a566f26f9d451d4b7d386bb70e2f023f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 29

Virtual Private Networks Globalizing LANs Timothy Hohman

What is A VPN? ► Tell me about it Microsoft: § “A virtual private network (VPN) is the extension of a private network that encompasses links across shared or public networks like the Internet. ” (Microsoft, 2001) ► It provides LAN access to end systems not physically located on the LAN ► An alternative to WAN (Wide Area Networks) which use leased lines to connect
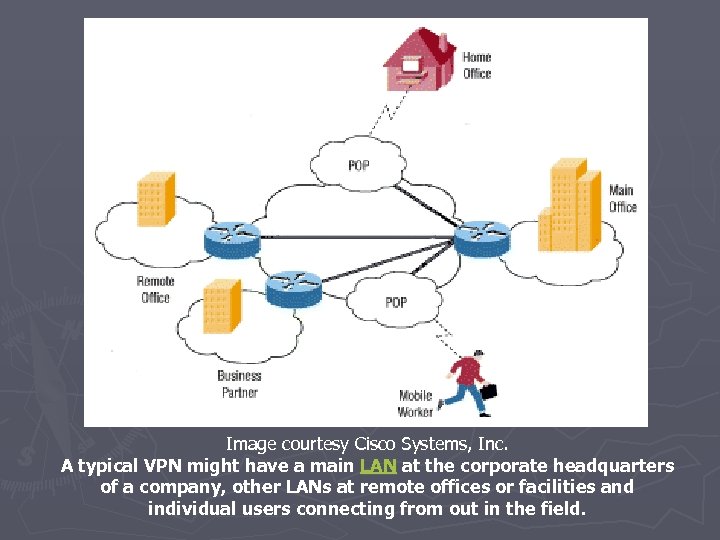
Image courtesy Cisco Systems, Inc. A typical VPN might have a main LAN at the corporate headquarters of a company, other LANs at remote offices or facilities and individual users connecting from out in the field.

How does it work? ► Data is encrypted (cannot be deciphered without the key) ► Virtual Point to Point Connection § To the user, it acts like a point to point connection ► Data is packaged with a header

Benefits of Using VPN Expand Globally ► Costs reduced ► § No dedicated lines necessary Easier ► Technology is on the end systems, which makes it more scalable ► No single point of failure ► Easier Network Management ►

Types of VPN ► Two Types: § Site to Site VPN § Remote Access VPN

Remote Access VPN ► Essentially provides LAN access through dial -up connection § Typically done by purchasing a NAS (Network Access Server) with a toll free number § Can instead be done through normal ISP connection using the VPN software to make a virtual connection to the LAN

Site to Site VPN ► Connects two LANs over local ISP connections ► Very useful if you need to connect a branch to a main hub (Big business) ► Much less expensive than purchasing one dedicated line between the hub and branch ► Intranet connects remote locations from one company Extranet connects two companies (partners) into one shared Private Network
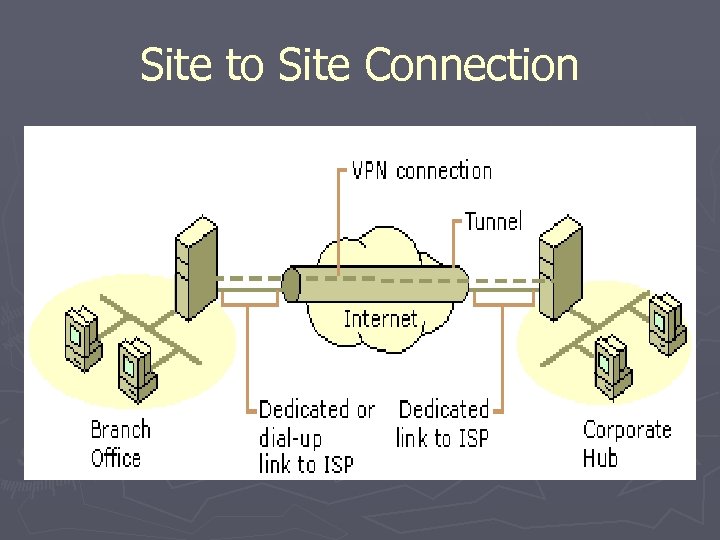
Site to Site Connection

Two Ways to “Get it Done” ► Two Tunneling protocols can be used § PPTP (Point to Point Tunneling Protocol) § L 2 TP (Layer Two Tunneling Protocol) § Tunneling encapsulates frames in an extra header to be passed over the internet appearing as normal frames. The process includes: ►Encapsulation Decapsulation (adding extra frame), transmission,

Tunneling Protocols ► Both of these protocols support these methods: § User Authentication § Token Card Support (one time passwords) § Dynamic Address Assignment § Data Compression § Data Encryption § Key Management § Multi-protocol Support
Tunneling Protocols cont. ► Each are built on PPP (Point to Point Protocol) § 4 Phases ► 1) Link Establishment - a physical link between ends ► 2) User Authentication – Password protocols used § PAP, CHAP, MS-CHAP ► 3) Call Back Control – optional § Disconnects and server calls back after authentication ► 4) Data Transfer Phase – exactly what it sounds like
Tunneling Protocols cont. ► PPTP § Uses IP datagrams for encapsulation § Uses TCP for tunnel maintenance § Uses encryption and compression ► L 2 TP § Encapsulation in IP, ATM, Frame Relay, X. 25 ►IP when going over internet § UDP used for tunnel maintenance

