1f1820990b0ef91ea19a983395fcf44d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 45


Verb Terms you must know: n Infinitive – – this is the verb in the whole form, before it is conjugated n Subject pronouns – The person or thing doing the action of the verb Je is I Tu is you Il/he elle is she on means one nous is we vous you all/you formal ils/they elles/they n Conjugate – To make the verb match the subject pronoun. You sound stupid if you don’t do it right!!!

There are 2 types of verbs n Regular --- means they follow a pattern, like a math problem, you can count on the same pattern to get the right answer. § -er verbs § -ir verbs § -re verbs n Irregular --- they don’t follow a pattern, you have to learn each verb (memorize– beat it into your head!!!)
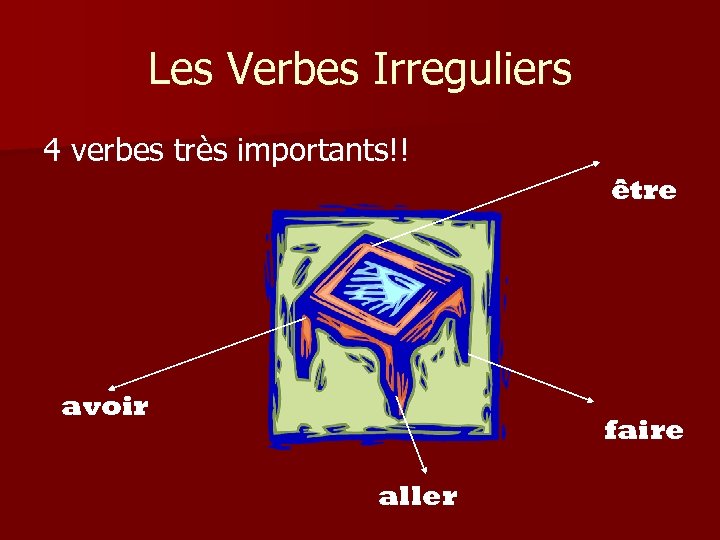
Les Verbes Irreguliers 4 verbes très importants!! être avoir faire aller

Create a reference sheet for each of these Irregular Verbs n Avoir n Etre n Faire n Aller n Savoir n Pouvoir n vouloir

Avoir – to have n J’ai n Tu as n Il a n Elle a n On a n Nous avons n Vous avez n Ils ont n Elles ont *** I have, I do have, I am having

être– to be n Je suis n Tu es n Il est n Elle est n On est n. I n Nous sommes n Vous êtes n Ils sont n Elles sont am, I am aming, I do am

faire – to do, to make n Je fais n Tu fais n Il fait n Elle fait n On fait n. I n Nous faisons n Vous faites n Ils font n Elles font do, I am doing, I do do n I make, I am making, I do making

Aller – to go n n Je vais n Tu vas n Il va n Elle va n On va n. I n Nous allons n Vous allez n Ils vont n Elles vont go, I do go, I am going
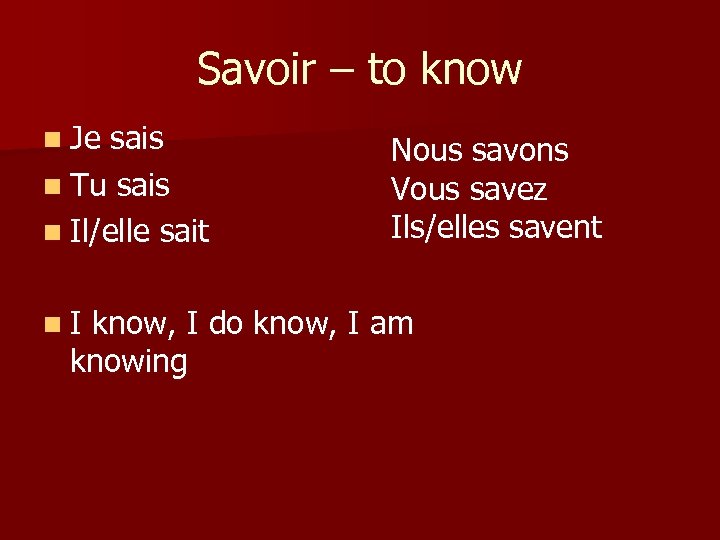
Savoir – to know n Je sais n Tu sais n Il/elle sait n. I Nous savons Vous savez Ils/elles savent know, I do know, I am knowing

pouvoir – can, to be able n Je peux n Tu peux n Il/elle peut n. I can n I am able Nous pouvons Vous pouvez Ils/elles peuvent

vouloir – to want, desire n Je veux n n Tu veux n Il/elle n. I veut Nous voulons Vous voulez Ils/elles veulent want, I do want, I am wanting

Les Verbes Vouloir to want et Pouvoir and to be able to

Le Verbe POUVOIR n What does it mean? n to be able to do n Je peux faire mon devoir. I can do my homework. n Je peux aller chez mon ami. I can go to my friend’s house.

