0f4698eea07b3a5d45175e035e9b3fb3.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 11
 v. FLIP vs c. FLIP Cleft 1 Edith Chan WIBR 1
v. FLIP vs c. FLIP Cleft 1 Edith Chan WIBR 1
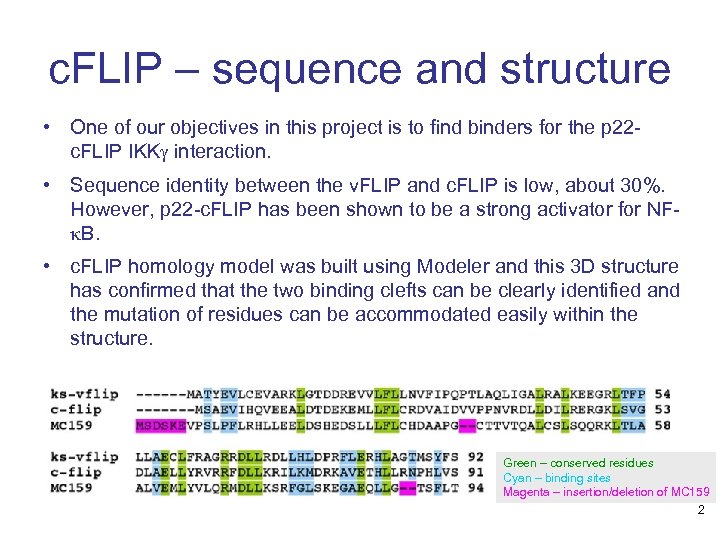 c. FLIP – sequence and structure • One of our objectives in this project is to find binders for the p 22 c. FLIP IKKg interaction. • Sequence identity between the v. FLIP and c. FLIP is low, about 30%. However, p 22 -c. FLIP has been shown to be a strong activator for NFk. B. • c. FLIP homology model was built using Modeler and this 3 D structure has confirmed that the two binding clefts can be clearly identified and the mutation of residues can be accommodated easily within the structure. Green – conserved residues Cyan – binding sites Magenta – insertion/deletion of MC 159 2
c. FLIP – sequence and structure • One of our objectives in this project is to find binders for the p 22 c. FLIP IKKg interaction. • Sequence identity between the v. FLIP and c. FLIP is low, about 30%. However, p 22 -c. FLIP has been shown to be a strong activator for NFk. B. • c. FLIP homology model was built using Modeler and this 3 D structure has confirmed that the two binding clefts can be clearly identified and the mutation of residues can be accommodated easily within the structure. Green – conserved residues Cyan – binding sites Magenta – insertion/deletion of MC 159 2
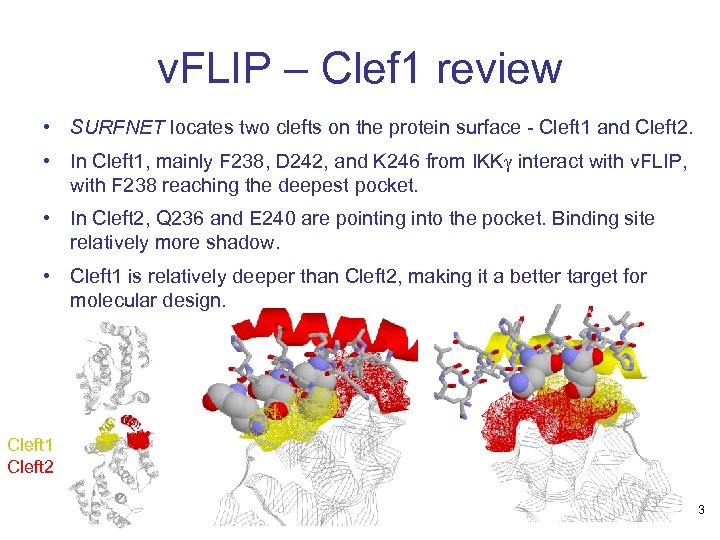 v. FLIP – Clef 1 review • SURFNET locates two clefts on the protein surface - Cleft 1 and Cleft 2. • In Cleft 1, mainly F 238, D 242, and K 246 from IKKg interact with v. FLIP, with F 238 reaching the deepest pocket. • In Cleft 2, Q 236 and E 240 are pointing into the pocket. Binding site relatively more shadow. • Cleft 1 is relatively deeper than Cleft 2, making it a better target for molecular design. Cleft 1 Cleft 2 3
