4f748cde035852c4753d047a9db0da42.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20
 Vasteras 2008 Cigre WG D 2. 24 EMS Architectures of the 21 st Century Alain P. STEVEN PJM Interconnection, LLC, USA CIGRE WG D 2. 24 Convenor Jay BRITTON AREVA T&D, USA TC 57, CIM expert Thierry LEFEBVRE RTE, France TC 57 chairman
Vasteras 2008 Cigre WG D 2. 24 EMS Architectures of the 21 st Century Alain P. STEVEN PJM Interconnection, LLC, USA CIGRE WG D 2. 24 Convenor Jay BRITTON AREVA T&D, USA TC 57, CIM expert Thierry LEFEBVRE RTE, France TC 57 chairman
 Outline WG D 2. 24 v Part 1: o o v Overview, goals Relationships with IECTC 57 (Thierry Lefebvre) Part 2 : o o CIM in CIGRE D 2. 24 Focus on the « Information Architecture » (Jay Britton)
Outline WG D 2. 24 v Part 1: o o v Overview, goals Relationships with IECTC 57 (Thierry Lefebvre) Part 2 : o o CIM in CIGRE D 2. 24 Focus on the « Information Architecture » (Jay Britton)
 WG D 2. 24 Cigré o o o IEC o o International Council on Large Electric Systems Facilitates, develops and synthesizes technical knowledge in all the fields related to HV generation and transmission Based in Paris, 80 member countries VLPGO o Several organizations sharing the same goal Very Large Power Grid Operators International initiative regrouping the world’s twelve largest grid operators Focus is on addressing challenges unique to the operation of very large power grids (> 50, 000 MW) International Electrotechnical Commission Prepares and publishes International Standards for all electrical, electronic and related technologies IRC/ITC o o IRC = North American ISO/RTO Council (CEO level) ITC = Information Technology Committee, reports to IRC (CIO level)
WG D 2. 24 Cigré o o o IEC o o International Council on Large Electric Systems Facilitates, develops and synthesizes technical knowledge in all the fields related to HV generation and transmission Based in Paris, 80 member countries VLPGO o Several organizations sharing the same goal Very Large Power Grid Operators International initiative regrouping the world’s twelve largest grid operators Focus is on addressing challenges unique to the operation of very large power grids (> 50, 000 MW) International Electrotechnical Commission Prepares and publishes International Standards for all electrical, electronic and related technologies IRC/ITC o o IRC = North American ISO/RTO Council (CEO level) ITC = Information Technology Committee, reports to IRC (CIO level)
