67bb03e0be562f20fd278e6010975fb1.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25
 Video
Video
 Using video o Carefully planned, well-executed video clips can make a dramatic difference in a multimedia project o Use video only when all other methods (text, still images) are not enough; don’t use it just because it’s possible
Using video o Carefully planned, well-executed video clips can make a dramatic difference in a multimedia project o Use video only when all other methods (text, still images) are not enough; don’t use it just because it’s possible
 Obtaining video clips o Shoot your own clips o Buy footage; this can be a nightmare since the licensing rights and permission may be difficult to obtain o On some projects you have no choice but to pay the price for required footage
Obtaining video clips o Shoot your own clips o Buy footage; this can be a nightmare since the licensing rights and permission may be difficult to obtain o On some projects you have no choice but to pay the price for required footage
 Some technical details o Light is converted into an electric signal by a sensor called a CCD o Good cameras have 3 CCD’s (RGB) o Component video is split into two separate chroma channels and a brightness channel o Composite video has all signals mixed together and carried on a single cable
Some technical details o Light is converted into an electric signal by a sensor called a CCD o Good cameras have 3 CCD’s (RGB) o Component video is split into two separate chroma channels and a brightness channel o Composite video has all signals mixed together and carried on a single cable
 Broadcast video standards o NTSC: Used in USA, Japan and some other countries o PAL: Europe, Australia, South Africa o SECAM: France, Russia and few other countries o HDTV: High Definition TV. 16: 9 aspect ratio.
Broadcast video standards o NTSC: Used in USA, Japan and some other countries o PAL: Europe, Australia, South Africa o SECAM: France, Russia and few other countries o HDTV: High Definition TV. 16: 9 aspect ratio.
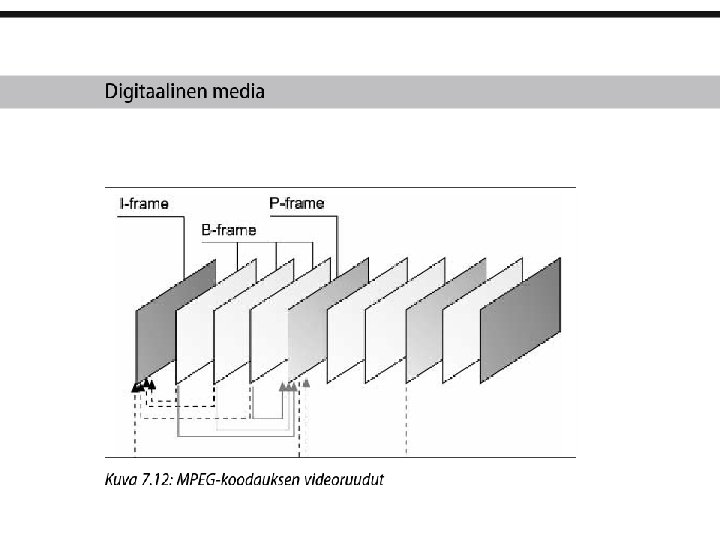
 Video compression o Even a small 10 -second clip of full-motion video requires transfer of an enormous amount of data in a very short amount of time o One frame of 24 -bits requires almost 1 MB of computer data, 30 seconds will require a one gigabyte o Full-size, full-motion video requires that the computer deliver data at about 30 MB per second o This technological bottleneck is overcome using digital video compression schemes or codecs (coders/decoders)
Video compression o Even a small 10 -second clip of full-motion video requires transfer of an enormous amount of data in a very short amount of time o One frame of 24 -bits requires almost 1 MB of computer data, 30 seconds will require a one gigabyte o Full-size, full-motion video requires that the computer deliver data at about 30 MB per second o This technological bottleneck is overcome using digital video compression schemes or codecs (coders/decoders)
