0ceaa8912ed98cb52f03793ffad0bf0f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 28
 Visual Knowledge Representation for Decision Support - from Cognitive Maps to Fuzzy Knowledge Maps Shamim Khan School of Computer Science khan_shamim@colstate. edu
Visual Knowledge Representation for Decision Support - from Cognitive Maps to Fuzzy Knowledge Maps Shamim Khan School of Computer Science khan_shamim@colstate. edu
 Introduction Ø The goal of Artificial Intelligence (AI) Ø Decision Support Systems and AI Ø Knowledge representation and reasoning Ø Schemes for knowledge representation l l 2/5/10 Rules Semantic Networks IT Seminar 3
Introduction Ø The goal of Artificial Intelligence (AI) Ø Decision Support Systems and AI Ø Knowledge representation and reasoning Ø Schemes for knowledge representation l l 2/5/10 Rules Semantic Networks IT Seminar 3
 Rule-based Knowledge Representation Ø A series of IF condition THEN action statements IF the stain of the organism is gramneg, and the morphology of the organism is rod, and the aerobicity of the organism is aerobic THEN there is strongly suggestive evidence (. 8) that the class of organism is enterocabateriaceae Ø An inference engine searches for patterns in the rules that match patterns in the data. 2/5/10 IT Seminar 4
Rule-based Knowledge Representation Ø A series of IF condition THEN action statements IF the stain of the organism is gramneg, and the morphology of the organism is rod, and the aerobicity of the organism is aerobic THEN there is strongly suggestive evidence (. 8) that the class of organism is enterocabateriaceae Ø An inference engine searches for patterns in the rules that match patterns in the data. 2/5/10 IT Seminar 4
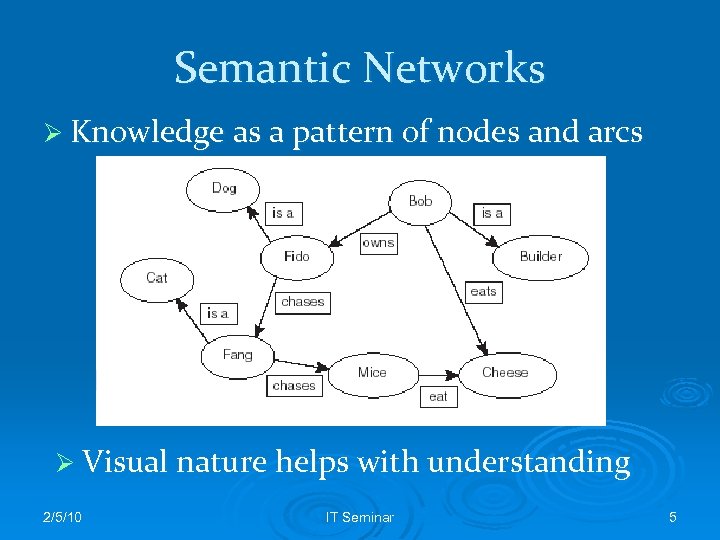 Semantic Networks Ø Knowledge as a pattern of nodes and arcs Ø Visual nature helps with understanding 2/5/10 IT Seminar 5
Semantic Networks Ø Knowledge as a pattern of nodes and arcs Ø Visual nature helps with understanding 2/5/10 IT Seminar 5
 Cognitive Maps - A causal view of knowledge Ø Knowledge as a network of concepts and their causal relationships Ø A visual representation scheme within a computational framework Ø First desribed as a decision support tool in (Axelrod 1976) 2/5/10 IT Seminar 6