 WG D 2. 24 10/03: First meeting of the VLPGO o o o EAS = Enterprise Architecture Standardization Complementary to the work of WG #2 01/07: VLPGO WG #2 becomes Cigré WG D 2. 24 o o CEO level Creation of WG #2 - EMS Architectures of the 21 st Century 01/06: IRC/ITC launches EAS project o (Cont’d) Expands membership to the rest of the industry Formalizes the work of WG #2 and provides a formal communication channel with IEC 06/07: EAS project merges with Cigré WG D 2. 24 o Provides a consistent description of the architecture, from the high level requirements down to the detailed message definitions
WG D 2. 24 10/03: First meeting of the VLPGO o o o EAS = Enterprise Architecture Standardization Complementary to the work of WG #2 01/07: VLPGO WG #2 becomes Cigré WG D 2. 24 o o CEO level Creation of WG #2 - EMS Architectures of the 21 st Century 01/06: IRC/ITC launches EAS project o (Cont’d) Expands membership to the rest of the industry Formalizes the work of WG #2 and provides a formal communication channel with IEC 06/07: EAS project merges with Cigré WG D 2. 24 o Provides a consistent description of the architecture, from the high level requirements down to the detailed message definitions
 WG D 2. 24 Mission & Scope q Mission Ø Ø Develop the vision for the architecture of the next generation of Energy Management and Market Management Systems, Gain broad adoption by the industry Facilitate its implementation as a de facto standard q Scope Ø Real-time Systems associated with the transmission and market operations Extendable to generation and distribution Ø Ø
WG D 2. 24 Mission & Scope q Mission Ø Ø Develop the vision for the architecture of the next generation of Energy Management and Market Management Systems, Gain broad adoption by the industry Facilitate its implementation as a de facto standard q Scope Ø Real-time Systems associated with the transmission and market operations Extendable to generation and distribution Ø Ø
 WG D 2. 24 Goals and Objectives Goal: to develop the vision for a highly interoperable and reusable architecture, and to facilitate its implementation through a common coordinated procurement process Objectives o o o Develop a common set of requirements Develop a description of the architecture and its standard components Facilitate its implementation and its funding through a coordinated procurement process along with a roadmap agreed upon between end users and manufacturers
WG D 2. 24 Goals and Objectives Goal: to develop the vision for a highly interoperable and reusable architecture, and to facilitate its implementation through a common coordinated procurement process Objectives o o o Develop a common set of requirements Develop a description of the architecture and its standard components Facilitate its implementation and its funding through a coordinated procurement process along with a roadmap agreed upon between end users and manufacturers
