032d3e6dabf0bbc20bcaf4efa124c7d5.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 21
 Value of Money in Cancer - IMRT as a case study Jean H. E. Yong, MASc Pharmacoeconomics Research Unit, Cancer Care Ontario Canadian Centre for Applied Research in Cancer Control Applied Health Research Centre, St. Michael’s Hospital
Value of Money in Cancer - IMRT as a case study Jean H. E. Yong, MASc Pharmacoeconomics Research Unit, Cancer Care Ontario Canadian Centre for Applied Research in Cancer Control Applied Health Research Centre, St. Michael’s Hospital
 Key messages § It is important to consider Value for Money when planning and coordinating cancer care § Assessing value for money is not difficult, but needs to be relevant to the context § Let’s try to provide value for money every step along the cancer journey
Key messages § It is important to consider Value for Money when planning and coordinating cancer care § Assessing value for money is not difficult, but needs to be relevant to the context § Let’s try to provide value for money every step along the cancer journey
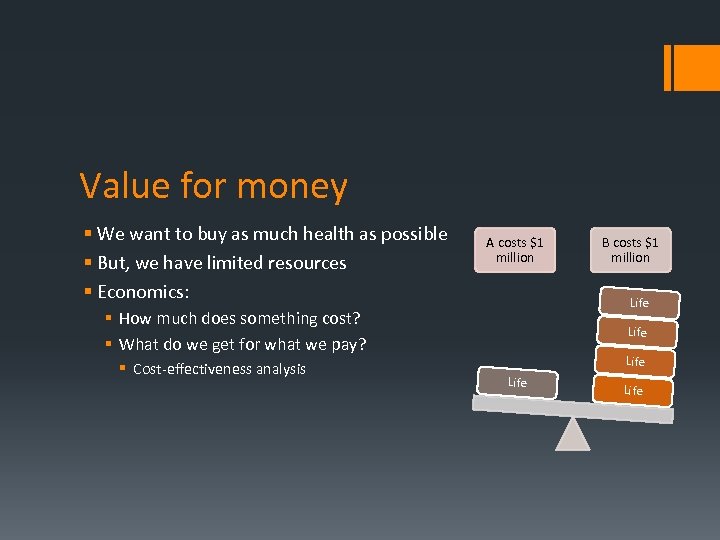 Value for money § We want to buy as much health as possible § But, we have limited resources § Economics: A costs $1 million Life § How much does something cost? § What do we get for what we pay? § Cost-effectiveness analysis B costs $1 million Life
Value for money § We want to buy as much health as possible § But, we have limited resources § Economics: A costs $1 million Life § How much does something cost? § What do we get for what we pay? § Cost-effectiveness analysis B costs $1 million Life
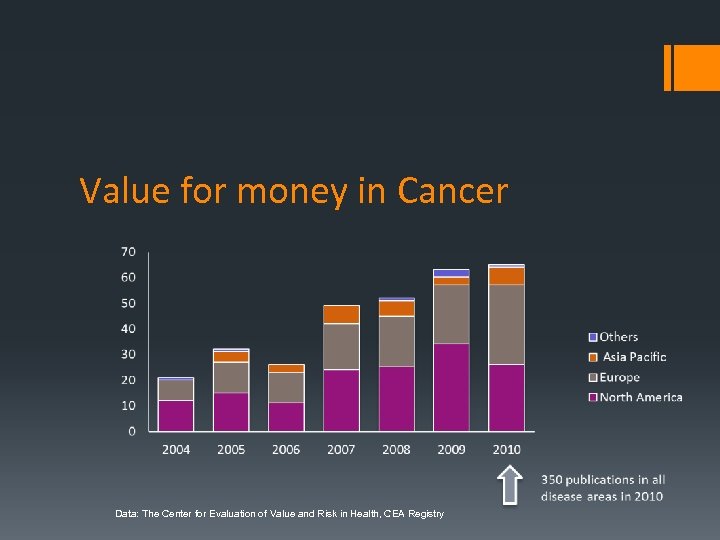 Value for money in Cancer Data: The Center for Evaluation of Value and Risk in Health, CEA Registry
Value for money in Cancer Data: The Center for Evaluation of Value and Risk in Health, CEA Registry
 Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT) § Introducing IMRT across Ontario § Which disease sites? § Is IMRT good value for money? § Can we afford it? Picture: Radiation Medical Group
Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT) § Introducing IMRT across Ontario § Which disease sites? § Is IMRT good value for money? § Can we afford it? Picture: Radiation Medical Group