Cognitive Maps - A causal view of knowledge Ø Knowledge as a network of concepts and their causal relationships Ø A visual representation scheme within a computational framework Ø First desribed as a decision support tool in (Axelrod 1976) 2/5/10 IT Seminar 6
 Robert Axelrod , BA(Math), Ph. D(Political Science) Professor for the Study of Human Understanding University of Michigan 2/5/10 IT Seminar 7
Robert Axelrod , BA(Math), Ph. D(Political Science) Professor for the Study of Human Understanding University of Michigan 2/5/10 IT Seminar 7
 Variants of Cognitive Maps Ø Also used in other fields – eg, psychology, geography Ø Axelrod's cognitive maps A mathematical model of a belief system l Lays out important concepts and relationships on a 2 D plane for “predictions, decisions and explanations” l 2/5/10 IT Seminar 8
Variants of Cognitive Maps Ø Also used in other fields – eg, psychology, geography Ø Axelrod's cognitive maps A mathematical model of a belief system l Lays out important concepts and relationships on a 2 D plane for “predictions, decisions and explanations” l 2/5/10 IT Seminar 8
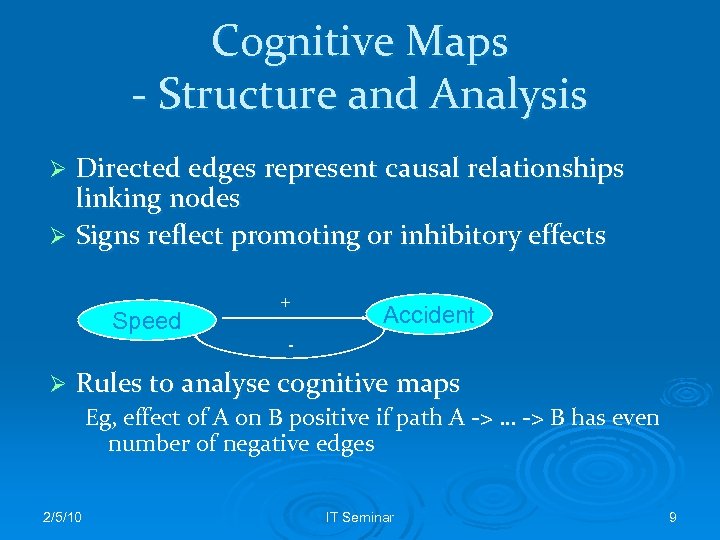 Cognitive Maps - Structure and Analysis Directed edges represent causal relationships linking nodes Ø Signs reflect promoting or inhibitory effects Ø Speed + Accident - Ø Rules to analyse cognitive maps Eg, effect of A on B positive if path A -> … -> B has even number of negative edges 2/5/10 IT Seminar 9
Cognitive Maps - Structure and Analysis Directed edges represent causal relationships linking nodes Ø Signs reflect promoting or inhibitory effects Ø Speed + Accident - Ø Rules to analyse cognitive maps Eg, effect of A on B positive if path A -> … -> B has even number of negative edges 2/5/10 IT Seminar 9
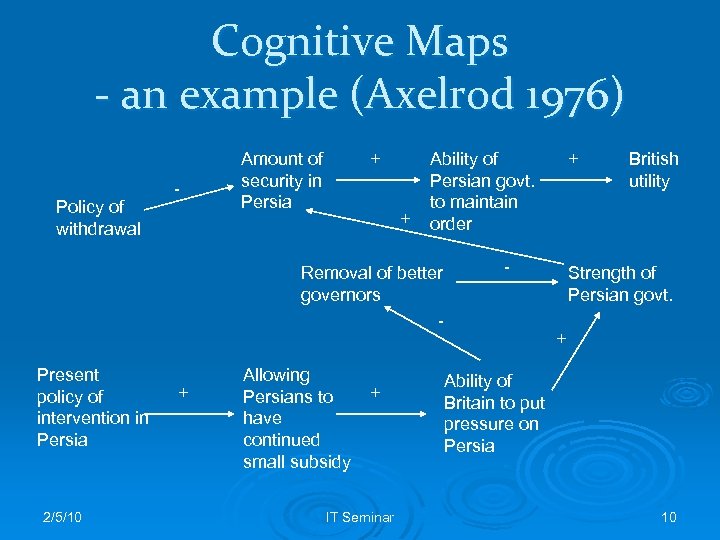 Cognitive Maps - an example (Axelrod 1976) Policy of withdrawal - Amount of security in Persia + + Ability of Persian govt. to maintain order Removal of better governors Present policy of intervention in Persia 2/5/10 + Allowing Persians to have continued small subsidy + IT Seminar + - British utility Strength of Persian govt. + Ability of Britain to put pressure on Persia 10
