c5c7713673c932e5f7451817fe0f8c02.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 64
Virtualization and Grid @ GRID 08, Bangalore Organized by PBS Grid. Works, Altair Presentation by S. THAMRAI SELVI Professor and Head Department of Information Technology MIT Campus, Anna University Chromepet, Chennai on 31. 08. 2008 GRID 08 - Grid Virtualization by S. T. Selvi, MIT, Anna University 1

Agenda n n n Introduction Virtualization Trust management in Grid Semantic discovery of Resources in Grid Conclusion 31. 08. 2008 GRID 08 - Grid Virtualization by S. T. Selvi, MIT, Anna University 2

The laws influencing Information Technology n The laws that are generally accepted as governing the spread of technology: 1. 2. 3. 4. 31. 08. 2008 Moore's Law Gilder's Law Metcalfe's Law Disk Law GRID 08 - Grid Virtualization by S. T. Selvi, MIT, Anna University 3
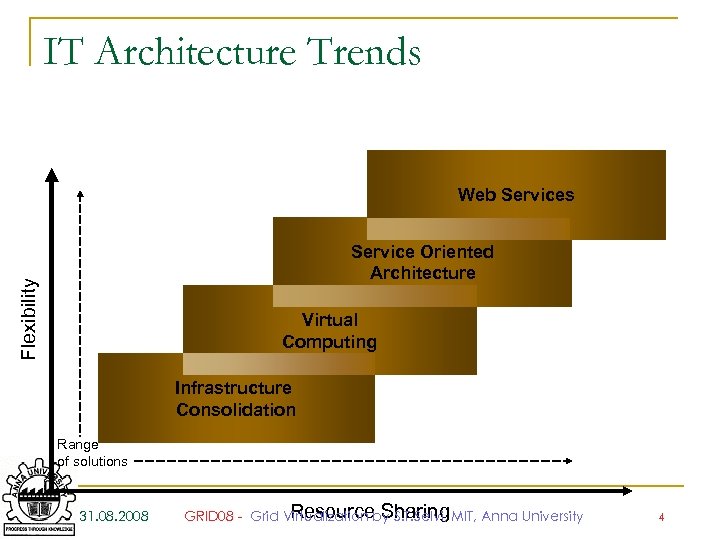
IT Architecture Trends Web Services Flexibility Service Oriented Architecture Virtual Computing Infrastructure Consolidation Range of solutions 31. 08. 2008 Resource Sharing GRID 08 - Grid Virtualization by S. T. Selvi, MIT, Anna University 4
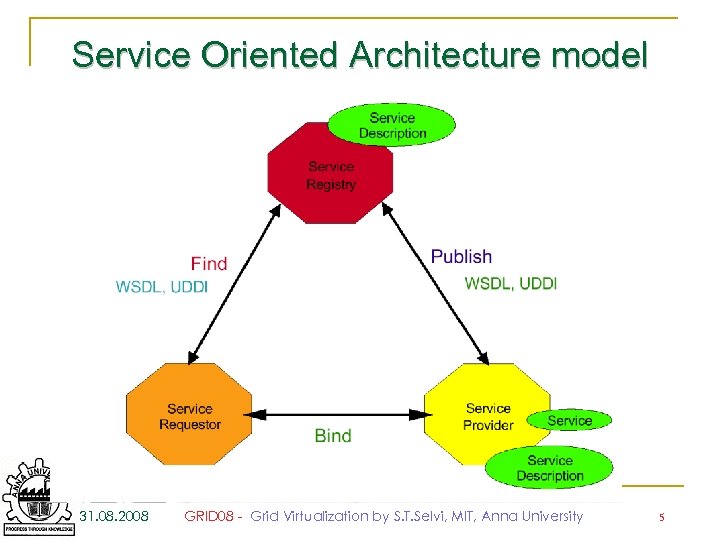
Service Oriented Architecture model 31. 08. 2008 GRID 08 - Grid Virtualization by S. T. Selvi, MIT, Anna University 5
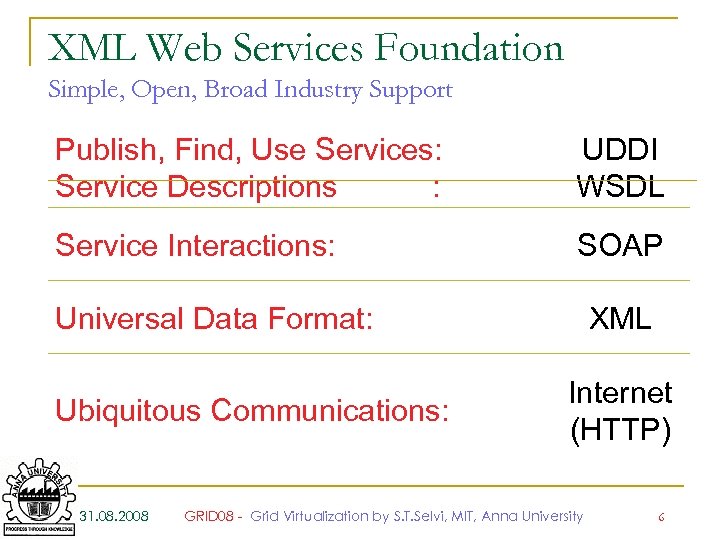
XML Web Services Foundation Simple, Open, Broad Industry Support Publish, Find, Use Services: Service Descriptions : UDDI WSDL Service Interactions: SOAP Universal Data Format: Ubiquitous Communications: 31. 08. 2008 XML Internet (HTTP) GRID 08 - Grid Virtualization by S. T. Selvi, MIT, Anna University 6