 Video compression o A codec is the algorithm used to compress a video for delivery and then decode it in real-time for fast playback o All popular codecs employ lossy compression algorithms o Popular codecs: MPEG, Divx, Real. Video, DVI/Indeo, Cinepak
Video compression o A codec is the algorithm used to compress a video for delivery and then decode it in real-time for fast playback o All popular codecs employ lossy compression algorithms o Popular codecs: MPEG, Divx, Real. Video, DVI/Indeo, Cinepak
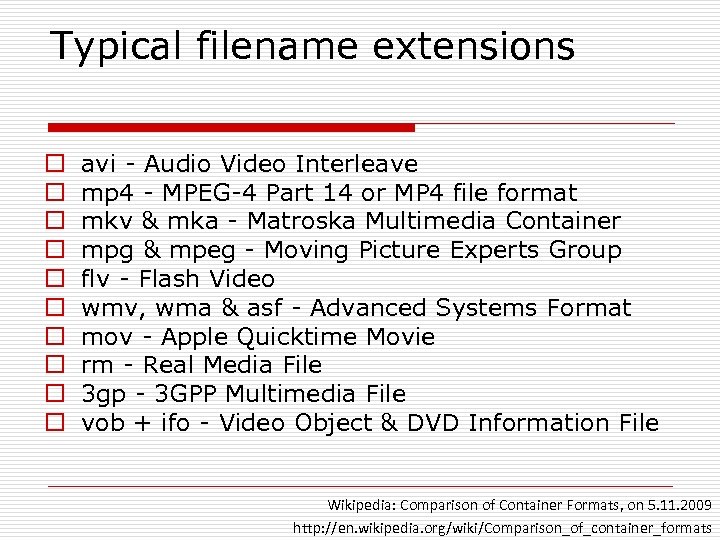 Typical filename extensions o o o o o avi - Audio Video Interleave mp 4 - MPEG-4 Part 14 or MP 4 file format mkv & mka - Matroska Multimedia Container mpg & mpeg - Moving Picture Experts Group flv - Flash Video wmv, wma & asf - Advanced Systems Format mov - Apple Quicktime Movie rm - Real Media File 3 gp - 3 GPP Multimedia File vob + ifo - Video Object & DVD Information File Wikipedia: Comparison of Container Formats, on 5. 11. 2009 http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/Comparison_of_container_formats
Typical filename extensions o o o o o avi - Audio Video Interleave mp 4 - MPEG-4 Part 14 or MP 4 file format mkv & mka - Matroska Multimedia Container mpg & mpeg - Moving Picture Experts Group flv - Flash Video wmv, wma & asf - Advanced Systems Format mov - Apple Quicktime Movie rm - Real Media File 3 gp - 3 GPP Multimedia File vob + ifo - Video Object & DVD Information File Wikipedia: Comparison of Container Formats, on 5. 11. 2009 http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/Comparison_of_container_formats

 (Net videos, CD-ROM videos, oldish) (DVD, digital TV, HDTV) (multimedia, digi-tv, mobile)
(Net videos, CD-ROM videos, oldish) (DVD, digital TV, HDTV) (multimedia, digi-tv, mobile)
 (Edition software) (Post production software)
(Edition software) (Post production software)
 Use of video in multimedia (good video is illustrative) (use static video, near shots) (less than 1 min clips) (video is confirming and creates mental images) (divide long video into clips with interactivity)
Use of video in multimedia (good video is illustrative) (use static video, near shots) (less than 1 min clips) (video is confirming and creates mental images) (divide long video into clips with interactivity)
 Animation
Animation
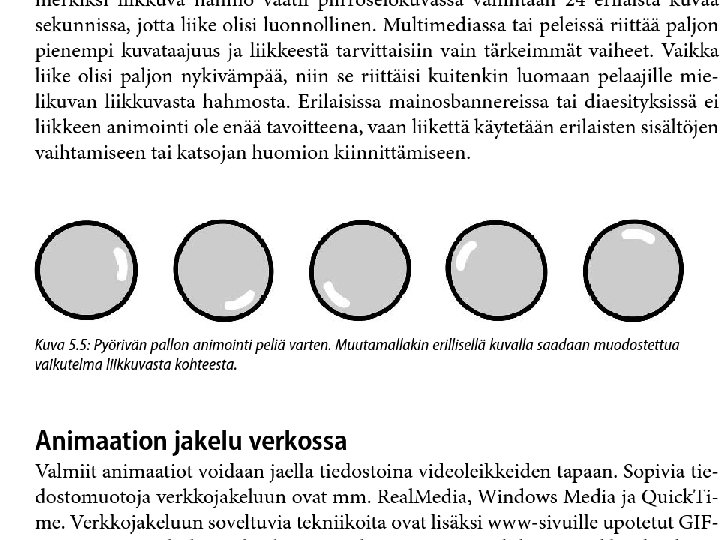
 Principles of animation o Animation is possible because of a biological phenomenon known as persistence of vision and a psychological phenomenon called phi o An object seen by the human eye remains chemically mapped on the eye’s retina for a brief time after viewing o Combined with the human mind’s need to conceptually complete a perceived action, this makes it possible for a series of images to blend together into a visual illusion of movement