Cognitive Maps - an example (Axelrod 1976) Policy of withdrawal - Amount of security in Persia + + Ability of Persian govt. to maintain order Removal of better governors Present policy of intervention in Persia 2/5/10 + Allowing Persians to have continued small subsidy + IT Seminar + - British utility Strength of Persian govt. + Ability of Britain to put pressure on Persia 10
 Limitations of Axelrod’s cognitive maps Ø Difficulty handling multiple paths between two nodes l Ø Static - do not evolve with time l Ø Real-life scenarios may also involve feedback Use of bivalent (true/false) logic l Ø Conflicting inferences Real-life causalities often expressed in inexact (fuzzy) terms Proposed solution: Kosko’s Fuzzy Cognitive Maps (Kosko 1986) 2/5/10 IT Seminar 11
Limitations of Axelrod’s cognitive maps Ø Difficulty handling multiple paths between two nodes l Ø Static - do not evolve with time l Ø Real-life scenarios may also involve feedback Use of bivalent (true/false) logic l Ø Conflicting inferences Real-life causalities often expressed in inexact (fuzzy) terms Proposed solution: Kosko’s Fuzzy Cognitive Maps (Kosko 1986) 2/5/10 IT Seminar 11
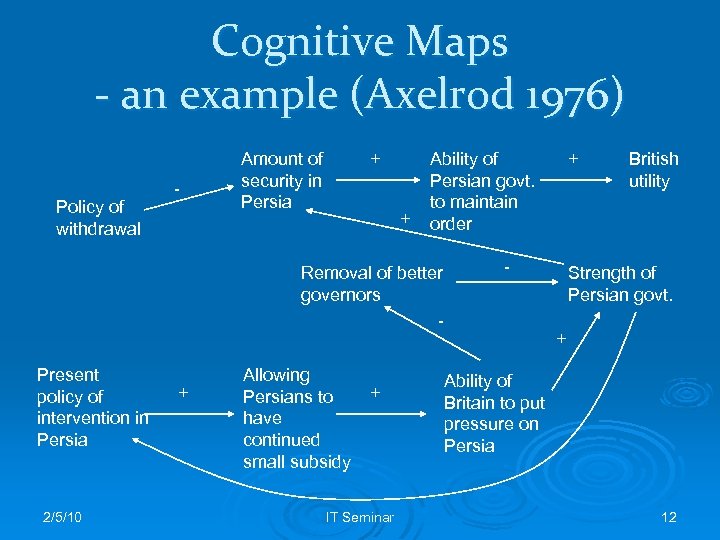 Cognitive Maps - an example (Axelrod 1976) Policy of withdrawal - Amount of security in Persia + + Ability of Persian govt. to maintain order Removal of better governors Present policy of intervention in Persia 2/5/10 + Allowing Persians to have continued small subsidy + IT Seminar + - British utility Strength of Persian govt. + Ability of Britain to put pressure on Persia 12
Cognitive Maps - an example (Axelrod 1976) Policy of withdrawal - Amount of security in Persia + + Ability of Persian govt. to maintain order Removal of better governors Present policy of intervention in Persia 2/5/10 + Allowing Persians to have continued small subsidy + IT Seminar + - British utility Strength of Persian govt. + Ability of Britain to put pressure on Persia 12
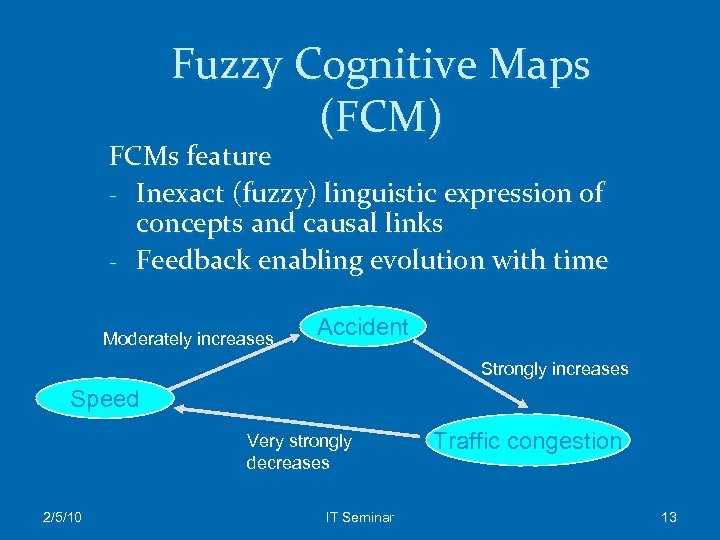 Fuzzy Cognitive Maps (FCM) FCMs feature - Inexact (fuzzy) linguistic expression of concepts and causal links - Feedback enabling evolution with time Moderately increases Accident Strongly increases Speed Very strongly decreases 2/5/10 IT Seminar Traffic congestion 13
