0b13fdc17ab0a6e2e7684fd62eb7940a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 16
 Virtual Organization Approach for Running HEP Applications in Grid Environment Łukasz Skitał1, Łukasz Dutka 1, Renata Słota 2, Krzysztof Korcyl 3, Maciej Janusz 2, Jacek Kitowski 1, 2 1 ACC CYFRONET AGH, Cracow 2 Institute of Computer Science AGH-UST, Cracow 3 Institute of Nuclear Physics PAN, Cracow Institute of Computer Science AGH-UST
Virtual Organization Approach for Running HEP Applications in Grid Environment Łukasz Skitał1, Łukasz Dutka 1, Renata Słota 2, Krzysztof Korcyl 3, Maciej Janusz 2, Jacek Kitowski 1, 2 1 ACC CYFRONET AGH, Cracow 2 Institute of Computer Science AGH-UST, Cracow 3 Institute of Nuclear Physics PAN, Cracow Institute of Computer Science AGH-UST
 Outline n n Introduction Application Requirements ¨ Architecture ¨ n Virtual Organization Requirements ¨ Certification ¨ Monitoring ¨ Dynamic Processing Tasks Pool ¨ n Summary/Conclusions
Outline n n Introduction Application Requirements ¨ Architecture ¨ n Virtual Organization Requirements ¨ Certification ¨ Monitoring ¨ Dynamic Processing Tasks Pool ¨ n Summary/Conclusions
 Introduction n n Part of int. eu. grid project State of Art. – current interactive applications in GRID Crossgrid ¨ Reality Grid ¨ Grid. PP ¨ n Why grid? Gain more resources ¨ Use resources for different purposes when ATLAS is off ¨ n Why VO? ¨ n Provides stable, but dynamic environment for an application HEP application is to process all events without any loss of data
Introduction n n Part of int. eu. grid project State of Art. – current interactive applications in GRID Crossgrid ¨ Reality Grid ¨ Grid. PP ¨ n Why grid? Gain more resources ¨ Use resources for different purposes when ATLAS is off ¨ n Why VO? ¨ n Provides stable, but dynamic environment for an application HEP application is to process all events without any loss of data
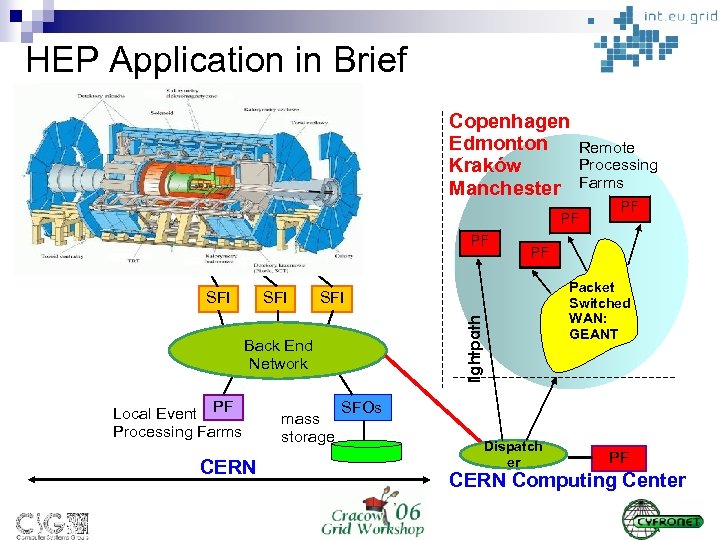 HEP Application in Brief Copenhagen Edmonton Kraków Manchester PF PF SFI Local Event PF Processing Farms CERN Packet Switched WAN: GEANT SFI Back End Network mass storage PF PF l i g ht p a t h SFI Remote Processing Farms SFOs Dispatch er PF CERN Computing Center
HEP Application in Brief Copenhagen Edmonton Kraków Manchester PF PF SFI Local Event PF Processing Farms CERN Packet Switched WAN: GEANT SFI Back End Network mass storage PF PF l i g ht p a t h SFI Remote Processing Farms SFOs Dispatch er PF CERN Computing Center
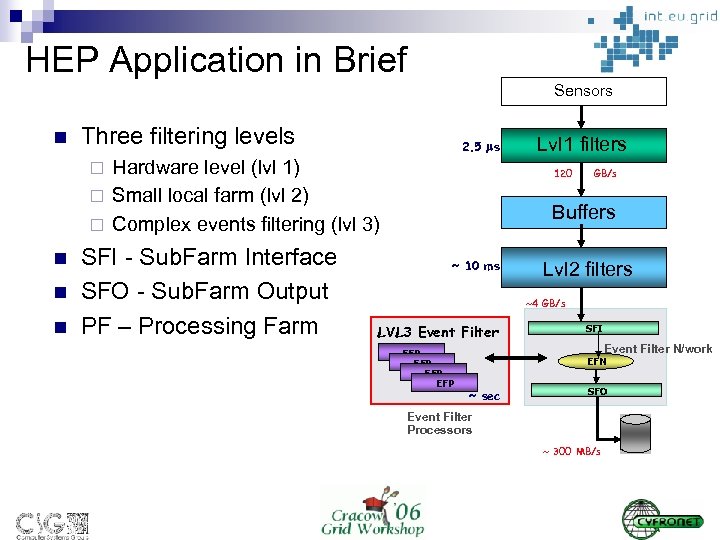 HEP Application in Brief Sensors n Three filtering levels 2. 5 s Hardware level (lvl 1) ¨ Small local farm (lvl 2) ¨ Complex events filtering (lvl 3) ¨ n n n SFI - Sub. Farm Interface SFO - Sub. Farm Output PF – Processing Farm Lvl 1 filters 120 GB/s Buffers ~ 10 ms Lvl 2 filters ~4 GB/s LVL 3 Event Filter EFP EFP SFI Event Filter N/work EFN ~ sec SFO Event Filter Processors ~ 300 MB/s
HEP Application in Brief Sensors n Three filtering levels 2. 5 s Hardware level (lvl 1) ¨ Small local farm (lvl 2) ¨ Complex events filtering (lvl 3) ¨ n n n SFI - Sub. Farm Interface SFO - Sub. Farm Output PF – Processing Farm Lvl 1 filters 120 GB/s Buffers ~ 10 ms Lvl 2 filters ~4 GB/s LVL 3 Event Filter EFP EFP SFI Event Filter N/work EFN ~ sec SFO Event Filter Processors ~ 300 MB/s
