4241b95931d4961032cbd687c747a1a4.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 21
 Version 1/9/2001 FINANCIAL ENGINEERING: DERIVATIVES AND RISK MANAGEMENT (J. Wiley, 2001) K. Cuthbertson and D. Nitzsche LECTURE T-Bond Futures 1
Version 1/9/2001 FINANCIAL ENGINEERING: DERIVATIVES AND RISK MANAGEMENT (J. Wiley, 2001) K. Cuthbertson and D. Nitzsche LECTURE T-Bond Futures 1
 Topics Details of Contracts and Terminology Hedging with T-Bond Futures Pricing T-Bond Futures Market Timing 2
Topics Details of Contracts and Terminology Hedging with T-Bond Futures Pricing T-Bond Futures Market Timing 2
 Details of Contracts and Terminology 3
Details of Contracts and Terminology 3
 Contract and its Uses Long T-bond futures position Holder can take delivery of a long maturity T-bond at expiration, at a price F 0 agreed at t=0. Speculation Think long rates will fall in the future, then buy a T-Bond future If rates do fall, then F increases and close out at profit Hedging Lock in a price today, for delivery or sale of the underlying T-Bonds Arbitrage Keeps the cash market T-bond price (S) and the futures price, F broadly moving together 4
Contract and its Uses Long T-bond futures position Holder can take delivery of a long maturity T-bond at expiration, at a price F 0 agreed at t=0. Speculation Think long rates will fall in the future, then buy a T-Bond future If rates do fall, then F increases and close out at profit Hedging Lock in a price today, for delivery or sale of the underlying T-Bonds Arbitrage Keeps the cash market T-bond price (S) and the futures price, F broadly moving together 4
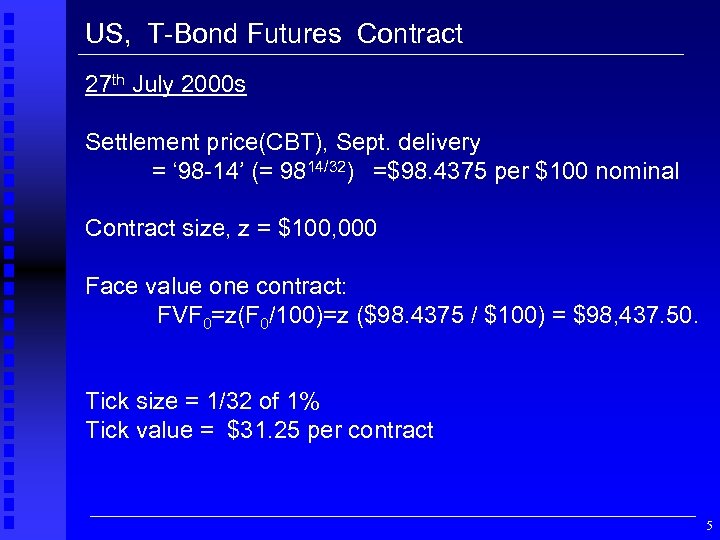 US, T-Bond Futures Contract 27 th July 2000 s Settlement price(CBT), Sept. delivery = ‘ 98 -14’ (= 9814/32) =$98. 4375 per $100 nominal Contract size, z = $100, 000 Face value one contract: FVF 0=z(F 0/100)=z ($98. 4375 / $100) = $98, 437. 50. Tick size = 1/32 of 1% Tick value = $31. 25 per contract 5
US, T-Bond Futures Contract 27 th July 2000 s Settlement price(CBT), Sept. delivery = ‘ 98 -14’ (= 9814/32) =$98. 4375 per $100 nominal Contract size, z = $100, 000 Face value one contract: FVF 0=z(F 0/100)=z ($98. 4375 / $100) = $98, 437. 50. Tick size = 1/32 of 1% Tick value = $31. 25 per contract 5
 . 6
. 6
 Conversion Factor, CF Adjusts price of actual bond to be delivered by assuming it has an 8% yield to maturity, , which then matches that of the notional bond in the futures contract. (also with maturity > 15 yrs) If the coupon on the bond actually delivered > 8% then CF > 1 If the coupon on the bond actually delivered < 8% then CF < 1 7
Conversion Factor, CF Adjusts price of actual bond to be delivered by assuming it has an 8% yield to maturity, , which then matches that of the notional bond in the futures contract. (also with maturity > 15 yrs) If the coupon on the bond actually delivered > 8% then CF > 1 If the coupon on the bond actually delivered < 8% then CF < 1 7
