1188993386f4d7d8a9059867477f466c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 14
 Vancouver’s Advantages and Challenges u Advantages • • u High quality of life Excellent universities Skilled technical staff and project managers , low development costs Few leaders competing for new markets with new product concepts. Threats • Brain Drain impacts design, marketing, and business resources. • Many investors are unfamiliar with technology opportunities. • Conservative business culture limits risk-taking u Challenges • Effective investment and business strategy requires insider understanding of markets and competitors • Business plan execution requires rapid user-centred design and risk reduction software engineering know-how 1
Vancouver’s Advantages and Challenges u Advantages • • u High quality of life Excellent universities Skilled technical staff and project managers , low development costs Few leaders competing for new markets with new product concepts. Threats • Brain Drain impacts design, marketing, and business resources. • Many investors are unfamiliar with technology opportunities. • Conservative business culture limits risk-taking u Challenges • Effective investment and business strategy requires insider understanding of markets and competitors • Business plan execution requires rapid user-centred design and risk reduction software engineering know-how 1
 Understanding Tech Markets and Competitors • Supporting the business plan competition and evaluation process - Market briefs and competitive analysis research for judges and competitors bring them up-to-date on latest market trends, new technologies, competitive environment - Technical feasibility analysis and estimates of development cost and time-to-market will identify the most cost-effective opportunities • Helping new companies to create a unique selling proposition - Understanding the customer opportunity and building a competitive strategy - Identification of critical success factors and needed assets - Merging and partnering companies, ideas, and teams for best opportunities 2
Understanding Tech Markets and Competitors • Supporting the business plan competition and evaluation process - Market briefs and competitive analysis research for judges and competitors bring them up-to-date on latest market trends, new technologies, competitive environment - Technical feasibility analysis and estimates of development cost and time-to-market will identify the most cost-effective opportunities • Helping new companies to create a unique selling proposition - Understanding the customer opportunity and building a competitive strategy - Identification of critical success factors and needed assets - Merging and partnering companies, ideas, and teams for best opportunities 2
 Business Plan Execution • Create a process for building new technology solutions for customer needs - Refining the business plan with marketing analyses, business modeling and earnings forecasts - Design plans and prototypes, independent and accurate timelines and cost estimates, risk-reduction development models - Project management support • Overcoming investor reluctance - Solid market, strategy, and design models build investor confidence Facilitating potential business partners and customer contacts Search for financial partners Facilitation of IPO • Alternative commercialization models - Auctioning of the idea and business plan on the Internet - Merger with new or existing project/company 3
Business Plan Execution • Create a process for building new technology solutions for customer needs - Refining the business plan with marketing analyses, business modeling and earnings forecasts - Design plans and prototypes, independent and accurate timelines and cost estimates, risk-reduction development models - Project management support • Overcoming investor reluctance - Solid market, strategy, and design models build investor confidence Facilitating potential business partners and customer contacts Search for financial partners Facilitation of IPO • Alternative commercialization models - Auctioning of the idea and business plan on the Internet - Merger with new or existing project/company 3
 Core Capabilities of Support Organization u Ongoing customer research to anticipate market opportunities u Expertise in customer-centred design and user experience assessment targets opportunities with solutions u State-of-the-art risk reduction and rapid development software engineering methods gives: • TIMELINESS: First mover advantage • WIDE CHANCES: platform to combine ideas, recycle old ideas, technology, and market information • WHOLE_PRODUCT DESIGNS: Design for evolving markets u Competitive Intelligence and flexible design/execution models synergize for rapid response to competitors 4