 HEP Requirements n n Real-time application High throughput (estimated) ¨ ¨ n 3500 event per second 1. 5 MB per event Average 1 second to compute one event on typical processor Infrastructure monitoring (for load balancing) Efficient way to distribute events to worker nodes ¨ Grid job submission mechanism is not sufficient n n n Simple job submission takes minutes Have seconds. . . Failure recovery ¨ ¨ ¨ Malfunctions of single nodes are acceptable, but have to be detected Application monitoring Infrastructure monitoring (for availability checks)
HEP Requirements n n Real-time application High throughput (estimated) ¨ ¨ n 3500 event per second 1. 5 MB per event Average 1 second to compute one event on typical processor Infrastructure monitoring (for load balancing) Efficient way to distribute events to worker nodes ¨ Grid job submission mechanism is not sufficient n n n Simple job submission takes minutes Have seconds. . . Failure recovery ¨ ¨ ¨ Malfunctions of single nodes are acceptable, but have to be detected Application monitoring Infrastructure monitoring (for availability checks)
 HEP application integration with GRID n n Job submission for each event is too slow Job submission for bunch of event is still too slow We need interactive communication Pilot job idea ¨ ¨ One job to allocate a node and start PT (Processing Task) Dedicated queue in LRMS for HEP pilot jobs (HEP VO) One PT processes many events Direct communication between PT and ATLAS experiment n n ¨ Faster than job submission ATLAS experiment provides event (1. 5 MB/event) PT responds with events analysis results (1 Kb/event) Asynchronous communication with events buffering Limited lifetime of PT to allow dynamic resource allocation n Lifetime set by queue or PT configuration
HEP application integration with GRID n n Job submission for each event is too slow Job submission for bunch of event is still too slow We need interactive communication Pilot job idea ¨ ¨ One job to allocate a node and start PT (Processing Task) Dedicated queue in LRMS for HEP pilot jobs (HEP VO) One PT processes many events Direct communication between PT and ATLAS experiment n n ¨ Faster than job submission ATLAS experiment provides event (1. 5 MB/event) PT responds with events analysis results (1 Kb/event) Asynchronous communication with events buffering Limited lifetime of PT to allow dynamic resource allocation n Lifetime set by queue or PT configuration
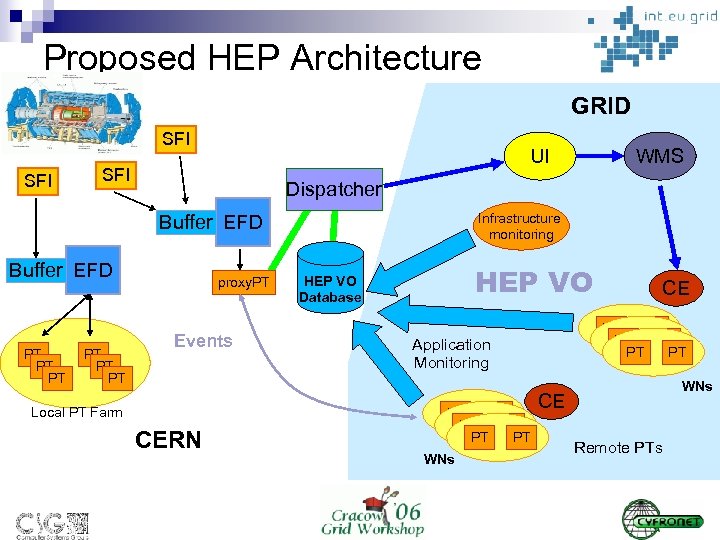 Proposed HEP Architecture GRID SFI UI SFI Dispatcher Infrastructure monitoring Buffer EFD PT PT PT WMS proxy. PT Events Local PT Farm CERN HEP VO Database PT PT PT Application Monitoring PT PT PT WNs CE Remote PTs
Proposed HEP Architecture GRID SFI UI SFI Dispatcher Infrastructure monitoring Buffer EFD PT PT PT WMS proxy. PT Events Local PT Farm CERN HEP VO Database PT PT PT Application Monitoring PT PT PT WNs CE Remote PTs
