ed4bbfc708872244356e59197ada3d49.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 107
 Uttar Pradesh 26 th May, 2008 1
Uttar Pradesh 26 th May, 2008 1
 Trends in State Finances 2
Trends in State Finances 2
 Fiscal Consolidation The FRBM Act envisages elimination of revenue deficit and reduction of the fiscal deficit/GSDP ratio to 3. 0% by the year 2008 -09 l Both the targets have been achieved two years in advance in 2006 -07 and the level of consolidation achieved is most likely to be maintained l Important features of changes in fiscal stance of the State l Ø Improvement in tax performance Ø Major jump in plan expenditure Ø Sustained increase in capital outlays Ø Debt/GSDP ratio begins to fall 3
Fiscal Consolidation The FRBM Act envisages elimination of revenue deficit and reduction of the fiscal deficit/GSDP ratio to 3. 0% by the year 2008 -09 l Both the targets have been achieved two years in advance in 2006 -07 and the level of consolidation achieved is most likely to be maintained l Important features of changes in fiscal stance of the State l Ø Improvement in tax performance Ø Major jump in plan expenditure Ø Sustained increase in capital outlays Ø Debt/GSDP ratio begins to fall 3
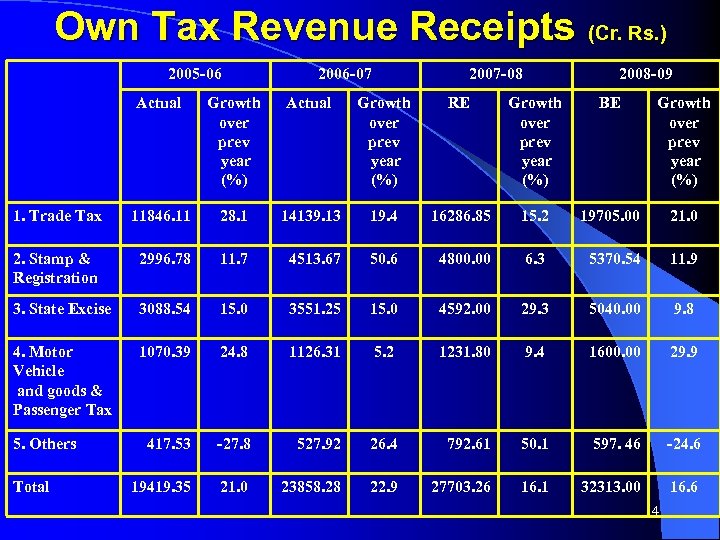 Own Tax Revenue Receipts (Cr. Rs. ) 2005 -06 2006 -07 2007 -08 2008 -09 Actual Growth over prev year (%) RE Growth over prev year (%) BE Growth over prev year (%) 1. Trade Tax 11846. 11 28. 1 14139. 13 19. 4 16286. 85 15. 2 19705. 00 21. 0 2. Stamp & Registration 2996. 78 11. 7 4513. 67 50. 6 4800. 00 6. 3 5370. 54 11. 9 3. State Excise 3088. 54 15. 0 3551. 25 15. 0 4592. 00 29. 3 5040. 00 9. 8 4. Motor Vehicle and goods & Passenger Tax 1070. 39 24. 8 1126. 31 5. 2 1231. 80 9. 4 1600. 00 29. 9 417. 53 -27. 8 527. 92 26. 4 792. 61 50. 1 597. 46 -24. 6 19419. 35 21. 0 23858. 28 22. 9 27703. 26 16. 1 32313. 00 16. 6 5. Others Total 4
Own Tax Revenue Receipts (Cr. Rs. ) 2005 -06 2006 -07 2007 -08 2008 -09 Actual Growth over prev year (%) RE Growth over prev year (%) BE Growth over prev year (%) 1. Trade Tax 11846. 11 28. 1 14139. 13 19. 4 16286. 85 15. 2 19705. 00 21. 0 2. Stamp & Registration 2996. 78 11. 7 4513. 67 50. 6 4800. 00 6. 3 5370. 54 11. 9 3. State Excise 3088. 54 15. 0 3551. 25 15. 0 4592. 00 29. 3 5040. 00 9. 8 4. Motor Vehicle and goods & Passenger Tax 1070. 39 24. 8 1126. 31 5. 2 1231. 80 9. 4 1600. 00 29. 9 417. 53 -27. 8 527. 92 26. 4 792. 61 50. 1 597. 46 -24. 6 19419. 35 21. 0 23858. 28 22. 9 27703. 26 16. 1 32313. 00 16. 6 5. Others Total 4
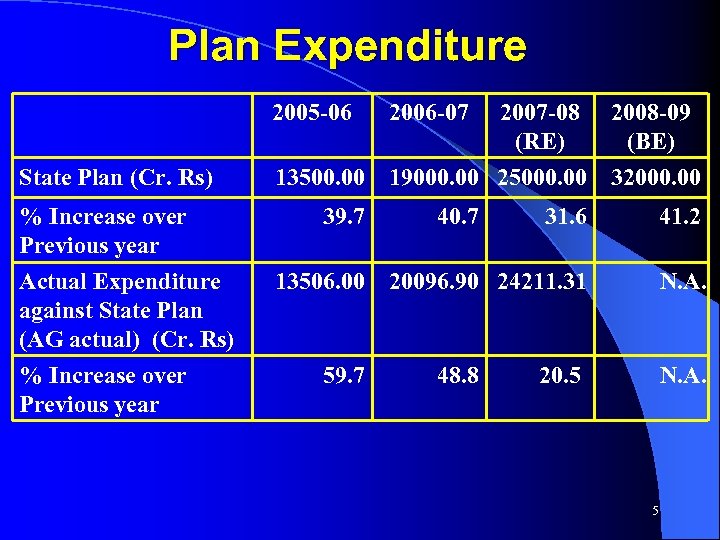 Plan Expenditure 2005 -06 State Plan (Cr. Rs) 13500. 00 % Increase over Previous year Actual Expenditure against State Plan (AG actual) (Cr. Rs) % Increase over Previous year 39. 7 13506. 00 59. 7 2006 -07 2007 -08 (RE) 19000. 00 25000. 00 40. 7 2008 -09 (BE) 32000. 00 31. 6 41. 2 20096. 90 24211. 31 N. A. 48. 8 20. 5 N. A. 5
Plan Expenditure 2005 -06 State Plan (Cr. Rs) 13500. 00 % Increase over Previous year Actual Expenditure against State Plan (AG actual) (Cr. Rs) % Increase over Previous year 39. 7 13506. 00 59. 7 2006 -07 2007 -08 (RE) 19000. 00 25000. 00 40. 7 2008 -09 (BE) 32000. 00 31. 6 41. 2 20096. 90 24211. 31 N. A. 48. 8 20. 5 N. A. 5
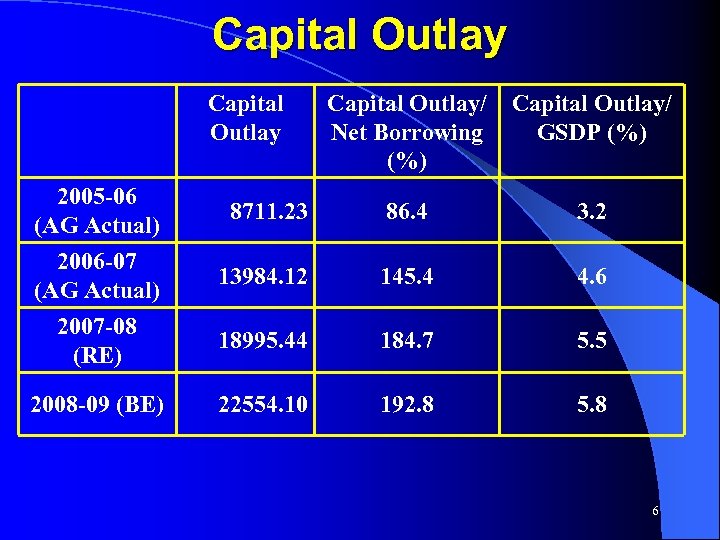 Capital Outlay Capital Outlay/ Net Borrowing (%) Capital Outlay/ GSDP (%) 2005 -06 (AG Actual) 8711. 23 86. 4 3. 2 2006 -07 (AG Actual) 13984. 12 145. 4 4. 6 2007 -08 (RE) 18995. 44 184. 7 5. 5 2008 -09 (BE) 22554. 10 192. 8 5. 8 6
Capital Outlay Capital Outlay/ Net Borrowing (%) Capital Outlay/ GSDP (%) 2005 -06 (AG Actual) 8711. 23 86. 4 3. 2 2006 -07 (AG Actual) 13984. 12 145. 4 4. 6 2007 -08 (RE) 18995. 44 184. 7 5. 5 2008 -09 (BE) 22554. 10 192. 8 5. 8 6
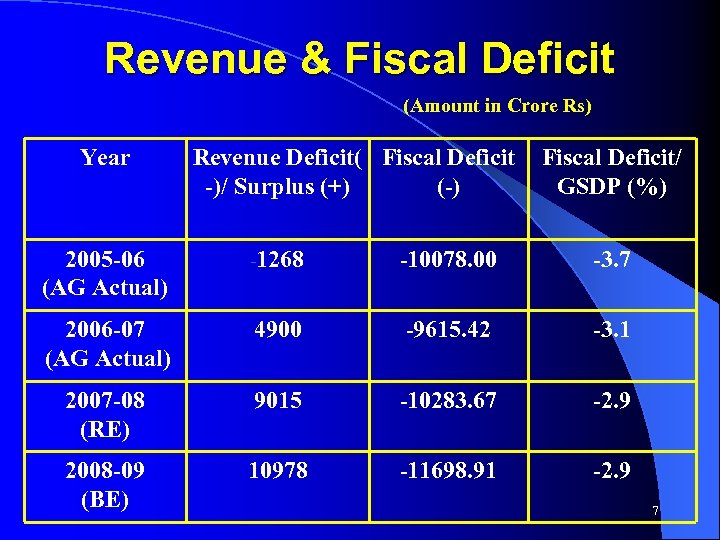 Revenue & Fiscal Deficit (Amount in Crore Rs) Year Revenue Deficit( Fiscal Deficit/ -)/ Surplus (+) (-) GSDP (%) 2005 -06 (AG Actual) -1268 -10078. 00 -3. 7 2006 -07 (AG Actual) 4900 -9615. 42 -3. 1 2007 -08 (RE) 9015 -10283. 67 -2. 9 2008 -09 (BE) 10978 -11698. 91 -2. 9 7
Revenue & Fiscal Deficit (Amount in Crore Rs) Year Revenue Deficit( Fiscal Deficit/ -)/ Surplus (+) (-) GSDP (%) 2005 -06 (AG Actual) -1268 -10078. 00 -3. 7 2006 -07 (AG Actual) 4900 -9615. 42 -3. 1 2007 -08 (RE) 9015 -10283. 67 -2. 9 2008 -09 (BE) 10978 -11698. 91 -2. 9 7
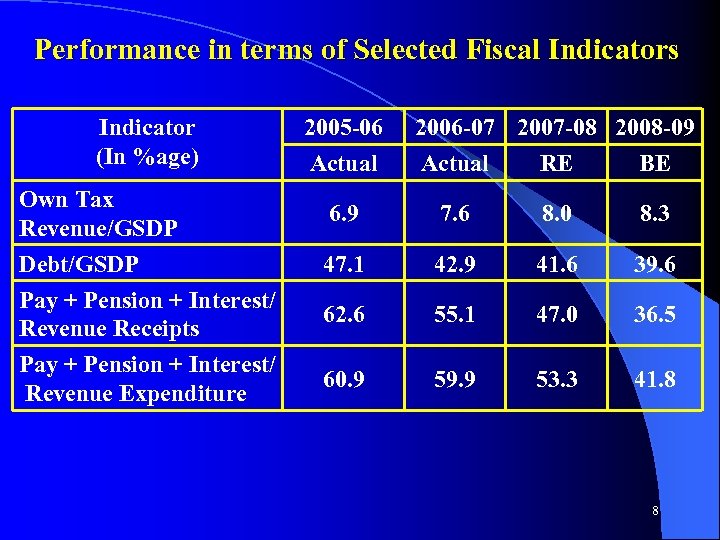 Performance in terms of Selected Fiscal Indicators Indicator (In %age) Own Tax Revenue/GSDP Debt/GSDP Pay + Pension + Interest/ Revenue Receipts Pay + Pension + Interest/ Revenue Expenditure 2005 -06 Actual 2006 -07 2007 -08 2008 -09 Actual RE BE 6. 9 7. 6 8. 0 8. 3 47. 1 42. 9 41. 6 39. 6 62. 6 55. 1 47. 0 36. 5 60. 9 59. 9 53. 3 41. 8 8
Performance in terms of Selected Fiscal Indicators Indicator (In %age) Own Tax Revenue/GSDP Debt/GSDP Pay + Pension + Interest/ Revenue Receipts Pay + Pension + Interest/ Revenue Expenditure 2005 -06 Actual 2006 -07 2007 -08 2008 -09 Actual RE BE 6. 9 7. 6 8. 0 8. 3 47. 1 42. 9 41. 6 39. 6 62. 6 55. 1 47. 0 36. 5 60. 9 59. 9 53. 3 41. 8 8
 Debt Waiver Total Debt waiver admissible to Go. UP under TFC award (Crore Rs. ) 1063. 71 per year Actual Debt Waiver received so far For the year 2004 -05 1063. 71 For the year 2005 -06 1063. 71 For the year 2006 -07 1063. 91 9
Debt Waiver Total Debt waiver admissible to Go. UP under TFC award (Crore Rs. ) 1063. 71 per year Actual Debt Waiver received so far For the year 2004 -05 1063. 71 For the year 2005 -06 1063. 71 For the year 2006 -07 1063. 91 9
 OUR STRENGTHS • Fertile land water resources • Largest producer of wheat, sugarcane, potato, mango, vegetables and milk. • Largest skilled/un-skilled manpower • Immense potential for tourism development • Good prospects for dairy development, meat production, horticulture development, food processing and agro based industries • Largest market for consumer goods 10
OUR STRENGTHS • Fertile land water resources • Largest producer of wheat, sugarcane, potato, mango, vegetables and milk. • Largest skilled/un-skilled manpower • Immense potential for tourism development • Good prospects for dairy development, meat production, horticulture development, food processing and agro based industries • Largest market for consumer goods 10
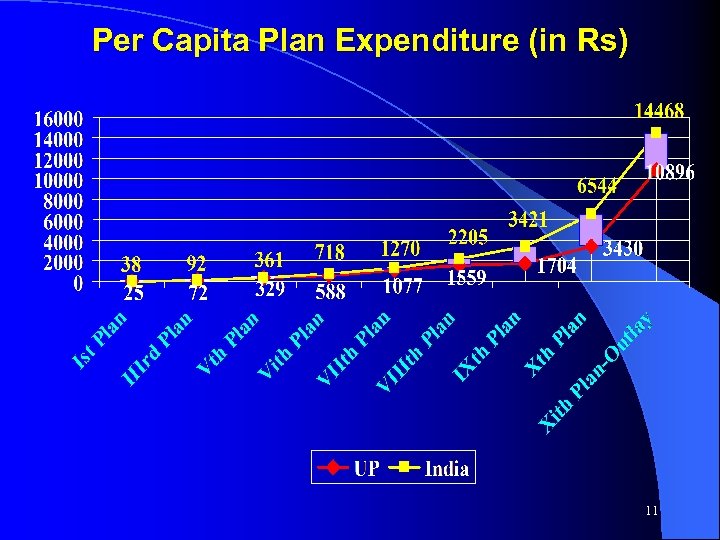 Per Capita Plan Expenditure (in Rs) 11
Per Capita Plan Expenditure (in Rs) 11
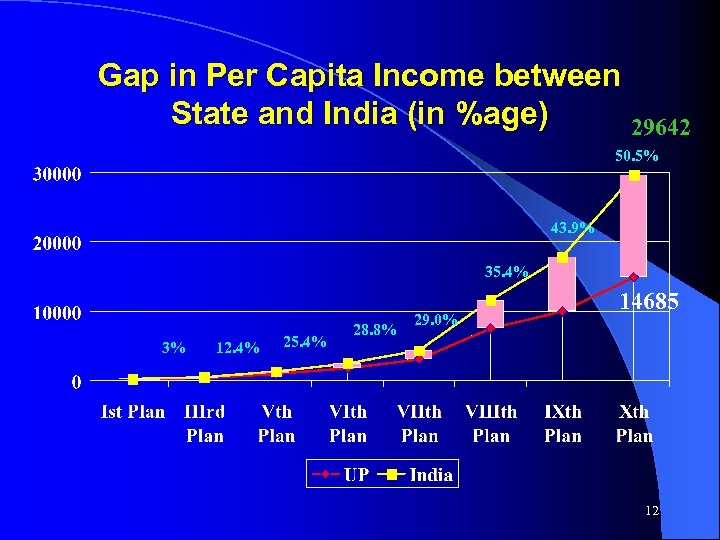 Gap in Per Capita Income between State and India (in %age) 29642 50. 5% 43. 9% 35. 4% 3% 12. 4% 25. 4% 28. 8% 29. 0% 14685 12
Gap in Per Capita Income between State and India (in %age) 29642 50. 5% 43. 9% 35. 4% 3% 12. 4% 25. 4% 28. 8% 29. 0% 14685 12
 MAJOR CHALLENGES • • • Bridging the increasing gap in per capita income of the State and India Placing the state on high growth trajectory Creating adequate power generation & quality power supply Reducing regional disparities Minimising poverty level Accelerating growth in agriculture and allied sectors. Strengthening of urban and rural infrastructure Creating sustainable employment opportunities To improve human development indices keeping in view the MDG - IMR, MMR, TFR, anaemia, mal-nutrition, gender gap in literacy, sex ratio 13
MAJOR CHALLENGES • • • Bridging the increasing gap in per capita income of the State and India Placing the state on high growth trajectory Creating adequate power generation & quality power supply Reducing regional disparities Minimising poverty level Accelerating growth in agriculture and allied sectors. Strengthening of urban and rural infrastructure Creating sustainable employment opportunities To improve human development indices keeping in view the MDG - IMR, MMR, TFR, anaemia, mal-nutrition, gender gap in literacy, sex ratio 13
