464c4a509fe08c78cf294b5649854cb7.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 42

VAD Test Loop: Detailed Design Review Team Members: Jon Klein Nguyen Vu Kyle Menges Christine Lowry Chris Stein Priya Narasimhan Julie Coggshall

Overview Meeting Timeline Start Time Topic of Review 10: 00 Introductions, Review Agenda 10: 02 Design Review 1 Action Items 10: 03 System Design and BOM 10: 15 Fluids Analysis – Electrical Simulation, Results 10: 35 Blood Tank – Bubble Rise Time, Fluid Extraction 10: 40 Water Bath – Heat Transfer 10: 45 Tubing – Heat Transfer Automated Resistance - Linear motor’s force 10: 50 approximation Compliance Tank – Arterial Tank Dimensioning, 11: 00 Electrical Equivalent Model 11: 15 Custom LVAD Connection 11: 20 System Drain – Saline Flush 11: 25 Pressure, Flow, and Temperature Sensors and DAQ 11: 50 Lab. View Front Panel Concept 11: 55 Wrap-up Pg. 1

Expectations To review the detailed design proposal to ensure design adequacy. Pg. 1

Project Objectives 1. Generate pressure and flow curves for static system (automatically adjusted) 2. Extracting fluids while running to determine damage to blood 3. Process data to generate pressure and flow curve for dynamic system (scaled model of the physiological circulatory system working with a PVS) Pg. 2
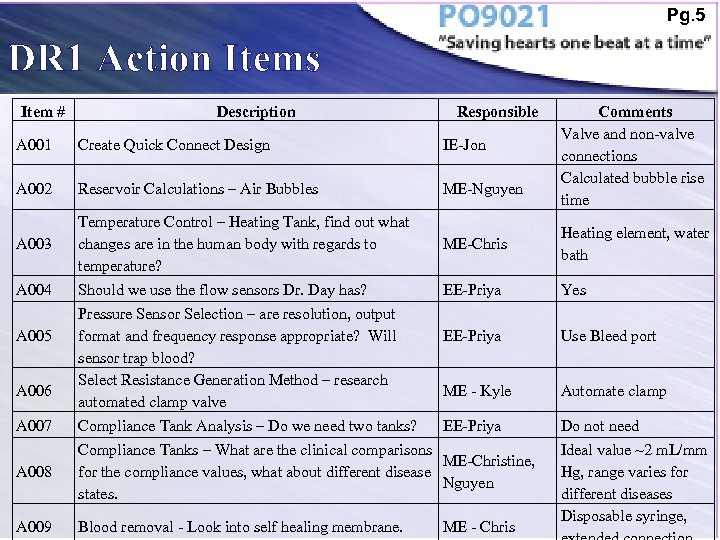
Pg. 5 DR 1 Action Items Item # Description Responsible Comments Valve and non-valve connections Calculated bubble rise time A 001 Create Quick Connect Design IE-Jon A 002 Reservoir Calculations – Air Bubbles ME-Nguyen A 003 Temperature Control – Heating Tank, find out what changes are in the human body with regards to temperature? ME-Chris Heating element, water bath A 004 Should we use the flow sensors Dr. Day has? EE-Priya Yes EE-Priya Use Bleed port ME - Kyle Automate clamp EE-Priya Do not need Ideal value ~2 m. L/mm Hg, range varies for different diseases Disposable syringe, A 005 A 006 A 007 A 008 A 009 Pressure Sensor Selection – are resolution, output format and frequency response appropriate? Will sensor trap