53aaaaaee5712586da4072c617f3e11e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25
 Verifying Atomicity via Data Independence Ohad Shacham Eran Yahav Guy Gueta Alex Aiken Nathan Bronson Mooly Sagiv Martin Vechev Yahoo Labs, Israel Technion, Israel Yahoo Labs, Israel Stanford University, USA Tel Aviv University, Israel ETH, Zurich
Verifying Atomicity via Data Independence Ohad Shacham Eran Yahav Guy Gueta Alex Aiken Nathan Bronson Mooly Sagiv Martin Vechev Yahoo Labs, Israel Technion, Israel Yahoo Labs, Israel Stanford University, USA Tel Aviv University, Israel ETH, Zurich
 Concurrent Data Structures • Writing highly concurrent data structures is complicated • Modern programming languages provide efficient concurrent collections with atomic operations … … … …… . .
Concurrent Data Structures • Writing highly concurrent data structures is complicated • Modern programming languages provide efficient concurrent collections with atomic operations … … … …… . .
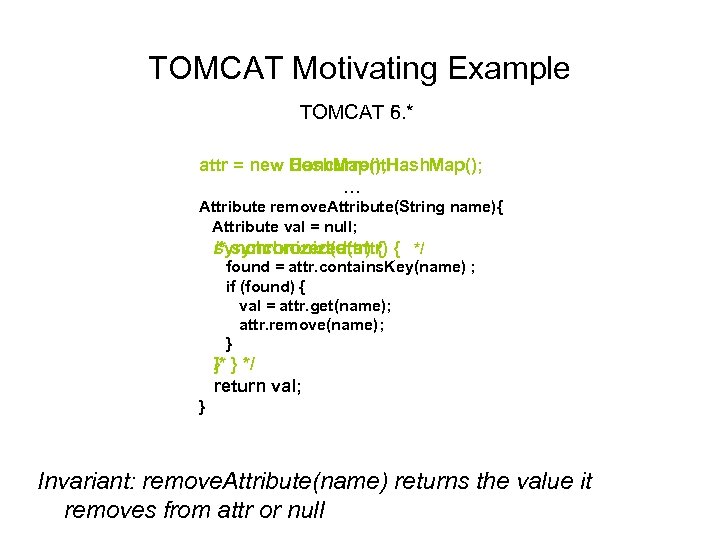 TOMCAT Motivating Example TOMCAT 5. * 6. * attr = new Hash. Map(); Concurrent. Hash. Map(); … Attribute remove. Attribute(String name){ Attribute val = null; /* synchronized(attr) { { */ found = attr. contains. Key(name) ; if (found) { val = attr. get(name); attr. remove(name); } /* } } */ return val; } Invariant: remove. Attribute(name) returns the value it removes from attr or null
TOMCAT Motivating Example TOMCAT 5. * 6. * attr = new Hash. Map(); Concurrent. Hash. Map(); … Attribute remove. Attribute(String name){ Attribute val = null; /* synchronized(attr) { { */ found = attr. contains. Key(name) ; if (found) { val = attr. get(name); attr. remove(name); } /* } } */ return val; } Invariant: remove. Attribute(name) returns the value it removes from attr or null
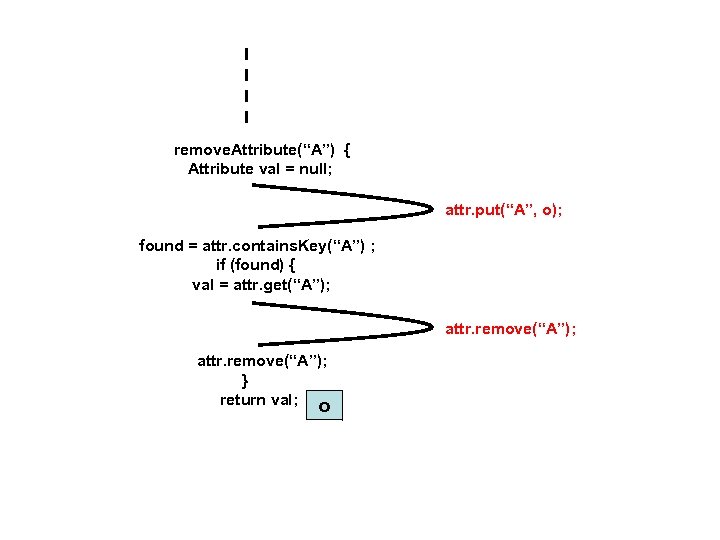 remove. Attribute(“A”) { Attribute val = null; attr. put(“A”, o); found = attr. contains. Key(“A”) ; if (found) { val = attr. get(“A”); attr. remove(“A”); } return val; o
remove. Attribute(“A”) { Attribute val = null; attr. put(“A”, o); found = attr. contains. Key(“A”) ; if (found) { val = attr. get(“A”); attr. remove(“A”); } return val; o
 Violation Detection • Testing Atomicity of Composed Concurrent Operation – OOPSLA’ 11 • Use library influence specification for POR • Many violations we found in real applications • Many were already fixed
Violation Detection • Testing Atomicity of Composed Concurrent Operation – OOPSLA’ 11 • Use library influence specification for POR • Many violations we found in real applications • Many were already fixed
 Challenge Verifying the atomicity of composed operations … … … ……
