8ab52bff6d3367444aa3e718ff130f55.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 12
 Video Value Chains Case Study Update: The Evolution of Video Services Natalie Klym Research Associate, MIT nklym@cfp. mit. edu May 31, 2007 Philadelphia, PA
Video Value Chains Case Study Update: The Evolution of Video Services Natalie Klym Research Associate, MIT nklym@cfp. mit. edu May 31, 2007 Philadelphia, PA
 The goals of today’s talk • Give an overview of the video case study • Look at today’s changes in historical context • Present a framework for video platforms • Examine current competitive dynamics among video services • Discuss future trends
The goals of today’s talk • Give an overview of the video case study • Look at today’s changes in historical context • Present a framework for video platforms • Examine current competitive dynamics among video services • Discuss future trends
 Overview of video case study • The evolution of the U. S. TV industry can be broken down into three phases – Original broadcast model (1930 s-1940 s) – First reinvention of television (1940 s-1990 s) – Second reinvention of television (1990 s – present) • Each phase includes a combination of – TV extensions – New delivery platforms – New content providers • General trend towards value chain fragmentation • Today’s video landscape is messy and complex, and changing quickly
Overview of video case study • The evolution of the U. S. TV industry can be broken down into three phases – Original broadcast model (1930 s-1940 s) – First reinvention of television (1940 s-1990 s) – Second reinvention of television (1990 s – present) • Each phase includes a combination of – TV extensions – New delivery platforms – New content providers • General trend towards value chain fragmentation • Today’s video landscape is messy and complex, and changing quickly
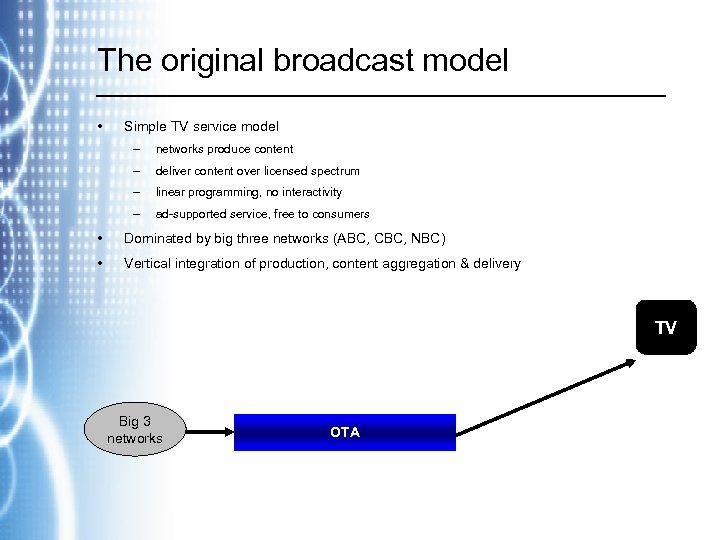 The original broadcast model • Simple TV service model – networks produce content – deliver content over licensed spectrum – linear programming, no interactivity – ad-supported service, free to consumers • Dominated by big three networks (ABC, CBC, NBC) • Vertical integration of production, content aggregation & delivery TV Big 3 networks OTA
The original broadcast model • Simple TV service model – networks produce content – deliver content over licensed spectrum – linear programming, no interactivity – ad-supported service, free to consumers • Dominated by big three networks (ABC, CBC, NBC) • Vertical integration of production, content aggregation & delivery TV Big 3 networks OTA