blood? Select Resistance Generation Method – research automated clamp valve Compliance Tank Analysis – Do we need two tanks? Compliance Tanks – What are the clinical comparisons for the compliance values, what about different disease states. Blood removal - Look into self healing membrane. ME-Christine, Nguyen ME - Chris
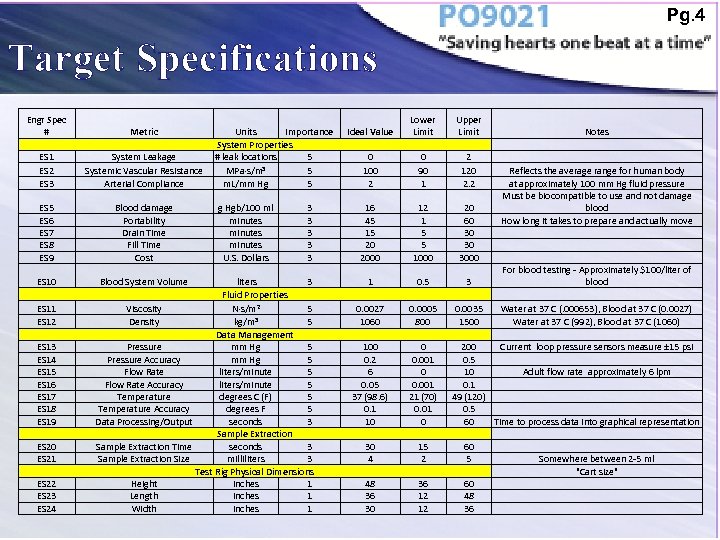
Pg. 4 Target Specifications Engr Spec # Metric ES 1 ES 2 ES 3 System Leakage Systemic Vascular Resistance Arterial Compliance ES 5 ES 6 ES 7 ES 8 ES 9 Blood damage Portability Drain Time Fill Time Cost ES 10 Blood System Volume ES 11 ES 12 ES 13 ES 14 ES 15 ES 16 ES 17 ES 18 ES 19 ES 20 ES 21 ES 22 ES 23 ES 24 Units Importance System Properties # leak locations 5 MPa·s/m 3 5 m. L/mm Hg 5 g Hgb/100 ml minutes U. S. Dollars 3 3 3 liters 3 Fluid Properties Viscosity N·s/m 2 5 3 Density kg/m 5 Data Management Pressure mm Hg 5 Pressure Accuracy mm Hg 5 Flow Rate liters/minute 5 Flow Rate Accuracy liters/minute 5 Temperature degrees C (F) 5 Temperature Accuracy degrees F 5 Data Processing/Output seconds 3 Sample Extraction Time seconds 3 Sample Extraction Size milliliters 3 Test Rig Physical Dimensions Height inches 1 Length inches 1 Width inches 1 Ideal Value Lower Limit 0 100 2 0 90 1 16 45 15 20 2000 12 1 5 5 1000 1 0. 5 0. 0027 1060 0. 0005 800 100 0. 2 6 0. 05 37 (98. 6) 0. 1 10 0 0. 001 21 (70) 0. 01 0 30 4 15 2 48 36 30 36 12 12 Upper Limit Notes 2 120 Reflects the average range for human body 2. 2 at approximately 100 mm Hg fluid pressure Must be biocompatible to use and not damage 20 blood 60 How long it takes to prepare and actually move 30 3000 For blood testing - Approximately $100/liter of 3 blood 0. 0035 Water at 37 C (. 000653), Blood at 37 C (0. 0027) 1500 Water at 37 C (992), Blood at 37 C (1060) 200 Current loop pressure sensors measure ± 15 psi 0. 5 10 Adult flow rate approximately 6 lpm 0. 1 49 (120) 0. 5 60 Time to process data into graphical representation 60 5 Somewhere between 2 -5 ml "Cart size" 60 48 36
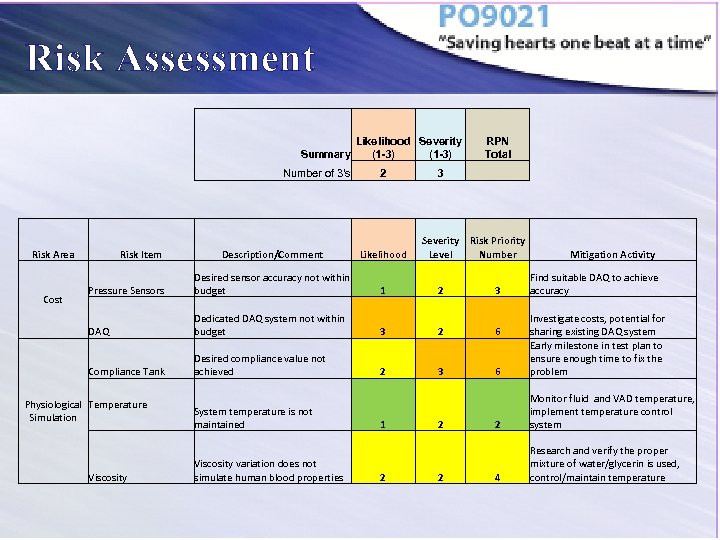
