c2b10b10ba8d6c1cc5a3c355ea99b68f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 50
 Value Stream Mapping
Value Stream Mapping
 Aims for session • Introduce the concept of Value Stream Mapping • Consider identification of value and waste
Aims for session • Introduce the concept of Value Stream Mapping • Consider identification of value and waste
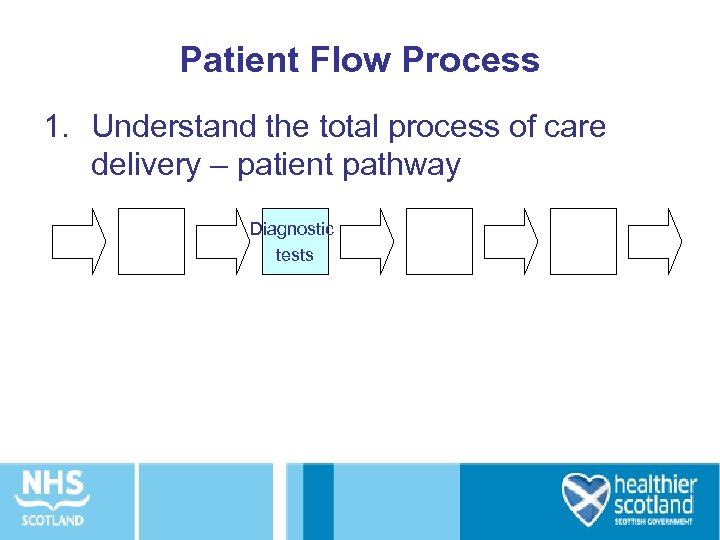 Patient Flow Process 1. Understand the total process of care delivery – patient pathway Diagnostic tests
Patient Flow Process 1. Understand the total process of care delivery – patient pathway Diagnostic tests
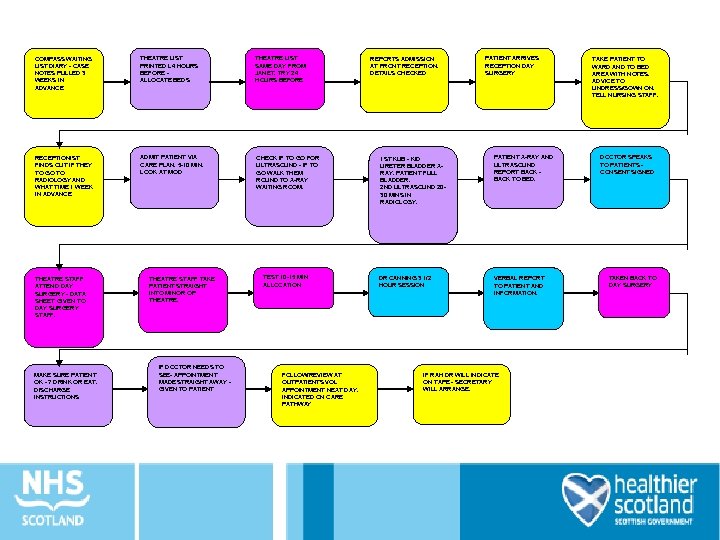 COMPASS WAITING LIST DIARY - CASE NOTES PULLED 3 WEEKS IN ADVANCE THEATRE LIST PRINTED L 4 HOURS BEFORE ALLOCATE BEDS THEATRE LIST SAME DAY FROM JANET. TRY 24 HOURS BEFORE RECEPTIONIST FINDS OUT IF THEY TO GO TO RADIOLOGY AND WHAT TIME 1 WEEK IN ADVANCE ADMIT PATIENT VIA CARE PLAN. 5 -10 MIN. LOOK AT MOD CHECK IF TO GO FOR ULTRASOUND - IF TO GO WALK THEM ROUND TO X-RAY WAITING ROOM. THEATRE STAFF ATTEND DAY SURGERY - DATA SHEET GIVEN TO DAY SURGERY STAFF. MAKE SURE PATIENT OK - ? DRINK OR EAT. DISCHARGE INSTRUCTIONS THEATRE STAFF TAKE PATIENT STRAIGHT INTO MINOR OP THEATRE. IF DOCTOR NEEDS TO SEE- APPOINTMENT MADE STRAIGHT AWAY GIVEN TO PATIENT TEST 10 -15 MIN ALLOCATION FOLLOW/REVIEW AT OUTPATIENTS VOL APPOINTMENT NEXT DAY. INDICATED ON CARE PATHWAY REPORTS ADMISSION AT FRONT RECEPTION. DETAILS CHECKED 1 ST KUB - KID URETER BLADDER XRAY. PATIENT FULL BLADDER. 2 ND ULTRASOUND 2030 MINS IN RADIOLOGY. DR CANNING 3 1/2 HOUR SESSION PATIENT ARRIVES RECEPTION DAY SURGERY PATIENT X-RAY AND ULTRASOUND REPORT BACK TO BED. VERBAL REPORT TO PATIENT AND INFORMATION. IF RAH DR WILL INDICATE ON TAPE - SECRETARY WILL ARRANGE. TAKE PATIENT TO WARD AND TO BED AREA WITH NOTES. ADVICE TO UNDRESS/GOWN ON. TELL NURSING STAFF. DOCTOR SPEAKS TO PATIENTS CONSENT SIGNED TAKEN BACK TO DAY SURGERY
