e5f141e9f5b62f5a6e6650010cbedeaa.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 17
 Version 11/9/2001 Lecture Options Pricing 1
Version 11/9/2001 Lecture Options Pricing 1
 Topics Valuation and Pricing (Black Scholes) Speculation Delta Hedging Copyright K. Cuthbertson, D. Nitzsche. 2
Topics Valuation and Pricing (Black Scholes) Speculation Delta Hedging Copyright K. Cuthbertson, D. Nitzsche. 2
 Valuation/Pricing of Options Copyright K. Cuthbertson, D. Nitzsche. 3
Valuation/Pricing of Options Copyright K. Cuthbertson, D. Nitzsche. 3
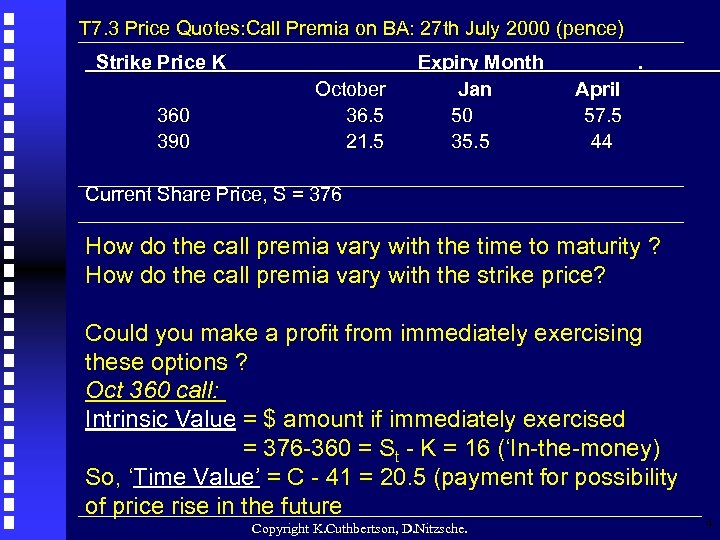 T 7. 3 Price Quotes: Call Premia on BA: 27 th July 2000 (pence) Strike Price K 360 390 ___ October 36. 5 21. 5 Expiry Month Jan 50 35. 5 . April 57. 5 44 Current Share Price, S = 376 How do the call premia vary with the time to maturity ? How do the call premia vary with the strike price? Could you make a profit from immediately exercising these options ? Oct 360 call: Intrinsic Value = $ amount if immediately exercised = 376 -360 = St - K = 16 (‘In-the-money) So, ‘Time Value’ = C - 41 = 20. 5 (payment for possibility of price rise in the future Copyright K. Cuthbertson, D. Nitzsche. 4
T 7. 3 Price Quotes: Call Premia on BA: 27 th July 2000 (pence) Strike Price K 360 390 ___ October 36. 5 21. 5 Expiry Month Jan 50 35. 5 . April 57. 5 44 Current Share Price, S = 376 How do the call premia vary with the time to maturity ? How do the call premia vary with the strike price? Could you make a profit from immediately exercising these options ? Oct 360 call: Intrinsic Value = $ amount if immediately exercised = 376 -360 = St - K = 16 (‘In-the-money) So, ‘Time Value’ = C - 41 = 20. 5 (payment for possibility of price rise in the future Copyright K. Cuthbertson, D. Nitzsche. 4
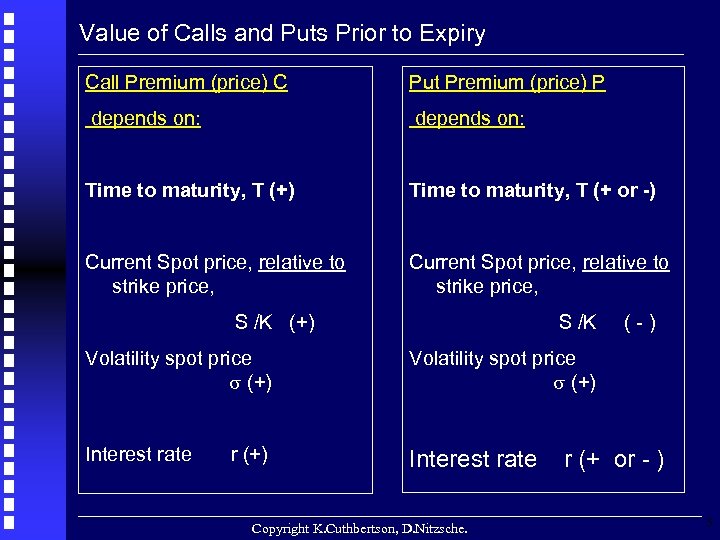 Value of Calls and Puts Prior to Expiry Call Premium (price) C Put Premium (price) P depends on: Time to maturity, T (+) Time to maturity, T (+ or -) Current Spot price, relative to strike price, S /K (+) S /K Volatility spot price (+) Interest rate (-) r (+) Copyright K. Cuthbertson, D. Nitzsche. r (+ or - ) 5
