4c15d69aa55d6679d828a9ab3ba3b7eb.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 27
 VELO Software Overview & Shutdown Planning • Organisation • Milestones • 3 Critical Areas Chris Parkes for VELO software Group
VELO Software Overview & Shutdown Planning • Organisation • Milestones • 3 Critical Areas Chris Parkes for VELO software Group
 Areas & Responsibilities • • • • Overall Co-ord: CP PVSS: Stefano De Capua DAQ Recipes: Karol Hennessy Timing & Gain: Kazu Akiba Error Bank Analyses: Ann van Lysebetten Online Monitoring: Kurt Rinnert Data Quality: Eduardo Rodrigues Simulation & Reconstruction: Tomasz Szumlak Tracking: David Hutchcroft Alignment: Silvia Borghi Closing Strategy: Malcolm John > 20 people contributing Milestones defined for each, with one person responsible and priorities assigned 2
Areas & Responsibilities • • • • Overall Co-ord: CP PVSS: Stefano De Capua DAQ Recipes: Karol Hennessy Timing & Gain: Kazu Akiba Error Bank Analyses: Ann van Lysebetten Online Monitoring: Kurt Rinnert Data Quality: Eduardo Rodrigues Simulation & Reconstruction: Tomasz Szumlak Tracking: David Hutchcroft Alignment: Silvia Borghi Closing Strategy: Malcolm John > 20 people contributing Milestones defined for each, with one person responsible and priorities assigned 2
 Organisation • Weekly Monday commissioning meeting – Report on previous week milestones – News from all, forum for discussing issues – Work plans for the week • Integration Days: Thursdays – Integrate weekly releases (if any) at pit – Release: PVSS, recipes, Vetra • Brief report bi-weekly Friday meeting – Report progress to whole group, no details – Specific presentations on items of general interest • Shutdown progress logged on milestone Twiki page https: //lbtwiki/bin/view/VELO/Software. Milestones 3