Web 2. 0: Evolution Towards a Read/Write Platform Web 1. 0 Web 2. 0 (1993 -2003) (2003 - beyond) Pretty much HTML pages viewed through a browser Web pages, plus a lot of other “content” shared over the web, with more interactivity; more like an application than a “page” “Read” Mode “Write” & Contribute “Page” Primary Unit of content “Post / record” “static” State “dynamic” Web browser Viewed through… Browsers, RSS Readers, anything “Client Server” Architecture “Web Services” Web Coders Content Created by… Everyone “geeks” Domain of… “mass amatuerization” 31. 08. 2008 GRID 08 - Grid Virtualization by S. T. Selvi, MIT, Anna University 7
Core concepts used in Web 2. 0 n AJAX- Asynchronous Java. Script + XML (User interface/Portal) n n n JSON - Java. Script Object Notation (SOAP) REST Representational State Transfer (WSDL). REST proposes to use Internet as programming platform with only HTTP Widgets, Gadgets, Start page for Portal 31. 08. 2008 GRID 08 - Grid Virtualization by S. T. Selvi, MIT, Anna University 8
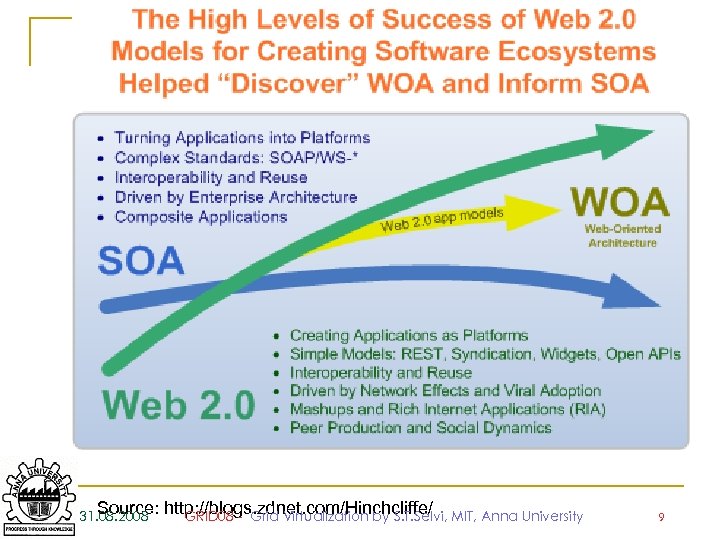
Source: 31. 08. 2008 http: //blogs. zdnet. com/Hinchcliffe/ MIT, Anna University GRID 08 - Grid Virtualization by S. T. Selvi, 9
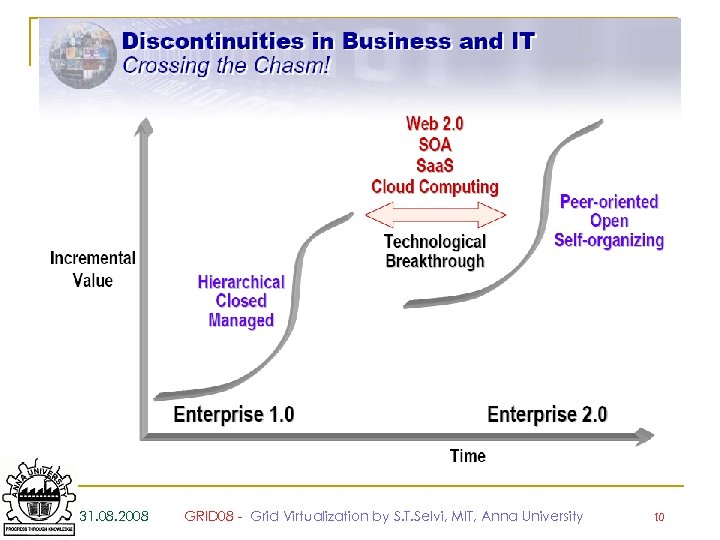
31. 08. 2008 GRID 08 - Grid Virtualization by S. T. Selvi, MIT, Anna University 10
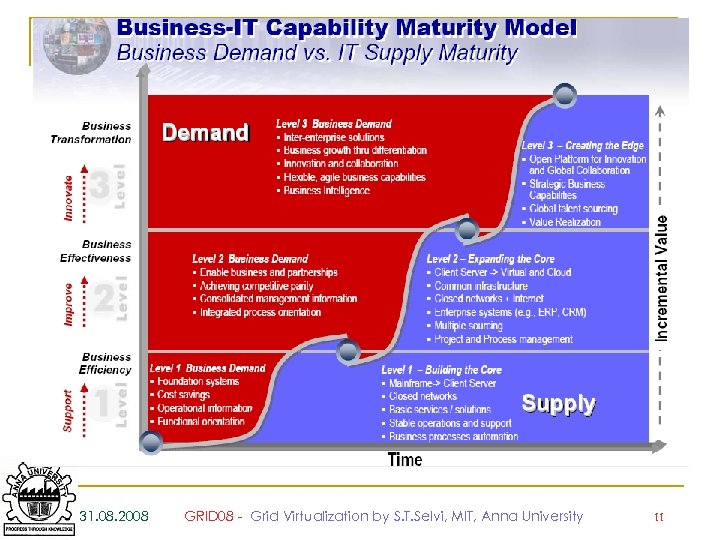
31. 08. 2008 GRID 08 - Grid Virtualization by S. T. Selvi, MIT, Anna University 11

31. 08. 2008 GRID 08 - Grid Virtualization by S. T. Selvi, MIT, Anna University 12

31. 08. 2008 GRID 08 - Grid Virtualization by S. T. Selvi, MIT, Anna University 13
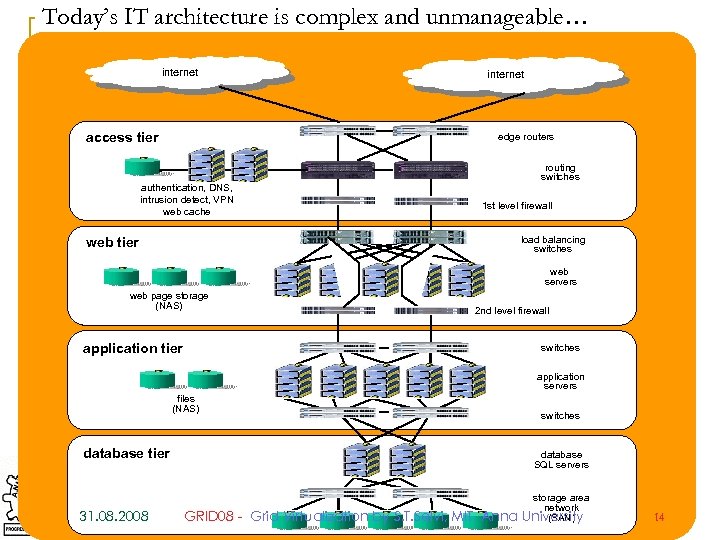
Today’s IT architecture is complex and unmanageable… internet access tier internet edge routers authentication, DNS, intrusion detect, VPN web cache routing switches 1 st level firewall load balancing switches web tier web servers web page storage (NAS) 2 nd level firewall application tier switches application servers files (NAS) database tier 31. 08. 2008 switches database SQL servers GRID 08 - Grid Virtualization by S. T. Selvi, MIT, Anna storage area network (SAN) University 14
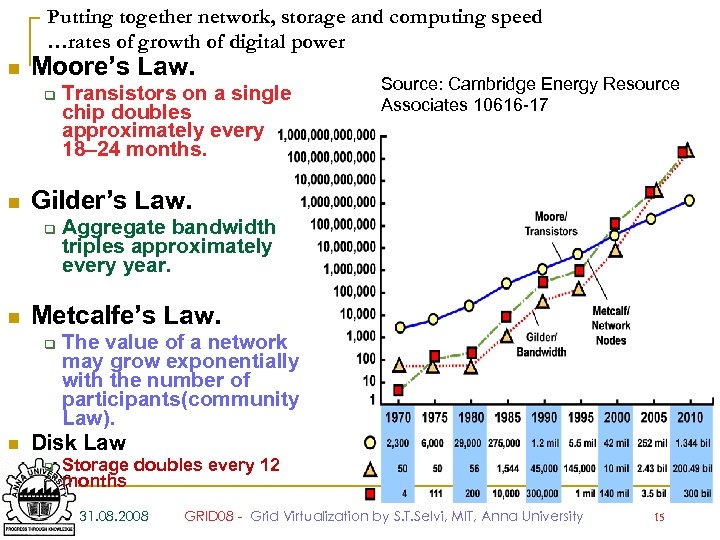
Putting together network, storage and computing speed …rates of growth of digital power n Moore’s Law. q n Transistors on a single chip doubles approximately every 18– 24 months. Source: Cambridge Energy Resource Associates 10616 -17 Gilder’s Law. q Aggregate bandwidth triples approximately every year. n Metcalfe’s Law. n The value of a network may grow exponentially with the number of participants(community Law). Disk Law q q Storage doubles every 12 months 31. 08. 2008 GRID 08 - Grid Virtualization by S. T. Selvi, MIT, Anna University 15
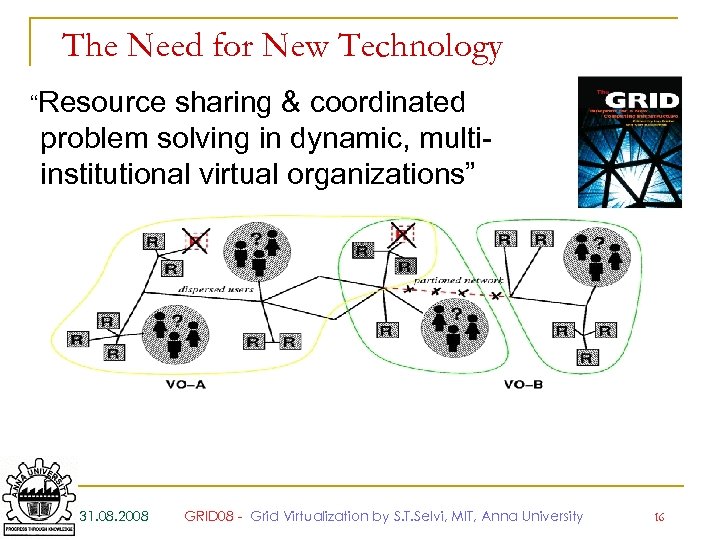
The Need for New Technology “Resource sharing & coordinated problem solving in dynamic, multiinstitutional virtual organizations” 31. 08. 2008 GRID 08 - Grid Virtualization by S. T. Selvi, MIT, Anna University 16

