34e42f03dde57e9ad731d9c92c9049a9.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 34

Viewing Malware Management as a Business Practice Copyright 2002

The Prophecy Computer viruses are the first and only form of artificial life to have had a measurable impact on society. Jeffrey Kephart, 1994 Copyright 2002
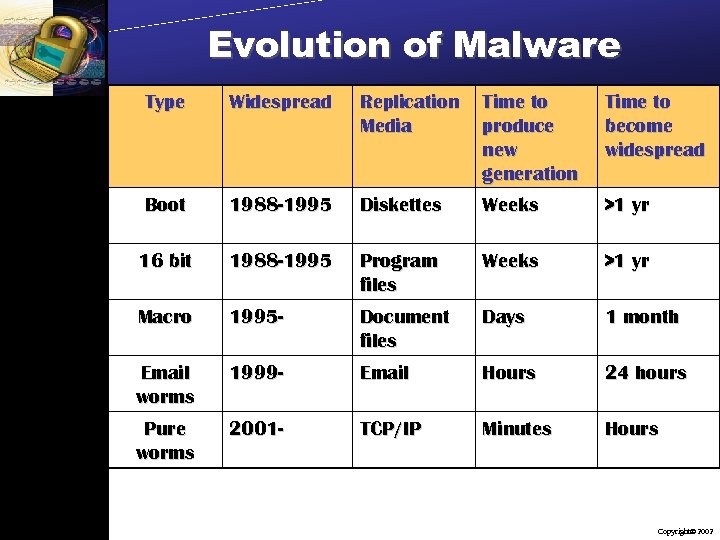
Evolution of Malware Type Widespread Replication Media Time to produce new generation Time to become widespread Boot 1988 -1995 Diskettes Weeks >1 yr 16 bit 1988 -1995 Program files Weeks >1 yr Macro 1995 - Document files Days 1 month Email worms 1999 - Email Hours 24 hours Pure worms 2001 - TCP/IP Minutes Hours Copyright 2002
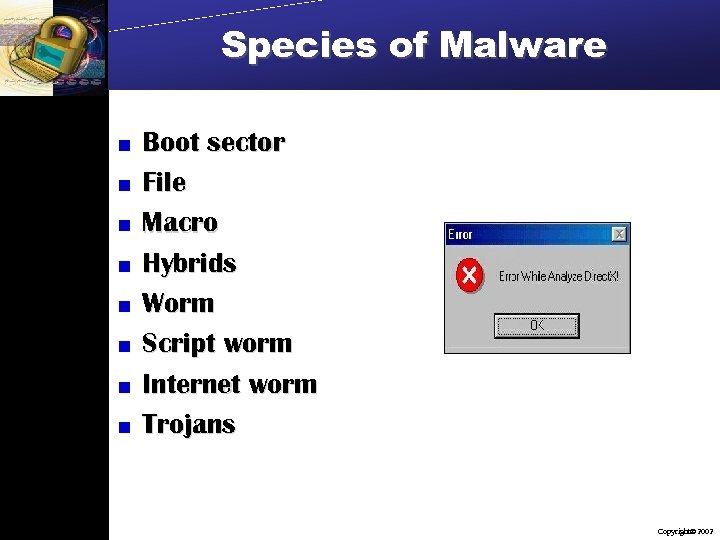
Species of Malware Boot sector File Macro Hybrids Worm Script worm Internet worm Trojans Copyright 2002
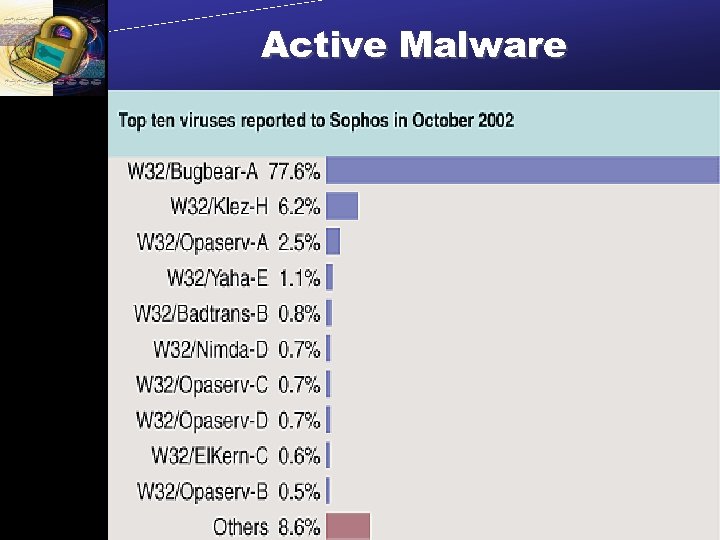
Active Malware Copyright 2002