Organisation • Weekly Monday commissioning meeting – Report on previous week milestones – News from all, forum for discussing issues – Work plans for the week • Integration Days: Thursdays – Integrate weekly releases (if any) at pit – Release: PVSS, recipes, Vetra • Brief report bi-weekly Friday meeting – Report progress to whole group, no details – Specific presentations on items of general interest • Shutdown progress logged on milestone Twiki page https: //lbtwiki/bin/view/VELO/Software. Milestones 3
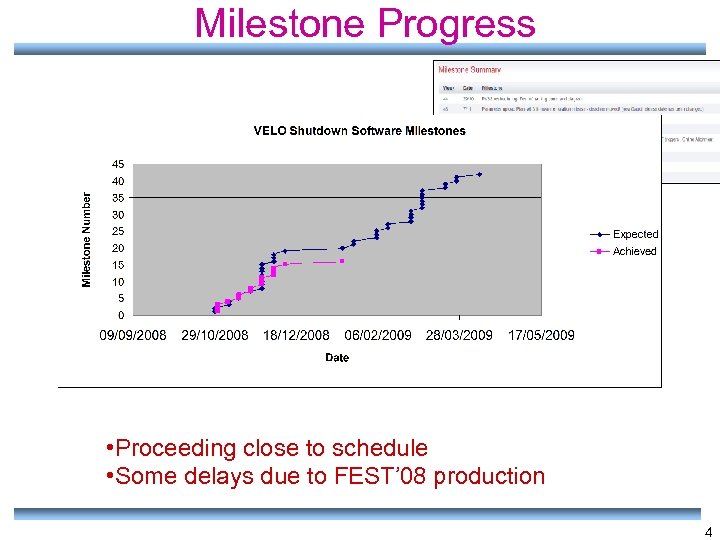 Milestone Progress • Proceeding close to schedule • Some delays due to FEST’ 08 production 4
Milestone Progress • Proceeding close to schedule • Some delays due to FEST’ 08 production 4
 Critical Path • In September identified three key areas where progress is needed before we start running this year – Timing – TELL 1 Parameter Uploading – Monitoring 5
Critical Path • In September identified three key areas where progress is needed before we start running this year – Timing – TELL 1 Parameter Uploading – Monitoring 5
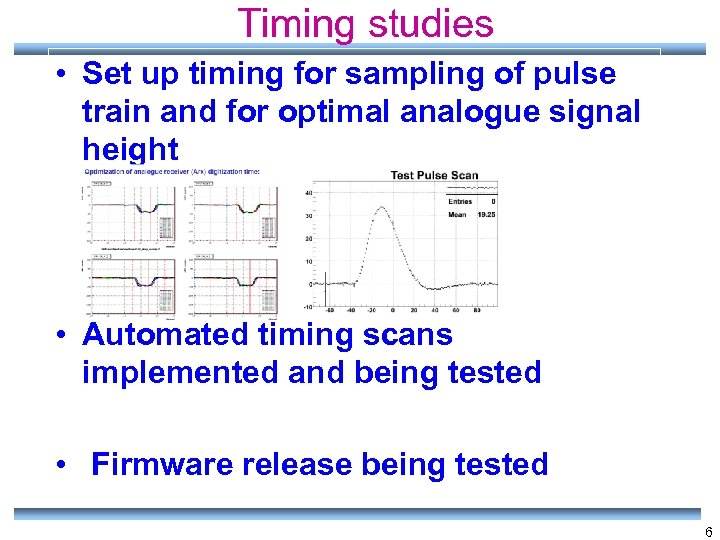 Timing studies • Set up timing for sampling of pulse train and for optimal analogue signal height • Automated timing scans implemented and being tested • Firmware release being tested 6
Timing studies • Set up timing for sampling of pulse train and for optimal analogue signal height • Automated timing scans implemented and being tested • Firmware release being tested 6
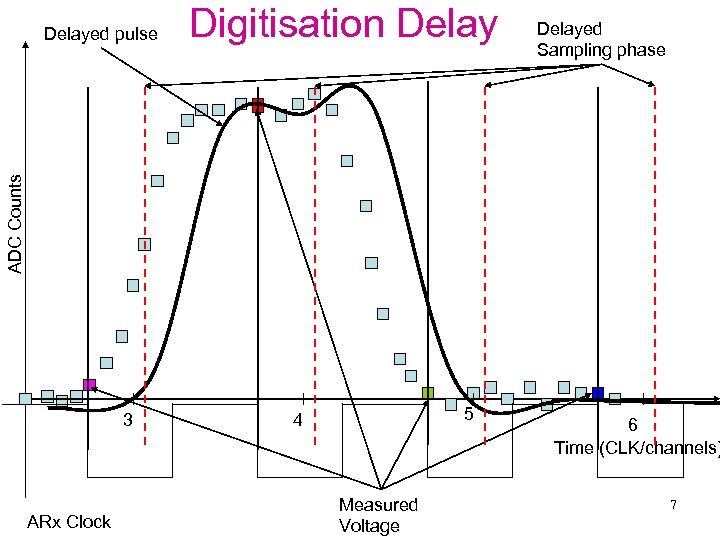 Digitisation Delayed Sampling phase ADC Counts Delayed pulse 3 ARx Clock 5 4 Measured Voltage 6 Time (CLK/channels) 7
Digitisation Delayed Sampling phase ADC Counts Delayed pulse 3 ARx Clock 5 4 Measured Voltage 6 Time (CLK/channels) 7
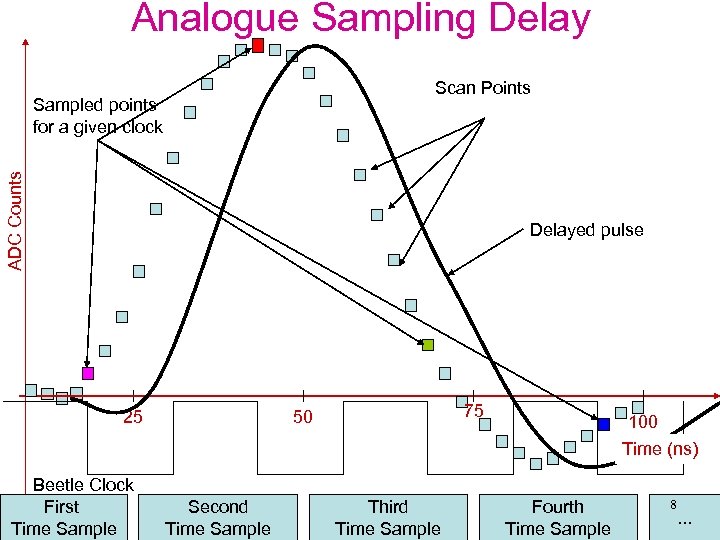 Analogue Sampling Delay Scan Points ADC Counts Sampled points for a given clock Delayed pulse 25 Beetle Clock First Time Sample 75 50 Second Time Sample Third Time Sample 100 Time (ns) Fourth Time Sample 8 . . .