Le verbe VOULOIR n What does it mean? n to n n n want Je veux du lait. I want some milk. Je ne veux pas de lait. I do not want any milk. Tu veux du chocolat. You want some chocolate. Tu ne veux pas de chocolat. You do not want any chocolate. Il veut du poisson. He wants some fish. Il ne veut pas de poisson. He does not want any fish.

How do I conjugate them? n n n POUVOIR je peux tu peux il/elle/on peut nous pouvons vous pouvez ils/elles peuvent n n n VOULOIR je veux tu veux il/elle/on veut nous voulons voulez ils/elles veulent The ne…. pas goes around the verb. Je ne peux pas aller au cinéma

Essayons de faire quelques exemples avec VOULOIR! n n n n n What does VOULOIR mean? to want I want an apple. Je veux une pomme. You want the book. Tu veux le livre. She wants some strawberries. Elle veut des fraises. He does not want any strawberries. Il ne veut pas de fraises.

Continuons avec les exemples! n This time you will see the French and you will translate the sentences into English. n Nous voulons des frites. n We want fries. n Vous voulez aller au cinéma? n Do you want to go to the movies? n EIles veulent faire un gâteau. n They want to make a cake. n Je veux du jus d’orange. n I want some orange juice.

Exemples avec POUVOIR n Est-ce que tu peux aller avec moi? n Can you go with me? n Elle peut faire son devoir. n She can do her homework. n Il peut jouer de la guitare. n He can play the guitar.

n They can make some sandwiches. n Ils peuvent faire des sandwiches. n You can’t go with me. n Tu ne peux pas aller avec moi. n We can’t go to the movies. n Nous ne pouvons pas aller au cinéma.

Regular –er verbs Marcher 1. Drop the –er 2. Add the endings –e, -es, -e, -ons, -ez –ent Je marche nous marchons Tu marches vous marchez Il/elle marche ils/elles marchent I walk, I do walk, I am walking

Regular –ir verbs Finir 1. Drop the –ir 2. Add the endings –is, -it, -issons, 3. -issez –issent Je finis nous finissons Tu finis vous finissez Il/elle finit ils/elles finissent I finish, I do finish, I am finishing

Regular –re verbs Attendre – to wait for 1. Drop the –re 2. Add the endings –s, - , -ons, -ez – ent J’ attends nous attendons Tu attends vous attendez Il/elle attend ils/elles attendent I wait for, I do wait for, I am waiting for

3 ways to translate the verb directly Do + verb Form verb -ing
avoir PRESENT PASSE COMPOSE FUTUR CONDITIONAL IMPARFAIT

Le Passé Composé Describing past actions

Qu’est-ce que c’est le passé composé? n You use the passé composé to talk about an action that began and was completed. n The reason why it must be clarified that this is to talk about an action that began and was completed, is because there is another way to express things that one used to do in the past that do not specify a beginning and end. We will learn that later. n Apprenons comment faire le passé composé!

How to form the passé composé n The majority of verbs use avoir to form the passé composé, but there are some that use être. n For now, we are only going to concentrate on verbs that use avoir. Ex: n I ate a croque monsieur. n J’ai mangé un croque monsieur. n Where in the phrase do you see the verb avoir? AVOIR is the helping verb because you need it in order to form the passé composé.

How to form the passé composé: n To form the passé composé you use the present tense of the verb avoir. n Conjugons le verbe avoir! j’ ai tu as elle/il a nous avons vous avez elles/ils ont

Passé Composé n Now that you remember how to conjugate avoir, you now must add the past participle of the verb (action) that happened in the past. Ex: n We ate a pizza. n Nous avons mangé un pizza. n What word in that sentence is the past participle? n Where is the verb avoir? n How do I form the past participle?

Le Participe Passé des verbes réguliers The Past Participle of regular verbs -ER é -IR I 1. drop the –er 2. add the é 1. drop the –ir 2. add the i parler finir parlé fini -RE u 1. drop the –re 2. add the u attendre attendu aimer aimé perdre perdu choisir choisi ! Remember that these are only verbs that take avoir as the helping verb !

