2926bdf66b6b25f88b96ad485351cf0b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 37
 Verifying Safety Policies with Size Properties and Alias Controls Wei Ngan Chin 1, 2, Siau-Cheng Khoo 1, Shengchao Qin 3, Corneliu Popeea 1, Huu Hai Nguyen 2 1 National University of Singapore 2 Singapore-MIT Alliance 3 University of Durham
Verifying Safety Policies with Size Properties and Alias Controls Wei Ngan Chin 1, 2, Siau-Cheng Khoo 1, Shengchao Qin 3, Corneliu Popeea 1, Huu Hai Nguyen 2 1 National University of Singapore 2 Singapore-MIT Alliance 3 University of Durham
![Background • Uses of Size Analysis : • array bound check elimin. [Xi-Pfenning'98] • Background • Uses of Size Analysis : • array bound check elimin. [Xi-Pfenning'98] •](https://present5.com/presentation/2926bdf66b6b25f88b96ad485351cf0b/image-2.jpg) Background • Uses of Size Analysis : • array bound check elimin. [Xi-Pfenning'98] • data structure invariance [Xi-Pfenning'99] • termination analysis [Lee-Jones'01] • space complexity [Hofman-Jost'03] analyse and verify • Current Status : • mostly for declarative languages (functional + logic) • restricted imperative language (e. g. Xanadu) 2
Background • Uses of Size Analysis : • array bound check elimin. [Xi-Pfenning'98] • data structure invariance [Xi-Pfenning'99] • termination analysis [Lee-Jones'01] • space complexity [Hofman-Jost'03] analyse and verify • Current Status : • mostly for declarative languages (functional + logic) • restricted imperative language (e. g. Xanadu) 2