 Membership WG D 2. 24 End Users o British Columbia TC o California ISO* o Cemig (Brazil) o Duke Energy o EPRI o ERCOT o Fingrid Oyj o Hydro-Quebec o Israel Electric Coorporation o ISO/RTO Council o KPX (Korea)* o Midwest ISO* o National Grid Company* o ONS (Brazil)* o PJM Interconnection* o Power Grid Corporation of India* o Red Electrica Espana* o RTE (France)* o SO-CDO for UES of Russia* o State Grid Corporation of China* Statnett SF o Swedish Center of Excellence o Tepco (Japan)* o Terna (Italy)* o Transba SA (Argentina) o Transpower (NZ) System Suppliers o ABB o Areva T&D o GE o Siemens Application Suppliers o Power. World Consultants o Grid Engineering o Kema Academic o Texas A&M o * VLPGO Member
Membership WG D 2. 24 End Users o British Columbia TC o California ISO* o Cemig (Brazil) o Duke Energy o EPRI o ERCOT o Fingrid Oyj o Hydro-Quebec o Israel Electric Coorporation o ISO/RTO Council o KPX (Korea)* o Midwest ISO* o National Grid Company* o ONS (Brazil)* o PJM Interconnection* o Power Grid Corporation of India* o Red Electrica Espana* o RTE (France)* o SO-CDO for UES of Russia* o State Grid Corporation of China* Statnett SF o Swedish Center of Excellence o Tepco (Japan)* o Terna (Italy)* o Transba SA (Argentina) o Transpower (NZ) System Suppliers o ABB o Areva T&D o GE o Siemens Application Suppliers o Power. World Consultants o Grid Engineering o Kema Academic o Texas A&M o * VLPGO Member
 WG D 2. 24 Common Issues o o o WG-2 Initial Findings High development and maintenance/support costs Lack of modularity and interoperability among multiple vendors Limited innovation Limited number of viable vendors Inadequate security Multiplicity of user interfaces Perceived Root Causes o o o Limited standardization (Market requirements as well as vendor products) Limited market(s) size Real-time performance imperatives High investment in legacy products Limited software reuseability
WG D 2. 24 Common Issues o o o WG-2 Initial Findings High development and maintenance/support costs Lack of modularity and interoperability among multiple vendors Limited innovation Limited number of viable vendors Inadequate security Multiplicity of user interfaces Perceived Root Causes o o o Limited standardization (Market requirements as well as vendor products) Limited market(s) size Real-time performance imperatives High investment in legacy products Limited software reuseability
 WG D 2. 24 Design Principles Component based, Services Oriented Architecture for integration and reusability within the Enterprise Modularity based on businesses processes componentization High Speed Bus for real-time message exchange Common Information Model for data standards Security layer Built on industry standards Common User Interface Common Modeling tools integrating display and data maintenance Transportable to future technologies Scalable
