VALVULARHEARTDISEASE InternalMedicineDidactics August 12, 2009 StevenR. BruhlMD,

































































valvular_heart_disease_im_8-12.ppt
- Размер: 4.3 Mегабайта
- Количество слайдов: 80
Описание презентации VALVULARHEARTDISEASE InternalMedicineDidactics August 12, 2009 StevenR. BruhlMD, по слайдам
 VALVULARHEARTDISEASE Internal. Medicine. Didactics August 12, 2009 Steven. R. Bruhl. MD, MS
VALVULARHEARTDISEASE Internal. Medicine. Didactics August 12, 2009 Steven. R. Bruhl. MD, MS
 Overview • Aortic. Stenosis • Mitral. Stenosis • Aortic. Regurgitation – Acuteand. Chronic • Mitral. Regurgitation – Acuteand. Chronic
Overview • Aortic. Stenosis • Mitral. Stenosis • Aortic. Regurgitation – Acuteand. Chronic • Mitral. Regurgitation – Acuteand. Chronic
 • Etiology • Pathophysiology • Physical. Exam • Natural. History • Testing • Treatment
• Etiology • Pathophysiology • Physical. Exam • Natural. History • Testing • Treatment
 Aortic. Stenosis
Aortic. Stenosis

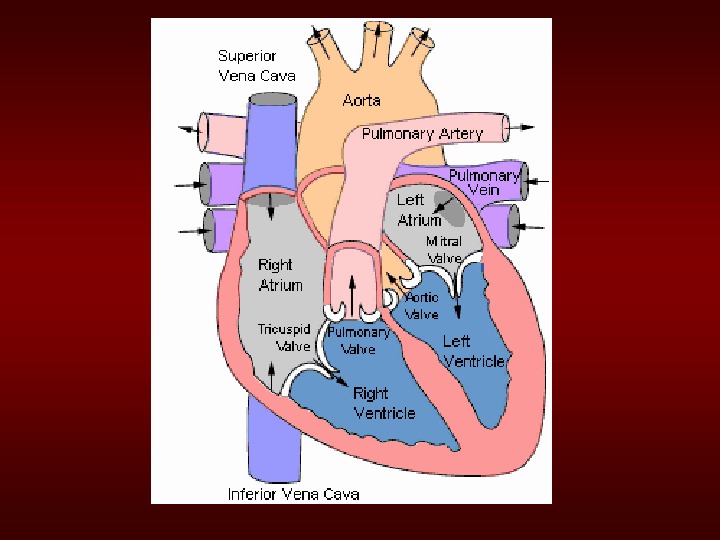
 Aortic. Stenosis. Overview: • Normal. Aortic. Valve. Area: 34 cm 2 • Symptoms: Occurwhenvalveareais 1/4 th ofnormalarea. • Types: – Supravalvular – Subvalvular – Valvular
Aortic. Stenosis. Overview: • Normal. Aortic. Valve. Area: 34 cm 2 • Symptoms: Occurwhenvalveareais 1/4 th ofnormalarea. • Types: – Supravalvular – Subvalvular – Valvular
 Etiologyof. Aortic. Stenosis • Congenital • Rheumatic • Degenerative/Calcific Patientsunder 70: >50%haveacongenital cause Patientsover 70: 50%duetodegenerative
Etiologyof. Aortic. Stenosis • Congenital • Rheumatic • Degenerative/Calcific Patientsunder 70: >50%haveacongenital cause Patientsover 70: 50%duetodegenerative




 Pathophysiologyof. Aortic. Stenosis • Apressuregradientdevelopsbetweenthe leftventricleandtheaorta. (increased afterload) • LVfunctioninitiallymaintainedby compensatorypressurehypertrophy • Whencompensatorymechanisms exhausted, LVfunctiondeclines.
Pathophysiologyof. Aortic. Stenosis • Apressuregradientdevelopsbetweenthe leftventricleandtheaorta. (increased afterload) • LVfunctioninitiallymaintainedby compensatorypressurehypertrophy • Whencompensatorymechanisms exhausted, LVfunctiondeclines.
 Presentationof. Aortic. Stenosis Syncope: (exertional) Angina: (increasedmyocardialoxygen demand; demand/supplymismatch) Dyspnea: onexertionduetoheartfailure (systolicanddiastolic) Suddendeath
Presentationof. Aortic. Stenosis Syncope: (exertional) Angina: (increasedmyocardialoxygen demand; demand/supplymismatch) Dyspnea: onexertionduetoheartfailure (systolicanddiastolic) Suddendeath
 Physical. Findingsin. Aortic. Stenosis • Slowrisingcarotidpulse( pulsustardus )& decreasedpulseamplitude( pulsusparvus ) • Heartsoundssoftandsplitsecondheart sound, S 4 gallopdueto. LVH. • Systolicejectionmurmur cresendodecrescendocharacter. This peaks lateras the severity ofthestenosis increases. – Loudnessdoes. NOTtellyouanythingabout severity
Physical. Findingsin. Aortic. Stenosis • Slowrisingcarotidpulse( pulsustardus )& decreasedpulseamplitude( pulsusparvus ) • Heartsoundssoftandsplitsecondheart sound, S 4 gallopdueto. LVH. • Systolicejectionmurmur cresendodecrescendocharacter. This peaks lateras the severity ofthestenosis increases. – Loudnessdoes. NOTtellyouanythingabout severity
 Natural. History • Mild. ASto. Severe. AS: – 8%in 10 years – 22%in 22 years – 38%in 25 years • Theonsetofsymptomsisapoorprognostic indicator.
Natural. History • Mild. ASto. Severe. AS: – 8%in 10 years – 22%in 22 years – 38%in 25 years • Theonsetofsymptomsisapoorprognostic indicator.