COMPASS WAITING LIST DIARY - CASE NOTES PULLED 3 WEEKS IN ADVANCE THEATRE LIST PRINTED L 4 HOURS BEFORE ALLOCATE BEDS THEATRE LIST SAME DAY FROM JANET. TRY 24 HOURS BEFORE RECEPTIONIST FINDS OUT IF THEY TO GO TO RADIOLOGY AND WHAT TIME 1 WEEK IN ADVANCE ADMIT PATIENT VIA CARE PLAN. 5 -10 MIN. LOOK AT MOD CHECK IF TO GO FOR ULTRASOUND - IF TO GO WALK THEM ROUND TO X-RAY WAITING ROOM. THEATRE STAFF ATTEND DAY SURGERY - DATA SHEET GIVEN TO DAY SURGERY STAFF. MAKE SURE PATIENT OK - ? DRINK OR EAT. DISCHARGE INSTRUCTIONS THEATRE STAFF TAKE PATIENT STRAIGHT INTO MINOR OP THEATRE. IF DOCTOR NEEDS TO SEE- APPOINTMENT MADE STRAIGHT AWAY GIVEN TO PATIENT TEST 10 -15 MIN ALLOCATION FOLLOW/REVIEW AT OUTPATIENTS VOL APPOINTMENT NEXT DAY. INDICATED ON CARE PATHWAY REPORTS ADMISSION AT FRONT RECEPTION. DETAILS CHECKED 1 ST KUB - KID URETER BLADDER XRAY. PATIENT FULL BLADDER. 2 ND ULTRASOUND 2030 MINS IN RADIOLOGY. DR CANNING 3 1/2 HOUR SESSION PATIENT ARRIVES RECEPTION DAY SURGERY PATIENT X-RAY AND ULTRASOUND REPORT BACK TO BED. VERBAL REPORT TO PATIENT AND INFORMATION. IF RAH DR WILL INDICATE ON TAPE - SECRETARY WILL ARRANGE. TAKE PATIENT TO WARD AND TO BED AREA WITH NOTES. ADVICE TO UNDRESS/GOWN ON. TELL NURSING STAFF. DOCTOR SPEAKS TO PATIENTS CONSENT SIGNED TAKEN BACK TO DAY SURGERY
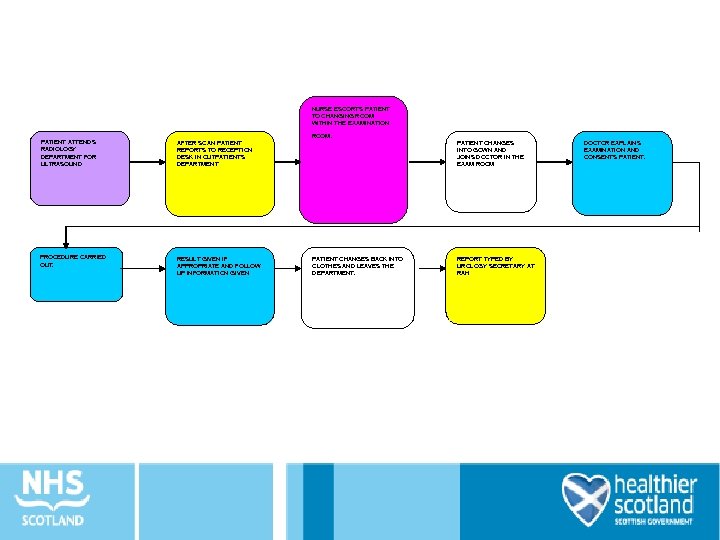 NURSE ESCORTS PATIENT TO CHANGING ROOM WITHIN THE EXAMINATION PATIENT ATTENDS RADIOLOGY DEPARTMENT FOR ULTRASOUND AFTER SCAN PATIENT REPORTS TO RECEPTION DESK IN OUTPATIENTS DEPARTMENT PROCEDURE CARRIED OUT. RESULT GIVEN IF APPROPRIATE AND FOLLOW UP INFORMATION GIVEN . ROOM PATIENT CHANGES BACK INTO CLOTHES AND LEAVES THE DEPARTMENT. PATIENT CHANGES INTO GOWN AND JOINS DOCTOR IN THE EXAM ROOM REPORT TYPED BY UROLOGY SECRETARY AT RAH DOCTOR EXPLAINS EXAMINATION AND CONSENTS PATIENT.
NURSE ESCORTS PATIENT TO CHANGING ROOM WITHIN THE EXAMINATION PATIENT ATTENDS RADIOLOGY DEPARTMENT FOR ULTRASOUND AFTER SCAN PATIENT REPORTS TO RECEPTION DESK IN OUTPATIENTS DEPARTMENT PROCEDURE CARRIED OUT. RESULT GIVEN IF APPROPRIATE AND FOLLOW UP INFORMATION GIVEN . ROOM PATIENT CHANGES BACK INTO CLOTHES AND LEAVES THE DEPARTMENT. PATIENT CHANGES INTO GOWN AND JOINS DOCTOR IN THE EXAM ROOM REPORT TYPED BY UROLOGY SECRETARY AT RAH DOCTOR EXPLAINS EXAMINATION AND CONSENTS PATIENT.
