884fdc18881134b6ff56f0e6182c81ff.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 22
 Value creation from IS Integration: From ASP to Web Services? Wendy. L. Currie Warwick Business School Presentation at ESRC Seminar – Nottingham University Business School, UK June 2004
Value creation from IS Integration: From ASP to Web Services? Wendy. L. Currie Warwick Business School Presentation at ESRC Seminar – Nottingham University Business School, UK June 2004
 Overview n n EPSRC and ESRC Funded Research Project 2000 -2004 The ASP market - A Flawed e-business model? Web Services - Integration: The Missing Link? Case Study – Implementing A Compliance System in the Financial Services Sector
Overview n n EPSRC and ESRC Funded Research Project 2000 -2004 The ASP market - A Flawed e-business model? Web Services - Integration: The Missing Link? Case Study – Implementing A Compliance System in the Financial Services Sector
 Research studies n n £ 193, 000 from EPSRC: ‘Assessing the deployment, hosting and integration of business-critical information systems by application service providers’ (BC-ASP). October 01 -September 03. £ 258, 000 (plus £ 195, 000 to Fullard Learning Ltd and DCS. com Ltd) from ESRC: ‘Developing a riskassessment framework for deploying, hosting and integrating vertical and horizontal information systems by application service providers’ (ASP-VH). March 02 -February 04.
Research studies n n £ 193, 000 from EPSRC: ‘Assessing the deployment, hosting and integration of business-critical information systems by application service providers’ (BC-ASP). October 01 -September 03. £ 258, 000 (plus £ 195, 000 to Fullard Learning Ltd and DCS. com Ltd) from ESRC: ‘Developing a riskassessment framework for deploying, hosting and integrating vertical and horizontal information systems by application service providers’ (ASP-VH). March 02 -February 04.
 ASP Definition “An ASP manages and delivers application capabilities to multiple entities from data centres across a wide area network (WAN)”. ASP Industry Consortium
ASP Definition “An ASP manages and delivers application capabilities to multiple entities from data centres across a wide area network (WAN)”. ASP Industry Consortium
 Ecosystem For Hosted Applications
Ecosystem For Hosted Applications
 Early predictions – ASP Market $24 Billion by 2005 $18 Billion by 2005 $23 Billion by 2003 $22. 7 Billion by 2003 $19. 2 Billion by 2003 IDC, 2001 Gartner Group, 2001 Forrester, 2000 Data. Quest, 2000 Yankee Group, 2000
Early predictions – ASP Market $24 Billion by 2005 $18 Billion by 2005 $23 Billion by 2003 $22. 7 Billion by 2003 $19. 2 Billion by 2003 IDC, 2001 Gartner Group, 2001 Forrester, 2000 Data. Quest, 2000 Yankee Group, 2000