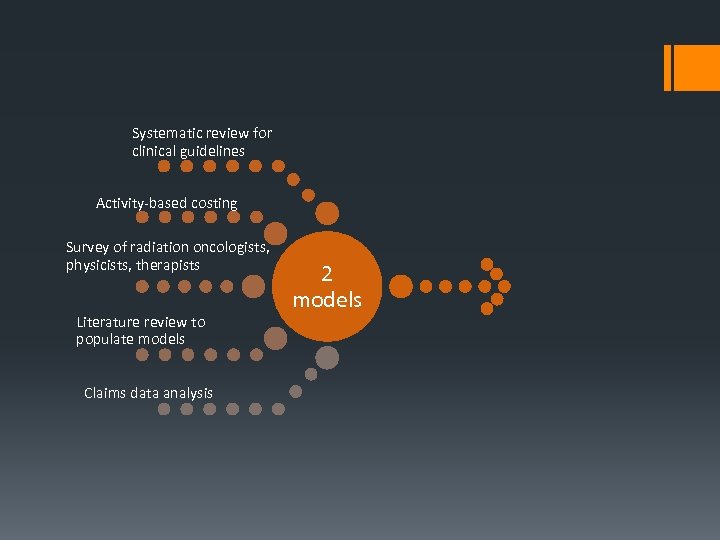 Systematic review for clinical guidelines Activity-based costing Survey of radiation oncologists, physicists, therapists Literature review to populate models Claims data analysis 2 models
Systematic review for clinical guidelines Activity-based costing Survey of radiation oncologists, physicists, therapists Literature review to populate models Claims data analysis 2 models
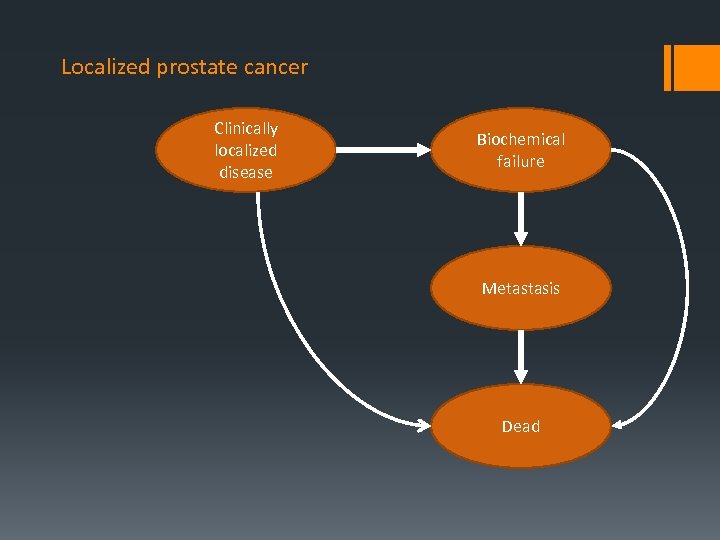 Localized prostate cancer Clinically localized disease Biochemical failure Metastasis Dead
Localized prostate cancer Clinically localized disease Biochemical failure Metastasis Dead
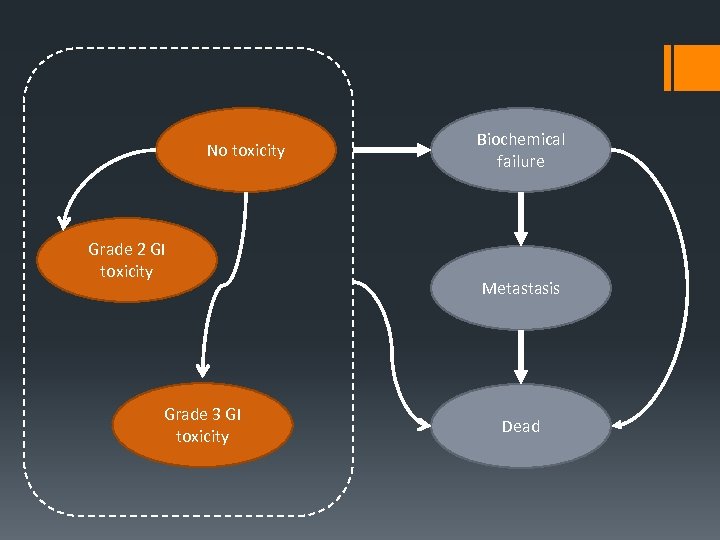 No toxicity Grade 2 GI toxicity Grade 3 GI toxicity Biochemical failure Metastasis Dead
No toxicity Grade 2 GI toxicity Grade 3 GI toxicity Biochemical failure Metastasis Dead
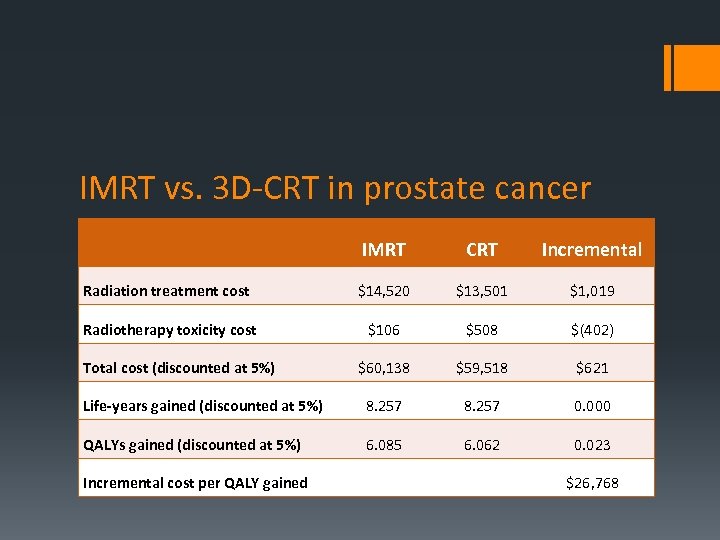 IMRT vs. 3 D-CRT in prostate cancer IMRT CRT Incremental Radiation treatment cost $14, 520 $13, 501 $1, 019 Radiotherapy toxicity cost $106 $508 $(402) $60, 138 $59, 518 $621 Life-years gained (discounted at 5%) 8. 257 0. 000 QALYs gained (discounted at 5%) 6. 085 6. 062 0. 023 Incremental cost per QALY gained $26, 768 Total cost (discounted at 5%)
IMRT vs. 3 D-CRT in prostate cancer IMRT CRT Incremental Radiation treatment cost $14, 520 $13, 501 $1, 019 Radiotherapy toxicity cost $106 $508 $(402) $60, 138 $59, 518 $621 Life-years gained (discounted at 5%) 8. 257 0. 000 QALYs gained (discounted at 5%) 6. 085 6. 062 0. 023 Incremental cost per QALY gained $26, 768 Total cost (discounted at 5%)
 Sensitivity analysis § Results were sensitive to the disease control assumption and treatment cost difference § When IMRT is delivered at a higher dose than CRT, it is cost saving and is more effective § When we add Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy to IMRT, IMRT has shorter treatment time than CRT and becomes cost saving § We estimated cost of IMRT for a mature program. In a start-up program scenario, IMRT costs $279, 850 per QALY.