WG D 2. 24 Design Principles Component based, Services Oriented Architecture for integration and reusability within the Enterprise Modularity based on businesses processes componentization High Speed Bus for real-time message exchange Common Information Model for data standards Security layer Built on industry standards Common User Interface Common Modeling tools integrating display and data maintenance Transportable to future technologies Scalable
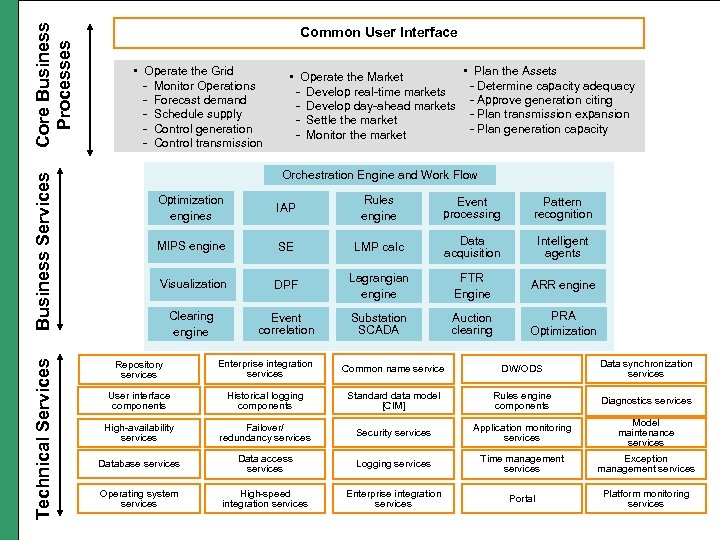 Core Business Processes Business Services Technical Services Common User Interface • Operate the Grid - Monitor Operations WG D 2. 24 - Forecast demand - Schedule supply - Control generation - Control transmission • Plan the Assets • Operate the Market - Determine capacity adequacy - Develop real-time markets - Develop day-ahead markets - Approve generation citing - Plan transmission expansion - Settle the market - Plan generation capacity - Monitor the market Orchestration Engine and Work Flow Optimization engines IAP Rules engine Event processing Pattern recognition MIPS engine SE LMP calc Data acquisition Intelligent agents Visualization DPF Lagrangian engine FTR Engine ARR engine Clearing engine Event correlation Substation SCADA Auction clearing PRA Optimization Repository services Enterprise integration services Common name service DW/ODS Data synchronization services User interface components Historical logging components Standard data model [CIM] Rules engine components Diagnostics services High-availability services Failover/ redundancy services Security services Application monitoring services Model maintenance services Database services Data access services Logging services Time management services Exception management services Operating system services High-speed integration services Enterprise integration services Portal Platform monitoring services
Core Business Processes Business Services Technical Services Common User Interface • Operate the Grid - Monitor Operations WG D 2. 24 - Forecast demand - Schedule supply - Control generation - Control transmission • Plan the Assets • Operate the Market - Determine capacity adequacy - Develop real-time markets - Develop day-ahead markets - Approve generation citing - Plan transmission expansion - Settle the market - Plan generation capacity - Monitor the market Orchestration Engine and Work Flow Optimization engines IAP Rules engine Event processing Pattern recognition MIPS engine SE LMP calc Data acquisition Intelligent agents Visualization