![Cheapest to Deliver CTD bond is one with smallest raw basis: [6. 1] Raw Cheapest to Deliver CTD bond is one with smallest raw basis: [6. 1] Raw](https://present5.com/presentation/4241b95931d4961032cbd687c747a1a4/image-8.jpg) Cheapest to Deliver CTD bond is one with smallest raw basis: [6. 1] Raw Basis = BT – FT CFT BT = spot (“clean”) price of eligible bond for delivery FT = settlement futures price CFT = conversion factor of a deliverable bond. 8
Cheapest to Deliver CTD bond is one with smallest raw basis: [6. 1] Raw Basis = BT – FT CFT BT = spot (“clean”) price of eligible bond for delivery FT = settlement futures price CFT = conversion factor of a deliverable bond. 8
 Hedging with T-Bond Futures 9
Hedging with T-Bond Futures 9
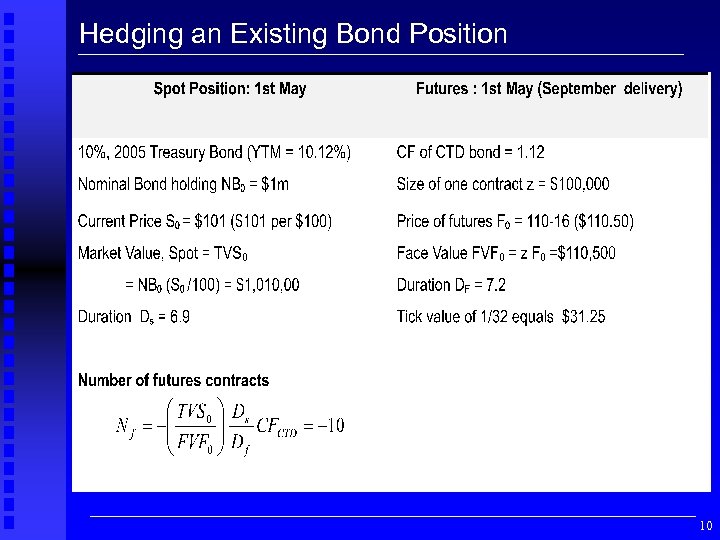 Hedging an Existing Bond Position 10
Hedging an Existing Bond Position 10
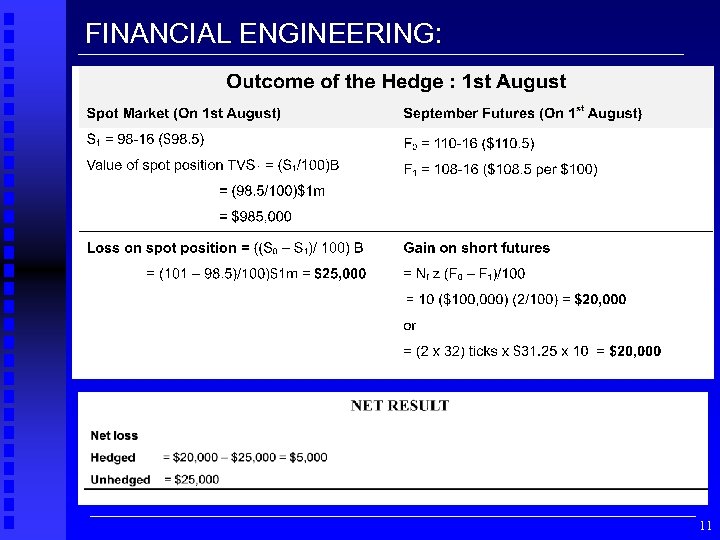 FINANCIAL ENGINEERING: 11
FINANCIAL ENGINEERING: 11
 Risks in the Hedge ·the hedge period (eg. 3 months from May to August) may not correspond to the maturity of the futures contract (eg. September contract) ·the exact bond to be delivered in the futures contract is not known, neither is the precise delivery date ·all of the methods for calculating the relative price response in the spot and futures markets are subject to some error, in part because it is difficult to ascertain the CTD bond (and hence its duration) ·shifts in the yield curve may not be parallel, so we cannot always assume, ys = y. F. 12
Risks in the Hedge ·the hedge period (eg. 3 months from May to August) may not correspond to the maturity of the futures contract (eg. September contract) ·the exact bond to be delivered in the futures contract is not known, neither is the precise delivery date ·all of the methods for calculating the relative price response in the spot and futures markets are subject to some error, in part because it is difficult to ascertain the CTD bond (and hence its duration) ·shifts in the yield curve may not be parallel, so we cannot always assume, ys = y. F. 12
 Wild Card Play Position Day : The short notifies the Clearing House of intention to deliver, two business days later Notice of Intention Day : The Clearing House assigns a trader who is long to accept delivery. The short is now obligated to deliver the next business day. Delivery Day Bonds are delivered (with the last possible delivery day being the business day prior to the last 7 days in the delivery month). 13
Wild Card Play Position Day : The short notifies the Clearing House of intention to deliver, two business days later Notice of Intention Day : The Clearing House assigns a trader who is long to accept delivery. The short is now obligated to deliver the next business day. Delivery Day Bonds are delivered (with the last possible delivery day being the business day prior to the last 7 days in the delivery month). 13