Sensitivity analysis § Results were sensitive to the disease control assumption and treatment cost difference § When IMRT is delivered at a higher dose than CRT, it is cost saving and is more effective § When we add Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy to IMRT, IMRT has shorter treatment time than CRT and becomes cost saving § We estimated cost of IMRT for a mature program. In a start-up program scenario, IMRT costs $279, 850 per QALY.
 IMRT vs. 2 D-RT in head and neck cancers § Compared with 2 D-RT, IMRT reduces xerostomia and improves quality of life § IMRT is less expensive than CRT § saves $1100 per patient § IMRT takes longer to plan but less time to deliver § Results are most sensitive to the cost difference between treatment § In a start up program scenario: $162, 000 per QALY
IMRT vs. 2 D-RT in head and neck cancers § Compared with 2 D-RT, IMRT reduces xerostomia and improves quality of life § IMRT is less expensive than CRT § saves $1100 per patient § IMRT takes longer to plan but less time to deliver § Results are most sensitive to the cost difference between treatment § In a start up program scenario: $162, 000 per QALY
 Discussion § Results are specific to the research questions § Not generalizable to other indications § Specific to the comparator § Radiotherapy costs vary across countries § Validate model § Literature review and sensitivity analysis
Discussion § Results are specific to the research questions § Not generalizable to other indications § Specific to the comparator § Radiotherapy costs vary across countries § Validate model § Literature review and sensitivity analysis
 Success Factors § An in house health economics unit § Effective partnerships with many stakeholders § Academics § Community providers § Evaluation part of an implementation strategy
Success Factors § An in house health economics unit § Effective partnerships with many stakeholders § Academics § Community providers § Evaluation part of an implementation strategy
 Cancer journey Prevention Screening Diagnosis Treatment Recovery and palliative
Cancer journey Prevention Screening Diagnosis Treatment Recovery and palliative
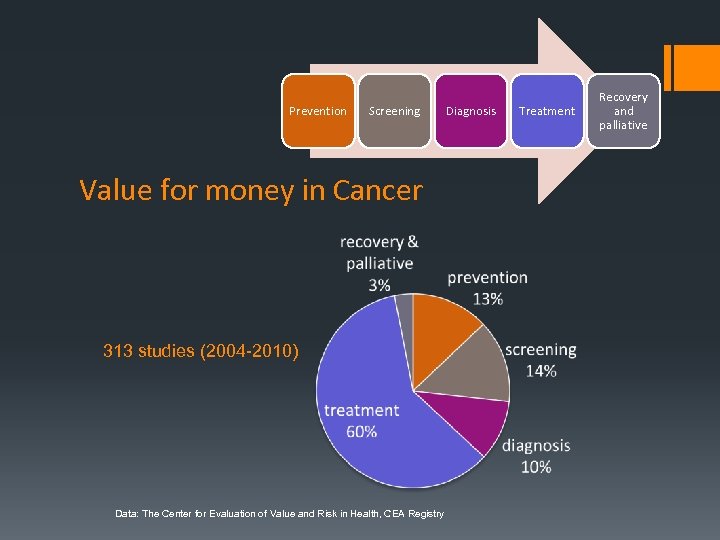 Prevention Screening Value for money in Cancer 313 studies (2004 -2010) Data: The Center for Evaluation of Value and Risk in Health, CEA Registry Diagnosis Treatment Recovery and palliative