 Evaluationof. AS • Echocardiographyisthemostvaluabletest fordiagnosis, quantificationandfollowup ofpatientswith. AS. • Twomeasurementsobtainedare: a) Leftventricularsizeandfunction: LVH, Dilation, and. EF b) Dopplerderivedgradientandvalvearea (AVA)
Evaluationof. AS • Echocardiographyisthemostvaluabletest fordiagnosis, quantificationandfollowup ofpatientswith. AS. • Twomeasurementsobtainedare: a) Leftventricularsizeandfunction: LVH, Dilation, and. EF b) Dopplerderivedgradientandvalvearea (AVA)
 Evaluationof. AS Cardiaccatheterization: Shouldonlybedoneforadirect measurementifsymptomseverityandechoseveritydon’t match. ORpriortoreplacementwhenreplacementisplanned.
Evaluationof. AS Cardiaccatheterization: Shouldonlybedoneforadirect measurementifsymptomseverityandechoseveritydon’t match. ORpriortoreplacementwhenreplacementisplanned.
 Managementof. AS • General IEprophylaxisindentalprocedures withaprosthetic. AVorhistoryofendocarditis. • Medical limitedrolesince. ASisamechanical problem. Vasodilatorsare relatively contraindicated insevere. AS • Aortic. Balloon. Valvotomy showslittle benefit. • Surgical. Replacement: Definitivetreatment
Managementof. AS • General IEprophylaxisindentalprocedures withaprosthetic. AVorhistoryofendocarditis. • Medical limitedrolesince. ASisamechanical problem. Vasodilatorsare relatively contraindicated insevere. AS • Aortic. Balloon. Valvotomy showslittle benefit. • Surgical. Replacement: Definitivetreatment
 Echo. Surveillance • Mild: Every 5 years • Moderate: Every 2 years • Severe: Every 6 monthsto 1 year
Echo. Surveillance • Mild: Every 5 years • Moderate: Every 2 years • Severe: Every 6 monthsto 1 year

 Simplified Indicationsfor. Surgery in. Aortic. Stenosis • Any. SYMPTOMATICpatientwithsevere AS(includessymptomswithexercise) • Anypatientwithdecreasing. EF • Anypatientundergoing. CABGwith moderateorsevere. AS
Simplified Indicationsfor. Surgery in. Aortic. Stenosis • Any. SYMPTOMATICpatientwithsevere AS(includessymptomswithexercise) • Anypatientwithdecreasing. EF • Anypatientundergoing. CABGwith moderateorsevere. AS
 Summary • Diseaseofaging • Lookforthesignsonphysicalexam • Echocardiogramtoassessseverity • Asymptomatic: Medicalmanagementand surveillance • Symptomatic: Ao. Vreplacement(evenin elderlyand. CHF)
Summary • Diseaseofaging • Lookforthesignsonphysicalexam • Echocardiogramtoassessseverity • Asymptomatic: Medicalmanagementand surveillance • Symptomatic: Ao. Vreplacement(evenin elderlyand. CHF)
 Mitral. Stenosis
Mitral. Stenosis
 Mitral. Stenosis. Overview • Definition: Obstructionof. LVinflowthat preventsproperfillingduringdiastole • Normal. MVArea: 46 cm 2 • Transmitralgradientsandsymptomsbegin atareaslessthan 2 cm 2 • Rheumaticcarditisisthepredominantcause • Prevalenceandincidence: decreasingdue toareductionofrheumaticheartdisease.
Mitral. Stenosis. Overview • Definition: Obstructionof. LVinflowthat preventsproperfillingduringdiastole • Normal. MVArea: 46 cm 2 • Transmitralgradientsandsymptomsbegin atareaslessthan 2 cm 2 • Rheumaticcarditisisthepredominantcause • Prevalenceandincidence: decreasingdue toareductionofrheumaticheartdisease.
 Etiologyof. Mitral. Stenosis • Rheumaticheartdisease: 7799%ofall cases • Infectiveendocarditis: 3. 3% • Mitralannularcalcification: 2. 7%
Etiologyof. Mitral. Stenosis • Rheumaticheartdisease: 7799%ofall cases • Infectiveendocarditis: 3. 3% • Mitralannularcalcification: 2. 7%