Technologies influencing a new era in computing… n n n n Microprocessor Technology Optical Networking Technology Storage Technology Wireless Technology Sensor Technology Global Internet Infrastructure WWW and Web Services (SOA) Open Source Movements 31. 08. 2008 GRID 08 - Grid Virtualization by S. T. Selvi, MIT, Anna University 17

Grid A kind of open standard distributed infrastructure that enables flexible, secure, coordinated resource sharing among dynamic collections of trusted resources belonging to diverse organizations across the globe ensuring user’s Quality of Service requirements. 31. 08. 2008 GRID 08 - Grid Virtualization by S. T. Selvi, MIT, Anna University 18

Grid enables … n n Virtual Organization Dynamic Resource sharing 31. 08. 2008 GRID 08 - Grid Virtualization by S. T. Selvi, MIT, Anna University 19
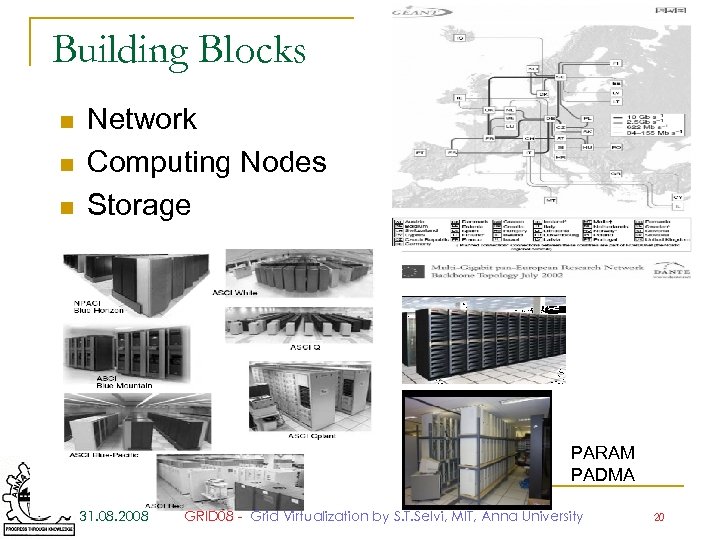
Building Blocks n n n Network Computing Nodes Storage PARAM PADMA 31. 08. 2008 GRID 08 - Grid Virtualization by S. T. Selvi, MIT, Anna University 20
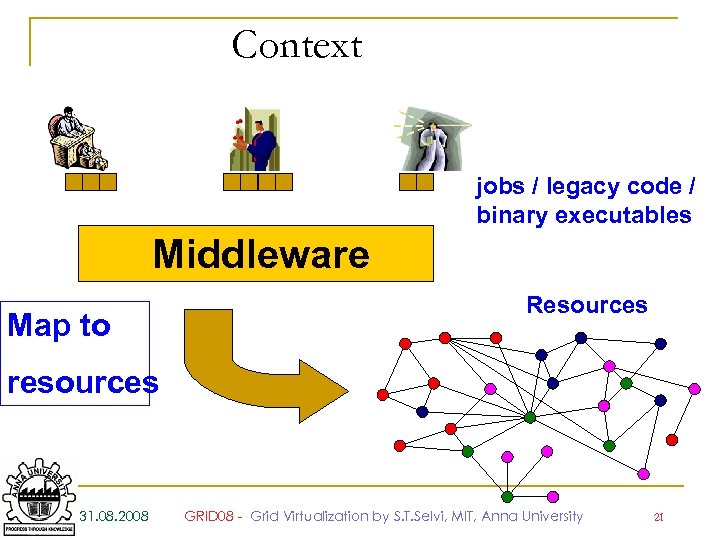
Context jobs / legacy code / binary executables Middleware Map to Resources resources 31. 08. 2008 GRID 08 - Grid Virtualization by S. T. Selvi, MIT, Anna University 21
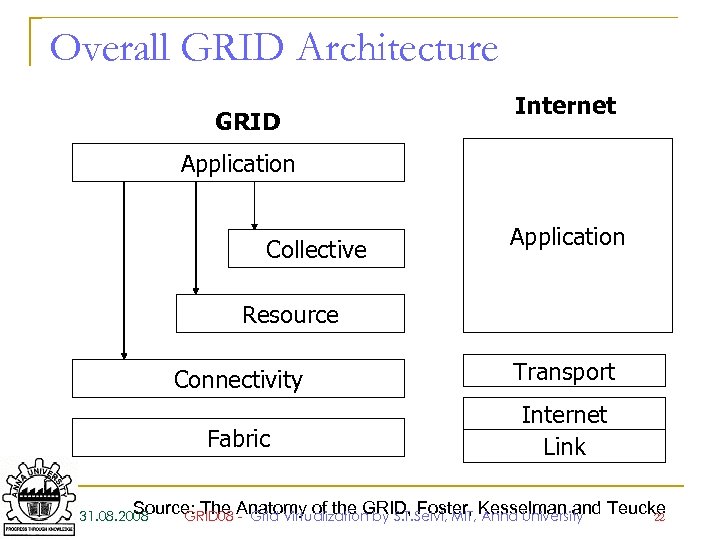
Overall GRID Architecture GRID Internet Application Collective Application Resource Connectivity Transport Fabric Internet Link Source: The Anatomy of the GRID, Foster, Kesselman and 31. 08. 2008 GRID 08 - Grid Virtualization by S. T. Selvi, MIT, Anna University Teucke 22
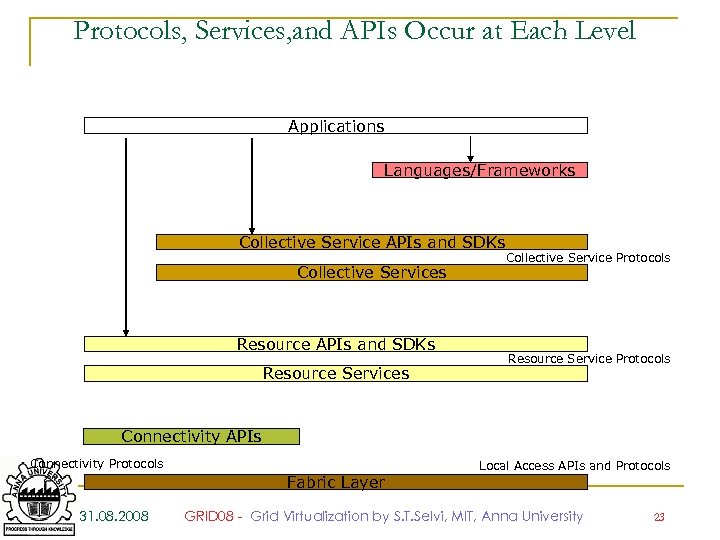
Protocols, Services, and APIs Occur at Each Level Applications Languages/Frameworks Collective Service APIs and SDKs Collective Services Resource APIs and SDKs Resource Services Collective Service Protocols Resource Service Protocols Connectivity APIs Connectivity Protocols Local Access APIs and Protocols Fabric Layer 31. 08. 2008 GRID 08 - Grid Virtualization by S. T. Selvi, MIT, Anna University 23
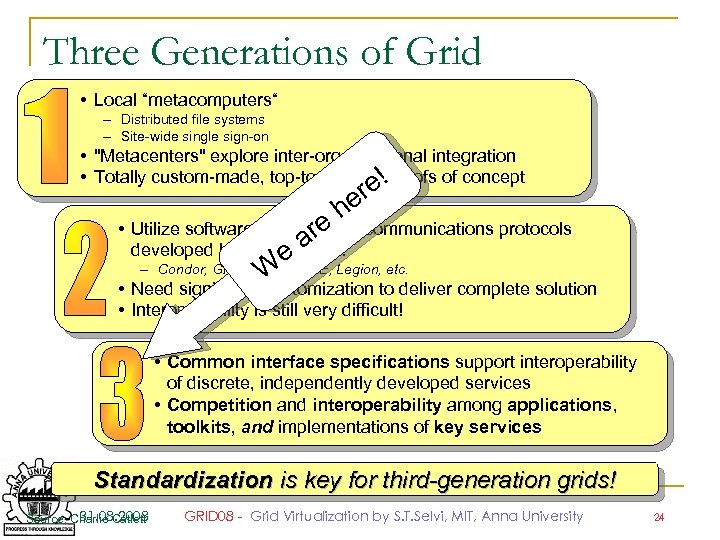
Three Generations of Grid • Local “metacomputers“ – Distributed file systems – Site-wide single sign-on • "Metacenters" explore inter-organizational integration • Totally custom-made, top-to-bottom: !proofs of concept re e h • Utilize software servicese r and communications protocols a developed by grid projects: e W – Condor, Globus, UNICORE, Legion, etc. • Need significant customization to deliver complete solution • Interoperability is still very difficult! • Common interface specifications support interoperability of discrete, independently developed services • Competition and interoperability among applications, toolkits, and implementations of key services Standardization is key for third-generation grids! 31. 08. 2008 Source: Charlie Catlett GRID 08 - Grid Virtualization by S. T. Selvi, MIT, Anna University 24