 Our Goal • Static Verification for Object-Based Programs • Main Challenges : • objects may mutate • objects may be aliased • Our Approach Use size analysis and alias controls to specify and verify safety policies 3
Our Goal • Static Verification for Object-Based Programs • Main Challenges : • objects may mutate • objects may be aliased • Our Approach Use size analysis and alias controls to specify and verify safety policies 3
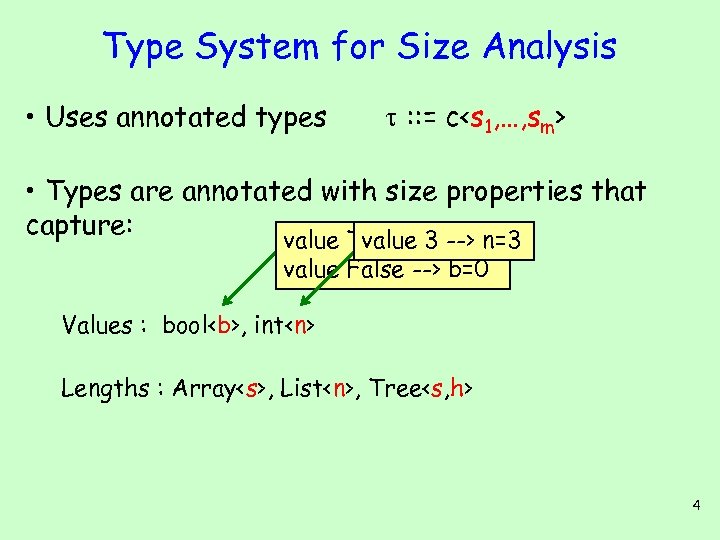 Type System for Size Analysis • Uses annotated types : : = c
Type System for Size Analysis • Uses annotated types : : = c • Types are annotated with size properties that capture: value True --> b=1 n=3 value 3 --> value False --> b=0 Values : bool, int, List
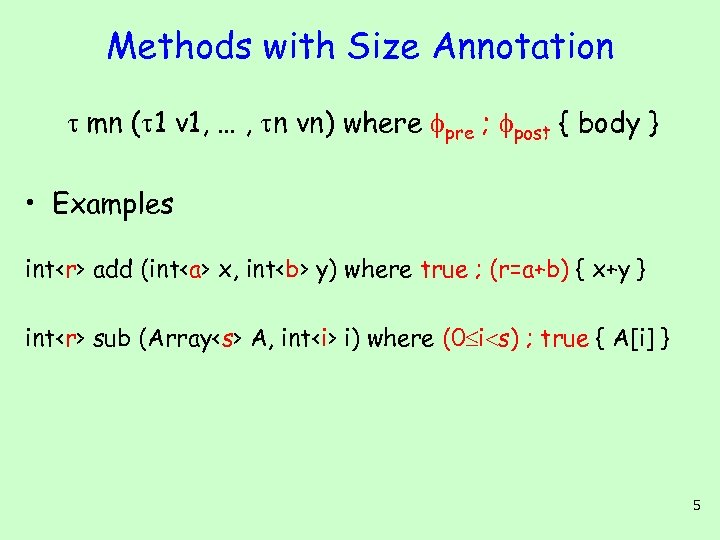 Methods with Size Annotation mn ( 1 v 1, … , n vn) where pre ; post { body } • Examples int
Methods with Size Annotation mn ( 1 v 1, … , n vn) where pre ; post { body } • Examples int A, int i) where (0 i s) ; true { A[i] } 5
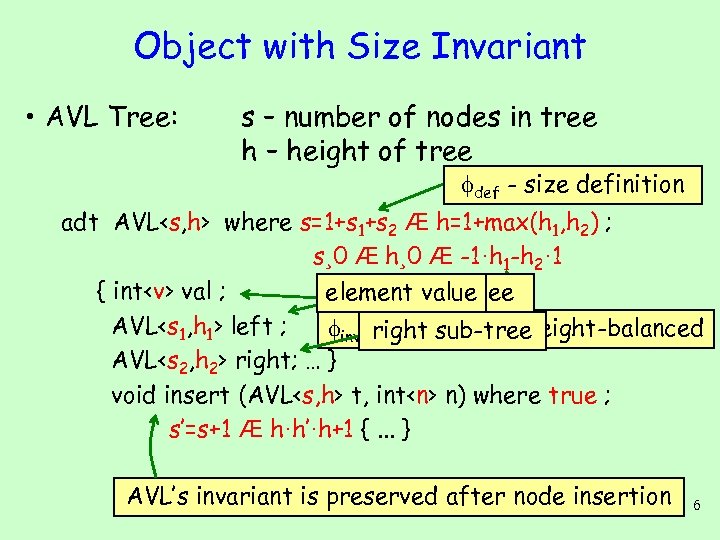 Object with Size Invariant • AVL Tree: s – number of nodes in tree h – height of tree def - size definition adt AVL
Object with Size Invariant • AVL Tree: s – number of nodes in tree h – height of tree def - size definition adt AVL left ; inv - AVL sub-tree right Tree is height-balanced AVL right; … } void insert (AVL
 Mutability & Aliasing adt List
Mutability & Aliasing adt List
 Alias Controls Goal: precisely and soundly capture size-properties. Adopted annotations : Immutability + Uniqueness Each reference (field/param/local var) is marked: • • Read-Only (R) : always refers to the same object. Unique (U) : sole reference to an object. Shared (S) : maybe globally aliased. Lent-Once (L) : unique parameter temporarily lent. 8