Value of Calls and Puts Prior to Expiry Call Premium (price) C Put Premium (price) P depends on: Time to maturity, T (+) Time to maturity, T (+ or -) Current Spot price, relative to strike price, S /K (+) S /K Volatility spot price (+) Interest rate (-) r (+) Copyright K. Cuthbertson, D. Nitzsche. r (+ or - ) 5
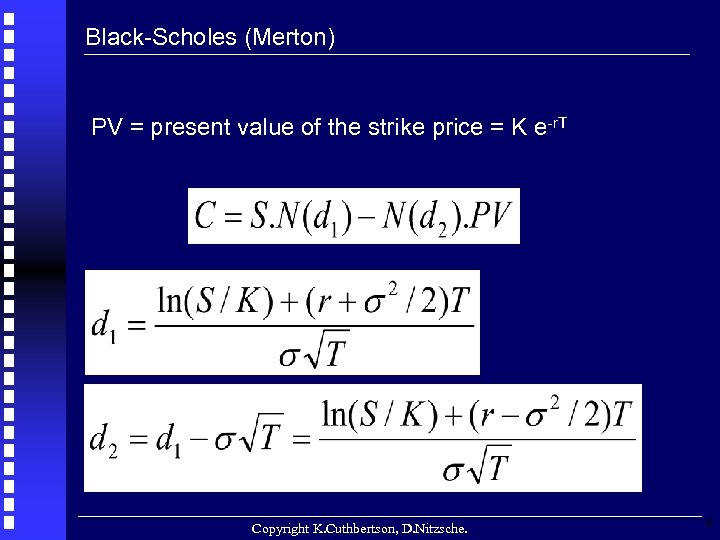 Black-Scholes (Merton) PV = present value of the strike price = K e-r. T Copyright K. Cuthbertson, D. Nitzsche. 6
Black-Scholes (Merton) PV = present value of the strike price = K e-r. T Copyright K. Cuthbertson, D. Nitzsche. 6
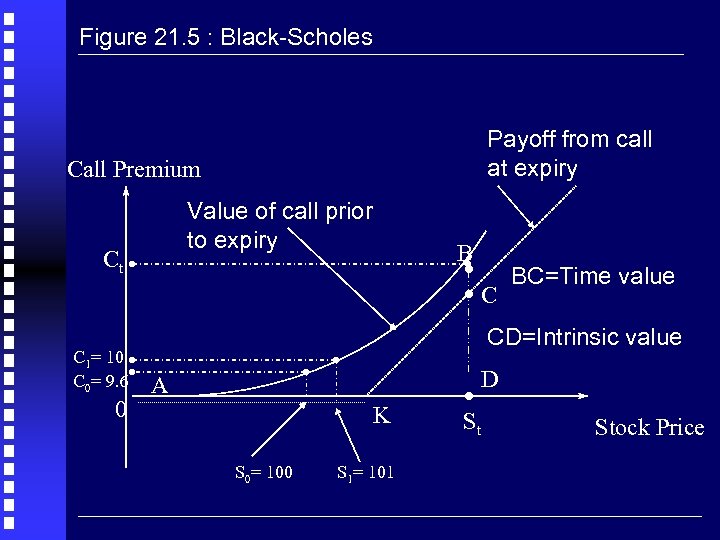 Figure 21. 5 : Black-Scholes Payoff from call at expiry Call Premium Value of call prior to expiry Ct C 1= 10 C 0= 9. 6 0 . BC=Time value. C B CD=Intrinsic value A K S 0= 100 S 1= 101 . D St Stock Price
Figure 21. 5 : Black-Scholes Payoff from call at expiry Call Premium Value of call prior to expiry Ct C 1= 10 C 0= 9. 6 0 . BC=Time value. C B CD=Intrinsic value A K S 0= 100 S 1= 101 . D St Stock Price
 Black-Scholes Key results are CALLS Call premium increases as stock price increases (but less than one-for-one) Call premium increases if the volatility of the stock increases PUTS Put premium falls as stock price increases (but less than one-for-one) Put premium increases if the volatility of the stock increases
Black-Scholes Key results are CALLS Call premium increases as stock price increases (but less than one-for-one) Call premium increases if the volatility of the stock increases PUTS Put premium falls as stock price increases (but less than one-for-one) Put premium increases if the volatility of the stock increases
 Speculation with Options Copyright K. Cuthbertson, D. Nitzsche. 9
Speculation with Options Copyright K. Cuthbertson, D. Nitzsche. 9
 Speculation with Options (Before Maturity) Buy low and sell high Expect a bull market - then buy a call and close out the position before maturity ( that is, sell the call at a higher call premium) Profit (before maturity) = C 1 - C 0 = 5. 2 - 5. 0 Your net position of ‘zero’ is noted by the Clearing House which sends you the $0. 2 (and cancels any ‘delivery’ to you) Sell high and buy low Expect a bear market then sell a call at C 0 = 10 and close out the position by buying back a call at C 1 = 9. 8 (prior to maturity) Copyright K. Cuthbertson, D. Nitzsche. 10