Grids – Where to ? n n n Grid 1. 0 – concerned with the virtualization, aggregation and sharing or compute resources Grid 2. 0 – focused on the virtualization, aggregation and sharing of all compute, storage, network and data resources The promise is that in Grid 2. 0 the resources will be easier to define, test, install, transport and adjust on demand. 31. 08. 2008 GRID 08 - Grid Virtualization by S. T. Selvi, MIT, Anna University 25
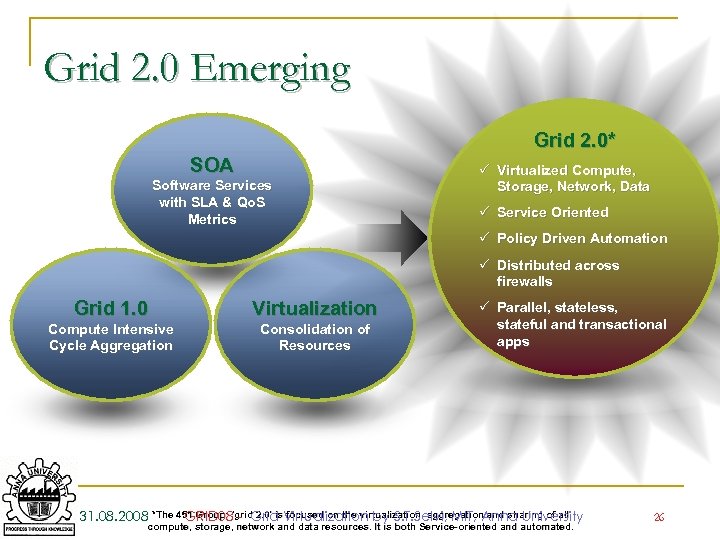
Grid 2. 0 Emerging Grid 2. 0* SOA Software Services with SLA & Qo. S Metrics P Virtualized Compute, Storage, Network, Data P Service Oriented P Policy Driven Automation P Distributed across firewalls Grid 1. 0 Virtualization Compute Intensive Cycle Aggregation Consolidation of Resources P Parallel, stateless, stateful and transactional apps 31. 08. 2008 *The 451 Group: 'grid 2. 0' is. Virtualization by S. T. Selvi, MIT, Anna University GRID 08 - Grid focused on the virtualization, aggregation and sharing of all compute, storage, network and data resources. It is both Service-oriented and automated. 26
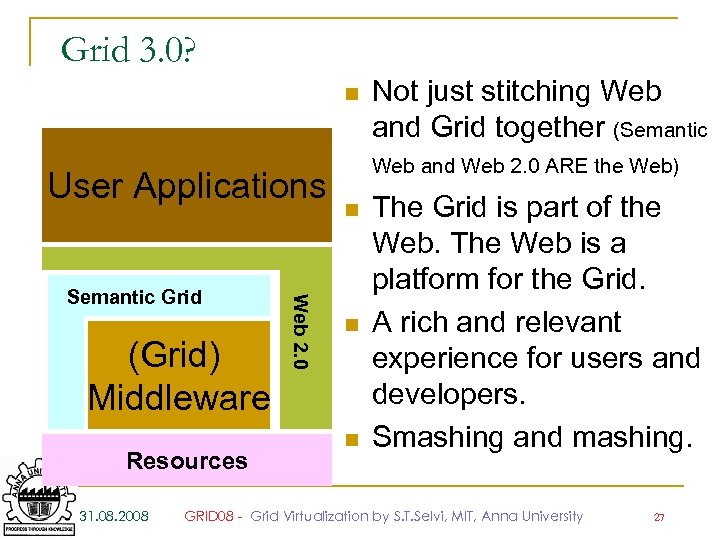
Grid 3. 0? n User Applications (Grid) Middleware Resources 31. 08. 2008 Web 2. 0 Semantic Grid Not just stitching Web and Grid together (Semantic Web and Web 2. 0 ARE the Web) n n n The Grid is part of the Web. The Web is a platform for the Grid. A rich and relevant experience for users and developers. Smashing and mashing. GRID 08 - Grid Virtualization by S. T. Selvi, MIT, Anna University 27
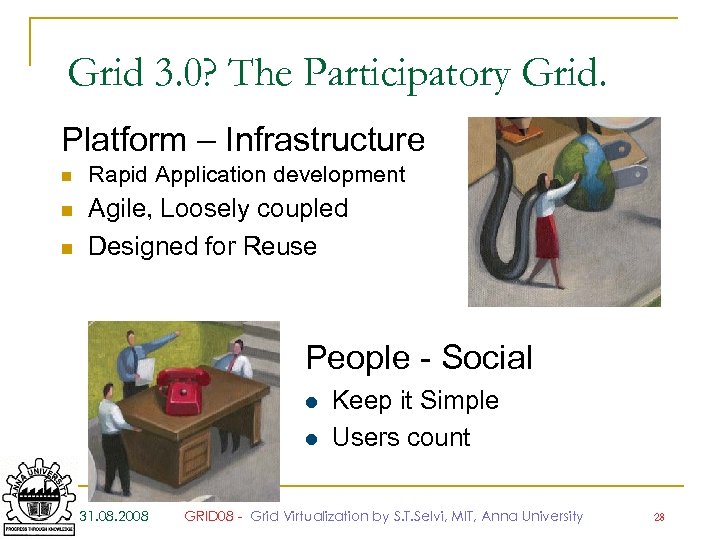
Grid 3. 0? The Participatory Grid. Platform – Infrastructure n n n Rapid Application development Agile, Loosely coupled Designed for Reuse People - Social l l 31. 08. 2008 Keep it Simple Users count GRID 08 - Grid Virtualization by S. T. Selvi, MIT, Anna University 28
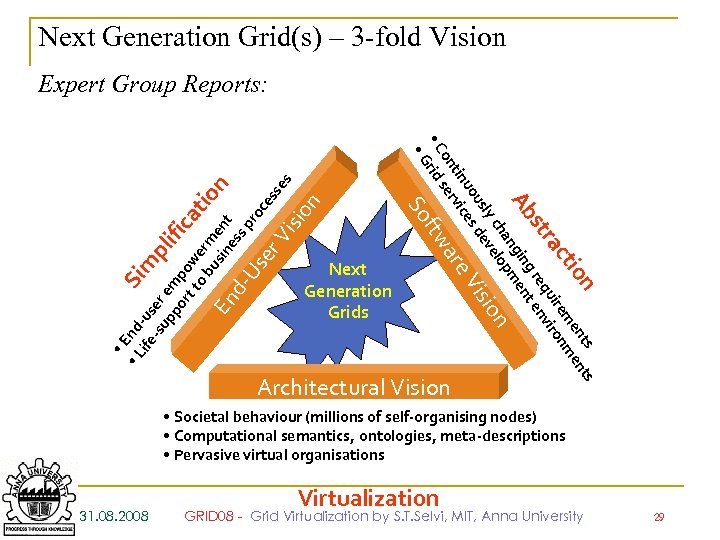
Next Generation Grid(s) – 3 -fold Vision n sio Next Generation Grids n ents io ct uiremironm ra st g req t env Ab angin pmen ch velo ly ion us de Vis uo es tin vic are on ser • C rid ftw • G So • E Si • L nd ife -us m -su er pl pp em ifi or po ca tt w o b er t us me ion En in nt d- ess p Us ro ce er Vi sses Expert Group Reports: Architectural Vision • Societal behaviour (millions of self-organising nodes) • Computational semantics, ontologies, meta-descriptions • Pervasive virtual organisations 31. 08. 2008 Virtualization GRID 08 - Grid Virtualization by S. T. Selvi, MIT, Anna University 29