Alias Controls Goal: precisely and soundly capture size-properties. Adopted annotations : Immutability + Uniqueness Each reference (field/param/local var) is marked: • • Read-Only (R) : always refers to the same object. Unique (U) : sole reference to an object. Shared (S) : maybe globally aliased. Lent-Once (L) : unique parameter temporarily lent. 8
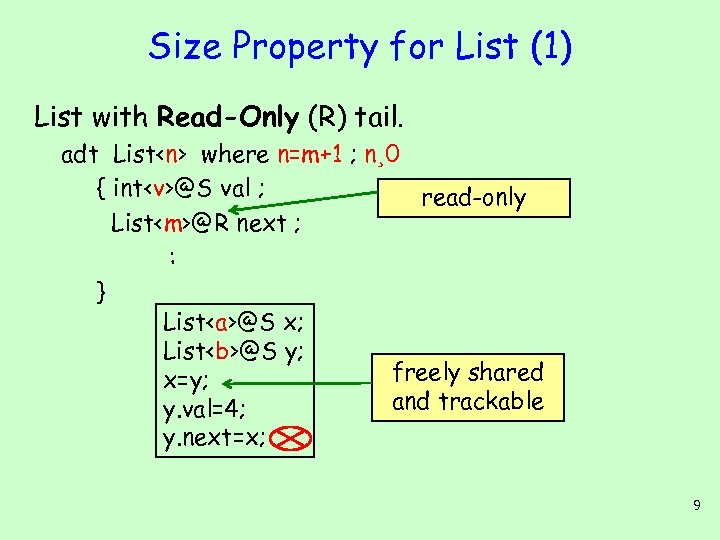 Size Property for List (1) List with Read-Only (R) tail. adt List
Size Property for List (1) List with Read-Only (R) tail. adt List
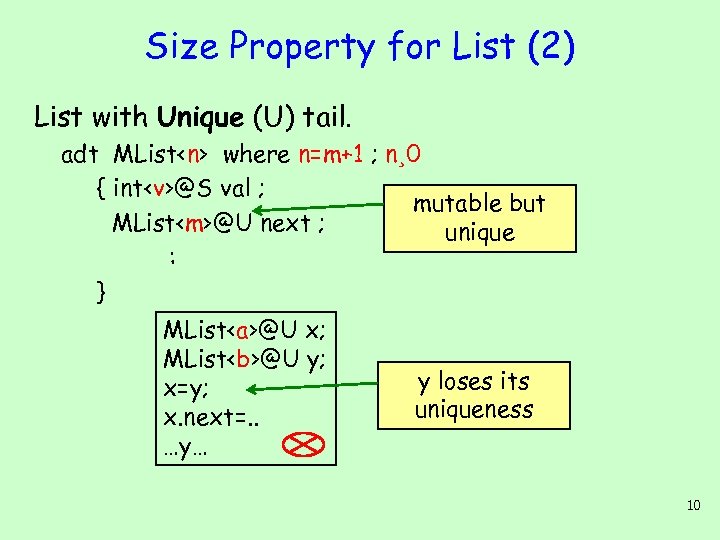 Size Property for List (2) List with Unique (U) tail. adt MList
Size Property for List (2) List with Unique (U) tail. adt MList
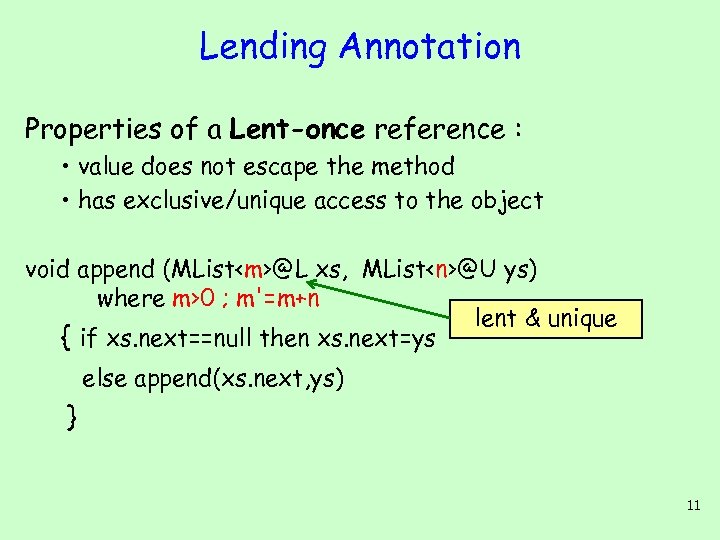 Lending Annotation Properties of a Lent-once reference : • value does not escape the method • has exclusive/unique access to the object void append (MList
Lending Annotation Properties of a Lent-once reference : • value does not escape the method • has exclusive/unique access to the object void append (MList
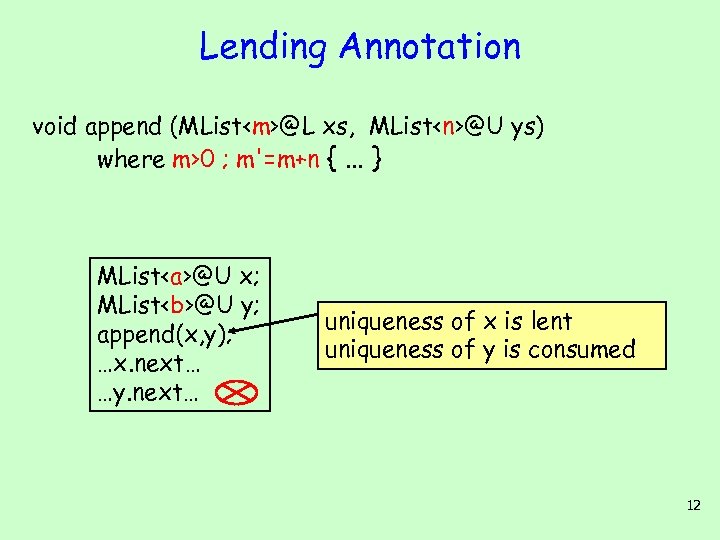 Lending Annotation void append (MList
Lending Annotation void append (MList
 Classification of Size-Variables Three possible groups Vobj( hs*i) = (SI, ST, SN) (i) Size-Immutable (freely shared) (ii) Trackable (mutable and unique) (iii) Non-Trackable (mutable and globally aliased) 13
Classification of Size-Variables Three possible groups Vobj( hs*i) = (SI, ST, SN) (i) Size-Immutable (freely shared) (ii) Trackable (mutable and unique) (iii) Non-Trackable (mutable and globally aliased) 13