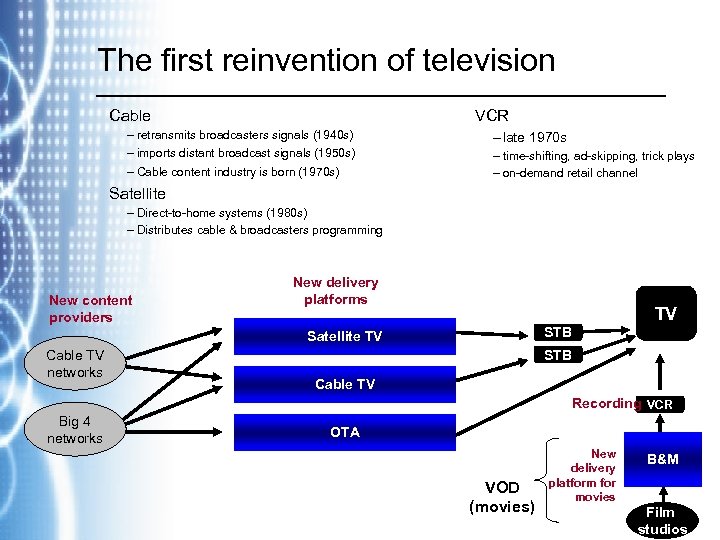 The first reinvention of television Cable VCR – retransmits broadcasters signals (1940 s) – imports distant broadcast signals (1950 s) – Cable content industry is born (1970 s) – late 1970 s – time-shifting, ad-skipping, trick plays – on-demand retail channel Satellite – Direct-to-home systems (1980 s) – Distributes cable & broadcasters programming New content providers New delivery platforms TV STB Satellite TV Cable TV networks STB Cable TV Recording VCR Big 4 networks OTA VOD (movies) New delivery platform for movies B&M Film studios
The first reinvention of television Cable VCR – retransmits broadcasters signals (1940 s) – imports distant broadcast signals (1950 s) – Cable content industry is born (1970 s) – late 1970 s – time-shifting, ad-skipping, trick plays – on-demand retail channel Satellite – Direct-to-home systems (1980 s) – Distributes cable & broadcasters programming New content providers New delivery platforms TV STB Satellite TV Cable TV networks STB Cable TV Recording VCR Big 4 networks OTA VOD (movies) New delivery platform for movies B&M Film studios
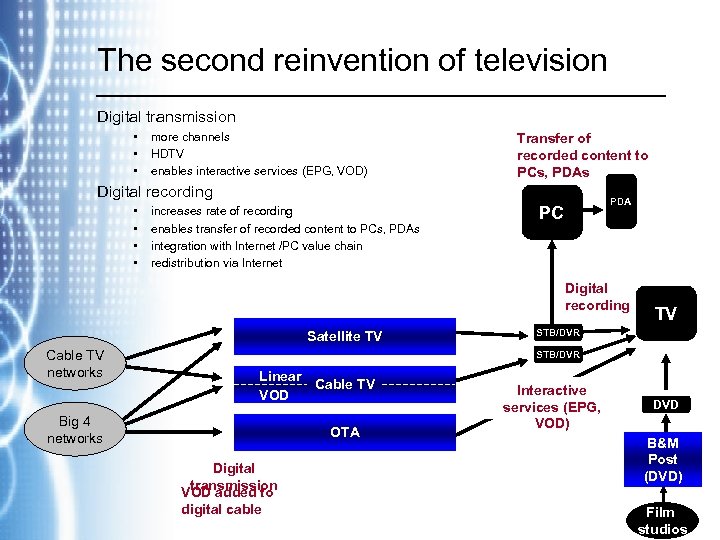 The second reinvention of television Digital transmission • • • more channels HDTV enables interactive services (EPG, VOD) Transfer of recorded content to PCs, PDAs Digital recording • • increases rate of recording enables transfer of recorded content to PCs, PDAs integration with Internet /PC value chain redistribution via Internet PDA PC Digital recording Satellite TV Cable TV networks TV STB/DVR Linear Cable TV VOD Big 4 networks OTA Digital transmission VOD added to digital cable Interactive services (EPG, VOD) DVD B&M Post (DVD) Film studios
The second reinvention of television Digital transmission • • • more channels HDTV enables interactive services (EPG, VOD) Transfer of recorded content to PCs, PDAs Digital recording • • increases rate of recording enables transfer of recorded content to PCs, PDAs integration with Internet /PC value chain redistribution via Internet PDA PC Digital recording Satellite TV Cable TV networks TV STB/DVR Linear Cable TV VOD Big 4 networks OTA Digital transmission VOD added to digital cable Interactive services (EPG, VOD) DVD B&M Post (DVD) Film studios