Principles of animation o Animation is possible because of a biological phenomenon known as persistence of vision and a psychological phenomenon called phi o An object seen by the human eye remains chemically mapped on the eye’s retina for a brief time after viewing o Combined with the human mind’s need to conceptually complete a perceived action, this makes it possible for a series of images to blend together into a visual illusion of movement
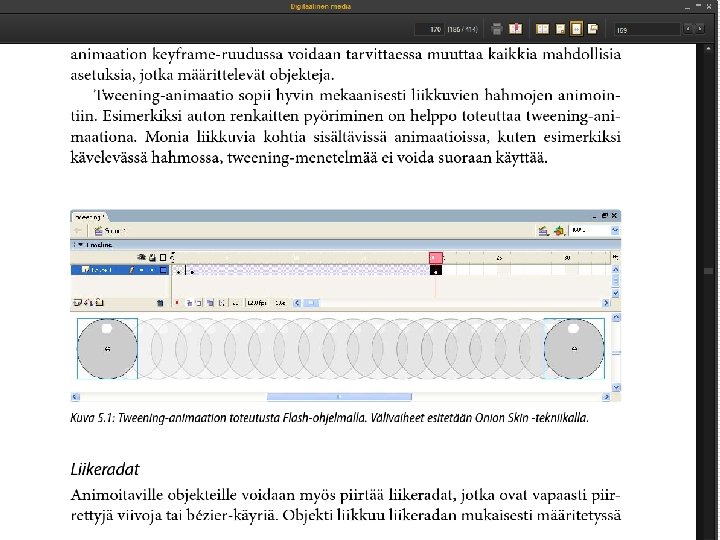
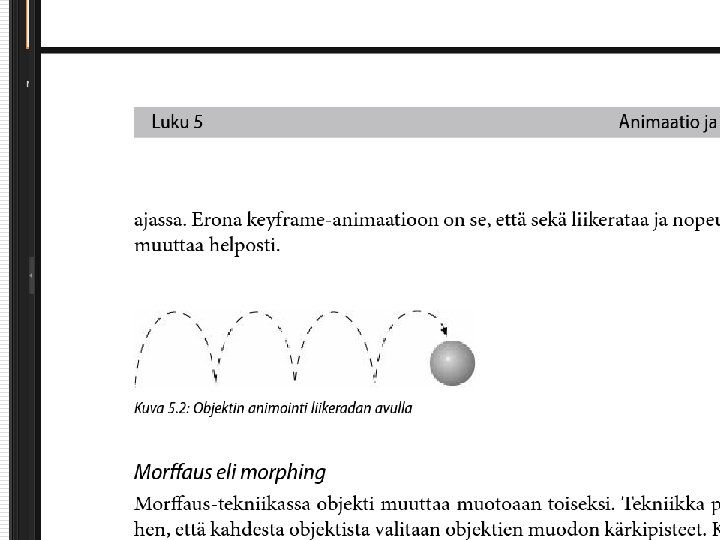
 Computer animation o Computer animation programs typically use layers, keyframes and tweening techniques o These methods are commonly used also with traditional animations that are done without computers o You can usually set your own framerate, but the rate at which changes are computed and screens actully refreshed will depend on the power of your display platform and hardware o The smaller the object, the faster it can move
Computer animation o Computer animation programs typically use layers, keyframes and tweening techniques o These methods are commonly used also with traditional animations that are done without computers o You can usually set your own framerate, but the rate at which changes are computed and screens actully refreshed will depend on the power of your display platform and hardware o The smaller the object, the faster it can move
 Animation file formats o Some file formats are designed specially for animations; they can be often ported among applications and platforms o Popular animation formats: Director (. dir and. dcr), 3 D Studio Max (. max), Windows Audio Video Interleave (. avi), Machintosh Quicktime (. mov), Motion Video (. mpg), Flash (. swf)
Animation file formats o Some file formats are designed specially for animations; they can be often ported among applications and platforms o Popular animation formats: Director (. dir and. dcr), 3 D Studio Max (. max), Windows Audio Video Interleave (. avi), Machintosh Quicktime (. mov), Motion Video (. mpg), Flash (. swf)
 Video vs. animation o Video includes something that is real; an animation has no limits o. When to choose video, when animation? o http: //streams. metropolia. fi/old/opto metria/skiaskopia/
Video vs. animation o Video includes something that is real; an animation has no limits o. When to choose video, when animation? o http: //streams. metropolia. fi/old/opto metria/skiaskopia/
 (Animation software) , Blender. (Camtasia Studio, Captivate)
(Animation software) , Blender. (Camtasia Studio, Captivate)


 Example: o 2 D Visualization of nuclear power plant components o 3 D visualization of a wood pressing machine
Example: o 2 D Visualization of nuclear power plant components o 3 D visualization of a wood pressing machine