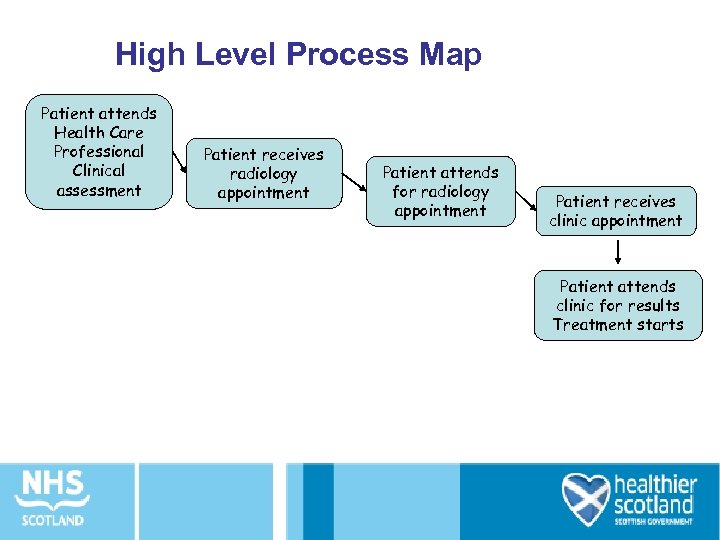 High Level Process Map Patient attends Health Care Professional Clinical assessment Patient receives radiology appointment Patient attends for radiology appointment Patient receives clinic appointment Patient attends clinic for results Treatment starts
High Level Process Map Patient attends Health Care Professional Clinical assessment Patient receives radiology appointment Patient attends for radiology appointment Patient receives clinic appointment Patient attends clinic for results Treatment starts
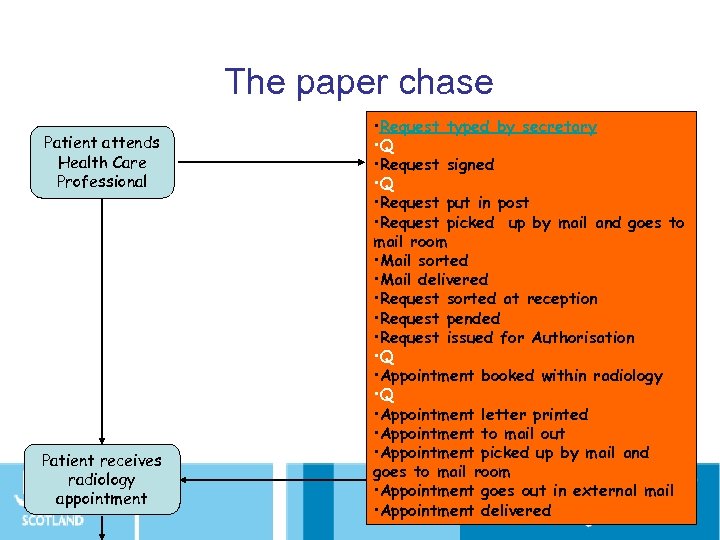 The paper chase Patient attends Health Care Professional Patient receives radiology appointment • Request typed by secretary • Q • Request signed • Q • Request put in post • Request picked up by mail and goes to mail room • Mail sorted • Mail delivered • Request sorted at reception • Request pended • Request issued for Authorisation • Q • Appointment booked within radiology • Q • Appointment letter printed • Appointment to mail out • Appointment picked up by mail and goes to mail room • Appointment goes out in external mail • Appointment delivered
The paper chase Patient attends Health Care Professional Patient receives radiology appointment • Request typed by secretary • Q • Request signed • Q • Request put in post • Request picked up by mail and goes to mail room • Mail sorted • Mail delivered • Request sorted at reception • Request pended • Request issued for Authorisation • Q • Appointment booked within radiology • Q • Appointment letter printed • Appointment to mail out • Appointment picked up by mail and goes to mail room • Appointment goes out in external mail • Appointment delivered
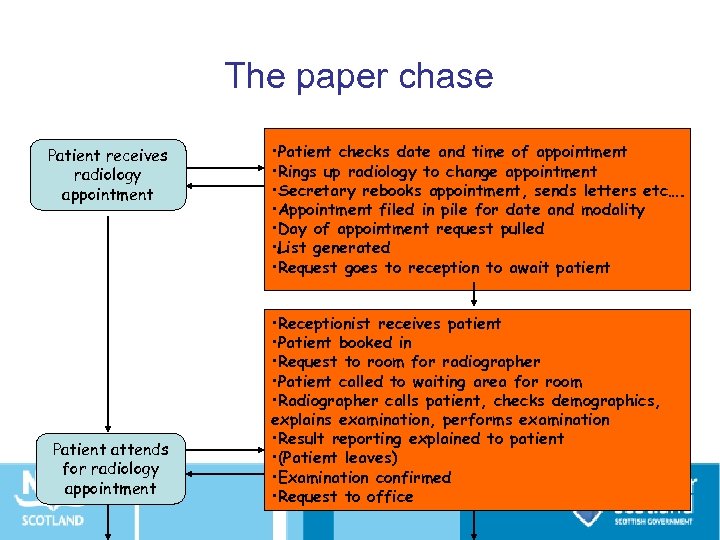 The paper chase Patient receives radiology appointment Patient attends for radiology appointment • Patient checks date and time of appointment • Rings up radiology to change appointment • Secretary rebooks appointment, sends letters etc…. • Appointment filed in pile for date and modality • Day of appointment request pulled • List generated • Request goes to reception to await patient • Receptionist receives patient • Patient booked in • Request to room for radiographer • Patient called to waiting area for room • Radiographer calls patient, checks demographics, explains examination, performs examination • Result reporting explained to patient • (Patient leaves) • Examination confirmed • Request to office
The paper chase Patient receives radiology appointment Patient attends for radiology appointment • Patient checks date and time of appointment • Rings up radiology to change appointment • Secretary rebooks appointment, sends letters etc…. • Appointment filed in pile for date and modality • Day of appointment request pulled • List generated • Request goes to reception to await patient • Receptionist receives patient • Patient booked in • Request to room for radiographer • Patient called to waiting area for room • Radiographer calls patient, checks demographics, explains examination, performs examination • Result reporting explained to patient • (Patient leaves) • Examination confirmed • Request to office