Speculation with Options (Before Maturity) Buy low and sell high Expect a bull market - then buy a call and close out the position before maturity ( that is, sell the call at a higher call premium) Profit (before maturity) = C 1 - C 0 = 5. 2 - 5. 0 Your net position of ‘zero’ is noted by the Clearing House which sends you the $0. 2 (and cancels any ‘delivery’ to you) Sell high and buy low Expect a bear market then sell a call at C 0 = 10 and close out the position by buying back a call at C 1 = 9. 8 (prior to maturity) Copyright K. Cuthbertson, D. Nitzsche. 10
 Delta Hedging with Options Copyright K. Cuthbertson, D. Nitzsche. 11
Delta Hedging with Options Copyright K. Cuthbertson, D. Nitzsche. 11
 Delta Hedging with Options Problem: You currently hold shares but you fear high volatility of stock prices over the next month. You want to protect the current value of your stock position until the market returns to ‘normal’. Can you “hedge” your stock position using options ? A call option on the share is available with a “delta” of 0. 4 which implies: When S increases by +$1 (e. g. from 100 to 101), then C increases by $0. 4 (e. g. from 9. 6 to 10) Copyright K. Cuthbertson, D. Nitzsche. 12
Delta Hedging with Options Problem: You currently hold shares but you fear high volatility of stock prices over the next month. You want to protect the current value of your stock position until the market returns to ‘normal’. Can you “hedge” your stock position using options ? A call option on the share is available with a “delta” of 0. 4 which implies: When S increases by +$1 (e. g. from 100 to 101), then C increases by $0. 4 (e. g. from 9. 6 to 10) Copyright K. Cuthbertson, D. Nitzsche. 12
 Delta Hedging with Options Note: The ‘contract size’ for one call option contract is for 100 shares But the price of the call option C is quoted as if there was only one share underlying the option (i. e. we need to multiply C by 100 to get the invoice price of the option) Copyright K. Cuthbertson, D. Nitzsche. 13
Delta Hedging with Options Note: The ‘contract size’ for one call option contract is for 100 shares But the price of the call option C is quoted as if there was only one share underlying the option (i. e. we need to multiply C by 100 to get the invoice price of the option) Copyright K. Cuthbertson, D. Nitzsche. 13
