55810ff3179dec3f06afa4265051e4b3.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 23
 Virtual Agents for Social Tutoring Honours Project in Computer Science By Marissa Milne Artificial Intelligence Laboratory
Virtual Agents for Social Tutoring Honours Project in Computer Science By Marissa Milne Artificial Intelligence Laboratory
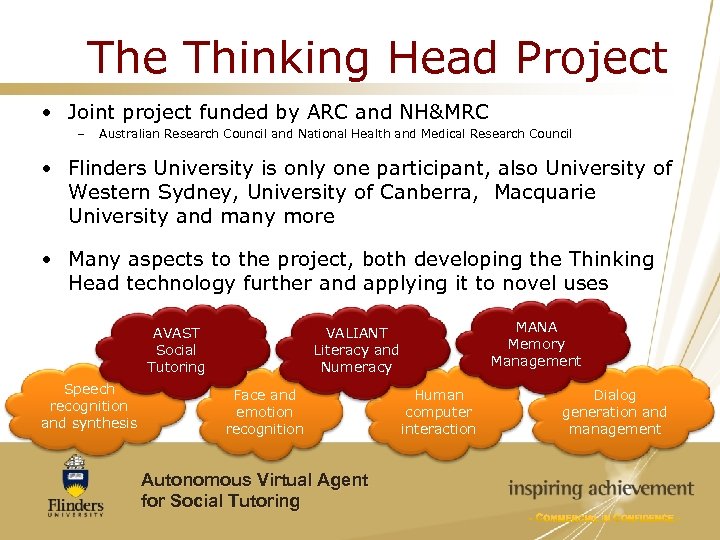 The Thinking Head Project • Joint project funded by ARC and NH&MRC – Australian Research Council and National Health and Medical Research Council • Flinders University is only one participant, also University of Western Sydney, University of Canberra, Macquarie University and many more • Many aspects to the project, both developing the Thinking Head technology further and applying it to novel uses AVAST Social Tutoring Speech recognition and synthesis MANA Memory Management VALIANT Literacy and Numeracy Face and emotion recognition Autonomous Virtual Agent for Social Tutoring Human computer interaction Dialog generation and management
The Thinking Head Project • Joint project funded by ARC and NH&MRC – Australian Research Council and National Health and Medical Research Council • Flinders University is only one participant, also University of Western Sydney, University of Canberra, Macquarie University and many more • Many aspects to the project, both developing the Thinking Head technology further and applying it to novel uses AVAST Social Tutoring Speech recognition and synthesis MANA Memory Management VALIANT Literacy and Numeracy Face and emotion recognition Autonomous Virtual Agent for Social Tutoring Human computer interaction Dialog generation and management
 Origins of AVAST Autonomous Virtual Agents for Social Tutoring • Suggested by Novita for hearing impaired children – Prototype focuses on children with autism – Proposal for future development includes a range of special needs, including hearing impaired children • Prototype is one of the first practical applications of the Thinking Head technology Autonomous Virtual Agent for Social Tutoring
Origins of AVAST Autonomous Virtual Agents for Social Tutoring • Suggested by Novita for hearing impaired children – Prototype focuses on children with autism – Proposal for future development includes a range of special needs, including hearing impaired children • Prototype is one of the first practical applications of the Thinking Head technology Autonomous Virtual Agent for Social Tutoring
 Why Virtual Agents? • Individuals with ASD often enjoy computers • Always available for practice • Consistent and predictable • Can control level of complexity – lesson content – appearance of people and interface • Can aid generalisation – e. g. variety of virtual people to practice reading facial expressions with • Learner can work at their own pace Autonomous Virtual Agent for Social Tutoring
Why Virtual Agents? • Individuals with ASD often enjoy computers • Always available for practice • Consistent and predictable • Can control level of complexity – lesson content – appearance of people and interface • Can aid generalisation – e. g. variety of virtual people to practice reading facial expressions with • Learner can work at their own pace Autonomous Virtual Agent for Social Tutoring
