67bf3c73ffff4e1aca46a064ebfc37dc.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 41

Value creating processes conceptual framework

About the Syllabus n Two lecturers: n n András István Kun, Ph. D, assistant professor Ágnes Kotsis, assistant lecturer 1 lecture and 2 seminar in every week Monday in room C/9 Syllabus and slides will be available on the internet: oktato. econ. unideb. hu/kunandras/BAINMBA/MVCP. htm n Calculator is needed on the classes!

Requirements n The calculation of the final grade is as follows: n n Written exam 100% Exams will be organized via neptun in the exam period. The exams contain all of the topics discussed during the whole semester. The final result will be evaluated according to the following schedule: <51%– 1 51%– 2 65%– 3 75%– 4 85%– 5

What is this course about? n Introductory course to operations management. Key issues: n n n n n The Value Chain Concept Competitiveness, strategy, productivity Capacity Planning Constraint management Quality Management Supply Chain Management and logistics Inventory Management LEAN Operations Basics of process and project management

Roots of operations management n n Industrial revolution (1770’s) – Europe Scientific management (1911) – USA n n n Mass production Standardization Division of labor Human relations (HR) movement (1920 -60) Decision models (1915, 1960 -70’s) Influence of Japanese management philosophy and techinques

Roots of operations management n n Production management n Production: creation of finished goods (and services) using the factors of production: land, labor, capital (+ enterpreneurship, knowledge) n Production magagement: Planning, implementation, and control of industrial production processes to ensure smooth and efficient operation (the activites of managers do to help their firms create goods). Ensures that goods (and services) are produced efficiently; that they are of the right quality, quantity, cost; and that they are produced on time. Hence service sector becomes larger, concepts of (industrial) production management become influenced by it.

Operations management n n Includes the production of services. The term production has been repleaced by operations. Specialized area in management that converts or transforms resources into goods and services. It managing systems and processes as well.
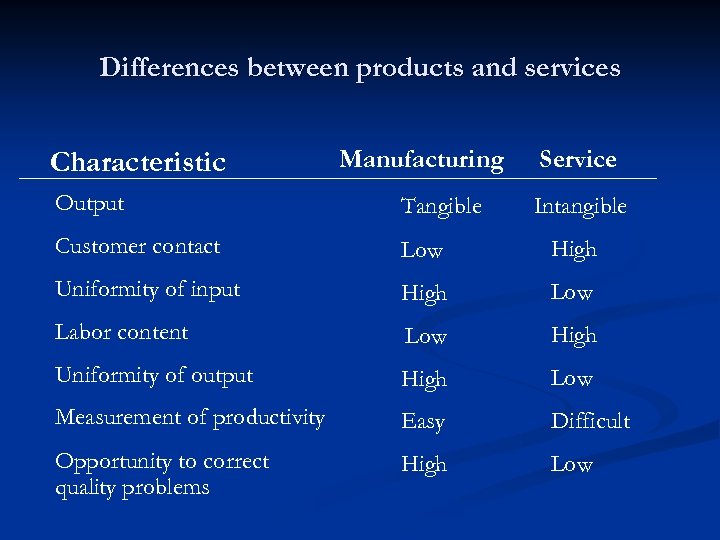
Differences between products and services Characteristic Manufacturing Service Output Tangible Customer contact Low High Uniformity of input High Low Labor content Low High Uniformity of output High Low Measurement of productivity Easy Difficult Opportunity to correct quality problems High Low Intangible

Goods-service Continuum Steel production Home remodeling Auto Repair Maid Service Teaching Automobile fabrication Retail sales Appliance repair Manual car wash Lawn mowing High percentage goods Low percentage service Low percentage goods High percentage service
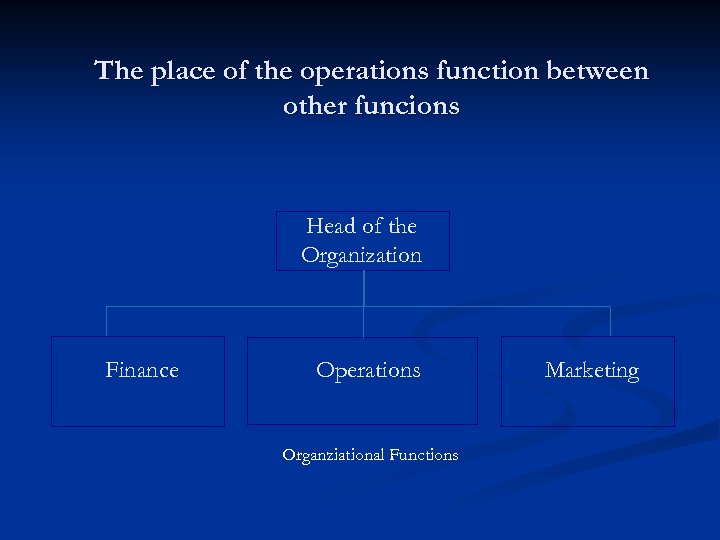
The place of the operations function between other funcions Head of the Organization Finance Operations Organziational Functions Marketing