 Spending on ASPs n n n IDC says companies spent roughly $245 million on application service provider (ASP) services in 2001 Manufacturers spent $221 million on ASP services in 2001 But 60% of ASPs predicted not to survive! (Gartner Group)
Spending on ASPs n n n IDC says companies spent roughly $245 million on application service provider (ASP) services in 2001 Manufacturers spent $221 million on ASP services in 2001 But 60% of ASPs predicted not to survive! (Gartner Group)
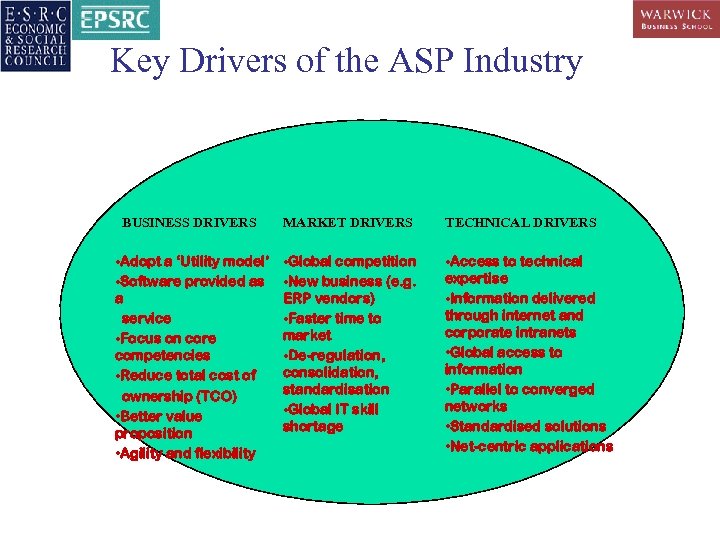 Key Drivers of the ASP Industry BUSINESS DRIVERS MARKET DRIVERS TECHNICAL DRIVERS • Adopt a ‘Utility model’ • Software provided as a service • Focus on core competencies • Reduce total cost of ownership (TCO) • Better value proposition • Agility and flexibility • Global competition • New business (e. g. ERP vendors) • Faster time to market • De-regulation, consolidation, standardisation • Global IT skill shortage • Access to technical expertise • Information delivered through internet and corporate intranets • Global access to information • Parallel to converged networks • Standardised solutions • Net-centric applications
Key Drivers of the ASP Industry BUSINESS DRIVERS MARKET DRIVERS TECHNICAL DRIVERS • Adopt a ‘Utility model’ • Software provided as a service • Focus on core competencies • Reduce total cost of ownership (TCO) • Better value proposition • Agility and flexibility • Global competition • New business (e. g. ERP vendors) • Faster time to market • De-regulation, consolidation, standardisation • Global IT skill shortage • Access to technical expertise • Information delivered through internet and corporate intranets • Global access to information • Parallel to converged networks • Standardised solutions • Net-centric applications
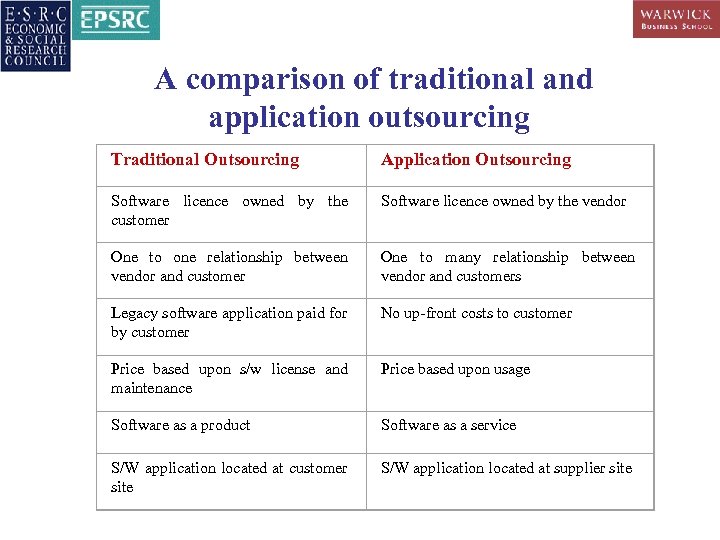 A comparison of traditional and application outsourcing Traditional Outsourcing Application Outsourcing Software licence owned by the customer Software licence owned by the vendor One to one relationship between vendor and customer One to many relationship between vendor and customers Legacy software application paid for by customer No up-front costs to customer Price based upon s/w license and maintenance Price based upon usage Software as a product Software as a service S/W application located at customer site S/W application located at supplier site
