78ab7f694a5cc5f5864f1fb42d201541.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 73
 virginity , pregnancy & delivery
virginity , pregnancy & delivery
 virginity • Also known as Virgo Intacta. • definition: Virgin is sexual intercourse. a female who has not experienced ØSigns of virginity : 1. Extra genital signs (in breast) 2. Genital signs
virginity • Also known as Virgo Intacta. • definition: Virgin is sexual intercourse. a female who has not experienced ØSigns of virginity : 1. Extra genital signs (in breast) 2. Genital signs
 GENITALS • LABIA MAJORA • LABIA MINORA • VAGINAL WALL • VESTIBULE • POSTERIOR COMMISURE • FORCHETTE • FOSSA NAVICULARIS • HYMEN
GENITALS • LABIA MAJORA • LABIA MINORA • VAGINAL WALL • VESTIBULE • POSTERIOR COMMISURE • FORCHETTE • FOSSA NAVICULARIS • HYMEN
 TYPES OF HYMEN 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) 8) SEMILUNAR ANNULAR INFANTILE CRIBRIFORM VERTICAL SEPTATE IMPERFORATE CARUNCULAE MYRTIFORMIS
TYPES OF HYMEN 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) 8) SEMILUNAR ANNULAR INFANTILE CRIBRIFORM VERTICAL SEPTATE IMPERFORATE CARUNCULAE MYRTIFORMIS
 features virginity Defloration 1. Basic difference No experience of sexual intercourse Have experience of sexual intercourse 2. hymen Intact Torn except in false virgin 3. introitus Does not admit more than tip of little finger, it is painful May admit 2 fingers , it is painless 4. vagina. Marked rugosity on wall Full length of a finger cannot be admitted Rugosity diminishes Full length of finger can be admitted 5. Fossa navicularis Less conspicuous More conspicuous after sexual intercourse 6. Fourchette Intact Healed tear 7. Labia minora Smaller pinkish, covered with majora enlarged, pigmented, not covered 8. Labia majora Thick, fleshy, both majora are in close apposition Less fleshy, not in full apposition 9. Breasts Smaller, firm, pinkish smaller areola, and small nipple Larger, flabby, pendulous, wider areola, large and raised nipple
features virginity Defloration 1. Basic difference No experience of sexual intercourse Have experience of sexual intercourse 2. hymen Intact Torn except in false virgin 3. introitus Does not admit more than tip of little finger, it is painful May admit 2 fingers , it is painless 4. vagina. Marked rugosity on wall Full length of a finger cannot be admitted Rugosity diminishes Full length of finger can be admitted 5. Fossa navicularis Less conspicuous More conspicuous after sexual intercourse 6. Fourchette Intact Healed tear 7. Labia minora Smaller pinkish, covered with majora enlarged, pigmented, not covered 8. Labia majora Thick, fleshy, both majora are in close apposition Less fleshy, not in full apposition 9. Breasts Smaller, firm, pinkish smaller areola, and small nipple Larger, flabby, pendulous, wider areola, large and raised nipple
 ØOther conditions which may affect signs of virginity v. Trauma or Accident v. Surgical operation or Gynaecological examination v. Sanitary tampons v. Foreign body – sola pith (APTAE VARIS) v. Scratching due to irritation from uncleaniness v. Masturbation v. Ulceration – d/t diphtheria , fungus, etc.
ØOther conditions which may affect signs of virginity v. Trauma or Accident v. Surgical operation or Gynaecological examination v. Sanitary tampons v. Foreign body – sola pith (APTAE VARIS) v. Scratching due to irritation from uncleaniness v. Masturbation v. Ulceration – d/t diphtheria , fungus, etc.
 false virgins • Hymen is intact but the woman has had sexual intercourse.
false virgins • Hymen is intact but the woman has had sexual intercourse.
 Point of difference True virgin False virgin 1. Basic difference The woman has no experience of sexual intercourse Has experience of sexual intercourse 2. Hymen Not ruptured. It is thin flap of tissue of Not ruptured. It is thick , fleshy or fibrous regular shape and appearance elastic with folds 3. Introitus Does not admit more than the tip of little finger, it is painful May admit 2 fingers, it is not painful 4. Vagina. Marked rugosity on wall Full length of a finger cannot be admitted Rugosity diminishes Full length of finger can be admitted
Point of difference True virgin False virgin 1. Basic difference The woman has no experience of sexual intercourse Has experience of sexual intercourse 2. Hymen Not ruptured. It is thin flap of tissue of Not ruptured. It is thick , fleshy or fibrous regular shape and appearance elastic with folds 3. Introitus Does not admit more than the tip of little finger, it is painful May admit 2 fingers, it is not painful 4. Vagina. Marked rugosity on wall Full length of a finger cannot be admitted Rugosity diminishes Full length of finger can be admitted
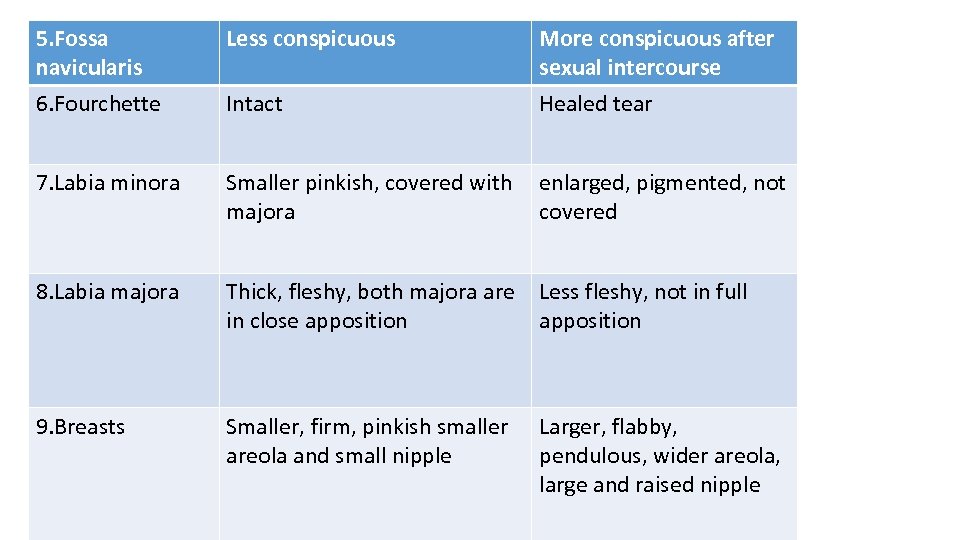 5. Fossa navicularis 6. Fourchette Less conspicuous Intact More conspicuous after sexual intercourse Healed tear 7. Labia minora Smaller pinkish, covered with majora enlarged, pigmented, not covered 8. Labia majora Thick, fleshy, both majora are in close apposition Less fleshy, not in full apposition 9. Breasts Smaller, firm, pinkish smaller areola and small nipple Larger, flabby, pendulous, wider areola, large and raised nipple
5. Fossa navicularis 6. Fourchette Less conspicuous Intact More conspicuous after sexual intercourse Healed tear 7. Labia minora Smaller pinkish, covered with majora enlarged, pigmented, not covered 8. Labia majora Thick, fleshy, both majora are in close apposition Less fleshy, not in full apposition 9. Breasts Smaller, firm, pinkish smaller areola and small nipple Larger, flabby, pendulous, wider areola, large and raised nipple
 medico legal importance of virginity in civil cases: 1. 2. 3. 4. Nullity of marriage Divorce Defamation of character Rape
medico legal importance of virginity in civil cases: 1. 2. 3. 4. Nullity of marriage Divorce Defamation of character Rape
 pregnancy • It is a physiological condition develops in a female with in her child bearing age due to fertilisation of ova by spermatozoa results in developing embryo or foetus in the uterus till its birth. • Signs of pregnancy in living: 1. Presumptive signs 2. Probable signs 3. Positive or conclusive signs
pregnancy • It is a physiological condition develops in a female with in her child bearing age due to fertilisation of ova by spermatozoa results in developing embryo or foetus in the uterus till its birth. • Signs of pregnancy in living: 1. Presumptive signs 2. Probable signs 3. Positive or conclusive signs
 presumptive signs of pregnancy • Amenorrhoea • Morning sickness • Changes in breasts • Changes in the Vagina • Urinary disturbances- increased frequency of micturition • Chloasma - 24 th week • Quickening - 16 – 20 weeks • Linea nigra - 20 th week • Striae gravidarum • Sympathetic change -increased salivation -PICA (perverted appetite) -irritable temper.