The operations function Consists of all activities directly related to producing goods or providing services
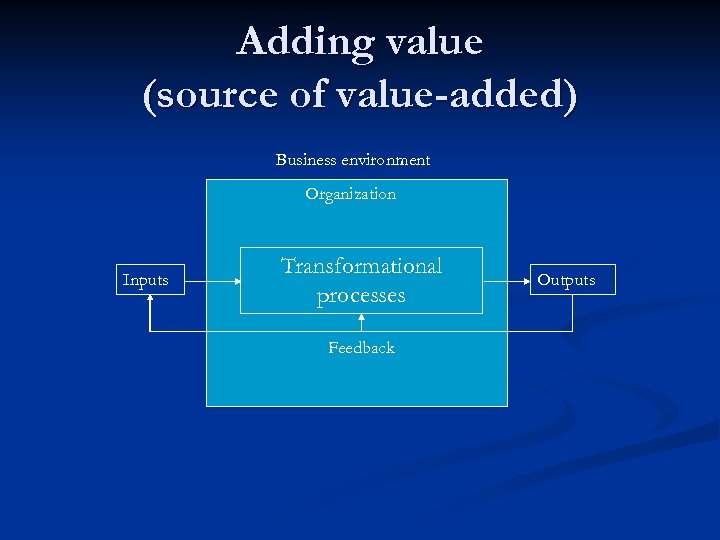
Adding value (source of value-added) Business environment Organization Inputs Transformational processes Feedback Outputs
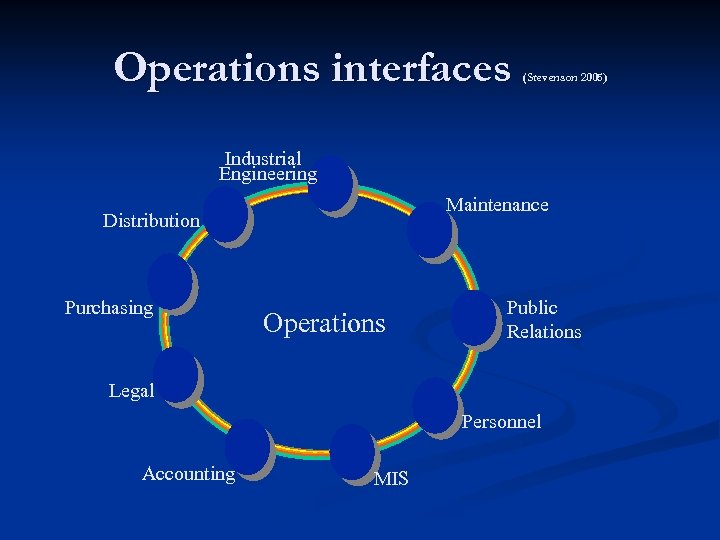
Operations interfaces (Stevenson 2005) Industrial Engineering Maintenance Distribution Purchasing Operations Public Relations Legal Personnel Accounting MIS
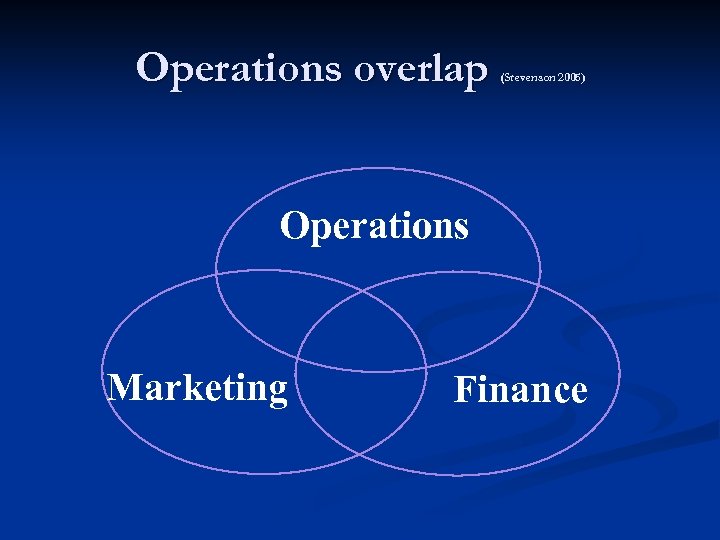
Operations overlap (Stevenson 2005) Operations Marketing Finance