Overview of Attack Trends Speed of attack tools Sophistication of attack tools Faster discovery of vulnerabilities Asymmetric threat Copyright 2002
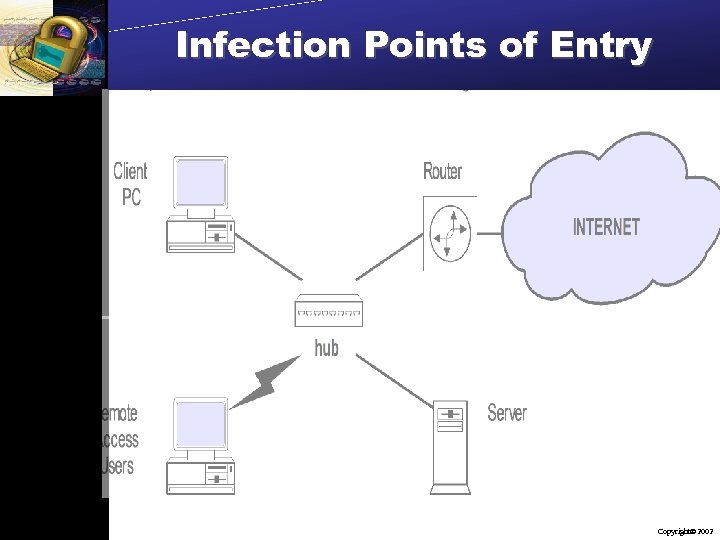
Infection Points of Entry Copyright 2002
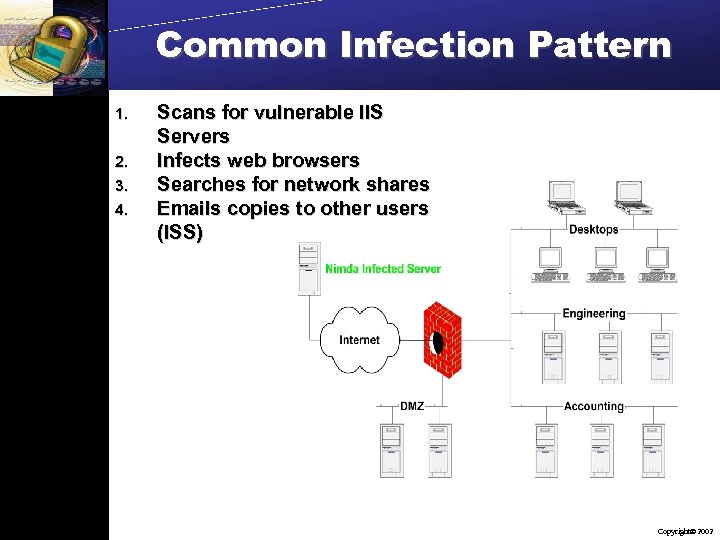
Common Infection Pattern 1. 2. 3. 4. Scans for vulnerable IIS Servers Infects web browsers Searches for network shares Emails copies to other users (ISS) Copyright 2002

Managing Infection Points Home computers Laptops used in travel PDAs Cell phones Internet appliances Printers Copyright 2002

The Problem with Malware Virus writer Manager-business side Security Administrator User Copyright 2002

Virus Perpetrator Characteristics Challenge and curiosity Fame and power Protest and anarchy Proof of concept Political motives Copyright 2002

Infecting Machines by Hacking Humans Email IM Software downloads Remote access AV patches Loss of hardware Copyright 2002

Why Attack a PC? E-mail client and address book Potential zombie host Container for stolen information Staging ground for attack Copyright 2002