Challenge Verifying the atomicity of composed operations … … … ……
 Challenges in Verification • What do we want to check? – Specifying software correctness • Scalability of static checking – Large programs • Many sources of unboundedness – Inputs – # threads – # operations
Challenges in Verification • What do we want to check? – Specifying software correctness • Scalability of static checking – Large programs • Many sources of unboundedness – Inputs – # threads – # operations
 Challenges in Verification • What do we want to check? – Specifying software correctness • Scalability of static checking – Large programs • Many sources of unboundedness – Inputs – # threads – # operations
Challenges in Verification • What do we want to check? – Specifying software correctness • Scalability of static checking – Large programs • Many sources of unboundedness – Inputs – # threads – # operations
![Linearizability • Check that composed operations are Linearizable [Herlihy & Wing, TOPLAS’ 90] – Linearizability • Check that composed operations are Linearizable [Herlihy & Wing, TOPLAS’ 90] –](https://present5.com/presentation/53aaaaaee5712586da4072c617f3e11e/image-9.jpg) Linearizability • Check that composed operations are Linearizable [Herlihy & Wing, TOPLAS’ 90] – Returns the same result as some sequential run
Linearizability • Check that composed operations are Linearizable [Herlihy & Wing, TOPLAS’ 90] – Returns the same result as some sequential run
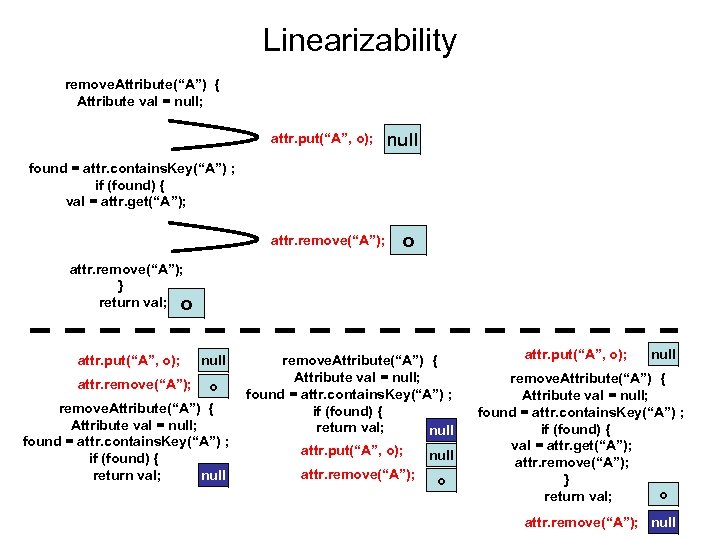 Linearizability remove. Attribute(“A”) { Attribute val = null; attr. put(“A”, o); null found = attr. contains. Key(“A”) ; if (found) { val = attr. get(“A”); attr. remove(“A”); o attr. remove(“A”); } return val; o attr. put(“A”, o); attr. remove(“A”); null o remove. Attribute(“A”) { Attribute val = null; found = attr. contains. Key(“A”) ; if (found) { return val; null attr. put(“A”, o); null attr. remove(“A”); o attr. put(“A”, o); null remove. Attribute(“A”) { Attribute val = null; found = attr. contains. Key(“A”) ; if (found) { val = attr. get(“A”); attr. remove(“A”); } o return val; attr. remove(“A”); null
Linearizability remove. Attribute(“A”) { Attribute val = null; attr. put(“A”, o); null found = attr. contains. Key(“A”) ; if (found) { val = attr. get(“A”); attr. remove(“A”); o attr. remove(“A”); } return val; o attr. put(“A”, o); attr. remove(“A”); null o remove. Attribute(“A”) { Attribute val = null; found = attr. contains. Key(“A”) ; if (found) { return val; null attr. put(“A”, o); null attr. remove(“A”); o attr. put(“A”, o); null remove. Attribute(“A”) { Attribute val = null; found = attr. contains. Key(“A”) ; if (found) { val = attr. get(“A”); attr. remove(“A”); } o return val; attr. remove(“A”); null