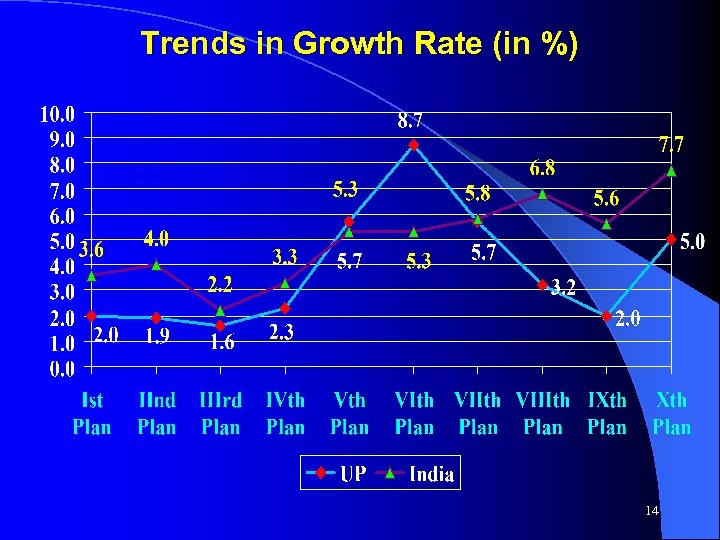 Trends in Growth Rate (in %) 14
Trends in Growth Rate (in %) 14
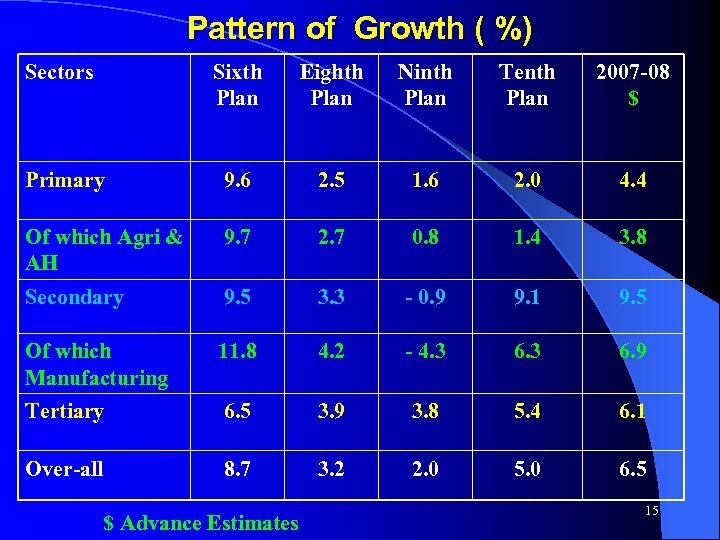 Pattern of Growth ( %) Sectors Sixth Plan Eighth Plan Ninth Plan Tenth Plan 2007 -08 $ Primary 9. 6 2. 5 1. 6 2. 0 4. 4 Of which Agri & AH 9. 7 2. 7 0. 8 1. 4 3. 8 Secondary 9. 5 3. 3 - 0. 9 9. 1 9. 5 Of which Manufacturing 11. 8 4. 2 - 4. 3 6. 9 Tertiary 6. 5 3. 9 3. 8 5. 4 6. 1 Over-all 8. 7 3. 2 2. 0 5. 0 6. 5 $ Advance Estimates 15
Pattern of Growth ( %) Sectors Sixth Plan Eighth Plan Ninth Plan Tenth Plan 2007 -08 $ Primary 9. 6 2. 5 1. 6 2. 0 4. 4 Of which Agri & AH 9. 7 2. 7 0. 8 1. 4 3. 8 Secondary 9. 5 3. 3 - 0. 9 9. 1 9. 5 Of which Manufacturing 11. 8 4. 2 - 4. 3 6. 9 Tertiary 6. 5 3. 9 3. 8 5. 4 6. 1 Over-all 8. 7 3. 2 2. 0 5. 0 6. 5 $ Advance Estimates 15
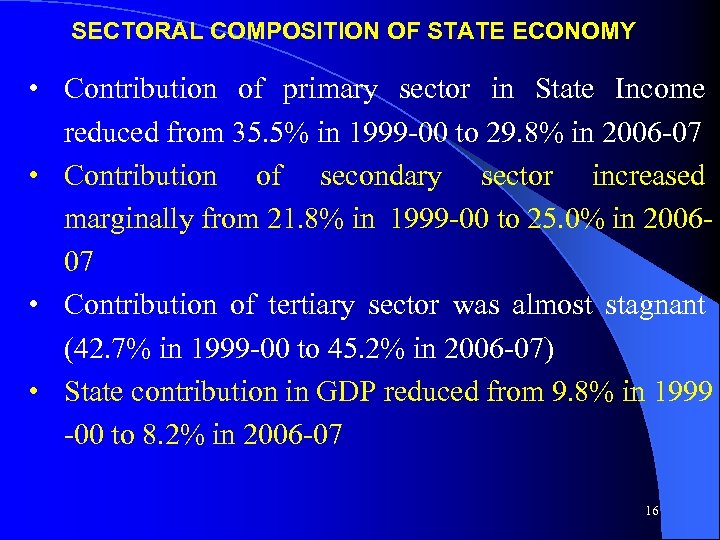 SECTORAL COMPOSITION OF STATE ECONOMY • Contribution of primary sector in State Income reduced from 35. 5% in 1999 -00 to 29. 8% in 2006 -07 • Contribution of secondary sector increased marginally from 21. 8% in 1999 -00 to 25. 0% in 200607 • Contribution of tertiary sector was almost stagnant (42. 7% in 1999 -00 to 45. 2% in 2006 -07) • State contribution in GDP reduced from 9. 8% in 1999 -00 to 8. 2% in 2006 -07 16
SECTORAL COMPOSITION OF STATE ECONOMY • Contribution of primary sector in State Income reduced from 35. 5% in 1999 -00 to 29. 8% in 2006 -07 • Contribution of secondary sector increased marginally from 21. 8% in 1999 -00 to 25. 0% in 200607 • Contribution of tertiary sector was almost stagnant (42. 7% in 1999 -00 to 45. 2% in 2006 -07) • State contribution in GDP reduced from 9. 8% in 1999 -00 to 8. 2% in 2006 -07 16
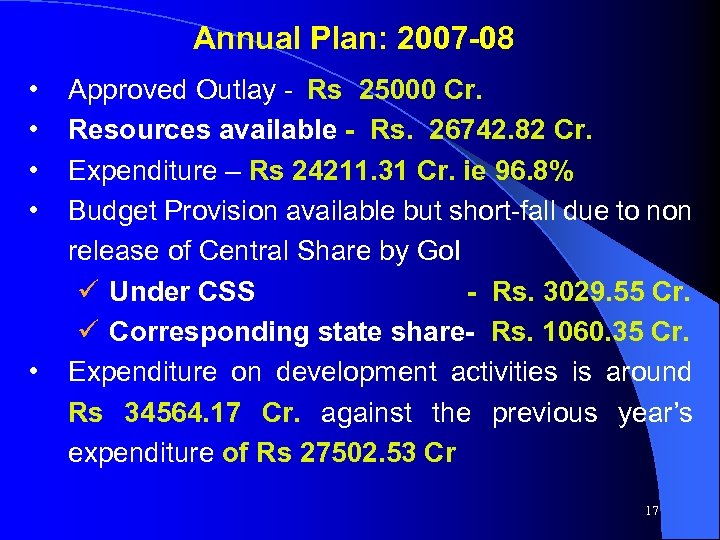 Annual Plan: 2007 -08 • • • Approved Outlay - Rs 25000 Cr. Resources available - Rs. 26742. 82 Cr. Expenditure – Rs 24211. 31 Cr. ie 96. 8% Budget Provision available but short-fall due to non release of Central Share by Go. I ü Under CSS - Rs. 3029. 55 Cr. ü Corresponding state share- Rs. 1060. 35 Cr. Expenditure on development activities is around Rs 34564. 17 Cr. against the previous year’s expenditure of Rs 27502. 53 Cr 17
Annual Plan: 2007 -08 • • • Approved Outlay - Rs 25000 Cr. Resources available - Rs. 26742. 82 Cr. Expenditure – Rs 24211. 31 Cr. ie 96. 8% Budget Provision available but short-fall due to non release of Central Share by Go. I ü Under CSS - Rs. 3029. 55 Cr. ü Corresponding state share- Rs. 1060. 35 Cr. Expenditure on development activities is around Rs 34564. 17 Cr. against the previous year’s expenditure of Rs 27502. 53 Cr 17
 MAJOR POLICY INITIATIVES TAKEN BY THE STATE GOVERNMENT • VAT introduced in the State from 1 st January, 2008 • To promote agricultural research and extension work in Bundelkhand area, a new agricultural university is being established in Banda district. On the pattern of National Horticulture Mission, State Horticultural Mission launched in the remaining 31 districts through state resources. On the pattern of IAY, a special state funded rural housing scheme Mahamaya Awas Yojana launched and one lakh houses already constructed. All villages to be saturated with basic amenities/services under Dr Ambedkar Gram Sabha Samagra Vikas Yojana in a phased manner. Minimum wage for unskilled labour increased from Rs 58 to Rs 100 per day. To rejuvenate urban infrastructure and services, a special state funded scheme- Manyavar Sri Kanshi Ramji Shahri Samagra Vikas Yojana launched. • • • 18
MAJOR POLICY INITIATIVES TAKEN BY THE STATE GOVERNMENT • VAT introduced in the State from 1 st January, 2008 • To promote agricultural research and extension work in Bundelkhand area, a new agricultural university is being established in Banda district. On the pattern of National Horticulture Mission, State Horticultural Mission launched in the remaining 31 districts through state resources. On the pattern of IAY, a special state funded rural housing scheme Mahamaya Awas Yojana launched and one lakh houses already constructed. All villages to be saturated with basic amenities/services under Dr Ambedkar Gram Sabha Samagra Vikas Yojana in a phased manner. Minimum wage for unskilled labour increased from Rs 58 to Rs 100 per day. To rejuvenate urban infrastructure and services, a special state funded scheme- Manyavar Sri Kanshi Ramji Shahri Samagra Vikas Yojana launched. • • • 18
 MAJOR POLICY INITIATIVES TAKEN BY THE STATE GOVERNMENT • • For integrated development of smaller towns with less than one lakh population, a special state funded scheme- Adarsh Nagar Yojana launched. All villages to be covered by a new scheme of CC roads and KC drains Scholarship distribution computerised by direct transfer of funds to students accounts through banking network thereby ensuring transparency and savings of about Rs 600 Cr during 2007 -08. E-procurement being introduced in the State in six major departments. Several major infrastructure projects being taken-up under PPP mode - Roads and Bridges, Medical, Transport, Power Generation, Airport, Tourism, urban rejuvenation etc. Special initiatives taken for drought proofing in Bundelkhand Vindhyanchal region. Old age and Widow pension rates doubled from Rs 150 to Rs 300 per month and all eligible BPL beneficiary are being covered. More than 50 lakh benefitted. English language as a subject introduced from Class I. 19
MAJOR POLICY INITIATIVES TAKEN BY THE STATE GOVERNMENT • • For integrated development of smaller towns with less than one lakh population, a special state funded scheme- Adarsh Nagar Yojana launched. All villages to be covered by a new scheme of CC roads and KC drains Scholarship distribution computerised by direct transfer of funds to students accounts through banking network thereby ensuring transparency and savings of about Rs 600 Cr during 2007 -08. E-procurement being introduced in the State in six major departments. Several major infrastructure projects being taken-up under PPP mode - Roads and Bridges, Medical, Transport, Power Generation, Airport, Tourism, urban rejuvenation etc. Special initiatives taken for drought proofing in Bundelkhand Vindhyanchal region. Old age and Widow pension rates doubled from Rs 150 to Rs 300 per month and all eligible BPL beneficiary are being covered. More than 50 lakh benefitted. English language as a subject introduced from Class I. 19
 SPECIAL DROUGHT RELIEF /DROUGHT PROOFING MEASURES • Food-grain bank introduced in every village in the drought affected districts in Bundelkhand Mirzapur regions. 15 kg of food-grain per month being distributed free of cost to all destitute persons. • Community kitchen established in every village to provide cooked food to destitute persons. • Mid-day meal facility extended during summer vacations. • Cattle camp established in the affected areas. • More than Rs 600 Cr sanctioned for drought relief works and agriculture input subsidy. • 100 percent subsidy being provided in Bundelkhand for drip and sprinkler irrigation to SC/ST families and 75 % subsidy to small and marginal farmers. • Medical kit distributed to 8 lakh school children. • Augmentation of drinking water in rural and urban areas by way of improving the piped water supply system, installation/re-boring of hand-pumps. • Development and improvement of water tanks and village ponds, deepening of wells through blasting. • More than 3000 private tube-wells energised to augment drinking water supply. • More than 500 tankers deployed for drinking water supply in the urban and rural areas. 20