presumptive signs of pregnancy • Amenorrhoea • Morning sickness • Changes in breasts • Changes in the Vagina • Urinary disturbances- increased frequency of micturition • Chloasma - 24 th week • Quickening - 16 – 20 weeks • Linea nigra - 20 th week • Striae gravidarum • Sympathetic change -increased salivation -PICA (perverted appetite) -irritable temper.
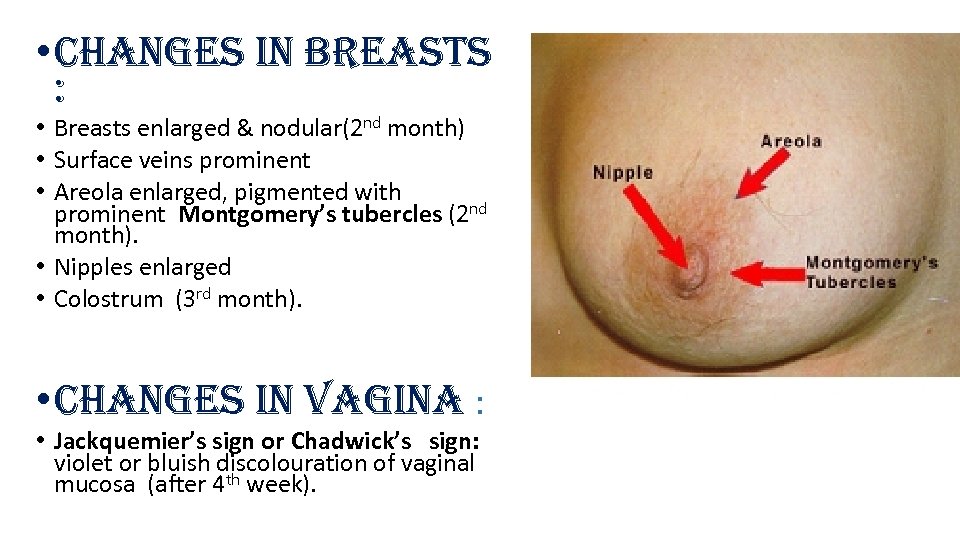 • changes in Breasts : • Breasts enlarged & nodular(2 nd month) • Surface veins prominent • Areola enlarged, pigmented with prominent Montgomery’s tubercles (2 nd month). • Nipples enlarged • Colostrum (3 rd month). • changes in vagina : • Jackquemier’s sign or Chadwick’s sign: violet or bluish discolouration of vaginal mucosa (after 4 th week).
• changes in Breasts : • Breasts enlarged & nodular(2 nd month) • Surface veins prominent • Areola enlarged, pigmented with prominent Montgomery’s tubercles (2 nd month). • Nipples enlarged • Colostrum (3 rd month). • changes in vagina : • Jackquemier’s sign or Chadwick’s sign: violet or bluish discolouration of vaginal mucosa (after 4 th week).
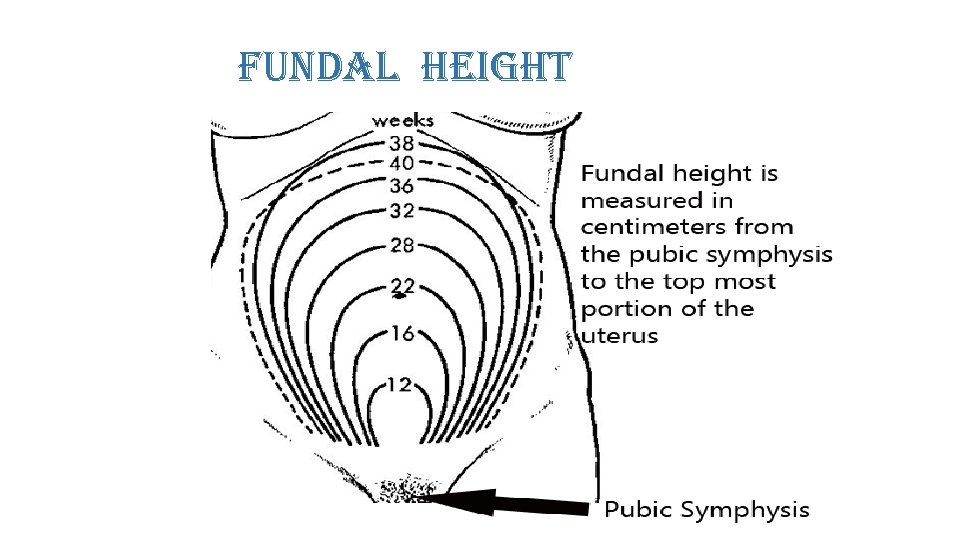
 probable signs of pregnancy • Enlargement of abdomen • Height of uterus. • Palmer’s sign- regular rhythmic contractions of uterus at 4 th to 8 th week.
probable signs of pregnancy • Enlargement of abdomen • Height of uterus. • Palmer’s sign- regular rhythmic contractions of uterus at 4 th to 8 th week.
