2dbfa3667aa765afbd1557f44e10f3ad.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 30
 Vehicle Technology: 2 and 3 Wheelers in Asia: Current and Future Greenhouse Gas Emissions Narayan Iyer, Adviser (Technical), Bajaj Auto Ltd, Pune, India Workshop on Climate Change Mitigation in the Transport Sector 24 and 25 May, 2006 Asian Development Bank, Manila
Vehicle Technology: 2 and 3 Wheelers in Asia: Current and Future Greenhouse Gas Emissions Narayan Iyer, Adviser (Technical), Bajaj Auto Ltd, Pune, India Workshop on Climate Change Mitigation in the Transport Sector 24 and 25 May, 2006 Asian Development Bank, Manila
 Presentation Contents • Structure of 2 & 3 wheeler fleet in terms of types of vehicles, engines, technologies and fuels • Known, potential and emerging technologies and their evolution • Estimations of co 2 emissions and fuel consumption of new technologies • Available estimates of transport GHG emissions in India
Presentation Contents • Structure of 2 & 3 wheeler fleet in terms of types of vehicles, engines, technologies and fuels • Known, potential and emerging technologies and their evolution • Estimations of co 2 emissions and fuel consumption of new technologies • Available estimates of transport GHG emissions in India
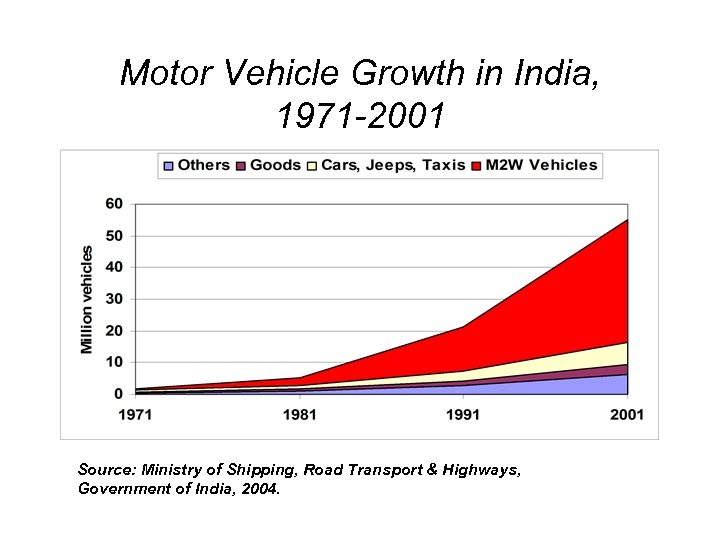 Motor Vehicle Growth in India, 1971 -2001 Source: Ministry of Shipping, Road Transport & Highways, Government of India, 2004.
Motor Vehicle Growth in India, 1971 -2001 Source: Ministry of Shipping, Road Transport & Highways, Government of India, 2004.
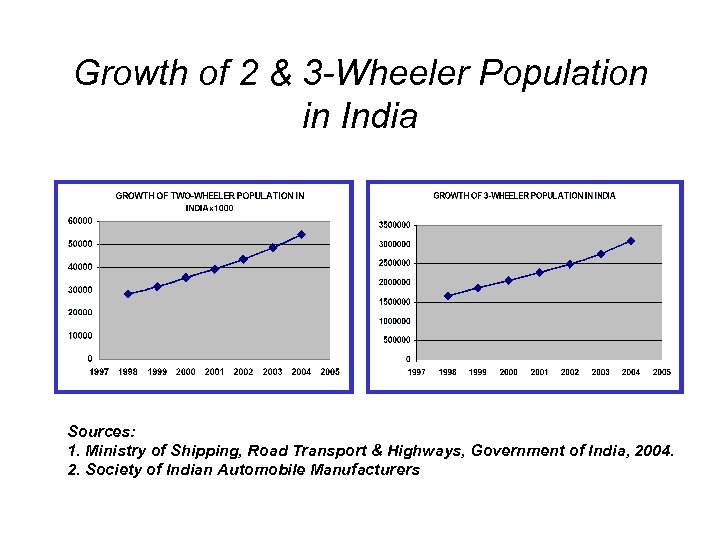 Growth of 2 & 3 -Wheeler Population in India Sources: 1. Ministry of Shipping, Road Transport & Highways, Government of India, 2004. 2. Society of Indian Automobile Manufacturers
Growth of 2 & 3 -Wheeler Population in India Sources: 1. Ministry of Shipping, Road Transport & Highways, Government of India, 2004. 2. Society of Indian Automobile Manufacturers
