5_Vectorization.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 12

Vector digitazing or vectorization

Objectives: What is vectorization? Point, Polygon, Line, Curve; Vector Output; Conclusion.

What is vectorization? A complete raster to vector conversion process includes image acquisition, pre-processing, line tracing, text extraction (OCR), shape recognition, topology creation and attribute assignment is called “VECTORIZATION” or “VECTOR DIGITAIZING”. There are several ways and methods of vectorization. They are: - Manual digitizing; - Heads-Up Digitizing and Interactive Tracing; - Automatic Raster to Vector Conversion. → http: //www. ablesw. com/r 2 v/rasvect. html

Visualization; Interpretation; Classification; Estimation. Vectorization steps:
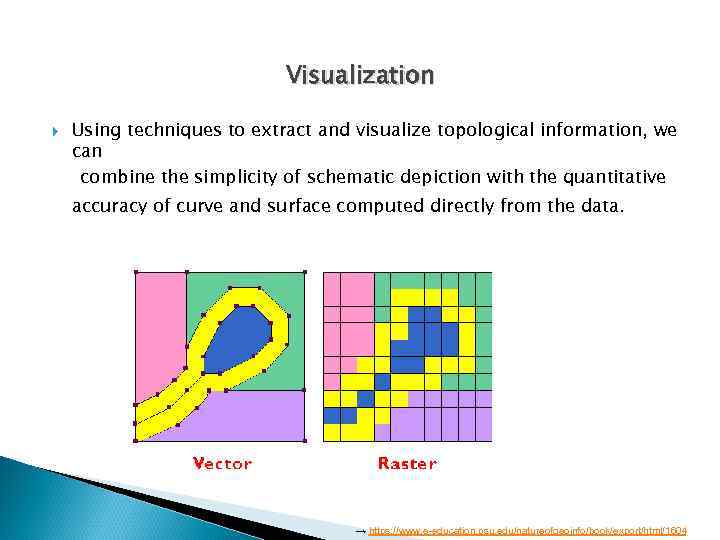
Visualization Using techniques to extract and visualize topological information, we can combine the simplicity of schematic depiction with the quantitative accuracy of curve and surface computed directly from the data. → https: //www. e-education. psu. edu/natureofgeoinfo/book/export/html/1604

Interpretation Photographic interpretation can be defined as: “the act of examining photographic images for the purpose of identifying objects and judging their significance”. The most basic of these principles are the elements of image interpretation. They are: location, size, shape, shadow, tone/color, texture, pattern, height/depth and site/situation/association. These are routinely used when interpreting an aerial photo or analyzing a photo-like image. A welltrained image interpreter uses many of these elements during his or her analysis without really thinking about them. However, a beginner may not only have to force himself or herself to consciously evaluate an unknown object with respect to these elements, but also analyze its significance in relation to the other objects or phenomena in the photo or image.

Classification is the labeling of a pixel or a group of pixels based on its value. Classification is one of the most often used methods of information extraction. In Classification, usually multiple features are used for a set of pixels. Classification is of two types namely, ◦ Supervised classification. ◦ Unsupervised classification. → http: //video. yandex. ru/#search? where=all&text=free%20 powerpoint%20 image%20 processing%20 -vectorization