SPECIAL DROUGHT RELIEF /DROUGHT PROOFING MEASURES • Food-grain bank introduced in every village in the drought affected districts in Bundelkhand Mirzapur regions. 15 kg of food-grain per month being distributed free of cost to all destitute persons. • Community kitchen established in every village to provide cooked food to destitute persons. • Mid-day meal facility extended during summer vacations. • Cattle camp established in the affected areas. • More than Rs 600 Cr sanctioned for drought relief works and agriculture input subsidy. • 100 percent subsidy being provided in Bundelkhand for drip and sprinkler irrigation to SC/ST families and 75 % subsidy to small and marginal farmers. • Medical kit distributed to 8 lakh school children. • Augmentation of drinking water in rural and urban areas by way of improving the piped water supply system, installation/re-boring of hand-pumps. • Development and improvement of water tanks and village ponds, deepening of wells through blasting. • More than 3000 private tube-wells energised to augment drinking water supply. • More than 500 tankers deployed for drinking water supply in the urban and rural areas. 20
 Highlights of Annual Plan (2007 -08) Performance • • • State economy grew at 6. 4 % Food-grains production reached the level of 419. 64 lakh tonnes. Work started on the site of 1000 MW Anpara’C’ by the private developer. AT&C losses reduced by 3. 4% in 2007 -08 24. 98 lakh employment generated through various development programmes. Under NREGA, 13. 63 crore man-days generated and Rs 1898. 25 Cr spent and more than 40 lakh families got employment. Under PMGSY, an expenditure of Rs 1186 Cr incurred and 2657 km roads constructed and 1093 habitations connected by all weather roads. 7000 kms new village roads constructed, 10000 km village roads reconstructed and 80 bridges constructed 2. 55 lakh Indira Awas constructed and additional one lakh houses constructed through state resources under Mahamaya Awas Yojana. 21. 51 lakh toilets constructed under Total Sanitation Campaign and 51% coverage achieved. 2. 37 lakh new hand-pumps installed and 1075 quality affected habitations covered. 21
Highlights of Annual Plan (2007 -08) Performance • • • State economy grew at 6. 4 % Food-grains production reached the level of 419. 64 lakh tonnes. Work started on the site of 1000 MW Anpara’C’ by the private developer. AT&C losses reduced by 3. 4% in 2007 -08 24. 98 lakh employment generated through various development programmes. Under NREGA, 13. 63 crore man-days generated and Rs 1898. 25 Cr spent and more than 40 lakh families got employment. Under PMGSY, an expenditure of Rs 1186 Cr incurred and 2657 km roads constructed and 1093 habitations connected by all weather roads. 7000 kms new village roads constructed, 10000 km village roads reconstructed and 80 bridges constructed 2. 55 lakh Indira Awas constructed and additional one lakh houses constructed through state resources under Mahamaya Awas Yojana. 21. 51 lakh toilets constructed under Total Sanitation Campaign and 51% coverage achieved. 2. 37 lakh new hand-pumps installed and 1075 quality affected habitations covered. 21
 Highlights of Annual Plan (2007 -08) Performance • As per Constitutional requirements, District Planning Committees constituted and made functional with nominated and elected members. • 813 primary and 5510 upper primary schools opened and 31535 additional class-rooms constructed. • 60000 additional teachers selected • 183. 76 lakh children in primary schools and 39. 60 lakh children in upper primary schools covered under MDM • 60 private degree colleges and 150 colleges under Self financing scheme opened • Under Janani Suraksha Yojana, against 1. 68 lakh institutional delivery in 2006 -07, 9. 64 lakh institutional delivery achieved in 2007 -08 • 1. 31 lakh ASHA selected and 1. 25 lakh trained • Contractual appointment of 1410 Staff nurses, 960 ANMs , 155 lady doctors and 82 lab technicians. • Out of 897 ICDS projects, hot cooked meal is being provided in 470 projects. • 13. 52 lakh BPL destitute women being provided pension • 25. 36 lakh beneficiaries covered under old age pension scheme 22
Highlights of Annual Plan (2007 -08) Performance • As per Constitutional requirements, District Planning Committees constituted and made functional with nominated and elected members. • 813 primary and 5510 upper primary schools opened and 31535 additional class-rooms constructed. • 60000 additional teachers selected • 183. 76 lakh children in primary schools and 39. 60 lakh children in upper primary schools covered under MDM • 60 private degree colleges and 150 colleges under Self financing scheme opened • Under Janani Suraksha Yojana, against 1. 68 lakh institutional delivery in 2006 -07, 9. 64 lakh institutional delivery achieved in 2007 -08 • 1. 31 lakh ASHA selected and 1. 25 lakh trained • Contractual appointment of 1410 Staff nurses, 960 ANMs , 155 lady doctors and 82 lab technicians. • Out of 897 ICDS projects, hot cooked meal is being provided in 470 projects. • 13. 52 lakh BPL destitute women being provided pension • 25. 36 lakh beneficiaries covered under old age pension scheme 22
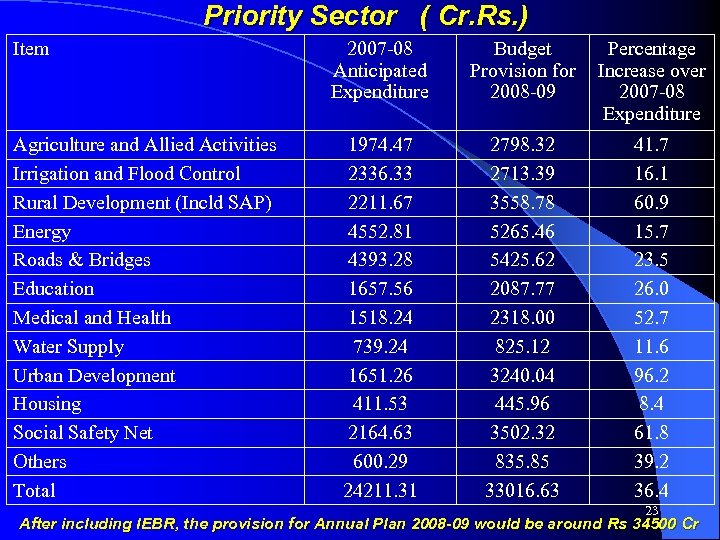 Priority Sector ( Cr. Rs. ) Item Agriculture and Allied Activities Irrigation and Flood Control Rural Development (Incld SAP) Energy Roads & Bridges Education Medical and Health Water Supply Urban Development Housing Social Safety Net Others Total 2007 -08 Anticipated Expenditure 1974. 47 2336. 33 2211. 67 4552. 81 4393. 28 1657. 56 1518. 24 739. 24 1651. 26 411. 53 2164. 63 600. 29 24211. 31 Budget Percentage Provision for Increase over 2008 -09 2007 -08 Expenditure 2798. 32 2713. 39 3558. 78 5265. 46 5425. 62 2087. 77 2318. 00 825. 12 3240. 04 445. 96 3502. 32 835. 85 33016. 63 41. 7 16. 1 60. 9 15. 7 23. 5 26. 0 52. 7 11. 6 96. 2 8. 4 61. 8 39. 2 36. 4 23 After including IEBR, the provision for Annual Plan 2008 -09 would be around Rs 34500 Cr
Priority Sector ( Cr. Rs. ) Item Agriculture and Allied Activities Irrigation and Flood Control Rural Development (Incld SAP) Energy Roads & Bridges Education Medical and Health Water Supply Urban Development Housing Social Safety Net Others Total 2007 -08 Anticipated Expenditure 1974. 47 2336. 33 2211. 67 4552. 81 4393. 28 1657. 56 1518. 24 739. 24 1651. 26 411. 53 2164. 63 600. 29 24211. 31 Budget Percentage Provision for Increase over 2008 -09 2007 -08 Expenditure 2798. 32 2713. 39 3558. 78 5265. 46 5425. 62 2087. 77 2318. 00 825. 12 3240. 04 445. 96 3502. 32 835. 85 33016. 63 41. 7 16. 1 60. 9 15. 7 23. 5 26. 0 52. 7 11. 6 96. 2 8. 4 61. 8 39. 2 36. 4 23 After including IEBR, the provision for Annual Plan 2008 -09 would be around Rs 34500 Cr
 Action Plan : 2008 -09 • Additional increase in food-grains production by 77. 43 lakh tonnes • To increase milk production from the present level of 187. 82 lakh MT to 218. 95 lakh MT • Creation of additional irrigation potential of 6. 76 lakh ha • To reduce T&D losses by 4 % • To open 3033 primary and 4398 upper primary schools and construct 17310 additional class rooms • Mid day meal scheme extended to all upper primary schools • To provide hot cooked food in all the remaining 427 ICDS projects to achieve 100% coverage • To construct 7500 km new village roads, 5200 km reconstruction of village roads, 2600 km widening / strengthening of roads and 100 bridges. • Additional employment opportunity to 25. 00 lakh • Computer education to commence in 700 Upper Primary Schools. • Training of 9000 Urdu Special BTC trainees in 2008 -09. • In-service training of 1. 35 lakh elementary school teachers. • To cover 15 lakh beneficiaries under Janani Suraksha Yojana • To make at-least 2 FRUs functional in each district. • To establish one Adolescent Counselling Centre in each district • To launch a pilot programme of CCT scheme for addressing mal-nutrition 24 among girls.