v. FLIP – Clef 1 review • SURFNET locates two clefts on the protein surface - Cleft 1 and Cleft 2. • In Cleft 1, mainly F 238, D 242, and K 246 from IKKg interact with v. FLIP, with F 238 reaching the deepest pocket. • In Cleft 2, Q 236 and E 240 are pointing into the pocket. Binding site relatively more shadow. • Cleft 1 is relatively deeper than Cleft 2, making it a better target for molecular design. Cleft 1 Cleft 2 3
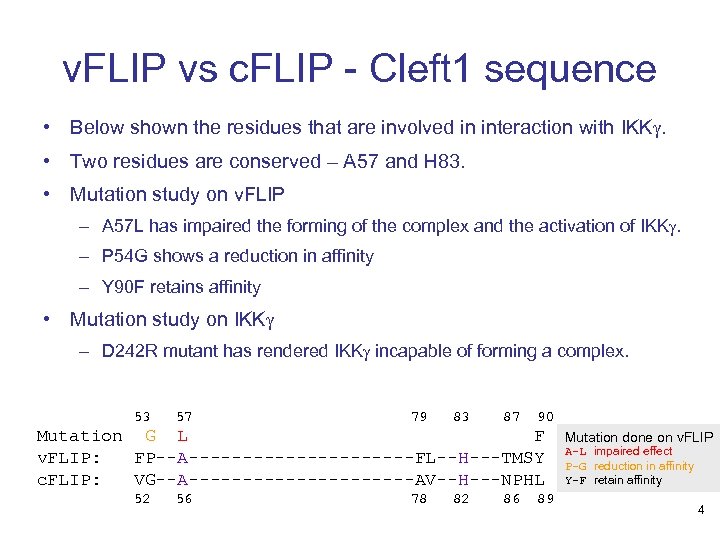 v. FLIP vs c. FLIP - Cleft 1 sequence • Below shown the residues that are involved in interaction with IKKg. • Two residues are conserved – A 57 and H 83. • Mutation study on v. FLIP – A 57 L has impaired the forming of the complex and the activation of IKKg. – P 54 G shows a reduction in affinity – Y 90 F retains affinity • Mutation study on IKKg – D 242 R mutant has rendered IKKg incapable of forming a complex. 53 57 79 83 87 90 Mutation G L F v. FLIP: FP--A-----------FL--H---TMSY c. FLIP: VG--A-----------AV--H---NPHL 52 56 78 82 86 89 Mutation done on v. FLIP A-L impaired effect P-G reduction in affinity Y-F retain affinity 4
v. FLIP vs c. FLIP - Cleft 1 sequence • Below shown the residues that are involved in interaction with IKKg. • Two residues are conserved – A 57 and H 83. • Mutation study on v. FLIP – A 57 L has impaired the forming of the complex and the activation of IKKg. – P 54 G shows a reduction in affinity – Y 90 F retains affinity • Mutation study on IKKg – D 242 R mutant has rendered IKKg incapable of forming a complex. 53 57 79 83 87 90 Mutation G L F v. FLIP: FP--A-----------FL--H---TMSY c. FLIP: VG--A-----------AV--H---NPHL 52 56 78 82 86 89 Mutation done on v. FLIP A-L impaired effect P-G reduction in affinity Y-F retain affinity 4