 Why Virtual Agents? • Children with ASD have difficulties with social skills – Children need help in recognizing social cues – Children need scaffolding in learning to avoid being overwhelmed by information • Interacting with a computerized avatar is less threatening – Computerized avatar can be arbitrarily human- or cartoon-like – Children often have an enthusiasm for computers/cartoons • Interacting with a computer conserves human resources – Therapists can specify computerized programs and interventions – A computer is non-threatening and non-judgmental Autonomous Virtual Agent for Social Tutoring
Why Virtual Agents? • Children with ASD have difficulties with social skills – Children need help in recognizing social cues – Children need scaffolding in learning to avoid being overwhelmed by information • Interacting with a computerized avatar is less threatening – Computerized avatar can be arbitrarily human- or cartoon-like – Children often have an enthusiasm for computers/cartoons • Interacting with a computer conserves human resources – Therapists can specify computerized programs and interventions – A computer is non-threatening and non-judgmental Autonomous Virtual Agent for Social Tutoring
 Existing Virtual Peer Interventions • Autonomous versus Authorable virtual peers • Sam: authorable for social skills (Tartaro and Cassell 2008) • Baldi and Timo: autonomous for vocabulary development (Bosseler and Massaro 2003) Autonomous Virtual Agent for Social Tutoring
Existing Virtual Peer Interventions • Autonomous versus Authorable virtual peers • Sam: authorable for social skills (Tartaro and Cassell 2008) • Baldi and Timo: autonomous for vocabulary development (Bosseler and Massaro 2003) Autonomous Virtual Agent for Social Tutoring
 Lesson Content Motivation: Difficulty reading non-verbal cues ‘Theory of Mind’ issues – trouble understanding that other people do not always feel the way they do Can lack social skills needed to make friends – exposed to bullies Choices: Conversation Skills Recognising faces indicating boredom, interest or turn requesting behaviour and choosing appropriate actions to take Dealing with Bullying Discriminating between friendly/bullying behaviour and laughing with/laughing at Learning a simple 3 step strategy to deal with bullying Autonomous Virtual Agent for Social Tutoring
Lesson Content Motivation: Difficulty reading non-verbal cues ‘Theory of Mind’ issues – trouble understanding that other people do not always feel the way they do Can lack social skills needed to make friends – exposed to bullies Choices: Conversation Skills Recognising faces indicating boredom, interest or turn requesting behaviour and choosing appropriate actions to take Dealing with Bullying Discriminating between friendly/bullying behaviour and laughing with/laughing at Learning a simple 3 step strategy to deal with bullying Autonomous Virtual Agent for Social Tutoring
 Design Considerations Sensory tolerance Keep interface simple, avoid unnecessary use of colour, sound, movement, etc. . Communication impairments Use of icons to facilitate understanding Allow for different interaction options Keep dialogue simple Able to read aloud displayed options or repeat last question Generalisation Each of the three rounds is presented by a different tutor Some randomization in generation of dialogue Autonomous Virtual Agent for Social Tutoring
