54255f3bfa97cc5cc1acd0890843e2ad.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 33
 Valves In Industry (Part 1)
Valves In Industry (Part 1)
 Contents 1) 2) 3) 4) Process control & instrumentation terminology/definition What valve means? How it’s work? Classification of valves? 2
Contents 1) 2) 3) 4) Process control & instrumentation terminology/definition What valve means? How it’s work? Classification of valves? 2
 Process Control & Instrumentation Terminology/Definition n Control Valve (automated valve)- is referring to a control valve assembly which typically consists of valve body, the internal trim parts, an actuator and variety of additional valve accessories which can include positioners, transducer, supply pressure regulators, air sets, limit switches, etc. The control valve manipulates a flowing fluid, such as gas, steam, water, or chemical compounds, to compensate for the load disturbance and keep the regulated process variable as close as possible to the desired set point. 3
Process Control & Instrumentation Terminology/Definition n Control Valve (automated valve)- is referring to a control valve assembly which typically consists of valve body, the internal trim parts, an actuator and variety of additional valve accessories which can include positioners, transducer, supply pressure regulators, air sets, limit switches, etc. The control valve manipulates a flowing fluid, such as gas, steam, water, or chemical compounds, to compensate for the load disturbance and keep the regulated process variable as close as possible to the desired set point. 3
 Process Control & Instrumentation Terminology/Definition n Actuator- n Positioner- A pneumatic, hydraulic, or electrically powered device that supplies force and motion to open or close a valve. A position controller that is mechanically connected to a moving part of a final control element (valve/control valve) or its actuator and that automatically adjusts its output to the actuator to maintain a desired position in proportion to the input signal. 4
Process Control & Instrumentation Terminology/Definition n Actuator- n Positioner- A pneumatic, hydraulic, or electrically powered device that supplies force and motion to open or close a valve. A position controller that is mechanically connected to a moving part of a final control element (valve/control valve) or its actuator and that automatically adjusts its output to the actuator to maintain a desired position in proportion to the input signal. 4
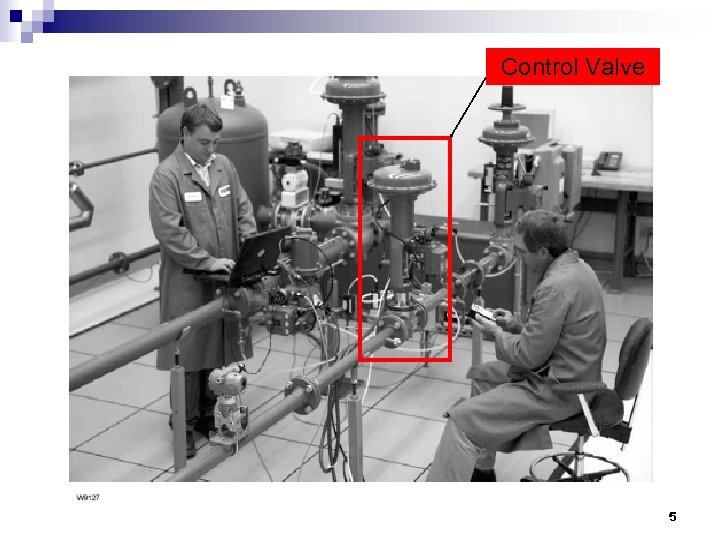 Control Valve 5
Control Valve 5
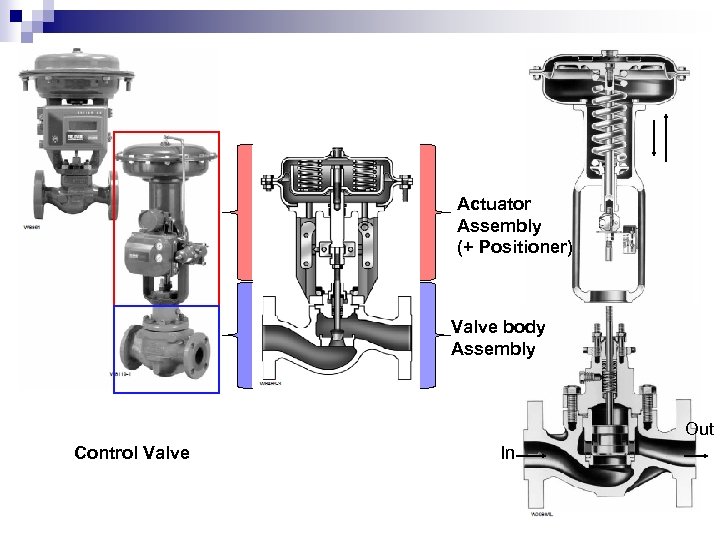 Actuator Assembly (+ Positioner) Valve body Assembly Out Control Valve In 6
Actuator Assembly (+ Positioner) Valve body Assembly Out Control Valve In 6
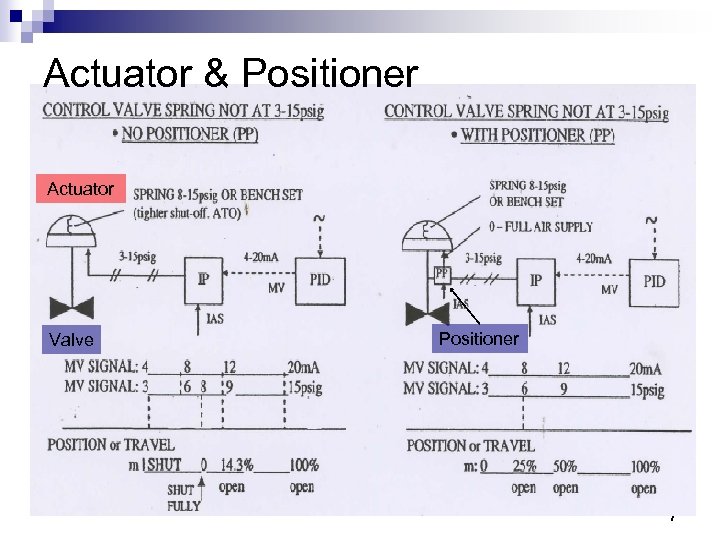 Actuator & Positioner Actuator Valve Positioner 7
Actuator & Positioner Actuator Valve Positioner 7
 Introduction to Valves Mechanical devices specifically designed to direct, start, stop, mix or regulate the flow, pressure or temperature of a process fluid. n Manufactured from various materials, mostly made from steel, iron, plastic, brass, bronze and special alloys. n 8
Introduction to Valves Mechanical devices specifically designed to direct, start, stop, mix or regulate the flow, pressure or temperature of a process fluid. n Manufactured from various materials, mostly made from steel, iron, plastic, brass, bronze and special alloys. n 8
 Valves Classification According To; Function 2) Application 3) Motion 1) 9
Valves Classification According To; Function 2) Application 3) Motion 1) 9
 Valves Classification According To Function n i) iii) n Categorized into three areas: On-Off Valves Non return Valves Throttling Valves Specific valve-body designs may fit into one, two, or all three category. 10
Valves Classification According To Function n i) iii) n Categorized into three areas: On-Off Valves Non return Valves Throttling Valves Specific valve-body designs may fit into one, two, or all three category. 10
 Valves Classification According To Function 1) On-Off Valves Ø Start or stop the flow of the medium through the process. Ø Example: gate, plug, ball and pressurerelief valves. Ø Can be hand-operated or automated with the addition of an actuator. 11
Valves Classification According To Function 1) On-Off Valves Ø Start or stop the flow of the medium through the process. Ø Example: gate, plug, ball and pressurerelief valves. Ø Can be hand-operated or automated with the addition of an actuator. 11