 MSPathophysiology • Progressive. Dyspnea(70%): LAdilation pulmonarycongestion(reducedemptying) – worsewithexercise, fever, tachycardia, andpregnancy • Increased. Transmitral. Pressures: Leadstoleft atrialenlargementandatrialfibrillation. • Rightheartfailuresymptoms: dueto Pulmonaryvenous. HTN • Hemoptysis: duetoruptureofbronchialvessels duetoelevatedpulmonarypressure
MSPathophysiology • Progressive. Dyspnea(70%): LAdilation pulmonarycongestion(reducedemptying) – worsewithexercise, fever, tachycardia, andpregnancy • Increased. Transmitral. Pressures: Leadstoleft atrialenlargementandatrialfibrillation. • Rightheartfailuresymptoms: dueto Pulmonaryvenous. HTN • Hemoptysis: duetoruptureofbronchialvessels duetoelevatedpulmonarypressure
 Natural. Historyof. MS • Diseaseofplateaus: – Mild. MS: 10 yearsafterinitial. RHDinsult – Moderate: 10 yearslater – Severe: 10 yearslater • Mortality: Duetoprogressivepulmonary congestion, infection, andthromboembolism.
Natural. Historyof. MS • Diseaseofplateaus: – Mild. MS: 10 yearsafterinitial. RHDinsult – Moderate: 10 yearslater – Severe: 10 yearslater • Mortality: Duetoprogressivepulmonary congestion, infection, andthromboembolism.
 Physical. Exam. Findingsof. MS • prominent»a»waveinjugularvenouspulsations : Duetopulmonaryhypertensionandrightventricular hypertrophy • Signsofrightsidedheartfailure: inadvanced disease • Mitralfacies: When. MSissevereandthecardiac outputisdiminished, thereisvasoconstriction, resultinginpinkishpurplepatchesonthecheeks
Physical. Exam. Findingsof. MS • prominent»a»waveinjugularvenouspulsations : Duetopulmonaryhypertensionandrightventricular hypertrophy • Signsofrightsidedheartfailure: inadvanced disease • Mitralfacies: When. MSissevereandthecardiac outputisdiminished, thereisvasoconstriction, resultinginpinkishpurplepatchesonthecheeks
 • Diastolicmurmur: – Lowpitched diastolicrumble mostprominentat theapex. – Heardbestwiththepatientlyingontheleftside inheldexpiration – Intensityofthediastolicmurmur doesnot correlate withtheseverityofthestenosis. Heart. Soundsin. MS
• Diastolicmurmur: – Lowpitched diastolicrumble mostprominentat theapex. – Heardbestwiththepatientlyingontheleftside inheldexpiration – Intensityofthediastolicmurmur doesnot correlate withtheseverityofthestenosis. Heart. Soundsin. MS
 • Loud. Opening. S 1 snap: heardattheapexwhen leafletsarestillmobile – Duetotheabrupthaltinleafletmotioninearly diastole, afterrapidinitialrapidopening, dueto fusionattheleaflettips. – Ashorter. S 2 toopeningsnapintervalindicates moreseveredisease. Heart. Soundsin. MS
• Loud. Opening. S 1 snap: heardattheapexwhen leafletsarestillmobile – Duetotheabrupthaltinleafletmotioninearly diastole, afterrapidinitialrapidopening, dueto fusionattheleaflettips. – Ashorter. S 2 toopeningsnapintervalindicates moreseveredisease. Heart. Soundsin. MS
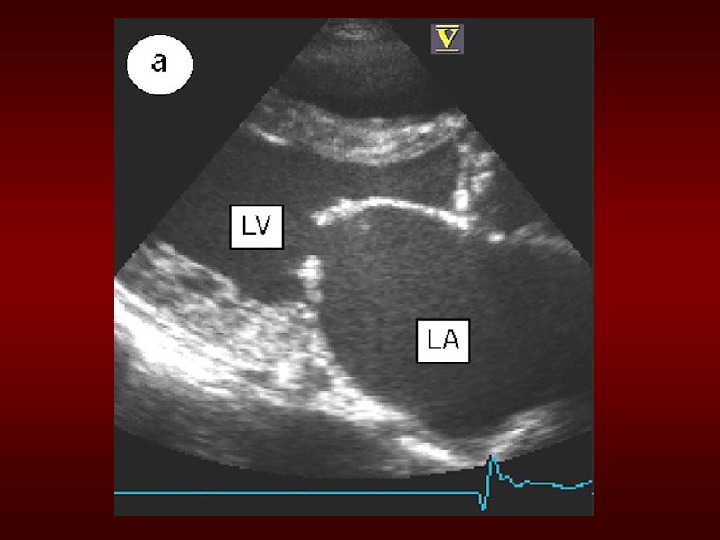
 Evaluationof. MS • ECG : mayshowatrialfibrillationand. LA enlargement • CXR : LAenlargementandpulmonary congestion. Occasionallycalcified. MV • ECHO : The GOLDSTANDARD for diagnosis. Assesmitralvalvemobility, gradientandmitralvalvearea
Evaluationof. MS • ECG : mayshowatrialfibrillationand. LA enlargement • CXR : LAenlargementandpulmonary congestion. Occasionallycalcified. MV • ECHO : The GOLDSTANDARD for diagnosis. Assesmitralvalvemobility, gradientandmitralvalvearea

 Managementof. MS Serialechocardiography: – Mild: 35 years – Moderate: 12 years – Severe: yearly • Medications: MSlike. ASisamechanicalproblem andmedicaltherapydoesnotpreventprogression blockers, CCBs, Digoxinwhichcontrolheart rateandhenceprolongdiastoleforimproved diastolicfilling – Duireticsforfluidoverload
Managementof. MS Serialechocardiography: – Mild: 35 years – Moderate: 12 years – Severe: yearly • Medications: MSlike. ASisamechanicalproblem andmedicaltherapydoesnotpreventprogression blockers, CCBs, Digoxinwhichcontrolheart rateandhenceprolongdiastoleforimproved diastolicfilling – Duireticsforfluidoverload
 Managementof. MS • Identifypatientearlywhomightbenefitfrom percutaneousmitralballoonvalvotomy. • IEprophylaxis: Patientswithprostheticvalvesor a. Hxof. IEfordentalprocedures.
Managementof. MS • Identifypatientearlywhomightbenefitfrom percutaneousmitralballoonvalvotomy. • IEprophylaxis: Patientswithprostheticvalvesor a. Hxof. IEfordentalprocedures.