 Components n EFD (Event Filter Dataflow) ¨ ¨ ¨ n Processing Task (PT) ¨ ¨ n Coordinates task distribution from EFD to PTs Infrastructure Monitoring ¨ n Interface to remote PT Dispatcher ¨ n Runs on worker nodes (WNs) Process events and answers with short analysis data Proxy. PT ¨ n Takes event from SFI and place them in local buffer Events are distributed to PT (local or remote) Depending on PT's answer event is stored or flushed Network load/status, WNs status Application Monitoring ¨ PT application state
Components n EFD (Event Filter Dataflow) ¨ ¨ ¨ n Processing Task (PT) ¨ ¨ n Coordinates task distribution from EFD to PTs Infrastructure Monitoring ¨ n Interface to remote PT Dispatcher ¨ n Runs on worker nodes (WNs) Process events and answers with short analysis data Proxy. PT ¨ n Takes event from SFI and place them in local buffer Events are distributed to PT (local or remote) Depending on PT's answer event is stored or flushed Network load/status, WNs status Application Monitoring ¨ PT application state
 HEP Virtual Organization n Purpose Provides runtime environment for HEP application ¨ Fulfills application’s requirements ¨ Realizes site certification process ¨ n Architecture ¨ High level (static) - sites n n ¨ Certification Agreements Configuration guidelines Functional tests Low level (dynamic) - resources n n Runtime environment Dynamic resource allocation Monitoring and failover Load balancing
HEP Virtual Organization n Purpose Provides runtime environment for HEP application ¨ Fulfills application’s requirements ¨ Realizes site certification process ¨ n Architecture ¨ High level (static) - sites n n ¨ Certification Agreements Configuration guidelines Functional tests Low level (dynamic) - resources n n Runtime environment Dynamic resource allocation Monitoring and failover Load balancing
 Site certification - Requirements n n n Long-term ability to provide services and resources Legal issues/agreements LRMS configuration ¨ n Dedicated high priority (but short) queues on computing elements for jobs from HEP VO Ability to safely communicate between site's WNs and CERN HEP nodes: Opened specified port on CERN side ¨ Opened specified port on site side ¨ Trusted proxy to setup two way communication ¨ Channel encryption ¨
Site certification - Requirements n n n Long-term ability to provide services and resources Legal issues/agreements LRMS configuration ¨ n Dedicated high priority (but short) queues on computing elements for jobs from HEP VO Ability to safely communicate between site's WNs and CERN HEP nodes: Opened specified port on CERN side ¨ Opened specified port on site side ¨ Trusted proxy to setup two way communication ¨ Channel encryption ¨
 HEP VO site operation process n Certification phase Long term tests for reliability performance and updates (application, databases) ¨ Sites tested using artificial/calibration data ¨ Communication between site's WNs and CERN HEP nodes ¨ n Operation phase with runtime environment monitoring Operates on production data ¨ Checks during PTs startup ¨ n Proper environment, up-to-date application, databases, etc. Infrastructure and application monitoring ¨ Dynamic resource allocation ¨ Excluding nodes/sites which are frequently unavailable ¨ n Temporary excluded sites/nodes can not process real data, but they can still receive test jobs