 Outline • Background on Size Analysis • Size Tracking with Alias Controls • Kernel Language and Protocol Specification • Type System for Verification • Implementation and Conclusion. 14
Outline • Background on Size Analysis • Size Tracking with Alias Controls • Kernel Language and Protocol Specification • Type System for Verification • Implementation and Conclusion. 14
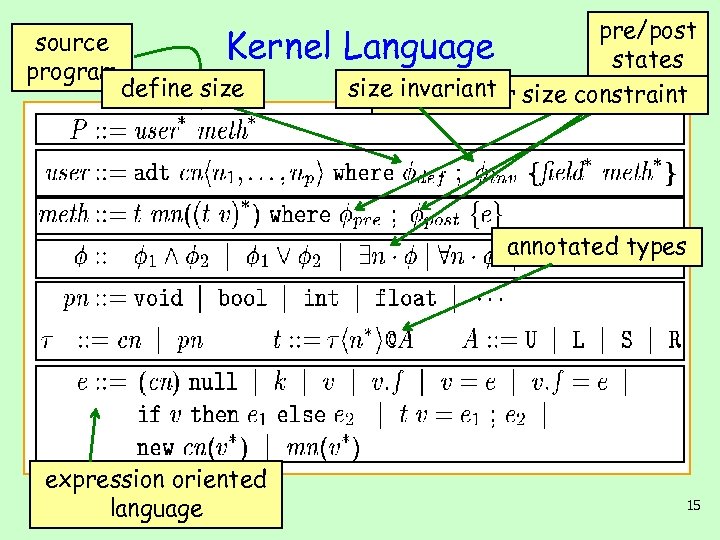 source program Kernel define size pre/post Language states size. Presburger size constraint invariant annotated types expression oriented language 15
source program Kernel define size pre/post Language states size. Presburger size constraint invariant annotated types expression oriented language 15
 How are Safety Policies Specified? • Popular approach - finite state machine. • Our approach : ADT with (i) Object’s Size Invariant. (ii) Methods’ Preconditions. • Benefits: Relational Properties Infinite-State Policies 16
How are Safety Policies Specified? • Popular approach - finite state machine. • Our approach : ADT with (i) Object’s Size Invariant. (ii) Methods’ Preconditions. • Benefits: Relational Properties Infinite-State Policies 16
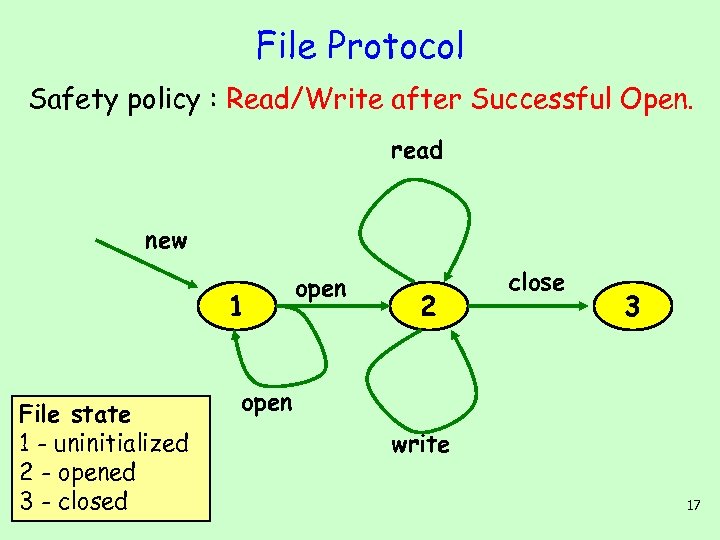 File Protocol Safety policy : Read/Write after Successful Open. read new 1 File state 1 - uninitialized 2 - opened 3 - closed open 2 close 3 open write 17
File Protocol Safety policy : Read/Write after Successful Open. read new 1 File state 1 - uninitialized 2 - opened 3 - closed open 2 close 3 open write 17
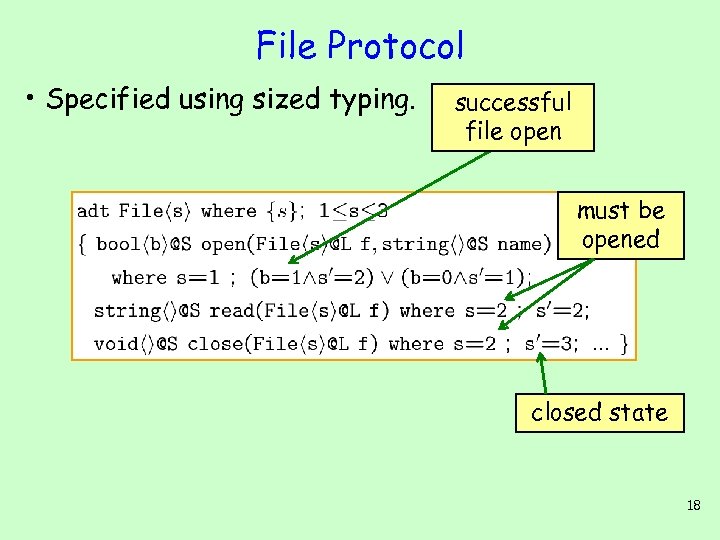 File Protocol • Specified using sized typing. successful file open must be opened closed state 18
