 Valve Regurgitation Echocardiographic Calculations Rami Khouzam, MD
Valve Regurgitation Echocardiographic Calculations Rami Khouzam, MD
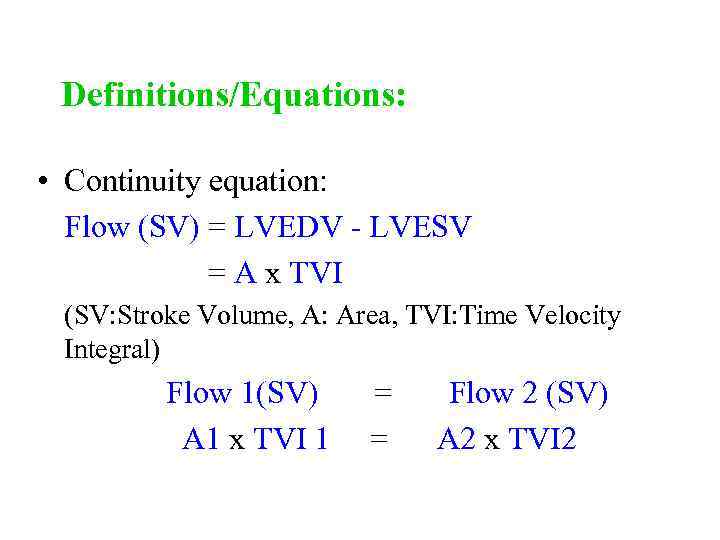 Definitions/Equations: • Continuity equation: Flow (SV) = LVEDV - LVESV = A x TVI (SV: Stroke Volume, A: Area, TVI: Time Velocity Integral) Flow 1(SV) A 1 x TVI 1 = = Flow 2 (SV) A 2 x TVI 2
Definitions/Equations: • Continuity equation: Flow (SV) = LVEDV - LVESV = A x TVI (SV: Stroke Volume, A: Area, TVI: Time Velocity Integral) Flow 1(SV) A 1 x TVI 1 = = Flow 2 (SV) A 2 x TVI 2
 TVI • Time Velocity Integral = stroke distance (cm). The distance over which blood travels in one cardiac cycle: the cycle velocity (cm/s) divided by time (s). Usually represents Mean gradient. • Different than V (Velocity): m/s or cm/s. Usually represents Peak Instantaneous gradient.
TVI • Time Velocity Integral = stroke distance (cm). The distance over which blood travels in one cardiac cycle: the cycle velocity (cm/s) divided by time (s). Usually represents Mean gradient. • Different than V (Velocity): m/s or cm/s. Usually represents Peak Instantaneous gradient.
 Area = r 2 = 3. 14 r 2 (radius) = 0. 785 d 2 (diameter)
Area = r 2 = 3. 14 r 2 (radius) = 0. 785 d 2 (diameter)