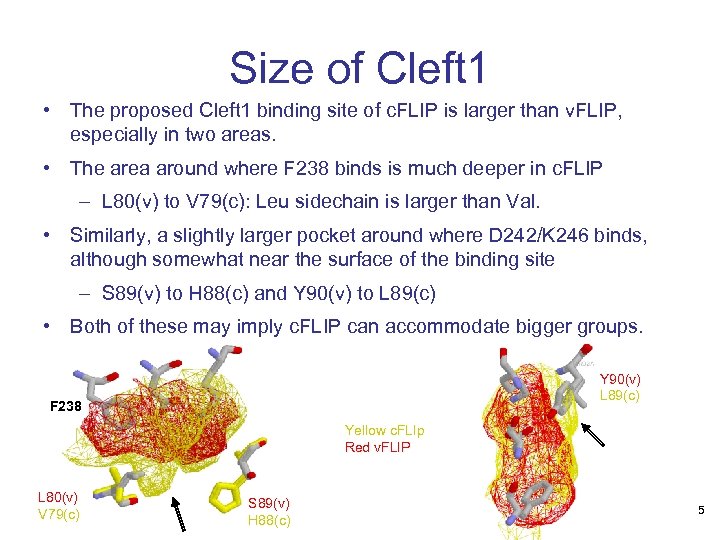 Size of Cleft 1 • The proposed Cleft 1 binding site of c. FLIP is larger than v. FLIP, especially in two areas. • The area around where F 238 binds is much deeper in c. FLIP – L 80(v) to V 79(c): Leu sidechain is larger than Val. • Similarly, a slightly larger pocket around where D 242/K 246 binds, although somewhat near the surface of the binding site – S 89(v) to H 88(c) and Y 90(v) to L 89(c) • Both of these may imply c. FLIP can accommodate bigger groups. Y 90(v) L 89(c) F 238 Yellow c. FLIp Red v. FLIP L 80(v) V 79(c) S 89(v) H 88(c) 5
Size of Cleft 1 • The proposed Cleft 1 binding site of c. FLIP is larger than v. FLIP, especially in two areas. • The area around where F 238 binds is much deeper in c. FLIP – L 80(v) to V 79(c): Leu sidechain is larger than Val. • Similarly, a slightly larger pocket around where D 242/K 246 binds, although somewhat near the surface of the binding site – S 89(v) to H 88(c) and Y 90(v) to L 89(c) • Both of these may imply c. FLIP can accommodate bigger groups. Y 90(v) L 89(c) F 238 Yellow c. FLIp Red v. FLIP L 80(v) V 79(c) S 89(v) H 88(c) 5
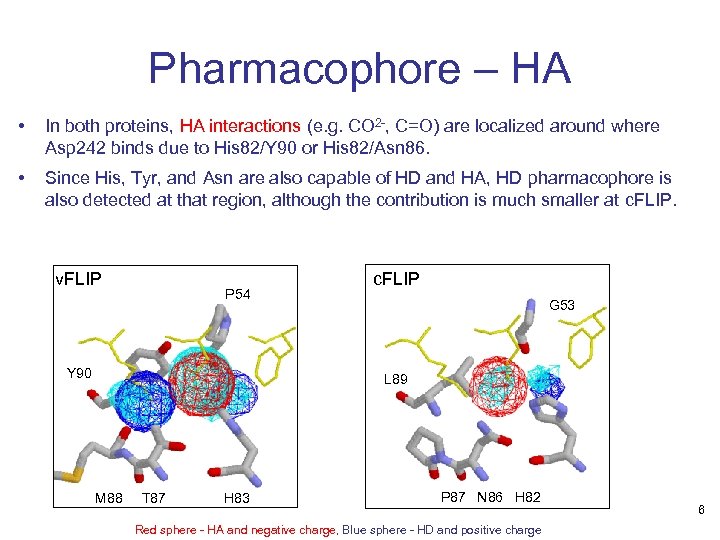 Pharmacophore – HA • In both proteins, HA interactions (e. g. CO 2 -, C=O) are localized around where Asp 242 binds due to His 82/Y 90 or His 82/Asn 86. • Since His, Tyr, and Asn are also capable of HD and HA, HD pharmacophore is also detected at that region, although the contribution is much smaller at c. FLIP. v. FLIP P 54 Y 90 c. FLIP G 53 L 89 M 88 T 87 H 83 P 87 N 86 H 82 Red sphere - HA and negative charge, Blue sphere - HD and positive charge 6
Pharmacophore – HA • In both proteins, HA interactions (e. g. CO 2 -, C=O) are localized around where Asp 242 binds due to His 82/Y 90 or His 82/Asn 86. • Since His, Tyr, and Asn are also capable of HD and HA, HD pharmacophore is also detected at that region, although the contribution is much smaller at c. FLIP. v. FLIP P 54 Y 90 c. FLIP G 53 L 89 M 88 T 87 H 83 P 87 N 86 H 82 Red sphere - HA and negative charge, Blue sphere - HD and positive charge 6