File Protocol • Specified using sized typing. successful file open must be opened closed state 18
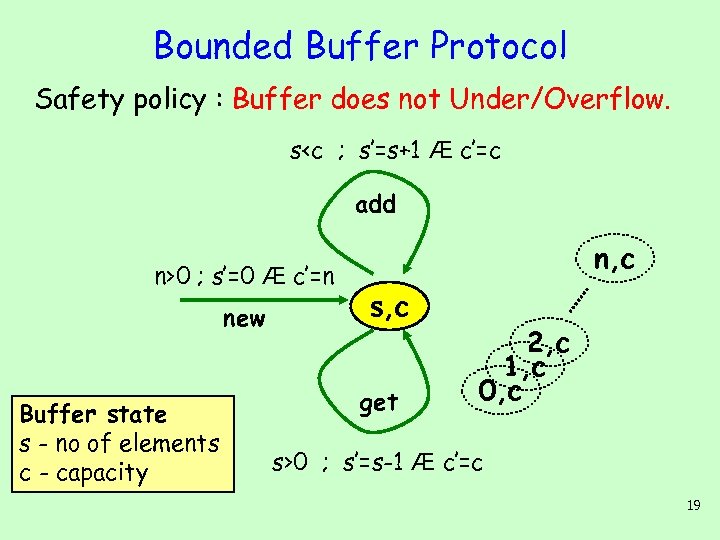 Bounded Buffer Protocol Safety policy : Buffer does not Under/Overflow. s
Bounded Buffer Protocol Safety policy : Buffer does not Under/Overflow. s
 Outline • Background on Size Analysis • Size Tracking with Alias Controls • Kernel Language and Protocol Specification • Type System for Verification • Implementation and Conclusion. 20
Outline • Background on Size Analysis • Size Tracking with Alias Controls • Kernel Language and Protocol Specification • Type System for Verification • Implementation and Conclusion. 20
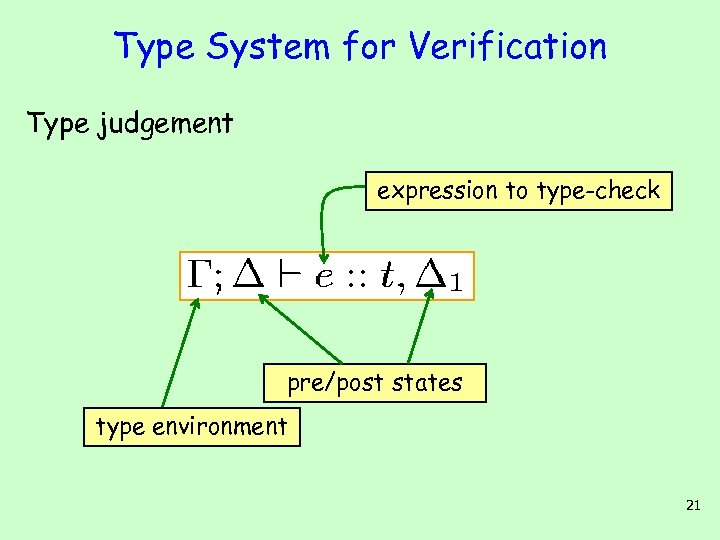 Type System for Verification Type judgement expression to type-check pre/post states type environment 21
Type System for Verification Type judgement expression to type-check pre/post states type environment 21
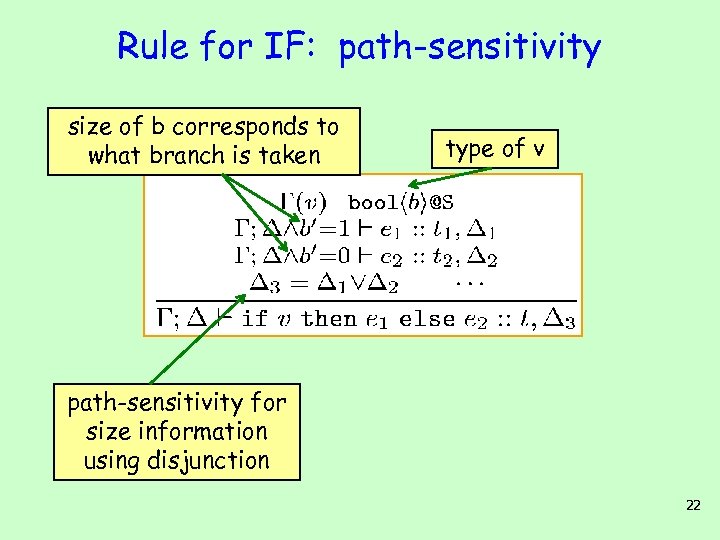 Rule for IF: path-sensitivity size of b corresponds to what branch is taken type of v path-sensitivity for size information using disjunction 22
Rule for IF: path-sensitivity size of b corresponds to what branch is taken type of v path-sensitivity for size information using disjunction 22
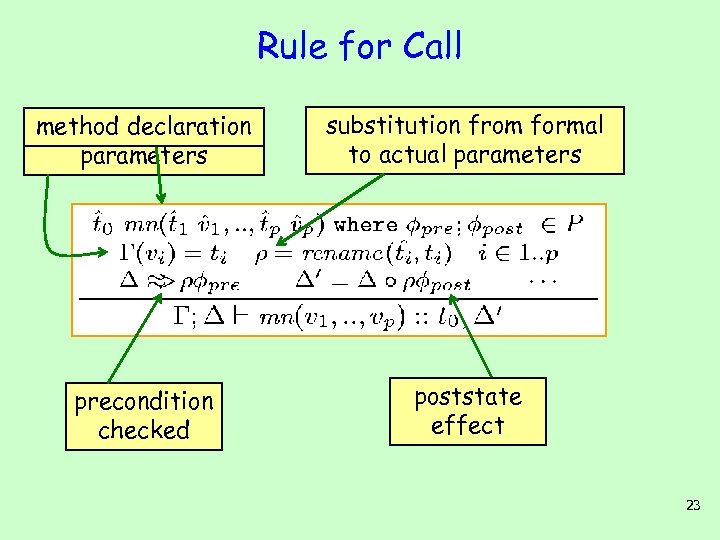 Rule for Call types declaration method for actual parameters substitution from formal to actual parameters precondition checked poststate effect 23
Rule for Call types declaration method for actual parameters substitution from formal to actual parameters precondition checked poststate effect 23