Analogue Sampling Delay Scan Points ADC Counts Sampled points for a given clock Delayed pulse 25 Beetle Clock First Time Sample 75 50 Second Time Sample Third Time Sample 100 Time (ns) Fourth Time Sample 8 . . .
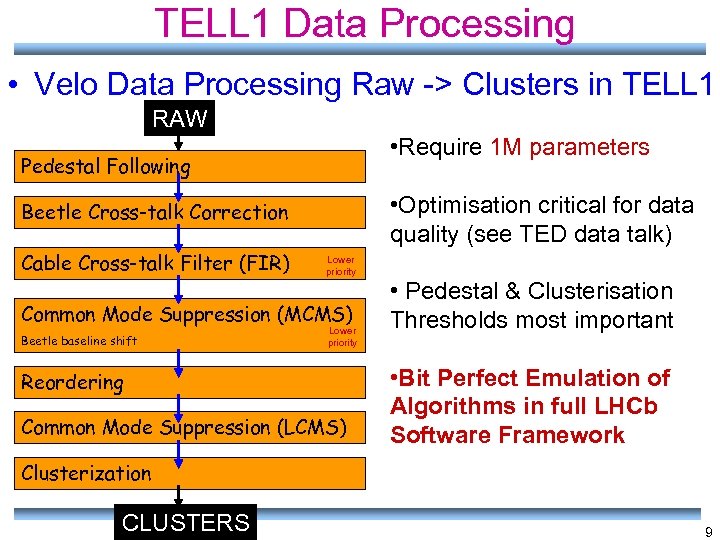 TELL 1 Data Processing • Velo Data Processing Raw -> Clusters in TELL 1 RAW • Require 1 M parameters Pedestal Following • Optimisation critical for data quality (see TED data talk) Beetle Cross-talk Correction Cable Cross-talk Filter (FIR) Lower priority Common Mode Suppression (MCMS) Beetle baseline shift Lower priority Reordering Common Mode Suppression (LCMS) • Pedestal & Clusterisation Thresholds most important • Bit Perfect Emulation of Algorithms in full LHCb Software Framework Clusterization CLUSTERS 9
TELL 1 Data Processing • Velo Data Processing Raw -> Clusters in TELL 1 RAW • Require 1 M parameters Pedestal Following • Optimisation critical for data quality (see TED data talk) Beetle Cross-talk Correction Cable Cross-talk Filter (FIR) Lower priority Common Mode Suppression (MCMS) Beetle baseline shift Lower priority Reordering Common Mode Suppression (LCMS) • Pedestal & Clusterisation Thresholds most important • Bit Perfect Emulation of Algorithms in full LHCb Software Framework Clusterization CLUSTERS 9
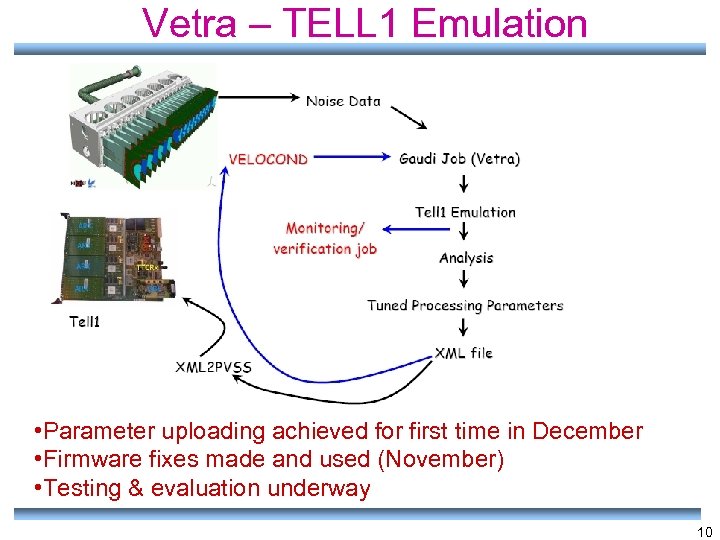 Vetra – TELL 1 Emulation • Parameter uploading achieved for first time in December • Firmware fixes made and used (November) • Testing & evaluation underway 10