DPF Lagrangian engine FTR Engine ARR engine Clearing engine Event correlation Substation SCADA Auction clearing PRA Optimization Repository services Enterprise integration services Common name service DW/ODS Data synchronization services User interface components Historical logging components Standard data model [CIM] Rules engine components Diagnostics services High-availability services Failover/ redundancy services Security services Application monitoring services Model maintenance services Database services Data access services Logging services Time management services Exception management services Operating system services High-speed integration services Enterprise integration services Portal Platform monitoring services
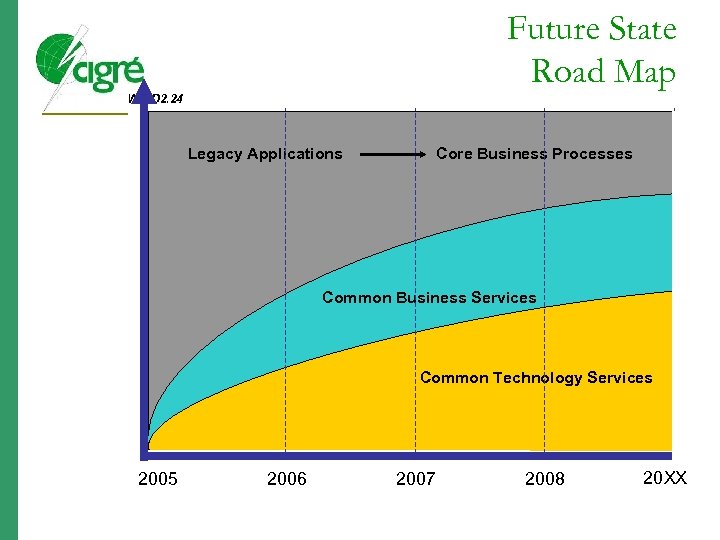 Future State Road Map WG D 2. 24 Legacy Applications Core Business Processes Common Business Services Common Technology Services 2005 2006 2007 2008 20 XX
Future State Road Map WG D 2. 24 Legacy Applications Core Business Processes Common Business Services Common Technology Services 2005 2006 2007 2008 20 XX
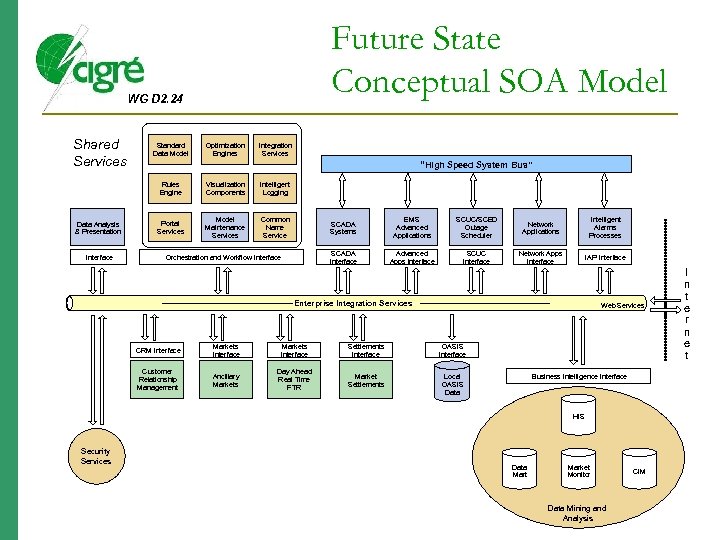 Future State Conceptual SOA Model WG D 2. 24 Shared Services Standard Data Model Optimization Engines Integration Services “High Speed System Bus” Rules Engine Data Analysis & Presentation Interface Visualization Components Intelligent Logging Portal Services Model Maintenance Services Common Name Service SCADA Systems SCUC/SCED Outage Scheduler Network Applications Intelligent Alarms Processes SCADA Interface Orchestration and Workflow Interface EMS Advanced Applications Advanced Apps Interface SCUC Interface Network Apps Interface IAP Interface Enterprise Integration Services Web Services CRM Interface Markets Interface Settlements Interface OASIS Interface Customer Relationship Management Ancillary Markets Day Ahead Real Time FTR Market Settlements Local OASIS Data Business Intelligence Interface HIS Security Services Data Mart Market Monitor Data Mining and Analysis CIM I n t e r n e t
Future State Conceptual SOA Model WG D 2. 24 Shared Services Standard Data Model Optimization Engines Integration Services “High Speed System Bus” Rules Engine Data Analysis & Presentation Interface Visualization Components Intelligent Logging Portal Services Model Maintenance Services Common Name Service SCADA Systems SCUC/SCED Outage Scheduler Network Applications Intelligent Alarms Processes SCADA Interface Orchestration and Workflow Interface EMS Advanced Applications Advanced Apps Interface SCUC Interface Network Apps Interface IAP Interface Enterprise Integration Services Web Services CRM Interface Markets Interface Settlements Interface OASIS Interface Customer Relationship Management Ancillary Markets Day Ahead Real Time FTR Market Settlements Local OASIS Data Business Intelligence Interface HIS Security Services Data Mart Market Monitor Data Mining and Analysis CIM I n t e r n e t