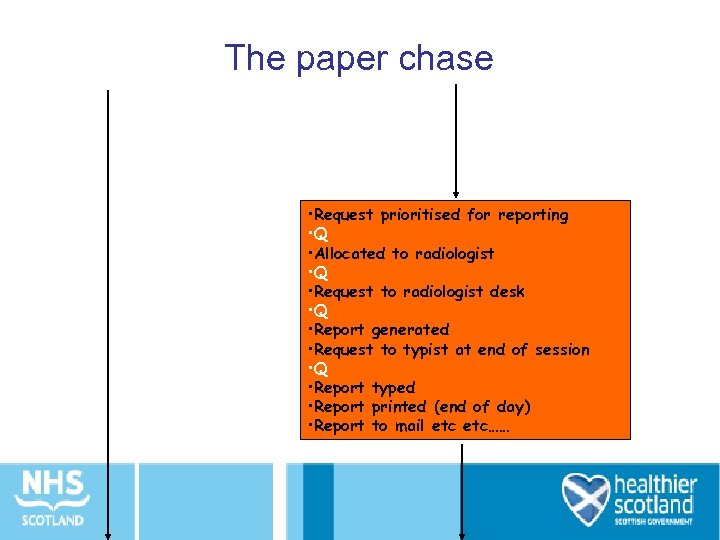 The paper chase • Request prioritised for reporting • Q • Allocated to radiologist • Q • Request to radiologist desk • Q • Report generated • Request to typist at end of session • Q • Report typed • Report printed (end of day) • Report to mail etc……
The paper chase • Request prioritised for reporting • Q • Allocated to radiologist • Q • Request to radiologist desk • Q • Report generated • Request to typist at end of session • Q • Report typed • Report printed (end of day) • Report to mail etc……
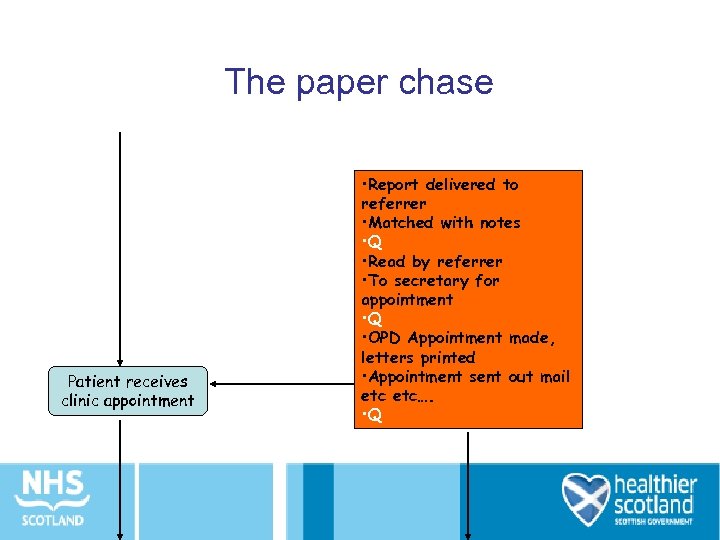 The paper chase Patient receives clinic appointment • Report delivered to referrer • Matched with notes • Q • Read by referrer • To secretary for appointment • Q • OPD Appointment made, letters printed • Appointment sent out mail etc…. • Q
The paper chase Patient receives clinic appointment • Report delivered to referrer • Matched with notes • Q • Read by referrer • To secretary for appointment • Q • OPD Appointment made, letters printed • Appointment sent out mail etc…. • Q
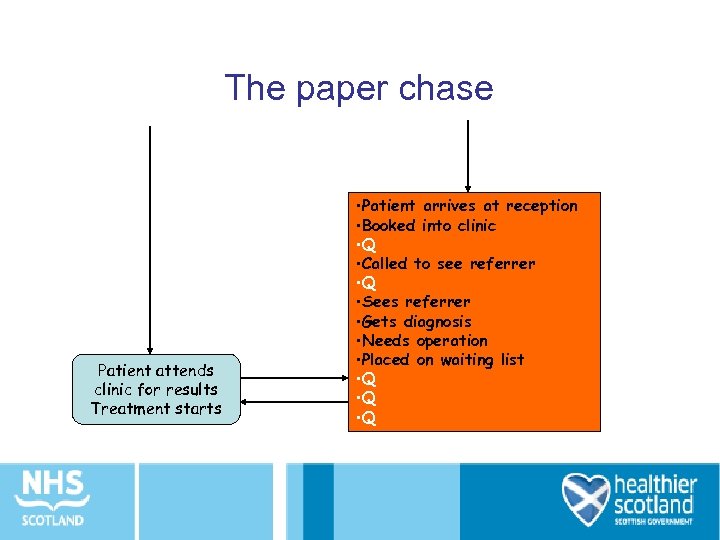 The paper chase Patient attends clinic for results Treatment starts • Patient arrives at reception • Booked into clinic • Q • Called to see referrer • Q • Sees referrer • Gets diagnosis • Needs operation • Placed on waiting list • Q • Q
The paper chase Patient attends clinic for results Treatment starts • Patient arrives at reception • Booked into clinic • Q • Called to see referrer • Q • Sees referrer • Gets diagnosis • Needs operation • Placed on waiting list • Q • Q
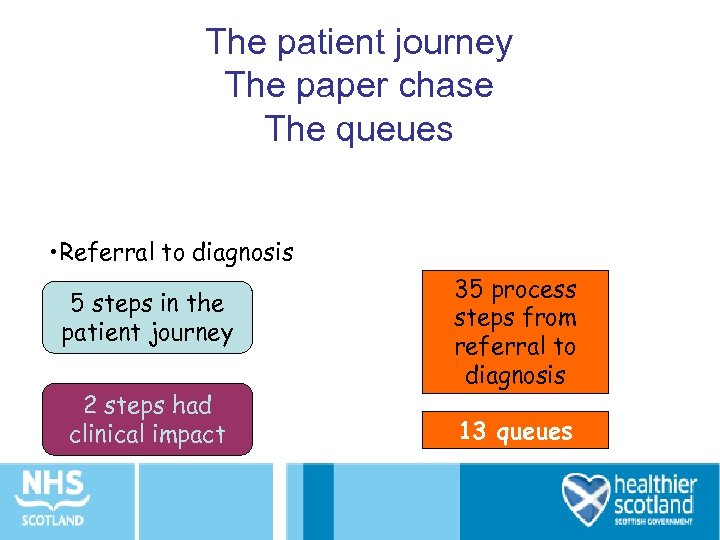 The patient journey The paper chase The queues • Referral to diagnosis 5 steps in the patient journey 2 steps had clinical impact 35 process steps from referral to diagnosis 13 queues
The patient journey The paper chase The queues • Referral to diagnosis 5 steps in the patient journey 2 steps had clinical impact 35 process steps from referral to diagnosis 13 queues
 What is value? • The activity is done right first time • The activity transforms the patient and moves them towards the next defined outcome • The activity is something that the patient cares about
What is value? • The activity is done right first time • The activity transforms the patient and moves them towards the next defined outcome • The activity is something that the patient cares about
 Activity: Identifying Value • Have a look at the process map • Which steps add value for the patient? • How many are there? • Which steps are necessary but don’t add value? • How many are there? • How long does the whole process take? • How much time adds value for the patient?