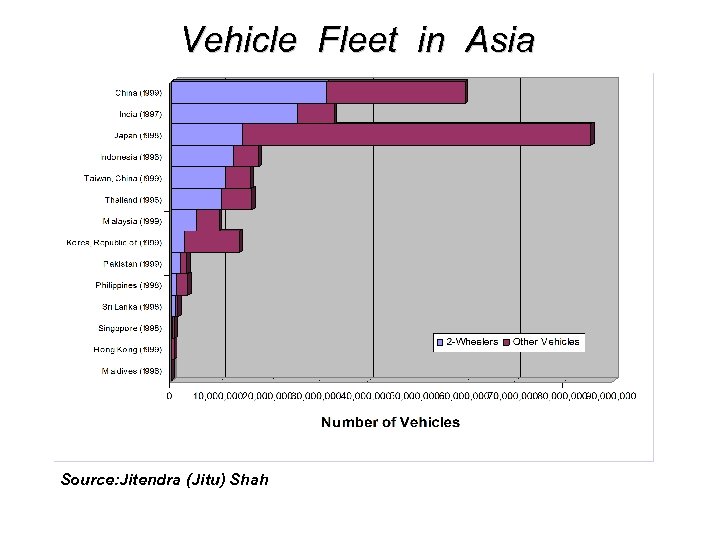 Vehicle Fleet in Asia Source: Jitendra (Jitu) Shah
Vehicle Fleet in Asia Source: Jitendra (Jitu) Shah
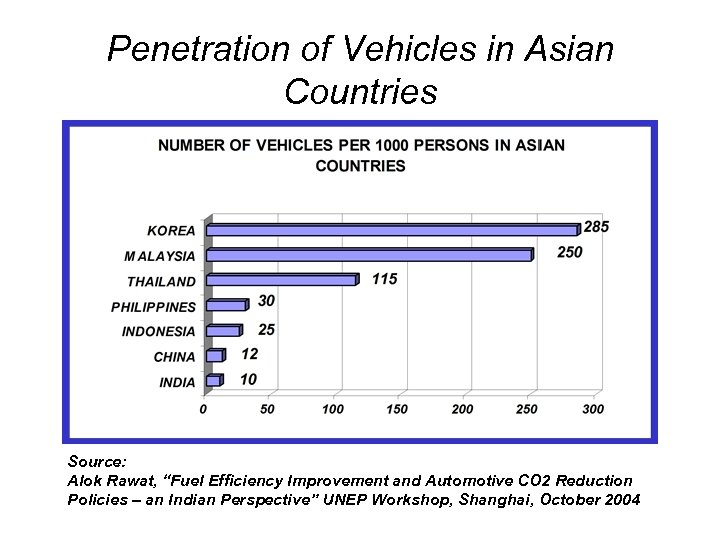 Penetration of Vehicles in Asian Countries Source: Alok Rawat, “Fuel Efficiency Improvement and Automotive CO 2 Reduction Policies – an Indian Perspective” UNEP Workshop, Shanghai, October 2004
Penetration of Vehicles in Asian Countries Source: Alok Rawat, “Fuel Efficiency Improvement and Automotive CO 2 Reduction Policies – an Indian Perspective” UNEP Workshop, Shanghai, October 2004
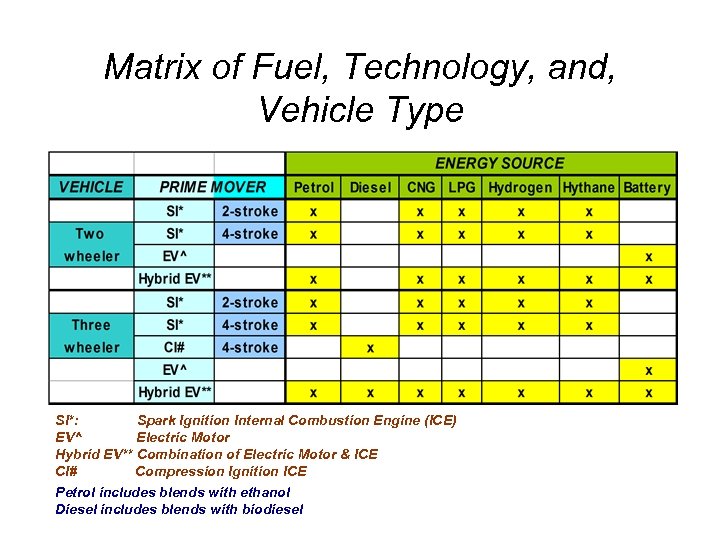 Matrix of Fuel, Technology, and, Vehicle Type SI*: Spark Ignition Internal Combustion Engine (ICE) EV^ Electric Motor Hybrid EV** Combination of Electric Motor & ICE CI# Compression Ignition ICE Petrol includes blends with ethanol Diesel includes blends with biodiesel
Matrix of Fuel, Technology, and, Vehicle Type SI*: Spark Ignition Internal Combustion Engine (ICE) EV^ Electric Motor Hybrid EV** Combination of Electric Motor & ICE CI# Compression Ignition ICE Petrol includes blends with ethanol Diesel includes blends with biodiesel
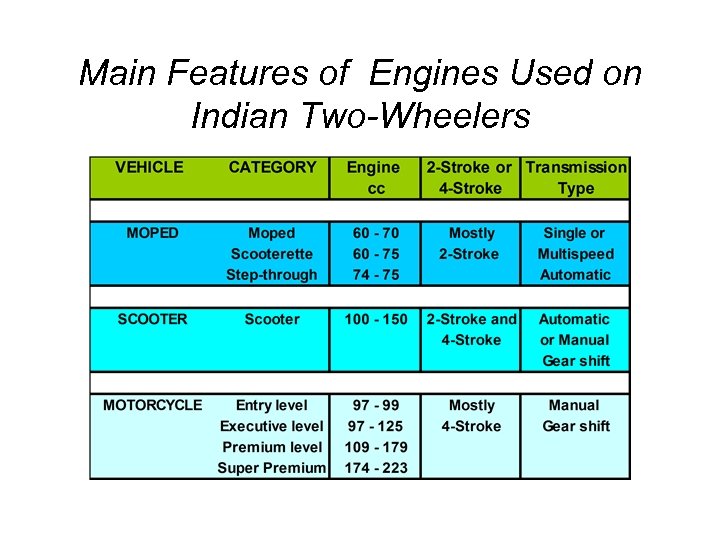 Main Features of Engines Used on Indian Two-Wheelers
Main Features of Engines Used on Indian Two-Wheelers
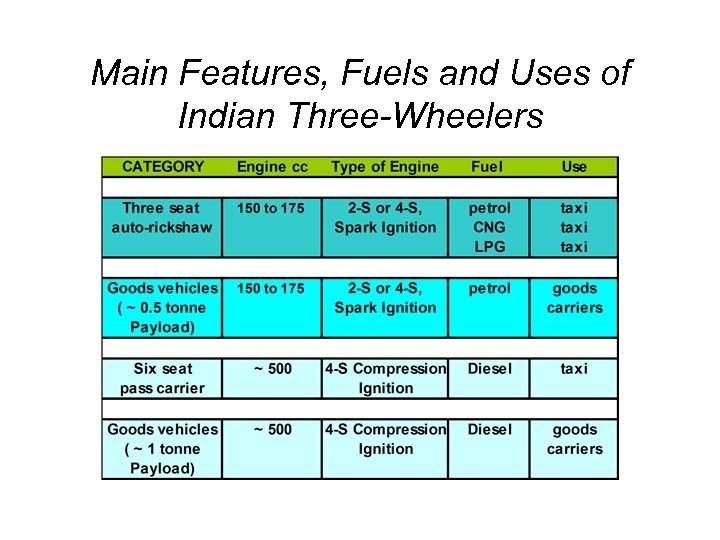 Main Features, Fuels and Uses of Indian Three-Wheelers
Main Features, Fuels and Uses of Indian Three-Wheelers
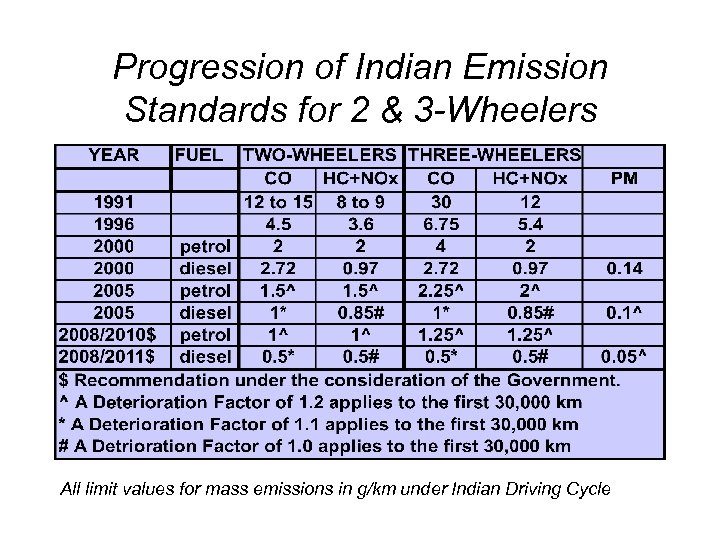 Progression of Indian Emission Standards for 2 & 3 -Wheelers All limit values for mass emissions in g/km under Indian Driving Cycle
Progression of Indian Emission Standards for 2 & 3 -Wheelers All limit values for mass emissions in g/km under Indian Driving Cycle
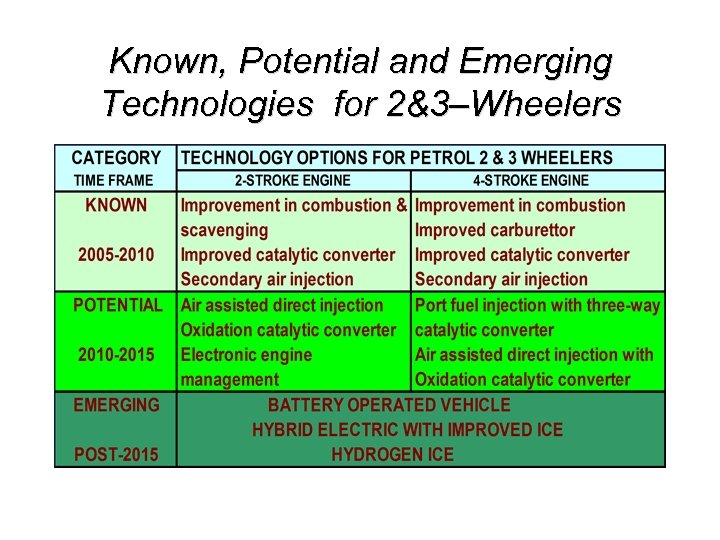 Known, Potential and Emerging Technologies for 2&3–Wheelers
Known, Potential and Emerging Technologies for 2&3–Wheelers