Vetra – TELL 1 Emulation • Parameter uploading achieved for first time in December • Firmware fixes made and used (November) • Testing & evaluation underway 10
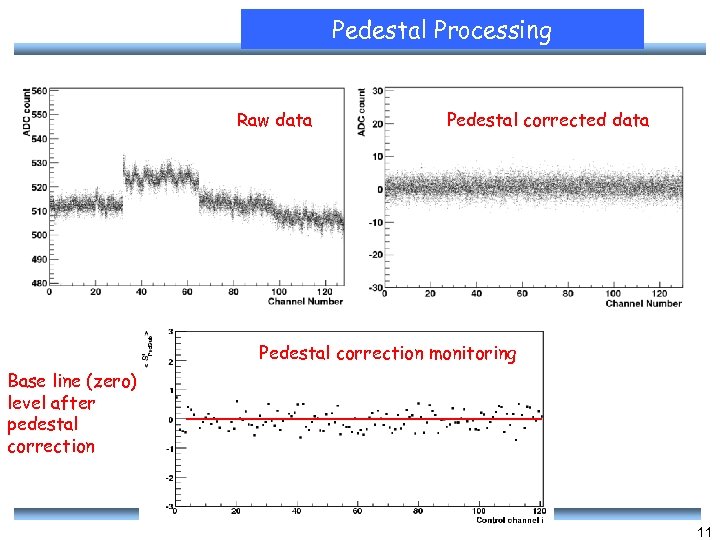 Pedestal Processing Raw data Pedestal corrected data Pedestal correction monitoring Base line (zero) level after pedestal correction 11
Pedestal Processing Raw data Pedestal corrected data Pedestal correction monitoring Base line (zero) level after pedestal correction 11
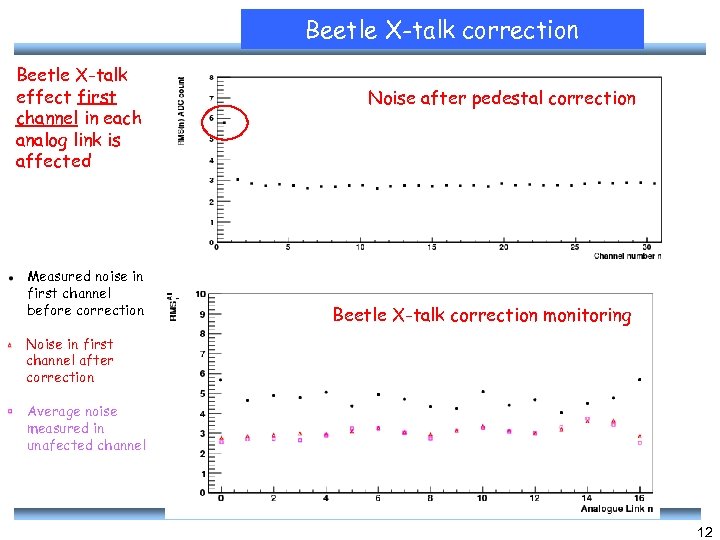 Beetle X-talk correction Beetle X-talk effect first channel in each analog link is affected Measured noise in first channel before correction Noise after pedestal correction Beetle X-talk correction monitoring Noise in first channel after correction Average noise measured in unafected channel 12
Beetle X-talk correction Beetle X-talk effect first channel in each analog link is affected Measured noise in first channel before correction Noise after pedestal correction Beetle X-talk correction monitoring Noise in first channel after correction Average noise measured in unafected channel 12
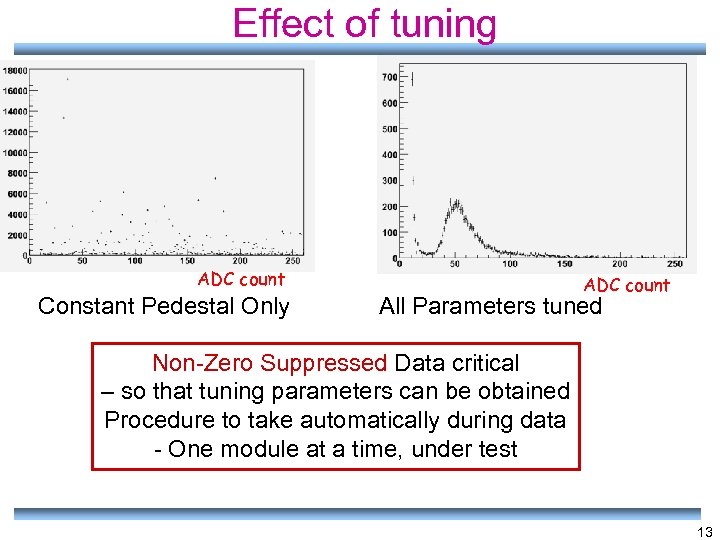 Effect of tuning ADC count Constant Pedestal Only ADC count All Parameters tuned Non-Zero Suppressed Data critical – so that tuning parameters can be obtained Procedure to take automatically during data - One module at a time, under test 13