Action Plan : 2008 -09 • Additional increase in food-grains production by 77. 43 lakh tonnes • To increase milk production from the present level of 187. 82 lakh MT to 218. 95 lakh MT • Creation of additional irrigation potential of 6. 76 lakh ha • To reduce T&D losses by 4 % • To open 3033 primary and 4398 upper primary schools and construct 17310 additional class rooms • Mid day meal scheme extended to all upper primary schools • To provide hot cooked food in all the remaining 427 ICDS projects to achieve 100% coverage • To construct 7500 km new village roads, 5200 km reconstruction of village roads, 2600 km widening / strengthening of roads and 100 bridges. • Additional employment opportunity to 25. 00 lakh • Computer education to commence in 700 Upper Primary Schools. • Training of 9000 Urdu Special BTC trainees in 2008 -09. • In-service training of 1. 35 lakh elementary school teachers. • To cover 15 lakh beneficiaries under Janani Suraksha Yojana • To make at-least 2 FRUs functional in each district. • To establish one Adolescent Counselling Centre in each district • To launch a pilot programme of CCT scheme for addressing mal-nutrition 24 among girls.
 Investment & Infrastructure through PPP 25
Investment & Infrastructure through PPP 25
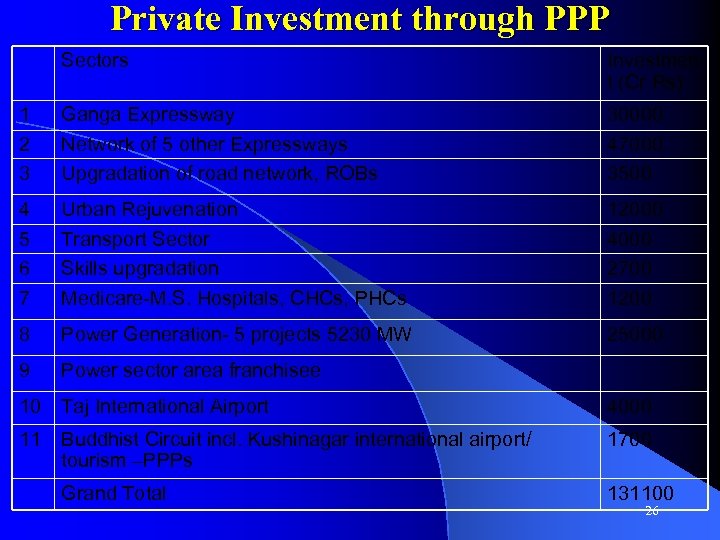 Private Investment through PPP Sectors Investmen t (Cr Rs) 1 2 3 Ganga Expressway Network of 5 other Expressways Upgradation of road network, ROBs 30000 47000 3500 4 5 6 7 Urban Rejuvenation Transport Sector Skills upgradation Medicare-M. S. Hospitals, CHCs, PHCs 12000 4000 2700 1200 8 Power Generation- 5 projects 5230 MW 25000 9 Power sector area franchisee 10 Taj International Airport 4000 11 Buddhist Circuit incl. Kushinagar international airport/ tourism –PPPs 1700 Grand Total 131100 26
Private Investment through PPP Sectors Investmen t (Cr Rs) 1 2 3 Ganga Expressway Network of 5 other Expressways Upgradation of road network, ROBs 30000 47000 3500 4 5 6 7 Urban Rejuvenation Transport Sector Skills upgradation Medicare-M. S. Hospitals, CHCs, PHCs 12000 4000 2700 1200 8 Power Generation- 5 projects 5230 MW 25000 9 Power sector area franchisee 10 Taj International Airport 4000 11 Buddhist Circuit incl. Kushinagar international airport/ tourism –PPPs 1700 Grand Total 131100 26
 Power Sector
Power Sector
 Generation Sector Achievements 1. Generation Capacity of 732 MW Added § 210 MW - Unit no. IV of Parichha Thermal Commissioned. § 100 MW - R&M of Obra unit no VI. § 422 MW -Sugar mills installed cogeneration plant. 2. Projects of 3930 MW under Construction A- State Sector - 2000 MW § 500 MW (2 x 250)Parichha Thermal Power Project (Ext. ) 500 MW (2 x 250) Harduaganj Thermal Power Project (Ext. ) 1000 MW (2 x 500) Anpara’D’ Thermal Power Project. B- Private sector projects 1930 MW § 2 x 300 MW Roza Thermal Power Project, 4 x 82. 5 MW Srinagar Hydro Power Project, 2 x 500 (2 x 600) MW Anpara ‘C’ Project. 3. Projects of 5940 MW are in the final stages of startup § 1320 MW in joint sector with NTPC at Meja, 1320 MW Tanda Thermal Ext. Project. NTPC. (U. P. Share 65%), 1980 MW (3 x 660)Bara Thermal Power Project at Allahabad 1320 MW (2 x 660) Karchana Thermal Power Project at Allahabad). 4. Startup Activity on Projects of 7000 MW § § 1000 MW Obra C thermal power project. 4000 MW UMPP in Bundelkhand Region(Joint Venture) 2000 MW Thermal Power Project of at Fatehpur (Joint Venture). 28
Generation Sector Achievements 1. Generation Capacity of 732 MW Added § 210 MW - Unit no. IV of Parichha Thermal Commissioned. § 100 MW - R&M of Obra unit no VI. § 422 MW -Sugar mills installed cogeneration plant. 2. Projects of 3930 MW under Construction A- State Sector - 2000 MW § 500 MW (2 x 250)Parichha Thermal Power Project (Ext. ) 500 MW (2 x 250) Harduaganj Thermal Power Project (Ext. ) 1000 MW (2 x 500) Anpara’D’ Thermal Power Project. B- Private sector projects 1930 MW § 2 x 300 MW Roza Thermal Power Project, 4 x 82. 5 MW Srinagar Hydro Power Project, 2 x 500 (2 x 600) MW Anpara ‘C’ Project. 3. Projects of 5940 MW are in the final stages of startup § 1320 MW in joint sector with NTPC at Meja, 1320 MW Tanda Thermal Ext. Project. NTPC. (U. P. Share 65%), 1980 MW (3 x 660)Bara Thermal Power Project at Allahabad 1320 MW (2 x 660) Karchana Thermal Power Project at Allahabad). 4. Startup Activity on Projects of 7000 MW § § 1000 MW Obra C thermal power project. 4000 MW UMPP in Bundelkhand Region(Joint Venture) 2000 MW Thermal Power Project of at Fatehpur (Joint Venture). 28
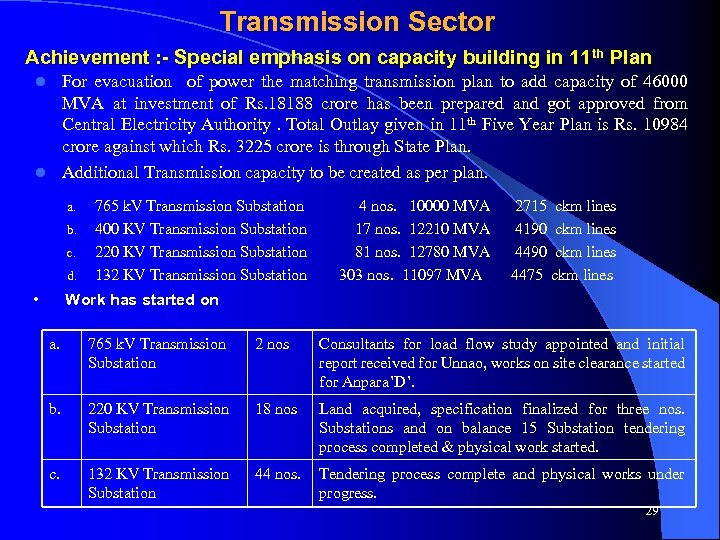 Transmission Sector Achievement : - Special emphasis on capacity building in 11 th Plan For evacuation of power the matching transmission plan to add capacity of 46000 MVA at investment of Rs. 18188 crore has been prepared and got approved from Central Electricity Authority. Total Outlay given in 11 th Five Year Plan is Rs. 10984 crore against which Rs. 3225 crore is through State Plan. l Additional Transmission capacity to be created as per plan. l a. b. c. d. • 765 k. V Transmission Substation 4 nos. 10000 MVA 2715 ckm lines 400 KV Transmission Substation 17 nos. 12210 MVA 4190 ckm lines 220 KV Transmission Substation 81 nos. 12780 MVA 4490 ckm lines 132 KV Transmission Substation 303 nos. 11097 MVA 4475 ckm lines Work has started on a. 765 k. V Transmission Substation 2 nos Consultants for load flow study appointed and initial report received for Unnao, works on site clearance started for Anpara’D’. b. 220 KV Transmission Substation 18 nos Land acquired, specification finalized for three nos. Substations and on balance 15 Substation tendering process completed & physical work started. c. 132 KV Transmission Substation 44 nos. Tendering process complete and physical works under progress. 29
Transmission Sector Achievement : - Special emphasis on capacity building in 11 th Plan For evacuation of power the matching transmission plan to add capacity of 46000 MVA at investment of Rs. 18188 crore has been prepared and got approved from Central Electricity Authority. Total Outlay given in 11 th Five Year Plan is Rs. 10984 crore against which Rs. 3225 crore is through State Plan. l Additional Transmission capacity to be created as per plan. l a. b. c. d. • 765 k. V Transmission Substation 4 nos. 10000 MVA 2715 ckm lines 400 KV Transmission Substation 17 nos. 12210 MVA 4190 ckm lines 220 KV Transmission Substation 81 nos. 12780 MVA 4490 ckm lines 132 KV Transmission Substation 303 nos. 11097 MVA 4475 ckm lines Work has started on a. 765 k. V Transmission Substation 2 nos Consultants for load flow study appointed and initial report received for Unnao, works on site clearance started for Anpara’D’. b. 220 KV Transmission Substation 18 nos Land acquired, specification finalized for three nos. Substations and on balance 15 Substation tendering process completed & physical work started. c. 132 KV Transmission Substation 44 nos. Tendering process complete and physical works under progress. 29
 Distribution Sector l l l l With no tariff increase in the last three years revenue has increased by more than Rs. 1100 crore which is 14% improvement over last year. Target for 2008 -09 to improve collections by 27% over last year. The AT&C Loss which was more than 53% at the time of un bundling of UPSEB in Jan 2000 has reduced to around 37% in 2007 -08. 313 Collection Based Franchisee and 2 Input Based Rural Franchisee covering around 15000 villages have been appointed which resulted in increase in collection efficiency of the area from 50% to average 84%. Target to expand collection based franchisee to cover 50000 villages and Input based franchisee in one pocket of Kaval towns by March 2009. More than 20000 RGGVY villages have been energized. Tariff increase of around 10% has been implemented so that cost coverage can increase from 58% to 68%. About 5 lacs new connection have been released during 2007 -08. 5000 km Arial Bunch Conductors are in place. Target for laying of Arial Bunch Conductor of 11500 Km in year 2008 -09. Segregation of agricultural and domestic/ commercial load in rural area taken-up in 5 districts and 50, 000 prepaid meters to be installed. 33 KV Urban sub- stations to be covered under input based franchisee on pilot basis in 2008 -09 and further to be extended by end of 11 th Five year Plan. Metering of all Urban Transformers in Phase- I. Rural Electrification Plan for 100% electrification and strengthening of rural back bone in next three years. Massive plan for metering of Domestic light and fan consumers, installation of high capacity meters for small and medium category consumers Unified billing system with complete I. T. application. 30
Distribution Sector l l l l With no tariff increase in the last three years revenue has increased by more than Rs. 1100 crore which is 14% improvement over last year. Target for 2008 -09 to improve collections by 27% over last year. The AT&C Loss which was more than 53% at the time of un bundling of UPSEB in Jan 2000 has reduced to around 37% in 2007 -08. 313 Collection Based Franchisee and 2 Input Based Rural Franchisee covering around 15000 villages have been appointed which resulted in increase in collection efficiency of the area from 50% to average 84%. Target to expand collection based franchisee to cover 50000 villages and Input based franchisee in one pocket of Kaval towns by March 2009. More than 20000 RGGVY villages have been energized. Tariff increase of around 10% has been implemented so that cost coverage can increase from 58% to 68%. About 5 lacs new connection have been released during 2007 -08. 5000 km Arial Bunch Conductors are in place. Target for laying of Arial Bunch Conductor of 11500 Km in year 2008 -09. Segregation of agricultural and domestic/ commercial load in rural area taken-up in 5 districts and 50, 000 prepaid meters to be installed. 33 KV Urban sub- stations to be covered under input based franchisee on pilot basis in 2008 -09 and further to be extended by end of 11 th Five year Plan. Metering of all Urban Transformers in Phase- I. Rural Electrification Plan for 100% electrification and strengthening of rural back bone in next three years. Massive plan for metering of Domestic light and fan consumers, installation of high capacity meters for small and medium category consumers Unified billing system with complete I. T. application. 30
 Important Issues l l l l l Development of Chendipada Coal Block, jointly allocated to the three States, hampered as due to one or other reason SPV not yet formed - Coal Block should be allocated to Uttar Pradesh exclusively. Allocation of Power from Central Sector Station to the State has no relevance with reference to, Area and Population of State – needs more emphasis on population. 15% Unallocated Share of central undertakings being allocated by Mo. P needs allocation according to Demand Availability of Power in the State in corresponding to population and size of the State. The rural electrification scheme of Mazras– Mo. P / REC to review the scheme of Uttar Pradesh and issue sanction. Proposal of Uttar Pradesh for Rs. 5892 crore submitted. Only Sultanpur and Rae-bareily have been sanctioned. Recovery of Cost by Central generating Station on the basis of Parameters rather than on Actuals- should be revised so that burden of State Discoms and consumers is reduced. Guidelines for 100% funding of APDRP II be considered for immediate implementation to achieve target for completion of APDRP schemes covering 232 towns of 30000 or more population having total population of more than 3. 5 crore which require funds of Rs. 1300 crore. 4000 MW power project at Lalitpur in joint sector with NTPC needs to be expedited. The expansion of capacity of Narora Atomic Plant from present 2 x 220 MW to 2 x 700 MW was raised by Uttar Pradesh. Government of India informed that the matter was examined and Department of Atomic Energy has found the present site suitable. It needs urgent finalization for earliest execution. The project of 6480 MW capacity on river Sharda(Mahakali) power house at Pancheshwar and 10800 MW power generation project at river Ghaghra(Karnali) near Cheesapani (Nepal), which promise benefits of irrigation, power and flood control to the State need to be pursued at the level of Government of India with the 31 Government of Nepal for speedy approval and execution.