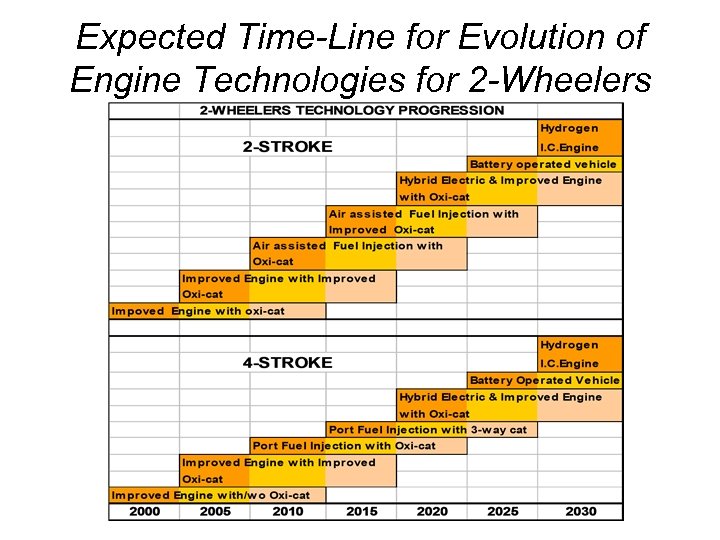 Expected Time-Line for Evolution of Engine Technologies for 2 -Wheelers
Expected Time-Line for Evolution of Engine Technologies for 2 -Wheelers
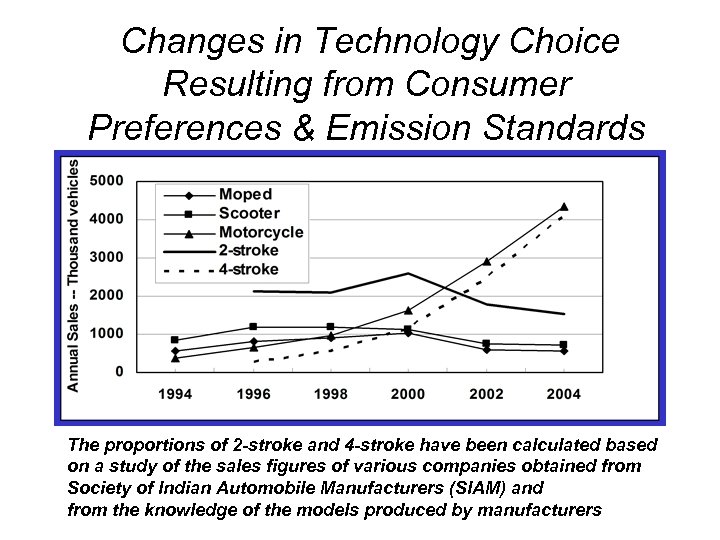 Changes in Technology Choice Resulting from Consumer Preferences & Emission Standards The proportions of 2 -stroke and 4 -stroke have been calculated based on a study of the sales figures of various companies obtained from Society of Indian Automobile Manufacturers (SIAM) and from the knowledge of the models produced by manufacturers
Changes in Technology Choice Resulting from Consumer Preferences & Emission Standards The proportions of 2 -stroke and 4 -stroke have been calculated based on a study of the sales figures of various companies obtained from Society of Indian Automobile Manufacturers (SIAM) and from the knowledge of the models produced by manufacturers
 Methodology for the Estimation of Fuel Consumption and CO 2 Emissions – 1/2 • (a) Baseline fuel consumption of current technologies is average of “Type Approval Test” results of several models published by the Automotive Research Association of India (ARAI)*. • ARAI calculates fuel consumption in km/litre using the ‘carbon balance method’ from measured exhaust emission levels under “Indian Driving Cycle” run on a chassis dynamometer • (b) The baseline data for average CO 2 emissions (tail pipe only) of each category of vehicle has also been determined from the same source of data * Source: Bhanot B, Kulkarni U. , ”Indian Auto Emission Profile”, Symposium on International Vehicle Technology, Automotive Research Association of India, 2001
Methodology for the Estimation of Fuel Consumption and CO 2 Emissions – 1/2 • (a) Baseline fuel consumption of current technologies is average of “Type Approval Test” results of several models published by the Automotive Research Association of India (ARAI)*. • ARAI calculates fuel consumption in km/litre using the ‘carbon balance method’ from measured