 Simplified Indicationsfor. Mitral valvereplacement • ANYSYMPTOMATIC Patientwith NYHAClass. IIIor. IVSymptoms • Asymptomaticmoderateor. Severe. MSwith apliablevalvesuitablefor. PMBV
Simplified Indicationsfor. Mitral valvereplacement • ANYSYMPTOMATIC Patientwith NYHAClass. IIIor. IVSymptoms • Asymptomaticmoderateor. Severe. MSwith apliablevalvesuitablefor. PMBV
 Aortic. Regurgitation
Aortic. Regurgitation

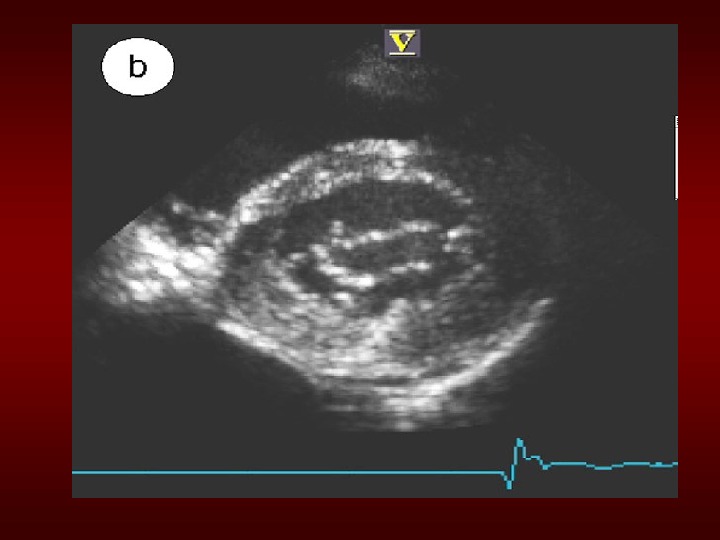
 Aortic. Regurgitation. Overview • Definition: Leakageofbloodinto. LVduring diastoleduetoineffectivecoaptationofthe aorticcusps
Aortic. Regurgitation. Overview • Definition: Leakageofbloodinto. LVduring diastoleduetoineffectivecoaptationofthe aorticcusps
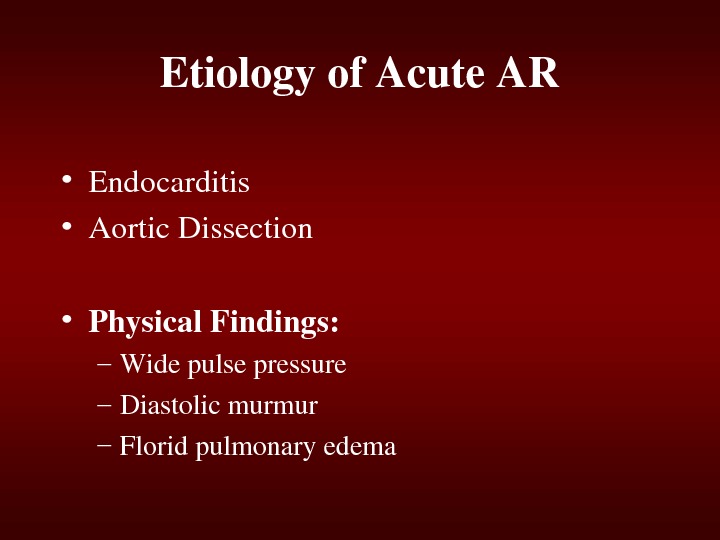
 Etiologyof. Acute. AR • Endocarditis • Aortic. Dissection • Physical. Findings: – Widepulsepressure – Diastolicmurmur – Floridpulmonaryedema
Etiologyof. Acute. AR • Endocarditis • Aortic. Dissection • Physical. Findings: – Widepulsepressure – Diastolicmurmur – Floridpulmonaryedema
 Treatmentof. Acute. AR • True. Surgical. Emergency: • Positiveinotrope: (eg, dopamine, dobutamine) • Vasodilators: (eg, nitroprusside) • Avoidbetablockers • Donotevenconsideraballoonpump
Treatmentof. Acute. AR • True. Surgical. Emergency: • Positiveinotrope: (eg, dopamine, dobutamine) • Vasodilators: (eg, nitroprusside) • Avoidbetablockers • Donotevenconsideraballoonpump