 Wild Card Play by the ‘short’ On any 'position day'. If the spot price of bonds falls between 3 pm and 5 pm, the short buys the “low price” CTD bond in the cash market and issues a notice of intention to deliver knowing that upon delivery she will receive the “high” futures settlement price determined as of 3 pm that day. However, if the spot (bond) price does not decline, she can wait until the next day and repeat this strategy (until the final business day before the final delivery day in the month). the short has an implicit option that is exercisable during the delivery month, while the long has increased risk because she does not know the exact price (ie. value) of the bond that will be delivered. 14
Wild Card Play by the ‘short’ On any 'position day'. If the spot price of bonds falls between 3 pm and 5 pm, the short buys the “low price” CTD bond in the cash market and issues a notice of intention to deliver knowing that upon delivery she will receive the “high” futures settlement price determined as of 3 pm that day. However, if the spot (bond) price does not decline, she can wait until the next day and repeat this strategy (until the final business day before the final delivery day in the month). the short has an implicit option that is exercisable during the delivery month, while the long has increased risk because she does not know the exact price (ie. value) of the bond that will be delivered. 14
 Pricing T-Bond Futures 15
Pricing T-Bond Futures 15
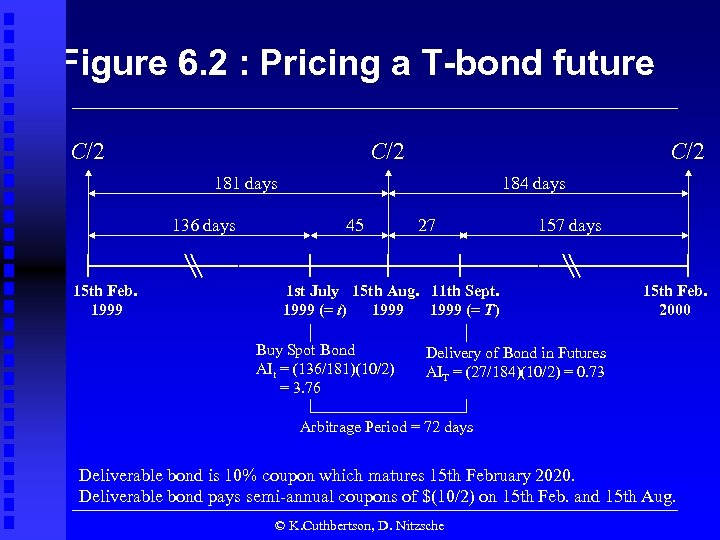 Figure 6. 2 : Pricing a T-bond future C/2 C/2 181 days 136 days 15 th Feb. 1999 184 days 45 27 157 days 1 st July 15 th Aug. 11 th Sept. 1999 (= t) 1999 (= T) Buy Spot Bond AIt = (136/181)(10/2) = 3. 76 15 th Feb. 2000 Delivery of Bond in Futures AIT = (27/184)(10/2) = 0. 73 Arbitrage Period = 72 days Deliverable bond is 10% coupon which matures 15 th February 2020. Deliverable bond pays semi-annual coupons of $(10/2) on 15 th Feb. and 15 th Aug. © K. Cuthbertson, D. Nitzsche
Figure 6. 2 : Pricing a T-bond future C/2 C/2 181 days 136 days 15 th Feb. 1999 184 days 45 27 157 days 1 st July 15 th Aug. 11 th Sept. 1999 (= t) 1999 (= T) Buy Spot Bond AIt = (136/181)(10/2) = 3. 76 15 th Feb. 2000 Delivery of Bond in Futures AIT = (27/184)(10/2) = 0. 73 Arbitrage Period = 72 days Deliverable bond is 10% coupon which matures 15 th February 2020. Deliverable bond pays semi-annual coupons of $(10/2) on 15 th Feb. and 15 th Aug. © K. Cuthbertson, D. Nitzsche