Core Capabilities of Support Organization u Ongoing customer research to anticipate market opportunities u Expertise in customer-centred design and user experience assessment targets opportunities with solutions u State-of-the-art risk reduction and rapid development software engineering methods gives: • TIMELINESS: First mover advantage • WIDE CHANCES: platform to combine ideas, recycle old ideas, technology, and market information • WHOLE_PRODUCT DESIGNS: Design for evolving markets u Competitive Intelligence and flexible design/execution models synergize for rapid response to competitors 4
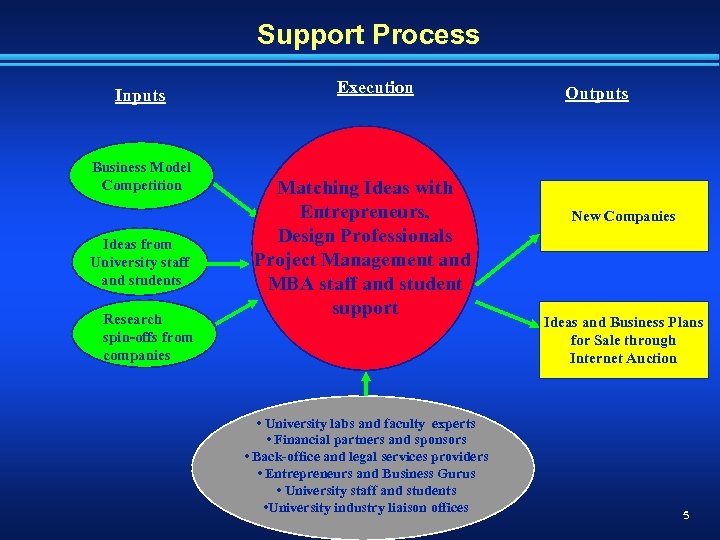 Support Process Inputs Business Model Competition Ideas from University staff and students Research spin-offs from companies Execution Matching Ideas with Entrepreneurs, Design Professionals Project Management and MBA staff and student support • University labs and faculty experts • Financial partners and sponsors • Back-office and legal services providers • Entrepreneurs and Business Gurus • University staff and students • University industry liaison offices Outputs New Companies Ideas and Business Plans for Sale through Internet Auction 5
Support Process Inputs Business Model Competition Ideas from University staff and students Research spin-offs from companies Execution Matching Ideas with Entrepreneurs, Design Professionals Project Management and MBA staff and student support • University labs and faculty experts • Financial partners and sponsors • Back-office and legal services providers • Entrepreneurs and Business Gurus • University staff and students • University industry liaison offices Outputs New Companies Ideas and Business Plans for Sale through Internet Auction 5
 Focus Areas The -BC business plan competition will be open to all kind of ideas, however the support organization will initially be focused on internet and related technology-based offerings. • Initially Telelearning, Internet, New media and entertainment products and services • Expand or clone for new opportunities - Information appliance software and hardware - New energy products and services - New Bio-pharmacy and Medical offerings 6
Focus Areas The -BC business plan competition will be open to all kind of ideas, however the support organization will initially be focused on internet and related technology-based offerings. • Initially Telelearning, Internet, New media and entertainment products and services • Expand or clone for new opportunities - Information appliance software and hardware - New energy products and services - New Bio-pharmacy and Medical offerings 6
 Key Aspects of Entrepreneur Support Inc. u Time-sharing experts spreads the expertise over may startups • Create business and design documents that can be implemented offline by local talent • “Checkups” and “booster shots” for young companies as needed u Processes, knowledge assets build over time to further enhance effectiveness u Stable teams of experts outperform consultants, new groups • Efficiency of model enables ESI to hire, incent, and retain top talent. • Challenging work and diversification of share options retains them u University links give access to business, design, customer understanding and technology talent and IP 7
Key Aspects of Entrepreneur Support Inc. u Time-sharing experts spreads the expertise over may startups • Create business and design documents that can be implemented offline by local talent • “Checkups” and “booster shots” for young companies as needed u Processes, knowledge assets build over time to further enhance effectiveness u Stable teams of experts outperform consultants, new groups • Efficiency of model enables ESI to hire, incent, and retain top talent. • Challenging work and diversification of share options retains them u University links give access to business, design, customer understanding and technology talent and IP 7
 Impact of User Experience Research u "Usability is critical for any application, but for mass-market software, usability spells success or failure more clearly than any other feature. " Dr. Jerold M. Grochow, Chief Technology Officer, American Management Systems u “ Industry data show that each dollar spent on user studies during product design saves $10 on problem fixes during product development, or $100 or more in rework after product release. . . It's estimated that 80% of maintenance costs are spent on unforeseen user requirements, while only 20% are due to bugs. “ IBM Web Site u “Massive, new effort is needed in HCI education, research, and practice. . . Universities should be encouraged to perceive HCI as a ‘critical technology’ and the accompanying skills and knowledge as fundamental to a student's education and preparation for jobs in the information age. ” 1994 report of the US National Science Foundation Interactive Systems and Applications of Advanced Technology Program, in collaboration with the Software and Intelligent Systems Technology Office, Advanced Research Projects Agency 8