Virus Risk Assessment Does the company provide Internet and email access for all employees? Does the company scan email attachments for viruses? Is there an in-house specialist or department responsible for virus protection? Is there a way to automatically propagate updates throughout the network? Is virus protection centrally managed? Do you know the number of viruses detected on the network each year? Copyright 2002
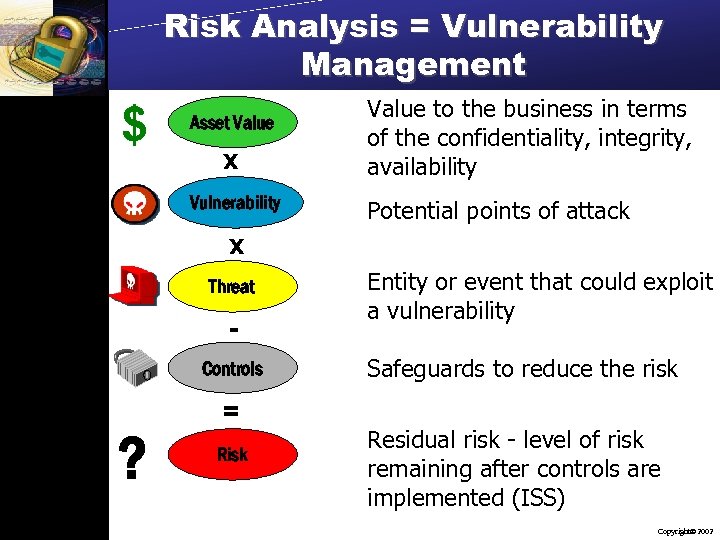
Risk Analysis = Vulnerability Management $ Asset Value x Vulnerability Value to the business in terms of the confidentiality, integrity, availability Potential points of attack x Threat Controls ? = Risk Entity or event that could exploit a vulnerability Safeguards to reduce the risk Residual risk - level of risk remaining after controls are implemented (ISS) Copyright 2002

Integrated Management Approach Each organization has a unique set of risks Threats should be tied to an organization’s mission and business objectives Tradeoffs will be required between business and security issues when creating policy Copyright 2002

Payload Damage is the Business Risk Attacks on availability • • Deletion Renaming Encryption Unauthorized calls to system software Attacks on integrity • • • Corruption of system files and areas Data diddling Corruption of application files Attacks on confidentiality • • Capturing and forwarding passwords Forwarding personal and confidential files Copyright 2002
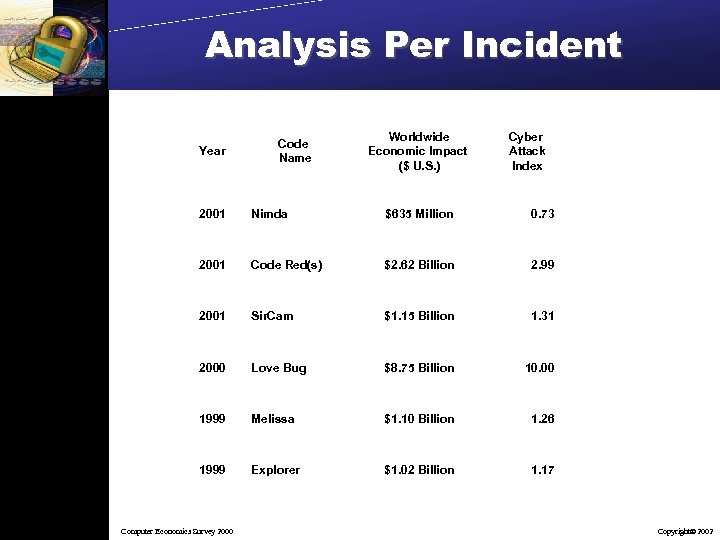
Analysis Per Incident Year Code Name Worldwide Economic Impact ($ U. S. ) Cyber Attack Index 2001 Nimda $635 Million 0. 73 2001 Code Red(s) $2. 62 Billion 2. 99 2001 Sir. Cam $1. 15 Billion 1. 31 2000 Love Bug $8. 75 Billion 10. 00 1999 Melissa $1. 10 Billion 1. 26 1999 Explorer $1. 02 Billion 1. 17 Computer Economics Survey 2000 Copyright 2002

Malware Management Solution Categories Technological Educational Political Copyright 2002

Managing Malware with Technology Current AV model is reactive Attack-response cycle places a business at risk Ø Virus released vendors get samples vendors analyze generate detection and disinfection distribute fix Helpless against fast-burners Desktop is defacto defense Multiple network solutions have a high cost Copyright 2002