 fundal height
fundal height
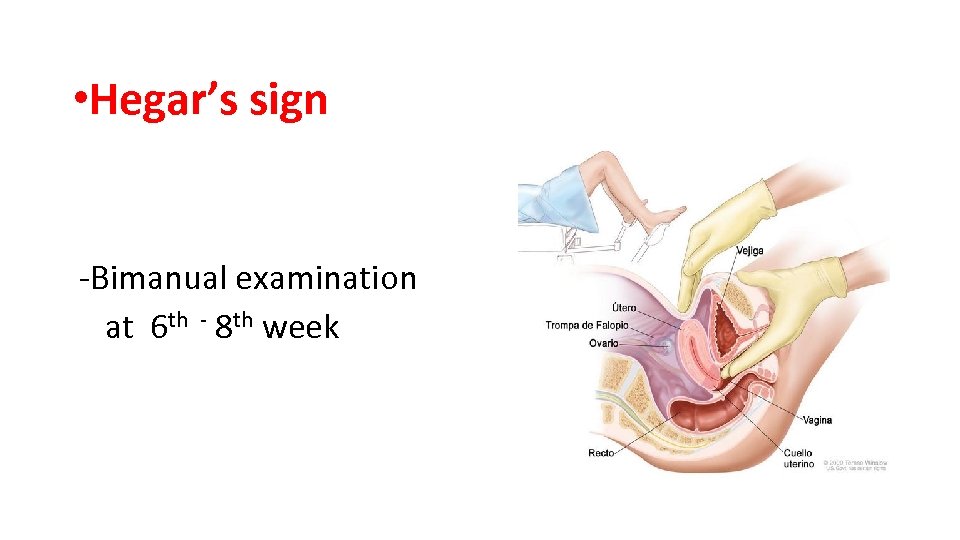 • Hegar’s sign -Bimanual examination at 6 th - 8 th week
• Hegar’s sign -Bimanual examination at 6 th - 8 th week
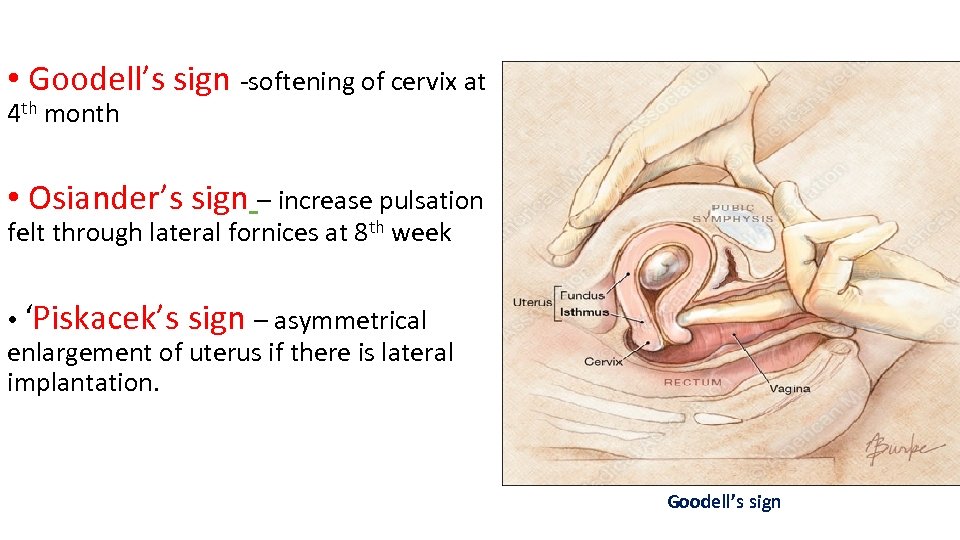 • Goodell’s sign -softening of cervix at 4 th month • Osiander’s sign – increase pulsation felt through lateral fornices at 8 th week • ‘Piskacek’s sign – asymmetrical enlargement of uterus if there is lateral implantation. Goodell’s sign
• Goodell’s sign -softening of cervix at 4 th month • Osiander’s sign – increase pulsation felt through lateral fornices at 8 th week • ‘Piskacek’s sign – asymmetrical enlargement of uterus if there is lateral implantation. Goodell’s sign
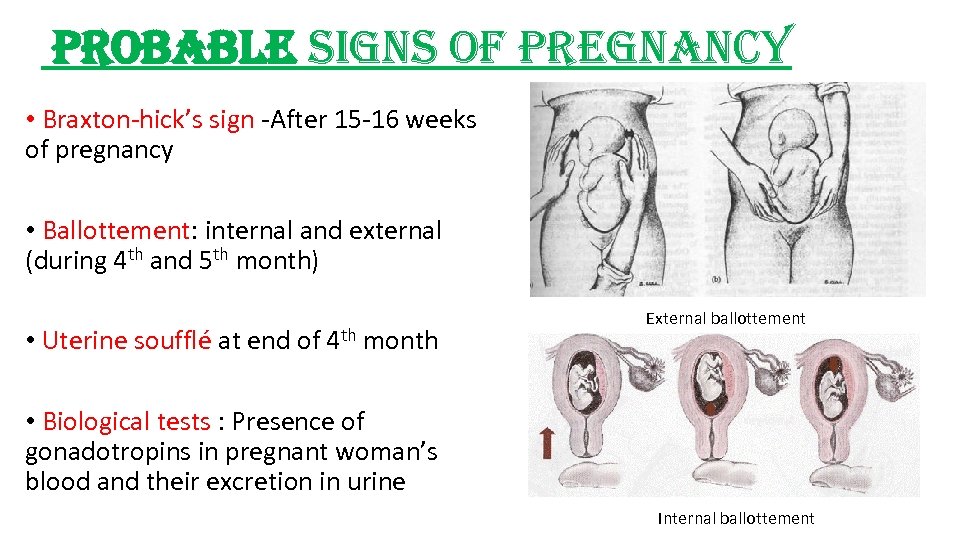 probable signs of pregnancy • Braxton-hick’s sign -After 15 -16 weeks of pregnancy • Ballottement: internal and external (during 4 th and 5 th month) • Uterine soufflé at end of 4 th month External ballottement • Biological tests : Presence of gonadotropins in pregnant woman’s blood and their excretion in urine Internal ballottement
probable signs of pregnancy • Braxton-hick’s sign -After 15 -16 weeks of pregnancy • Ballottement: internal and external (during 4 th and 5 th month) • Uterine soufflé at end of 4 th month External ballottement • Biological tests : Presence of gonadotropins in pregnant woman’s blood and their excretion in urine Internal ballottement
 • Immunological tests : a) Inhibition (Indirect) Latex slide test b) Direct Latex slide test • Haemagglutination inhibition test. • RIA and ELISA
• Immunological tests : a) Inhibition (Indirect) Latex slide test b) Direct Latex slide test • Haemagglutination inhibition test. • RIA and ELISA
 positive signs of pregnancy • Auscultation of foetal heart sounds- positive after 18 -20 wks • Palpation of foetal part • Feeling foetal movements • Radiograph of foetus -after 3 months • USG : 6 wks - Gestational sac 7 wks - Embryo 10 wks - Heart beat 14 wks - Head and Thorax • Presence of foetal cells in mother’s blood.
positive signs of pregnancy • Auscultation of foetal heart sounds- positive after 18 -20 wks • Palpation of foetal part • Feeling foetal movements • Radiograph of foetus -after 3 months • USG : 6 wks - Gestational sac 7 wks - Embryo 10 wks - Heart beat 14 wks - Head and Thorax • Presence of foetal cells in mother’s blood.