exhaust emission levels under “Indian Driving Cycle” run on a chassis dynamometer • (b) The baseline data for average CO 2 emissions (tail pipe only) of each category of vehicle has also been determined from the same source of data * Source: Bhanot B, Kulkarni U. , ”Indian Auto Emission Profile”, Symposium on International Vehicle Technology, Automotive Research Association of India, 2001
 Methodology for the Estimation of Fuel Consumption and CO 2 Emissions – 2/2 • (c ) The fuel consumption of new Internal Combustion Engine (ICE) technologies based on the indications in literature. • (d) All the fuel consumption values converted to MJ/km by using appropriate values of density and Lower Heating Values of the respective fuels. • (e) CO 2 emissions of new ICE technologies derived from the fuel consumption by establishing a relationship between fuel consumption and CO 2 emissions
Methodology for the Estimation of Fuel Consumption and CO 2 Emissions – 2/2 • (c ) The fuel consumption of new Internal Combustion Engine (ICE) technologies based on the indications in literature. • (d) All the fuel consumption values converted to MJ/km by using appropriate values of density and Lower Heating Values of the respective fuels. • (e) CO 2 emissions of new ICE technologies derived from the fuel consumption by establishing a relationship between fuel consumption and CO 2 emissions
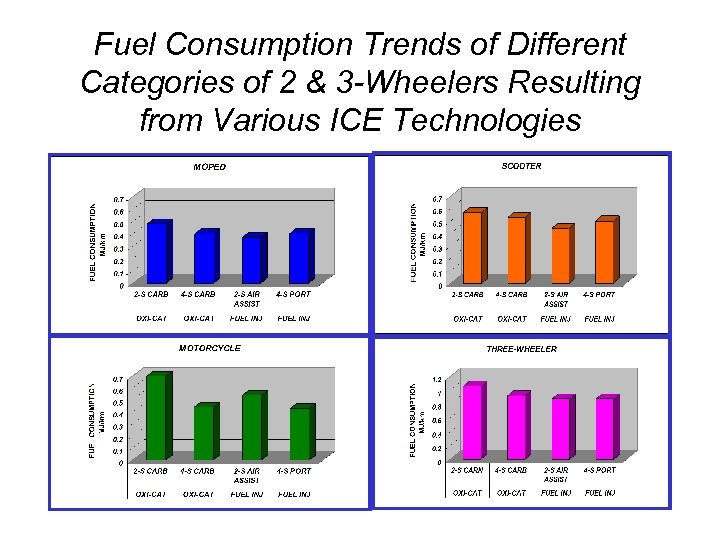 Fuel Consumption Trends of Different Categories of 2 & 3 -Wheelers Resulting from Various ICE Technologies
Fuel Consumption Trends of Different Categories of 2 & 3 -Wheelers Resulting from Various ICE Technologies
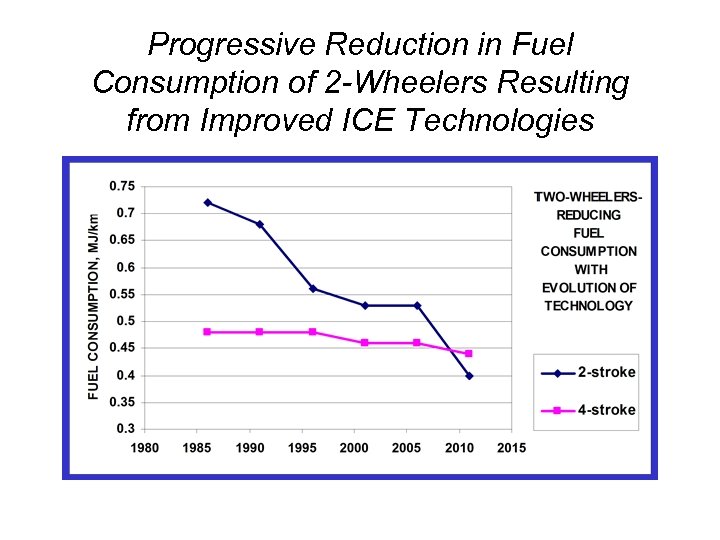 Progressive Reduction in Fuel Consumption of 2 -Wheelers Resulting from Improved ICE Technologies
Progressive Reduction in Fuel Consumption of 2 -Wheelers Resulting from Improved ICE Technologies
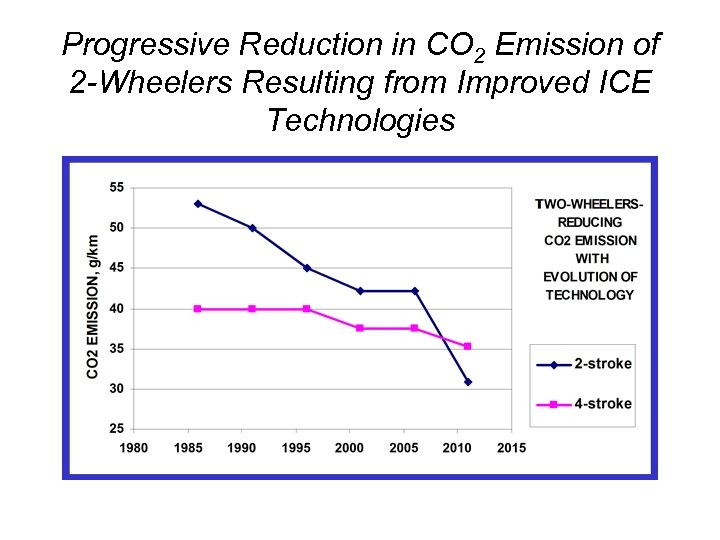 Progressive Reduction in CO 2 Emission of 2 -Wheelers Resulting from Improved ICE Technologies