 Challenges in Verification • What do we want to check? – Specifying software correctness • Scalability of static checking – Large programs • Many sources of unboundedness – Inputs – # threads – # operations
Challenges in Verification • What do we want to check? – Specifying software correctness • Scalability of static checking – Large programs • Many sources of unboundedness – Inputs – # threads – # operations
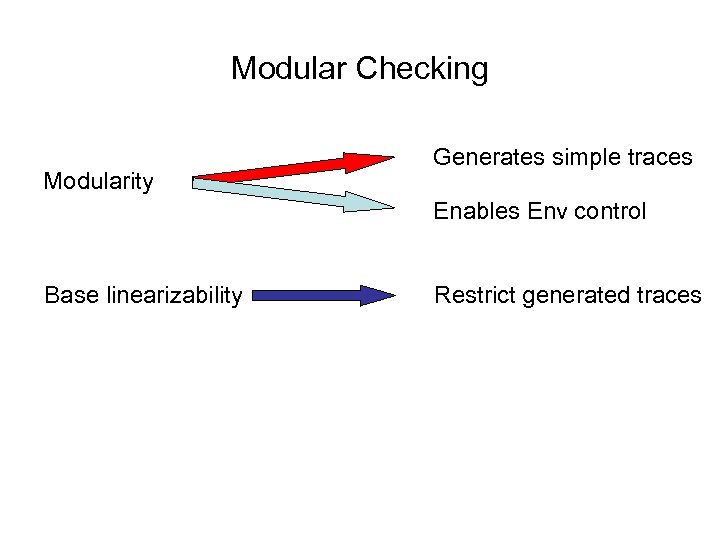 Modular Checking Modularity Generates simple traces Enables Env control Base linearizability Restrict generated traces
Modular Checking Modularity Generates simple traces Enables Env control Base linearizability Restrict generated traces
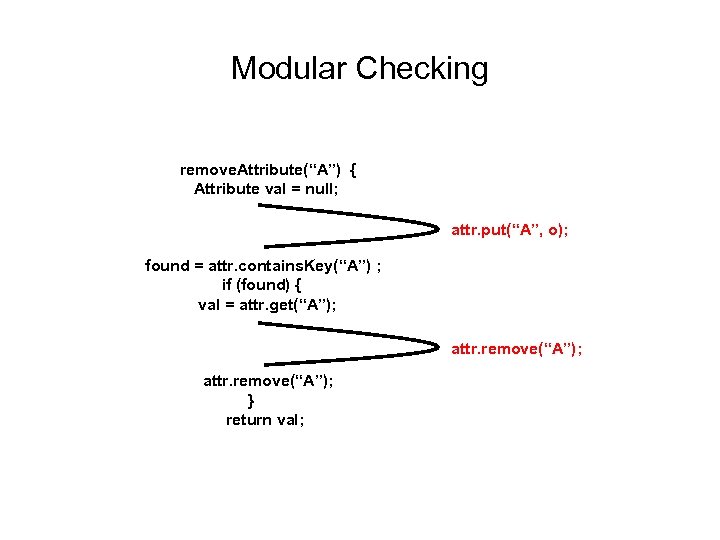 Modular Checking remove. Attribute(“A”) { Attribute val = null; attr. put(“A”, o); found = attr. contains. Key(“A”) ; if (found) { val = attr. get(“A”); attr. remove(“A”); } return val;
Modular Checking remove. Attribute(“A”) { Attribute val = null; attr. put(“A”, o); found = attr. contains. Key(“A”) ; if (found) { val = attr. get(“A”); attr. remove(“A”); } return val;
 Challenges in Verification • What do we want to check? – Specifying software correctness • Scalability of static checking – Large programs • Many sources of unboundedness – Inputs – # threads – # operations
Challenges in Verification • What do we want to check? – Specifying software correctness • Scalability of static checking – Large programs • Many sources of unboundedness – Inputs – # threads – # operations
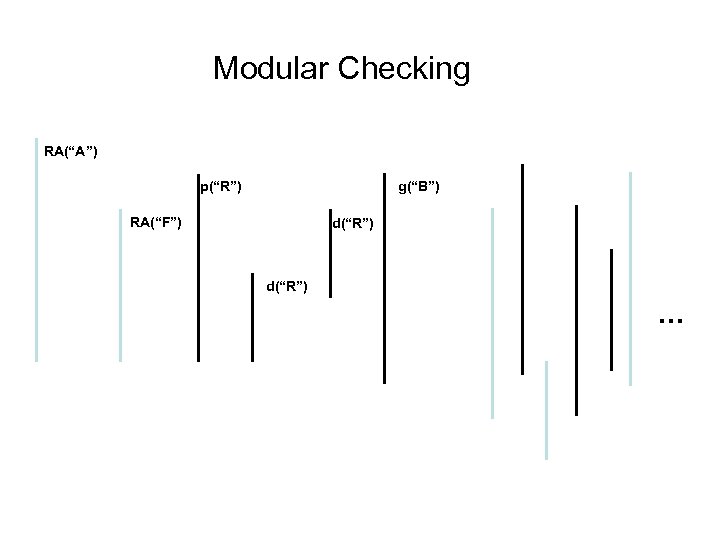 Modular Checking RA(“A”) g(“B”) p(“R”) RA(“F”) d(“R”) …
Modular Checking RA(“A”) g(“B”) p(“R”) RA(“F”) d(“R”) …
 Modular Checking RA(“A”) g(“B”) p(“R”) d(“R”) …
Modular Checking RA(“A”) g(“B”) p(“R”) d(“R”) …
 Modular Checking RA(“A”) p(“A”) d(“A”)
Modular Checking RA(“A”) p(“A”) d(“A”)
![Data Independence [Wolper, POPL’ 86] Attribute remove. Attribute(String name){{ name) Attribute val = null; Data Independence [Wolper, POPL’ 86] Attribute remove. Attribute(String name){{ name) Attribute val = null;](https://present5.com/presentation/53aaaaaee5712586da4072c617f3e11e/image-18.jpg) Data Independence [Wolper, POPL’ 86] Attribute remove. Attribute(String name){{ name) Attribute val = null; found = attr. contains. Key(name) ; if (found) { val = attr. get(name); attr. remove(name); } return val; } Program behaves the same for all Inputs
Data Independence [Wolper, POPL’ 86] Attribute remove. Attribute(String name){{ name) Attribute val = null; found = attr. contains. Key(name) ; if (found) { val = attr. get(name); attr. remove(name); } return val; } Program behaves the same for all Inputs