Anti-Virus Software Missed Goner, Nimda, Sir. Cam, My. Party Copyright 2002

How Anti-Virus Programs Work GENERIC ANTIVIRAL PROGRAM flags activities--such as the alteration of critical sites in RAM or particular files on disk--that are likely to arise from a virus in action. SIGNATURE SCANNER searches a user's disks looking for fragments of program code that appear in known viruses. BEHAVIOR BLOCKING Monitors real-time execution of program code and blocks actions if a delete, modification, format, initiate network connections. Copyright 2002
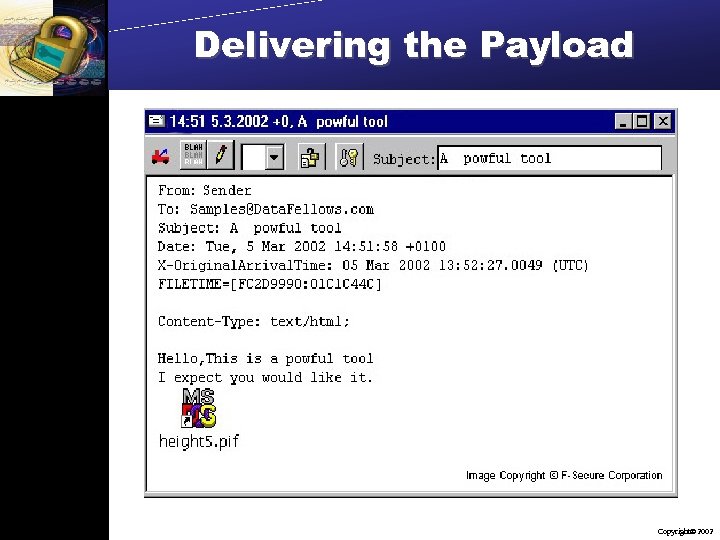
Delivering the Payload Copyright 2002

The ability of an organization to achieve its mission and meet its business objectives is directly and strategically linked to the state of the computing infrastructure and to the manner in which people interact with that infrastructure. Christopher Alberts, Viewing Security Management as a Business Practice Copyright 2002

Managing Malware with Education Social engineering Spam techniques User cooperation Copyright 2002
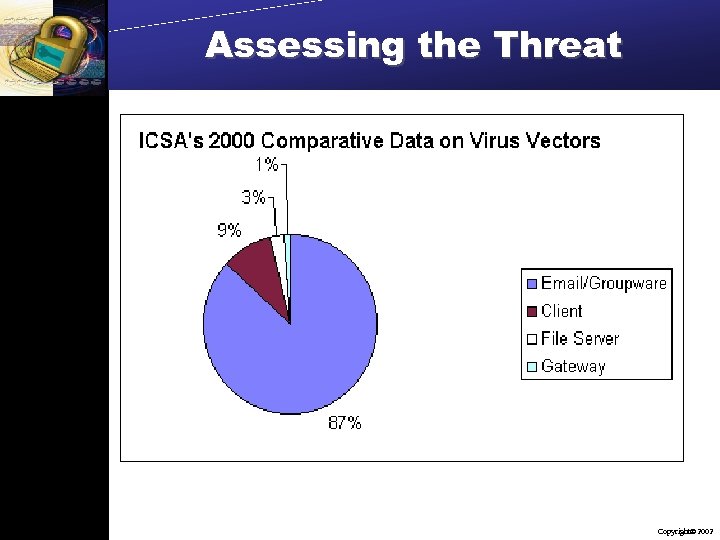
Assessing the Threat Copyright 2002

Social Engineering From: sdekih@iteoka. i> To: Patricia LOGAN Date : Tuesday - May 28, 2002 10: 44 PM <HTML><HEAD></HEAD><BODY> Subj ect: Worm Klez. E immunity Mime. 822 (1 639 bytes) [View] [Save As] <FONT>KLEZ. E files. Because of its very smart stealth and anti-virus technic, most common AV software can't detect or clean it. We developed this free immunity tool to defeat the malicious virus. You only need to run this tool once, and then Klez will never come into your PC. NOTE: Because this tool acts as a fake Klez to fool the real worm, some AV monitor maybe cry when you run it. If so, Ignore the warning, and select 'continue'. If you have any question, please <a href=3 Dmailto: sdekih@iteoka. i>mail to me</a>. </FONT></BODY></HTML> bat attachment detected and blocked YOU JUST DODGED A BULLET Your computer has just been saved from a possible virus infection. This message contained attachments that have been blocked. Please contact Computing Support at 626 -7777 if you have questions WSU Systems / Network Management Copyright 2002
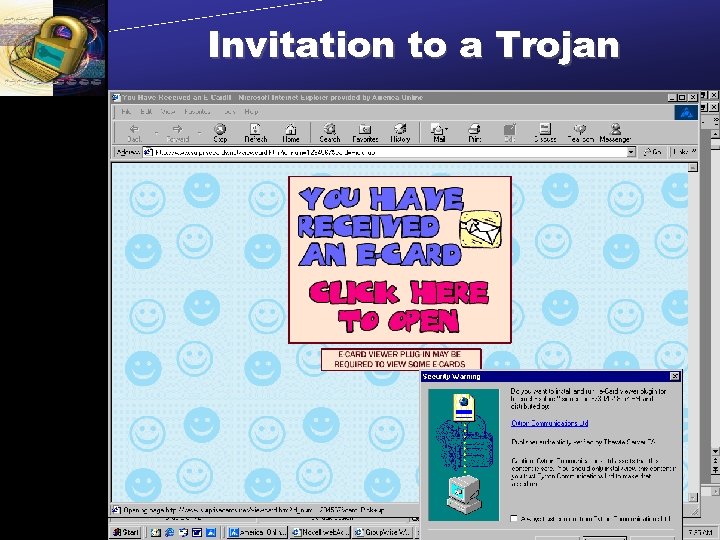
Invitation to a Trojan Copyright 2002