Virtualization 31. 08. 2008 GRID 08 - Grid Virtualization by S. T. Selvi, MIT, Anna University 30

Virtualization is a framework or methodology of dividing the resources of a computer into multiple execution environments, by applying one or more concepts or technologies such as hardware and software partitioning, timesharing, partial or complete machine simulation, emulation, quality of service (Source: Wiki) 31. 08. 2008 GRID 08 - Grid Virtualization by S. T. Selvi, MIT, Anna University 31
Benefits from Virtualization n Load balancing q n Increased Resource utilization q n Create VM in the under utilized resources Reusable q n Create VM for new work loads One VM created can be reused somewhere else Isolation q Destruction of one VM doesn’t affect the other VM 31. 08. 2008 GRID 08 - Grid Virtualization by S. T. Selvi, MIT, Anna University 32

Continued… n High Availability q n Improved ROI q n Reduction in downtime More production with less Investment, operational and maintenance Reduced TCO q Eliminate the need of new Infrasturctures such as Server 31. 08. 2008 GRID 08 - Grid Virtualization by S. T. Selvi, MIT, Anna University 33

Continued… n Live migration q n Persistent and Non Persistent q n Support suspend resume and migration of created VMs Support for keep/drop the changes made in VM images Undoable and Append q Allows undo and append options in VM imagaes 31. 08. 2008 GRID 08 - Grid Virtualization by S. T. Selvi, MIT, Anna University 34

Motivation for our Research “If you want people to use your system then make it as easy as possible to use. ” Werner Vogels, Amazon CTO Simple to use is not the same as simple Yes, Grids are doing complicated hard stuff. But why make the developer and user suffer so? Also, Trust is another major issue 31. 08. 2008 GRID 08 - Grid Virtualization by S. T. Selvi, MIT, Anna University 35

CARE Resource Broker (CRB ) A Grid Meta Scheduler 31. 08. 2008 GRID 08 - Grid Virtualization by S. T. Selvi, MIT, Anna University 36
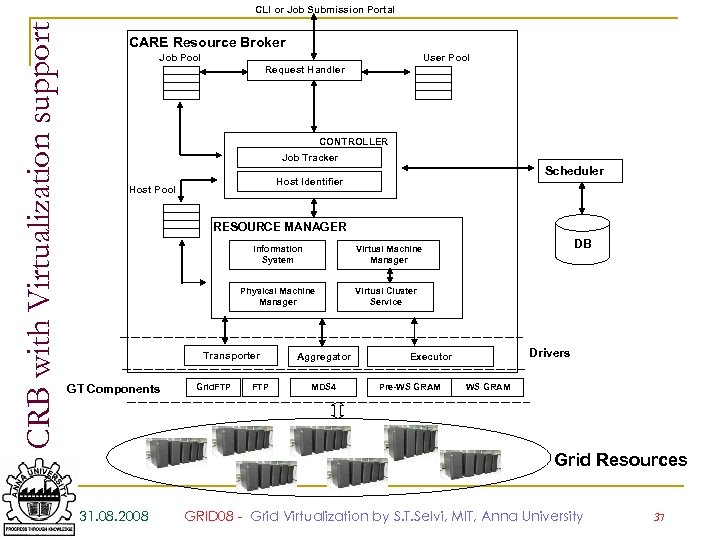
CRB with Virtualization support CLI or Job Submission Portal CARE Resource Broker Job Pool User Pool Request Handler CONTROLLER Job Tracker Scheduler Host Identifier Host Pool RESOURCE MANAGER Information System Physical Machine Manager Transporter GT Components Grid. FTP DB Virtual Machine Manager Aggregator MDS 4 Virtual Cluster Service Drivers Executor Pre-WS GRAM Grid Resources 31. 08. 2008 GRID 08 - Grid Virtualization by S. T. Selvi, MIT, Anna University 37

CRB Request Handler: n Gets the Job request, create Job instance and store it in the Job Pool. Controller: n Initiates the Aggregator to collect the information about all available resources and updates the Host object and Host Pool object. 31. 08. 2008 GRID 08 - Grid Virtualization by S. T. Selvi, MIT, Anna University 38

Continued … Scheduler: Gets the unordered resource list and orders the resources based on their trust value and return back to Controller. Virtual Cluster Service: The controller gives the resource list to the VCS in order to create virtual cluster. 31. 08. 2008 GRID 08 - Grid Virtualization by S. T. Selvi, MIT, Anna University 39
Continued… Transporter Initializes the RFT and transfer the input and executables into selected host Executor: Initializes the GRAM to submit the job into local scheduler. Aggregator Initializes MDS to get the resource information in the Grid 31. 08. 2008 GRID 08 - Grid Virtualization by S. T. Selvi, MIT, Anna University 40

Trust Management System 31. 08. 2008 GRID 08 - Grid Virtualization by S. T. Selvi, MIT, Anna University 41