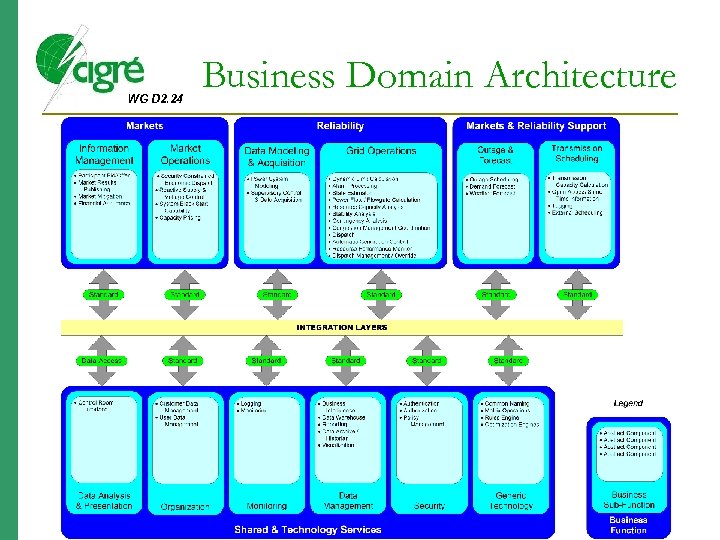 WG D 2. 24 Business Domain Architecture
WG D 2. 24 Business Domain Architecture
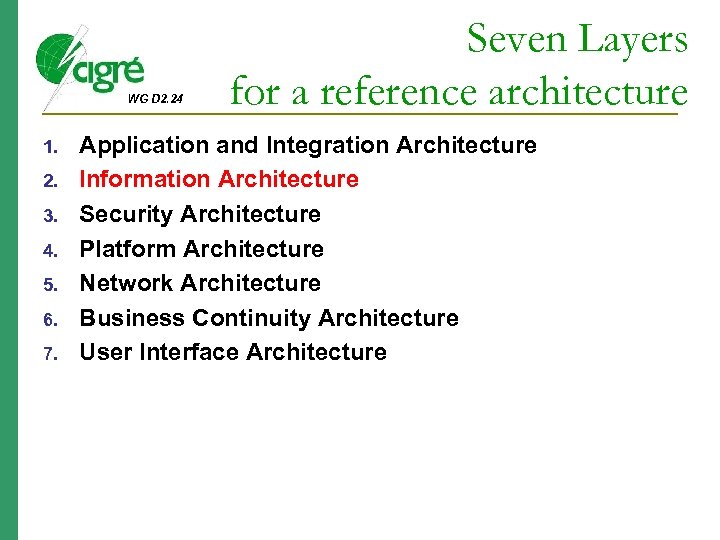 WG D 2. 24 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Seven Layers for a reference architecture Application and Integration Architecture Information Architecture Security Architecture Platform Architecture Network Architecture Business Continuity Architecture User Interface Architecture
WG D 2. 24 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Seven Layers for a reference architecture Application and Integration Architecture Information Architecture Security Architecture Platform Architecture Network Architecture Business Continuity Architecture User Interface Architecture
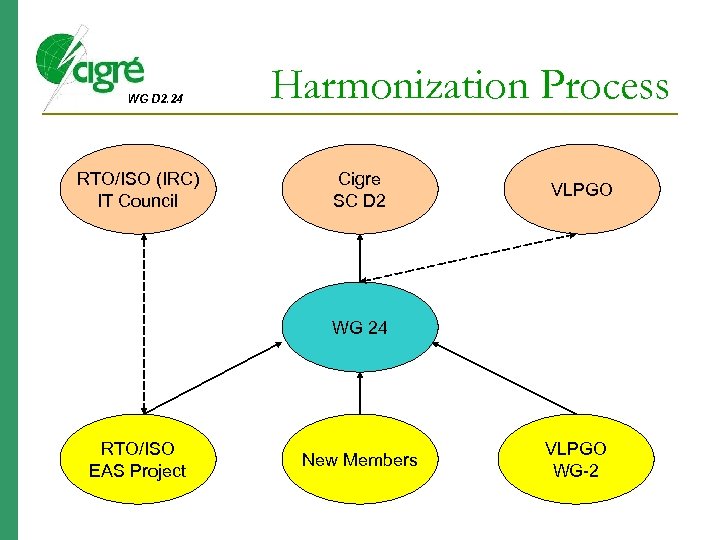 WG D 2. 24 RTO/ISO (IRC) IT Council Harmonization Process Cigre SC D 2 VLPGO WG 24 RTO/ISO EAS Project New Members VLPGO WG-2
WG D 2. 24 RTO/ISO (IRC) IT Council Harmonization Process Cigre SC D 2 VLPGO WG 24 RTO/ISO EAS Project New Members VLPGO WG-2
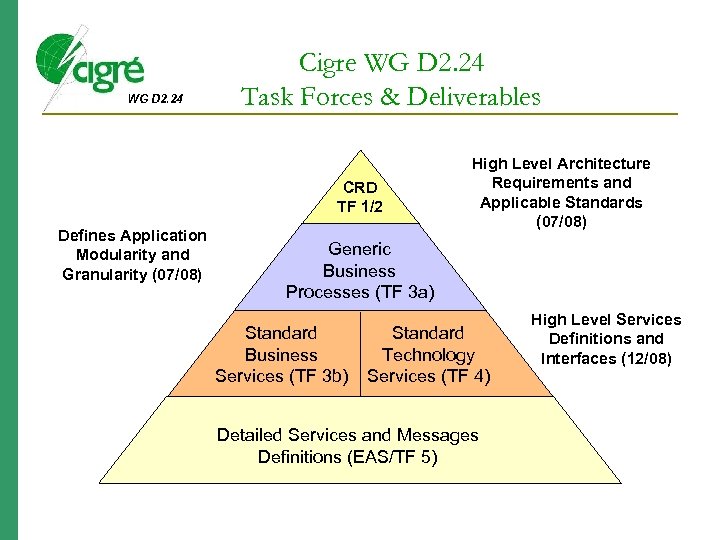 WG D 2. 24 Cigre WG D 2. 24 Task Forces & Deliverables CRD TF 1/2 Defines Application Modularity and Granularity (07/08) High Level Architecture Requirements and Applicable Standards (07/08) Generic Business Processes (TF 3 a) Standard Business Services (TF 3 b) Standard Technology Services (TF 4) Detailed Services and Messages Definitions (EAS/TF 5) High Level Services Definitions and Interfaces (12/08)
WG D 2. 24 Cigre WG D 2. 24 Task Forces & Deliverables CRD TF 1/2 Defines Application Modularity and Granularity (07/08) High Level Architecture Requirements and Applicable Standards (07/08) Generic Business Processes (TF 3 a) Standard Business Services (TF 3 b) Standard Technology Services (TF 4) Detailed Services and Messages Definitions (EAS/TF 5) High Level Services Definitions and Interfaces (12/08)
 WG D 2. 24
WG D 2. 24
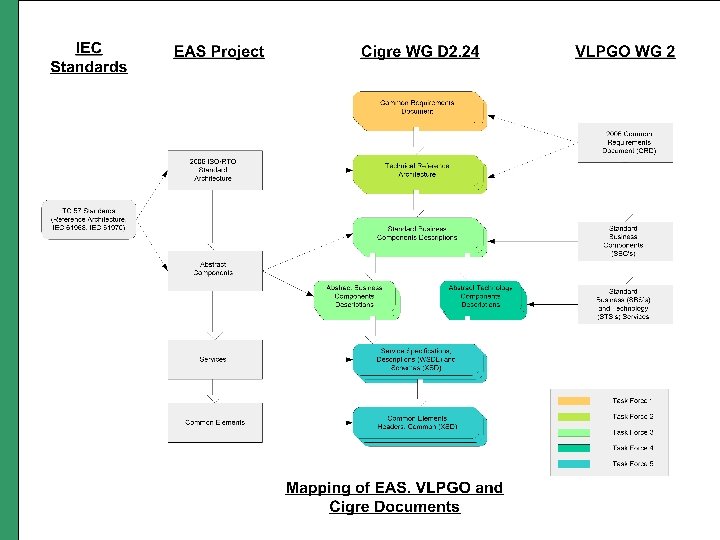
 Industry Coordination WG D 2. 24 sets the vision and requirements, not the standards Objectives o o Standard Committees/Initiatives Align with current and emerging standards, and leverage work done Produce a complete and consistent specification of the architecture Coordination with o o IEC TC-57 related working groups (mainly CIM) North American ISO/RTO Council EAS Project