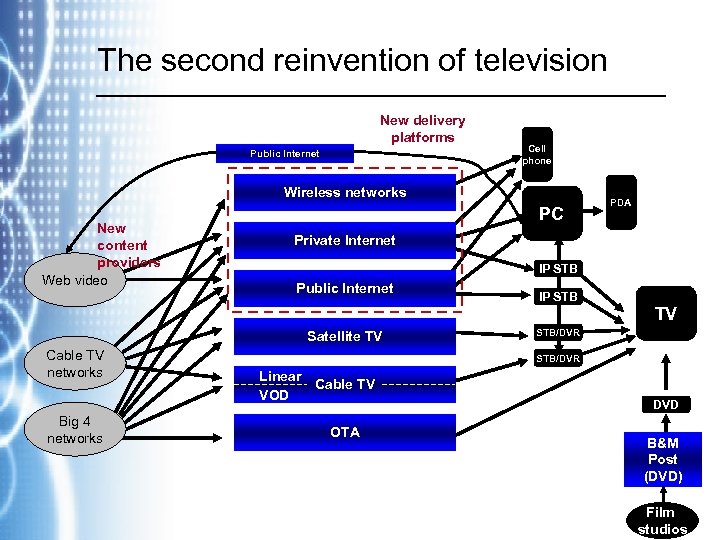 The second reinvention of television New delivery platforms Public Internet Cell phone Wireless networks New content providers Web video PC PDA Private Internet IP STB Public Internet IP STB TV Satellite TV Cable TV networks Big 4 networks STB/DVR Linear Cable TV VOD OTA DVD B&M Post (DVD) Film studios
The second reinvention of television New delivery platforms Public Internet Cell phone Wireless networks New content providers Web video PC PDA Private Internet IP STB Public Internet IP STB TV Satellite TV Cable TV networks Big 4 networks STB/DVR Linear Cable TV VOD OTA DVD B&M Post (DVD) Film studios
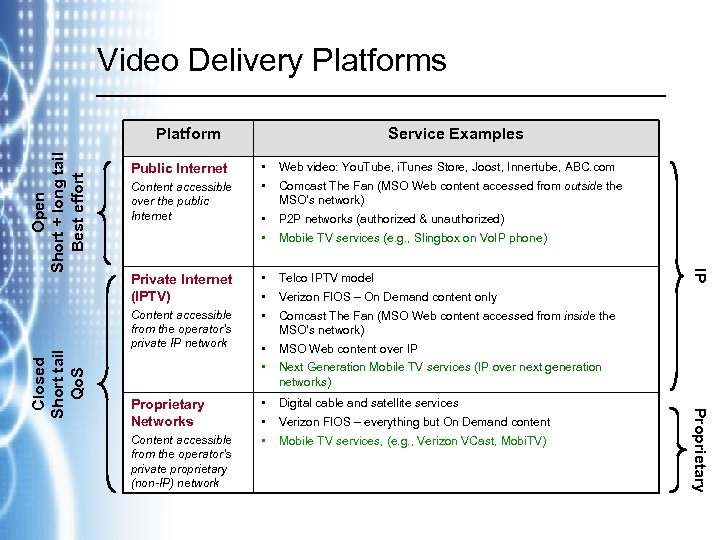 Video Delivery Platforms Content accessible over the public Internet Private Internet (IPTV) Content accessible from the operator’s private IP network Proprietary Networks Content accessible from the operator’s private proprietary (non-IP) network • • Web video: You. Tube, i. Tunes Store, Joost, Innertube, ABC. com • • P 2 P networks (authorized & unauthorized) • • • Telco IPTV model • • MSO Web content over IP • • • Digital cable and satellite services Comcast The Fan (MSO Web content accessed from outside the MSO’s network) Mobile TV services (e. g. , Slingbox on Vo. IP phone) Verizon FIOS – On Demand content only Comcast The Fan (MSO Web content accessed from inside the MSO’s network) Next Generation Mobile TV services (IP over next generation networks) Verizon FIOS – everything but On Demand content Mobile TV services, (e. g. , Verizon VCast, Mobi. TV) Proprietary Closed Short tail Qo. S Public Internet Service Examples IP Open Short + long tail Best effort Platform
Video Delivery Platforms Content accessible over the public Internet Private Internet (IPTV) Content accessible from the operator’s private IP network Proprietary Networks Content accessible from the operator’s private proprietary (non-IP) network • • Web video: You. Tube, i. Tunes Store, Joost, Innertube, ABC. com • • P 2 P networks (authorized & unauthorized) • • • Telco IPTV model • • MSO Web content over IP • • • Digital cable and satellite services Comcast The Fan (MSO Web content accessed from outside the MSO’s network) Mobile TV services (e. g. , Slingbox on Vo. IP phone) Verizon FIOS – On Demand content only Comcast The Fan (MSO Web content accessed from inside the MSO’s network) Next Generation Mobile TV services (IP over next generation networks) Verizon FIOS – everything but On Demand content Mobile TV services, (e. g. , Verizon VCast, Mobi. TV) Proprietary Closed Short tail Qo. S Public Internet Service Examples IP Open Short + long tail Best effort Platform
