a10e40261278b6bd2cbda58b8e4552fc.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 17
 Value Chain and IS/IT V. T. Raja, Ph. D. , Information Management Oregon State University
Value Chain and IS/IT V. T. Raja, Ph. D. , Information Management Oregon State University
 Value Chain l Discussion questions: – – – What is the Value Chain (VC)? Identify the activities of the VC How is the “service” activity different from “marketing and sales”? (Don’t “sales” people provide “service”? ) Differentiate between “procurement” activity and “inbound logistics” Why study about Value Chain in an IS/IT class? Explain value chain linkages (internal and external) with the help of examples.
Value Chain l Discussion questions: – – – What is the Value Chain (VC)? Identify the activities of the VC How is the “service” activity different from “marketing and sales”? (Don’t “sales” people provide “service”? ) Differentiate between “procurement” activity and “inbound logistics” Why study about Value Chain in an IS/IT class? Explain value chain linkages (internal and external) with the help of examples.
 Value Chain Activities l Inbound Logistics – l Operations – l Involve relationships with suppliers and include all activities required to receive, store, and disseminate inputs All activities required to transform inputs into outputs Outbound Logistics – All activities required to collect, store, and distribute output
Value Chain Activities l Inbound Logistics – l Operations – l Involve relationships with suppliers and include all activities required to receive, store, and disseminate inputs All activities required to transform inputs into outputs Outbound Logistics – All activities required to collect, store, and distribute output
 Value Chain Activities (Continued) l Marketing and Sales Inform buyers about products/services – Induce buyers to purchase products/services and facilitate their purchase (Stimulate demand for products/services) – Collect and pass customer feed back to various units in firm – Estimate expected sales volume – l Service – Activities required to keep the product/service working effectively for the buyer after it is sold and delivered
Value Chain Activities (Continued) l Marketing and Sales Inform buyers about products/services – Induce buyers to purchase products/services and facilitate their purchase (Stimulate demand for products/services) – Collect and pass customer feed back to various units in firm – Estimate expected sales volume – l Service – Activities required to keep the product/service working effectively for the buyer after it is sold and delivered
 Value Chain Activities (Continued) l Procurement – l Acquisition (actual purchase) of inputs, or resources, for the firm Human Resource Management – Activities involved in recruiting, training, developing, compensating, laying off personnel
Value Chain Activities (Continued) l Procurement – l Acquisition (actual purchase) of inputs, or resources, for the firm Human Resource Management – Activities involved in recruiting, training, developing, compensating, laying off personnel
 Value Chain Activities (Continued) l Technological Development – l Technology purchased/adopted/developed to bear in the firm’s transformation of inputs into outputs Infrastructure (General Administration) – Activities include accounting, legal, finance, planning , public affairs, government relations, quality assurance and general management
Value Chain Activities (Continued) l Technological Development – l Technology purchased/adopted/developed to bear in the firm’s transformation of inputs into outputs Infrastructure (General Administration) – Activities include accounting, legal, finance, planning , public affairs, government relations, quality assurance and general management
 Value Chain and IS/IT: Examples l Inbound Logistics – – l Operations – l Automated Warehousing System; JIT inventory systems Computer-Controlled Machining Systems Outbound Logistics – – Automated Shipment Scheduling Systems Tracking Systems
Value Chain and IS/IT: Examples l Inbound Logistics – – l Operations – l Automated Warehousing System; JIT inventory systems Computer-Controlled Machining Systems Outbound Logistics – – Automated Shipment Scheduling Systems Tracking Systems
 Value Chain and IS/IT Examples (Continued) l Sales and Marketing – – l Service – l On-line Ordering Systems for customer Sales forecasting Equipment maintenance systems Procurement – Computerized Ordering Systems and EDI
Value Chain and IS/IT Examples (Continued) l Sales and Marketing – – l Service – l On-line Ordering Systems for customer Sales forecasting Equipment maintenance systems Procurement – Computerized Ordering Systems and EDI
 Value Chain and IS/IT Examples (Continued) l Technology Development – l Human Resource Management – – – l Computer-Aided Design Systems Multi-media database systems On-line recruiting Intranet for employee benefits (retirement benefits, medical benefits etc. ) Infrastructure – Electronic scheduling; financial systems, accounting systems, decision support systems etc.