Effect of tuning ADC count Constant Pedestal Only ADC count All Parameters tuned Non-Zero Suppressed Data critical – so that tuning parameters can be obtained Procedure to take automatically during data - One module at a time, under test 13
 Monitoring • Monitoring package – Package for “high-level” (= ZS) data • Monitoring based on clusters and tracks – Package for NZS data • Noise calculation, time alignment study, beetle pulse shape, … • Scripts and macros are being developed to analyse data • Wiki pages with documentation and How. To’s Review of Monitoring status in February 14
Monitoring • Monitoring package – Package for “high-level” (= ZS) data • Monitoring based on clusters and tracks – Package for NZS data • Noise calculation, time alignment study, beetle pulse shape, … • Scripts and macros are being developed to analyse data • Wiki pages with documentation and How. To’s Review of Monitoring status in February 14
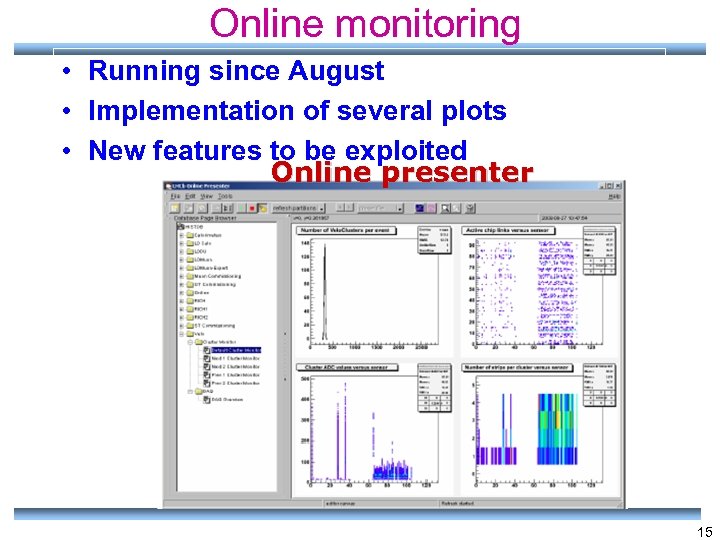 Online monitoring • Running since August • Implementation of several plots • New features to be exploited Online presenter 15
Online monitoring • Running since August • Implementation of several plots • New features to be exploited Online presenter 15