A comparison of traditional and application outsourcing Traditional Outsourcing Application Outsourcing Software licence owned by the customer Software licence owned by the vendor One to one relationship between vendor and customer One to many relationship between vendor and customers Legacy software application paid for by customer No up-front costs to customer Price based upon s/w license and maintenance Price based upon usage Software as a product Software as a service S/W application located at customer site S/W application located at supplier site
 ASP and Integration n n n Integration of applications across multiple platforms, sites and environments Business process re-design through integration To create a ‘seamless’ IT organisation Integration of billing information into auditing and reporting systems To create an infrastructure for better manageability To achieve faster software application implementation Resultant synergy from combination of applications
ASP and Integration n n n Integration of applications across multiple platforms, sites and environments Business process re-design through integration To create a ‘seamless’ IT organisation Integration of billing information into auditing and reporting systems To create an infrastructure for better manageability To achieve faster software application implementation Resultant synergy from combination of applications
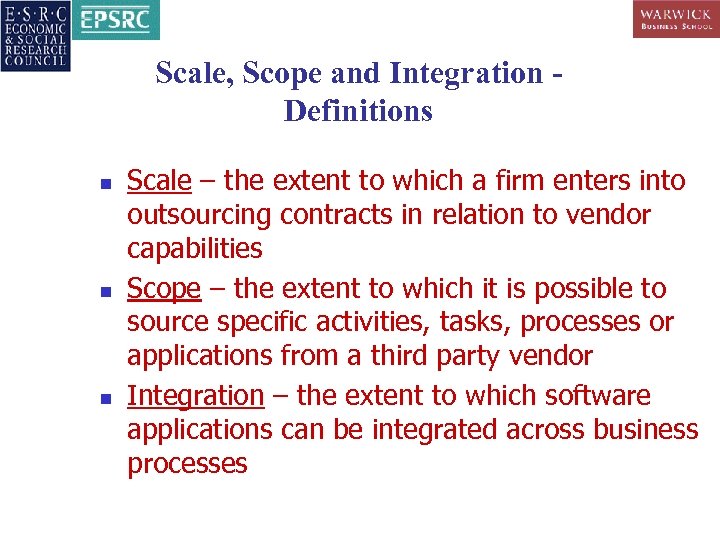 Scale, Scope and Integration Definitions n n n Scale – the extent to which a firm enters into outsourcing contracts in relation to vendor capabilities Scope – the extent to which it is possible to source specific activities, tasks, processes or applications from a third party vendor Integration – the extent to which software applications can be integrated across business processes
Scale, Scope and Integration Definitions n n n Scale – the extent to which a firm enters into outsourcing contracts in relation to vendor capabilities Scope – the extent to which it is possible to source specific activities, tasks, processes or applications from a third party vendor Integration – the extent to which software applications can be integrated across business processes
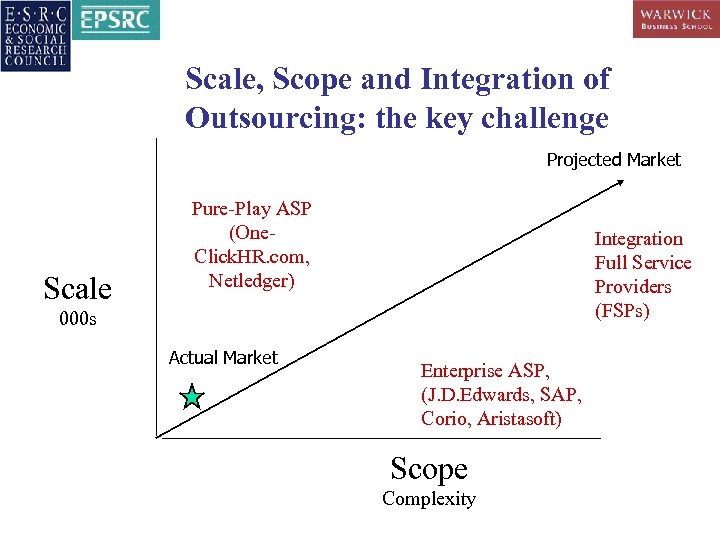 Scale, Scope and Integration of Outsourcing: the key challenge Projected Market Scale Pure-Play ASP (One. Click. HR. com, Netledger) Integration Full Service Providers (FSPs) 000 s Actual Market Enterprise ASP, (J. D. Edwards, SAP, Corio, Aristasoft) Scope Complexity
Scale, Scope and Integration of Outsourcing: the key challenge Projected Market Scale Pure-Play ASP (One. Click. HR. com, Netledger) Integration Full Service Providers (FSPs) 000 s Actual Market Enterprise ASP, (J. D. Edwards, SAP, Corio, Aristasoft) Scope Complexity