Activity: Identifying Value • Have a look at the process map • Which steps add value for the patient? • How many are there? • Which steps are necessary but don’t add value? • How many are there? • How long does the whole process take? • How much time adds value for the patient?
 Who to Involve • Small team 8 -12 people, mixed disciplines • Represent people at all the steps you will look at • ‘Fresh eyes’ • Patients/ carers • Nominate a team and clinical lead
Who to Involve • Small team 8 -12 people, mixed disciplines • Represent people at all the steps you will look at • ‘Fresh eyes’ • Patients/ carers • Nominate a team and clinical lead
 What to Measure Agree beforehand improvements in - Journey time for patients - Time spent on non value adding work - Throughput (productivity) - Morale / staff satisfaction
What to Measure Agree beforehand improvements in - Journey time for patients - Time spent on non value adding work - Throughput (productivity) - Morale / staff satisfaction
 Observe and Gather Data • Walk the patient journey - see the actual work place • Follow and make notes about each component – What happens to the patient – What staff are doing – What the information / communication flow is • Take photos of wastes
Observe and Gather Data • Walk the patient journey - see the actual work place • Follow and make notes about each component – What happens to the patient – What staff are doing – What the information / communication flow is • Take photos of wastes
 Measure the distance patients / staff have to travel
Measure the distance patients / staff have to travel
 Track both the patient and information flows
Track both the patient and information flows
 Take the cameras on the walkabout, you’ll never convey this verbally!
Take the cameras on the walkabout, you’ll never convey this verbally!
 What do patients actually experience and say about the process?
What do patients actually experience and say about the process?
 Ask staff at each step for their views on ‘show stoppers’, frustrations and positives
Ask staff at each step for their views on ‘show stoppers’, frustrations and positives
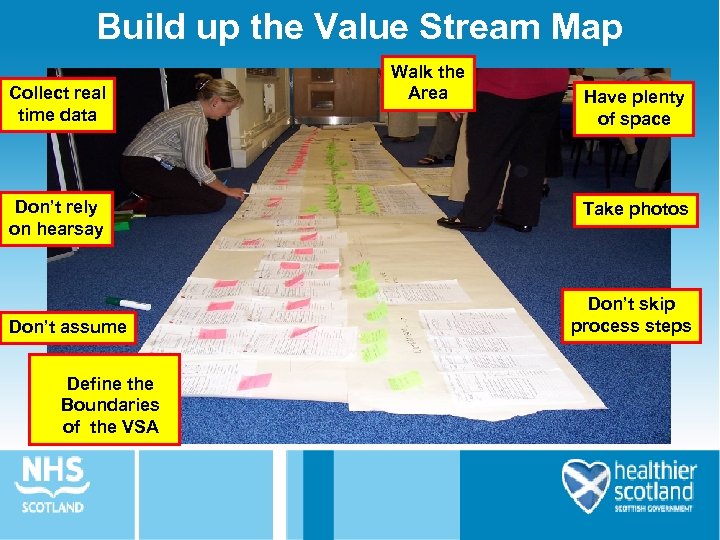 Build up the Value Stream Map Collect real time data Don’t rely on hearsay Don’t assume Define the Boundaries of the VSA Walk the Area Have plenty of space Take photos Don’t skip process steps
Build up the Value Stream Map Collect real time data Don’t rely on hearsay Don’t assume Define the Boundaries of the VSA Walk the Area Have plenty of space Take photos Don’t skip process steps
 Understanding your Current State Map: • Add value • Remove waste
Understanding your Current State Map: • Add value • Remove waste