The Trust… We definedegree of belief in the resource provider’s competence to complete user’s task dependably, securely and reliably in a specific context at a given time Agent / Resource Broker users Resources 31. 08. 2008 GRID 08 - Grid Virtualization by S. T. Selvi, MIT, Anna University 42
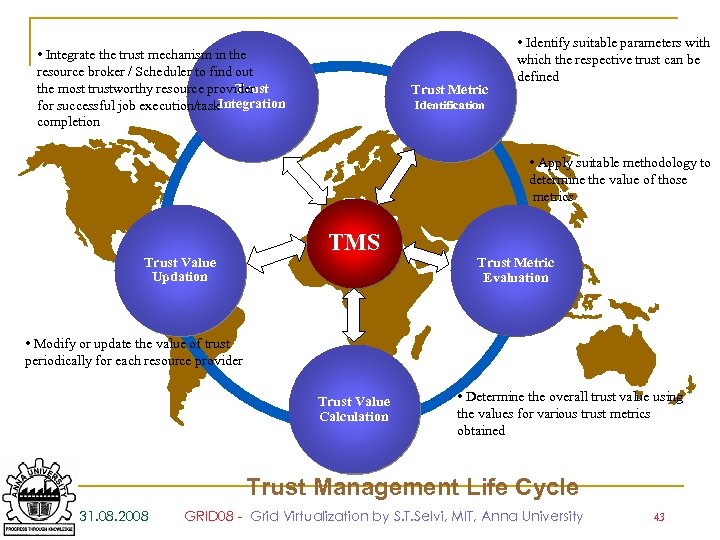
• Integrate the trust mechanism in the resource broker / Scheduler to find out the most trustworthy resource provider Trust Integration for successful job execution/task completion Trust Metric • Identify suitable parameters with which the respective trust can be defined Identification • Apply suitable methodology to determine the value of those metrics Trust Value Updation TMS Trust Metric Evaluation • Modify or update the value of trust periodically for each resource provider Trust Value Calculation • Determine the overall trust value using the values for various trust metrics obtained Trust Management Life Cycle 31. 08. 2008 GRID 08 - Grid Virtualization by S. T. Selvi, MIT, Anna University 43
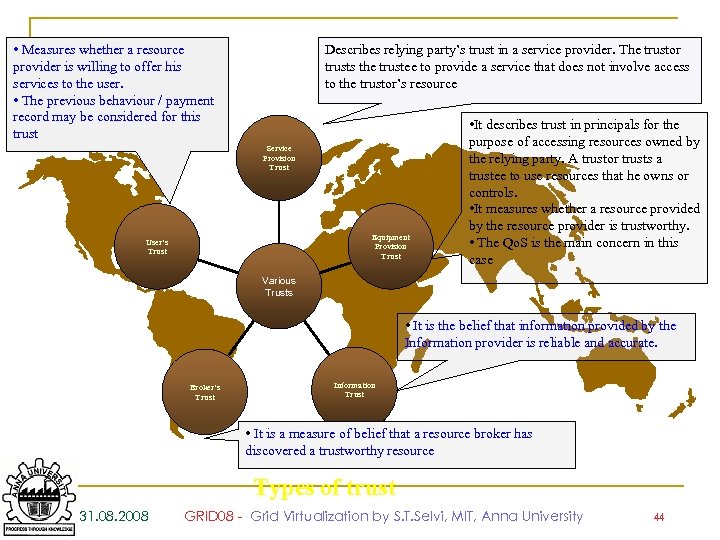
• Measures whether a resource provider is willing to offer his services to the user. • The previous behaviour / payment record may be considered for this trust Describes relying party’s trust in a service provider. The trustor trusts the trustee to provide a service that does not involve access to the trustor’s resource Service Provision Trust Equipment Provision Trust User’s Trust • It describes trust in principals for the purpose of accessing resources owned by the relying party. A trustor trusts a trustee to use resources that he owns or controls. • It measures whether a resource provided by the resource provider is trustworthy. • The Qo. S is the main concern in this case Various Trusts • It is the belief that information provided by the Information provider is reliable and accurate. Broker’s Trust Information Trust • It is a measure of belief that a resource broker has discovered a trustworthy resource Types of trust 31. 08. 2008 GRID 08 - Grid Virtualization by S. T. Selvi, MIT, Anna University 44
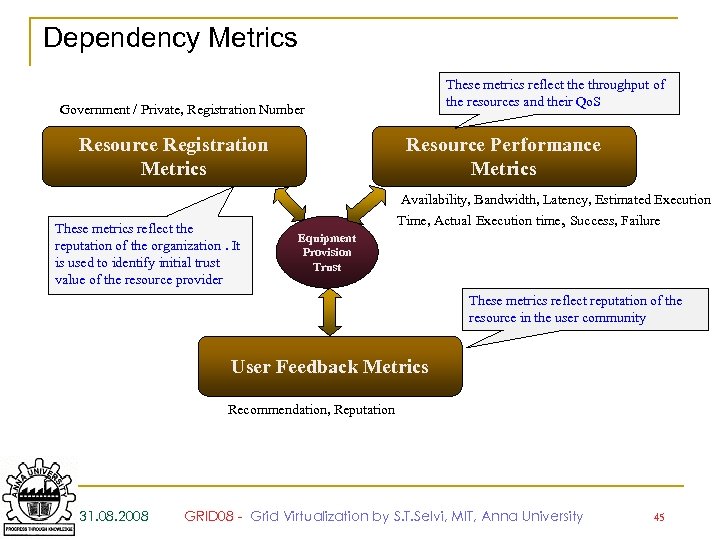
Dependency Metrics These metrics reflect the throughput of the resources and their Qo. S Government / Private, Registration Number Resource Registration Metrics These metrics reflect the reputation of the organization. It is used to identify initial trust value of the resource provider Resource Performance Metrics Availability, Bandwidth, Latency, Estimated Execution Time, Actual Execution time, Success, Failure Equipment Provision Trust These metrics reflect reputation of the resource in the user community User Feedback Metrics Recommendation, Reputation 31. 08. 2008 GRID 08 - Grid Virtualization by S. T. Selvi, MIT, Anna University 45
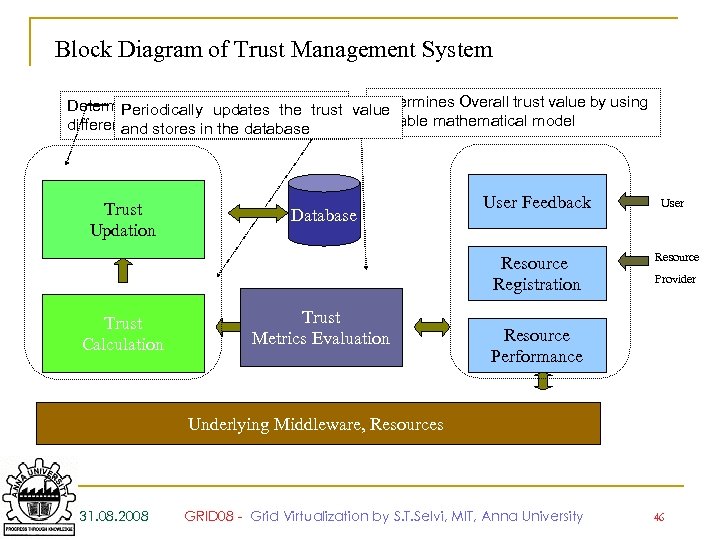
Block Diagram of Trust Management System Determines Overall trust value by using Determines values updates the trust value Periodically of metrics using suitable mathematical model Trust Metrics Identification different methodologies database and stores in the Trust Updation Database User Feedback Resource Registration Trust Calculation Trust Metrics Evaluation User Resource Provider Resource Performance Underlying Middleware, Resources 31. 08. 2008 GRID 08 - Grid Virtualization by S. T. Selvi, MIT, Anna University 46
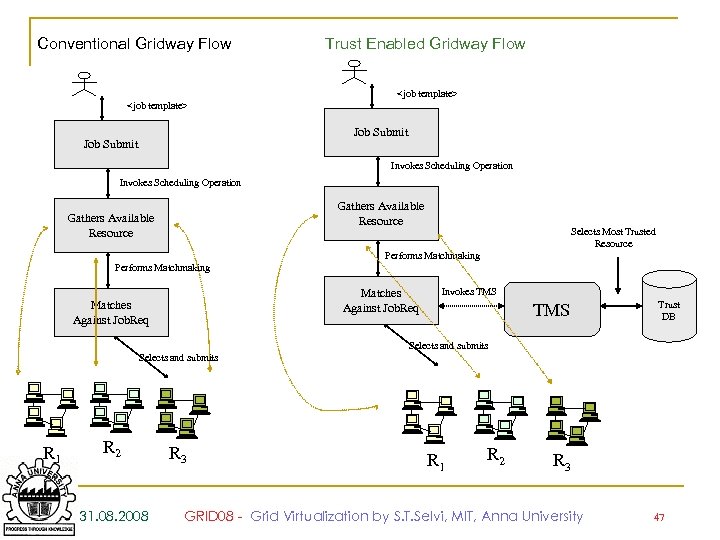
Conventional Gridway Flow Trust Enabled Gridway Flow <job template> Job Submit Invokes Scheduling Operation Gathers Available Resource Selects Most Trusted Resource Performs Matchmaking Matches Against Job. Req Invokes TMS Trust DB Selects and submits R 1 R 2 31. 08. 2008 R 3 R 1 R 2 R 3 GRID 08 - Grid Virtualization by S. T. Selvi, MIT, Anna University 47