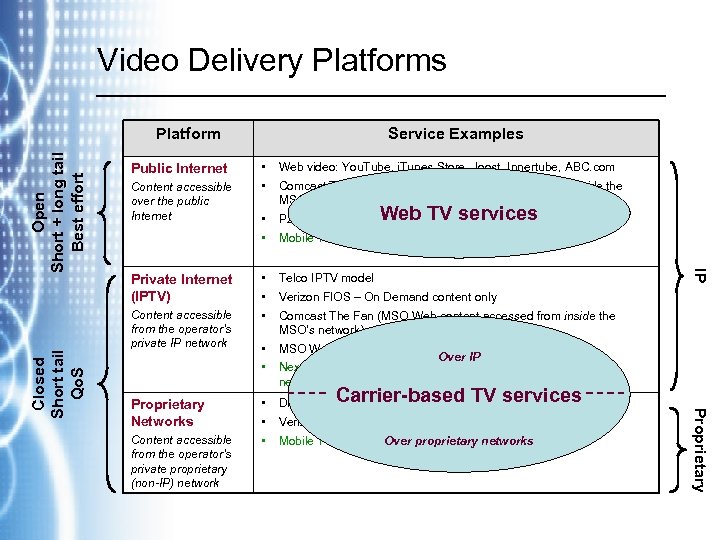 Video Delivery Platforms Content accessible over the public Internet Private Internet (IPTV) Content accessible from the operator’s private IP network Proprietary Networks Content accessible from the operator’s private proprietary (non-IP) network • • Web video: You. Tube, i. Tunes Store, Joost, Innertube, ABC. com • • P 2 P networks (authorized & unauthorized) • • • Telco IPTV model • • MSO Web content over IP • • • Digital cable and satellite services Comcast The Fan (MSO Web content accessed from outside the MSO’s network) Web TV services Mobile TV services (e. g. , Slingbox on Vo. IP phone) Verizon FIOS – On Demand content only Comcast The Fan (MSO Web content accessed from inside the MSO’s network) Over IP Next Generation Mobile TV services (IP over next generation networks) Carrier-based TV services Verizon FIOS – everything but On Demand content Mobile TV services, Over proprietary networks (e. g. , Verizon VCast, Mobi. TV) Proprietary Closed Short tail Qo. S Public Internet Service Examples IP Open Short + long tail Best effort Platform
Video Delivery Platforms Content accessible over the public Internet Private Internet (IPTV) Content accessible from the operator’s private IP network Proprietary Networks Content accessible from the operator’s private proprietary (non-IP) network • • Web video: You. Tube, i. Tunes Store, Joost, Innertube, ABC. com • • P 2 P networks (authorized & unauthorized) • • • Telco IPTV model • • MSO Web content over IP • • • Digital cable and satellite services Comcast The Fan (MSO Web content accessed from outside the MSO’s network) Web TV services Mobile TV services (e. g. , Slingbox on Vo. IP phone) Verizon FIOS – On Demand content only Comcast The Fan (MSO Web content accessed from inside the MSO’s network) Over IP Next Generation Mobile TV services (IP over next generation networks) Carrier-based TV services Verizon FIOS – everything but On Demand content Mobile TV services, Over proprietary networks (e. g. , Verizon VCast, Mobi. TV) Proprietary Closed Short tail Qo. S Public Internet Service Examples IP Open Short + long tail Best effort Platform
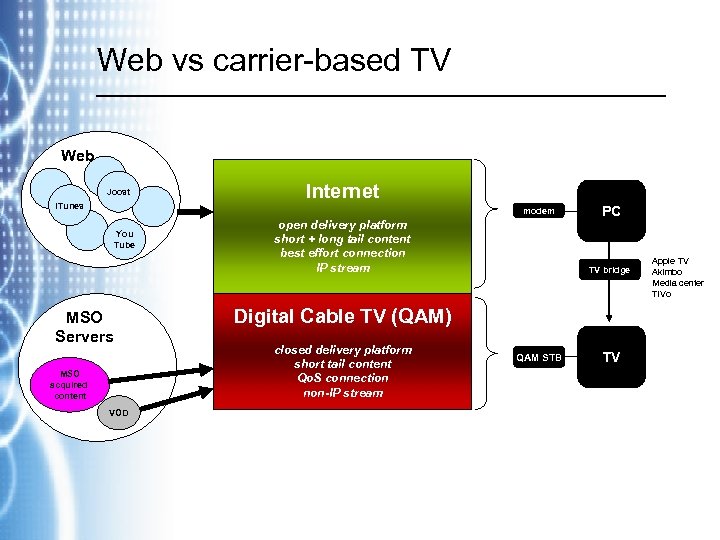 Web vs carrier-based TV Web Joost i. Tunes Internet modem You Tube MSO Servers MSO acquired content VOD open delivery platform short + long tail content best effort connection IP stream PC TV bridge Digital Cable TV (QAM) closed delivery platform short tail content Qo. S connection non-IP stream QAM STB TV Apple TV Akimbo Media center Ti. Vo