Important Issues l l l l l Development of Chendipada Coal Block, jointly allocated to the three States, hampered as due to one or other reason SPV not yet formed - Coal Block should be allocated to Uttar Pradesh exclusively. Allocation of Power from Central Sector Station to the State has no relevance with reference to, Area and Population of State – needs more emphasis on population. 15% Unallocated Share of central undertakings being allocated by Mo. P needs allocation according to Demand Availability of Power in the State in corresponding to population and size of the State. The rural electrification scheme of Mazras– Mo. P / REC to review the scheme of Uttar Pradesh and issue sanction. Proposal of Uttar Pradesh for Rs. 5892 crore submitted. Only Sultanpur and Rae-bareily have been sanctioned. Recovery of Cost by Central generating Station on the basis of Parameters rather than on Actuals- should be revised so that burden of State Discoms and consumers is reduced. Guidelines for 100% funding of APDRP II be considered for immediate implementation to achieve target for completion of APDRP schemes covering 232 towns of 30000 or more population having total population of more than 3. 5 crore which require funds of Rs. 1300 crore. 4000 MW power project at Lalitpur in joint sector with NTPC needs to be expedited. The expansion of capacity of Narora Atomic Plant from present 2 x 220 MW to 2 x 700 MW was raised by Uttar Pradesh. Government of India informed that the matter was examined and Department of Atomic Energy has found the present site suitable. It needs urgent finalization for earliest execution. The project of 6480 MW capacity on river Sharda(Mahakali) power house at Pancheshwar and 10800 MW power generation project at river Ghaghra(Karnali) near Cheesapani (Nepal), which promise benefits of irrigation, power and flood control to the State need to be pursued at the level of Government of India with the 31 Government of Nepal for speedy approval and execution.
 Irrigation & Flood Control
Irrigation & Flood Control
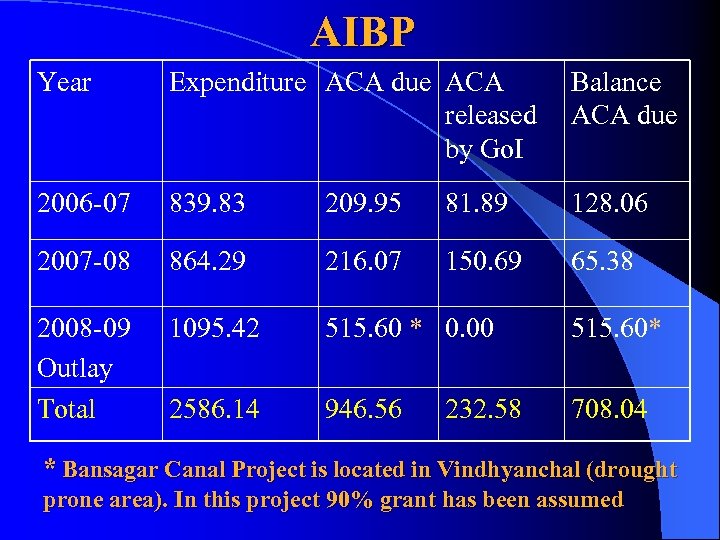 AIBP Year Expenditure ACA due ACA Balance released ACA due by Go. I 2006 -07 839. 83 209. 95 81. 89 128. 06 2007 -08 864. 29 216. 07 150. 69 65. 38 2008 -09 Outlay Total 1095. 42 515. 60 * 0. 00 515. 60* 2586. 14 946. 56 708. 04 232. 58 * Bansagar Canal Project is located in Vindhyanchal (drought prone area). In this project 90% grant has been assumed
AIBP Year Expenditure ACA due ACA Balance released ACA due by Go. I 2006 -07 839. 83 209. 95 81. 89 128. 06 2007 -08 864. 29 216. 07 150. 69 65. 38 2008 -09 Outlay Total 1095. 42 515. 60 * 0. 00 515. 60* 2586. 14 946. 56 708. 04 232. 58 * Bansagar Canal Project is located in Vindhyanchal (drought prone area). In this project 90% grant has been assumed
 ISSUES As per guide-lines of A. I. B. P. , projects benefitting drought prone areas or flood prone areas are eligible for central grant @ 90% of project cost. Bundelkhand Vindhyanchal region of U. P. is a drought prone area. Similarly North-eastern parts of U. P. , especially those bordering Nepal are prone to recurrent floods. Therefore, irrigation projects benefitting these areas should qualify for central grant @ 90% instead of 25% as at present. l There is a need to improve the flood forecasting and warning system with more hydro-meteorological stations in Nepalese territory and speed up the pending Indo-Nepal joint multi-purpose projects l 34
ISSUES As per guide-lines of A. I. B. P. , projects benefitting drought prone areas or flood prone areas are eligible for central grant @ 90% of project cost. Bundelkhand Vindhyanchal region of U. P. is a drought prone area. Similarly North-eastern parts of U. P. , especially those bordering Nepal are prone to recurrent floods. Therefore, irrigation projects benefitting these areas should qualify for central grant @ 90% instead of 25% as at present. l There is a need to improve the flood forecasting and warning system with more hydro-meteorological stations in Nepalese territory and speed up the pending Indo-Nepal joint multi-purpose projects l 34
 Roads & Bridges
Roads & Bridges
 ROADS & BRIDGES l l l l l State has 162893 Kms road against 290973 km of road length including earthen tracks. Villages having population of more than 500 are 26078 out of which 12690 villages are still to be connected with all weather roads With an expenditure of Rs. 5, 842 Cr, construction of 7862 km of link roads were completed providing connectivity to 3114 villages. Improvement and repair of 30, 033 kms of existing link roads of 13, 211 villages were completed. Strengthening and widening of 2200 km of existing roads completed 77 major bridges & 3 ROBs were completed. The entire amount of Rs 195 Cr sanctioned by Go. I under inter-state connectivity for improvement and reconstruction were spent. Go. I sanctioned Rs 227 Cr for widening and strengthening of 351 kms of roads under CRF. Construction of expressways ( Balia to Noida) in progress. 36
ROADS & BRIDGES l l l l l State has 162893 Kms road against 290973 km of road length including earthen tracks. Villages having population of more than 500 are 26078 out of which 12690 villages are still to be connected with all weather roads With an expenditure of Rs. 5, 842 Cr, construction of 7862 km of link roads were completed providing connectivity to 3114 villages. Improvement and repair of 30, 033 kms of existing link roads of 13, 211 villages were completed. Strengthening and widening of 2200 km of existing roads completed 77 major bridges & 3 ROBs were completed. The entire amount of Rs 195 Cr sanctioned by Go. I under inter-state connectivity for improvement and reconstruction were spent. Go. I sanctioned Rs 227 Cr for widening and strengthening of 351 kms of roads under CRF. Construction of expressways ( Balia to Noida) in progress. 36
 v v v v v NEW INITIATIVES & WORK PLAN U. P. State highway authority (UPSHA) revitalized on NHAI pattern to take over all PPP projects. Institutional development and strategies (IDS) cell created for capacity building & efficient delivery. Research & quality control facilities strengthened at district, regional and head quarter levels. Performance based maintenance system on major highways planned on PMGSY pattern. 2, 800 kms. of core road network for rehabilitation/upgradation under externally aided state road project (World Bank) - Rs. 2, 920 Cr. Widening & strengthening of 900 kms. Of S. H. /M. D. R. under CRF scheme. For construction of roads and drains in urban areas- Rs 175 Cr. For construction/reconstruction of link roads in 3800 gram sabha- Rs 1350 Cr For widening & strengthening of 2600 kms of state highway and other important roads- Rs 1462 Cr. For construction of 100 major bridges – Rs 545 Cr. 37
v v v v v NEW INITIATIVES & WORK PLAN U. P. State highway authority (UPSHA) revitalized on NHAI pattern to take over all PPP projects. Institutional development and strategies (IDS) cell created for capacity building & efficient delivery. Research & quality control facilities strengthened at district, regional and head quarter levels. Performance based maintenance system on major highways planned on PMGSY pattern. 2, 800 kms. of core road network for rehabilitation/upgradation under externally aided state road project (World Bank) - Rs. 2, 920 Cr. Widening & strengthening of 900 kms. Of S. H. /M. D. R. under CRF scheme. For construction of roads and drains in urban areas- Rs 175 Cr. For construction/reconstruction of link roads in 3800 gram sabha- Rs 1350 Cr For widening & strengthening of 2600 kms of state highway and other important roads- Rs 1462 Cr. For construction of 100 major bridges – Rs 545 Cr. 37
 ISSUES v v Project for 477 kms Indo-Nepal border roads pending with Ministry of Home ( Rs 900 Cr) NHAI Act has no provision for solatium or negotiation with farmers. NHAI has not adopted 2007 rehabilitation policy of Go. I. NH roads are poorly maintained due to paucity of funds. Diesel cess should be allocated for upgradation of NH roads. Approximately 98 ROB proposals pending with Ministry of Railways for 50: 50 cost sharing. 38
ISSUES v v Project for 477 kms Indo-Nepal border roads pending with Ministry of Home ( Rs 900 Cr) NHAI Act has no provision for solatium or negotiation with farmers. NHAI has not adopted 2007 rehabilitation policy of Go. I. NH roads are poorly maintained due to paucity of funds. Diesel cess should be allocated for upgradation of NH roads. Approximately 98 ROB proposals pending with Ministry of Railways for 50: 50 cost sharing. 38
 Agriculture 39
Agriculture 39
 AGRICULTURE IN UP l 2. 1% growth in 10 th Plan. l 5. 1% growth projected for 11 th Pan. l 3+% growth expected in the year 2007 -08. l State Agriculture budget increased fourfold since 2006 ( from Rs. 269 crores in 2006 -07 to Rs 826 crores in 2007 -08 to Rs 1575 crores in 2008 -09). l However, productivity stagnant for the last 5 years. 40