Key decisions n What to produce / amount to produce n When to produce / to order / to supply n Where Is the best location for work / process / store etc. n How designed n Who to do the work (or which team)

Measures & methods Operations research (mathematical basis) n Models and abstraction n Performance metrics n Trade-off analysis n System approach n

The Value Chain Concept

„A Focus on Value Creation is a starting point to make the business feasible and real. ”

Economic activity n n Economy is a subsystem of society, that consists in producing, exchanging, distributing, and consuming goods and services. The function of this kind of human activity is to satisfy the needs of humanity under scarce and unequally distributed resources. Transformation of resources is a key to deal with scarcity. In market economies the primary actors of economy are the firm, the worker and customers. We will focus on the first.

The firm n n n Main goal is to earn profit through producing goods and services to satisfy customers’ demand. Vision statement: outlines what the organization wants to be, or how it wants the world – in which it operates – to be. It concentrates on the future. It is a source of inspiration. It provides clear decisionmaking criteria. „Where do we want to go? ” Mission: Defines the fundamental purpose of an organization or an enterprise, succinctly describing why it exists and what it does to achieve its Vision. It also describes the customers. „What and for whom do we want to do? ” Shared values: Beliefs that are shared among the stakeholders of an organization. Values drive an organization's culture and priorities. Strategy: A combination of the measurable ends (goals) for which the firm is striving and the means (policies) by which it is seeking to get there.
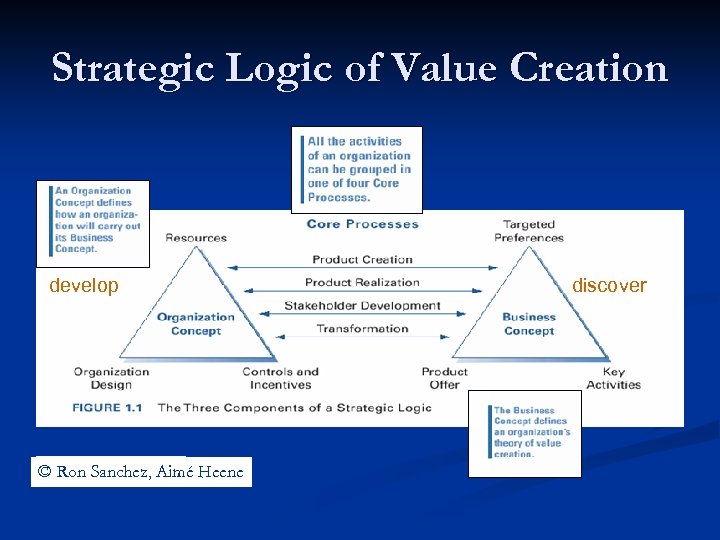
Strategic Logic of Value Creation develop © Wiley © Ron Sanchez, Aimé Heene discover

3 interrelated components of a value creating strategy: • Business concept: identifies • • Organizational concept: defines • • • customers, the product/service offers and key activities the resources, the organization design for co-ordinating its activities, the controls to monitor its value-creating activities, and the incentives – or plan for value distribution – that the organization will offer to attract and motivate resource providers. The core processes of product creation, product realization, stakeholder development, and organizational transformation through which an organization tries to create and distribute value on a sustainable basis.