Risk Assessment Summary Number of 3's Likelihood Severity (1 -3) RPN Total 2 3 Description/Comment Likelihood Severity Level Risk Priority Number Pressure Sensors Desired sensor accuracy not within budget 1 2 3 DAQ Dedicated DAQ system not within budget 3 2 6 Compliance Tank Desired compliance value not achieved 2 3 6 Investigate costs, potential for sharing existing DAQ system Early milestone in test plan to ensure enough time to fix the problem 2 Monitor fluid and VAD temperature, implement temperature control system 4 Research and verify the proper mixture of water/glycerin is used, control/maintain temperature Risk Area Cost Risk Item Physiological Temperature Simulation Viscosity System temperature is not maintained Viscosity variation does not simulate human blood properties 1 2 2 2 Mitigation Activity Find suitable DAQ to achieve accuracy
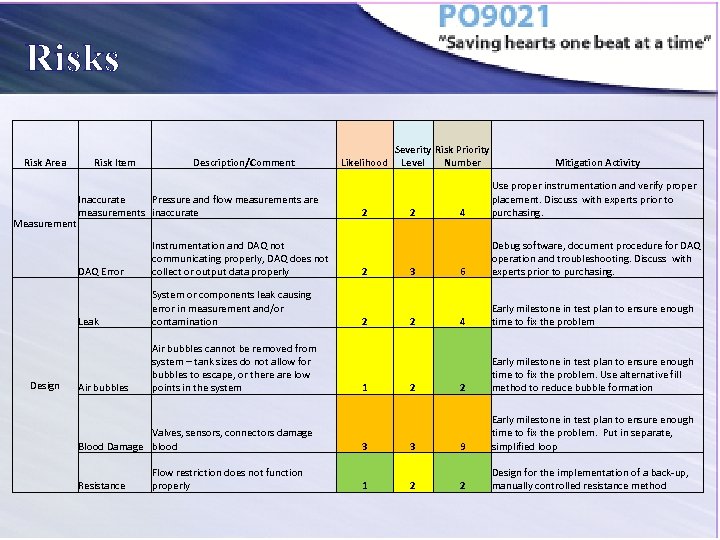
Risks Risk Area Measurement Risk Item Description/Comment Inaccurate Pressure and flow measurements are measurements inaccurate DAQ Error Leak Design Instrumentation and DAQ not communicating properly, DAQ does not collect or output data properly System or components leak causing error in measurement and/or contamination Air bubbles cannot be removed from system – tank sizes do not allow for bubbles to escape, or there are low points in the system Valves, sensors, connectors damage Blood Damage blood Resistance Flow restriction does not function properly Likelihood 2 2 2 1 Severity Risk Priority Level Number 2 3 2 2 Mitigation Activity 4 Use proper instrumentation and verify proper placement. Discuss with experts prior to purchasing. 6 Debug software, document procedure for DAQ operation and troubleshooting. Discuss with experts prior to purchasing. 4 Early milestone in test plan to ensure enough time to fix the problem 2 Early milestone in test plan to ensure enough time to fix the problem. Use alternative fill method to reduce bubble formation 3 3 9 Early milestone in test plan to ensure enough time to fix the problem. Put in separate, simplified loop 1 2 2 Design for the implementation of a back-up, manually controlled resistance method