AGRICULTURE IN UP l 2. 1% growth in 10 th Plan. l 5. 1% growth projected for 11 th Pan. l 3+% growth expected in the year 2007 -08. l State Agriculture budget increased fourfold since 2006 ( from Rs. 269 crores in 2006 -07 to Rs 826 crores in 2007 -08 to Rs 1575 crores in 2008 -09). l However, productivity stagnant for the last 5 years. 40
 PLAN FOR 2008 -09 l Plan to increase foodgrain production by 77 LMT in the current year, of which 30 LMT increase is projected for wheat and 21 LMT for rice. Rest will come from pulses and other grains like Jowar, Bajra etc. 41
PLAN FOR 2008 -09 l Plan to increase foodgrain production by 77 LMT in the current year, of which 30 LMT increase is projected for wheat and 21 LMT for rice. Rest will come from pulses and other grains like Jowar, Bajra etc. 41
 STRATEGY l Effective implementation of FSM and ISOPOM Programmes. l Accelerate seed replacement rate. l Extensive use of hybrids in rice. l Reclamation of 4 lakh hectares of degraded land through Kisan Hit Yojana. l Bring back 8 lakh hectares of land in Bundelkhand under cultivation which could not be sown due to failure of rains in 2007 -08. l Micro-planning for 4100 low-productivity Gram Panchayats in the State. 42
STRATEGY l Effective implementation of FSM and ISOPOM Programmes. l Accelerate seed replacement rate. l Extensive use of hybrids in rice. l Reclamation of 4 lakh hectares of degraded land through Kisan Hit Yojana. l Bring back 8 lakh hectares of land in Bundelkhand under cultivation which could not be sown due to failure of rains in 2007 -08. l Micro-planning for 4100 low-productivity Gram Panchayats in the State. 42
 HOW IT WILL BE ACHIEVED Promotion of System of Rice Intensification (SRI) Technique during Kharif in rain deficient regions. l Optimum utilisation of water resources by promoting use of sprinklers and drip systems. l Improvement in soil health and targeted use of fertilisers through an extensive campaign of soiltesting “Apni Mitti Pahchano Abhiyan’ in May. June 2008. 2. 40 lakh samples collected in a single day on 21 st May. Active public participation in the campaign. l Organisation of 5 day’s Krishi Melas in all agroclimatic zones for dissemination of latest knowhow. l 43
HOW IT WILL BE ACHIEVED Promotion of System of Rice Intensification (SRI) Technique during Kharif in rain deficient regions. l Optimum utilisation of water resources by promoting use of sprinklers and drip systems. l Improvement in soil health and targeted use of fertilisers through an extensive campaign of soiltesting “Apni Mitti Pahchano Abhiyan’ in May. June 2008. 2. 40 lakh samples collected in a single day on 21 st May. Active public participation in the campaign. l Organisation of 5 day’s Krishi Melas in all agroclimatic zones for dissemination of latest knowhow. l 43
 INITIATIVES l l l New Agriculture University at Banda, Bundelkhand. Special subsidy scheme for sprinkler and drip irrigation systems in drought affected Bundelkhand. Weather based Insurance Scheme for Bundelkhand. Adoption of PPP model for extension – 52, 000 Kisan Mitras, training of 40, 000 dealers for basic counselling of farmers and Farmer’s Field Schools. Exploration of new technologies like artificial rains in drought-hit areas and magnetic treatment of irrigation water. 44
INITIATIVES l l l New Agriculture University at Banda, Bundelkhand. Special subsidy scheme for sprinkler and drip irrigation systems in drought affected Bundelkhand. Weather based Insurance Scheme for Bundelkhand. Adoption of PPP model for extension – 52, 000 Kisan Mitras, training of 40, 000 dealers for basic counselling of farmers and Farmer’s Field Schools. Exploration of new technologies like artificial rains in drought-hit areas and magnetic treatment of irrigation water. 44
 ISSUES WITH GOI l l l l Adequate and timely supply of Phosphatic fertilisers. Expeditious decision on loan waiver scheme. Inclusion of notified hybrid seeds in subsidy under FSM. Permit subsidy on seeds over 10 years. Special incentives to pulse producers through free full package demonstrations Assistance for setting up Universities in each agro-climatic zone of the State. Revision of cost norms of projects under NRM Scheme in view of change of minimum wages in UP. Inclusion of Blue Bulls in category of vermins. 45
ISSUES WITH GOI l l l l Adequate and timely supply of Phosphatic fertilisers. Expeditious decision on loan waiver scheme. Inclusion of notified hybrid seeds in subsidy under FSM. Permit subsidy on seeds over 10 years. Special incentives to pulse producers through free full package demonstrations Assistance for setting up Universities in each agro-climatic zone of the State. Revision of cost norms of projects under NRM Scheme in view of change of minimum wages in UP. Inclusion of Blue Bulls in category of vermins. 45
 HORTICULTURE DEVELOPMENT l l l l Improving the quality of planting material including seed certification and standardisation. Up-gradation of traditional nurseries Adoption of post harvest management infrastructure including logistics support. Initiation of high tech horticulture Improving marketing facilities. Impetus to horticulture processing. Farmers awareness through training and visit programmes. 46
HORTICULTURE DEVELOPMENT l l l l Improving the quality of planting material including seed certification and standardisation. Up-gradation of traditional nurseries Adoption of post harvest management infrastructure including logistics support. Initiation of high tech horticulture Improving marketing facilities. Impetus to horticulture processing. Farmers awareness through training and visit programmes. 46
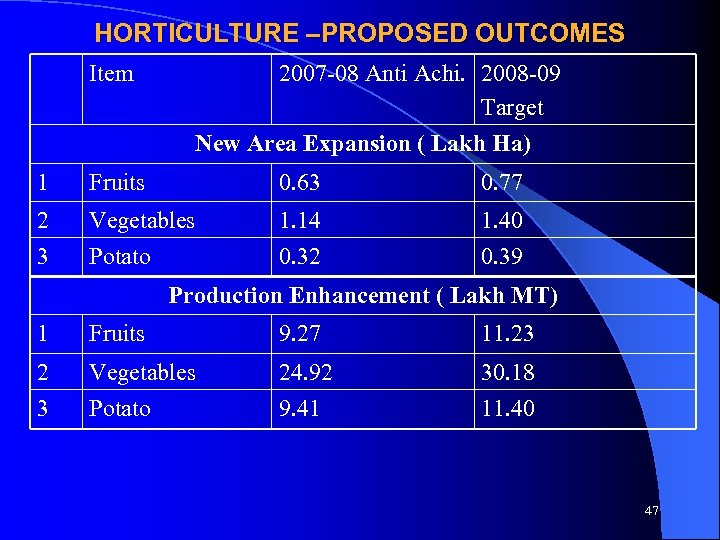 HORTICULTURE –PROPOSED OUTCOMES Item 2007 -08 Anti Achi. 2008 -09 Target New Area Expansion ( Lakh Ha) 1 Fruits 0. 63 0. 77 2 3 Vegetables Potato 1. 14 0. 32 1. 40 0. 39 Production Enhancement ( Lakh MT) 1 Fruits 9. 27 11. 23 2 3 Vegetables Potato 24. 92 9. 41 30. 18 11. 40 47
HORTICULTURE –PROPOSED OUTCOMES Item 2007 -08 Anti Achi. 2008 -09 Target New Area Expansion ( Lakh Ha) 1 Fruits 0. 63 0. 77 2 3 Vegetables Potato 1. 14 0. 32 1. 40 0. 39 Production Enhancement ( Lakh MT) 1 Fruits 9. 27 11. 23 2 3 Vegetables Potato 24. 92 9. 41 30. 18 11. 40 47
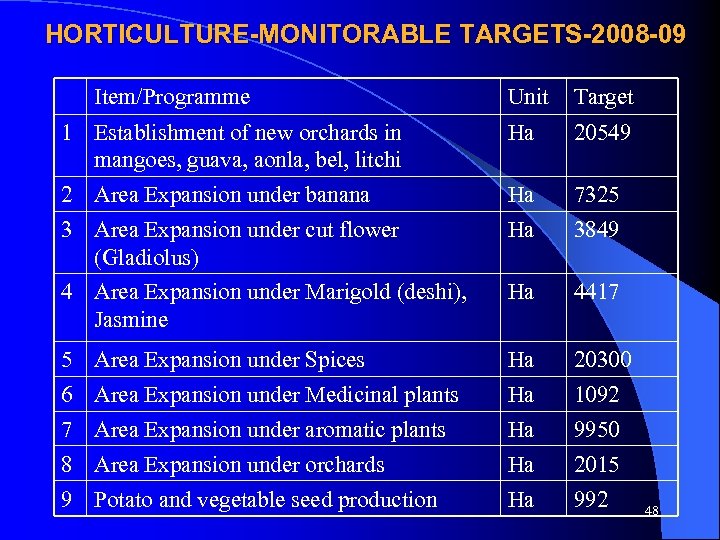 HORTICULTURE-MONITORABLE TARGETS-2008 -09 Item/Programme Unit Target 1 Establishment of new orchards in mangoes, guava, aonla, bel, litchi Ha 20549 2 Area Expansion under banana Ha 7325 3 Area Expansion under cut flower (Gladiolus) Ha 3849 4 Area Expansion under Marigold (deshi), Jasmine Ha 4417 5 Area Expansion under Spices Ha 20300 6 Area Expansion under Medicinal plants Ha 1092 7 Area Expansion under aromatic plants Ha 9950 8 Area Expansion under orchards Ha 2015 9 Potato and vegetable seed production Ha 992 48
HORTICULTURE-MONITORABLE TARGETS-2008 -09 Item/Programme Unit Target 1 Establishment of new orchards in mangoes, guava, aonla, bel, litchi Ha 20549 2 Area Expansion under banana Ha 7325 3 Area Expansion under cut flower (Gladiolus) Ha 3849 4 Area Expansion under Marigold (deshi), Jasmine Ha 4417 5 Area Expansion under Spices Ha 20300 6 Area Expansion under Medicinal plants Ha 1092 7 Area Expansion under aromatic plants Ha 9950 8 Area Expansion under orchards Ha 2015 9 Potato and vegetable seed production Ha 992 48
 Animal Husbandry - Constraints & Strategies Low productivity of livestock & lack of sufficient breeding coverage. § Increased coverage by artificial insemination from 27% to 30% and improvement of poultry breeds. § Invoke PPP projects. Inadequate availability of feed and fodder. § Ensuring better quality seed production and distribution system. § Rectifying imbalances in Bundelkhand Purvanchal. Low coverage of animal health, limited facility of disease surveillance and diagnostic network. § Establishing 400 new veterinary hospitals to add to 1782 existing ones. § Establishing 9 new disease diagnostic laboratories to add to 10 existing ones. § Reduction of infertility by administration of medicines. Lack of adequate training programmes & poor livestock extension. • Strengthening veterinary education, training and skill upgradation facilities through University of Veterinary Sciences. • Strengthening of R&D laboratories at the Directorate and university 49 level.
Animal Husbandry - Constraints & Strategies Low productivity of livestock & lack of sufficient breeding coverage. § Increased coverage by artificial insemination from 27% to 30% and improvement of poultry breeds. § Invoke PPP projects. Inadequate availability of feed and fodder. § Ensuring better quality seed production and distribution system. § Rectifying imbalances in Bundelkhand Purvanchal. Low coverage of animal health, limited facility of disease surveillance and diagnostic network. § Establishing 400 new veterinary hospitals to add to 1782 existing ones. § Establishing 9 new disease diagnostic laboratories to add to 10 existing ones. § Reduction of infertility by administration of medicines. Lack of adequate training programmes & poor livestock extension. • Strengthening veterinary education, training and skill upgradation facilities through University of Veterinary Sciences. • Strengthening of R&D laboratories at the Directorate and university 49 level.