 Correctness of Type System • Type Preservation – size type property is correctly preserved during reduction. • Progress – a well-typed program never goes wrong. Safety policies are guaranteed for well-typed programs. 24
Correctness of Type System • Type Preservation – size type property is correctly preserved during reduction. • Progress – a well-typed program never goes wrong. Safety policies are guaranteed for well-typed programs. 24
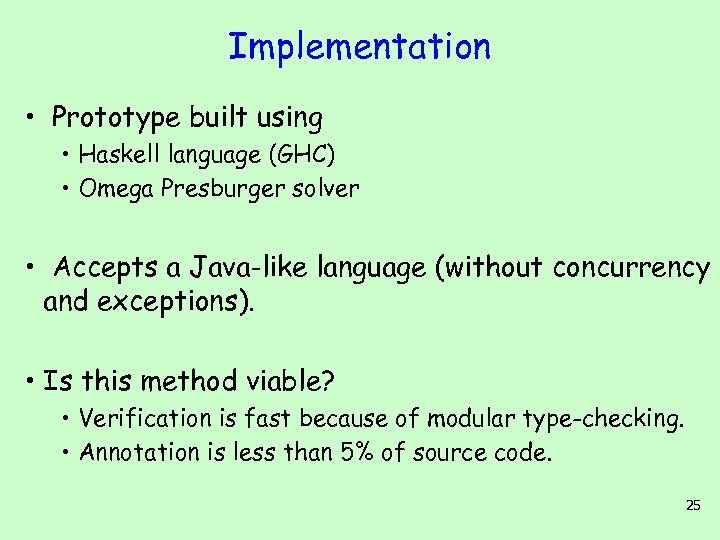 Implementation • Prototype built using • Haskell language (GHC) • Omega Presburger solver • Accepts a Java-like language (without concurrency and exceptions). • Is this method viable? • Verification is fast because of modular type-checking. • Annotation is less than 5% of source code. 25
Implementation • Prototype built using • Haskell language (GHC) • Omega Presburger solver • Accepts a Java-like language (without concurrency and exceptions). • Is this method viable? • Verification is fast because of modular type-checking. • Annotation is less than 5% of source code. 25
![Related Work Size analysis for immutable data structures [Hughes et. al'96, Xi-Pfenning'98, '99, Jost-Hofman'03] Related Work Size analysis for immutable data structures [Hughes et. al'96, Xi-Pfenning'98, '99, Jost-Hofman'03]](https://present5.com/presentation/2926bdf66b6b25f88b96ad485351cf0b/image-26.jpg) Related Work Size analysis for immutable data structures [Hughes et. al'96, Xi-Pfenning'98, '99, Jost-Hofman'03] Alias controls for program reasoning [Chan-Boyland'98, Aldrich-Kostadinov-Chambers'02] Other approaches to verification: • Finite type-state: Vault, Fugue [Fahndrich-De. Line'02, '04] • Theorem proving: ESC (may be unsound) [Flanagan-Leino-Lillibridge-Nelson et. al'02] • Model checking: Bogor (requires test harness) [Robby-Dwyer-Hatcliff-Rodriguez'03, '04] 26