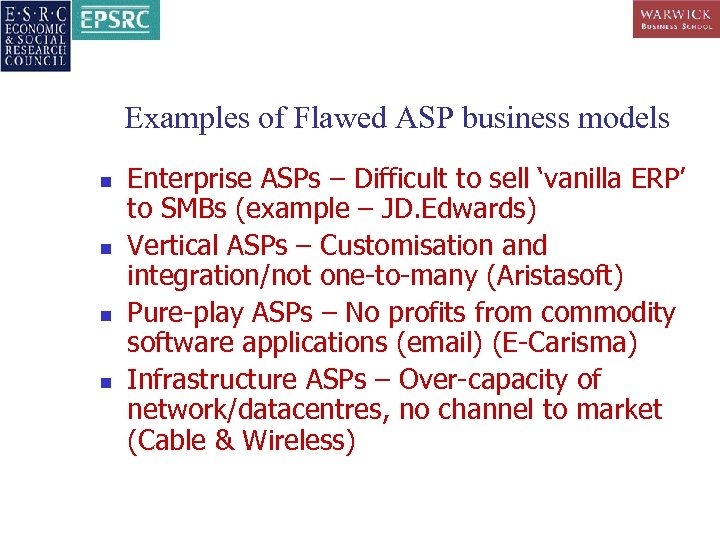 Examples of Flawed ASP business models n n Enterprise ASPs – Difficult to sell ‘vanilla ERP’ to SMBs (example – JD. Edwards) Vertical ASPs – Customisation and integration/not one-to-many (Aristasoft) Pure-play ASPs – No profits from commodity software applications (email) (E-Carisma) Infrastructure ASPs – Over-capacity of network/datacentres, no channel to market (Cable & Wireless)
Examples of Flawed ASP business models n n Enterprise ASPs – Difficult to sell ‘vanilla ERP’ to SMBs (example – JD. Edwards) Vertical ASPs – Customisation and integration/not one-to-many (Aristasoft) Pure-play ASPs – No profits from commodity software applications (email) (E-Carisma) Infrastructure ASPs – Over-capacity of network/datacentres, no channel to market (Cable & Wireless)
 The first-phase ASP market – a false start n n n One-to-many became same-for-all No profits from commodity software applications (email, MS office, etc) ASPs focused too much on marketing – not on revenue generation SMBs were unconvinced about the benefits of the ASP model ASPs failed to ‘create value’ for customers Technology platforms/software not webcentric
The first-phase ASP market – a false start n n n One-to-many became same-for-all No profits from commodity software applications (email, MS office, etc) ASPs focused too much on marketing – not on revenue generation SMBs were unconvinced about the benefits of the ASP model ASPs failed to ‘create value’ for customers Technology platforms/software not webcentric
 ASP and Web Services n n n Convergence between telecommunications and computing industries will continue Market consolidation of ASP vendors Web services will facilitate BPO Value creation through customization and integration ASP vendors need to develop business models which address scale, scope and integration
ASP and Web Services n n n Convergence between telecommunications and computing industries will continue Market consolidation of ASP vendors Web services will facilitate BPO Value creation through customization and integration ASP vendors need to develop business models which address scale, scope and integration
 ASP and Web Services • • • • • Commodity ASP 1990 s One-to-many – point solution 24 x 7 availability High scalability Economies of Scale Efficiency (of business applications) Individual performance improvement Utility pricing models Packaged ‘Stand-alone’ applications Functional data/information Application integration Remote C/V relationship Application outsourcing Service Level Agreement (SLA) Application-centric Continuous improvement Inter-departmental change Technology peripheral to core business Silo effect • • • • • Web Services 2000+ Many-to-many - Enterprise-wide 24 x 7 availability Unlimited Scalability Economies of Scale and Scope Adaptiveness (to business change) Enterprise-wide improvement Multiple, fluctuating pricing models Component based applications Business Intelligence Synergy of combination of applications Loosely-coupled C/V relationship Business process outsourcing Multiple SLAs Industry-centric Changing Industry/market dynamics Industry-wide change Mixed technology portfolio Synergistic (more than the sum of the parts)
ASP and Web Services • • • • • Commodity ASP 1990 s One-to-many – point solution 24 x 7 availability High scalability Economies of Scale Efficiency (of business applications) Individual performance improvement Utility pricing models Packaged ‘Stand-alone’ applications Functional data/information Application integration Remote C/V relationship Application outsourcing Service Level Agreement (SLA) Application-centric Continuous improvement Inter-departmental change Technology peripheral to core business Silo effect • • • • • Web Services 2000+ Many-to-many - Enterprise-wide 24 x 7 availability Unlimited Scalability Economies of Scale and Scope Adaptiveness (to business change) Enterprise-wide improvement Multiple, fluctuating pricing models Component based applications Business Intelligence Synergy of combination of applications Loosely-coupled C/V relationship Business process outsourcing Multiple SLAs Industry-centric Changing Industry/market dynamics Industry-wide change Mixed technology portfolio Synergistic (more than the sum of the parts)
 Web Services Definition ‘Web Services are loosely coupled software components delivered over Internet standard technologies. A Web Service represents a business function or business service and can be accessed by another application…over public networks using generally available protocols. . ’ (IDC, 2001).
Web Services Definition ‘Web Services are loosely coupled software components delivered over Internet standard technologies. A Web Service represents a business function or business service and can be accessed by another application…over public networks using generally available protocols. . ’ (IDC, 2001).
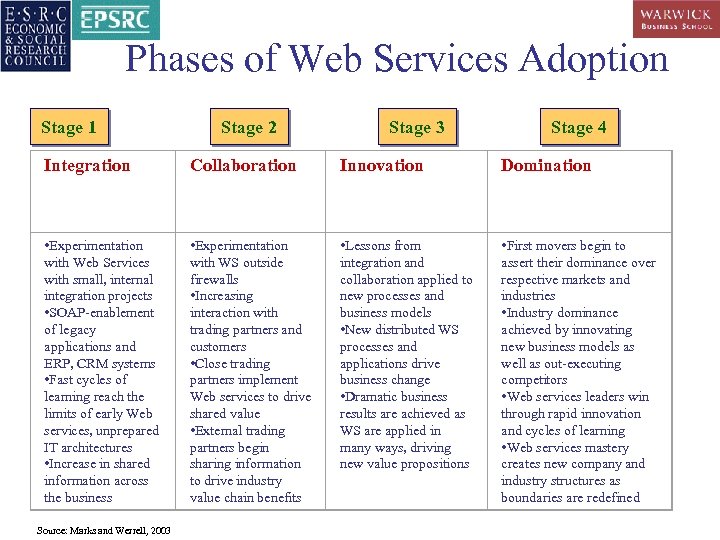 Phases of Web Services Adoption Stage 1 Stage 2 Stage 3 Stage 4 Integration Collaboration Innovation Domination • Experimentation with Web Services with small, internal integration projects • SOAP-enablement of legacy applications and ERP, CRM systems • Fast cycles of learning reach the limits of early Web services, unprepared IT architectures • Increase in shared information across