 Valves Classification According To Function (On-Off Valves) 12
Valves Classification According To Function (On-Off Valves) 12
 Valves Classification According To Function (On-Off Valves) Used in mixing applications where a number of fluids are combined for a predetermined amount of time (exact measurements are not required). Ø Used for immediate shut down of a system when an emergency situation occurs. Ø 13
Valves Classification According To Function (On-Off Valves) Used in mixing applications where a number of fluids are combined for a predetermined amount of time (exact measurements are not required). Ø Used for immediate shut down of a system when an emergency situation occurs. Ø 13
 Valves Classification According To Function (On-Off Valves) Ø Ø Ø Pressure-relief valves are self-actuated on-off valves that open only when a preset pressure is surpassed. Used for guarding against overpressurization of a liquid service. Applied in gas applications where overpressurization of the system shows a safety or process hazard and must be vented. 14
Valves Classification According To Function (On-Off Valves) Ø Ø Ø Pressure-relief valves are self-actuated on-off valves that open only when a preset pressure is surpassed. Used for guarding against overpressurization of a liquid service. Applied in gas applications where overpressurization of the system shows a safety or process hazard and must be vented. 14
 Valves Classification According To Function (On-Off Valves) 15
Valves Classification According To Function (On-Off Valves) 15
 Valves Classification According To Function 2) Non return Valves Ø Allow the fluid to flow only in the desired direction. Ø Any flow or pressure in the opposite direction is mechanically restricted from occurring. Ø All check valves are non return valves. 16
Valves Classification According To Function 2) Non return Valves Ø Allow the fluid to flow only in the desired direction. Ø Any flow or pressure in the opposite direction is mechanically restricted from occurring. Ø All check valves are non return valves. 16
 Valves Classification According To Function (Non-return Valves) 17
Valves Classification According To Function (Non-return Valves) 17
 Valves Classification According To Function (Non-return valves) Backflow of fluid is prevented to ensure the safety of equipment and the desired dynamic of the process. Ø Applied in process systems that have varying pressures, which must be kept separated. Ø 18
Valves Classification According To Function (Non-return valves) Backflow of fluid is prevented to ensure the safety of equipment and the desired dynamic of the process. Ø Applied in process systems that have varying pressures, which must be kept separated. Ø 18
 Valves Classification According To Function 3) Throttling Valves Ø Used for regulating the flow, temperature or pressure of the service. Ø Can be moved to any position within the stroke of the valve and hold that position, including the fully-open or fully-closed positions. 19
Valves Classification According To Function 3) Throttling Valves Ø Used for regulating the flow, temperature or pressure of the service. Ø Can be moved to any position within the stroke of the valve and hold that position, including the fully-open or fully-closed positions. 19
 Valves Classification According To Function (Throttling valves) Ø Ø Ø Also provided with actuation system for greater thrust and positioning capability (automatic control). Example: pressure regulator varies the valve’s position to maintain constant pressure downstream (close to decrease and open to increase the pressure). Control valves are valves that are capable of varying flow conditions to match the process requirements (always equipped with actuators). 20
Valves Classification According To Function (Throttling valves) Ø Ø Ø Also provided with actuation system for greater thrust and positioning capability (automatic control). Example: pressure regulator varies the valve’s position to maintain constant pressure downstream (close to decrease and open to increase the pressure). Control valves are valves that are capable of varying flow conditions to match the process requirements (always equipped with actuators). 20
 Valves Classification According To Function (Throttling Valves) 21
Valves Classification According To Function (Throttling Valves) 21
 Valves Classification According To Application Categorized into three: 1) General Service Valves 2) Special Service Valves 3) Severe Service Valves 22