Design Considerations Sensory tolerance Keep interface simple, avoid unnecessary use of colour, sound, movement, etc. . Communication impairments Use of icons to facilitate understanding Allow for different interaction options Keep dialogue simple Able to read aloud displayed options or repeat last question Generalisation Each of the three rounds is presented by a different tutor Some randomization in generation of dialogue Autonomous Virtual Agent for Social Tutoring
 Preliminary Evaluation • Evaluation of facial expressions with typically developed adults – Participants watched a virtual person display expressions while listening to a story – Provided with open ended questions then multiple choice questions – Results indicated that facial expressions used in the tutoring software were appropriate Autonomous Virtual Agent for Social Tutoring
Preliminary Evaluation • Evaluation of facial expressions with typically developed adults – Participants watched a virtual person display expressions while listening to a story – Provided with open ended questions then multiple choice questions – Results indicated that facial expressions used in the tutoring software were appropriate Autonomous Virtual Agent for Social Tutoring
 Expression Demonstration Bored Interested Autonomous Virtual Agent for Social Tutoring Wanting to Talk
Expression Demonstration Bored Interested Autonomous Virtual Agent for Social Tutoring Wanting to Talk
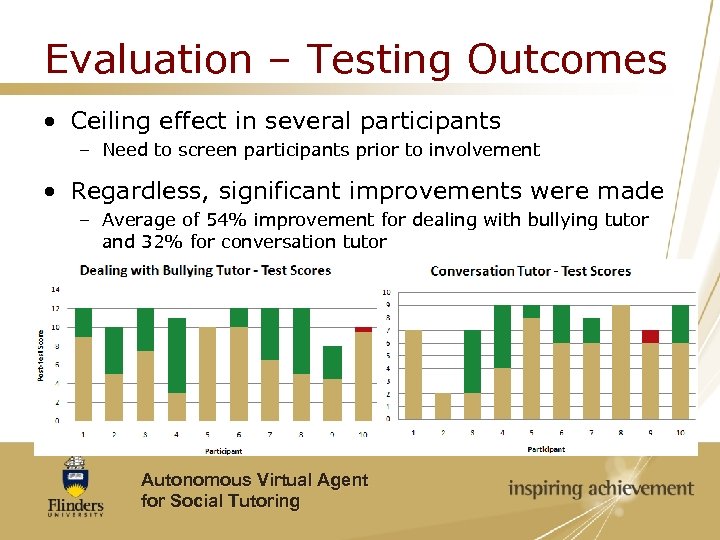 Evaluation – Testing Outcomes • Ceiling effect in several participants – Need to screen participants prior to involvement • Regardless, significant improvements were made – Average of 54% improvement for dealing with bullying tutor and 32% for conversation tutor Autonomous Virtual Agent for Social Tutoring
Evaluation – Testing Outcomes • Ceiling effect in several participants – Need to screen participants prior to involvement • Regardless, significant improvements were made – Average of 54% improvement for dealing with bullying tutor and 32% for conversation tutor Autonomous Virtual Agent for Social Tutoring
 Evaluation - Survey Outcomes (1 = strongly disagree, 7 = strongly agree) 1. Program was easy to use 2. Program was fun to use 3. It was easy to understand what the virtual tutors said 4. It was easy to understand what to do 5. The tutors were friendly 6. The program helped me to learn 7. What did you like best about the program? 8. What did you like least about the program? 9. Would you change anything about the program? If yes, what? Autonomous Virtual Agent for Social Tutoring Average score above ‘neutral’ midpoint for all questions Mode of 6 or more for all questions except for Question 6 in the Dealing with Bullying tutor.
Evaluation - Survey Outcomes (1 = strongly disagree, 7 = strongly agree) 1. Program was easy to use 2. Program was fun to use 3. It was easy to understand what the virtual tutors said 4. It was easy to understand what to do 5. The tutors were friendly 6. The program helped me to learn 7. What did you like best about the program? 8. What did you like least about the program? 9. Would you change anything about the program? If yes, what? Autonomous Virtual Agent for Social Tutoring Average score above ‘neutral’ midpoint for all questions Mode of 6 or more for all questions except for Question 6 in the Dealing with Bullying tutor.