Impact of User Experience Research u "Usability is critical for any application, but for mass-market software, usability spells success or failure more clearly than any other feature. " Dr. Jerold M. Grochow, Chief Technology Officer, American Management Systems u “ Industry data show that each dollar spent on user studies during product design saves $10 on problem fixes during product development, or $100 or more in rework after product release. . . It's estimated that 80% of maintenance costs are spent on unforeseen user requirements, while only 20% are due to bugs. “ IBM Web Site u “Massive, new effort is needed in HCI education, research, and practice. . . Universities should be encouraged to perceive HCI as a ‘critical technology’ and the accompanying skills and knowledge as fundamental to a student's education and preparation for jobs in the information age. ” 1994 report of the US National Science Foundation Interactive Systems and Applications of Advanced Technology Program, in collaboration with the Software and Intelligent Systems Technology Office, Advanced Research Projects Agency 8
 Impact of Risk-reduction Development u The Standish Group research shows a staggering 31. 1% of (software) projects will be canceled before they ever get completed. Further results indicate 52. 7% of projects will cost 189% of their original estimates. . . The three major reasons that a project will succeed are user involvement, executive management support, and a clear statement of requirements. “The Chaos Report” Standish Group 1995 u Some examples of impact on profits and productivity of a focus on improving software development processes (IEEE Computer 1995) • Lockheed cut development costs by 75%, reduced time-to-market by 40% and defects by 90% by implementing advanced design methods • Raytheon tripled productivity and increased ROI 8 fold • Similar results from Hughes, Loral, Motorola, Xerox 9
Impact of Risk-reduction Development u The Standish Group research shows a staggering 31. 1% of (software) projects will be canceled before they ever get completed. Further results indicate 52. 7% of projects will cost 189% of their original estimates. . . The three major reasons that a project will succeed are user involvement, executive management support, and a clear statement of requirements. “The Chaos Report” Standish Group 1995 u Some examples of impact on profits and productivity of a focus on improving software development processes (IEEE Computer 1995) • Lockheed cut development costs by 75%, reduced time-to-market by 40% and defects by 90% by implementing advanced design methods • Raytheon tripled productivity and increased ROI 8 fold • Similar results from Hughes, Loral, Motorola, Xerox 9
 Impact of Competitive Intelligence u “Competitive intelligence plays a crucial role in explaining why some companies won 67% of the contracts they went after, compared to the industry average of 18%” Price Waterhouse TQM/100 study, 1993 u “For the most part, information services and technology companies dominated the list of businesses that survey respondents believe make good use of business or competitive intelligence… 1997 Top Companies: #1 Microsoft, #2 Motorola, #3 IBM, #4 Proctor and Gamble, #5 GE, #6 Hewlett-Packard, #7 Coca-cola, #8 Intel” Futures group survey, 1997 u “Compared to other countries, Canada scores lower on the percentage of firms conducting world-class CI, training in CI, CI partnerships, , and CI culture. ” Industry Canada/Canadian Management Network 1999 10
Impact of Competitive Intelligence u “Competitive intelligence plays a crucial role in explaining why some companies won 67% of the contracts they went after, compared to the industry average of 18%” Price Waterhouse TQM/100 study, 1993 u “For the most part, information services and technology companies dominated the list of businesses that survey respondents believe make good use of business or competitive intelligence… 1997 Top Companies: #1 Microsoft, #2 Motorola, #3 IBM, #4 Proctor and Gamble, #5 GE, #6 Hewlett-Packard, #7 Coca-cola, #8 Intel” Futures group survey, 1997 u “Compared to other countries, Canada scores lower on the percentage of firms conducting world-class CI, training in CI, CI partnerships, , and CI culture. ” Industry Canada/Canadian Management Network 1999 10