Fuzzy Cognitive Maps (FCM) FCMs feature - Inexact (fuzzy) linguistic expression of concepts and causal links - Feedback enabling evolution with time Moderately increases Accident Strongly increases Speed Very strongly decreases 2/5/10 IT Seminar Traffic congestion 13
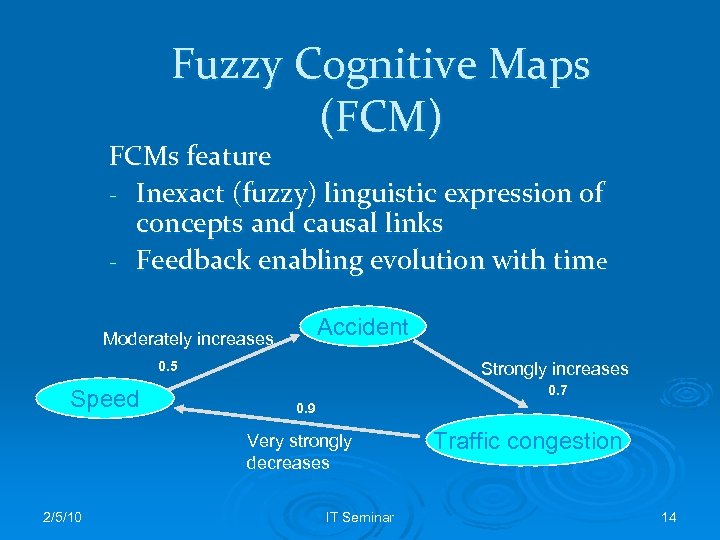 Fuzzy Cognitive Maps (FCM) FCMs feature - Inexact (fuzzy) linguistic expression of concepts and causal links - Feedback enabling evolution with time Accident Moderately increases 0. 5 Speed Strongly increases 0. 7 0. 9 Very strongly decreases 2/5/10 IT Seminar Traffic congestion 14
Fuzzy Cognitive Maps (FCM) FCMs feature - Inexact (fuzzy) linguistic expression of concepts and causal links - Feedback enabling evolution with time Accident Moderately increases 0. 5 Speed Strongly increases 0. 7 0. 9 Very strongly decreases 2/5/10 IT Seminar Traffic congestion 14
 FCM operation The state of a node determined by - sum of its inputs modified by causal link weights, and - a non-linear transfer function Fed with a stimulus state vector, the state of an FCM is continuously updated until it converges 2/5/10 IT Seminar 15
FCM operation The state of a node determined by - sum of its inputs modified by causal link weights, and - a non-linear transfer function Fed with a stimulus state vector, the state of an FCM is continuously updated until it converges 2/5/10 IT Seminar 15
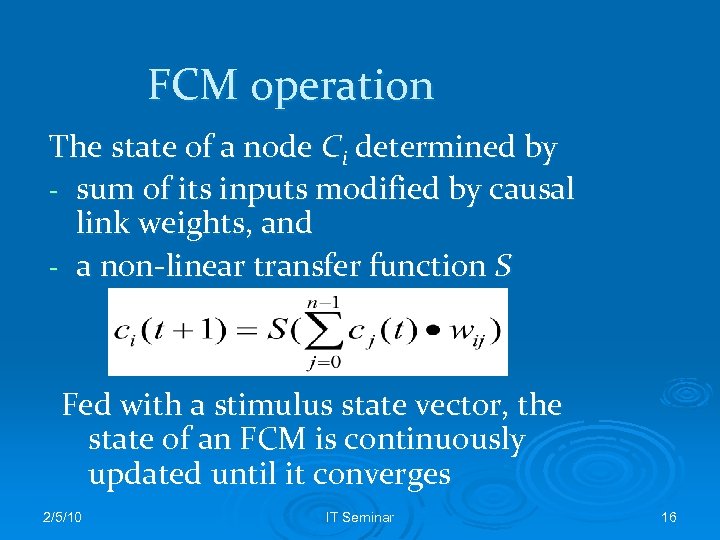 FCM operation The state of a node Ci determined by - sum of its inputs modified by causal link weights, and - a non-linear transfer function S Fed with a stimulus state vector, the state of an FCM is continuously updated until it converges 2/5/10 IT Seminar 16
FCM operation The state of a node Ci determined by - sum of its inputs modified by causal link weights, and - a non-linear transfer function S Fed with a stimulus state vector, the state of an FCM is continuously updated until it converges 2/5/10 IT Seminar 16
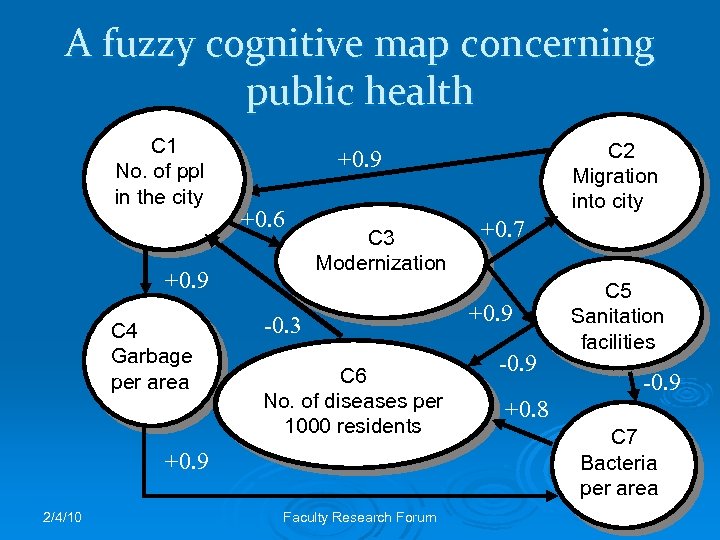 A fuzzy cognitive map concerning public health C 1 No. of ppl in the city +0. 9 +0. 6 +0. 9 C 4 Garbage per area +0. 9 2/4/10 C 3 Modernization -0. 3 C 6 No. of diseases per No. of diseases 1000 residents per 1000 residents Faculty Research Forum +0. 7 +0. 9 -0. 9 C 2 Migration into city C 5 Sanitation facilities -0. 9 +0. 8 C 7 Bacteria per area 17