Progressive Reduction in CO 2 Emission of 2 -Wheelers Resulting from Improved ICE Technologies
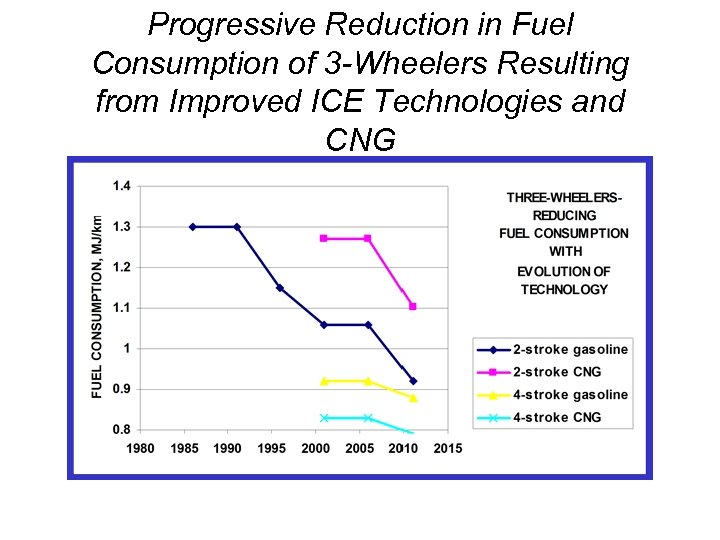 Progressive Reduction in Fuel Consumption of 3 -Wheelers Resulting from Improved ICE Technologies and CNG
Progressive Reduction in Fuel Consumption of 3 -Wheelers Resulting from Improved ICE Technologies and CNG
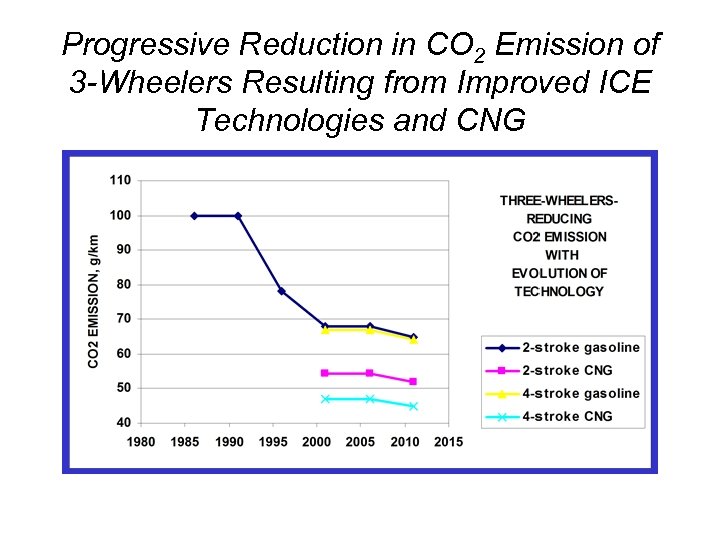 Progressive Reduction in CO 2 Emission of 3 -Wheelers Resulting from Improved ICE Technologies and CNG
Progressive Reduction in CO 2 Emission of 3 -Wheelers Resulting from Improved ICE Technologies and CNG
 Methodology for the Estimation of Fuel Consumption and CO 2 Emissions of EV and Hybrid EV • • • (a) The energy consumption (in MJ/km) of battery operated electric vehicle was considered to be 30% of the energy consumption of the basic ICE. This is based on the reported energy consumption of 0. 06 k. Wh/km of the Bajaj three wheeler(1). (b) The energy consumption of hybrid electric vehicles has been considered as 85% of that of the EV based on literature for both the hybrid and electric four wheelers (2). (c) CO 2 emission of EV and Hybrid EV based on ratio of the fuel consumption of the hybrid and corresponding basic ICE used in the category of vehicle Sources (1) Berry R. K. , Schweitzer Samuel, Basu Tapan, Bedewi Nabih, Vincent Daniel, Dhungana Atulya, “Indian Zero Emission Transportation Program – a driving force for change”, International Symposium on Automotive Electronics and Alternative Energy Vehicles, Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur, November 2001. (2) Ybema J. R. , Lako P. , Gielen D. J. , Oosterheert R. J. , Kram T. , “Prospects For Energy Technologies in the Netherlands, Volume 2, Technology characterizations and technology results”, ECN, August 1995