HEP VO site operation process n Certification phase Long term tests for reliability performance and updates (application, databases) ¨ Sites tested using artificial/calibration data ¨ Communication between site's WNs and CERN HEP nodes ¨ n Operation phase with runtime environment monitoring Operates on production data ¨ Checks during PTs startup ¨ n Proper environment, up-to-date application, databases, etc. Infrastructure and application monitoring ¨ Dynamic resource allocation ¨ Excluding nodes/sites which are frequently unavailable ¨ n Temporary excluded sites/nodes can not process real data, but they can still receive test jobs
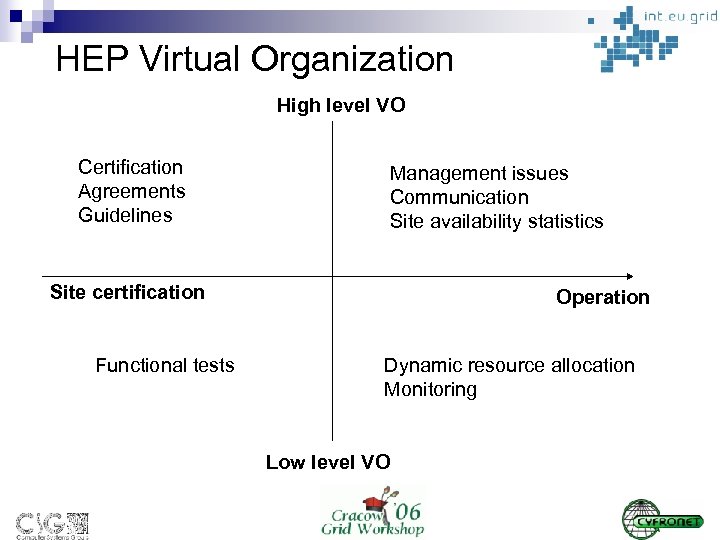 HEP Virtual Organization High level VO Certification Agreements Guidelines Management issues Communication Site availability statistics Site certification Functional tests Operation Dynamic resource allocation Monitoring Low level VO
HEP Virtual Organization High level VO Certification Agreements Guidelines Management issues Communication Site availability statistics Site certification Functional tests Operation Dynamic resource allocation Monitoring Low level VO
 Monitoring for HEP VO n Takes advantage of monitoring ¨ Monitoring using external tools ¨ Application Monitoring (with tool like J-OCM): n n provides information about current execution status n ¨ deployed on every worker node running HEP PT monitors computation time JIMS for Infrastructure Monitoring n n load of worker node n free memory n n availability of worker node network throughput between CERN and remote computing farm Failover
Monitoring for HEP VO n Takes advantage of monitoring ¨ Monitoring using external tools ¨ Application Monitoring (with tool like J-OCM): n n provides information about current execution status n ¨ deployed on every worker node running HEP PT monitors computation time JIMS for Infrastructure Monitoring n n load of worker node n free memory n n availability of worker node network throughput between CERN and remote computing farm Failover
 Dynamic resource allocation n Dynamic Processing Tasks pool Malfunctioning PT excluded from runtime environment (low level VO) PT lifetime limited by queue length (walltime) each ‘normal’ job has it’s own lifetime specified before execution ¨ ‘interactive’ type of job ¨ pool has to be refreshed periodically ¨ n Fair sharing of resources
Dynamic resource allocation n Dynamic Processing Tasks pool Malfunctioning PT excluded from runtime environment (low level VO) PT lifetime limited by queue length (walltime) each ‘normal’ job has it’s own lifetime specified before execution ¨ ‘interactive’ type of job ¨ pool has to be refreshed periodically ¨ n Fair sharing of resources
 Summary, conclusions n n n High/Low-level VO Site certification and software validation for HEP application HEP oriented site functionality tests On-line validation of site configuration Statistical analysis of HEP processing Dynamic Processing Task Pool
Summary, conclusions n n n High/Low-level VO Site certification and software validation for HEP application HEP oriented site functionality tests On-line validation of site configuration Statistical analysis of HEP processing Dynamic Processing Task Pool