 signs of pregnancy in dead • Products of conception • Enlarged Uterus & other uterine change. • Corpus luteum
signs of pregnancy in dead • Products of conception • Enlarged Uterus & other uterine change. • Corpus luteum
 medicolegal importance of pregnancy • in civil cases: • Nullity of marriage • Inheritance of property • Higher maintenance allowance in case of divorce • Compensation cases • Illegitimate baby • Maternity leave • Compensation case if allegation of pregnancy against unmarried woman or widow.
medicolegal importance of pregnancy • in civil cases: • Nullity of marriage • Inheritance of property • Higher maintenance allowance in case of divorce • Compensation cases • Illegitimate baby • Maternity leave • Compensation case if allegation of pregnancy against unmarried woman or widow.
 in criminal cases: • Execution of death sentence. • Advantage during trial in court. • It is positive proof in a trial of rape. • An unmarried pregnant woman bring a charge of criminal breach of trust against a man. • Adultery. • In criminal abortion and to foeticide or infanticide. • Motive for suicide or murder.
in criminal cases: • Execution of death sentence. • Advantage during trial in court. • It is positive proof in a trial of rape. • An unmarried pregnant woman bring a charge of criminal breach of trust against a man. • Adultery. • In criminal abortion and to foeticide or infanticide. • Motive for suicide or murder.
 • Pseudocyesis / False Pregnancy / Spurious Pregnancy / Phantom Pregnancy. • Superfoetation • Superfecundation • Foetus Papyraceous / Foetus Compressus
• Pseudocyesis / False Pregnancy / Spurious Pregnancy / Phantom Pregnancy. • Superfoetation • Superfecundation • Foetus Papyraceous / Foetus Compressus
 • QUESTIONS
• QUESTIONS
 1. Uterine soufflé may be heard by auscultation at the end ofa) 10 wks b) 12 wks c) 14 wks d) 16 wks 2. Foetal parts can be detected by X ray usually bya) 8 wks b) 12 wks c) 14 wks d) 16 wks
1. Uterine soufflé may be heard by auscultation at the end ofa) 10 wks b) 12 wks c) 14 wks d) 16 wks 2. Foetal parts can be detected by X ray usually bya) 8 wks b) 12 wks c) 14 wks d) 16 wks
 3. A pregnant woman sentenced to death cannot be hanged tilla) Delivery b) Delivery and attainment of 6 months of age by new born c) Delivery and one year after that d) None of the above 4. Pseudocyesis is found ina) Young married woman b) Aged unmarried girl c) Menopausal ladies d) Adolescent girl
3. A pregnant woman sentenced to death cannot be hanged tilla) Delivery b) Delivery and attainment of 6 months of age by new born c) Delivery and one year after that d) None of the above 4. Pseudocyesis is found ina) Young married woman b) Aged unmarried girl c) Menopausal ladies d) Adolescent girl
 5. Impregnation of an ovum discharged from a previous ovulation has been developed is calleda) Fecundation b) Superfecundation c) Super foetation d) None of the above 6. Which of the following statements is true for virgo intactaa) Breasts are large and nodular b) Labia majora not apposed with each other c) Fossa navicularis is disappeared d) Labia minora completely covered by labia majora
5. Impregnation of an ovum discharged from a previous ovulation has been developed is calleda) Fecundation b) Superfecundation c) Super foetation d) None of the above 6. Which of the following statements is true for virgo intactaa) Breasts are large and nodular b) Labia majora not apposed with each other c) Fossa navicularis is disappeared d) Labia minora completely covered by labia majora
 delivery • Definition : Expulsion of products of conception from within the uterus at term.
delivery • Definition : Expulsion of products of conception from within the uterus at term.
 Signs of Recent delivery in Living : General appearances of indisposition : Woman looks pale, exhausted and ill. Breasts : • Enlarged, full, firm, tense. • Darkening of areola. • Prominent Montgomery tubercles. • Surface veins are prominent. • Striae are seen. • Colostrum can be squeezed out for 2 -3 days after delivery.
Signs of Recent delivery in Living : General appearances of indisposition : Woman looks pale, exhausted and ill. Breasts : • Enlarged, full, firm, tense. • Darkening of areola. • Prominent Montgomery tubercles. • Surface veins are prominent. • Striae are seen. • Colostrum can be squeezed out for 2 -3 days after delivery.
 Abdomen: • Striae gravidarum (pink) • Lineae albicantes (silvery white) • Linea nigra (black) External genitalia : Labia are tender, swollen and lacerated. Fourchette is ruptured. Perineum is lacerated. Internal os begins to close within 24 hrs External os is patent admitting two fingers initially and later one finger with difficulty at the end of a week. • Vaginal discharge known as Lochia ( for 2 -3 weeks) : During first 4 -5 days -lochia rubra (red) During the next 4 days -lochia serosa (pale or serous) After 9 th day -lochia alba (yellowish grey or turbid) • • •