![Pricing T-Bond Futures Zero Coupon Bond [13 c] F = S exp( r (T-t) Pricing T-Bond Futures Zero Coupon Bond [13 c] F = S exp( r (T-t)](https://present5.com/presentation/4241b95931d4961032cbd687c747a1a4/image-17.jpg) Pricing T-Bond Futures Zero Coupon Bond [13 c] F = S exp( r (T-t) ) Coupon Paying Bond Synthetic bond future [6. 14] Net cost (at T) of ‘carry’ in cash market = (Ster(T-t) – FVCT) FVCT applies to the coupon payments which occur between t = 1 st of July and T = 11 th of September [6. 15] Invoice Price of Futures (at T): IPF = Ft CFt + AIT Actual futures contract and the synthetic futures both deliver one bond at T then their cost must be equal, otherwise riskless arbitrage profits would be possible. Equating [6. 14] and [6. 15] : [6. 16 a] [6. 16 b] Ft (CFt) + AIt = Ster(T-t) – FVCT F = (1/CFt) (Ster(T-t) – FVCT - AIT) 17
Pricing T-Bond Futures Zero Coupon Bond [13 c] F = S exp( r (T-t) ) Coupon Paying Bond Synthetic bond future [6. 14] Net cost (at T) of ‘carry’ in cash market = (Ster(T-t) – FVCT) FVCT applies to the coupon payments which occur between t = 1 st of July and T = 11 th of September [6. 15] Invoice Price of Futures (at T): IPF = Ft CFt + AIT Actual futures contract and the synthetic futures both deliver one bond at T then their cost must be equal, otherwise riskless arbitrage profits would be possible. Equating [6. 14] and [6. 15] : [6. 16 a] [6. 16 b] Ft (CFt) + AIt = Ster(T-t) – FVCT F = (1/CFt) (Ster(T-t) – FVCT - AIT) 17
![Pricing T-Bond Futures [6. 18] St = Bt + AIt [6. 19 b] St Pricing T-Bond Futures [6. 18] St = Bt + AIt [6. 19 b] St](https://present5.com/presentation/4241b95931d4961032cbd687c747a1a4/image-18.jpg) Pricing T-Bond Futures [6. 18] St = Bt + AIt [6. 19 b] St = $130 + $4. 14 = $134. 14 Net cost of carry in the cash market at T, is : [6. 20] (Ster(T-t) – FVCT) = $134. 14 e 0. 03(58/365) – $5. 022 = $129. 76 AIT because of the next coupon payment on 15 th of Feb 2000 is : [6. 21 a] AIT = (27/184) (10/2) = 0. 73 [6. 21 b] F = (1/CFt) (Ster(T-t) – FVCT - AIT) = (1/1. 22) ($129. 76 – $0. 73) = $105. 76 18
Pricing T-Bond Futures [6. 18] St = Bt + AIt [6. 19 b] St = $130 + $4. 14 = $134. 14 Net cost of carry in the cash market at T, is : [6. 20] (Ster(T-t) – FVCT) = $134. 14 e 0. 03(58/365) – $5. 022 = $129. 76 AIT because of the next coupon payment on 15 th of Feb 2000 is : [6. 21 a] AIT = (27/184) (10/2) = 0. 73 [6. 21 b] F = (1/CFt) (Ster(T-t) – FVCT - AIT) = (1/1. 22) ($129. 76 – $0. 73) = $105. 76 18
 Market Timing 19
Market Timing 19
 Market Timing Sell futures if you expect a rise in yields and therefore require a lower duration for your existing bond portfolio Buy futures if you expect a fall in yields and therefore require an increased duration for your bond portfolio. 20
Market Timing Sell futures if you expect a rise in yields and therefore require a lower duration for your existing bond portfolio Buy futures if you expect a fall in yields and therefore require an increased duration for your bond portfolio. 20
 END OF SLIDES 21
END OF SLIDES 21