A fuzzy cognitive map concerning public health C 1 No. of ppl in the city +0. 9 +0. 6 +0. 9 C 4 Garbage per area +0. 9 2/4/10 C 3 Modernization -0. 3 C 6 No. of diseases per No. of diseases 1000 residents per 1000 residents Faculty Research Forum +0. 7 +0. 9 -0. 9 C 2 Migration into city C 5 Sanitation facilities -0. 9 +0. 8 C 7 Bacteria per area 17
 Decision support using FCMs Given a stimulus vector, FCMs converge to one of three possibilities State vector remains unchanged 2. A sequence of state vectors keep repeating 3. The state vector keeps changing indefinitely 1. The evolved state(s) of an FCM can provide useful decision support 2/4/10 Faculty Research Forum 18
Decision support using FCMs Given a stimulus vector, FCMs converge to one of three possibilities State vector remains unchanged 2. A sequence of state vectors keep repeating 3. The state vector keeps changing indefinitely 1. The evolved state(s) of an FCM can provide useful decision support 2/4/10 Faculty Research Forum 18
 FCMs as decision support tools § Problem domain analysis - - - 2/4/10 How significant is concept A? What is the degree of influence of concept A on concept B? What will be the impact of a change in concept A on other concepts? Given a set of values for all concepts at a point in time, how will the system evolve with time? Faculty Research Forum 19
FCMs as decision support tools § Problem domain analysis - - - 2/4/10 How significant is concept A? What is the degree of influence of concept A on concept B? What will be the impact of a change in concept A on other concepts? Given a set of values for all concepts at a point in time, how will the system evolve with time? Faculty Research Forum 19
 FCMs as decision support tools (cont. ) § Goal oriented decision support (Khan et al 2004 a) – What state of affairs can lead to a given (goal) state? § Group decision support (Khan et al 2004 b) – FCMs can be merged 2/4/10 Faculty Research Forum 20
FCMs as decision support tools (cont. ) § Goal oriented decision support (Khan et al 2004 a) – What state of affairs can lead to a given (goal) state? § Group decision support (Khan et al 2004 b) – FCMs can be merged 2/4/10 Faculty Research Forum 20