Elements of the Value Creating Processes n The aim: Satisfying Customers’ Demand n Utility, demand value Competences of the Firm n Processes / Operations n
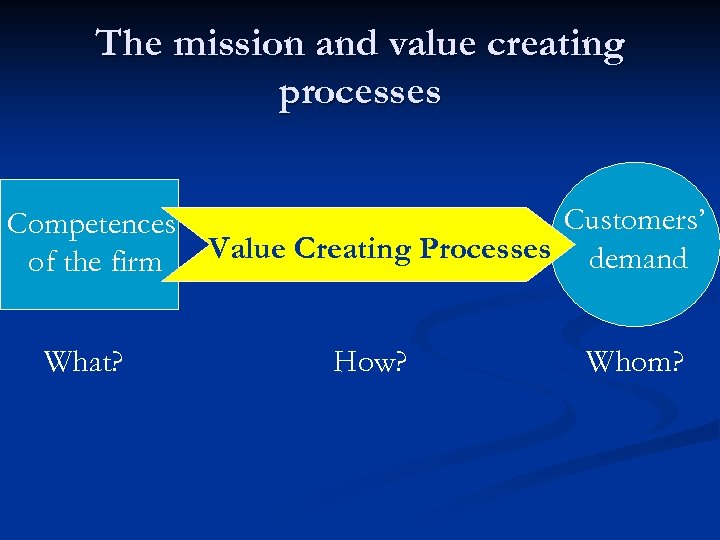
The mission and value creating processes Competences of the firm What? Customers’ Value Creating Processes demand How? Whom?

Measuring performance… n n n effectiveness: doing right things, setting right targets to achieve an overall goal (the effect). „How much a process leads to satisfy the customers? ” efficiency: doing things in the most economical way (input / output). „How profitable the process is? ” efficacy: getting things done, meeting targets

Basic notions of customer (consumer) value Utility (≈ benefits): a measure of the relative satisfaction from or desirability of consumption of various goods or services. Depends on the costumer and the situation (the same good has many possible values). n Demand: is the desire to own anything AND the ability to pay for it and willingness to pay at a given point of time. n Value: benefits / costs n

Customer (consumer) value is… n n n Subjective Linked to customers’ estimation Relational: n n Depends on: n n n n n high benefits with even higher costs gives lower value Technological characteristics Culture Reputation of the organization Staff representation Place and time Timing Additional services Offerings of the competitors Value of investment goods are tend to be more objective (and technological oriented)

Customer value characteristics n Consumer value: the subjective (perceived) utility of the good or service: n n n Consumer specific Changes in time Changes during consumer interactions Changes experience during and after consumption Dimensions of consumer value n n Value of use: linked to the ability of satisfying needs Value of place: geographical availability (softened by logistics) Value of time: provided when needed Ownership value: right of disposal

Organization concept n Efficiency needs design: division of labor (intra- or inter-firm) and n coordination (intra- or inter-firm): controls and incentives n resources: procurement, allocation, scheduling, invcentory n n n Transaction costs (comparative advantage) Vertical and horizontal integrations (in and out of the firm)
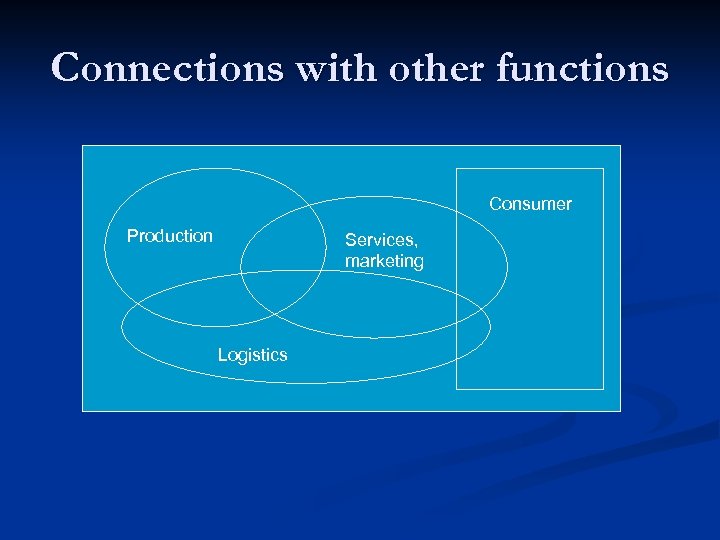
Connections with other functions Consumer Production Services, marketing Logistics