 Data Independence for CCC • Wolper’s definition is too restrictive for real life CCC • We defined a data independence of linearizability for CCC A CCC is linearizable for a single input iff it is linearizable for every input
Data Independence for CCC • Wolper’s definition is too restrictive for real life CCC • We defined a data independence of linearizability for CCC A CCC is linearizable for a single input iff it is linearizable for every input
 Data Independence Syntactic Rules • Data Independence detection is in general undecidable • Syntactic rules that imply a program as data-independent Attribute remove. Attribute(String name){ Attribute val = null; found = attr. contains. Key(name) ; if (found) { val = attr. get(name); attr. remove(name); } return val; }
Data Independence Syntactic Rules • Data Independence detection is in general undecidable • Syntactic rules that imply a program as data-independent Attribute remove. Attribute(String name){ Attribute val = null; found = attr. contains. Key(name) ; if (found) { val = attr. get(name); attr. remove(name); } return val; }
 Verifying Data Independent Operations Single Mutation Data independent Verified usingle input Influence CO adds one value Map elements are bounded
Verifying Data Independent Operations Single Mutation Data independent Verified usingle input Influence CO adds one value Map elements are bounded
 Verifying data independent operations • Small model reduction • Decidable when the local state is bounded • Explore all possible executions using: – One input key and finite number of values – Influenced based environment uses single value • Employ a model check
Verifying data independent operations • Small model reduction • Decidable when the local state is bounded • Explore all possible executions using: – One input key and finite number of values – Influenced based environment uses single value • Employ a model check
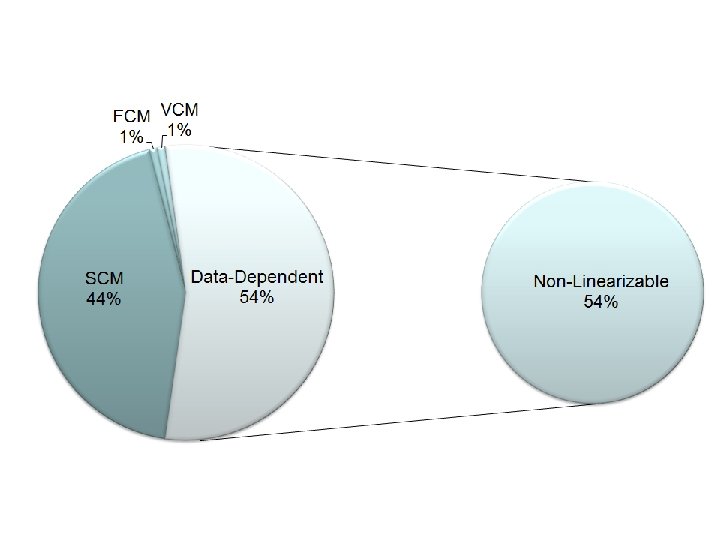
 Summary • • • Writing concurrent data structures is hard Employing atomic library operations is error prone Modular linearizability checking Leverage influence Leverage data independence • Prove the linearizability of several composed operations • Simple and efficient technique
Summary • • • Writing concurrent data structures is hard Employing atomic library operations is error prone Modular linearizability checking Leverage influence Leverage data independence • Prove the linearizability of several composed operations • Simple and efficient technique