PATENT Pending Filed Application for patent (Patent application No. 593/CHE/2007 A) n Title of the Invention: Trust Resource Broker n International Classification: G 06 F 17/30 n Patent has been published in Journal No. 16/2007 dated 20/04/2007. n 31. 08. 2008 GRID 08 - Grid Virtualization by S. T. Selvi, MIT, Anna University 48

Integrated with Gridway Meta Scheduler n http: //www. gridway. org/doku. php? id=related: related Developed by other projects n Trust Management q Description - This project provides Grid. Way with a mechanism to evalute the trust of the computational resources. The Trust module consists of modified host attribute parsers and match-making algorithms. Additionally the Trust module needs to modify the information providers of Grid resources. q Contact - This component has been developed by the team of Prof Dr. S. Thamarai Selvi (stselvi@annauniv. edu) at Madras Institute of Technology 31. 08. 2008 GRID 08 - Grid Virtualization by S. T. Selvi, MIT, Anna University 49

Semantic Component 31. 08. 2008 GRID 08 - Grid Virtualization by S. T. Selvi, MIT, Anna University 50
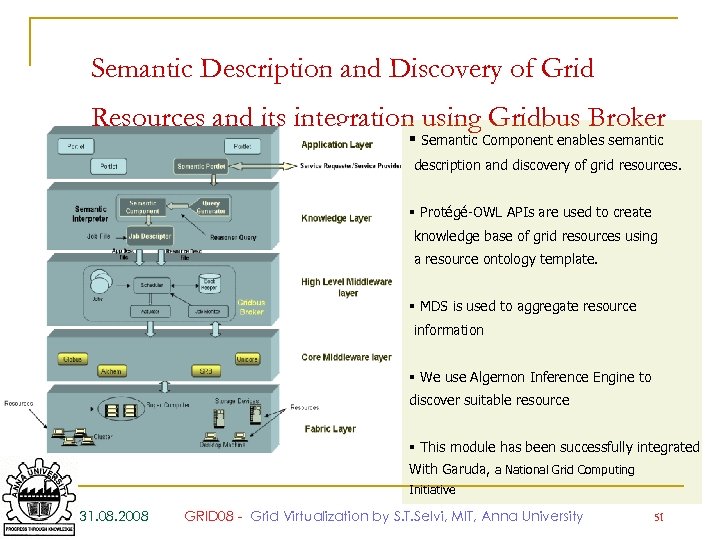
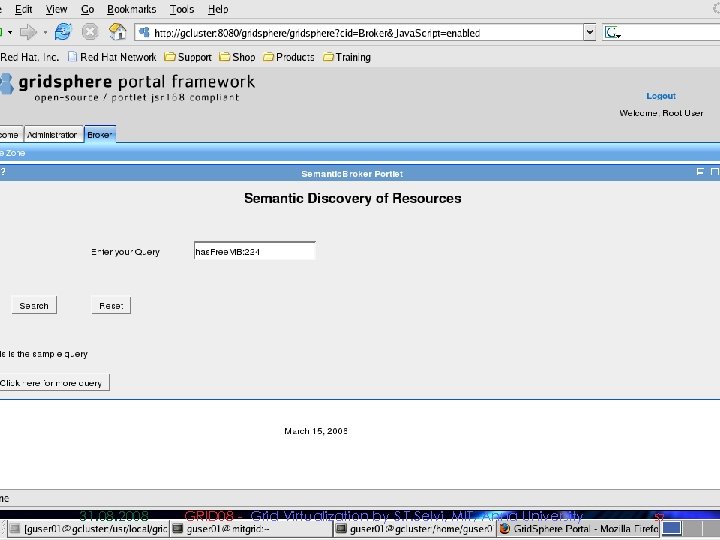
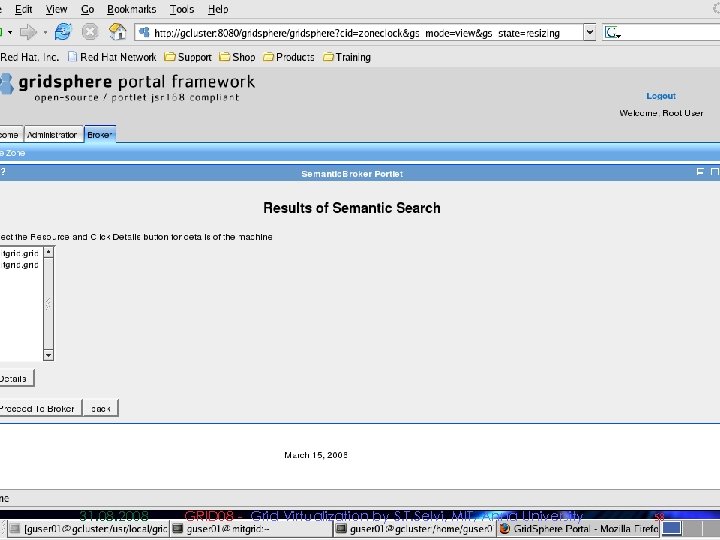
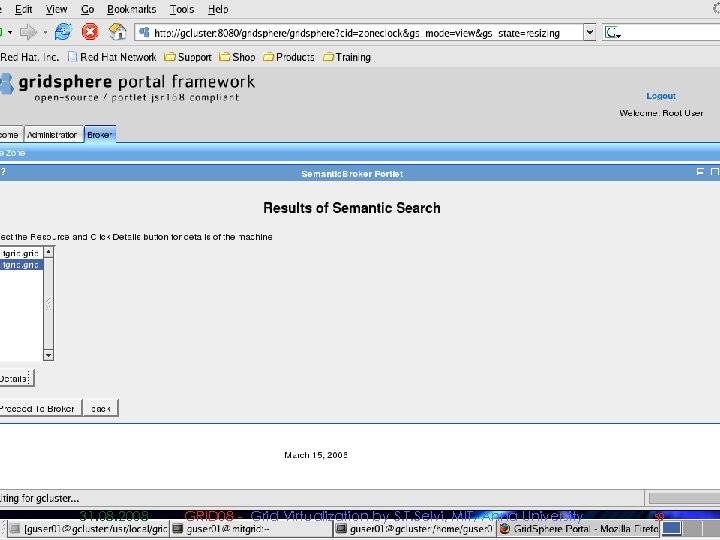
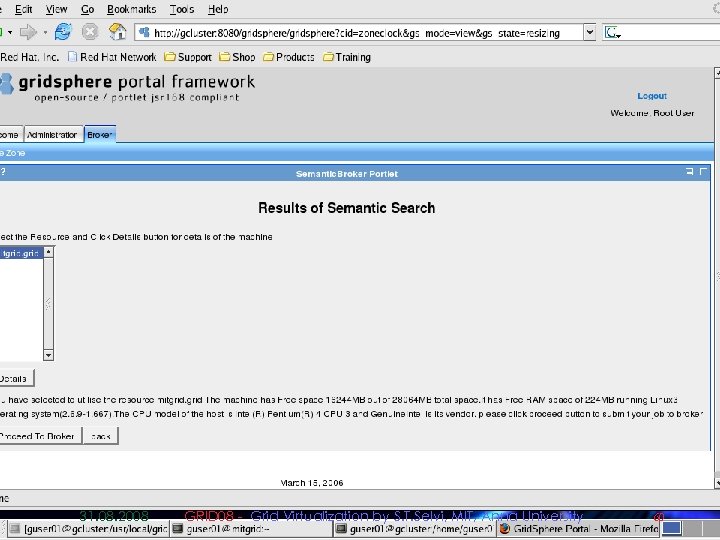
Semantic Description and Discovery of Grid Resources and its integration using Gridbus Broker § Semantic Component enables semantic description and discovery of grid resources. § Protégé-OWL APIs are used to create knowledge base of grid resources using a resource ontology template. § MDS is used to aggregate resource information § We use Algernon Inference Engine to discover suitable resource § This module has been successfully integrated With Garuda, a National Grid Computing Initiative 31. 08. 2008 GRID 08 - Grid Virtualization by S. T. Selvi, MIT, Anna University 51