Competencies of the firm n What could (and wants to) the firm offer to the customer: n n effectively (does the firm the right offer? ) and efficiently (is there a good input /output ratio? ) Core business: that organization's "main" or "essential" activity (stated in the mission) Core competency: a specific factor (ability, competency etc. ) that is central for a firm: n n n It contribute significantly to the end-products’ benefits It is not easy for competitors to imitate It can be leveraged widely to many products and markets. It provides the fundamental basis for the provision of added value In what processes is the firm better than the competitors on the long run!
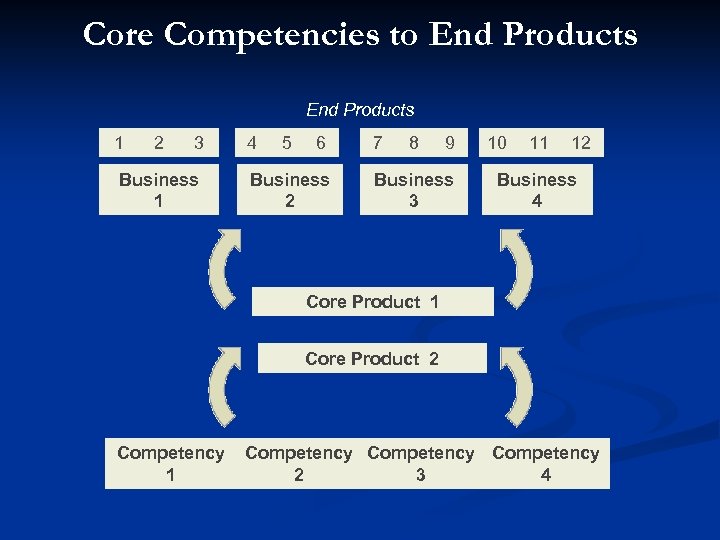
Core Competencies to End Products 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Business 2 Business 3 Business 4 Business 1 Core Product 1 Competency 1 Core Product 2 Competency 2 3 4

Value Creating Processes n Transforms the resources (and competencies) of the firm into consumer (customer) value. n Material processes (from inputs to value): production, logistics, inventory n n Informational processes (in both direction) n n Backwards: spoilage, wastage Planning, directing, controlling, documentation Feedback Value processes (from inputs to value): increase in the value of the product Other processes (R&D, finance etc. )

Value Chains n n n A value chain is a chain of activities for a firm operating in a specific industry. The business unit is the appropriate level for construction a value chain (we will discuss only the first). Products pass through all value activities of the chain in order and at each activity the product gains some value. Not to mix the concept of the value chain with the costs occurring throughout the activities. Supply chain: The value-chain concept has been extended beyond individual firms. It can apply to whole supply chains and distribution networks.
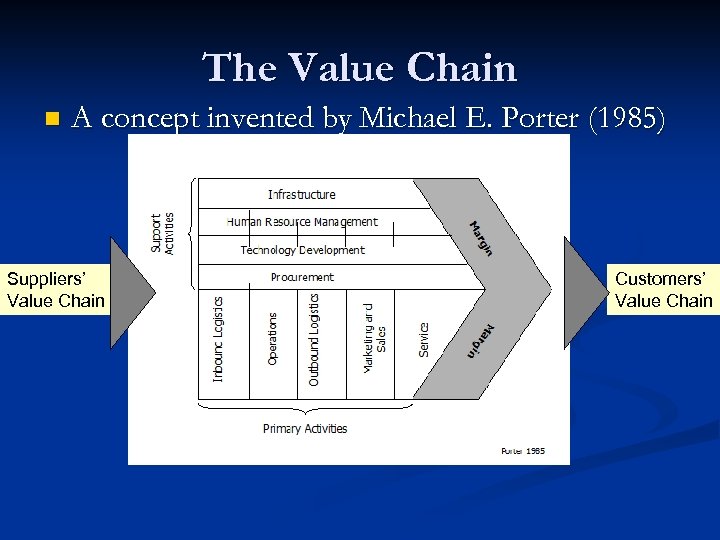
The Value Chain n A concept invented by Michael E. Porter (1985) Suppliers’ Value Chain Customers’ Value Chain