 Dairy Development • Highest Milk Production in the country, biggest single farm commodity by value. • Milk Production 187. 82 Lakh MT, which is roughly 18% of the total production in country. • Only 28% of marketable surplus is handled by organised sectorØ 120 plants in private sector (Capacity 119. 54 Lakh Lit. ) handled 23. 5% of surplus milk. Ø 52 plants in cooperative sector (Capacity 17. 50 Lakh Lit. ) handled only 4. 5% of marketable surplus. 50
Dairy Development • Highest Milk Production in the country, biggest single farm commodity by value. • Milk Production 187. 82 Lakh MT, which is roughly 18% of the total production in country. • Only 28% of marketable surplus is handled by organised sectorØ 120 plants in private sector (Capacity 119. 54 Lakh Lit. ) handled 23. 5% of surplus milk. Ø 52 plants in cooperative sector (Capacity 17. 50 Lakh Lit. ) handled only 4. 5% of marketable surplus. 50
 Major Initiatives • Programme of automation and development of infrastructure facilities will continue in 2008 -09. 2308 AMCU and 230 BMC’s are proposed to be installed in 2008 -09 • A new scheme “Ambedkar Dairy Development Self Employment Scheme” will be implemented from 200809 with outlay of Rs. 200 Crore. The scheme will help increase in milk production as well as self employment. 51
Major Initiatives • Programme of automation and development of infrastructure facilities will continue in 2008 -09. 2308 AMCU and 230 BMC’s are proposed to be installed in 2008 -09 • A new scheme “Ambedkar Dairy Development Self Employment Scheme” will be implemented from 200809 with outlay of Rs. 200 Crore. The scheme will help increase in milk production as well as self employment. 51
 COOPERATION - ISSUES FOR CONSIDERATION • Consequent upon declaration of loan waiver scheme by Go. I, flow of funds in form of recoveries from the farmers has almost choked. Therefore, Go. I is requested to: I. release an amount of Rs. 5329 Crore (1607 ST + 3722 LT) required by cooperative banks of the state to write off the loans of small & marginal farmers under Go. I debt waiver and debt relief scheme before 15 th June 2008 to ensure smooth flow of credit to farmers. II. IV. restructure the loan due for repayment to NABARD by State Cooperative Banks for three years. sanction separate line of credit in addition to normal cash credit for financing loan waiver scheme beneficiaries. enhance the level of NABARD refinance from 35% to 75% so as to overcome the liquidity crunch of the Co-operative Banks. 52
COOPERATION - ISSUES FOR CONSIDERATION • Consequent upon declaration of loan waiver scheme by Go. I, flow of funds in form of recoveries from the farmers has almost choked. Therefore, Go. I is requested to: I. release an amount of Rs. 5329 Crore (1607 ST + 3722 LT) required by cooperative banks of the state to write off the loans of small & marginal farmers under Go. I debt waiver and debt relief scheme before 15 th June 2008 to ensure smooth flow of credit to farmers. II. IV. restructure the loan due for repayment to NABARD by State Cooperative Banks for three years. sanction separate line of credit in addition to normal cash credit for financing loan waiver scheme beneficiaries. enhance the level of NABARD refinance from 35% to 75% so as to overcome the liquidity crunch of the Co-operative Banks. 52
 Contd… • • Interest rate on refinance by NABARD should be reduced to 2. 5% from the current rate of 3. 5% and restrict it to the level of 2. 5% for the coming years also. Interest subsidy on crop loan should be released well in time as the claims pertaining to the year 2007 - 08 are pending at NABARD level. Scope of interest subsidy scheme should be extended to medium term conversion loan as well as for the loans extended to farmers for other agriculture and allied activities. Farmers should be provided crop loan at 4% interest rate and interest subsidy required should be provided by Government of India as state government is not in a position to meet the above burden from own resources. Funds required during the residual year of 11 th Five Year Plan stands at Rs. 648. 82 Crore. 53
Contd… • • Interest rate on refinance by NABARD should be reduced to 2. 5% from the current rate of 3. 5% and restrict it to the level of 2. 5% for the coming years also. Interest subsidy on crop loan should be released well in time as the claims pertaining to the year 2007 - 08 are pending at NABARD level. Scope of interest subsidy scheme should be extended to medium term conversion loan as well as for the loans extended to farmers for other agriculture and allied activities. Farmers should be provided crop loan at 4% interest rate and interest subsidy required should be provided by Government of India as state government is not in a position to meet the above burden from own resources. Funds required during the residual year of 11 th Five Year Plan stands at Rs. 648. 82 Crore. 53
 Rural Development
Rural Development
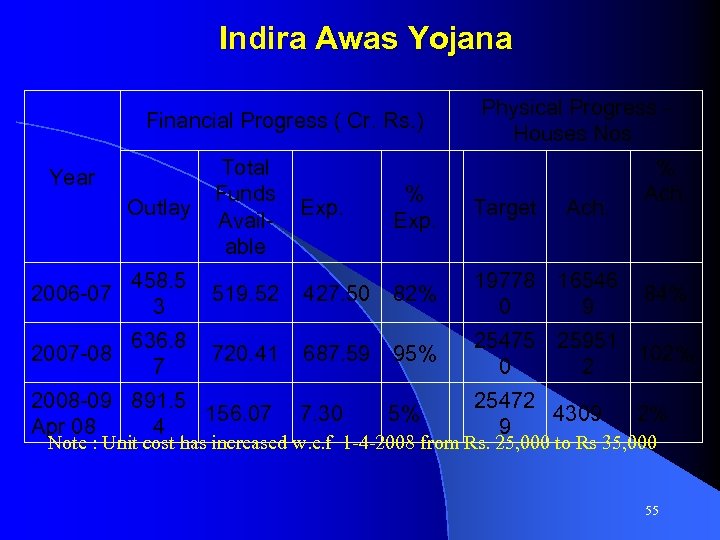 Indira Awas Yojana Financial Progress ( Cr. Rs. ) Year Outlay 458. 5 2006 -07 3 636. 8 2007 -08 7 Total Funds Exp. Available 519. 52 720. 41 2008 -09 891. 5 156. 07 Apr 08 4 427. 50 687. 59 7. 30 Physical Progress - Houses Nos. % Ach. % Exp. Target Ach. 82% 19778 0 16546 9 95% 25475 0 25951 102% 2 5% 25472 4309 9 84% 2% Note : Unit cost has increased w. e. f 1 -4 -2008 from Rs. 25, 000 to Rs 35, 000 55
Indira Awas Yojana Financial Progress ( Cr. Rs. ) Year Outlay 458. 5 2006 -07 3 636. 8 2007 -08 7 Total Funds Exp. Available 519. 52 720. 41 2008 -09 891. 5 156. 07 Apr 08 4 427. 50 687. 59 7. 30 Physical Progress - Houses Nos. % Ach. % Exp. Target Ach. 82% 19778 0 16546 9 95% 25475 0 25951 102% 2 5% 25472 4309 9 84% 2% Note : Unit cost has increased w. e. f 1 -4 -2008 from Rs. 25, 000 to Rs 35, 000 55
 Indira Awas: Issues • Total housing shortage in the State in permanent wait list is about 43 Lakh. To cover all the families during 11 th Five Year Plan there is need to construct 9 lakh houses every year while State is getting funds for construction of 56
Indira Awas: Issues • Total housing shortage in the State in permanent wait list is about 43 Lakh. To cover all the families during 11 th Five Year Plan there is need to construct 9 lakh houses every year while State is getting funds for construction of 56
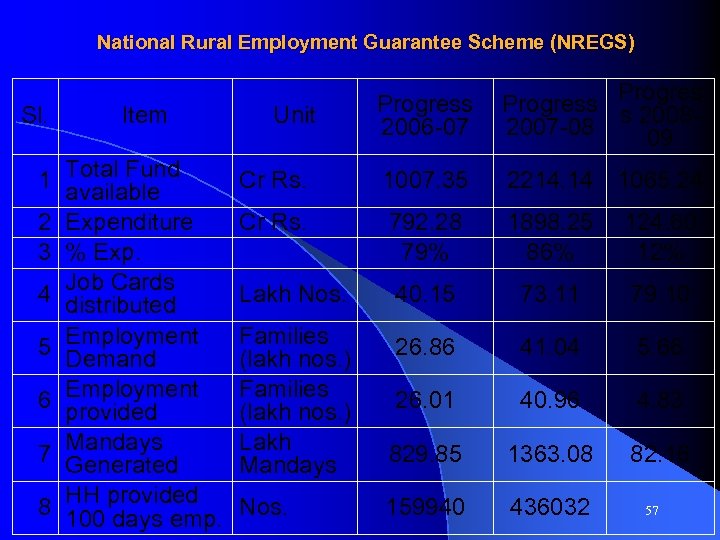 National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme (NREGS) Sl. Item 1 Total Fund available 2 Expenditure 3 % Exp. 4 Job Cards distributed 5 Employment Demand 6 Employment provided 7 Mandays Generated 8 HH provided 100 days emp. Unit Progress Progres 2006 -07 2007 -08 s 200809 Cr Rs. 1007. 35 2214. 14 1065. 24 Cr Rs. 792. 28 79% 1898. 25 86% 124. 60 12% Lakh Nos. 40. 15 73. 11 79. 10 Families (lakh nos. ) Lakh Mandays 26. 86 41. 04 5. 66 26. 01 40. 96 4. 83 829. 85 1363. 08 82. 16 Nos. 159940 436032 57
National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme (NREGS) Sl. Item 1 Total Fund available 2 Expenditure 3 % Exp. 4 Job Cards distributed 5 Employment Demand 6 Employment provided 7 Mandays Generated 8 HH provided 100 days emp. Unit Progress Progres 2006 -07 2007 -08 s 200809 Cr Rs. 1007. 35 2214. 14 1065. 24 Cr Rs. 792. 28 79% 1898. 25 86% 124. 60 12% Lakh Nos. 40. 15 73. 11 79. 10 Families (lakh nos. ) Lakh Mandays 26. 86 41. 04 5. 66 26. 01 40. 96 4. 83 829. 85 1363. 08 82. 16 Nos. 159940 436032 57
 National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme (NREGS) : Issues • • • Central Share amount of Rs. 3599. 86 crore approved in labour budget by Govt. of India for the year 2008 -09 be released in 2 installments so that sufficient funds are available at gram panchayat level. Bundelkhand Vindhyachal divisions being drought hit hence 100 days of employment is not sufficient in these areas. It is proposed that for these areas this condition be relaxed to 200 days of employment in a year State Council should be authorised to fix the priorities of works and add new works in prescribed list of works 58
National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme (NREGS) : Issues • • • Central Share amount of Rs. 3599. 86 crore approved in labour budget by Govt. of India for the year 2008 -09 be released in 2 installments so that sufficient funds are available at gram panchayat level. Bundelkhand Vindhyachal divisions being drought hit hence 100 days of employment is not sufficient in these areas. It is proposed that for these areas this condition be relaxed to 200 days of employment in a year State Council should be authorised to fix the priorities of works and add new works in prescribed list of works 58