Value Chain and IS/IT Examples (Continued) l Technology Development – l Human Resource Management – – – l Computer-Aided Design Systems Multi-media database systems On-line recruiting Intranet for employee benefits (retirement benefits, medical benefits etc. ) Infrastructure – Electronic scheduling; financial systems, accounting systems, decision support systems etc.
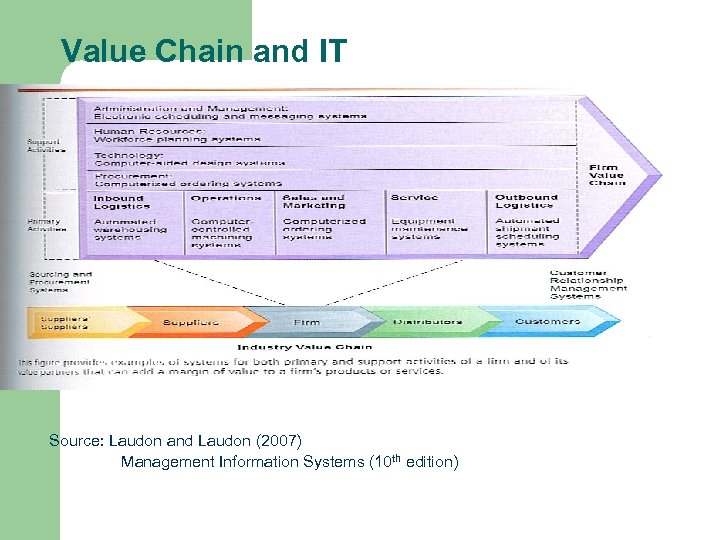 Value Chain and IT Source: Laudon and Laudon (2007) Management Information Systems (10 th edition)
Value Chain and IT Source: Laudon and Laudon (2007) Management Information Systems (10 th edition)
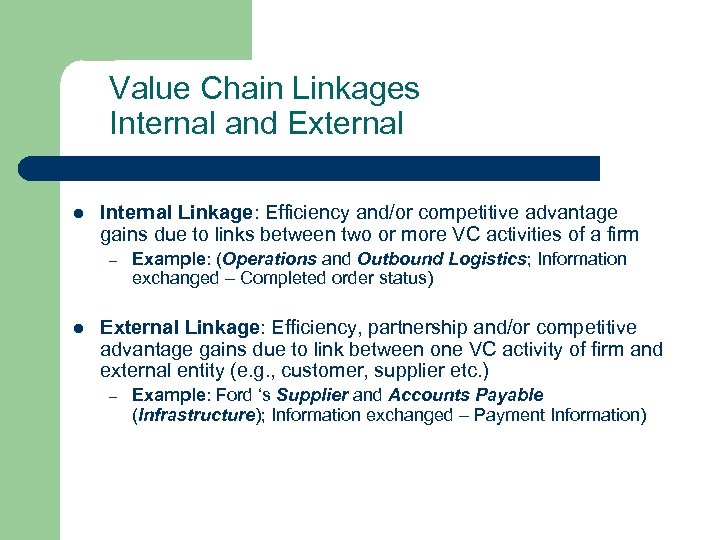 Value Chain Linkages Internal and External l Internal Linkage: Efficiency and/or competitive advantage gains due to links between two or more VC activities of a firm – l Example: (Operations and Outbound Logistics; Information exchanged – Completed order status) External Linkage: Efficiency, partnership and/or competitive advantage gains due to link between one VC activity of firm and external entity (e. g. , customer, supplier etc. ) – Example: Ford ‘s Supplier and Accounts Payable (Infrastructure); Information exchanged – Payment Information)
Value Chain Linkages Internal and External l Internal Linkage: Efficiency and/or competitive advantage gains due to links between two or more VC activities of a firm – l Example: (Operations and Outbound Logistics; Information exchanged – Completed order status) External Linkage: Efficiency, partnership and/or competitive advantage gains due to link between one VC activity of firm and external entity (e. g. , customer, supplier etc. ) – Example: Ford ‘s Supplier and Accounts Payable (Infrastructure); Information exchanged – Payment Information)
 Supply-Chain Management l Planning, organizing, directing, and controlling flows of materials and purchased parts or services – – – l Involves everyone in supply-chain – l Begins with raw materials Continues through internal operations Ends with distribution of finished goods Example: Your supplier’s supplier Objective: Maximize product value and decrease waste incurred in providing it.