Value analysis Eliminating anything that which causes cost but does not contribute to the value or function of the product or service (reducing costs while keeping the same level of benefits). n. Objective: purpose or reason of the product n. Basic function: without this, the product is useless n. Secondary funcions: support a basic function

Thank you for your attention

Some specific value chains
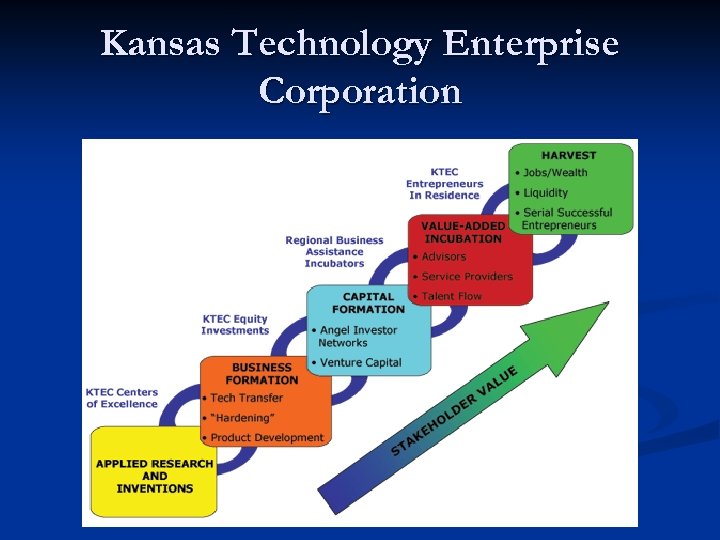
Kansas Technology Enterprise Corporation
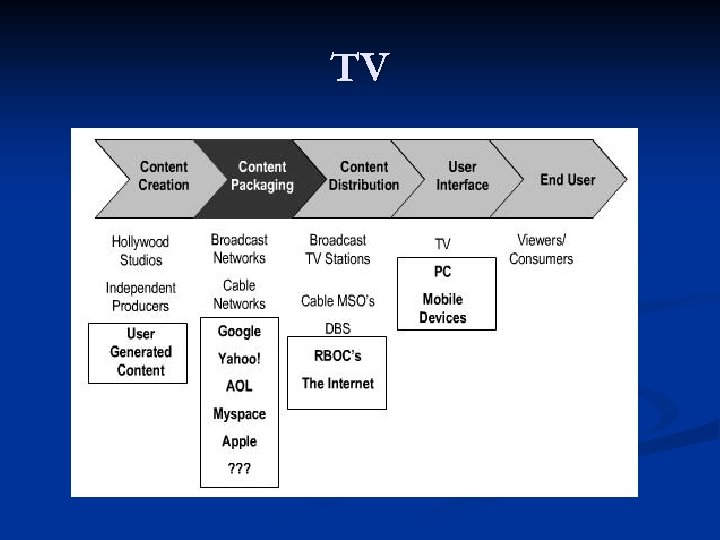
TV
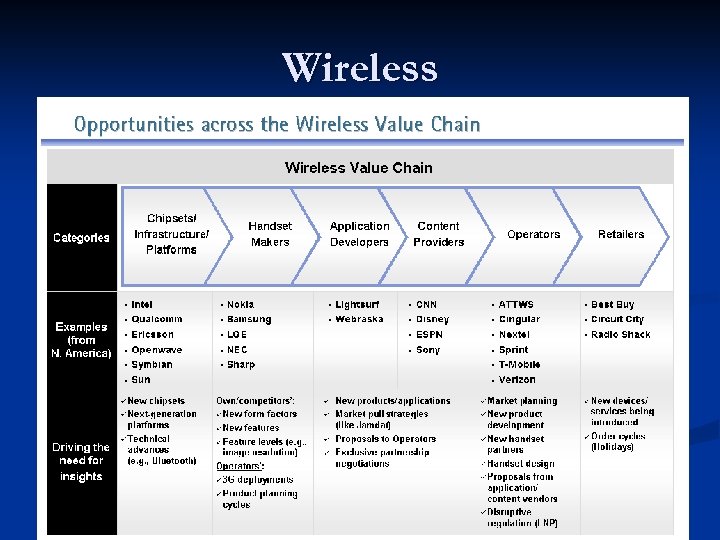
Wireless
67bf3c73ffff4e1aca46a064ebfc37dc.ppt