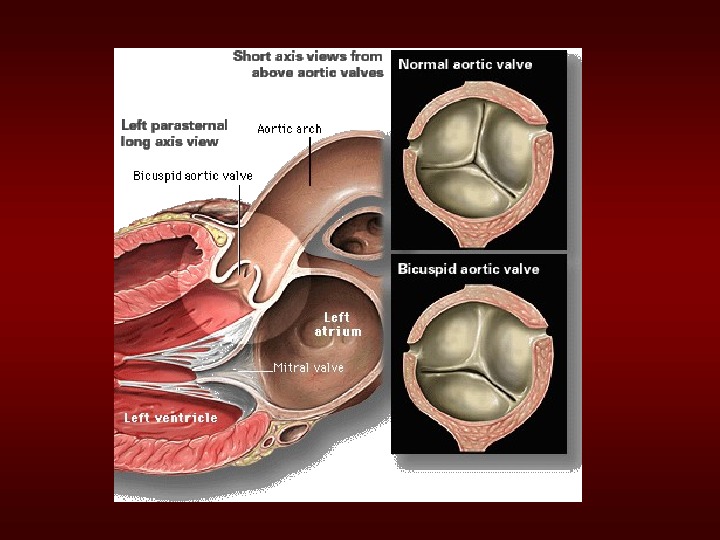
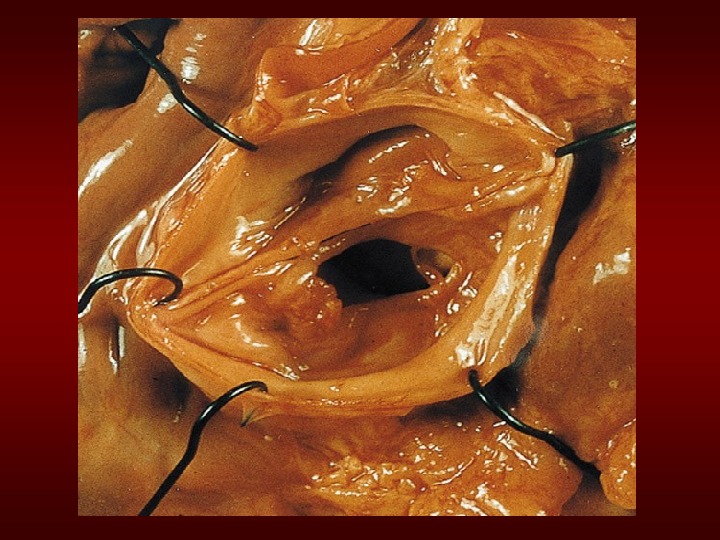
 Etiologyof. Chronic. AR • Bicuspidaorticvalve • Rheumatic • Infectiveendocarditis
Etiologyof. Chronic. AR • Bicuspidaorticvalve • Rheumatic • Infectiveendocarditis
 Pathophysiologyof. AR • Combinedpressure. ANDvolumeoverload • Compensatory. Mechanisms: LVdilation, LVH. Progressivedilationleadstoheart failure
Pathophysiologyof. AR • Combinedpressure. ANDvolumeoverload • Compensatory. Mechanisms: LVdilation, LVH. Progressivedilationleadstoheart failure
 Natural. Historyof. AR • Asymptomaticuntil 4 th or 5 th decade • Rateof. Progression: 46%peryear • Progressive. Symptomsinclude: Dyspnea: exertional, orthopnea, and paroxsymalnocturnaldyspnea Nocturnalangina: duetoslowingofheartrate andreductionofdiastolicbloodpressure Palpitations: duetoincreasedforceof contraction
Natural. Historyof. AR • Asymptomaticuntil 4 th or 5 th decade • Rateof. Progression: 46%peryear • Progressive. Symptomsinclude: Dyspnea: exertional, orthopnea, and paroxsymalnocturnaldyspnea Nocturnalangina: duetoslowingofheartrate andreductionofdiastolicbloodpressure Palpitations: duetoincreasedforceof contraction
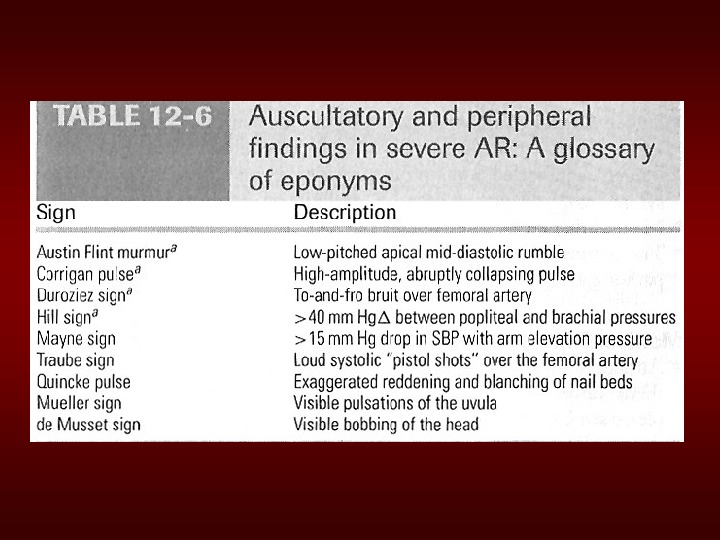
 Physical. Examfindingsof. AR • Widepulsepressure: mostsensitive • Hyperdynamicanddisplacedapicalimpulse • Auscultation – Diastolicblowingmurmur attheleftsternal border – Austinflintmurmur (apex): Regurgitantjet impingesonanterior. MVLcausingittovibrate – Systolicejectionmurmur : duetoincreasedflow acrosstheaorticvalve
Physical. Examfindingsof. AR • Widepulsepressure: mostsensitive • Hyperdynamicanddisplacedapicalimpulse • Auscultation – Diastolicblowingmurmur attheleftsternal border – Austinflintmurmur (apex): Regurgitantjet impingesonanterior. MVLcausingittovibrate – Systolicejectionmurmur : duetoincreasedflow acrosstheaorticvalve