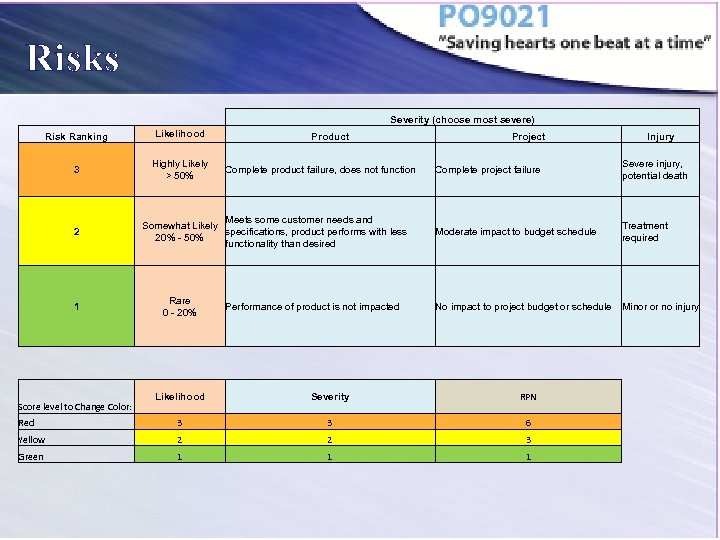
Risks Severity (choose most severe) Risk Ranking Likelihood 3 Highly Likely > 50% 2 1 Product Complete product failure, does not function Meets some customer needs and Somewhat Likely specifications, product performs with less 20% - 50% functionality than desired Rare 0 - 20% Performance of product is not impacted Project Complete project failure Severe injury, potential death Moderate impact to budget schedule Treatment required No impact to project budget or schedule Minor or no injury Likelihood Severity RPN Red 3 3 6 Yellow 2 2 3 Green 1 1 1 Score level to Change Color: Injury
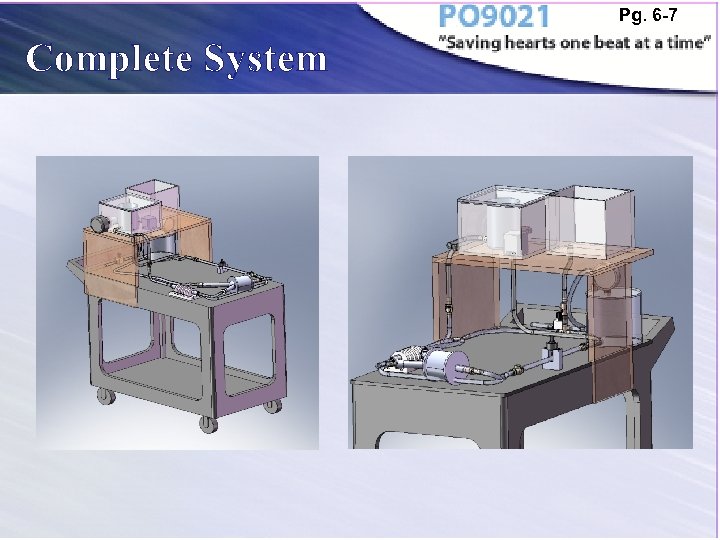
Pg. 6 -7 Complete System
![EW-30623 -79 Fittings/Connectors 3/4" to 1/2" Polypro reducing coupling (PVS inlet) [Mc. Master] 3/8" EW-30623 -79 Fittings/Connectors 3/4" to 1/2" Polypro reducing coupling (PVS inlet) [Mc. Master] 3/8"](https://present5.com/presentation/464c4a509fe08c78cf294b5649854cb7/image-11.jpg)
EW-30623 -79 Fittings/Connectors 3/4" to 1/2" Polypro reducing coupling (PVS inlet) [Mc. Master] 3/8" NPT x 1/2" Barbed threaded tank fitting [Eldon James] BOM Glycerin Tank - Barbed Tconnector (HDPE 1/2" x 1/2") [Cole -Parmer] 1" NPT x 1/2" Barbed threaded fitting for PVS (Nylon) [Mc. Master] Y connector [Eldon James]

Fittings/Connectors Reducer 1 to 1/2 plastic (HDPE) into PVS/Reducer 3/4 to 1/2 plastic (HDPE) Out of PVS [Cole-Parmer] Glycerine Tank - Shut-off Valve (1/2" to 1/2" barb)[Eldon James] BOM
![BOM Quick Connects Biocompatible Valve [Cole-Parmer] Biocompatible Non-valved [Cole-Parmer] BOM Quick Connects Biocompatible Valve [Cole-Parmer] Biocompatible Non-valved [Cole-Parmer]](https://present5.com/presentation/464c4a509fe08c78cf294b5649854cb7/image-13.jpg)
BOM Quick Connects Biocompatible Valve [Cole-Parmer] Biocompatible Non-valved [Cole-Parmer]
![Glycerin Tank 10 Qt [Mc. Master] BOM Glycerin Tank 10 Qt [Mc. Master] BOM](https://present5.com/presentation/464c4a509fe08c78cf294b5649854cb7/image-14.jpg)