Methodology for the Estimation of Fuel Consumption and CO 2 Emissions of EV and Hybrid EV • • • (a) The energy consumption (in MJ/km) of battery operated electric vehicle was considered to be 30% of the energy consumption of the basic ICE. This is based on the reported energy consumption of 0. 06 k. Wh/km of the Bajaj three wheeler(1). (b) The energy consumption of hybrid electric vehicles has been considered as 85% of that of the EV based on literature for both the hybrid and electric four wheelers (2). (c) CO 2 emission of EV and Hybrid EV based on ratio of the fuel consumption of the hybrid and corresponding basic ICE used in the category of vehicle Sources (1) Berry R. K. , Schweitzer Samuel, Basu Tapan, Bedewi Nabih, Vincent Daniel, Dhungana Atulya, “Indian Zero Emission Transportation Program – a driving force for change”, International Symposium on Automotive Electronics and Alternative Energy Vehicles, Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur, November 2001. (2) Ybema J. R. , Lako P. , Gielen D. J. , Oosterheert R. J. , Kram T. , “Prospects For Energy Technologies in the Netherlands, Volume 2, Technology characterizations and technology results”, ECN, August 1995
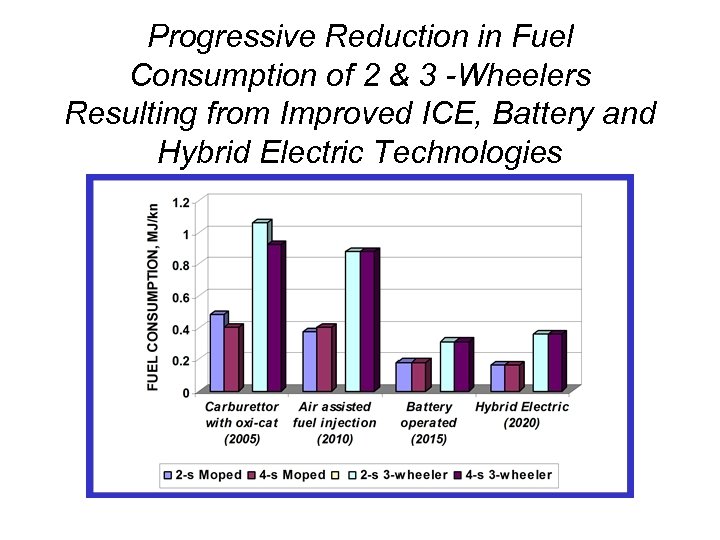 Progressive Reduction in Fuel Consumption of 2 & 3 -Wheelers Resulting from Improved ICE, Battery and Hybrid Electric Technologies
Progressive Reduction in Fuel Consumption of 2 & 3 -Wheelers Resulting from Improved ICE, Battery and Hybrid Electric Technologies
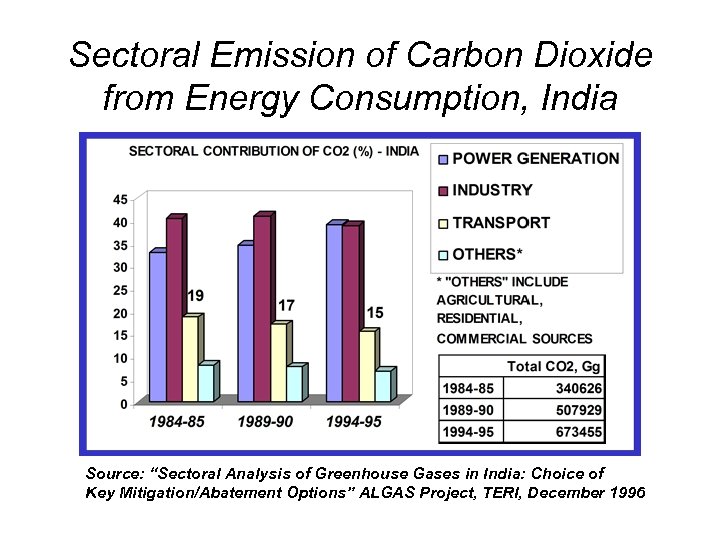 Sectoral Emission of Carbon Dioxide from Energy Consumption, India Source: “Sectoral Analysis of Greenhouse Gases in India: Choice of Key Mitigation/Abatement Options” ALGAS Project, TERI, December 1996
Sectoral Emission of Carbon Dioxide from Energy Consumption, India Source: “Sectoral Analysis of Greenhouse Gases in India: Choice of Key Mitigation/Abatement Options” ALGAS Project, TERI, December 1996