Deployment in Garuda Grid n Semantic component has been deployed in Garuda Grid 31. 08. 2008 GRID 08 - Grid Virtualization by S. T. Selvi, MIT, Anna University 52

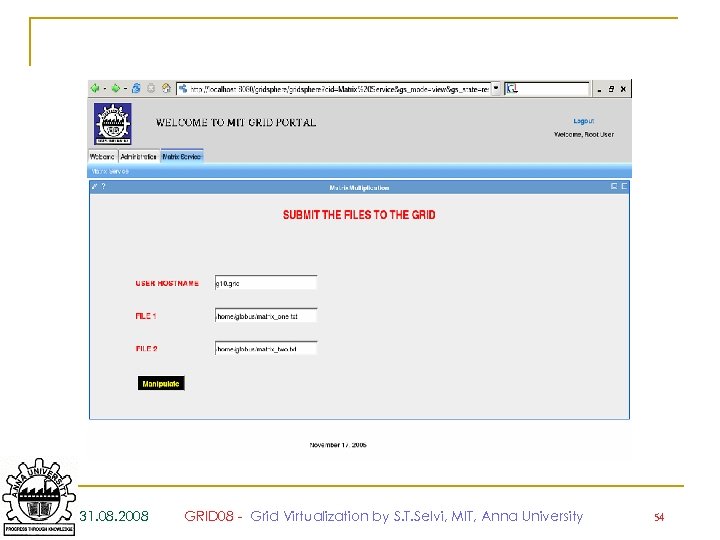
Sample Screenshots 31. 08. 2008 GRID 08 - Grid Virtualization by S. T. Selvi, MIT, Anna University 53
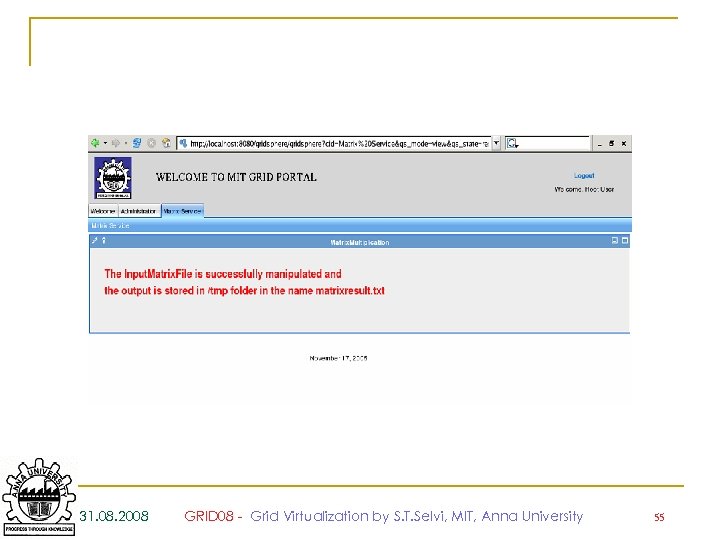
31. 08. 2008 GRID 08 - Grid Virtualization by S. T. Selvi, MIT, Anna University 54
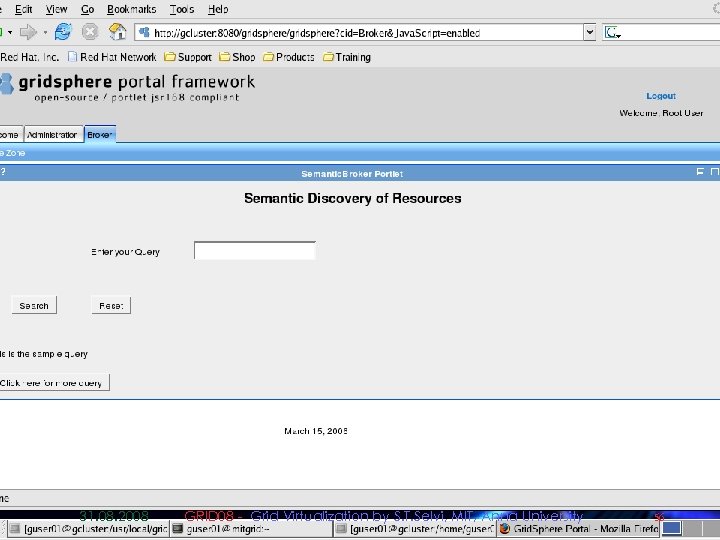
31. 08. 2008 GRID 08 - Grid Virtualization by S. T. Selvi, MIT, Anna University 55
31. 08. 2008 GRID 08 - Grid Virtualization by S. T. Selvi, MIT, Anna University 56
31. 08. 2008 GRID 08 - Grid Virtualization by S. T. Selvi, MIT, Anna University 57
31. 08. 2008 GRID 08 - Grid Virtualization by S. T. Selvi, MIT, Anna University 58
31. 08. 2008 GRID 08 - Grid Virtualization by S. T. Selvi, MIT, Anna University 59
31. 08. 2008 GRID 08 - Grid Virtualization by S. T. Selvi, MIT, Anna University 60
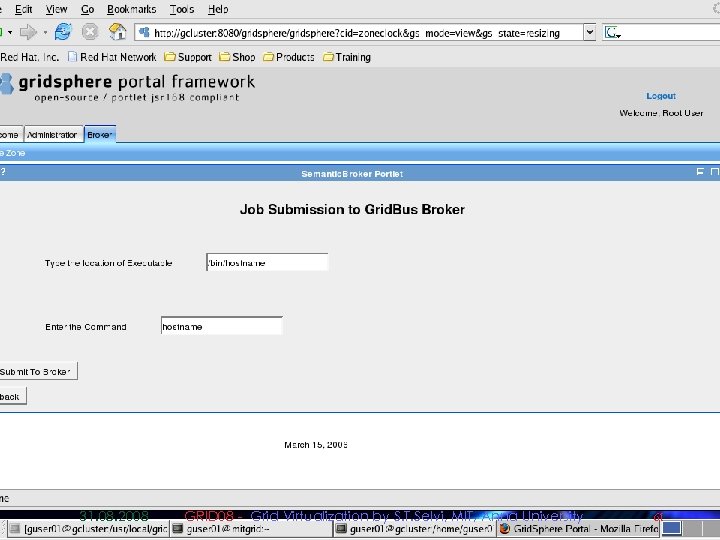
31. 08. 2008 GRID 08 - Grid Virtualization by S. T. Selvi, MIT, Anna University 61

31. 08. 2008 GRID 08 - Grid Virtualization by S. T. Selvi, MIT, Anna University 62

Contact E-Mail: stselvi@annauniv. edu Web site: www. annauniv. edu/care 31. 08. 2008 GRID 08 - Grid Virtualization by S. T. Selvi, MIT, Anna University 63

31. 08. 2008 GRID 08 - Grid Virtualization by S. T. Selvi, MIT, Anna University 64
c5c7713673c932e5f7451817fe0f8c02.ppt