Abdomen: • Striae gravidarum (pink) • Lineae albicantes (silvery white) • Linea nigra (black) External genitalia : Labia are tender, swollen and lacerated. Fourchette is ruptured. Perineum is lacerated. Internal os begins to close within 24 hrs External os is patent admitting two fingers initially and later one finger with difficulty at the end of a week. • Vaginal discharge known as Lochia ( for 2 -3 weeks) : During first 4 -5 days -lochia rubra (red) During the next 4 days -lochia serosa (pale or serous) After 9 th day -lochia alba (yellowish grey or turbid) • • •
 Signs of Recent delivery in Living : • Extent of signs depends upon whether the woman is primiparous or multiparous • Breast: pendulous • Hyperpigmentation present • Montgomery's tubercles are prominent • Stria are present • Abdomen: abdominal wall is lax • Linea albicantes • Linea nigra
Signs of Recent delivery in Living : • Extent of signs depends upon whether the woman is primiparous or multiparous • Breast: pendulous • Hyperpigmentation present • Montgomery's tubercles are prominent • Stria are present • Abdomen: abdominal wall is lax • Linea albicantes • Linea nigra
 Signs of Remote delivery in Living : • External genitalia: labia are lax • Vaginal rugae are lost • Fourchette is lost • Hymen: carunculae myrtiformis • Os in Nulliparous: - Internal os is well defined - External os is rounded and orifice closed • Os in Multiparous: -Internal os is not well defined External os is transverse irregular and may admit a tip of finger
Signs of Remote delivery in Living : • External genitalia: labia are lax • Vaginal rugae are lost • Fourchette is lost • Hymen: carunculae myrtiformis • Os in Nulliparous: - Internal os is well defined - External os is rounded and orifice closed • Os in Multiparous: -Internal os is not well defined External os is transverse irregular and may admit a tip of finger
 Sign of Recent delivery in the Dead : • Same as are found in living • Additional findings are found in uterus and its appendages • Uterus is firm and returns to a permanent reduced size • Placental site can be identified by its dark colour and coarse granular appearance and covered with blood clots, lymph and decidua. • Ovaries and fallopian tubes are congested • Histopathological examination: - trophoblastic cells and chorionic villi are present in endometrium - one large corpus luteum is present in one ovary
Sign of Recent delivery in the Dead : • Same as are found in living • Additional findings are found in uterus and its appendages • Uterus is firm and returns to a permanent reduced size • Placental site can be identified by its dark colour and coarse granular appearance and covered with blood clots, lymph and decidua. • Ovaries and fallopian tubes are congested • Histopathological examination: - trophoblastic cells and chorionic villi are present in endometrium - one large corpus luteum is present in one ovary
 Signs of Remote delivery in Dead : Same as are found in remote delivery in living Additional findings are present in uterus and its appendages Uterus is concave inwards. Fundus is above the line of fallopian tube Length of body is twice the length of cervix in multiparous and it is equal in nulliparous. • External os is enlarged, irregular and patulous and admits tip of finger • Internal os is not well defined • Arbor vitae: lost in parous woman • • •
Signs of Remote delivery in Dead : Same as are found in remote delivery in living Additional findings are present in uterus and its appendages Uterus is concave inwards. Fundus is above the line of fallopian tube Length of body is twice the length of cervix in multiparous and it is equal in nulliparous. • External os is enlarged, irregular and patulous and admits tip of finger • Internal os is not well defined • Arbor vitae: lost in parous woman • • •
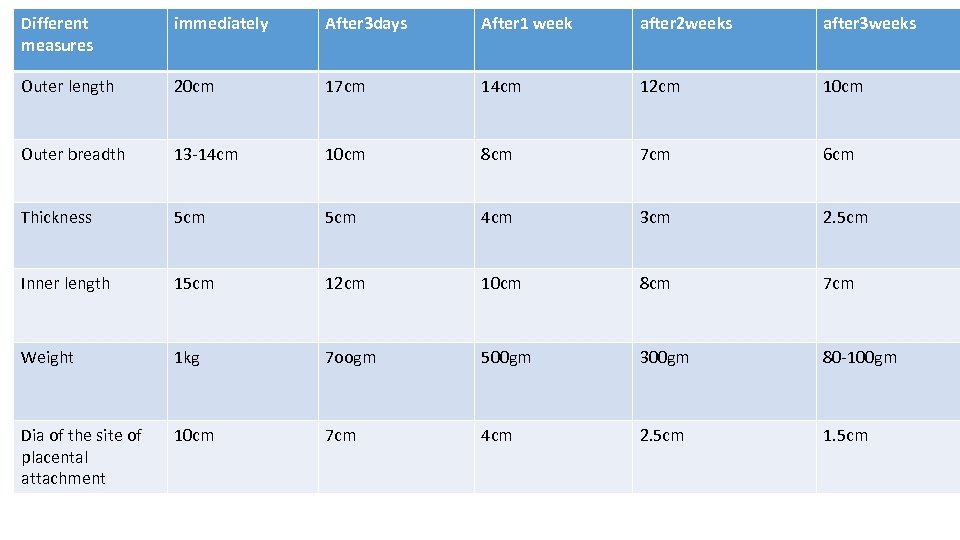 Different measures immediately After 3 days After 1 week after 2 weeks after 3 weeks Outer length 20 cm 17 cm 14 cm 12 cm 10 cm Outer breadth 13 -14 cm 10 cm 8 cm 7 cm 6 cm Thickness 5 cm 4 cm 3 cm 2. 5 cm Inner length 15 cm 12 cm 10 cm 8 cm 7 cm Weight 1 kg 7 oogm 500 gm 300 gm 80 -100 gm Dia of the site of placental attachment 10 cm 7 cm 4 cm 2. 5 cm 1. 5 cm
Different measures immediately After 3 days After 1 week after 2 weeks after 3 weeks Outer length 20 cm 17 cm 14 cm 12 cm 10 cm Outer breadth 13 -14 cm 10 cm 8 cm 7 cm 6 cm Thickness 5 cm 4 cm 3 cm 2. 5 cm Inner length 15 cm 12 cm 10 cm 8 cm 7 cm Weight 1 kg 7 oogm 500 gm 300 gm 80 -100 gm Dia of the site of placental attachment 10 cm 7 cm 4 cm 2. 5 cm 1. 5 cm
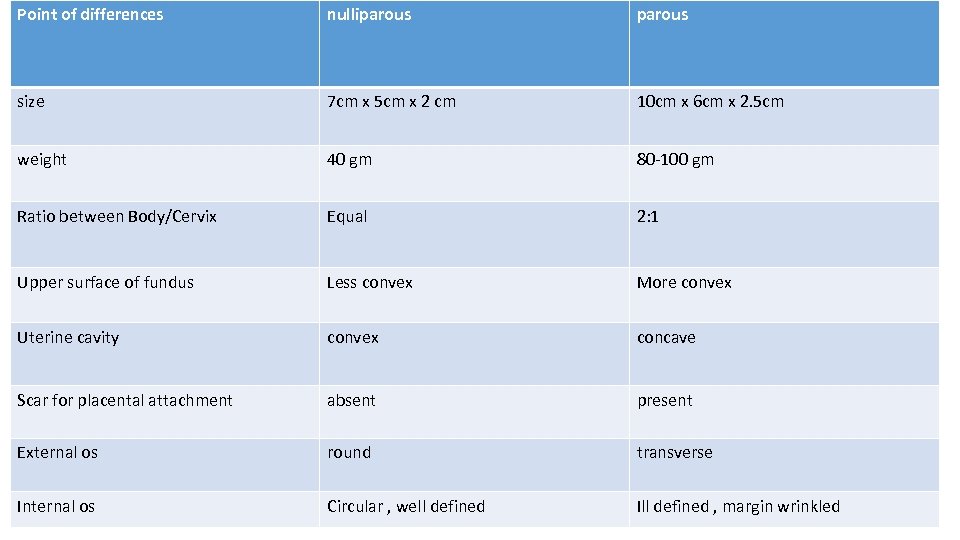 Point of differences nulliparous size 7 cm x 5 cm x 2 cm 10 cm x 6 cm x 2. 5 cm weight 40 gm 80 -100 gm Ratio between Body/Cervix Equal 2: 1 Upper surface of fundus Less convex More convex Uterine cavity convex concave Scar for placental attachment absent present External os round transverse Internal os Circular , well defined Ill defined , margin wrinkled