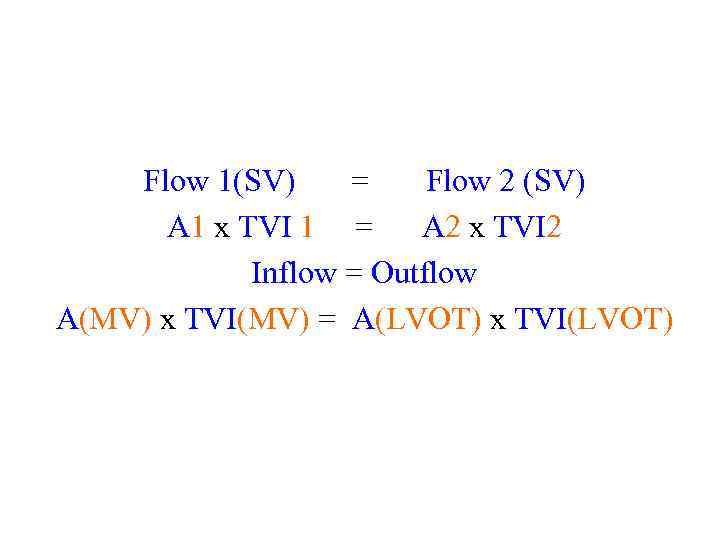 Flow 1(SV) = Flow 2 (SV) A 1 x TVI 1 = A 2 x TVI 2 Inflow = Outflow A(MV) x TVI(MV) = A(LVOT) x TVI(LVOT)
Flow 1(SV) = Flow 2 (SV) A 1 x TVI 1 = A 2 x TVI 2 Inflow = Outflow A(MV) x TVI(MV) = A(LVOT) x TVI(LVOT)
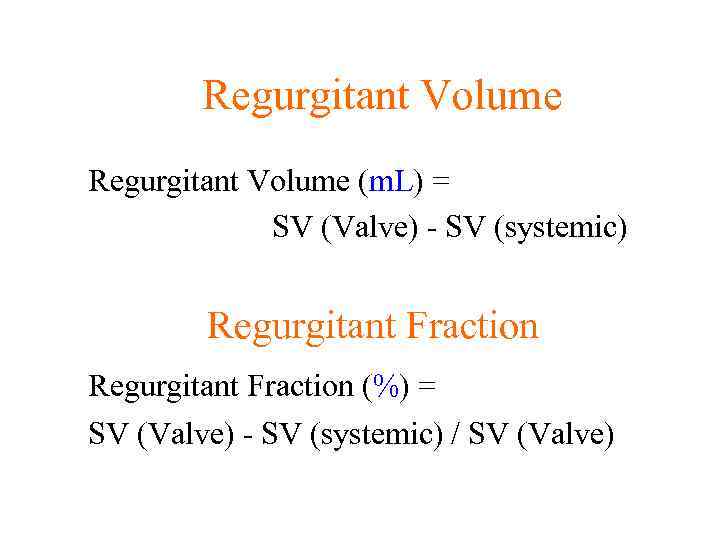 Regurgitant Volume (m. L) = SV (Valve) - SV (systemic) Regurgitant Fraction (%) = SV (Valve) - SV (systemic) / SV (Valve)
Regurgitant Volume (m. L) = SV (Valve) - SV (systemic) Regurgitant Fraction (%) = SV (Valve) - SV (systemic) / SV (Valve)
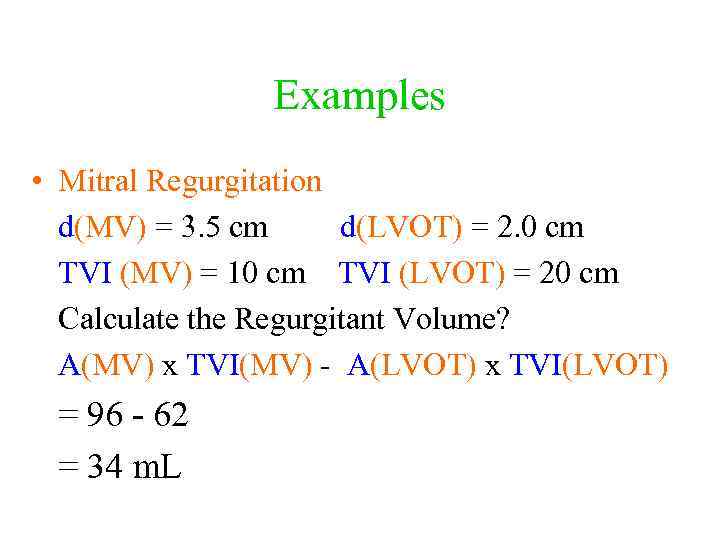 Examples • Mitral Regurgitation d(MV) = 3. 5 cm d(LVOT) = 2. 0 cm TVI (MV) = 10 cm TVI (LVOT) = 20 cm Calculate the Regurgitant Volume? A(MV) x TVI(MV) - A(LVOT) x TVI(LVOT) = 96 - 62 = 34 m. L
Examples • Mitral Regurgitation d(MV) = 3. 5 cm d(LVOT) = 2. 0 cm TVI (MV) = 10 cm TVI (LVOT) = 20 cm Calculate the Regurgitant Volume? A(MV) x TVI(MV) - A(LVOT) x TVI(LVOT) = 96 - 62 = 34 m. L
 • Aortic Regurgitation d(MV) = 3. 5 cm d(LVOT) = 2. 5 cm TVI (MV) = 8 cm TVI (LVOT) = 25 cm Calculate the Regurgitant Volume? A(LVOT) x TVI(LVOT) - A(MV) x TVI(MV) = 122 - 76 = 46 m. L
• Aortic Regurgitation d(MV) = 3. 5 cm d(LVOT) = 2. 5 cm TVI (MV) = 8 cm TVI (LVOT) = 25 cm Calculate the Regurgitant Volume? A(LVOT) x TVI(LVOT) - A(MV) x TVI(MV) = 122 - 76 = 46 m. L