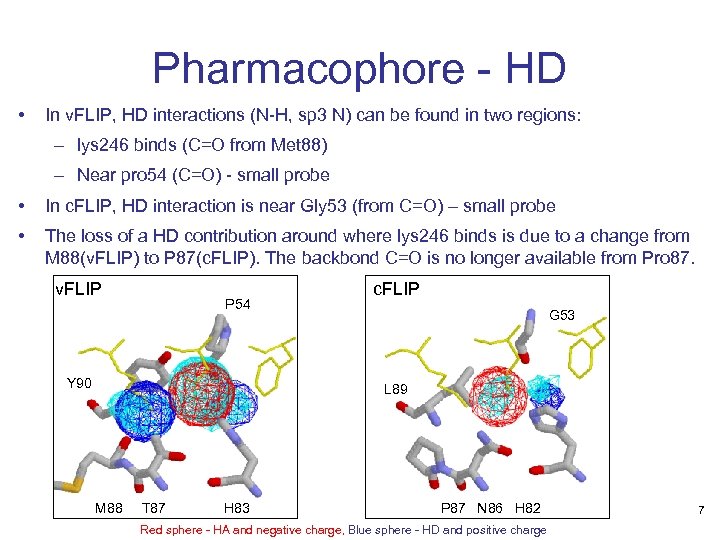 Pharmacophore - HD • In v. FLIP, HD interactions (N-H, sp 3 N) can be found in two regions: – lys 246 binds (C=O from Met 88) – Near pro 54 (C=O) - small probe • In c. FLIP, HD interaction is near Gly 53 (from C=O) – small probe • The loss of a HD contribution around where lys 246 binds is due to a change from M 88(v. FLIP) to P 87(c. FLIP). The backbond C=O is no longer available from Pro 87. v. FLIP P 54 Y 90 c. FLIP G 53 L 89 M 88 T 87 H 83 P 87 N 86 H 82 Red sphere - HA and negative charge, Blue sphere - HD and positive charge 7
Pharmacophore - HD • In v. FLIP, HD interactions (N-H, sp 3 N) can be found in two regions: – lys 246 binds (C=O from Met 88) – Near pro 54 (C=O) - small probe • In c. FLIP, HD interaction is near Gly 53 (from C=O) – small probe • The loss of a HD contribution around where lys 246 binds is due to a change from M 88(v. FLIP) to P 87(c. FLIP). The backbond C=O is no longer available from Pro 87. v. FLIP P 54 Y 90 c. FLIP G 53 L 89 M 88 T 87 H 83 P 87 N 86 H 82 Red sphere - HA and negative charge, Blue sphere - HD and positive charge 7
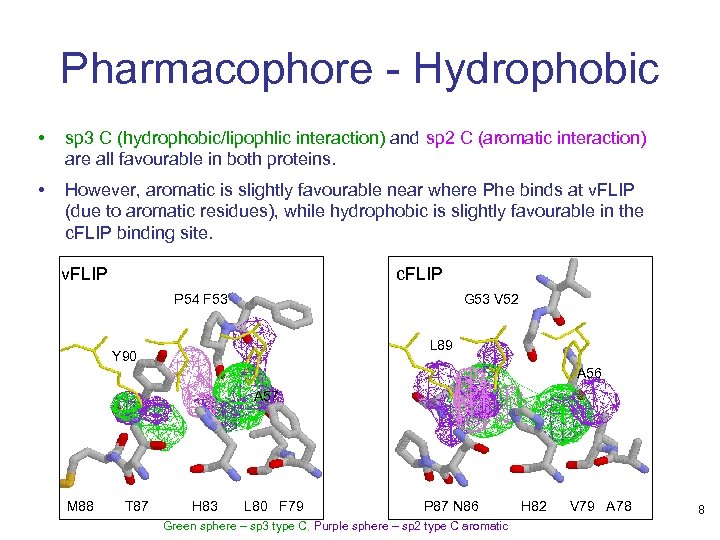 Pharmacophore - Hydrophobic • sp 3 C (hydrophobic/lipophlic interaction) and sp 2 C (aromatic interaction) are all favourable in both proteins. • However, aromatic is slightly favourable near where Phe binds at v. FLIP (due to aromatic residues), while hydrophobic is slightly favourable in the c. FLIP binding site. v. FLIP c. FLIP P 54 F 53 G 53 V 52 L 89 Y 90 A 56 A 57 M 88 T 87 H 83 L 80 F 79 P 87 N 86 Green sphere – sp 3 type C, Purple sphere – sp 2 type C aromatic H 82 V 79 A 78 8