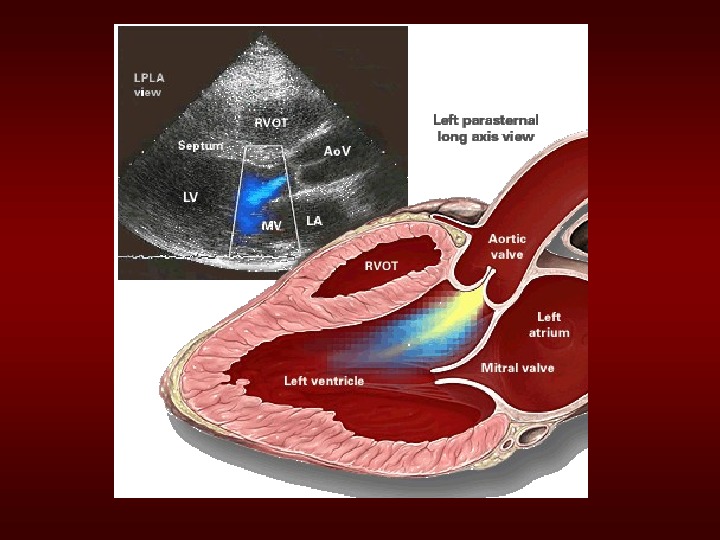
 MRIofthe. Heart. Revealinga. Central, High. Velocity. Jet. Projectingintothe. Left. Ventricular. Cavity. Thejetclearlystrikestheanteriormitralvalveleaflet, causingdistortionandprematureclosure duringdiastole.
MRIofthe. Heart. Revealinga. Central, High. Velocity. Jet. Projectingintothe. Left. Ventricular. Cavity. Thejetclearlystrikestheanteriormitralvalveleaflet, causingdistortionandprematureclosure duringdiastole.
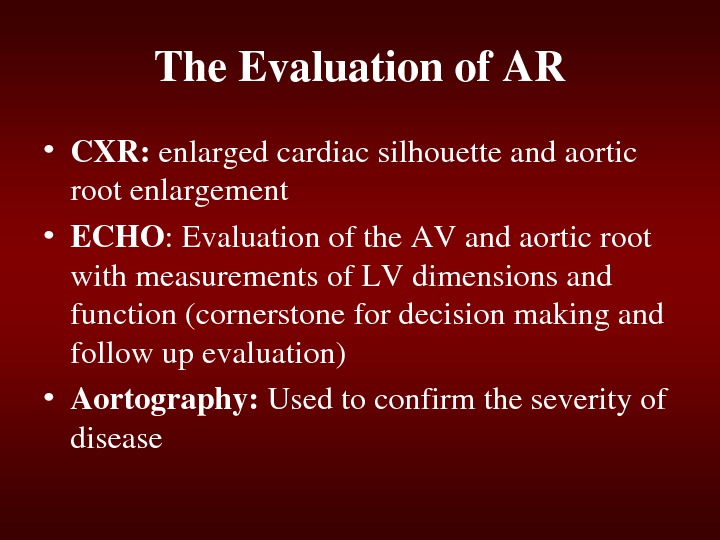
 The. Evaluationof. AR • CXR: enlargedcardiacsilhouetteandaortic rootenlargement • ECHO : Evaluationofthe. AVandaorticroot withmeasurementsof. LVdimensionsand function(cornerstonefordecisionmakingand followupevaluation) • Aortography: Usedtoconfirmtheseverityof disease
The. Evaluationof. AR • CXR: enlargedcardiacsilhouetteandaortic rootenlargement • ECHO : Evaluationofthe. AVandaorticroot withmeasurementsof. LVdimensionsand function(cornerstonefordecisionmakingand followupevaluation) • Aortography: Usedtoconfirmtheseverityof disease

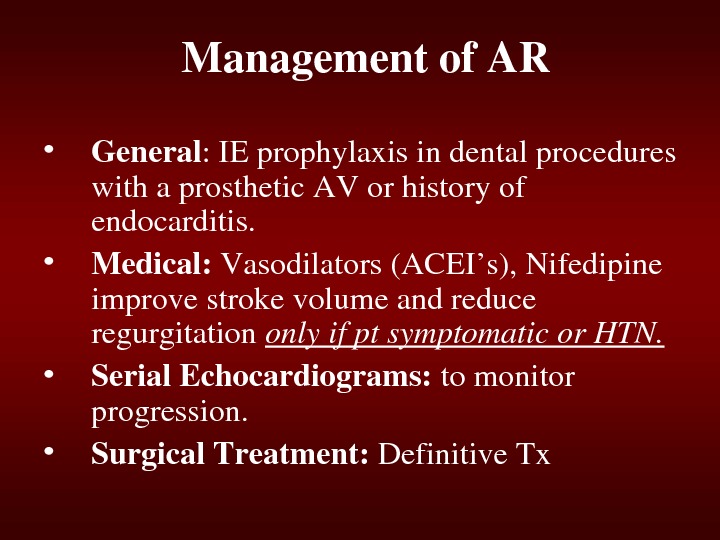
 Managementof. AR • General : IEprophylaxisindentalprocedures withaprosthetic. AVorhistoryof endocarditis. • Medical: Vasodilators(ACEI’s), Nifedipine improvestrokevolumeandreduce regurgitation onlyifptsymptomaticor. HTN. • Serial. Echocardiograms: tomonitor progression. • Surgical. Treatment: Definitive. Tx
Managementof. AR • General : IEprophylaxisindentalprocedures withaprosthetic. AVorhistoryof endocarditis. • Medical: Vasodilators(ACEI’s), Nifedipine improvestrokevolumeandreduce regurgitation onlyifptsymptomaticor. HTN. • Serial. Echocardiograms: tomonitor progression. • Surgical. Treatment: Definitive. Tx