 Coffee
Coffee
 Lean Tools Overview • • PDSA Glenday Sieve Workplace Organisation Rapid Improvement Events
Lean Tools Overview • • PDSA Glenday Sieve Workplace Organisation Rapid Improvement Events
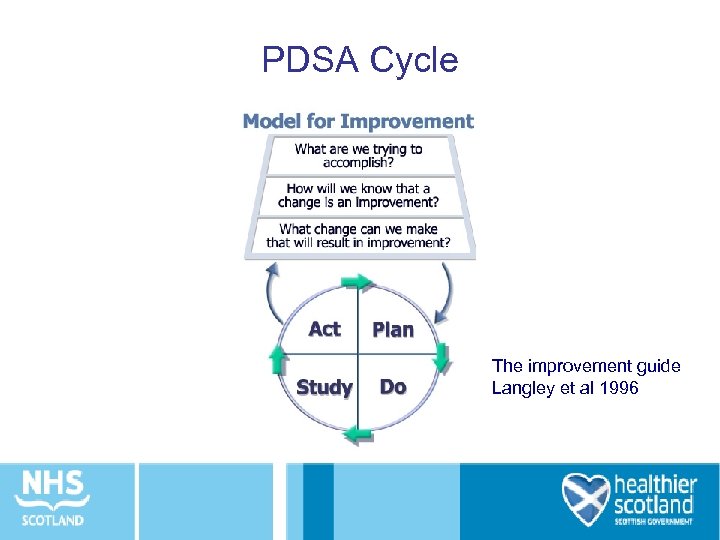 PDSA Cycle The improvement guide Langley et al 1996
PDSA Cycle The improvement guide Langley et al 1996
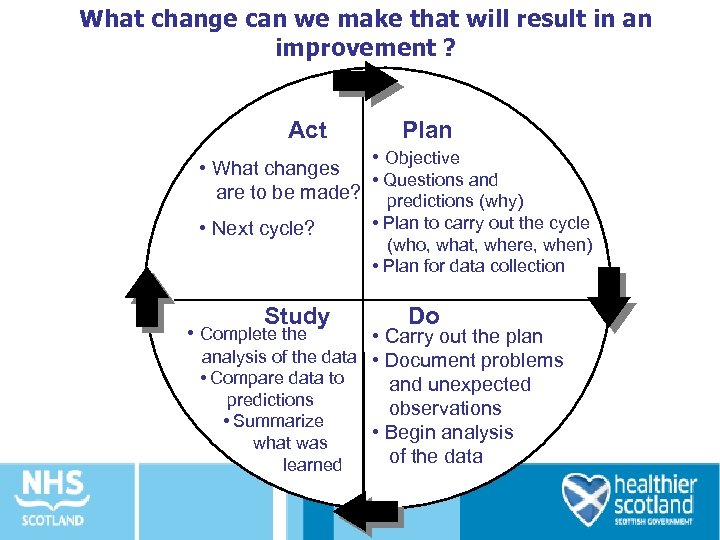 What change can we make that will result in an improvement ? Act Plan • Objective • What changes • Questions and are to be made? predictions (why) • Plan to carry out the cycle • Next cycle? (who, what, where, when) • Plan for data collection Study • Complete the Do • Carry out the plan analysis of the data • Document problems • Compare data to and unexpected predictions observations • Summarize • Begin analysis what was of the data learned
What change can we make that will result in an improvement ? Act Plan • Objective • What changes • Questions and are to be made? predictions (why) • Plan to carry out the cycle • Next cycle? (who, what, where, when) • Plan for data collection Study • Complete the Do • Carry out the plan analysis of the data • Document problems • Compare data to and unexpected predictions observations • Summarize • Begin analysis what was of the data learned
 PDSA Worksheet
PDSA Worksheet
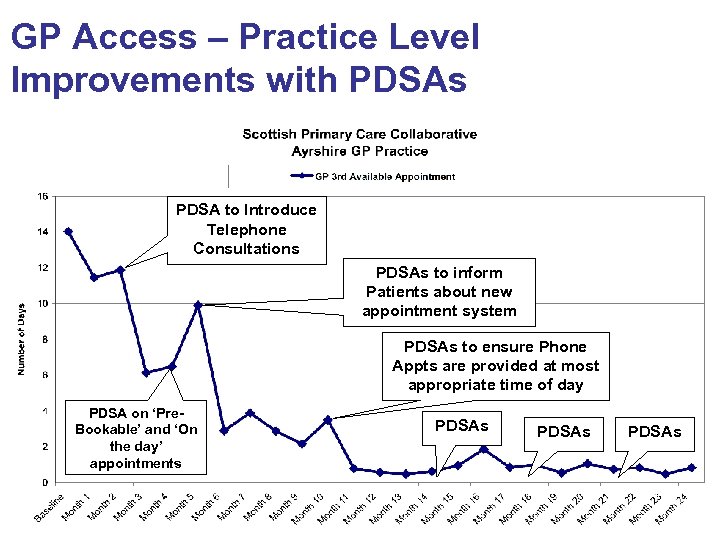 GP Access – Practice Level Improvements with PDSAs PDSA to Introduce Telephone Consultations PDSAs to inform Patients about new appointment system PDSAs to ensure Phone Appts are provided at most appropriate time of day PDSA on ‘Pre. Bookable’ and ‘On the day’ appointments PDSAs
GP Access – Practice Level Improvements with PDSAs PDSA to Introduce Telephone Consultations PDSAs to inform Patients about new appointment system PDSAs to ensure Phone Appts are provided at most appropriate time of day PDSA on ‘Pre. Bookable’ and ‘On the day’ appointments PDSAs
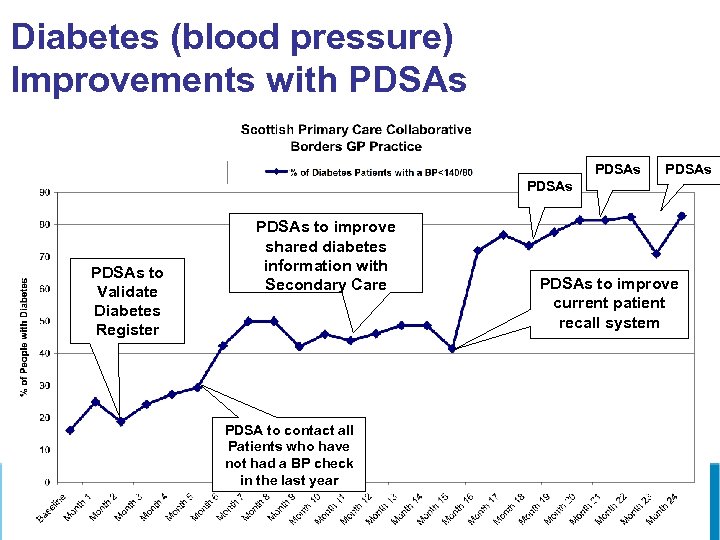 Diabetes (blood pressure) Improvements with PDSAs PDSAs to Validate Diabetes Register PDSAs to improve shared diabetes information with Secondary Care PDSA to contact all Patients who have not had a BP check in the last year PDSAs to improve current patient recall system
Diabetes (blood pressure) Improvements with PDSAs PDSAs to Validate Diabetes Register PDSAs to improve shared diabetes information with Secondary Care PDSA to contact all Patients who have not had a BP check in the last year PDSAs to improve current patient recall system
 Glenday Sieve • Heard of the Pareto (80/20 principle)? • Ladies – think of your wardrobe…. .
Glenday Sieve • Heard of the Pareto (80/20 principle)? • Ladies – think of your wardrobe…. .