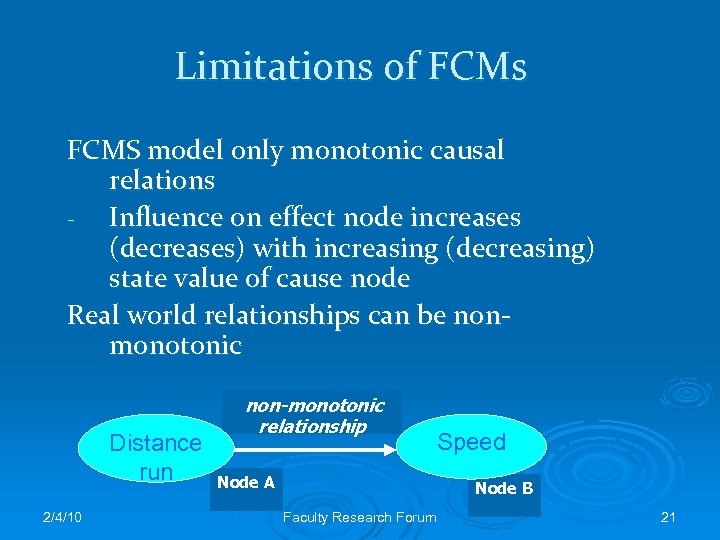 Limitations of FCMs FCMS model only monotonic causal relations - Influence on effect node increases (decreases) with increasing (decreasing) state value of cause node Real world relationships can be nonmonotonic Distance run 2/4/10 non-monotonic relationship Speed Node A Node B Faculty Research Forum 21
Limitations of FCMs FCMS model only monotonic causal relations - Influence on effect node increases (decreases) with increasing (decreasing) state value of cause node Real world relationships can be nonmonotonic Distance run 2/4/10 non-monotonic relationship Speed Node A Node B Faculty Research Forum 21
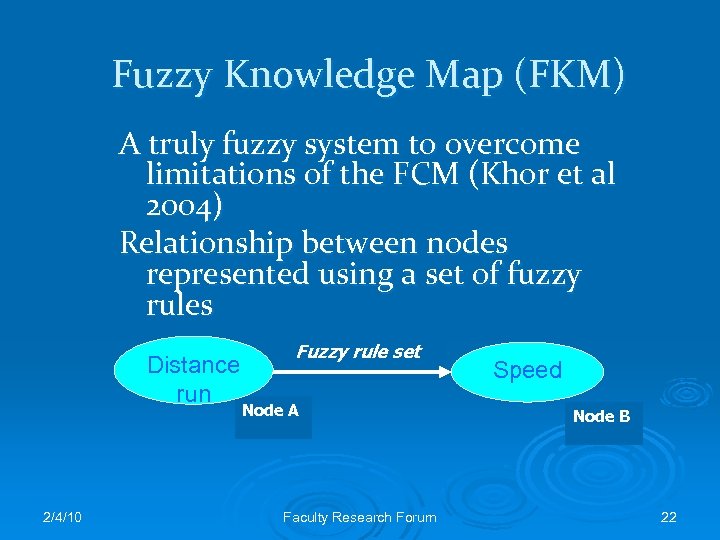 Fuzzy Knowledge Map (FKM) A truly fuzzy system to overcome limitations of the FCM (Khor et al 2004) Relationship between nodes represented using a set of fuzzy rules Distance run 2/4/10 Fuzzy rule set Node A Faculty Research Forum Speed Node B 22
Fuzzy Knowledge Map (FKM) A truly fuzzy system to overcome limitations of the FCM (Khor et al 2004) Relationship between nodes represented using a set of fuzzy rules Distance run 2/4/10 Fuzzy rule set Node A Faculty Research Forum Speed Node B 22
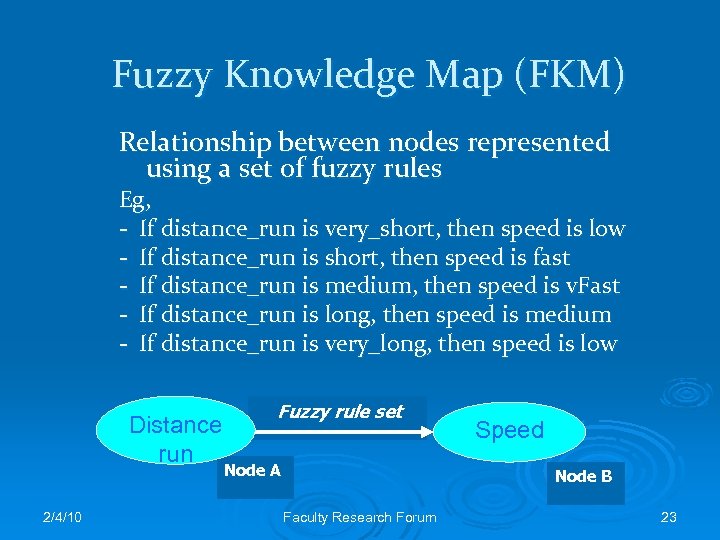 Fuzzy Knowledge Map (FKM) Relationship between nodes represented using a set of fuzzy rules Eg, - If distance_run is very_short, then speed is low - If distance_run is short, then speed is fast - If distance_run is medium, then speed is v. Fast - If distance_run is long, then speed is medium - If distance_run is very_long, then speed is low Distance run 2/4/10 Fuzzy rule set Node A Speed Node B Faculty Research Forum 23
Fuzzy Knowledge Map (FKM) Relationship between nodes represented using a set of fuzzy rules Eg, - If distance_run is very_short, then speed is low - If distance_run is short, then speed is fast - If distance_run is medium, then speed is v. Fast - If distance_run is long, then speed is medium - If distance_run is very_long, then speed is low Distance run 2/4/10 Fuzzy rule set Node A Speed Node B Faculty Research Forum 23
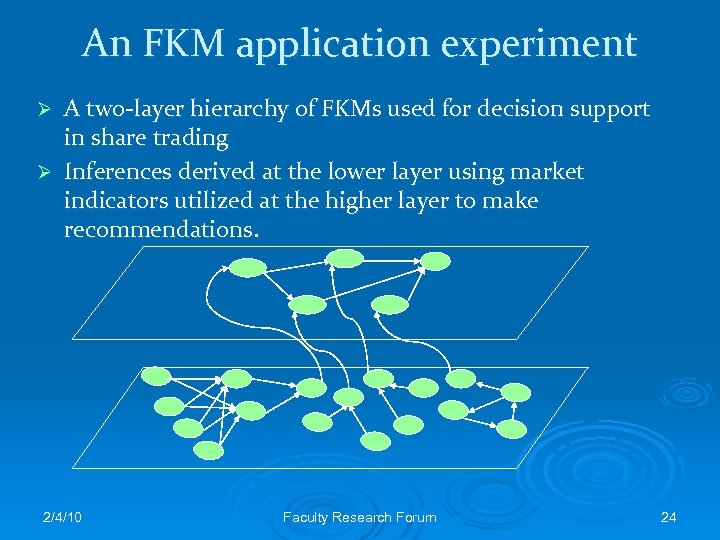 An FKM application experiment A two-layer hierarchy of FKMs used for decision support in share trading Ø Inferences derived at the lower layer using market indicators utilized at the higher layer to make recommendations. Ø 2/4/10 Faculty Research Forum 24