 Cluster Monitoring • Cluster information: – Cluster ADC value – Active chip links – Number of strip in a cluster – Cluster ADC value versus sampling – Number of cluster per events – More… Some of these distributions versus sensor number and/or sensor strip 16
Cluster Monitoring • Cluster information: – Cluster ADC value – Active chip links – Number of strip in a cluster – Cluster ADC value versus sampling – Number of cluster per events – More… Some of these distributions versus sensor number and/or sensor strip 16
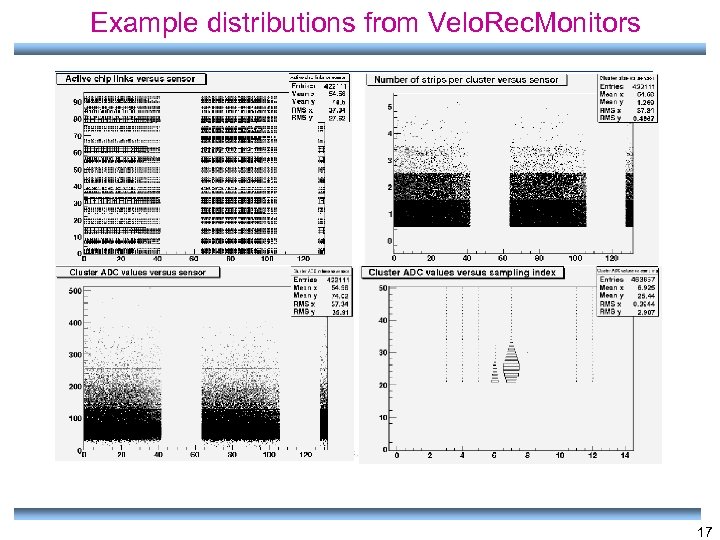 Example distributions from Velo. Rec. Monitors 17
Example distributions from Velo. Rec. Monitors 17
 Track Monitoring • Tracks – Number tracks – Pseudo-rapidity – Azimuthal Angle – Pseudo-efficiency – Biased and unbiased Residuals versus sensor number – Total number of R cluster per track – Vertex information – Hits distribution in xy and xz – Mean sigma of residuals versus of sensors – More… 18
Track Monitoring • Tracks – Number tracks – Pseudo-rapidity – Azimuthal Angle – Pseudo-efficiency – Biased and unbiased Residuals versus sensor number – Total number of R cluster per track – Vertex information – Hits distribution in xy and xz – Mean sigma of residuals versus of sensors – More… 18
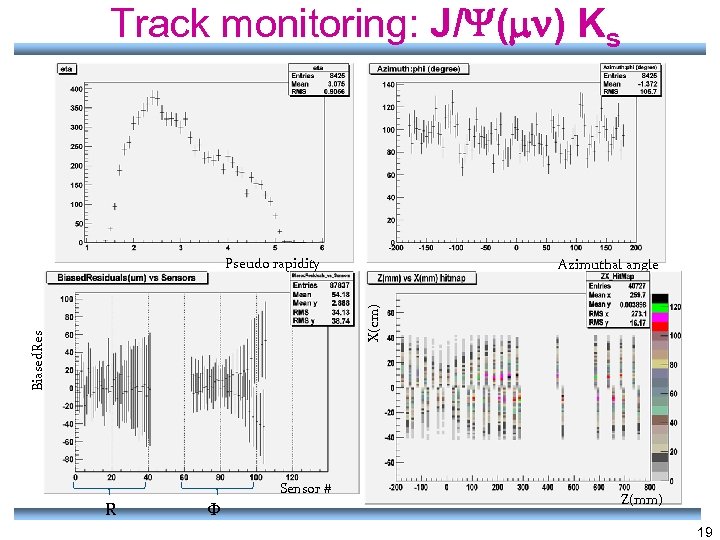 Track monitoring: J/ ( ) Ks Pseudo rapidity Biased. Res X(cm) Azimuthal angle Sensor # R Z(mm) 19
Track monitoring: J/ ( ) Ks Pseudo rapidity Biased. Res X(cm) Azimuthal angle Sensor # R Z(mm) 19