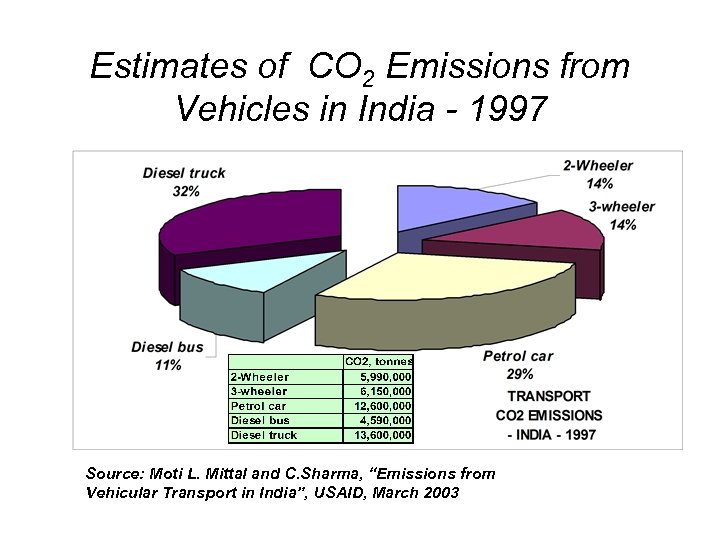 Estimates of CO 2 Emissions from Vehicles in India - 1997 Source: Moti L. Mittal and C. Sharma, “Emissions from Vehicular Transport in India”, USAID, March 2003
Estimates of CO 2 Emissions from Vehicles in India - 1997 Source: Moti L. Mittal and C. Sharma, “Emissions from Vehicular Transport in India”, USAID, March 2003
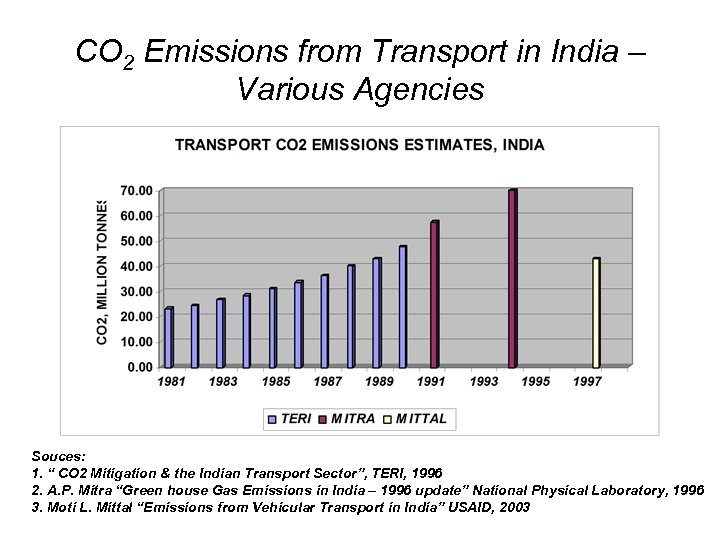 CO 2 Emissions from Transport in India – Various Agencies Souces: 1. “ CO 2 Mitigation & the Indian Transport Sector”, TERI, 1996 2. A. P. Mitra “Green house Gas Emissions in India – 1996 update” National Physical Laboratory, 1996 3. Moti L. Mittal “Emissions from Vehicular Transport in India” USAID, 2003
CO 2 Emissions from Transport in India – Various Agencies Souces: 1. “ CO 2 Mitigation & the Indian Transport Sector”, TERI, 1996 2. A. P. Mitra “Green house Gas Emissions in India – 1996 update” National Physical Laboratory, 1996 3. Moti L. Mittal “Emissions from Vehicular Transport in India” USAID, 2003
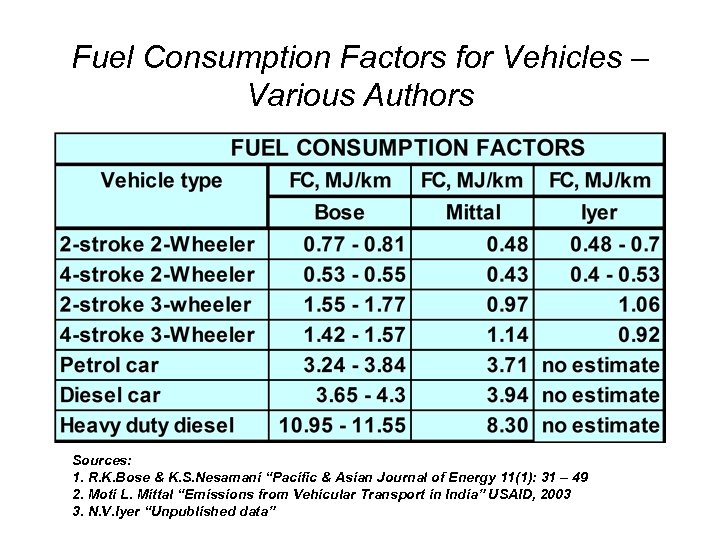 Fuel Consumption Factors for Vehicles – Various Authors Sources: 1. R. K. Bose & K. S. Nesamani “Pacific & Asian Journal of Energy 11(1): 31 – 49 2. Moti L. Mittal “Emissions from Vehicular Transport in India” USAID, 2003 3. N. V. Iyer “Unpublished data”
Fuel Consumption Factors for Vehicles – Various Authors Sources: 1. R. K. Bose & K. S. Nesamani “Pacific & Asian Journal of Energy 11(1): 31 – 49 2. Moti L. Mittal “Emissions from Vehicular Transport in India” USAID, 2003 3. N. V. Iyer “Unpublished data”
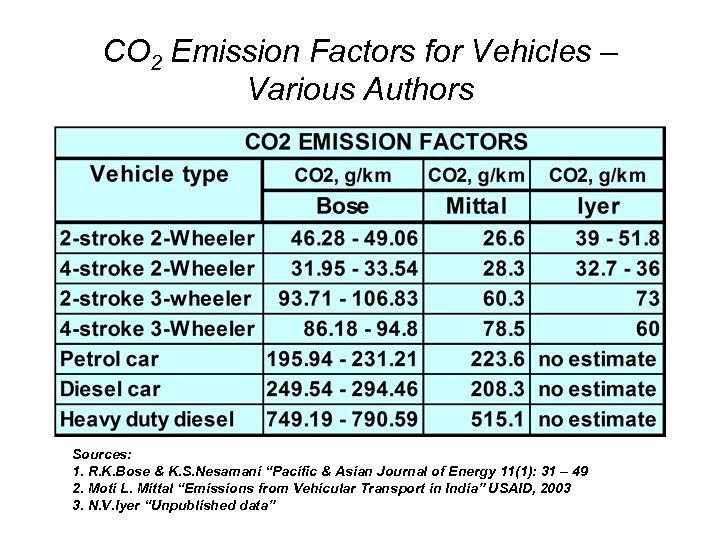 CO 2 Emission Factors for Vehicles – Various Authors Sources: 1. R. K. Bose & K. S. Nesamani “Pacific & Asian Journal of Energy 11(1): 31 – 49 2. Moti L. Mittal “Emissions from Vehicular Transport in India” USAID, 2003 3. N. V. Iyer “Unpublished data”
CO 2 Emission Factors for Vehicles – Various Authors Sources: 1. R. K. Bose & K. S. Nesamani “Pacific & Asian Journal of Energy 11(1): 31 – 49 2. Moti L. Mittal “Emissions from Vehicular Transport in India” USAID, 2003 3. N. V. Iyer “Unpublished data”