Valves Classification According To Application Categorized into three: 1) General Service Valves 2) Special Service Valves 3) Severe Service Valves 22
 Valves Classification According To Application 1) General Service Valves Ø Designed for the majority of the commonplace applications that have lower-pressure ratings, moderate-temperature ratings, noncorrosive fluids and common pressure drops that do not result in cavitation or flashing. Ø Had some degree of interchangeability and flexibility for wider range of applications. 23
Valves Classification According To Application 1) General Service Valves Ø Designed for the majority of the commonplace applications that have lower-pressure ratings, moderate-temperature ratings, noncorrosive fluids and common pressure drops that do not result in cavitation or flashing. Ø Had some degree of interchangeability and flexibility for wider range of applications. 23
 Valves Classification According To Application 2) Special Service Valves Ø Designed for a single application that is outside normal process applications (custom-engineered valves). Ø Handled a demanding temperature, high pressure or a corrosive medium. 24
Valves Classification According To Application 2) Special Service Valves Ø Designed for a single application that is outside normal process applications (custom-engineered valves). Ø Handled a demanding temperature, high pressure or a corrosive medium. 24
 Valves Classification According To Application 3) Severe Service Valves Ø Equipped with special features to handle volatile applications and high pressure drops (highly engineered trims). Ø Special actuation may be required to overcome the forces of the process. 25
Valves Classification According To Application 3) Severe Service Valves Ø Equipped with special features to handle volatile applications and high pressure drops (highly engineered trims). Ø Special actuation may be required to overcome the forces of the process. 25
 Valves Classification According To Motion Categorized into two: 1) 2) Linear-motion Valves Rotary-motion Valves 26
Valves Classification According To Motion Categorized into two: 1) 2) Linear-motion Valves Rotary-motion Valves 26
 Valves Classification According To Motion 1) Linear-motion Valves Ø Had a sliding-stem design that pushes a closure element into an open or closed position. Ø Simple design, easy maintenance, and versatile with various sizes, pressure class and design options. Ø Example: gate, globe, diaphragm, three-way. 27
Valves Classification According To Motion 1) Linear-motion Valves Ø Had a sliding-stem design that pushes a closure element into an open or closed position. Ø Simple design, easy maintenance, and versatile with various sizes, pressure class and design options. Ø Example: gate, globe, diaphragm, three-way. 27
 Valves Classification According To Motion (linear-motion valves) 28
Valves Classification According To Motion (linear-motion valves) 28
 Valves Classification According To Motion 2) Rotary-motion Valves Ø Used a closure element that rotates through a quarter-turn range to open and block the flow. Ø Limited to certain pressure drops. Ø Prone to cavitations and flashing problems. 29
Valves Classification According To Motion 2) Rotary-motion Valves Ø Used a closure element that rotates through a quarter-turn range to open and block the flow. Ø Limited to certain pressure drops. Ø Prone to cavitations and flashing problems. 29
 Valves Classification According To Motion (Rotary-motion valves) 30
Valves Classification According To Motion (Rotary-motion valves) 30
 THANK YOU… 31
THANK YOU… 31
 Assignments 1) Define the term of cavitation. (3 marks) 2) Discuss the conditions that cause the cavitation phenomenon. (6 marks) 3) Discuss the possible damages done by the cavitation phenomenon (8 marks) and how to control it. (8 marks) 32
Assignments 1) Define the term of cavitation. (3 marks) 2) Discuss the conditions that cause the cavitation phenomenon. (6 marks) 3) Discuss the possible damages done by the cavitation phenomenon (8 marks) and how to control it. (8 marks) 32
 Assignments 4) Define the term of flashing. (3 marks) 5) Discuss the conditions that cause the flashing phenomenon. (6 marks) 6) Discuss the possible damages done by the flashing phenomenon (8 marks) and how to control it. (8 marks) 33
Assignments 4) Define the term of flashing. (3 marks) 5) Discuss the conditions that cause the flashing phenomenon. (6 marks) 6) Discuss the possible damages done by the flashing phenomenon (8 marks) and how to control it. (8 marks) 33