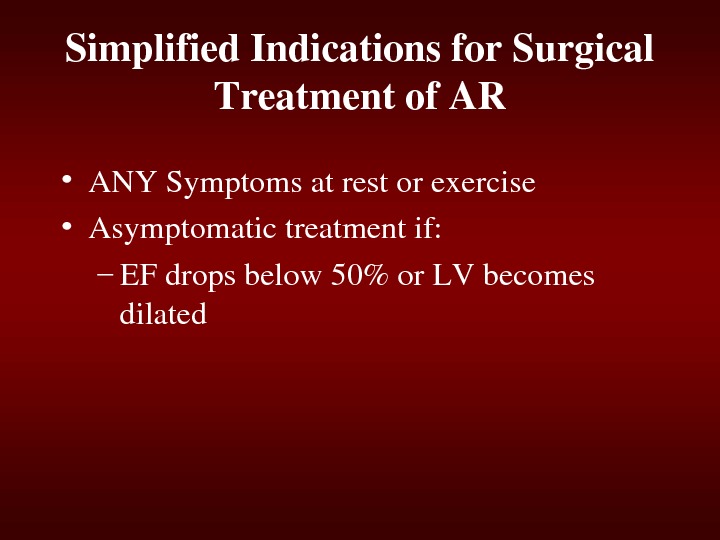
 Simplified. Indicationsfor. Surgical Treatmentof. AR • ANYSymptomsatrestorexercise • Asymptomatictreatmentif: – EFdropsbelow 50%or. LVbecomes dilated
Simplified. Indicationsfor. Surgical Treatmentof. AR • ANYSymptomsatrestorexercise • Asymptomatictreatmentif: – EFdropsbelow 50%or. LVbecomes dilated
 Mitral. Regurgitation
Mitral. Regurgitation
 • Definition: Backflowofbloodfromthe. LV tothe. LAduringsystole • Mild(physiological)MRisseenin 80%of normalindividuals. Chronic. Mitral. Regurgitation Overview
• Definition: Backflowofbloodfromthe. LV tothe. LAduringsystole • Mild(physiological)MRisseenin 80%of normalindividuals. Chronic. Mitral. Regurgitation Overview
 Acute. MR • Endocarditis • Acute. MI: • Malfunctionordisruptionofprosthetic valve
Acute. MR • Endocarditis • Acute. MI: • Malfunctionordisruptionofprosthetic valve
 Managementof. Acute. MR • Myocardialinfarction: Cardiaccathor thrombolytics • Mostothercasesofmitralregurgitation isafterloadreduction: – Diureticsandnitrates – nitroprusside, eveninthesettingofa normalbloodpressure.
Managementof. Acute. MR • Myocardialinfarction: Cardiaccathor thrombolytics • Mostothercasesofmitralregurgitation isafterloadreduction: – Diureticsandnitrates – nitroprusside, eveninthesettingofa normalbloodpressure.
 Managementof. Acute. MR • Donotattempttoalleviatetachycardia withbetablockers. Mildtomoderate tachycardiaisbeneficialinthesepatients becauseitallowslesstimefortheheartto havebackfill, whichlowersregurgitant volume.
Managementof. Acute. MR • Donotattempttoalleviatetachycardia withbetablockers. Mildtomoderate tachycardiaisbeneficialinthesepatients becauseitallowslesstimefortheheartto havebackfill, whichlowersregurgitant volume.
 Treatmentof. Acute. MR • Balloon. Pump • Nitroprussideevenifhypotensive • Emergent. Surgery
Treatmentof. Acute. MR • Balloon. Pump • Nitroprussideevenifhypotensive • Emergent. Surgery
 • Myxomatousdegeneration(MVP) • Ischemic. MR • Rheumaticheartdisease • Infective. Endocarditis Etiologiesof. Chronic. Mitral Regurgitation
• Myxomatousdegeneration(MVP) • Ischemic. MR • Rheumaticheartdisease • Infective. Endocarditis Etiologiesof. Chronic. Mitral Regurgitation
 Pathophysiologyof. MR • Pure. Volume. Overload • Compensatory. Mechanisms: Leftatrial enlargement, LVHandincreased contractility – Progressiveleftatrialdilationandright ventriculardysfunctionduetopulmonary hypertension. – Progressiveleftventricular volumeoverload leadstodilation andprogressiveheartfailure.
Pathophysiologyof. MR • Pure. Volume. Overload • Compensatory. Mechanisms: Leftatrial enlargement, LVHandincreased contractility – Progressiveleftatrialdilationandright ventriculardysfunctionduetopulmonary hypertension. – Progressiveleftventricular volumeoverload leadstodilation andprogressiveheartfailure.
 Physical. Examfindingsin. MR • Auscultation: soft. S 1 anda holosystolic murmurattheapexradiatingtotheaxilla – S 3(CHF/LAoverload) – Inchronic. MR, theintensityofthemurmur doescorrelate withtheseverity. • Exertion. Dyspnea: (exerciseintolerance) • Heart. Failure: Maycoincidewith increasedhemodynamicburdene. g. , pregnancy, infectionoratrialfibrillation
Physical. Examfindingsin. MR • Auscultation: soft. S 1 anda holosystolic murmurattheapexradiatingtotheaxilla – S 3(CHF/LAoverload) – Inchronic. MR, theintensityofthemurmur doescorrelate withtheseverity. • Exertion. Dyspnea: (exerciseintolerance) • Heart. Failure: Maycoincidewith increasedhemodynamicburdene. g. , pregnancy, infectionoratrialfibrillation
 The. Natural. Historyof. MR • Compensatoryphase: 1015 years • Patientswithasymptomaticsevere. MR havea 5%/yearmortalityrate • Oncethepatient’s. EFbecomes<60% and/orbecomessymptomatic, mortality risessharply • Mortality: Fromprogressivedyspneaand heartfailure
The. Natural. Historyof. MR • Compensatoryphase: 1015 years • Patientswithasymptomaticsevere. MR havea 5%/yearmortalityrate • Oncethepatient’s. EFbecomes<60% and/orbecomessymptomatic, mortality risessharply • Mortality: Fromprogressivedyspneaand heartfailure
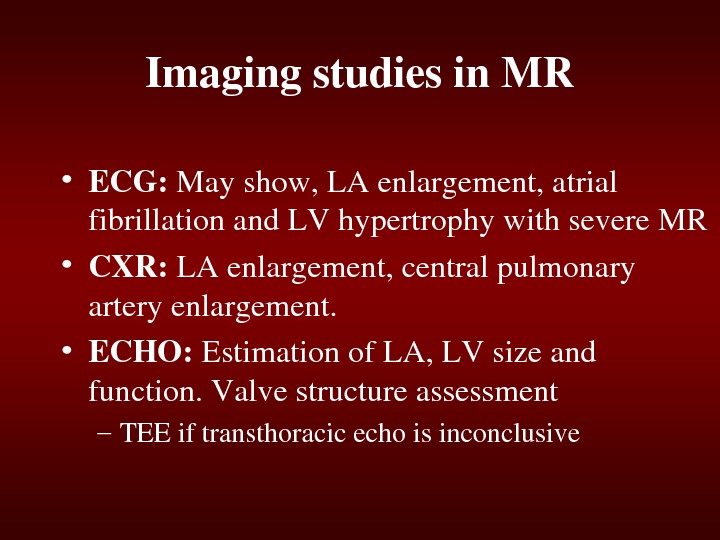
 Imagingstudiesin. MR • ECG: Mayshow, LAenlargement, atrial fibrillationand. LVhypertrophywithsevere. MR • CXR: LAenlargement, centralpulmonary arteryenlargement. • ECHO: Estimationof. LA, LVsizeand function. Valvestructureassessment – TEEiftransthoracicechoisinconclusive
Imagingstudiesin. MR • ECG: Mayshow, LAenlargement, atrial fibrillationand. LVhypertrophywithsevere. MR • CXR: LAenlargement, centralpulmonary arteryenlargement. • ECHO: Estimationof. LA, LVsizeand function. Valvestructureassessment – TEEiftransthoracicechoisinconclusive