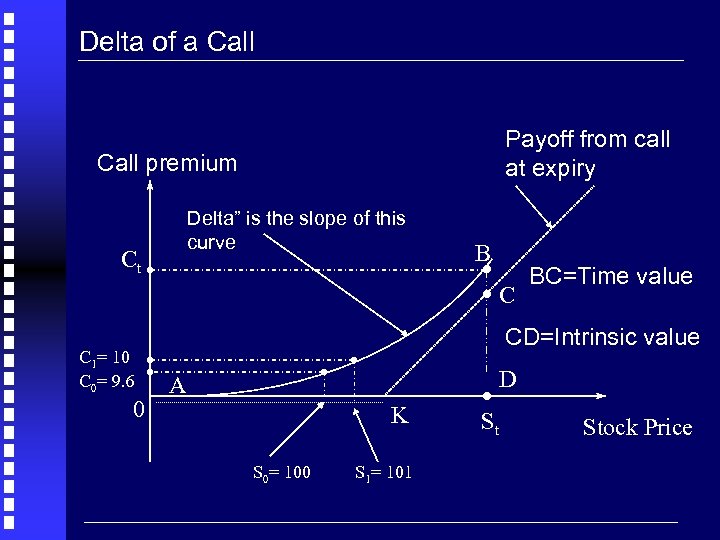 Delta of a Call Payoff from call at expiry Call premium Delta” is the slope of this curve Ct C 1= 10 C 0= 9. 6 0 . BC=Time value. C B CD=Intrinsic value A K S 0= 100 S 1= 101 . D St Stock Price
Delta of a Call Payoff from call at expiry Call premium Delta” is the slope of this curve Ct C 1= 10 C 0= 9. 6 0 . BC=Time value. C B CD=Intrinsic value A K S 0= 100 S 1= 101 . D St Stock Price
 Delta Hedging with Options Consider the following “portfolio” 40 -shares plus 1 written (sold) call option (at C 0 = 10) Suppose S falls by $1 over the next month THEN fall in C is 0. 4 ( = “delta” of the call) 9. 6 So C falls to C 1 = To close out you must now buy back at C 1 = 9. 6 Loss on 40 shares Gain on initial written call = 100 (C 0 - C 1 )= 100(0. 4) = $40 DELTA HEDGING YOUR 40 SHARES WITH 1 WRITTEN CALL OPTION MEANS THAT THE VALUE OF YOUR ‘POSITION’ WILL BE UNCHANGED. Copyright K. Cuthbertson, D. Nitzsche. 15
Delta Hedging with Options Consider the following “portfolio” 40 -shares plus 1 written (sold) call option (at C 0 = 10) Suppose S falls by $1 over the next month THEN fall in C is 0. 4 ( = “delta” of the call) 9. 6 So C falls to C 1 = To close out you must now buy back at C 1 = 9. 6 Loss on 40 shares Gain on initial written call = 100 (C 0 - C 1 )= 100(0. 4) = $40 DELTA HEDGING YOUR 40 SHARES WITH 1 WRITTEN CALL OPTION MEANS THAT THE VALUE OF YOUR ‘POSITION’ WILL BE UNCHANGED. Copyright K. Cuthbertson, D. Nitzsche. 15
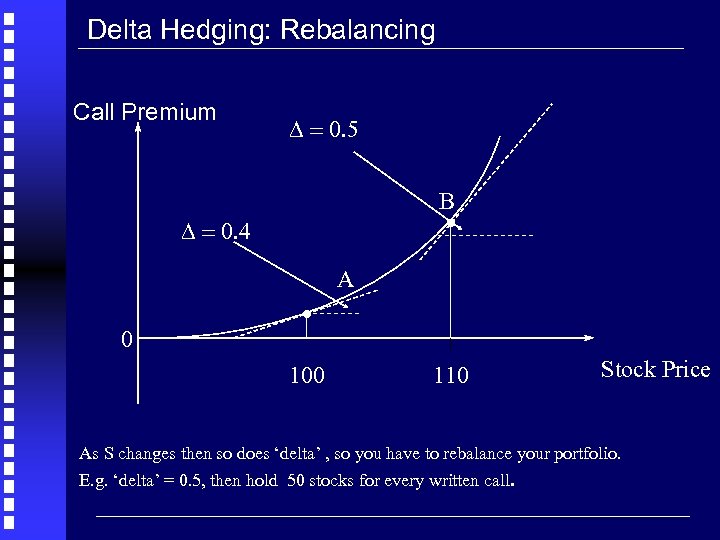 Delta Hedging: Rebalancing Call Premium D = 0. 5 . B D = 0. 4 0 . 100 A 110 Stock Price As S changes then so does ‘delta’ , so you have to rebalance your portfolio. E. g. ‘delta’ = 0. 5, then hold 50 stocks for every written call.
Delta Hedging: Rebalancing Call Premium D = 0. 5 . B D = 0. 4 0 . 100 A 110 Stock Price As S changes then so does ‘delta’ , so you have to rebalance your portfolio. E. g. ‘delta’ = 0. 5, then hold 50 stocks for every written call.
 END OF SLIDES Copyright K. Cuthbertson, D. Nitzsche. 17
END OF SLIDES Copyright K. Cuthbertson, D. Nitzsche. 17