Related Work Size analysis for immutable data structures [Hughes et. al'96, Xi-Pfenning'98, '99, Jost-Hofman'03] Alias controls for program reasoning [Chan-Boyland'98, Aldrich-Kostadinov-Chambers'02] Other approaches to verification: • Finite type-state: Vault, Fugue [Fahndrich-De. Line'02, '04] • Theorem proving: ESC (may be unsound) [Flanagan-Leino-Lillibridge-Nelson et. al'02] • Model checking: Bogor (requires test harness) [Robby-Dwyer-Hatcliff-Rodriguez'03, '04] 26
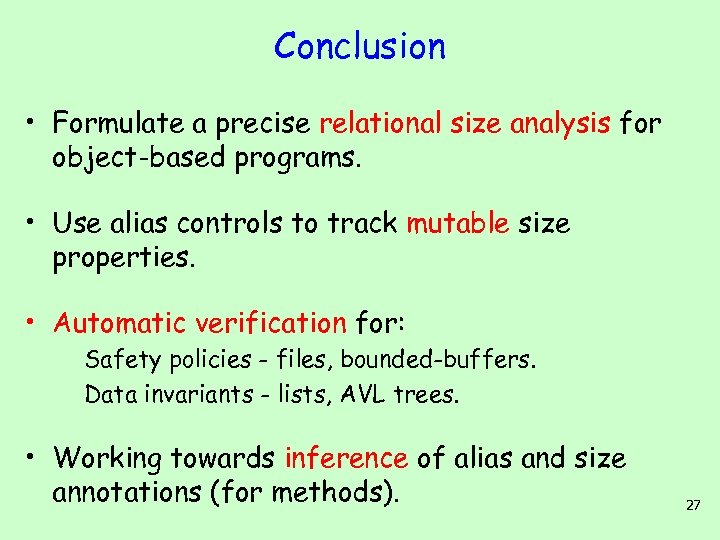 Conclusion • Formulate a precise relational size analysis for object-based programs. • Use alias controls to track mutable size properties. • Automatic verification for: Safety policies - files, bounded-buffers. Data invariants - lists, AVL trees. • Working towards inference of alias and size annotations (for methods). 27
Conclusion • Formulate a precise relational size analysis for object-based programs. • Use alias controls to track mutable size properties. • Automatic verification for: Safety policies - files, bounded-buffers. Data invariants - lists, AVL trees. • Working towards inference of alias and size annotations (for methods). 27
 End 28
End 28
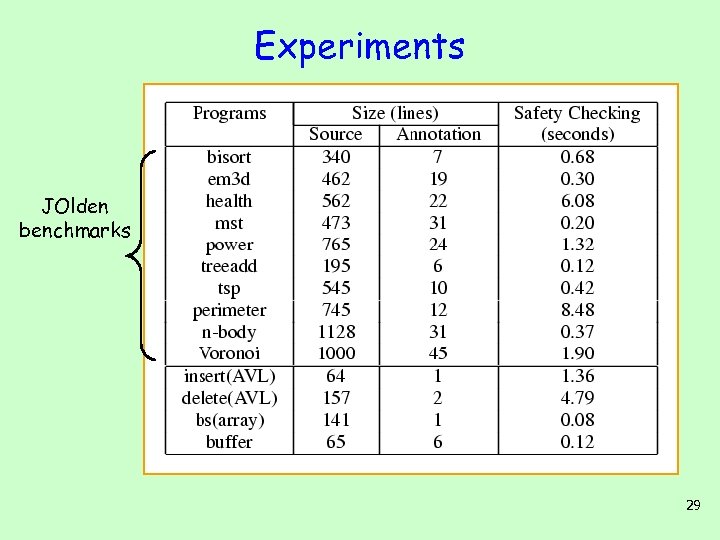 Experiments JOlden benchmarks 29
Experiments JOlden benchmarks 29
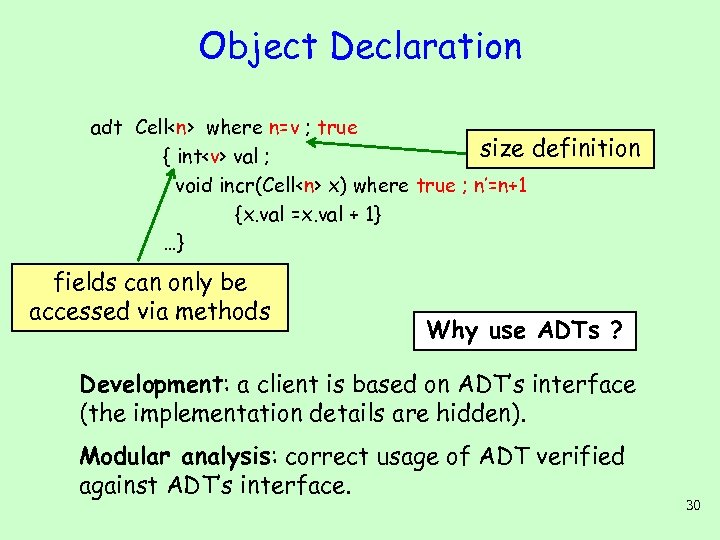 Object Declaration adt Cell
Object Declaration adt Cell