 Glenday Seive Green Actual volume of activity 50% Range of possible activities 6% 6% of possible activities accounts for 50% of actual work done Process Map the “Greens” and make them flow Create time for the difficult cases
Glenday Seive Green Actual volume of activity 50% Range of possible activities 6% 6% of possible activities accounts for 50% of actual work done Process Map the “Greens” and make them flow Create time for the difficult cases
 Glenday Sieve • Orthopaedics – Hips and knees • General Surgery – hernias and lap cholecystectomy • District Nurse – wound care, medication
Glenday Sieve • Orthopaedics – Hips and knees • General Surgery – hernias and lap cholecystectomy • District Nurse – wound care, medication
 MRI Team, NHS Tayside • 220 codes for appointments MRI RIE - 63% of MRI throughput from 2. 7% of procedure codes (i. e. 6 codes) • Group patients by the process they go through (rather than clinical condition)
MRI Team, NHS Tayside • 220 codes for appointments MRI RIE - 63% of MRI throughput from 2. 7% of procedure codes (i. e. 6 codes) • Group patients by the process they go through (rather than clinical condition)
 Surgery example • 213 cases over 8 months at Clatterbridge. – 52% of theatre throughput from 4. 2% of procedures • Group patients by the process they go through (rather than clinical condition) • Focus initially on smart process for the critical few [4. 2%]
Surgery example • 213 cases over 8 months at Clatterbridge. – 52% of theatre throughput from 4. 2% of procedures • Group patients by the process they go through (rather than clinical condition) • Focus initially on smart process for the critical few [4. 2%]
 Workplace organisation
Workplace organisation
 6 S – A Technique to • Promote workplace organisation • Set and ensure adherence to standards • Embed the spirit of continuous improvement • Improve Quality, Cost Delivery, Safety and Morale
6 S – A Technique to • Promote workplace organisation • Set and ensure adherence to standards • Embed the spirit of continuous improvement • Improve Quality, Cost Delivery, Safety and Morale
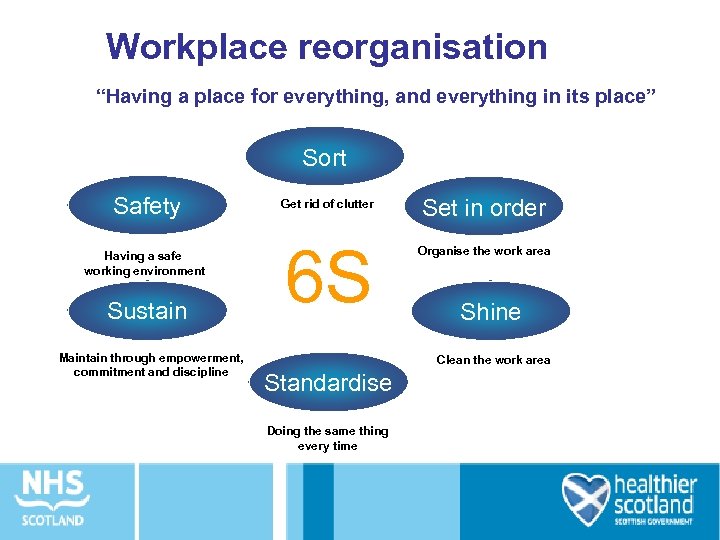 Workplace reorganisation “Having a place for everything, and everything in its place” Sort Safety Having a safe working environment Sustain Maintain through empowerment, commitment and discipline Get rid of clutter 6 S Set in order Organise the work area Shine Clean the work area Standardise Doing the same thing every time
Workplace reorganisation “Having a place for everything, and everything in its place” Sort Safety Having a safe working environment Sustain Maintain through empowerment, commitment and discipline Get rid of clutter 6 S Set in order Organise the work area Shine Clean the work area Standardise Doing the same thing every time
 Characteristics of a 6 S Workplace • • • Only have what is needed Clean enough to “eat off the floor” Everything is organised for the team Obvious to everyone when something is out of order Anything that is required can be retrieved within 30 seconds – No surprise shortages of supplies – visual management of stock levels • Responsibilities defined and everyone taking their responsibilities • Performance visible to all • Improvement ideas being routinely generated and implemented Adapted from Ross International, RIE Training material
Characteristics of a 6 S Workplace • • • Only have what is needed Clean enough to “eat off the floor” Everything is organised for the team Obvious to everyone when something is out of order Anything that is required can be retrieved within 30 seconds – No surprise shortages of supplies – visual management of stock levels • Responsibilities defined and everyone taking their responsibilities • Performance visible to all • Improvement ideas being routinely generated and implemented Adapted from Ross International, RIE Training material
 6 S Vision Taken from Ross International, RIE Training material Adapted from Ross International, RIE Training material
6 S Vision Taken from Ross International, RIE Training material Adapted from Ross International, RIE Training material