 Script and Macros • Analysis of the data for the evaluation for: – – – Time alignment study, Noise calculation, High voltage scan, beetle pulse shape, More… 20
Script and Macros • Analysis of the data for the evaluation for: – – – Time alignment study, Noise calculation, High voltage scan, beetle pulse shape, More… 20
 Noise monitoring macros – example of GUI 21
Noise monitoring macros – example of GUI 21
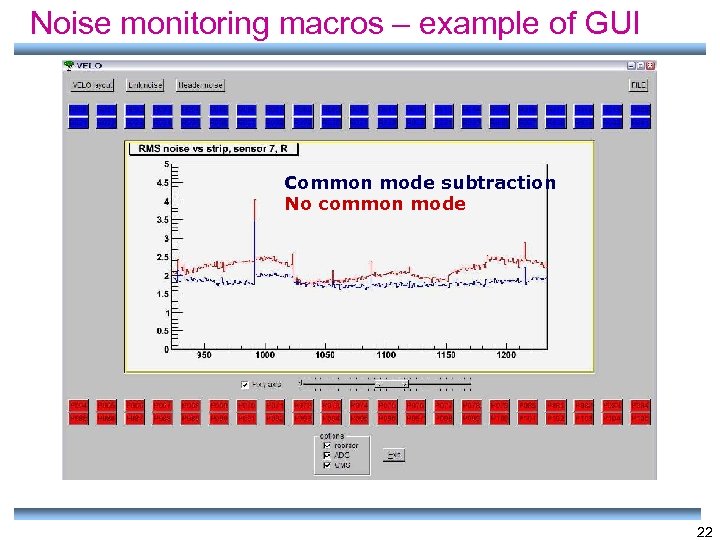 Noise monitoring macros – example of GUI Common mode subtraction No common mode 22
Noise monitoring macros – example of GUI Common mode subtraction No common mode 22
 Noise performance • Common mode pickup from beam requires data • At pit and in previous testbeams parameters highly stable HP 1 HP 2 HP 3 HP 4 23
Noise performance • Common mode pickup from beam requires data • At pit and in previous testbeams parameters highly stable HP 1 HP 2 HP 3 HP 4 23
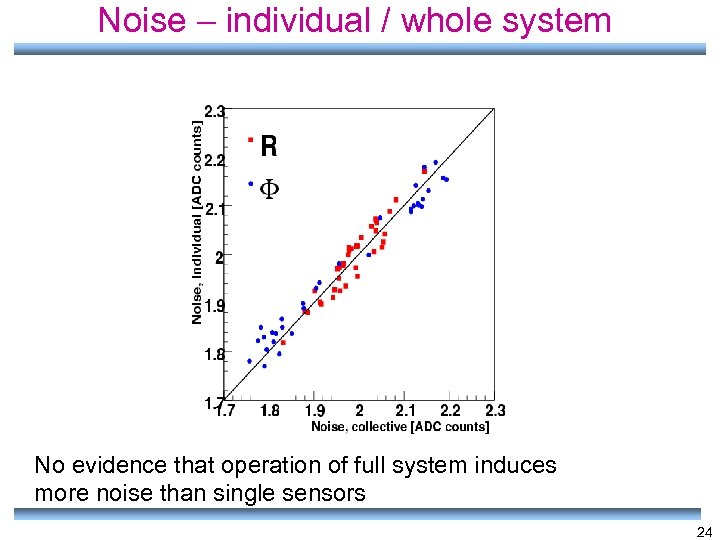 Noise – individual / whole system No evidence that operation of full system induces more noise than single sensors 24
Noise – individual / whole system No evidence that operation of full system induces more noise than single sensors 24
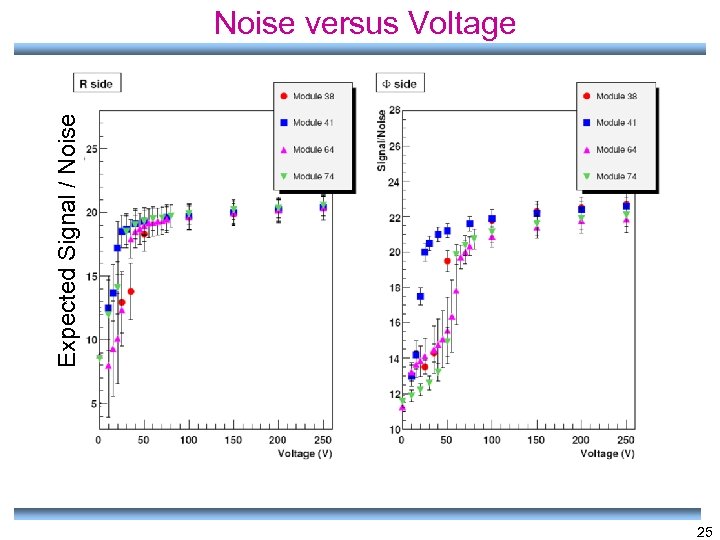 Expected Signal / Noise versus Voltage 25
Expected Signal / Noise versus Voltage 25