 ERO • Effective Regurgitant Orifice area (cm 2) = Regurgitant Volume (m. L) / TVI MR (cm) • Effective Regurgitant Orifice area (cm 2) = Flow (m. L/s) / V MR (cm/s)
ERO • Effective Regurgitant Orifice area (cm 2) = Regurgitant Volume (m. L) / TVI MR (cm) • Effective Regurgitant Orifice area (cm 2) = Flow (m. L/s) / V MR (cm/s)
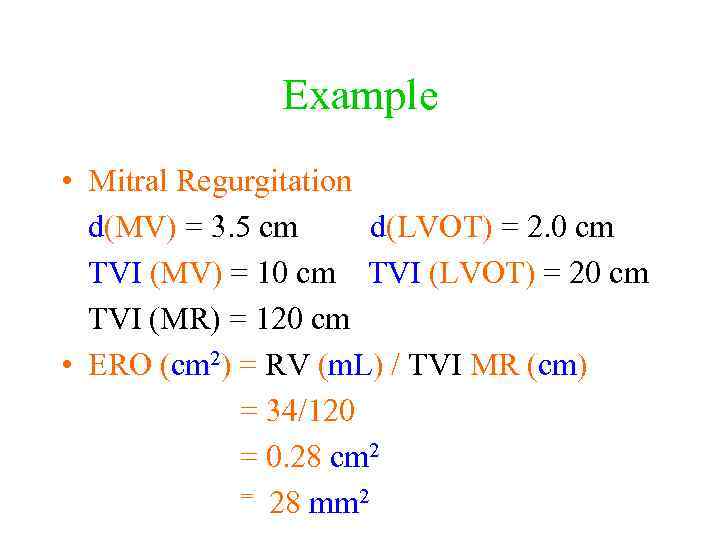 Example • Mitral Regurgitation d(MV) = 3. 5 cm d(LVOT) = 2. 0 cm TVI (MV) = 10 cm TVI (LVOT) = 20 cm TVI (MR) = 120 cm • ERO (cm 2) = RV (m. L) / TVI MR (cm) = 34/120 = 0. 28 cm 2 = 28 mm 2
Example • Mitral Regurgitation d(MV) = 3. 5 cm d(LVOT) = 2. 0 cm TVI (MV) = 10 cm TVI (LVOT) = 20 cm TVI (MR) = 120 cm • ERO (cm 2) = RV (m. L) / TVI MR (cm) = 34/120 = 0. 28 cm 2 = 28 mm 2
 • Aortic Regurgitation d(MV) = 3. 5 cm d(LVOT) = 2. 5 cm TVI (MV) = 8 cm TVI (LVOT) = 25 cm TVI (AR) = 188 cm • ERO (cm 2) = RV (m. L) / TVI AR (cm) = 46/188 = 0. 38 cm 2 = 38 mm 2
• Aortic Regurgitation d(MV) = 3. 5 cm d(LVOT) = 2. 5 cm TVI (MV) = 8 cm TVI (LVOT) = 25 cm TVI (AR) = 188 cm • ERO (cm 2) = RV (m. L) / TVI AR (cm) = 46/188 = 0. 38 cm 2 = 38 mm 2
 Tips • Inflow > Outflow : MR • Inflow < Outflow : AR
Tips • Inflow > Outflow : MR • Inflow < Outflow : AR
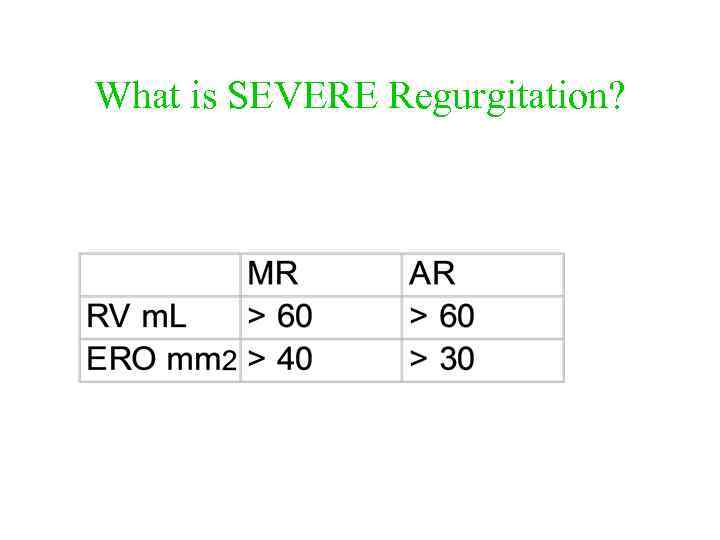 What is SEVERE Regurgitation?