Point of differences nulliparous size 7 cm x 5 cm x 2 cm 10 cm x 6 cm x 2. 5 cm weight 40 gm 80 -100 gm Ratio between Body/Cervix Equal 2: 1 Upper surface of fundus Less convex More convex Uterine cavity convex concave Scar for placental attachment absent present External os round transverse Internal os Circular , well defined Ill defined , margin wrinkled
 abortion • Definition: “Termination of pregnancy due to premature expulsion of product of conception at any time from the uterus. ”
abortion • Definition: “Termination of pregnancy due to premature expulsion of product of conception at any time from the uterus. ”
 TYPES OF ABORTION 1. SPONTANEOUS A)NATURAL B)ACCIDENTAL 2. INDUCED A)LEGAL B)CRIMINAL
TYPES OF ABORTION 1. SPONTANEOUS A)NATURAL B)ACCIDENTAL 2. INDUCED A)LEGAL B)CRIMINAL
 Medical termination of pregnancy (MTP)act 1971 • Came into force in 1972 • Amendments in 1975, 2002 and 2003 ØGrounds for MTP: • Therapeutic : risk to pregnant woman • Eugenic : risk to the child to be born • Humanitarian : pregnancy caused by rape • Socioeconomic : pregnancy due to failure of contraceptive, Unwanted pregnancy with low SE status • Environemental: no one to help from society
Medical termination of pregnancy (MTP)act 1971 • Came into force in 1972 • Amendments in 1975, 2002 and 2003 ØGrounds for MTP: • Therapeutic : risk to pregnant woman • Eugenic : risk to the child to be born • Humanitarian : pregnancy caused by rape • Socioeconomic : pregnancy due to failure of contraceptive, Unwanted pregnancy with low SE status • Environemental: no one to help from society
 Duration of pregnancy for MTP ØBelow 12 weeks : only one medical officer alone can take decision for MTP ØBetween 12 to 20 weeks: decision is taken by two medical officers for MTP ØAfter 20 weeks: MTP can not be done, except in emergency conditions. (In emergency conditions decision can be taken by only a single doctor. )
Duration of pregnancy for MTP ØBelow 12 weeks : only one medical officer alone can take decision for MTP ØBetween 12 to 20 weeks: decision is taken by two medical officers for MTP ØAfter 20 weeks: MTP can not be done, except in emergency conditions. (In emergency conditions decision can be taken by only a single doctor. )
 Places for MTP • Any government or semi-government hospital • Any non-government hospital approved by government or CMO or district health officer
Places for MTP • Any government or semi-government hospital • Any non-government hospital approved by government or CMO or district health officer
 Qualification and Experience of doctors for MTP • Up to 12 weeks: By any RMP who has performed at least 25 cases of MTP and out of which 5 have been performed independently in an approved place. • By doctor with any of the following: -PG degree or diploma in OBG -6 month of house surgency in OBG -Experience of one year or more in OBG at any hospital • In emergency cases: By any RMP , at any place , irrespective of duration of pregnancy.
Qualification and Experience of doctors for MTP • Up to 12 weeks: By any RMP who has performed at least 25 cases of MTP and out of which 5 have been performed independently in an approved place. • By doctor with any of the following: -PG degree or diploma in OBG -6 month of house surgency in OBG -Experience of one year or more in OBG at any hospital • In emergency cases: By any RMP , at any place , irrespective of duration of pregnancy.
 Consent • Only consent of pregnant woman is necessary • No need to obtain consent from her husband • In case of minor (less than 18 year of age), and mentally ill woman, consent from guardian is required
Consent • Only consent of pregnant woman is necessary • No need to obtain consent from her husband • In case of minor (less than 18 year of age), and mentally ill woman, consent from guardian is required
 Common methods of MTP • Medical : mifepristone and misoprostol • Dilatation and curettage (D&C) • Vacuum aspiration technique or surgical abortion • Intra-embryonic instillation of PG • Extra-embryonic instillation of hypertonic saline • Surgical
Common methods of MTP • Medical : mifepristone and misoprostol • Dilatation and curettage (D&C) • Vacuum aspiration technique or surgical abortion • Intra-embryonic instillation of PG • Extra-embryonic instillation of hypertonic saline • Surgical
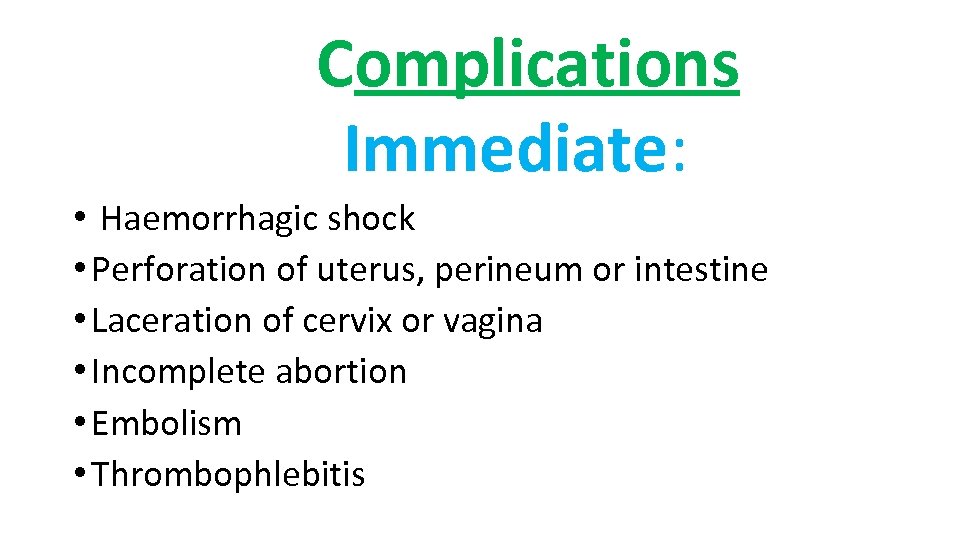 Complications Immediate: • Haemorrhagic shock • Perforation of uterus, perineum or intestine • Laceration of cervix or vagina • Incomplete abortion • Embolism • Thrombophlebitis
Complications Immediate: • Haemorrhagic shock • Perforation of uterus, perineum or intestine • Laceration of cervix or vagina • Incomplete abortion • Embolism • Thrombophlebitis
 Delayed: • • • PID Menstrual irregularities Sterility Endometritis Cervicitis Vaginitis
Delayed: • • • PID Menstrual irregularities Sterility Endometritis Cervicitis Vaginitis
 Criminal Abortion : • Abortion done against the provision of MTP act.
Criminal Abortion : • Abortion done against the provision of MTP act.