An FKM application experiment A two-layer hierarchy of FKMs used for decision support in share trading Ø Inferences derived at the lower layer using market indicators utilized at the higher layer to make recommendations. Ø 2/4/10 Faculty Research Forum 24
 Experiment Ø Indicators used: l l Ø Two data sets: l l Ø Commonwealth Bank of Australia Ltd. Telstra Corporation Ltd. Study period: l 2/4/10 Momentum, Relative strength index, Bollinger band, Moving averages. 3 years ( Jan 2002 to Dec 2004). Faculty Research Forum 25
Experiment Ø Indicators used: l l Ø Two data sets: l l Ø Commonwealth Bank of Australia Ltd. Telstra Corporation Ltd. Study period: l 2/4/10 Momentum, Relative strength index, Bollinger band, Moving averages. 3 years ( Jan 2002 to Dec 2004). Faculty Research Forum 25
 Results Performance of the FKM model over the 3 -year study period Ø FKM outperforms simple ‘Buy and hold’ strategy Ø 2/4/10 Faculty Research Forum 26
Results Performance of the FKM model over the 3 -year study period Ø FKM outperforms simple ‘Buy and hold’ strategy Ø 2/4/10 Faculty Research Forum 26
 Conclusion Ø Knowledge representation schemes can be more useful if they l l Ø Help us visualize a problem domain for analysis and inferencing Allow incorporation of inexact/qualitative human expert knowledge Fuzzy knowledge maps overcome the limitations of FCMs by allowing fuzzy expression of causal knowledge and fuzzy reasoning 2/4/10 Faculty Research Forum 27
Conclusion Ø Knowledge representation schemes can be more useful if they l l Ø Help us visualize a problem domain for analysis and inferencing Allow incorporation of inexact/qualitative human expert knowledge Fuzzy knowledge maps overcome the limitations of FCMs by allowing fuzzy expression of causal knowledge and fuzzy reasoning 2/4/10 Faculty Research Forum 27
 References • • • Axelrod, R. (1976), “Structure of Decision”, Princeton University Press, US. Kosko, B. (1986) "Fuzzy Cognitive Maps", Int. J. Man-Machine Studies, Vol. 24, pp. 65 -75. Khan, M. S. , Quaddus, M. A. , and Intrapairot, A. (2001) "Application of a Fuzzy Cognitive Map for Analysing Data Warehouse Diffusion", Proc. 19 th IASTED Int. Conf. on Applied Informatics, Innsbruck 19 -22 Feb. , pp. 32 -37. Khan, M. S. , and