Putting the helping verb and the past participle together n. I ate the apple. Lets take it one word at a time: n Je n ai (the helping verb goes in front of the past participle) n mangé (remember drop the –er from manger and add the é) n la pomme. n J’ai mangé la pomme.
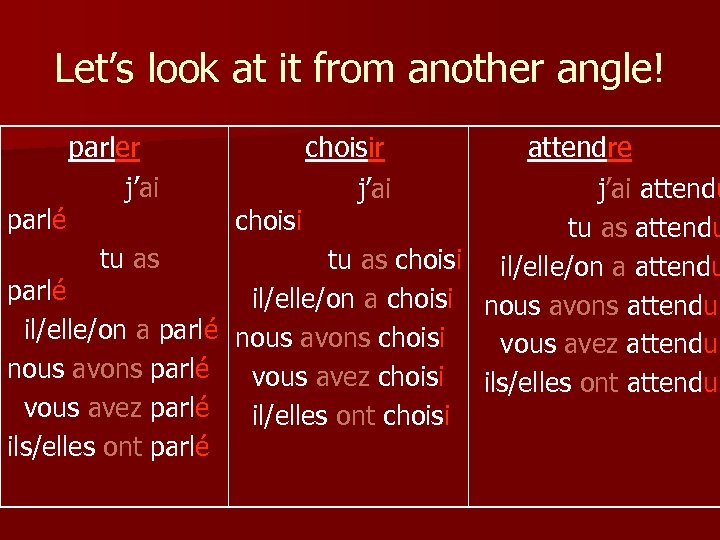
Let’s look at it from another angle! parlé parler j’ai tu as parlé il/elle/on a parlé nous avons parlé vous avez parlé ils/elles ont parlé choisir j’ai attendre j’ai attendu choisi tu as attendu tu as choisi il/elle/on a attendu il/elle/on a choisi nous avons attendu nous avons choisi vous avez attendu vous avez choisi ils/elles ont attendu il/elles ont choisi

n Il Exemples! a fini les devoirs. n He finished the homework. n Elle a mangé le sandwich au fromage. n She ate the cheese sandwich. n Nous avons parlé à Mme. Nelson. n We talked to Mme. Nelson. n Vous avez joué le futbol? n Did you play soccer? n Elles ont choisi le gâteau au chocolat. n They chose the chocolate cake.

étudier pour l’examen de français Il étudie pour l’examen de français. Il a étudié pour l’examen de français. Il n’a pas étudié pour l’examen de français.

détester Il déteste les devoirs. Il a détesté les devoirs. Il n’a pas détesté les devoirs.

oublier EIle oublie les devoirs. EIle a oublié les devoirs. Elle n’a pas oublié les devoirs.

donner une pomme au professeur Il donne une pomme au professeur. Il a donné une pomme au professeur. Il n’a pas donné une pomme au professeur.

What about the “ne…pas”? Do you remember the OREO cookie comparison? ne / n’ verb pas Je n’ai pas un oreo. Il ne veut pas un oreo.

When using “ne…pas” with the passé composé, that same rule applies. However, the p. p. goes after the “pas. ” ne + verb + past participle (avoir) Nous n’avons pas mangé d’oreos.

ne + (avoir) helping verb + past participle n Je n’ai pas mangé la pomme. n I did not eat the apple. n Il n’a pas fini ses devoirs. n He did not finish his homework. n Elles n’ont pas choisi un film. n They did not choose a movie. n Nous n’avons pas entendu le professeur. n We did not hear the professor.

Activité / Devoir verbes en - ER - aimer - étudier - oublier - manger - parler - donner - écouter - cher - regarder - trouver - acheter verbes en –IR - finir - choisir - obéir - réfléchir - réussir - grossir - remplir Choisissez 5 verbes de chaque famille et faites des phrases au passé composé. That is 15 sentences total. Make 5 of them negative. verbes en -RE -attendre -entendre -perdre -rendre -répondre -vendre

Pc verbes irregulier *take être not avoir in pc n n n n n Avoir - eu Être - été Faire - fait Aller – allé* Vouloir - voulu Pouvoir -pu Savoir - su Devoir - dû Dormir - dormi Voir - vu n n n n n Mettre - mis Prendre – pris Croire - cru Sortir – sorti* Partir – parti* Connaître - connu Venir – venu* Dire - dit Lire - lu Écrire - écrit

Assignment with irreg verbs n 10 sentences in pc

There about 17 verbs that take être in the pc Refer to your handout n Refer to the rap n
1f1820990b0ef91ea19a983395fcf44d.ppt