 Legal aspects of criminal abortion: ØSec. 312 IPC: Criminal abortion with the consent of patient • Punishment to both for upto 3 year, and +/- fine • If the woman is quick with child then may extend upto 7 years ØSec 313 IPC: if abortion done without her consent • Punishment upto 10 years and fine ØSec 314 IPC: if woman dies by this act • Punishment upto 10 years and fine
Legal aspects of criminal abortion: ØSec. 312 IPC: Criminal abortion with the consent of patient • Punishment to both for upto 3 year, and +/- fine • If the woman is quick with child then may extend upto 7 years ØSec 313 IPC: if abortion done without her consent • Punishment upto 10 years and fine ØSec 314 IPC: if woman dies by this act • Punishment upto 10 years and fine
 ØSec 315 IPC : Any act with the intent to prevent the child being born alive or cause its death before birth • Punishment : upto 10 years and/or fine. ØSec 316 IPC : any act which cause death of quick unborn child amount to culpable homicide • Imprisionment upto 10 years and fine
ØSec 315 IPC : Any act with the intent to prevent the child being born alive or cause its death before birth • Punishment : upto 10 years and/or fine. ØSec 316 IPC : any act which cause death of quick unborn child amount to culpable homicide • Imprisionment upto 10 years and fine
 Methods adopted for criminal abortion • I. Abortifacient drugs • Drugs acting directly on the Uterus • Irritants of Genito-Urinary tract • Irritants of GI tract • Drugs having poisonous effect on Body • II. General violence • III. Local violence
Methods adopted for criminal abortion • I. Abortifacient drugs • Drugs acting directly on the Uterus • Irritants of Genito-Urinary tract • Irritants of GI tract • Drugs having poisonous effect on Body • II. General violence • III. Local violence
 I. Abortifacient drugs: 1. Drugs acting directly on the Uterus : A. ECBOLICS : (Increase Uterine Contraction) Eg. Ergot Hydrastis canadensis Quinine Lead ( lead oleate or lead plaster) Decoction of cotton root bark Nitrobenzol Picrotoxin and strychnine
I. Abortifacient drugs: 1. Drugs acting directly on the Uterus : A. ECBOLICS : (Increase Uterine Contraction) Eg. Ergot Hydrastis canadensis Quinine Lead ( lead oleate or lead plaster) Decoction of cotton root bark Nitrobenzol Picrotoxin and strychnine
 • B. EMMENAGOGUES : (Increase Menstrual Flow) Eg. : - savin borex apiol rue laburum oestrogen sanguinarin caulophyllin hallebore
• B. EMMENAGOGUES : (Increase Menstrual Flow) Eg. : - savin borex apiol rue laburum oestrogen sanguinarin caulophyllin hallebore
 2. Irritants of Genito-urinary tract: • Oil of pennyroyal • Oil of tansy • Oil of turpentine • Cantharides • KMn. O 4
2. Irritants of Genito-urinary tract: • Oil of pennyroyal • Oil of tansy • Oil of turpentine • Cantharides • KMn. O 4
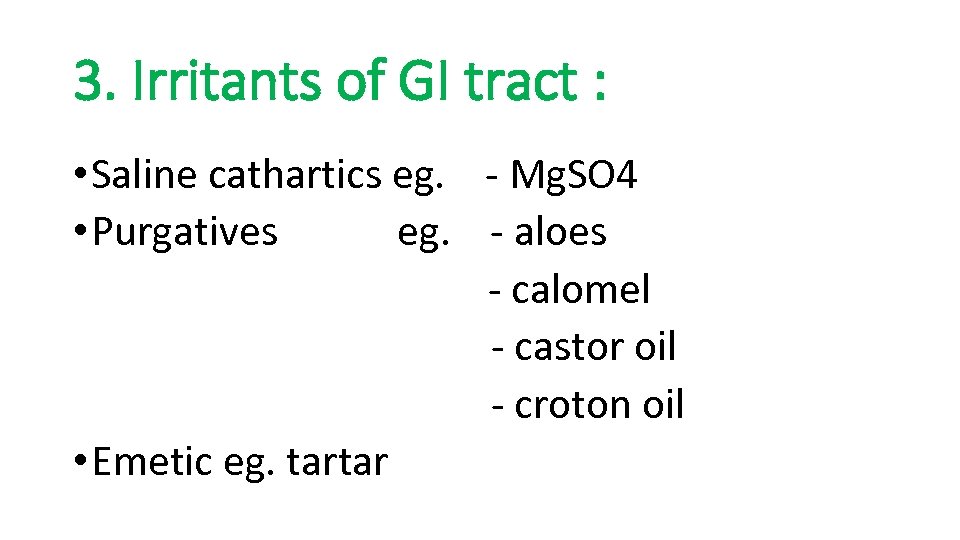 3. Irritants of GI tract : • Saline cathartics eg. - Mg. SO 4 • Purgatives eg. - aloes - calomel - castor oil - croton oil • Emetic eg. tartar
3. Irritants of GI tract : • Saline cathartics eg. - Mg. SO 4 • Purgatives eg. - aloes - calomel - castor oil - croton oil • Emetic eg. tartar
 4. Drugs having poisonous effect on Body: • Inorganic: Pb , Cu , Fe , Hg , Sb • Organic: cantharides , unripe fruits of papaya and pine apple, juice of calotropis , bark of plumbago rosea , methi , saffron
4. Drugs having poisonous effect on Body: • Inorganic: Pb , Cu , Fe , Hg , Sb • Organic: cantharides , unripe fruits of papaya and pine apple, juice of calotropis , bark of plumbago rosea , methi , saffron
 II. General violence: Intensional 1. Severe pressure on abdomen: by blow, kick, jumping or kneeling 2. Violent exercise: horse riding, cycling, jumping from height, severe jolting, carrying or lifting heavy weights 3. Cupping 4. Very hot and cold bath alternately
II. General violence: Intensional 1. Severe pressure on abdomen: by blow, kick, jumping or kneeling 2. Violent exercise: horse riding, cycling, jumping from height, severe jolting, carrying or lifting heavy weights 3. Cupping 4. Very hot and cold bath alternately
 III. Local violence : • Syringing: by Higginson’s syringe • Syringe aspiration • Vacuum aspiration • Rupture of membrane • Use of laminaria tent /slippery elm • Abortion sticks • Utus paste (thymol, iodine, salt of mercury) • Electric current
III. Local violence : • Syringing: by Higginson’s syringe • Syringe aspiration • Vacuum aspiration • Rupture of membrane • Use of laminaria tent /slippery elm • Abortion sticks • Utus paste (thymol, iodine, salt of mercury) • Electric current
 CAUSE OF DEATH AND DANGERS OF CRIMINAL ABORTION A. Cause of Rapid death: • Haemorrhage • Perforation • Vagal shock • Fat embolism • Air embolism
CAUSE OF DEATH AND DANGERS OF CRIMINAL ABORTION A. Cause of Rapid death: • Haemorrhage • Perforation • Vagal shock • Fat embolism • Air embolism
 B. Cause of delayed death • Peritonitis • Local infection getting complicated • Tetanus • Septicaemia • Pyaemia
B. Cause of delayed death • Peritonitis • Local infection getting complicated • Tetanus • Septicaemia • Pyaemia
 C. Remote causes : • Renal failure • Meningitis • Endocarditis • Pneumonitis • Hepatitis • D. Toxic effects of Abortifacient drugs: - causing early or delayed deaths
C. Remote causes : • Renal failure • Meningitis • Endocarditis • Pneumonitis • Hepatitis • D. Toxic effects of Abortifacient drugs: - causing early or delayed deaths
 Duties of doctor in suspected criminal abortion • Doctor must ask the patient to make a statement about the criminal abortion. • If she refuses, he should not pursue the matter, but inform the police. • He should keep all the information secret to maintain professional secrecy. • He must arrange to record the dying declaration in case woman’s condition is serious. • If woman dies, he must not issue the death certificate, but should inform police for post-mortem examination. • Any foreign materials collected from genitals should be kept preserved.
