7331274bddf69f73baf01ea6ba623b94.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 13

Validation and verification Requirements of ISO/IEC 17025 by Dr. Michael Scheutwinkel International Federation for Consulting Gmb. H IFC 1

5 Technical requirements 5. 1 5. 2 5. 3 5. 4 General Personnel Accommodation and environmental conditions Test and calibration methods and method validation 5. 5 Equipment 5. 6 Measurement traceability 5. 7 Sampling 5. 8 Handling of test and calibration items 5. 9 Assuring the quality of test and calibration results 5. 10 Reporting the results 2

5. 4 Test and calibration methods and method validation Appropriate methods for all tests / calibration within scope – with estimate of uncertainty; – Instructions for all equipment; – Up to date and readily available to personnel; – Deviations only if technically justified, authorized and accepted by the customer; – Methods must meet the needs of the customer; – Latest valid edition of national/international published standards is preferred. 3
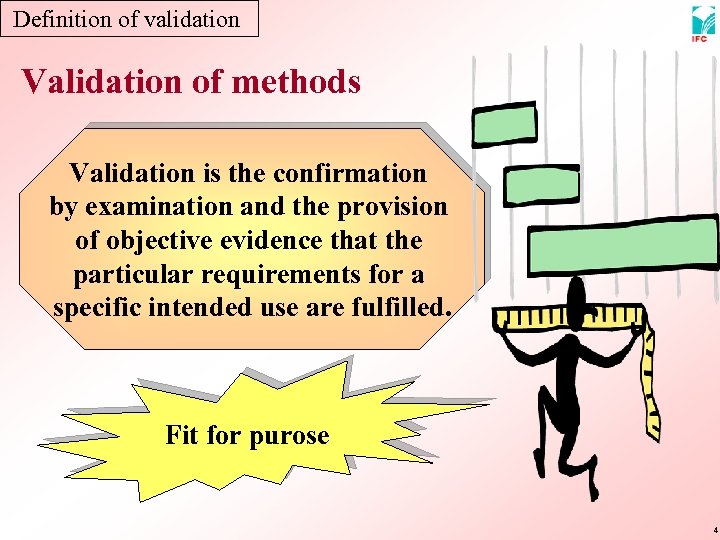
Definition of validation Validation of methods Validation is the confirmation by examination and the provision of objective evidence that the particular requirements for a specific intended use are fulfilled. Fit for purose 4

Validation of an analytical test method Validation is the process of establishing the • Performance characteristics; • Limitations of a method; • Identification of the influences which may change these characteristics and to what extent. Which analytes can be determined in which matrix in the presence of which interferences? Within these conditions what levels of precision and accuracy can be achieved? 5

Equipment and method valdiation Equipment validation DQ IQ Soft and hardware OQ PQ Method validation … different items 6

Do not forget: Self developed software or excel sheets have to be validated. Records for that must be available. 7

Verification of an analytical test method Verification is the process to demonstrate the competence in test performance of an already validated standardized test method. The tools are the same as for validation, the laboratory needs only to verify that the documented performance characteristics can be met (e. g. LOD, LOQ, accuracy, etc. ). 8

Validation is always a balance betwee costs, risks and technical possibilities. 9

Validation procedures according to CD 657/2002/EC Chapter 3 of Annex Examples for validation, models Conventional validation approach In-house validation approach Other approaches may be used provided that they achieve the same quality level of information 10

Commission Decision 2002/657/EC, validation Modelindependent Modeldependent performance parameters (Table 10) 11

Commission Decision 2002/657/EC Table 10 12

13
7331274bddf69f73baf01ea6ba623b94.ppt