Quaddus, M. (2004 a)“Group Decision Support using Fuzzy Cognitive Maps for Causal Reasoning”, Group Decision and Negotiation Journal, Vol. 13, No. 5, pp. 463 -480. Khan, M. S. , Khor, S. , and Chong, A. (2004 b)"Fuzzy Cognitive Maps with Genetic Algorithm for Goal-oriented Decision Support", International Journal of Uncertainty, Fuzziness and Knowledge-Based Systems, Vol. 12, October pp. 31 -42. Khan, M. S. , Khor, S. (2004 c)"A Framework for Fuzzy Rule-based Cognitive Maps", 8 th Pacific Rim International Conf. on Artificial Intelligence, Auckland, August 8 -13, pp. 454 -463. Khor, S. , Khan, M. S. , and Payakpate, J. (2004 d) “Fuzzy Knowledge Representation for Decision Support”, KBCS-2004 Fifth International Conference on Knowledge Based Computer Systems, Hyderabad, India, December 19 -22, 2004, pp. 186 -195. 2/4/10 Faculty Research Forum 28
References • • • Axelrod, R. (1976), “Structure of Decision”, Princeton University Press, US. Kosko, B. (1986) "Fuzzy Cognitive Maps", Int. J. Man-Machine Studies, Vol. 24, pp. 65 -75. Khan, M. S. , Quaddus, M. A. , and Intrapairot, A. (2001) "Application of a Fuzzy Cognitive Map for Analysing Data Warehouse Diffusion", Proc. 19 th IASTED Int. Conf. on Applied Informatics, Innsbruck 19 -22 Feb. , pp. 32 -37. Khan, M. S. , and Quaddus, M. (2004 a)“Group Decision Support using Fuzzy Cognitive Maps for Causal Reasoning”, Group Decision and Negotiation Journal, Vol. 13, No. 5, pp. 463 -480. Khan, M. S. , Khor, S. , and Chong, A. (2004 b)"Fuzzy Cognitive Maps with Genetic Algorithm for Goal-oriented Decision Support", International Journal of Uncertainty, Fuzziness and Knowledge-Based Systems, Vol. 12, October pp. 31 -42. Khan, M. S. , Khor, S. (2004 c)"A Framework for Fuzzy Rule-based Cognitive Maps", 8 th Pacific Rim International Conf. on Artificial Intelligence, Auckland, August 8 -13, pp. 454 -463. Khor, S. , Khan, M. S. , and Payakpate, J. (2004 d) “Fuzzy Knowledge Representation for Decision Support”, KBCS-2004 Fifth International Conference on Knowledge Based Computer Systems, Hyderabad, India, December 19 -22, 2004, pp. 186 -195. 2/4/10 Faculty Research Forum 28
 Questions? Thank you! 2/4/10 Faculty Research Forum 29
Questions? Thank you! 2/4/10 Faculty Research Forum 29