Glycerin Tank 10 Qt [Mc. Master] BOM

BOM Cart Dimensions: 43. 9”L x 25. 6” x 33. 3”H Weight: 42. 55 lbs. Sam’s Club

Loop Designs Blood Loop Pg. 8
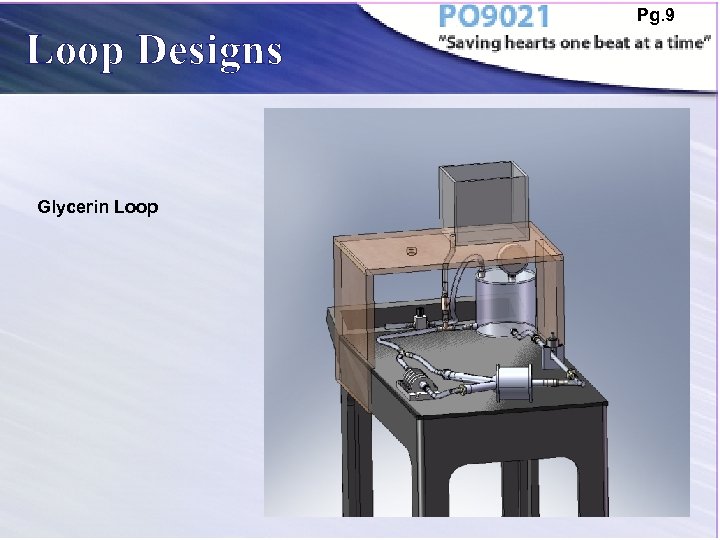
Loop Designs Glycerin Loop Pg. 9
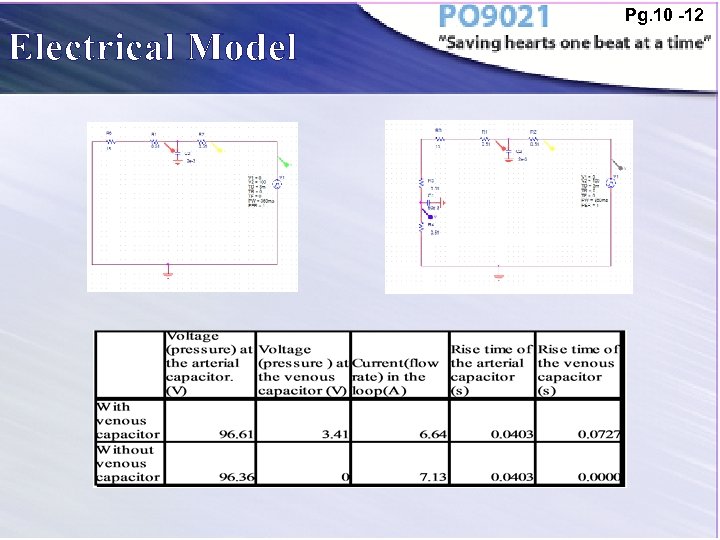
Electrical Model Pg. 10 -12
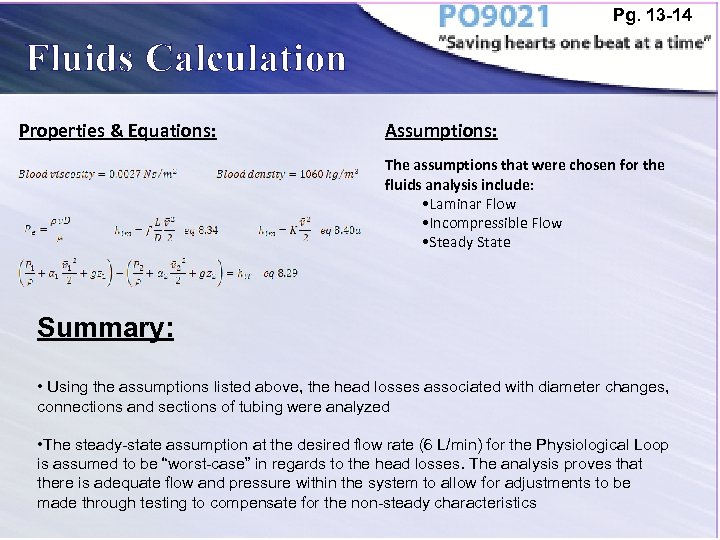
Pg. 13 -14 Fluids Calculation Properties & Equations: Assumptions: The assumptions that were chosen for the fluids analysis include: • Laminar Flow • Incompressible Flow • Steady State Summary: • Using the assumptions listed above, the head losses associated with diameter changes, connections and sections of tubing were analyzed • The steady-state assumption at the desired flow rate (6 L/min) for the Physiological Loop is assumed to be “worst-case” in regards to the head losses. The analysis proves that there is adequate flow and pressure within the system to allow for adjustments to be made through testing to compensate for the non-steady characteristics
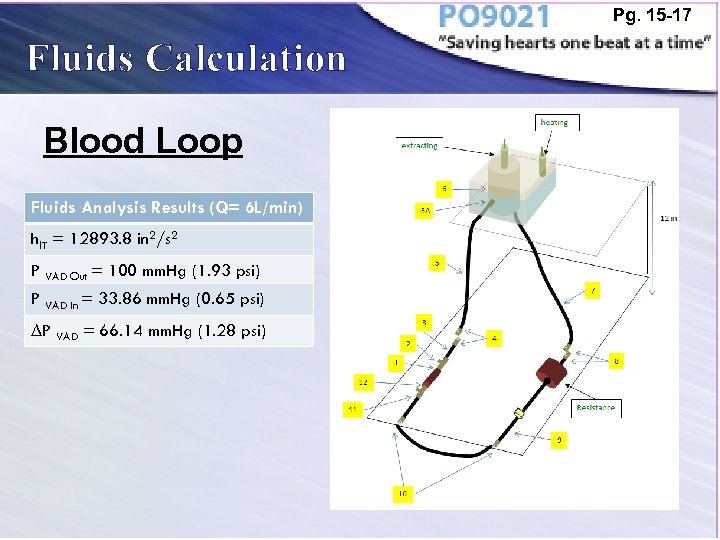
Pg. 15 -17 Fluids Calculation Blood Loop Fluids Analysis Results (Q= 6 L/min) hl. T = 12893. 8 in 2/s 2 P VAD Out = 100 mm. Hg (1. 93 psi) P VAD In = 33. 86 mm. Hg (0. 65 psi) ∆P VAD = 66. 14 mm. Hg (1. 28 psi)
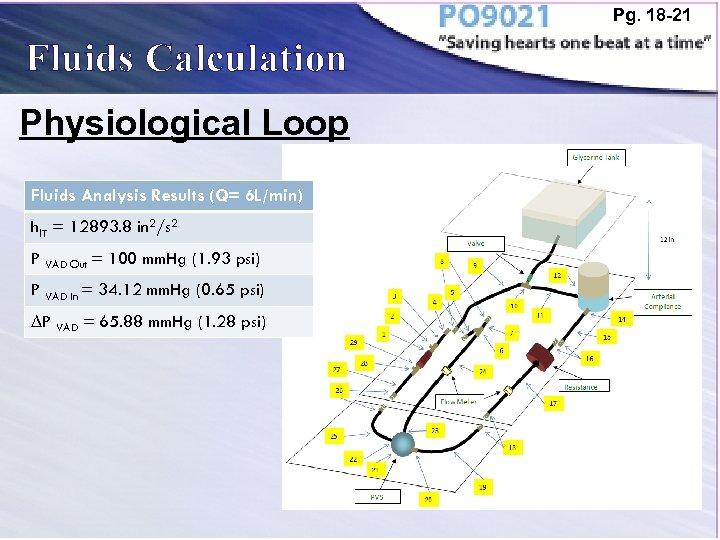
Pg. 18 -21 Fluids Calculation Physiological Loop Fluids Analysis Results (Q= 6 L/min) hl. T = 12893. 8 in 2/s 2 P VAD Out = 100 mm. Hg (1. 93 psi) P VAD In = 34. 12 mm. Hg (0. 65 psi) ∆P VAD = 65. 88 mm. Hg (1. 28 psi)
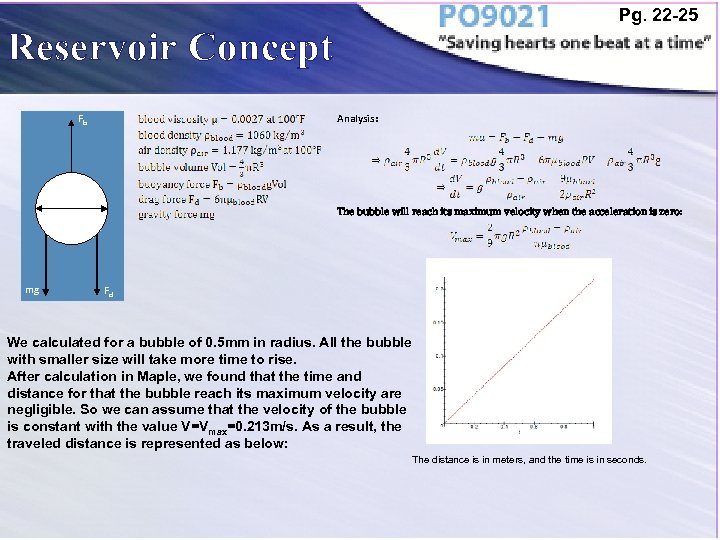
Pg. 22 -25 Reservoir Concept Fb Analysis: 2 R The bubble will reach its maximum velocity when the acceleration is zero: mg Fd We calculated for a bubble of 0. 5 mm in radius. All the bubble with smaller size will take more time to rise. After calculation in Maple, we found that the time and distance for that the bubble reach its maximum velocity are negligible. So we can assume that the velocity of the bubble is constant with the value V=Vmax=0. 213 m/s. As a result, the traveled distance is represented as below: The distance is in meters, and the time is in seconds.