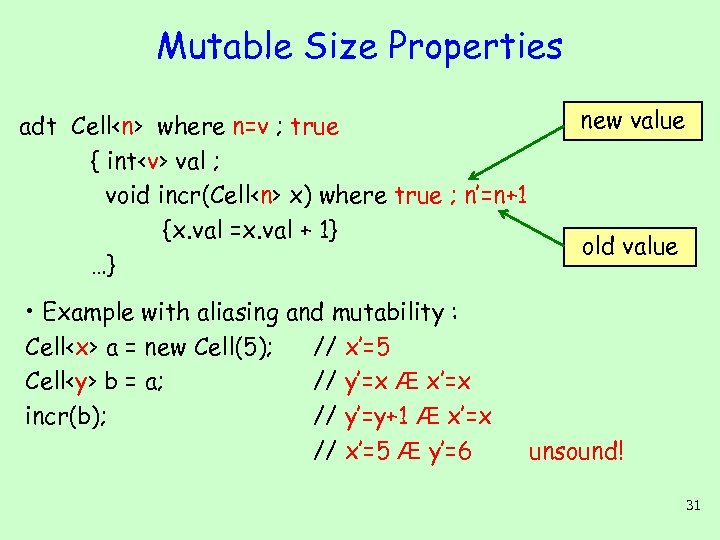 Mutable Size Properties adt Cell
Mutable Size Properties adt Cell
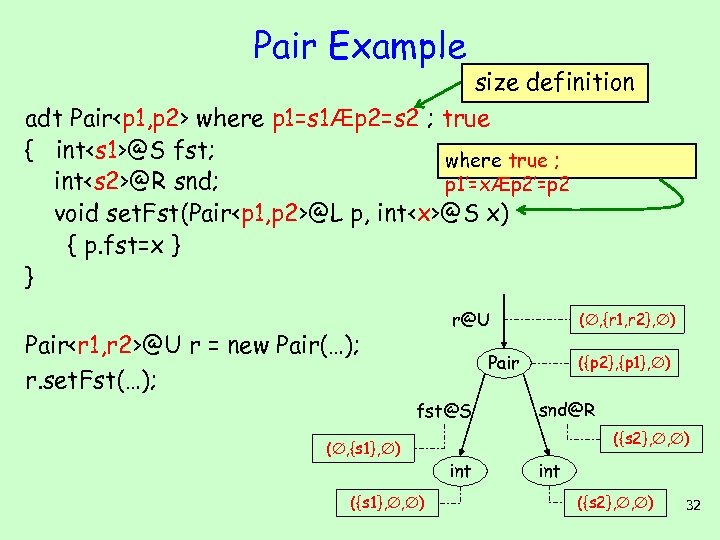 Pair Example size definition adt Pair
Pair Example size definition adt Pair
where p 1=s 1Æp 2=s 2 ; true { int@S fst; where true ; int@R snd; p 1’=xÆp 2’=p 2 void set. Fst(Pair
@L p, int
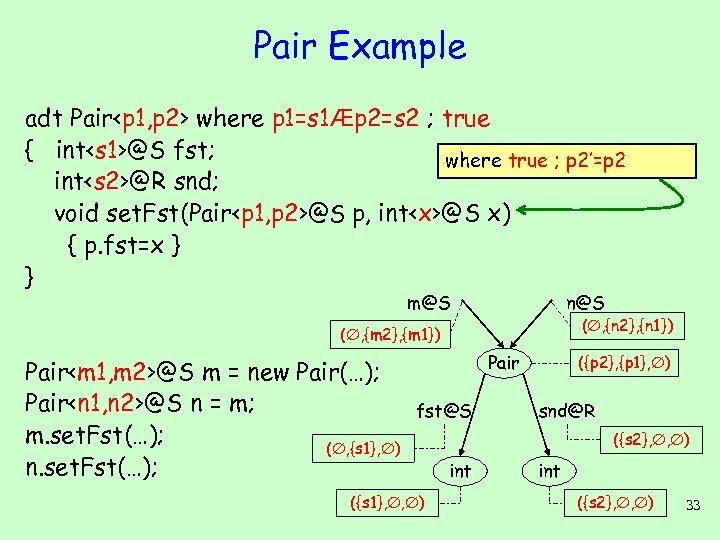 Pair Example adt Pair
Pair Example adt Pair
where p 1=s 1Æp 2=s 2 ; true { int@S fst; where true ; p 2’=p 2 int@R snd; void set. Fst(Pair
@S p, int
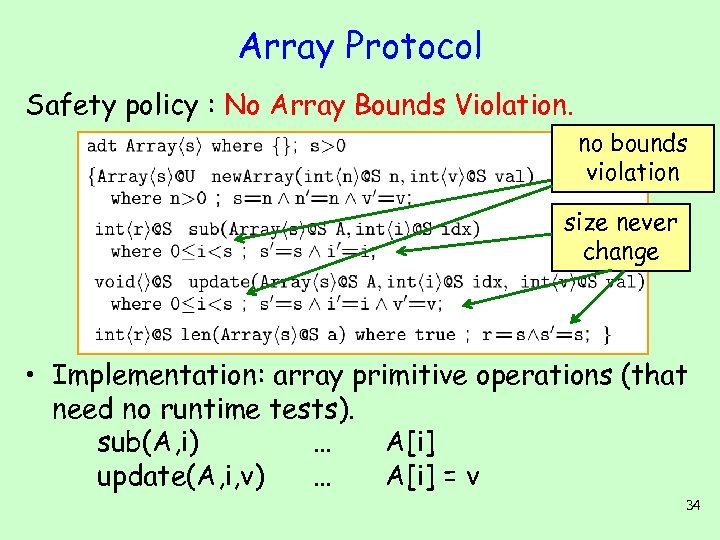 Array Protocol Safety policy : No Array Bounds Violation. no bounds violation size never change • Implementation: array primitive operations (that need no runtime tests). sub(A, i) … A[i] update(A, i, v) … A[i] = v 34
Array Protocol Safety policy : No Array Bounds Violation. no bounds violation size never change • Implementation: array primitive operations (that need no runtime tests). sub(A, i) … A[i] update(A, i, v) … A[i] = v 34
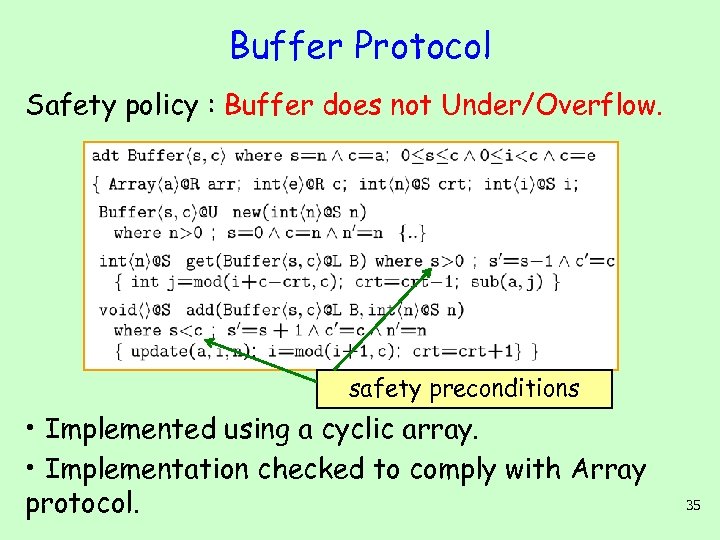 Buffer Protocol Safety policy : Buffer does not Under/Overflow. safety preconditions • Implemented using a cyclic array. • Implementation checked to comply with Array protocol. 35
Buffer Protocol Safety policy : Buffer does not Under/Overflow. safety preconditions • Implemented using a cyclic array. • Implementation checked to comply with Array protocol. 35
 Lock Protocol Safety policy : No double lock/unlock operations. 36
Lock Protocol Safety policy : No double lock/unlock operations. 36
 AVL Tree adt AVL
AVL Tree adt AVL@U left ; AVL@U right; void insert (AVL