Pharmacophore - Hydrophobic • sp 3 C (hydrophobic/lipophlic interaction) and sp 2 C (aromatic interaction) are all favourable in both proteins. • However, aromatic is slightly favourable near where Phe binds at v. FLIP (due to aromatic residues), while hydrophobic is slightly favourable in the c. FLIP binding site. v. FLIP c. FLIP P 54 F 53 G 53 V 52 L 89 Y 90 A 56 A 57 M 88 T 87 H 83 L 80 F 79 P 87 N 86 Green sphere – sp 3 type C, Purple sphere – sp 2 type C aromatic H 82 V 79 A 78 8
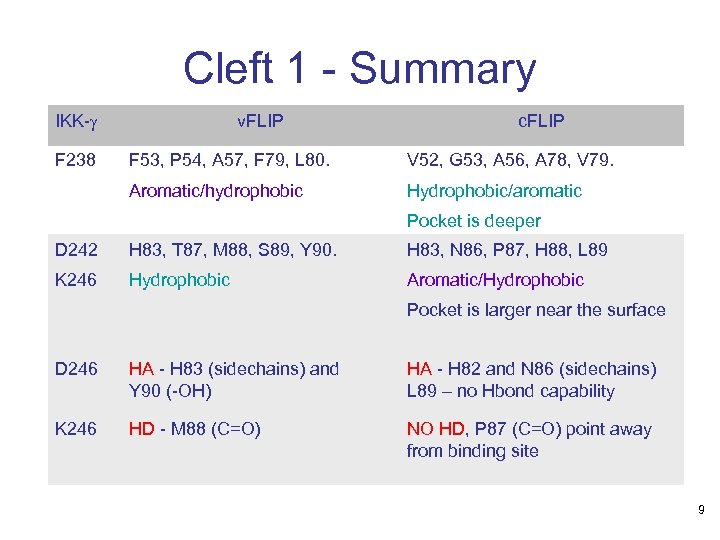 Cleft 1 - Summary IKK-g F 238 v. FLIP c. FLIP F 53, P 54, A 57, F 79, L 80. V 52, G 53, A 56, A 78, V 79. Aromatic/hydrophobic Hydrophobic/aromatic Pocket is deeper D 242 H 83, T 87, M 88, S 89, Y 90. H 83, N 86, P 87, H 88, L 89 K 246 Hydrophobic Aromatic/Hydrophobic Pocket is larger near the surface D 246 HA - H 83 (sidechains) and Y 90 (-OH) HA - H 82 and N 86 (sidechains) L 89 – no Hbond capability K 246 HD - M 88 (C=O) NO HD, P 87 (C=O) point away from binding site 9
Cleft 1 - Summary IKK-g F 238 v. FLIP c. FLIP F 53, P 54, A 57, F 79, L 80. V 52, G 53, A 56, A 78, V 79. Aromatic/hydrophobic Hydrophobic/aromatic Pocket is deeper D 242 H 83, T 87, M 88, S 89, Y 90. H 83, N 86, P 87, H 88, L 89 K 246 Hydrophobic Aromatic/Hydrophobic Pocket is larger near the surface D 246 HA - H 83 (sidechains) and Y 90 (-OH) HA - H 82 and N 86 (sidechains) L 89 – no Hbond capability K 246 HD - M 88 (C=O) NO HD, P 87 (C=O) point away from binding site 9
 Compounds to buy • Aryl sulfonamides • Isoindolinones – have not found suitable compounds to buy yet (Chem. Div) • Nutlins – wait for more compounds to be ordered at the same time 10
Compounds to buy • Aryl sulfonamides • Isoindolinones – have not found suitable compounds to buy yet (Chem. Div) • Nutlins – wait for more compounds to be ordered at the same time 10
 Sulfonamides • Chem. Bridge • 1 mg or 5 mg $38 • 10 compounds selected. 11
Sulfonamides • Chem. Bridge • 1 mg or 5 mg $38 • 10 compounds selected. 11