![BOM Blood Extraction Stainless Steel Lid [Mopec] Stainless Steel [Mopec] BOM Blood Extraction Stainless Steel Lid [Mopec] Stainless Steel [Mopec]](https://present5.com/presentation/464c4a509fe08c78cf294b5649854cb7/image-23.jpg)
BOM Blood Extraction Stainless Steel Lid [Mopec] Stainless Steel [Mopec]
![BOM Blood Extraction B-D Disposable Luer-Lock 5 m. L Syringe[Cole Parmer] Stainless steel cannula BOM Blood Extraction B-D Disposable Luer-Lock 5 m. L Syringe[Cole Parmer] Stainless steel cannula](https://present5.com/presentation/464c4a509fe08c78cf294b5649854cb7/image-24.jpg)
BOM Blood Extraction B-D Disposable Luer-Lock 5 m. L Syringe[Cole Parmer] Stainless steel cannula (13 gauge luer-lock) [Cole Parmer]
![Water Bath 10 Qt: [Mc. Master] BOM Water Bath 10 Qt: [Mc. Master] BOM](https://present5.com/presentation/464c4a509fe08c78cf294b5649854cb7/image-25.jpg)
Water Bath 10 Qt: [Mc. Master] BOM
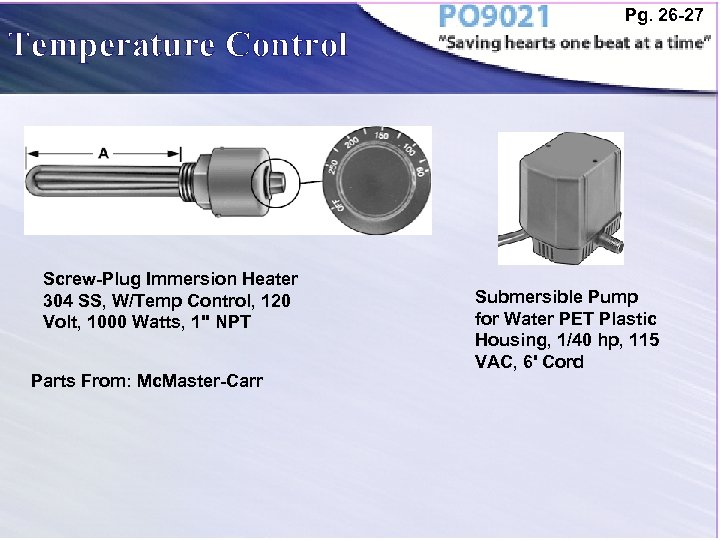
Temperature Control Screw-Plug Immersion Heater 304 SS, W/Temp Control, 120 Volt, 1000 Watts, 1" NPT Parts From: Mc. Master-Carr Pg. 26 -27 Submersible Pump for Water PET Plastic Housing, 1/40 hp, 115 VAC, 6' Cord
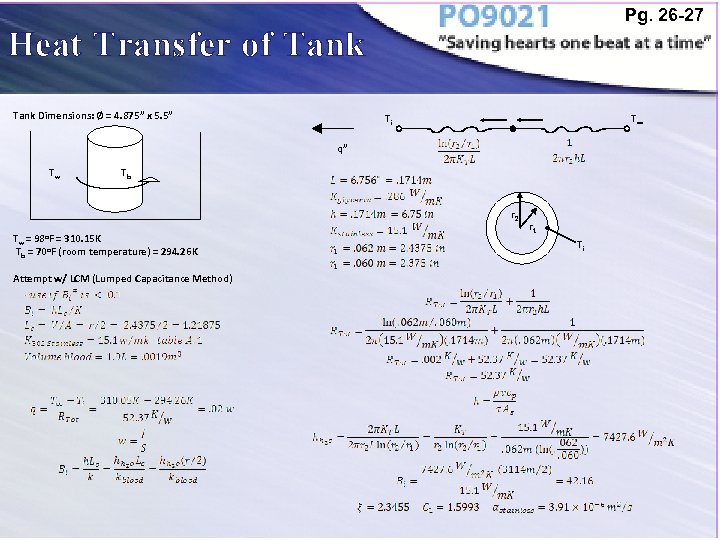
Pg. 26 -27 Heat Transfer of Tank Dimensions: Ø = 4. 875” x 5. 5” Ti T∞ q” Tw Tb r 2 Tw = 98 o. F = 310. 15 K Tb = 70 o. F (room temperature) = 294. 26 K Attempt w/ LCM (Lumped Capacitance Method) r 1 Ti

Pg. 26 -27 Heat Transfer of Tank Dimensions: Ø = 4. 875” x 5. 5” Tw Tb Results: • Time for the blood loop to heat less than 2 hours. Tw = 98 o. F = 310. 15 K Tb = 70 o. F (room temperature) = 294. 26 K Attempt w/ LCM (Lumped Capacitance Method) • Show temperature rise will be less likely to damage the blood.

Tubing Tygon 1/2" ID tubing (S-50 -HL Medical Grade) AAX 00037 Tygon 7/8" ID tubing (S-50 -HL Medical Grade BOM