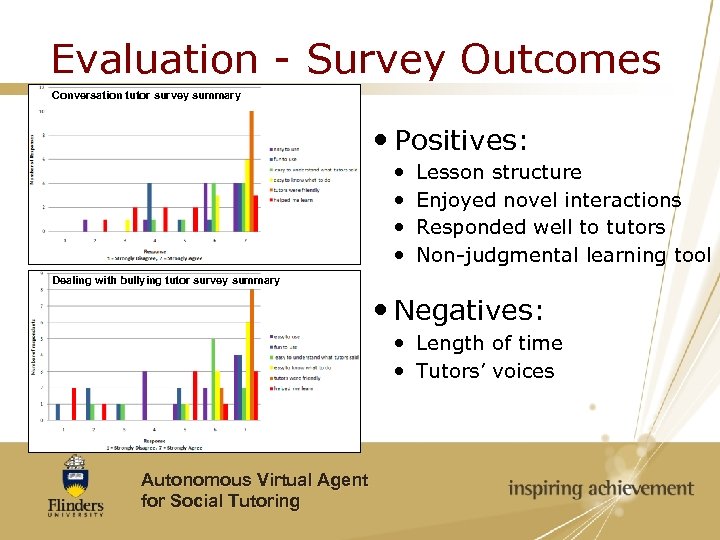 Evaluation - Survey Outcomes Conversation tutor survey summary Positives: Lesson structure Enjoyed novel interactions Responded well to tutors Non-judgmental learning tool Dealing with bullying tutor survey summary Negatives: Length of time Tutors’ voices Autonomous Virtual Agent for Social Tutoring
Evaluation - Survey Outcomes Conversation tutor survey summary Positives: Lesson structure Enjoyed novel interactions Responded well to tutors Non-judgmental learning tool Dealing with bullying tutor survey summary Negatives: Length of time Tutors’ voices Autonomous Virtual Agent for Social Tutoring
 Future Directions • Progress with the learner – Gradually introduce new content once existing content is sufficiently mastered – Modular social skills training • Can be tailored to different: – Social Contexts • The home, community, peer group – Applications • Social and communication skills learning, friendship skills, real world situations Autonomous Virtual Agent for Social Tutoring
Future Directions • Progress with the learner – Gradually introduce new content once existing content is sufficiently mastered – Modular social skills training • Can be tailored to different: – Social Contexts • The home, community, peer group – Applications • Social and communication skills learning, friendship skills, real world situations Autonomous Virtual Agent for Social Tutoring
 Modelling and Practice • Can demonstrate various social scenarios • Allows child to engage in role-play • Can give feedback on appropriate behaviour • Acts as a companion and helps solve problems • Gives training on how to be a friend • Allows practice of social skills in a group • Children interact with tutors and each other Autonomous Virtual Agent for Social Tutoring
Modelling and Practice • Can demonstrate various social scenarios • Allows child to engage in role-play • Can give feedback on appropriate behaviour • Acts as a companion and helps solve problems • Gives training on how to be a friend • Allows practice of social skills in a group • Children interact with tutors and each other Autonomous Virtual Agent for Social Tutoring
 Unique interface • User interacts with tutor by: – Speaking – Touch screen and natural actions/gestures – Moving physical objects • Human-like conversation: – Engaging – Interpersonal reinforcement – words, facial expression, gentle feedback • One-on-one tutoring/advice: – Monitors activities and offers help if needed Autonomous Virtual Agent for Social Tutoring
Unique interface • User interacts with tutor by: – Speaking – Touch screen and natural actions/gestures – Moving physical objects • Human-like conversation: – Engaging – Interpersonal reinforcement – words, facial expression, gentle feedback • One-on-one tutoring/advice: – Monitors activities and offers help if needed Autonomous Virtual Agent for Social Tutoring
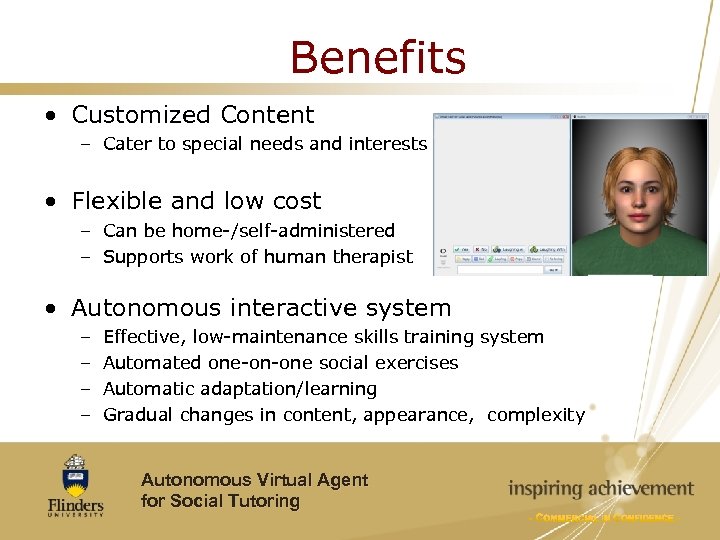 Benefits • Customized Content – Cater to special needs and interests • Flexible and low cost – Can be home-/self-administered – Supports work of human therapist • Autonomous interactive system – – Effective, low-maintenance skills training system Automated one-on-one social exercises Automatic adaptation/learning Gradual changes in content, appearance, complexity Autonomous Virtual Agent for Social Tutoring