Advantages ► PPTP: § § § No certificate infrastructure Can be used on more operating systems Can operate behind NATs ► L 2 TP: § More tools to guarantee packet integrity and data security § Require user and computer certificates § PPP authentication is encrypted (takes place after IP security check)

Security ► Many types of Security are offered including: § Firewalls § Encryption § IPSec § Certificates § AAA servers

Firewalls ► Can be used with VPN is right technology is set up on the router § Cisco 1700 router for example ► Can restrict: § The type of data being transferred § The number of ports open § Which protocols are allowed through

Encryption ► Symmetric Key Encryption (private key) § All communicating computers use the same key stored on their computer ► Asymmetric Key Encryption § Uses a Private key and a Public Key ►Private key on local computer ►Public key sent out to anyone who you want to communicate with ►Mathematically related through encryption algorithm ►Both must be used to decrypt anything sent

IPSec ► Made up of two parts § Authentication Header ►Verify data integrity § Encapsulation Security Payload ►Data integrity ►Data encryption
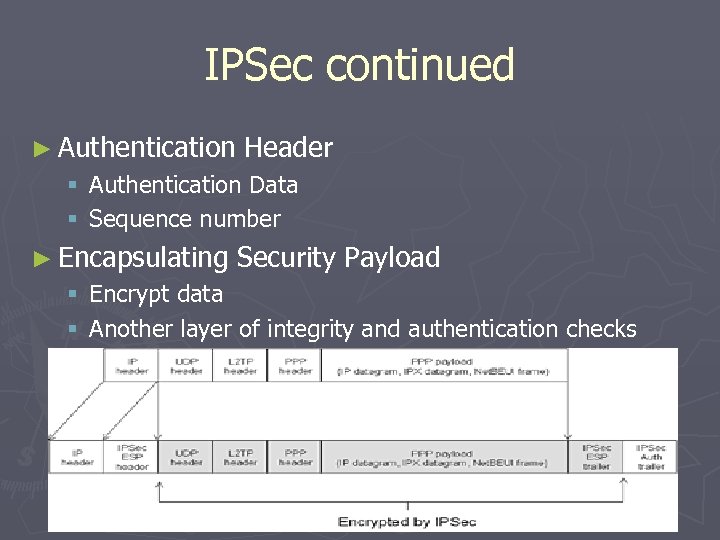
IPSec continued ► Authentication Header § Authentication Data § Sequence number ► Encapsulating Security Payload § Encrypt data § Another layer of integrity and authentication checks

Certificates ► Used alongside public keys § Contains: ► Certificate Name ► Owner of the public key ► Public key itself ► Expiration date ► Certificate authority § Verifies that information is coming from the private key § Can be distributed on disks, smart cards, or electronically

AAA Servers ► Authentication, Authorization, Accounting § These advanced servers ask each user who they are, what they are allowed to do, and what the actually want to do each time they connect § This allows the LAN to track usage from dial up connections and closely monitor those remotely connected as they would those physically connected.

How can I get this up and running? ► You need: § Software on each end system ►Windows: PPTP § Dedicated hardware (firewalls, routers, etc. ) § Dedicated VPN server § May need NAS

A Hardware Example ► http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=lq- Sh. HMof. EQ

An Example of VPN in Action ► 2001, CISCO direct-connect company filed for bankruptcy ► Changing over the 9000 employees to different direct-connect companies would be very costly and take 10 times the available staff to pull off

The VPN Solution User managed solution based on VPN software ► Users provide own internet connection ► Cisco provided IT support for VPN problems and provide gateway from internet to CISCO network ►

Benefits of the Change ► Productivity ► Employee Satisfaction § Able to work from home, making home work balance easier ► Globalization ► Flexibility ► Easier when letting employees go § Ex-employees do not have to have their dedicated line removed, rather they just lose Authentication to AAA server ► Cost, cost

Things to Come ► Expansion § China and India ► Faster Upgrades § Use of Microsoft installer ► Better encryption § Advanced encryption standard ► Better compression ► Voice and Video or VPN

Things to come cont. ► Wireless vendor support § Access to employees from anywhere ► PDA support § Possible software packages to be used on PDAs ► Hardware for home client § As shown in previous clip

References ► ► ► Cisco Systems (2004). Cisco VPN Client Brings Flexibility and Cost Reduction to Cisco Remote Access Solution. Retrieved from: http: //www. cisco. com/web/about/ciscoitatwork/downloads/ciscoitatwor k/pdf/Cisco_IT_Case_Study_VPN_Client_print. pdf Jeff Tyson (2007). How Virtual Private Network Work. Retrieved from: http: //computer. howstuffworks. com/vpn. htm Barrel, Matthew D. (2006). Take your network anywhere. PC Magazine, 25(21), p 122 -122. Calin, Doru; Mc. Gee, Andrew R. ; Chandrashekhar, Uma; Prasad, Ramjee (2006). MAGNET: An approach for secure personal networking in beyond 3 g wireless networks. Bell Labs Technical Journal, 11(1), pp. 79 – 98. Tanner, John C. (2006). Ethernet rides the NGN wave. America’s Network, 110(2), pp. 40 -43.
a566f26f9d451d4b7d386bb70e2f023f.ppt