Web vs carrier-based TV Web Joost i. Tunes Internet modem You Tube MSO Servers MSO acquired content VOD open delivery platform short + long tail content best effort connection IP stream PC TV bridge Digital Cable TV (QAM) closed delivery platform short tail content Qo. S connection non-IP stream QAM STB TV Apple TV Akimbo Media center Ti. Vo
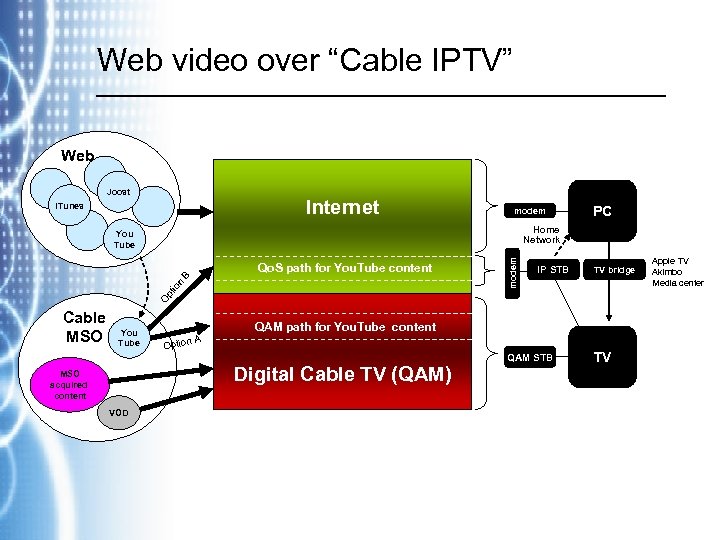 Web video over “Cable IPTV” Web Joost Internet i. Tunes modem PC Home Network IP STB TV bridge O pt io n B Qo. S path for You. Tube content modem You Tube Cable MSO You Tube QAM path for You. Tube content A Option Digital Cable TV (QAM) MSO acquired content VOD QAM STB TV Apple TV Akimbo Media center
Web video over “Cable IPTV” Web Joost Internet i. Tunes modem PC Home Network IP STB TV bridge O pt io n B Qo. S path for You. Tube content modem You Tube Cable MSO You Tube QAM path for You. Tube content A Option Digital Cable TV (QAM) MSO acquired content VOD QAM STB TV Apple TV Akimbo Media center
 Will Web TV compete with or complement carrierbased TV services? • “Unbundled value chains innovate faster. The Apple’s and Microsoft’s will provide experiences, not pipes and will be more agile than the network operators who provide more integrated services. ” • “The user has become the master. Consumers know how to put together their own bundle of services. It doesn’t have to be an integrated solution. ” • “We’re starting to see the tail wagging the dog – the terminal is driving consumer choices. In the future, Sony and Samsung will have TVs connected to the Internet. People will buy devices that happen to connect to content. ” • “At the end of the day, most people buy bundles of services. The consumer will buy the least costly package. ”
Will Web TV compete with or complement carrierbased TV services? • “Unbundled value chains innovate faster. The Apple’s and Microsoft’s will provide experiences, not pipes and will be more agile than the network operators who provide more integrated services. ” • “The user has become the master. Consumers know how to put together their own bundle of services. It doesn’t have to be an integrated solution. ” • “We’re starting to see the tail wagging the dog – the terminal is driving consumer choices. In the future, Sony and Samsung will have TVs connected to the Internet. People will buy devices that happen to connect to content. ” • “At the end of the day, most people buy bundles of services. The consumer will buy the least costly package. ”