Duties of doctor in suspected criminal abortion • Doctor must ask the patient to make a statement about the criminal abortion. • If she refuses, he should not pursue the matter, but inform the police. • He should keep all the information secret to maintain professional secrecy. • He must arrange to record the dying declaration in case woman’s condition is serious. • If woman dies, he must not issue the death certificate, but should inform police for post-mortem examination. • Any foreign materials collected from genitals should be kept preserved.
 Examination of Living individual • Requisition from the concerned authority • Identification of female • Written informed consent • A female must be present • Brief history • Clothing must be examined • Clinical examination: sign of ill health, GIT disturbances, exhaustion • Local examination • Laboratory investigations
Examination of Living individual • Requisition from the concerned authority • Identification of female • Written informed consent • A female must be present • Brief history • Clothing must be examined • Clinical examination: sign of ill health, GIT disturbances, exhaustion • Local examination • Laboratory investigations
 Examination of Dead body ØSudden death of a woman of child bearing age should give rise the suspicion of criminal abortion if: 1. The deceased was pregnant and deeply cyanosed 2. Instrument to procure the abortion or abortifacient drugs are found at scene of death. 3. Underclothing appears to be disturbed after death. 4. Fluid , soapy material or blood coming out of vagina.
Examination of Dead body ØSudden death of a woman of child bearing age should give rise the suspicion of criminal abortion if: 1. The deceased was pregnant and deeply cyanosed 2. Instrument to procure the abortion or abortifacient drugs are found at scene of death. 3. Underclothing appears to be disturbed after death. 4. Fluid , soapy material or blood coming out of vagina.
 ØFollowing points should be proved to convict the abortionist: 1. The dead woman was pregnant 2. The accused was responsible for the act which resulted in the interruption of pregnancy 3. The accused acted for purpose of procuring illegal abortion 4. Death occurred as a result of attempt to interrupt the pregnancy
ØFollowing points should be proved to convict the abortionist: 1. The dead woman was pregnant 2. The accused was responsible for the act which resulted in the interruption of pregnancy 3. The accused acted for purpose of procuring illegal abortion 4. Death occurred as a result of attempt to interrupt the pregnancy
 Medical evidence of Abortion In a Living victim : • Breasts-pigmented • Colostrum • Linea nigra and albicans may present • Congestion of labia majora and minora • Tags of membrane may be present in uterus • Swab taken from cervical canal may show chemical used • HCG in urine up to 7 days • Aborted material, if available , should be subjected to visual or histological examination.
Medical evidence of Abortion In a Living victim : • Breasts-pigmented • Colostrum • Linea nigra and albicans may present • Congestion of labia majora and minora • Tags of membrane may be present in uterus • Swab taken from cervical canal may show chemical used • HCG in urine up to 7 days • Aborted material, if available , should be subjected to visual or histological examination.
 Medical evidence of abortion In a dead victim (autopsy findings) • Face may appear pale. • Undergarment may show blood clots and fragments of product of conception. • Congestion of labia and post. commissure • Signs of peritonitis. • Vaginal fluid for chemical analysis. • In case of suspected air embolism X-ray & CT-Scan. • Uterus and ovary may also be sent for chemical analysis to detect abortifacients.
Medical evidence of abortion In a dead victim (autopsy findings) • Face may appear pale. • Undergarment may show blood clots and fragments of product of conception. • Congestion of labia and post. commissure • Signs of peritonitis. • Vaginal fluid for chemical analysis. • In case of suspected air embolism X-ray & CT-Scan. • Uterus and ovary may also be sent for chemical analysis to detect abortifacients.
 Factor suggestive of Spontaneous / natural Abortion • Blighted embryo • Degenerative change of chorionic villi • Hydatidiform mole • Attenuated trophoblastic layer and myxomatous avascular stroma • Macerated foetus and placenta • Foetal abnormalities
Factor suggestive of Spontaneous / natural Abortion • Blighted embryo • Degenerative change of chorionic villi • Hydatidiform mole • Attenuated trophoblastic layer and myxomatous avascular stroma • Macerated foetus and placenta • Foetal abnormalities
 Questions • 1. In India MTP act was first introduced in § a. 1947 § B. 1966 § C. 1971 § D. 1975 2. MTP act extends all over India , except, the city/state a. Delhi b. Mumbai c. Chennai d. Jammu and kashmir
Questions • 1. In India MTP act was first introduced in § a. 1947 § B. 1966 § C. 1971 § D. 1975 2. MTP act extends all over India , except, the city/state a. Delhi b. Mumbai c. Chennai d. Jammu and kashmir
 Questions(contd) • 3. under MTP act one doctor can terminate the pregnancy upto • A. six weeks • B. twelve weeks • C. Twenty weeks • D. Twenty weeks • 4. if criminal abortion is performed with the consent of the woman , the doctor will be charged under section • A. 310 IPC • B. 312 IPC • C. 313 IPC • D. 320 IPC
Questions(contd) • 3. under MTP act one doctor can terminate the pregnancy upto • A. six weeks • B. twelve weeks • C. Twenty weeks • D. Twenty weeks • 4. if criminal abortion is performed with the consent of the woman , the doctor will be charged under section • A. 310 IPC • B. 312 IPC • C. 313 IPC • D. 320 IPC
 Questions (contd) • 5. Age of pregnant woman to give consent in MTP act is • A. 12 years • B. 16 years • C. 18 years • D. 21 years • 6. Injection of soap water into vagina during criminal abortion cause • A. Air embolism • B. fat embolism • C. neurogenic shock • D. peritonitis
Questions (contd) • 5. Age of pregnant woman to give consent in MTP act is • A. 12 years • B. 16 years • C. 18 years • D. 21 years • 6. Injection of soap water into vagina during criminal abortion cause • A. Air embolism • B. fat embolism • C. neurogenic shock • D. peritonitis
 Questions (contd) • 7. Intra-amniotic injection of prostaglandins is successful in causing abortion in the • A. First trimester • B. Second trimester • C. Third trimester • D. After viability of fetus • 8. If criminal abortion is performed without the consent of woman , the doctor will be charged under section • A. 310 IPC • B. 312 IPC • C. 313 IPC • D. 320 IPC
Questions (contd) • 7. Intra-amniotic injection of prostaglandins is successful in causing abortion in the • A. First trimester • B. Second trimester • C. Third trimester • D. After viability of fetus • 8. If criminal abortion is performed without the consent of woman , the doctor will be charged under section • A. 310 IPC • B. 312 IPC • C. 313 IPC • D. 320 IPC
 Questions (contd) • 9. Under MTP act pregnancy can be terminated at any stage on the ground of • A. Eugenic • B. Therapeutic • C. Social • D. Humanitarian • 10 Consent required for termination of pregnancy , in an adult woman is • A. Husband herself • B. mother • C. Mother • D. Herself only
Questions (contd) • 9. Under MTP act pregnancy can be terminated at any stage on the ground of • A. Eugenic • B. Therapeutic • C. Social • D. Humanitarian • 10 Consent required for termination of pregnancy , in an adult woman is • A. Husband herself • B. mother • C. Mother • D. Herself only