Supply-Chain Management l Planning, organizing, directing, and controlling flows of materials and purchased parts or services – – – l Involves everyone in supply-chain – l Begins with raw materials Continues through internal operations Ends with distribution of finished goods Example: Your supplier’s supplier Objective: Maximize product value and decrease waste incurred in providing it.
 Nike’s (Simplified) Supply Chain Source: Laudon and Laudon (2007) Management Information Systems (10 th edition)
Nike’s (Simplified) Supply Chain Source: Laudon and Laudon (2007) Management Information Systems (10 th edition)
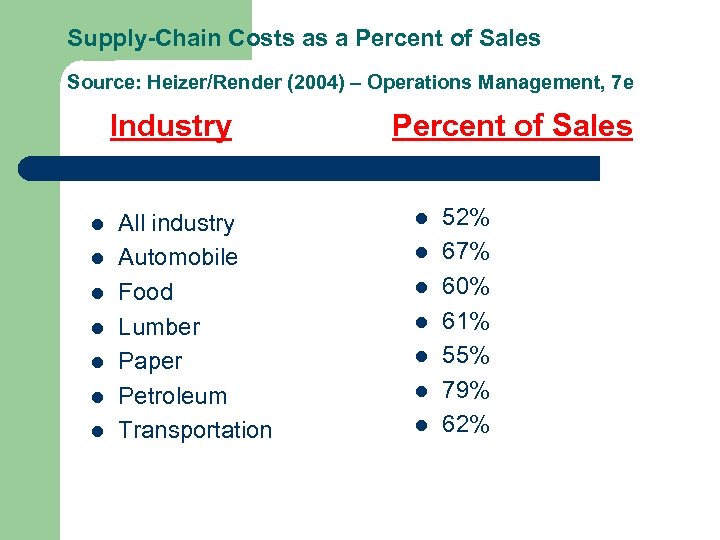 Supply-Chain Costs as a Percent of Sales Source: Heizer/Render (2004) – Operations Management, 7 e Industry l l l l All industry Automobile Food Lumber Paper Petroleum Transportation Percent of Sales l l l l 52% 67% 60% 61% 55% 79% 62%
Supply-Chain Costs as a Percent of Sales Source: Heizer/Render (2004) – Operations Management, 7 e Industry l l l l All industry Automobile Food Lumber Paper Petroleum Transportation Percent of Sales l l l l 52% 67% 60% 61% 55% 79% 62%
 Successful Supply-Chain Management Requires: l l l A mutual agreement with suppliers on goals Trust among all elements of the supply chain Compatible organizational cultures
Successful Supply-Chain Management Requires: l l l A mutual agreement with suppliers on goals Trust among all elements of the supply chain Compatible organizational cultures
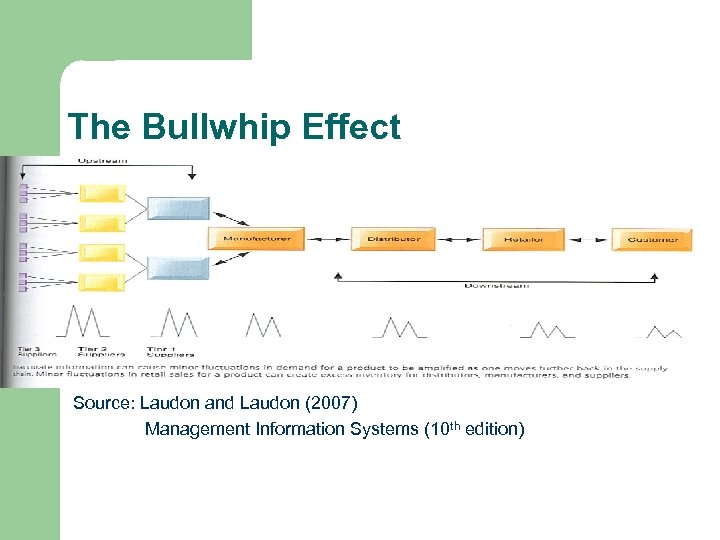 The Bullwhip Effect Source: Laudon and Laudon (2007) Management Information Systems (10 th edition)
The Bullwhip Effect Source: Laudon and Laudon (2007) Management Information Systems (10 th edition)
 Supply Chain Management
Supply Chain Management