Estimation This section is very significant part of vector digitizing. At this particular process we analyze and see how very severe the work has reached outcomes. If vectorization processing has done with 80 or 90 percent similarity then the data performed successfully. → http: //www. tankonyvtar. hu/hu/tartalom/tamop 425/0027_SAN 1/ch 01 s 05. html
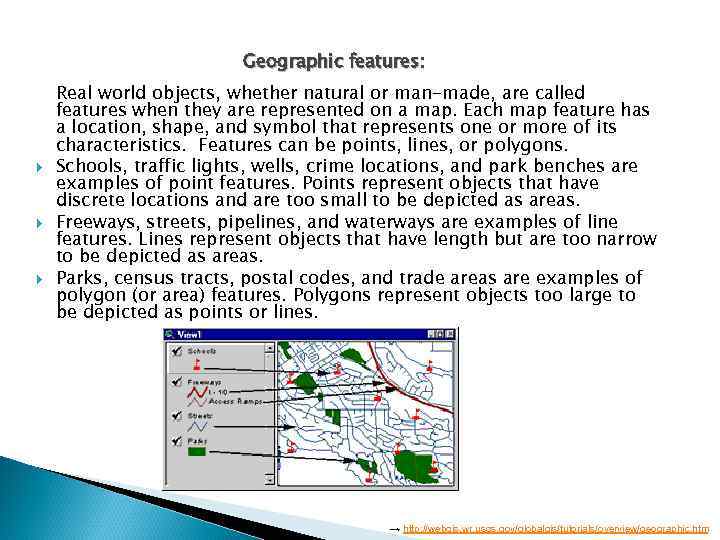
Geographic features: Real world objects, whether natural or man-made, are called features when they are represented on a map. Each map feature has a location, shape, and symbol that represents one or more of its characteristics. Features can be points, lines, or polygons. Schools, traffic lights, wells, crime locations, and park benches are examples of point features. Points represent objects that have discrete locations and are too small to be depicted as areas. Freeways, streets, pipelines, and waterways are examples of line features. Lines represent objects that have length but are too narrow to be depicted as areas. Parks, census tracts, postal codes, and trade areas are examples of polygon (or area) features. Polygons represent objects too large to be depicted as points or lines. → http: //webgis. wr. usgs. gov/globalgis/tutorials/overview/geographic. htm
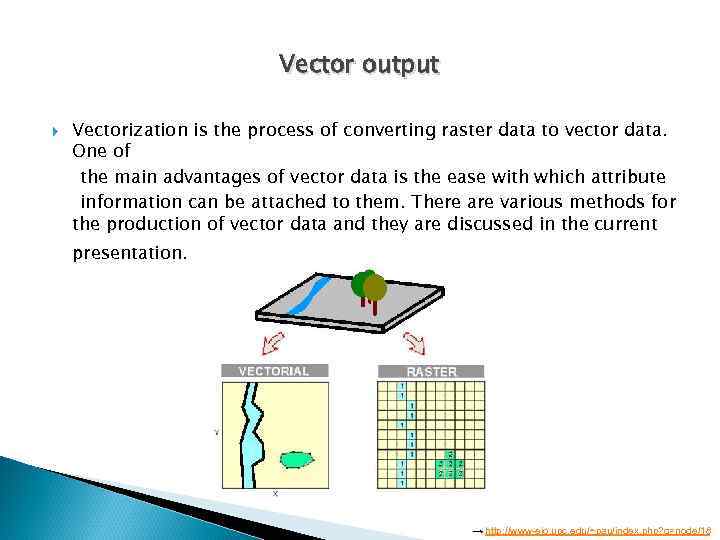
Vector output Vectorization is the process of converting raster data to vector data. One of the main advantages of vector data is the ease with which attribute information can be attached to them. There are various methods for the production of vector data and they are discussed in the current presentation. → http: //www-eio. upc. edu/~pau/index. php? q=node/18

Sum up If to talk raster to vector conversion process with its each details, then we may convert the raster data to the vector data by means of several ways and methods, as we talked it above (Manual digitizing, Heads-Up Digitizing and Interactive Tracing, Automatic Raster to Vector Conversion). Using these methods we process from simple image or photo absolutely different, understandable and clear maps. Each method has its advantages and disadvantages. Every user of these methods can choose appropriate one, depending on his or her ability and possibility.

Reference: → http: //www-eio. upc. edu/~pau/index. php? q=node/18 → http: //webgis. wr. usgs. gov/globalgis/tutorials/overview/geographic. htm → → http: //www. tankonyvtar. hu/hu/tartalom/tamop 425/0027_SAN 1/ch 01 s 0 5. html http: //video. yandex. ru/#search? where=all&text=free%20 powerpoint%20 imag e%20 processing%20 -vectorization → https: //www. eeducation. psu. edu/natureofgeoinfo/book/export/html/1604 → http: //www. ablesw. com/r 2 v/rasvect. html
5_Vectorization.ppt