 Alliances and relationships u Build alliances with incubators and think-tanks in Canada and US u Explore enhanced relationship with familiar collaborators: Philips, HRL, Sun, etc. u Seek closer ties to Canadian and US investors u Seek off-campus location, perhaps in False Creek tech park 11
Alliances and relationships u Build alliances with incubators and think-tanks in Canada and US u Explore enhanced relationship with familiar collaborators: Philips, HRL, Sun, etc. u Seek closer ties to Canadian and US investors u Seek off-campus location, perhaps in False Creek tech park 11
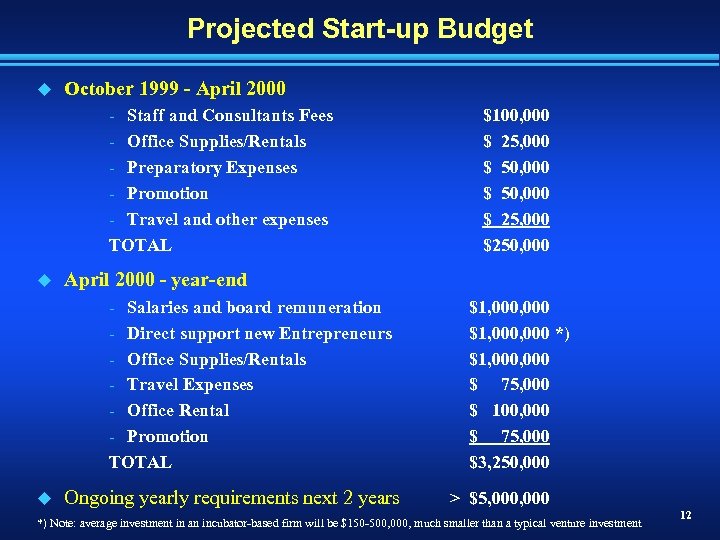 Projected Start-up Budget u October 1999 - April 2000 - Staff and Consultants Fees - Office Supplies/Rentals - Preparatory Expenses - Promotion - Travel and other expenses TOTAL u April 2000 - year-end - Salaries and board remuneration - Direct support new Entrepreneurs - Office Supplies/Rentals - Travel Expenses - Office Rental - Promotion TOTAL u $100, 000 $ 25, 000 $ 50, 000 $ 25, 000 $250, 000 Ongoing yearly requirements next 2 years $1, 000, 000 *) $1, 000 $ 75, 000 $ 100, 000 $ 75, 000 $3, 250, 000 > $5, 000 *) Note: average investment in an incubator-based firm will be $150 -500, 000, much smaller than a typical venture investment 12
Projected Start-up Budget u October 1999 - April 2000 - Staff and Consultants Fees - Office Supplies/Rentals - Preparatory Expenses - Promotion - Travel and other expenses TOTAL u April 2000 - year-end - Salaries and board remuneration - Direct support new Entrepreneurs - Office Supplies/Rentals - Travel Expenses - Office Rental - Promotion TOTAL u $100, 000 $ 25, 000 $ 50, 000 $ 25, 000 $250, 000 Ongoing yearly requirements next 2 years $1, 000, 000 *) $1, 000 $ 75, 000 $ 100, 000 $ 75, 000 $3, 250, 000 > $5, 000 *) Note: average investment in an incubator-based firm will be $150 -500, 000, much smaller than a typical venture investment 12
 Financing Sequence u First step is to guarantee launching capital from start-up sponsors by late 1999/early 2000 u Next, in May 2000, issuing $ 5 million of equity through sale of shares (to Venture Capitalists, Companies, Individuals, Institutions and others) u Second wave of ? ? $ million by year-end 2000/early 2001 u New companies must pay their bill in cash from investors through sale of shares and/or with shares as negotiated. u Board members, employees and key staff are given stock-options based upon performance as evaluated by colleagues and spin-off companies. For these stock-options a subordinate class of stock will be created. Options from this class will mature within 3 years. 14
Financing Sequence u First step is to guarantee launching capital from start-up sponsors by late 1999/early 2000 u Next, in May 2000, issuing $ 5 million of equity through sale of shares (to Venture Capitalists, Companies, Individuals, Institutions and others) u Second wave of ? ? $ million by year-end 2000/early 2001 u New companies must pay their bill in cash from investors through sale of shares and/or with shares as negotiated. u Board members, employees and key staff are given stock-options based upon performance as evaluated by colleagues and spin-off companies. For these stock-options a subordinate class of stock will be created. Options from this class will mature within 3 years. 14
 Questions u Under whose banner should this be launched: Government, Business Council BC, SFU, Vancouver Enterprise Forum, new independent joint initiative? u Staffing and board participation? u How to deal with intellectual property University u Who can help with lobbying for launching sponsors? u How to involve UBC and BC-IT? u How to involve other local incubators e. g. Idea. Park? u How to increase attractiveness for investors - local Venture Capitalists and others? u How to attract more capital from elsewhere (Toronto, US, Europe)? 16
Questions u Under whose banner should this be launched: Government, Business Council BC, SFU, Vancouver Enterprise Forum, new independent joint initiative? u Staffing and board participation? u How to deal with intellectual property University u Who can help with lobbying for launching sponsors? u How to involve UBC and BC-IT? u How to involve other local incubators e. g. Idea. Park? u How to increase attractiveness for investors - local Venture Capitalists and others? u How to attract more capital from elsewhere (Toronto, US, Europe)? 16