Benefits • Customized Content – Cater to special needs and interests • Flexible and low cost – Can be home-/self-administered – Supports work of human therapist • Autonomous interactive system – – Effective, low-maintenance skills training system Automated one-on-one social exercises Automatic adaptation/learning Gradual changes in content, appearance, complexity Autonomous Virtual Agent for Social Tutoring
 Reporting • Can provide reports to caregivers and professionals working with child – Potential to alert to new issues – Make even small gains visible – Can quantify progress by exercise type • Another TH project focuses on detecting gifted and talented in non-typical populations Autonomous Virtual Agent for Social Tutoring
Reporting • Can provide reports to caregivers and professionals working with child – Potential to alert to new issues – Make even small gains visible – Can quantify progress by exercise type • Another TH project focuses on detecting gifted and talented in non-typical populations Autonomous Virtual Agent for Social Tutoring
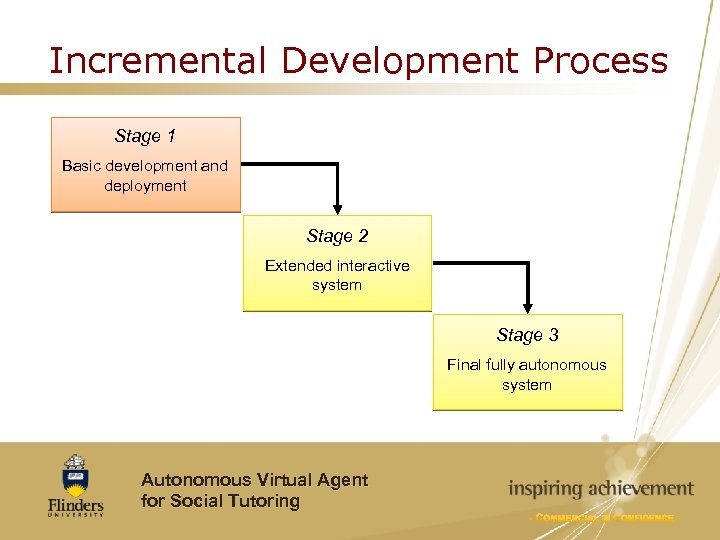 Incremental Development Process Stage 1 Basic development and deployment Stage 2 Extended interactive system Stage 3 Final fully autonomous system Autonomous Virtual Agent for Social Tutoring
Incremental Development Process Stage 1 Basic development and deployment Stage 2 Extended interactive system Stage 3 Final fully autonomous system Autonomous Virtual Agent for Social Tutoring
 Staged Development Process Stage 1 – no/limited camera or microphone use • Text In-Speech Out interactive system • Design and implement pilot modules Stage 2 – speech recognition and adaptation • More complex, less structured interactions • Test with expanded audience Autonomous Virtual Agent for Social Tutoring
Staged Development Process Stage 1 – no/limited camera or microphone use • Text In-Speech Out interactive system • Design and implement pilot modules Stage 2 – speech recognition and adaptation • More complex, less structured interactions • Test with expanded audience Autonomous Virtual Agent for Social Tutoring
 Staged Development Process Stage 3 –non-verbal cues, group interaction • Emotion, speech, face and object recognition • Situation awareness (person, expression, object) • Interface with system by manipulating objects • Group interaction modules ‒ Children interact with each other and tutors in a group • Final system deployment Autonomous Virtual Agent for Social Tutoring
Staged Development Process Stage 3 –non-verbal cues, group interaction • Emotion, speech, face and object recognition • Situation awareness (person, expression, object) • Interface with system by manipulating objects • Group interaction modules ‒ Children interact with each other and tutors in a group • Final system deployment Autonomous Virtual Agent for Social Tutoring
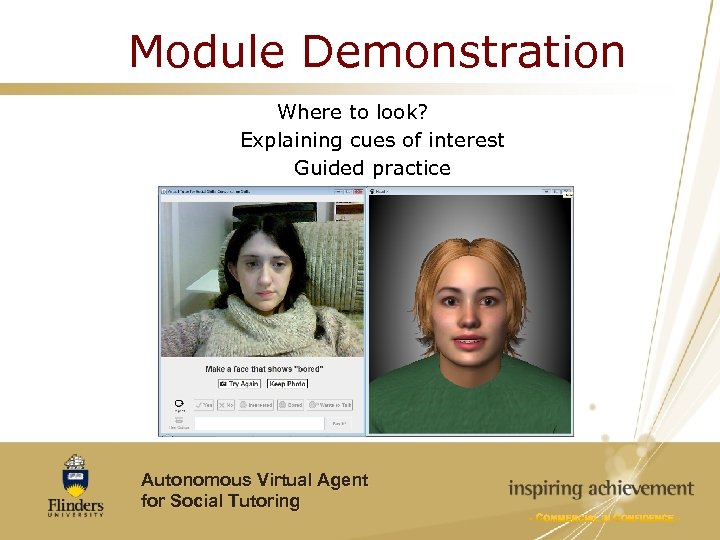 Module Demonstration Where to look? Explaining cues of interest Guided practice Autonomous Virtual Agent for Social Tutoring
Module Demonstration Where to look? Explaining cues of interest Guided practice Autonomous Virtual Agent for Social Tutoring
 Questions or Comments? If you would like any more information about the project or would like to contribute your ideas, please contact me: marissa. milne@flinders. edu. au Autonomous Virtual Agent for Social Tutoring
Questions or Comments? If you would like any more information about the project or would like to contribute your ideas, please contact me: marissa. milne@flinders. edu. au Autonomous Virtual Agent for Social Tutoring