the business • Experimentation with WS outside firewalls • Increasing interaction with trading partners and customers • Close trading partners implement Web services to drive shared value • External trading partners begin sharing information to drive industry value chain benefits • Lessons from integration and collaboration applied to new processes and business models • New distributed WS processes and applications drive business change • Dramatic business results are achieved as WS are applied in many ways, driving new value propositions • First movers begin to assert their dominance over respective markets and industries • Industry dominance achieved by innovating new business models as well as out-executing competitors • Web services leaders win through rapid innovation and cycles of learning • Web services mastery creates new company and industry structures as boundaries are redefined Source: Marks and Werrell, 2003
Phases of Web Services Adoption Stage 1 Stage 2 Stage 3 Stage 4 Integration Collaboration Innovation Domination • Experimentation with Web Services with small, internal integration projects • SOAP-enablement of legacy applications and ERP, CRM systems • Fast cycles of learning reach the limits of early Web services, unprepared IT architectures • Increase in shared information across the business • Experimentation with WS outside firewalls • Increasing interaction with trading partners and customers • Close trading partners implement Web services to drive shared value • External trading partners begin sharing information to drive industry value chain benefits • Lessons from integration and collaboration applied to new processes and business models • New distributed WS processes and applications drive business change • Dramatic business results are achieved as WS are applied in many ways, driving new value propositions • First movers begin to assert their dominance over respective markets and industries • Industry dominance achieved by innovating new business models as well as out-executing competitors • Web services leaders win through rapid innovation and cycles of learning • Web services mastery creates new company and industry structures as boundaries are redefined Source: Marks and Werrell, 2003