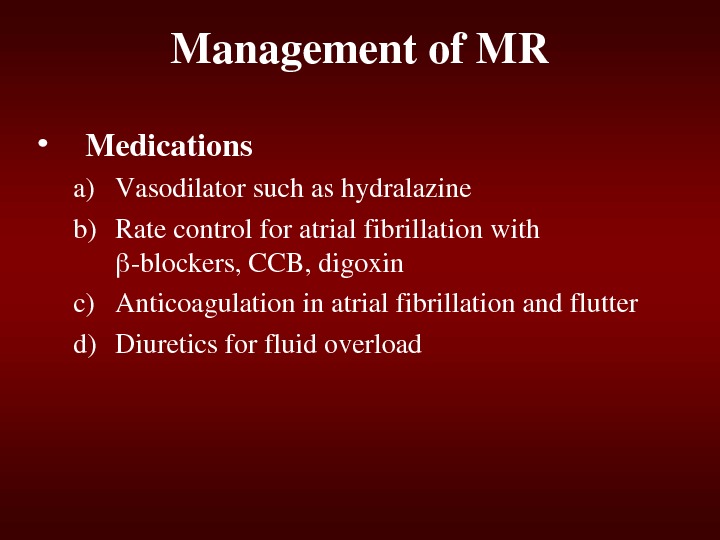
 Managementof. MR • Medications a) Vasodilatorsuchashydralazine b) Ratecontrolforatrialfibrillationwith blockers, CCB, digoxin c) Anticoagulationinatrialfibrillationandflutter d) Diureticsforfluidoverload
Managementof. MR • Medications a) Vasodilatorsuchashydralazine b) Ratecontrolforatrialfibrillationwith blockers, CCB, digoxin c) Anticoagulationinatrialfibrillationandflutter d) Diureticsforfluidoverload
 Managementof. MR • Serial. Echocardiography: – Mild: 23 years – Moderate: 12 years – Severe: 612 months • IEprophylaxis: Patientswithprosthetic valvesora. Hxof. IEfordentalprocedures.
Managementof. MR • Serial. Echocardiography: – Mild: 23 years – Moderate: 12 years – Severe: 612 months • IEprophylaxis: Patientswithprosthetic valvesora. Hxof. IEfordentalprocedures.


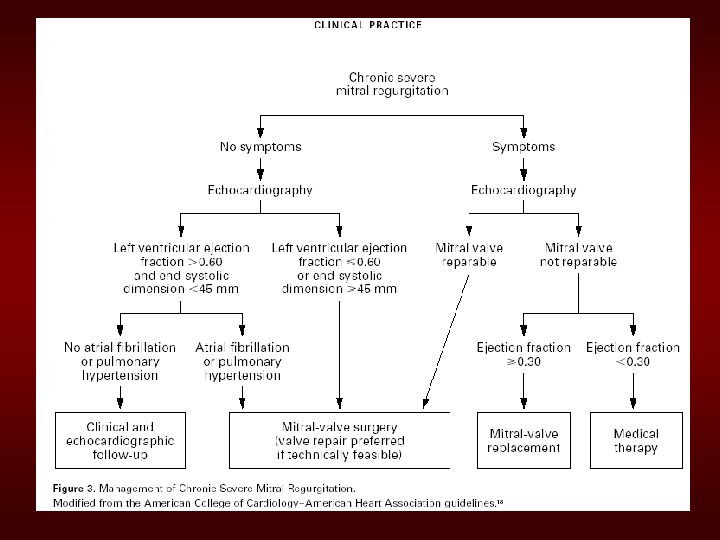
 Simplified. Indicationsfor. MV Replacementin. Severe. MR • ANYSymptoms atrestorexercisewith (repairiffeasible) • Asymptomatic: – If. EF<60% – Ifnewonsetatrialfibrillation
Simplified. Indicationsfor. MV Replacementin. Severe. MR • ANYSymptoms atrestorexercisewith (repairiffeasible) • Asymptomatic: – If. EF<60% – Ifnewonsetatrialfibrillation
 THANKYOU
THANKYOU