Prevention Screening Value for money in Cancer 313 studies (2004 -2010) Data: The Center for Evaluation of Value and Risk in Health, CEA Registry Diagnosis Treatment Recovery and palliative
 Key messages § It is important to consider Value for Money when planning and coordinating cancer care § Assessing value for money is not difficult, but needs to be relevant to the context § Let’s try to provide value for money every step along the cancer journey
Key messages § It is important to consider Value for Money when planning and coordinating cancer care § Assessing value for money is not difficult, but needs to be relevant to the context § Let’s try to provide value for money every step along the cancer journey
 Acknowledgements § Dr. Jeffrey Hoch & Jaclyn Beca § Cancer Care Ontario § Community practitioners § Radiation oncologists, physicists, therapists § Academic collaborators § Drs. Tom Mc. Gowan and Murray Krahn § IMRT Indications Expert Panel § Drs. Brian O’Sullivan and Glenn Bauman Ontario Ministry of Health and Long-Term Care
Acknowledgements § Dr. Jeffrey Hoch & Jaclyn Beca § Cancer Care Ontario § Community practitioners § Radiation oncologists, physicists, therapists § Academic collaborators § Drs. Tom Mc. Gowan and Murray Krahn § IMRT Indications Expert Panel § Drs. Brian O’Sullivan and Glenn Bauman Ontario Ministry of Health and Long-Term Care
 Jean. yong@cancercare. on. ca Thank you.
Jean. yong@cancercare. on. ca Thank you.
 Cancer Care in Canada § Universal health care § Limited access to interventions that are not covered by public payers § § Public health agency Provincial cancer agencies Provincial drug plans Hospitals
Cancer Care in Canada § Universal health care § Limited access to interventions that are not covered by public payers § § Public health agency Provincial cancer agencies Provincial drug plans Hospitals
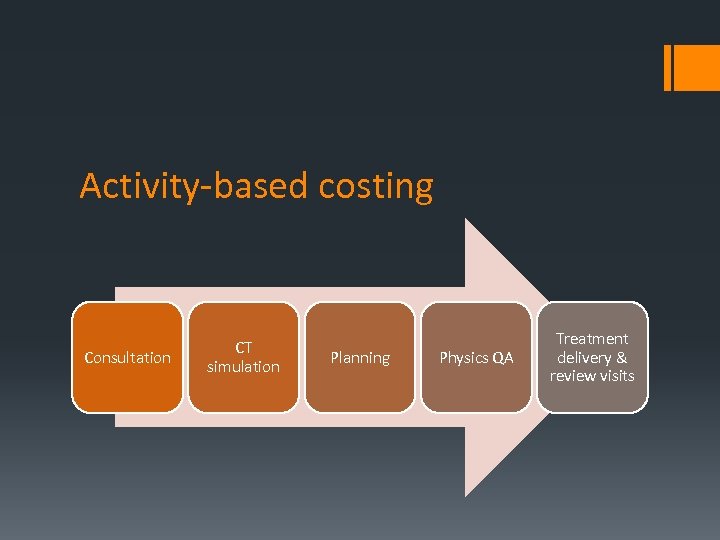 Activity-based costing Consultation CT simulation Planning Physics QA Treatment delivery & review visits
Activity-based costing Consultation CT simulation Planning Physics QA Treatment delivery & review visits