 Stracathro -Theatre Store Room Money is tied up in inventory gathering dust because of a supply chain process which is not aligned with the patient pathway value stream In amongst this is back up emergency equipment Clutter- time wasted trying to find things
Stracathro -Theatre Store Room Money is tied up in inventory gathering dust because of a supply chain process which is not aligned with the patient pathway value stream In amongst this is back up emergency equipment Clutter- time wasted trying to find things
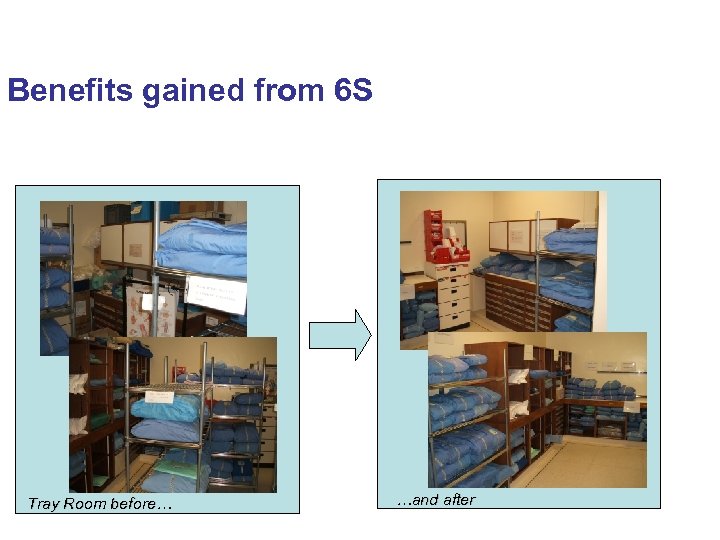 Benefits gained from 6 S Tray Room before… …and after
Benefits gained from 6 S Tray Room before… …and after

 Rapid Improvement Events (RIEs) – an overview
Rapid Improvement Events (RIEs) – an overview
 What are RIEs? • Common Lean tool to introduce Lean principles and thinking in organisations • RIEs select critical business areas and make real improvements for patients and staff • Process-focussed and brings together the team in a highly structured way • Results-focussed – establishing the root cause of problems, and achieving measurable improvements • Process which is action-orientated and data driven
What are RIEs? • Common Lean tool to introduce Lean principles and thinking in organisations • RIEs select critical business areas and make real improvements for patients and staff • Process-focussed and brings together the team in a highly structured way • Results-focussed – establishing the root cause of problems, and achieving measurable improvements • Process which is action-orientated and data driven
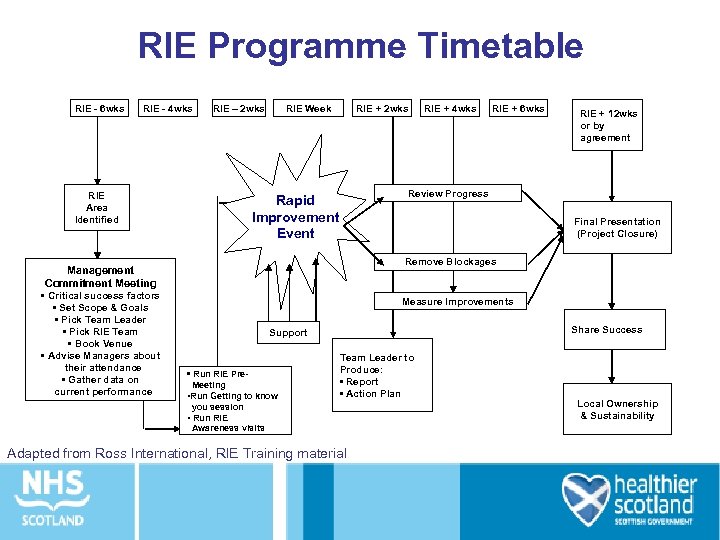 RIE Programme Timetable RIE - 6 wks RIE - 4 wks RIE – 2 wks RIE Area Identified RIE + 2 wks RIE + 4 wks RIE + 6 wks RIE + 12 wks or by agreement Review Progress Rapid Improvement Event Final Presentation (Project Closure) Remove Blockages Management Commitment Meeting • Critical success factors • Set Scope & Goals • Pick Team Leader • Pick RIE Team • Book Venue • Advise Managers about their attendance • Gather data on current performance RIE Week Measure Improvements Share Success Support • Run RIE Pre. Meeting • Run Getting to know Team Leader to Produce: • Report • Action Plan you session • Run RIE Awareness visits Adapted from Ross International, RIE Training material Local Ownership & Sustainability
RIE Programme Timetable RIE - 6 wks RIE - 4 wks RIE – 2 wks RIE Area Identified RIE + 2 wks RIE + 4 wks RIE + 6 wks RIE + 12 wks or by agreement Review Progress Rapid Improvement Event Final Presentation (Project Closure) Remove Blockages Management Commitment Meeting • Critical success factors • Set Scope & Goals • Pick Team Leader • Pick RIE Team • Book Venue • Advise Managers about their attendance • Gather data on current performance RIE Week Measure Improvements Share Success Support • Run RIE Pre. Meeting • Run Getting to know Team Leader to Produce: • Report • Action Plan you session • Run RIE Awareness visits Adapted from Ross International, RIE Training material Local Ownership & Sustainability
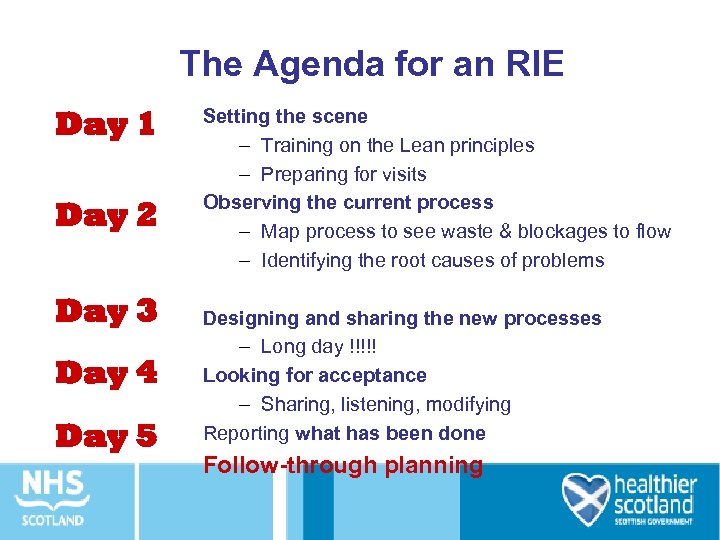 The Agenda for an RIE Day 1 Day 2 Day 3 Day 4 Day 5 Setting the scene – Training on the Lean principles – Preparing for visits Observing the current process – Map process to see waste & blockages to flow – Identifying the root causes of problems Designing and sharing the new processes – Long day !!!!! Looking for acceptance – Sharing, listening, modifying Reporting what has been done Follow-through planning
The Agenda for an RIE Day 1 Day 2 Day 3 Day 4 Day 5 Setting the scene – Training on the Lean principles – Preparing for visits Observing the current process – Map process to see waste & blockages to flow – Identifying the root causes of problems Designing and sharing the new processes – Long day !!!!! Looking for acceptance – Sharing, listening, modifying Reporting what has been done Follow-through planning
 One Team’s experience NHS Tayside Urology RIE
One Team’s experience NHS Tayside Urology RIE