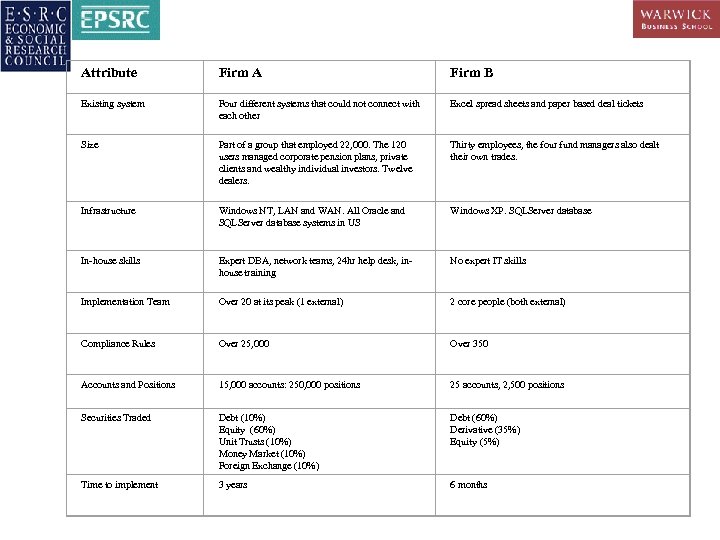 Attribute Firm A Firm B Existing system Four different systems that could not connect with each other Excel spread sheets and paper based deal tickets Size Part of a group that employed 22, 000. The 120 users managed corporate pension plans, private clients and wealthy individual investors. Twelve dealers. Thirty employees, the four fund managers also dealt their own trades. Infrastructure Windows NT, LAN and WAN. All Oracle and SQLServer database systems in US Windows XP. SQLServer database In-house skills Expert DBA, network teams, 24 hr help desk, inhouse training No expert IT skills Implementation Team Over 20 at its peak (1 external) 2 core people (both external) Compliance Rules Over 25, 000 Over 350 Accounts and Positions 15, 000 accounts: 250, 000 positions 25 accounts, 2, 500 positions Securities Traded Debt (10%) Equity (60%) Unit Trusts (10%) Money Market (10%) Foreign Exchange (10%) Debt (60%) Derivative (35%) Equity (5%) Time to implement 3 years 6 months
Attribute Firm A Firm B Existing system Four different systems that could not connect with each other Excel spread sheets and paper based deal tickets Size Part of a group that employed 22, 000. The 120 users managed corporate pension plans, private clients and wealthy individual investors. Twelve dealers. Thirty employees, the four fund managers also dealt their own trades. Infrastructure Windows NT, LAN and WAN. All Oracle and SQLServer database systems in US Windows XP. SQLServer database In-house skills Expert DBA, network teams, 24 hr help desk, inhouse training No expert IT skills Implementation Team Over 20 at its peak (1 external) 2 core people (both external) Compliance Rules Over 25, 000 Over 350 Accounts and Positions 15, 000 accounts: 250, 000 positions 25 accounts, 2, 500 positions Securities Traded Debt (10%) Equity (60%) Unit Trusts (10%) Money Market (10%) Foreign Exchange (10%) Debt (60%) Derivative (35%) Equity (5%) Time to implement 3 years 6 months
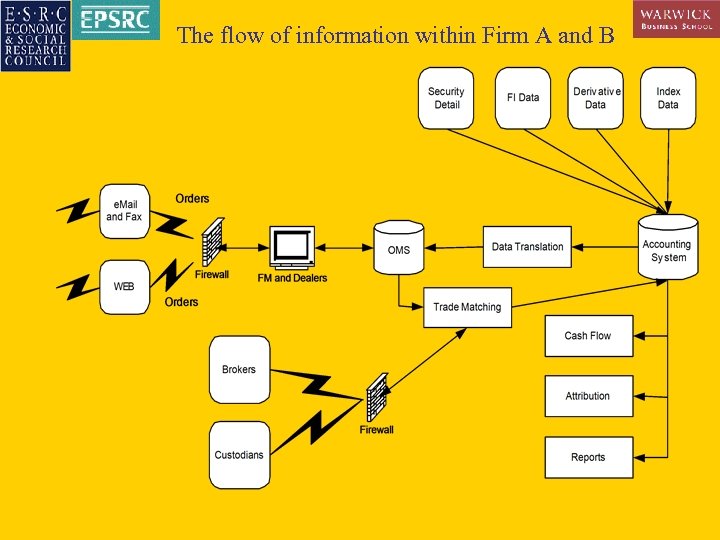 The flow of information within Firm A and B
The flow of information within Firm A and B
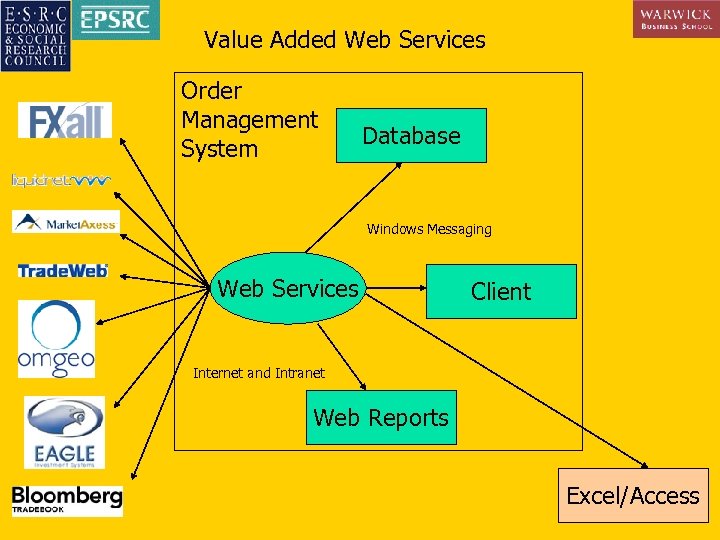 Value Added Web Services Order Management System Database Windows Messaging Web Services Client Internet and Intranet Web Reports Excel/Access
Value Added Web Services Order Management System Database Windows Messaging Web Services Client Internet and Intranet Web Reports Excel/Access
 Conclusion n n Market driven towards using Web services for straight through processing From One to Many (ASP) to Many (Web Services) Speed of Integration improved with standardisation of interfaces (XML) Increased liquidity (i. e. allows more buyers/sellers to trade simultaneously)
Conclusion n n Market driven towards using Web services for straight through processing From One to Many (ASP) to Many (Web Services) Speed of Integration improved with standardisation of interfaces (XML) Increased liquidity (i. e. allows more buyers/sellers to trade simultaneously)