![Tubing Clamps Stepless ear clamps [Oetiker] BOM Double Snap-Grip Nylon Hose and Tube Clamp[Mc. Tubing Clamps Stepless ear clamps [Oetiker] BOM Double Snap-Grip Nylon Hose and Tube Clamp[Mc.](https://present5.com/presentation/464c4a509fe08c78cf294b5649854cb7/image-30.jpg)
Tubing Clamps Stepless ear clamps [Oetiker] BOM Double Snap-Grip Nylon Hose and Tube Clamp[Mc. Master]
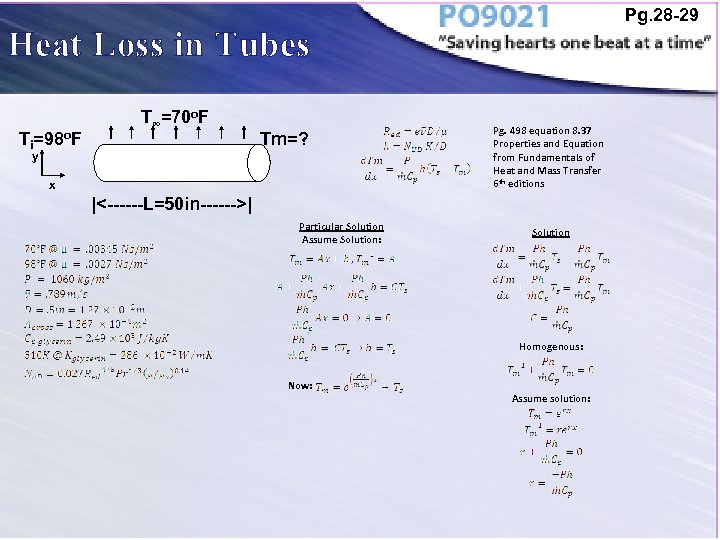
Pg. 28 -29 Heat Loss in Tubes Ti=98 o. F T∞=70 o. F Tm=? y x Pg. 498 equation 8. 37 Properties and Equation from Fundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer 6 th editions |<------L=50 in------>| Particular Solution Assume Solution: Solution Homogenous: Now: Assume solution:
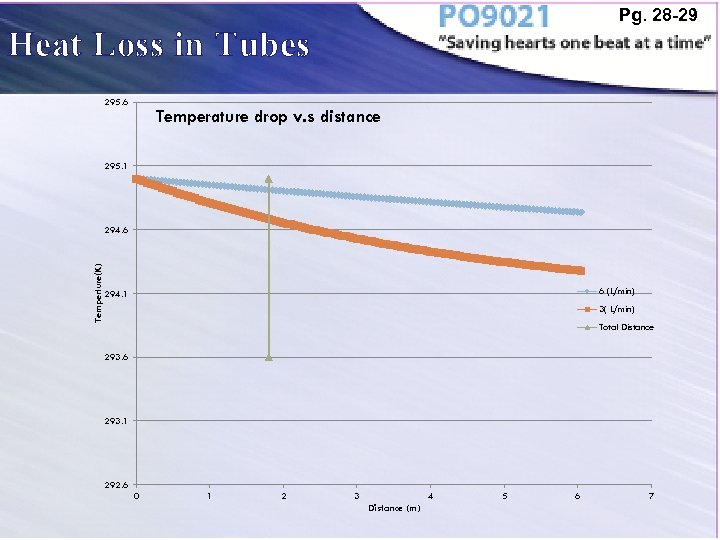
Pg. 28 -29 Heat Loss in Tubes 295. 6 Temperature drop v. s distance 295. 1 Temperture(K) 294. 6 6 (L/min) 294. 1 3( L/min) Total Distance 293. 6 293. 1 292. 6 0 1 2 3 4 Distance (m) 5 6 7

Pg. 30 Resistance Automated - linear actuator & stepper motor combination (Anaheim Automation) Back Up Manual Resistance Competitively priced, high resolution digital captive linear acutuators • Linear force up to 22. 5 lbs (100 N) • Linear step resolution of. 001”, . 002” and. 004” • Unipolar and bipolar coil constructions • Fast, powerful and precise positioning • Precision radial ball bearing design • Industry standard frame size • Customized designs available Parallax BASIC Stamp 2 microcontroller (to control stepper motor) http: //www. anaheimautomation. com/manuals/L 010451%20%20 TSMCA 42%20 Spec%20 Sheet. pdf http: //www. parallax. com/Store/Microcontrollers/BASICStamp. Programmin g. Kits/tabid/136/Category. ID/11/List/0/Sort. Field/0/Level/a/Product. ID/294/De fault. aspx

Pg. 31 Compliance Arterial Tank: Acrylic 7. 2 in tall 8 in OD 7. 75 in ID Bottom & Top: Acrylic 9 in OD 0. 236 thickness Bolts: Steel Hex Nut (1/4"-20, 7/16” width, 5/32" height) x 8 Washer: Stainless Steel x 8 Silicon O-Ring x 2 Barbed Hose Fitting (Stainless - pressure regulator hook-up) (53505 K 72) Quick-connect Air Hose fitting (3/8" NPT threaded) Low-Pressure SS Case. Gauge +/-1% Accuracy 4" Dial, 1/4" NPT (Mc. Master) Cole-Parmer Pressure Regulator