Industry Coordination WG D 2. 24 sets the vision and requirements, not the standards Objectives o o Standard Committees/Initiatives Align with current and emerging standards, and leverage work done Produce a complete and consistent specification of the architecture Coordination with o o IEC TC-57 related working groups (mainly CIM) North American ISO/RTO Council EAS Project
 WG D 2. 24 1. IEC-CIGRE Relationships Liaison type A between CIGRE D 2 and IEC TC 57 IEC Category A liaison for Organizations that make an effective contribution to the work of the Technical Committee for questions dealt with by this TC. Such organizations can exchange all relevant documentation and are invited to meetings. They may nominate experts to participate in a WG. 2. Mo. U to clarify organization & management General management: CIGRE: D 2. convenor => A. Steven IEC: TC 57 chairman => T. Lefebvre Operational management: CIGRE: S. Neuman (CIGRE member, TC 57 member) IEC: P. Skare (CIGRE member, TC 57 -WG 19 chairman) Members: Most of D 2. 24 members are TC 57 members
WG D 2. 24 1. IEC-CIGRE Relationships Liaison type A between CIGRE D 2 and IEC TC 57 IEC Category A liaison for Organizations that make an effective contribution to the work of the Technical Committee for questions dealt with by this TC. Such organizations can exchange all relevant documentation and are invited to meetings. They may nominate experts to participate in a WG. 2. Mo. U to clarify organization & management General management: CIGRE: D 2. convenor => A. Steven IEC: TC 57 chairman => T. Lefebvre Operational management: CIGRE: S. Neuman (CIGRE member, TC 57 member) IEC: P. Skare (CIGRE member, TC 57 -WG 19 chairman) Members: Most of D 2. 24 members are TC 57 members
 WG D 2. 24 In brief The ultimate goal of WG D 2. 24 is to deliver a complete specification for the next EMS/MMS architecture This specification will become a key building block for future EMS/MMS procurements WG D 2. 24 will work closely with the vendors to develop requirements and a time-based prioritized roadmap, which is technically and commercially viable WG D 2. 24 intends to leverage existing IEC TC-57 Standards. Conversely, new IEC TC-57 standardization efforts may emerge from the WG D 2. 24 work products
WG D 2. 24 In brief The ultimate goal of WG D 2. 24 is to deliver a complete specification for the next EMS/MMS architecture This specification will become a key building block for future EMS/MMS procurements WG D 2. 24 will work closely with the vendors to develop requirements and a time-based prioritized roadmap, which is technically and commercially viable WG D 2. 24 intends to leverage existing IEC TC-57 Standards. Conversely, new IEC TC-57 standardization efforts may emerge from the WG D 2. 24 work products