Payload Copyright 2002
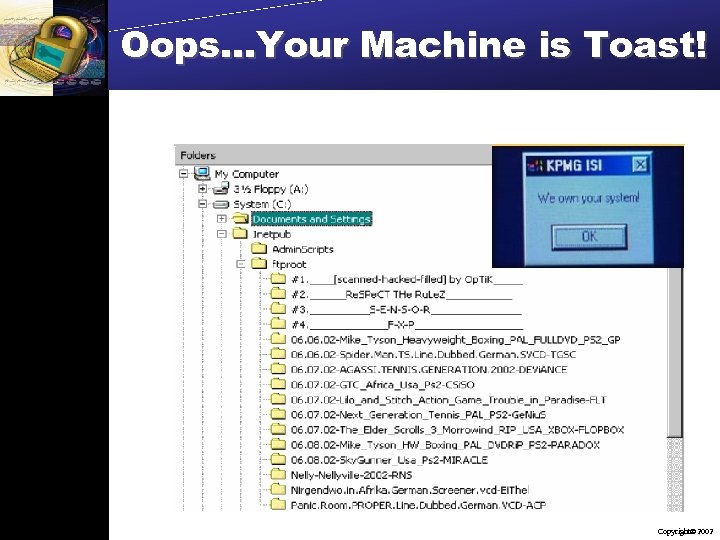
Oops…Your Machine is Toast! Copyright 2002

Political Issues and Malware Legislation Prosecution Multiple jurisdictions Downstream liability Copyright 2002

Goals of Malware Management Detection of incident Initial response Response strategy formulation Investigation Isolate and contain Recovery Report Lessons learned Copyright 2002
Costs of Malware Management Procurement Initial implementation Maintenance Impact (negative) to systems performance Ongoing postural reassessment cycle Copyright 2002
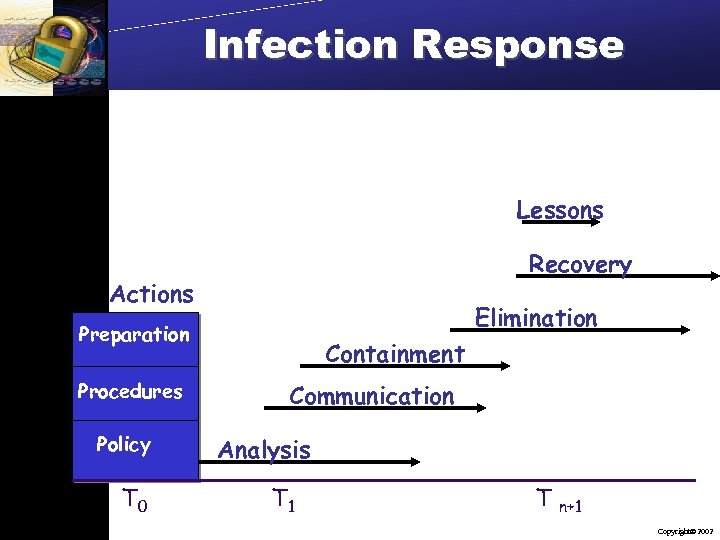
Infection Response Lessons Recovery Actions Elimination Preparation Procedures Policy T 0 Containment Communication Analysis T 1 T n+1 Copyright 2002
34e42f03dde57e9ad731d9c92c9049a9.ppt