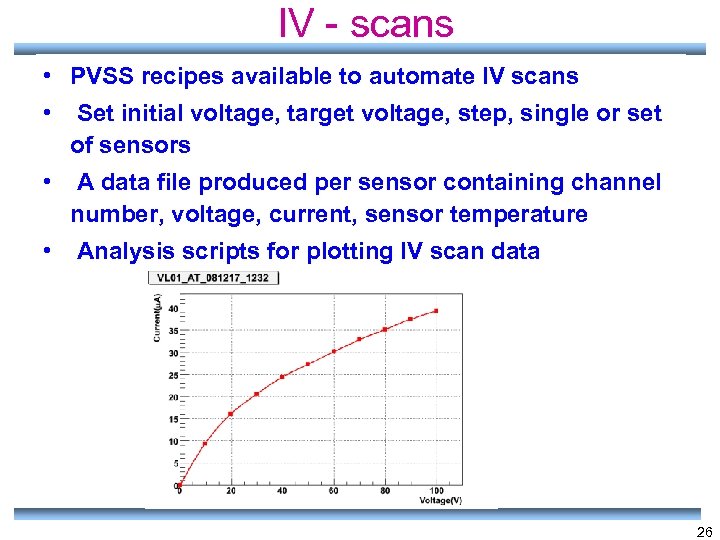 IV - scans • PVSS recipes available to automate IV scans • Set initial voltage, target voltage, step, single or set of sensors • A data file produced per sensor containing channel number, voltage, current, sensor temperature • Analysis scripts for plotting IV scan data 26
IV - scans • PVSS recipes available to automate IV scans • Set initial voltage, target voltage, step, single or set of sensors • A data file produced per sensor containing channel number, voltage, current, sensor temperature • Analysis scripts for plotting IV scan data 26
 Software Commissioning Summary • All baseline algorithms – Completed for summer ’ 08 • Commissioning software – Milestones for data readiness in April 2009 – 3 critical areas all proceeding according to plan • TED data are the VELO ‘cosmics’ Tremendous success of first tracks This sample has been very useful for comissioning TED data this summer will allow us to: Optimise timing Test and tune FPGA algorithms Increase alignment accuracy 27
Software Commissioning Summary • All baseline algorithms – Completed for summer ’ 08 • Commissioning software – Milestones for data readiness in April 2009 – 3 critical areas all proceeding according to plan • TED data are the VELO ‘cosmics’ Tremendous success of first tracks This sample has been very useful for comissioning TED data this summer will allow us to: Optimise timing Test and tune FPGA algorithms Increase alignment accuracy 27