What is SEVERE Regurgitation?
 More Examples A 65 yo M with NYHA class II symptoms. EF 55 %. d MV = 4 cm d LVOT = 2 cm TVI MV = 10 cm TVI LVOT = 20 cm V Ao = 1. 2 m/s • What’s next? a) Operate for MR b) Operate for AR c) Observe MR d) Observe combined AS/AR
More Examples A 65 yo M with NYHA class II symptoms. EF 55 %. d MV = 4 cm d LVOT = 2 cm TVI MV = 10 cm TVI LVOT = 20 cm V Ao = 1. 2 m/s • What’s next? a) Operate for MR b) Operate for AR c) Observe MR d) Observe combined AS/AR
 Regurgitant Volume? A(MV) x TVI(MV) - A(LVOT) x TVI(LVOT) = 125. 6 > 62. 8 = 62 m. L Inflow > Outflow: MR Answer: a
Regurgitant Volume? A(MV) x TVI(MV) - A(LVOT) x TVI(LVOT) = 125. 6 > 62. 8 = 62 m. L Inflow > Outflow: MR Answer: a
 A patient has: d MV = 4 cm TVI MV = 4 cm d LVOT = 2. 5 cm TVI LVOT = 25 cm V Ao = 2. 5 • This patient should have: a) Absent A 2 b) Opening snap c) Quincke’s pulse d) Large V-wave e) Clubbing
A patient has: d MV = 4 cm TVI MV = 4 cm d LVOT = 2. 5 cm TVI LVOT = 25 cm V Ao = 2. 5 • This patient should have: a) Absent A 2 b) Opening snap c) Quincke’s pulse d) Large V-wave e) Clubbing
 A(MV) x TVI(MV) - A(LVOT) x TVI(LVOT) = 50. 2 < 122. 6 = 72 m. L Inflow < Outflow: AR Answer: c
A(MV) x TVI(MV) - A(LVOT) x TVI(LVOT) = 50. 2 < 122. 6 = 72 m. L Inflow < Outflow: AR Answer: c