 Conclusions 1/2 • There is a rapid increase in the number of motor vehicles in India, the population being dominated by two wheelers, yet, vehicle penetration is among the lowest in the world • Progressively stringent emission standards and customer demand for fuel economy resulted in manufacturers adopting new technologies to reduce emissions and fuel consumption that have also resulted in reduction in CO 2 emissions
Conclusions 1/2 • There is a rapid increase in the number of motor vehicles in India, the population being dominated by two wheelers, yet, vehicle penetration is among the lowest in the world • Progressively stringent emission standards and customer demand for fuel economy resulted in manufacturers adopting new technologies to reduce emissions and fuel consumption that have also resulted in reduction in CO 2 emissions
 Conclusions 2/2 • Adoption of more stringent standards for 2&3 wheelers in the coming years is expected to lead to the adoption of newer technologies which are also expected to bring about further reductions in fuel consumption and CO 2 emissions. • CO 2 contribution of the Indian transport sector is estimated to be 15% of the total (1994 -95). While the rapidly increasing population of vehicles may lead to an increase in this, the progressively reducing levels of CO 2 emissions may have a compensating effect.
Conclusions 2/2 • Adoption of more stringent standards for 2&3 wheelers in the coming years is expected to lead to the adoption of newer technologies which are also expected to bring about further reductions in fuel consumption and CO 2 emissions. • CO 2 contribution of the Indian transport sector is estimated to be 15% of the total (1994 -95). While the rapidly increasing population of vehicles may lead to an increase in this, the progressively reducing levels of CO 2 emissions may have a compensating effect.