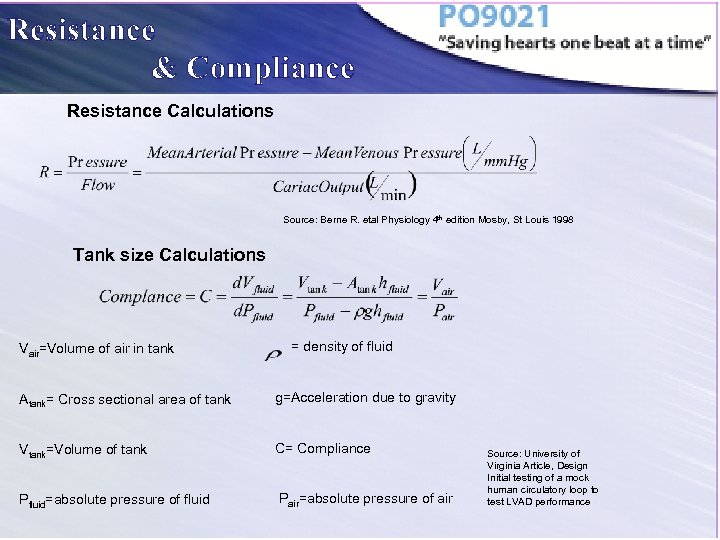
Resistance & Compliance Resistance Calculations Source: Berne R. etal Physiology 4 th edition Mosby, St Louis 1998 Tank size Calculations Vair=Volume of air in tank = density of fluid Atank= Cross sectional area of tank g=Acceleration due to gravity Vtank=Volume of tank C= Compliance Pfluid=absolute pressure of fluid Pair=absolute pressure of air Source: University of Virginia Article, Design Initial testing of a mock human circulatory loop to test LVAD performance
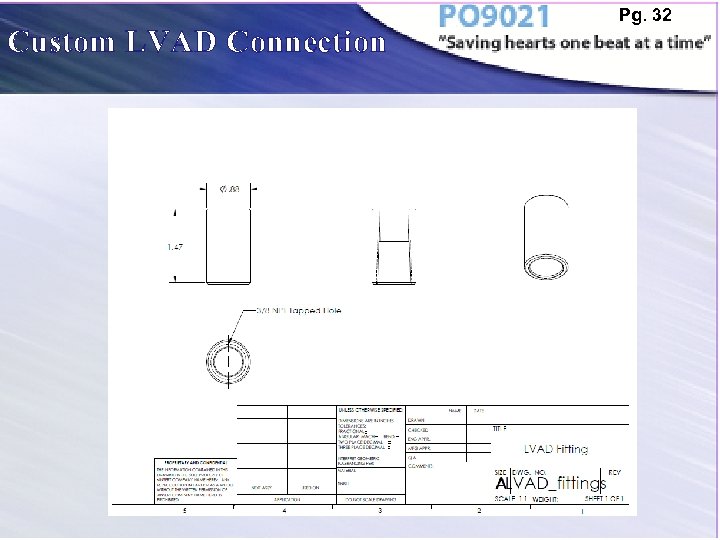
Custom LVAD Connection Pg. 32
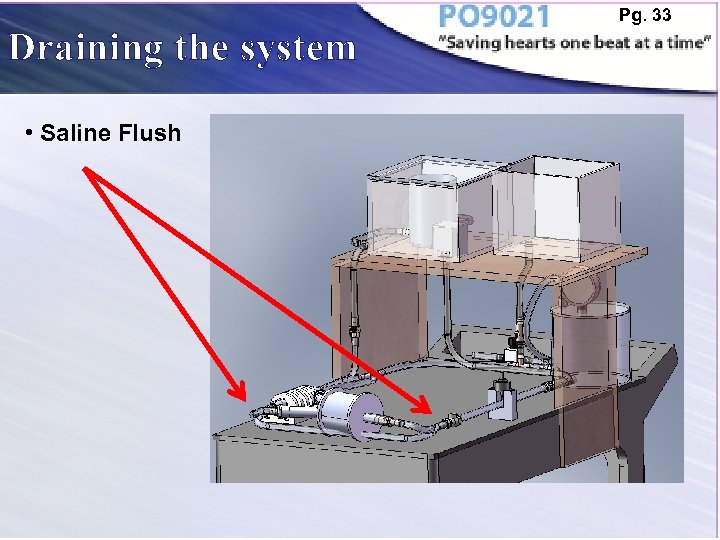
Draining the system • Saline Flush Pg. 33

Pg. 34 Flow Sensors Sensitivity - 0. 156 V/liter Resolution – 7. 8 m. V Flow sensor (Transducer+board digiflow-ext 1 ) Specs Resolution Output format Max measurement Model's specs 1 ml/min -5 V to 5 V Frequency 15 k. Hz to 18 MHz (transmitter frequency) Price Don’t need to purchase

Pg. 34 Pressure Sensors Sensitivity – 10 m. V/psi Resolution – 36. 1µV Pressure Sensor (Omega PX 26 -005 DV ) Specs Model's specs Output format (@10 V) 50 m. V Price $36. 00
Pg. 35 Temperature Sensors Thermocouple. (Omega - KMQSS-020 G-12) Specs Model's specs Type Ungrounded Price $28. 65 S 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24
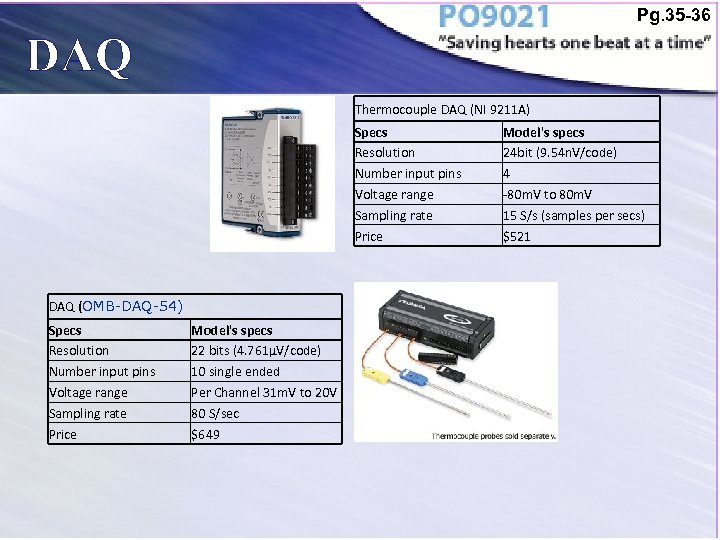
Pg. 35 -36 DAQ Thermocouple DAQ (NI 9211 A) Specs Resolution Number input pins Voltage range Sampling rate Price DAQ (OMB-DAQ-54) Specs Resolution Number input pins Voltage range Sampling rate Price Model's specs 22 bits (4. 761µV/code) 10 single ended Per Channel 31 m. V to 20 V 80 S/sec $649 Model's specs 24 bit (9. 54 n. V/code) 4 -80 m. V to 80 m. V 15 S/s (samples per secs) $521
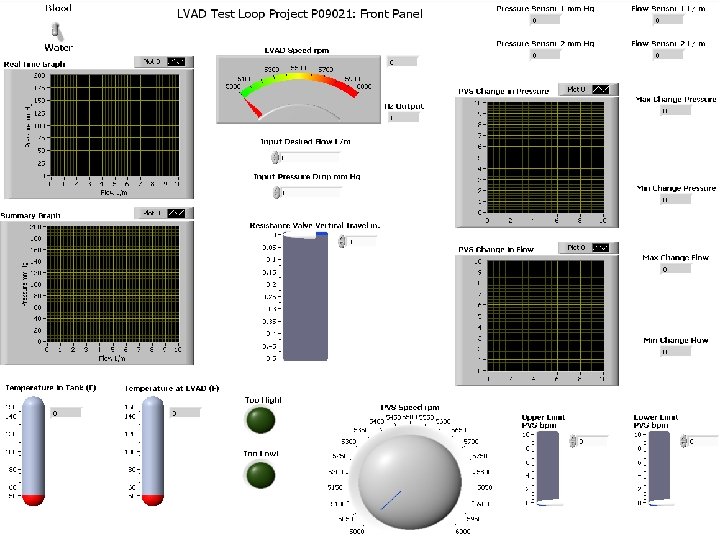
Pg. 11 DAQ ? More needed ? N 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 RISK Dedicated DAQ system not within budget Instrumentation and DAQ not communicating properly, DAQ does not collect or output data properly 6 6 13 14 15 16
464c4a509fe08c78cf294b5649854cb7.ppt