 Action taken for Smooth Implementation of Scheme Ø Ø Ø The appointment of APOs and other staff is under process. The notification of State Fund is under process and on both the above points decision will be taken in two weeks time. In remaining districts the vacant posts of P. O. will be filled shortly. 27151 Rojgar sevaks have been selected 4157 technical assistants empanelled. Separate Additional Commissioner (EGS) appointed by State Govt. Proposal is under consideration to appoint A. P. Os in each block. State Govt. has introduced the procedure of payment of wages through banks and post offices. Till date 5. 15 lakh accounts have been opened. Instructions have been issued to conduct Social Audit along with videography at least twice a year (April & October). Complaint cell and help line has been set up in every district under the Chairmanship of District Magistrates. 59 59
Action taken for Smooth Implementation of Scheme Ø Ø Ø The appointment of APOs and other staff is under process. The notification of State Fund is under process and on both the above points decision will be taken in two weeks time. In remaining districts the vacant posts of P. O. will be filled shortly. 27151 Rojgar sevaks have been selected 4157 technical assistants empanelled. Separate Additional Commissioner (EGS) appointed by State Govt. Proposal is under consideration to appoint A. P. Os in each block. State Govt. has introduced the procedure of payment of wages through banks and post offices. Till date 5. 15 lakh accounts have been opened. Instructions have been issued to conduct Social Audit along with videography at least twice a year (April & October). Complaint cell and help line has been set up in every district under the Chairmanship of District Magistrates. 59 59
 Information, Education & Communication (IEC) Ø Special gram sabha meetings convened in all GPs. Ø Pamphlets, Hoardings, Notice Boards, Wall writings etc. describing NREGA processes in local languages are being used for wider publicity of the scheme. Ø Salient features of NREGA were advertised in daily news papers / Gramin Bharat magzine, broadcast on Radio and local TV channels etc. Ø Wall Writing in each village. Ø Cultural programmes like Kathputli, magic shows, Folk Sangeet and Nukkad natak organized. 60 60
Information, Education & Communication (IEC) Ø Special gram sabha meetings convened in all GPs. Ø Pamphlets, Hoardings, Notice Boards, Wall writings etc. describing NREGA processes in local languages are being used for wider publicity of the scheme. Ø Salient features of NREGA were advertised in daily news papers / Gramin Bharat magzine, broadcast on Radio and local TV channels etc. Ø Wall Writing in each village. Ø Cultural programmes like Kathputli, magic shows, Folk Sangeet and Nukkad natak organized. 60 60
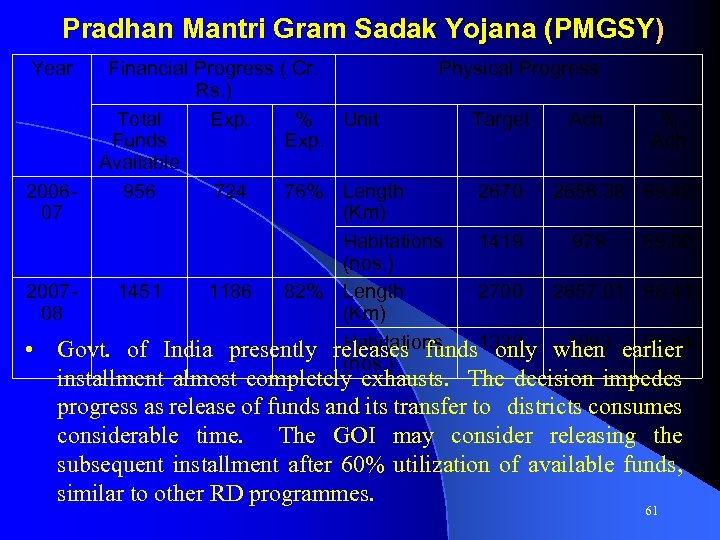 Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana (PMGSY) Year Financial Progress ( Cr. Physical Progress Rs. ) Total Exp. % Unit Target Ach. % Funds Exp. Ach Available 2006956 724 76% Length 2670 2656. 38 99. 48 07 (Km) Habitations 1419 979 69. 00 (nos. ) 20071451 1186 82% Length 2700 2657. 01 98. 41 08 (Km) Habitations 1338 1093 81. 64 • Govt. of India presently releases funds only when earlier (nos. ) installment almost completely exhausts. The decision impedes progress as release of funds and its transfer to districts consumes considerable time. The GOI may consider releasing the subsequent installment after 60% utilization of available funds, similar to other RD programmes. 61
Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana (PMGSY) Year Financial Progress ( Cr. Physical Progress Rs. ) Total Exp. % Unit Target Ach. % Funds Exp. Ach Available 2006956 724 76% Length 2670 2656. 38 99. 48 07 (Km) Habitations 1419 979 69. 00 (nos. ) 20071451 1186 82% Length 2700 2657. 01 98. 41 08 (Km) Habitations 1338 1093 81. 64 • Govt. of India presently releases funds only when earlier (nos. ) installment almost completely exhausts. The decision impedes progress as release of funds and its transfer to districts consumes considerable time. The GOI may consider releasing the subsequent installment after 60% utilization of available funds, similar to other RD programmes. 61
 Rural Drinking Water Scheme Regular reboring of failed hand pumps. l Ground water recharge and rainwater harvesting works to be made integral part of water supply system. l Legislation to control extraction of ground water, prevention of pollution of ground /surface water and disruption of water supply sources shall be enacted. l Rationalisation of tariff structure 62 l
Rural Drinking Water Scheme Regular reboring of failed hand pumps. l Ground water recharge and rainwater harvesting works to be made integral part of water supply system. l Legislation to control extraction of ground water, prevention of pollution of ground /surface water and disruption of water supply sources shall be enacted. l Rationalisation of tariff structure 62 l
 Education
Education
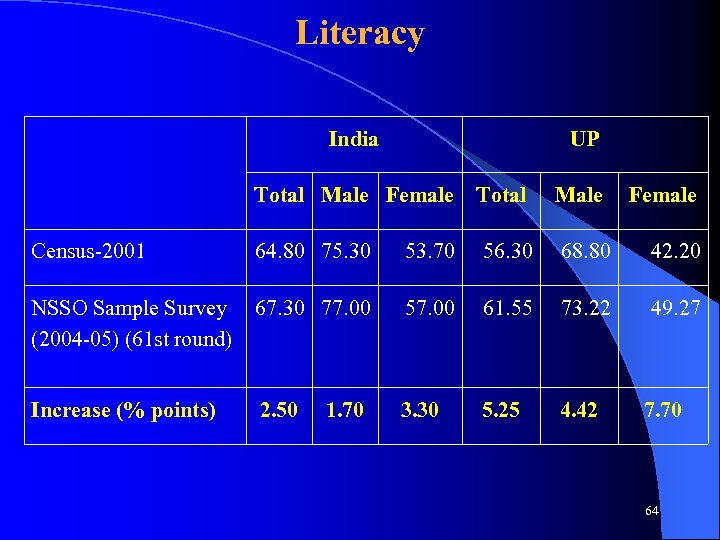 Literacy India UP Total Male Female Total Male Census-2001 64. 80 75. 30 53. 70 56. 30 68. 80 42. 20 NSSO Sample Survey (2004 -05) (61 st round) 67. 30 77. 00 57. 00 61. 55 73. 22 49. 27 Increase (% points) 2. 50 3. 30 5. 25 4. 42 1. 70 Female 7. 70 64
Literacy India UP Total Male Female Total Male Census-2001 64. 80 75. 30 53. 70 56. 30 68. 80 42. 20 NSSO Sample Survey (2004 -05) (61 st round) 67. 30 77. 00 57. 00 61. 55 73. 22 49. 27 Increase (% points) 2. 50 3. 30 5. 25 4. 42 1. 70 Female 7. 70 64
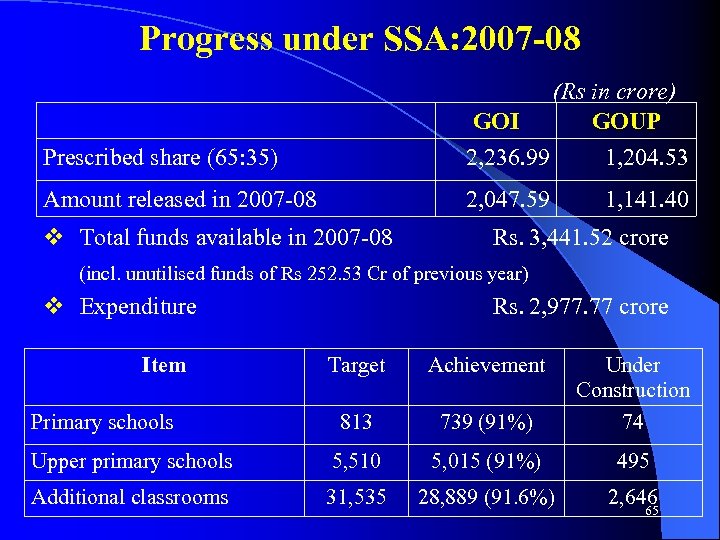 Progress under SSA: 2007 -08 Prescribed share (65: 35) (Rs in crore) GOI GOUP 2, 236. 99 1, 204. 53 Amount released in 2007 -08 2, 047. 59 1, 141. 40 v Total funds available in 2007 -08 Rs. 3, 441. 52 crore (incl. unutilised funds of Rs 252. 53 Cr of previous year) v Expenditure Rs. 2, 977. 77 crore Item Target Achievement 813 739 (91%) Under Construction 74 Upper primary schools 5, 510 5, 015 (91%) 495 Additional classrooms 31, 535 28, 889 (91. 6%) 2, 646 Primary schools 65
Progress under SSA: 2007 -08 Prescribed share (65: 35) (Rs in crore) GOI GOUP 2, 236. 99 1, 204. 53 Amount released in 2007 -08 2, 047. 59 1, 141. 40 v Total funds available in 2007 -08 Rs. 3, 441. 52 crore (incl. unutilised funds of Rs 252. 53 Cr of previous year) v Expenditure Rs. 2, 977. 77 crore Item Target Achievement 813 739 (91%) Under Construction 74 Upper primary schools 5, 510 5, 015 (91%) 495 Additional classrooms 31, 535 28, 889 (91. 6%) 2, 646 Primary schools 65
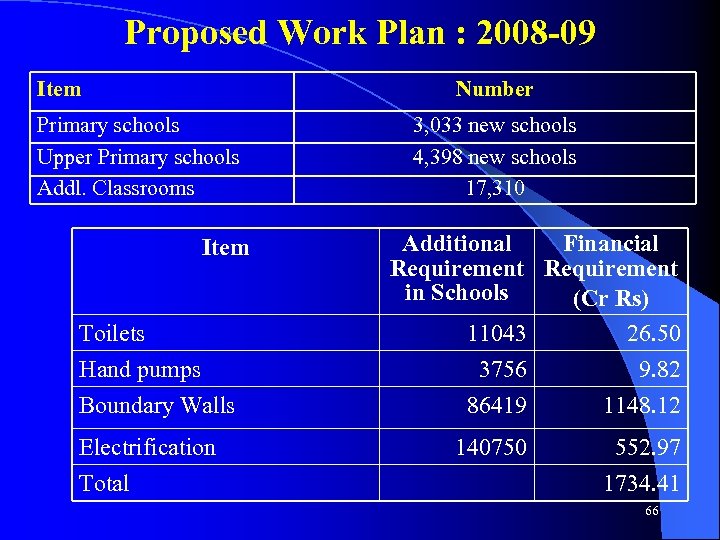 Proposed Work Plan : 2008 -09 Item Number Primary schools Upper Primary schools Addl. Classrooms Item Toilets Hand pumps Boundary Walls Electrification Total 3, 033 new schools 4, 398 new schools 17, 310 Additional Financial Requirement in Schools (Cr Rs) 11043 26. 50 3756 9. 82 86419 1148. 12 140750 552. 97 1734. 41 66
Proposed Work Plan : 2008 -09 Item Number Primary schools Upper Primary schools Addl. Classrooms Item Toilets Hand pumps Boundary Walls Electrification Total 3, 033 new schools 4, 398 new schools 17, 310 Additional Financial Requirement in Schools (Cr Rs) 11043 26. 50 3756 9. 82 86419 1148. 12 140750 552. 97 1734. 41 66
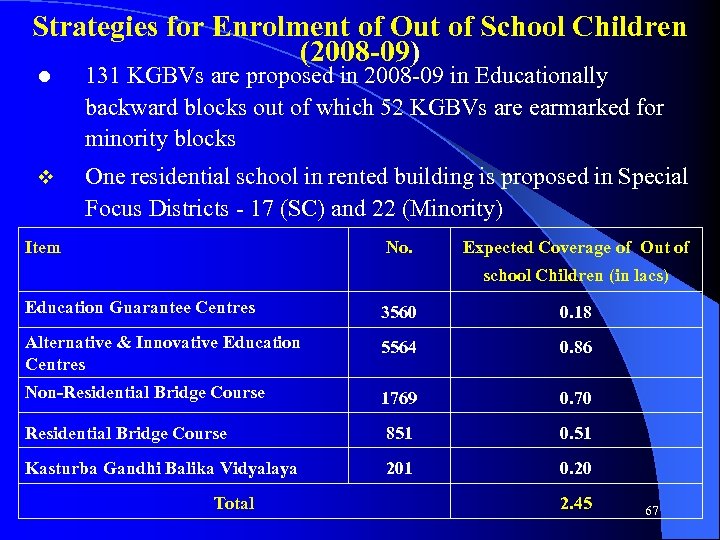 Strategies for Enrolment of Out of School Children (2008 -09) l 131 KGBVs are proposed in 2008 -09 in Educationally backward blocks out of which 52 KGBVs are earmarked for minority blocks v One residential school in rented building is proposed in Special Focus Districts - 17 (SC) and 22 (Minority) Item No. Expected Coverage of Out of school Children (in lacs) Education Guarantee Centres 3560 0. 18 Alternative & Innovative Education Centres 5564 0. 86 Non-Residential Bridge Course 1769 0. 70 Residential Bridge Course 851 0. 51 Kasturba Gandhi Balika Vidyalaya 201 0. 20 Total 2. 45 67
Strategies for Enrolment of Out of School Children (2008 -09) l 131 KGBVs are proposed in 2008 -09 in Educationally backward blocks out of which 52 KGBVs are earmarked for minority blocks v One residential school in rented building is proposed in Special Focus Districts - 17 (SC) and 22 (Minority) Item No. Expected Coverage of Out of school Children (in lacs) Education Guarantee Centres 3560 0. 18 Alternative & Innovative Education Centres 5564 0. 86 Non-Residential Bridge Course 1769 0. 70 Residential Bridge Course 851 0. 51 Kasturba Gandhi Balika Vidyalaya 201 0. 20 Total 2. 45 67
 Inclusive Education 2008 -09 v Special survey will be done by itinerant and resource teachers during May-June, 08 to identify more children with special needs. v 819 medical assessment camps are planned. v 70 residential bridge courses for Visually Impaired and Hiring Impaired children of 6 month duration. v Construction of ramps in 4565 schools. v Braille text books for blind children v Enlarge & bold print text books for low vision children v Strengthening of resource centre at the district level 68
Inclusive Education 2008 -09 v Special survey will be done by itinerant and resource teachers during May-June, 08 to identify more children with special needs. v 819 medical assessment camps are planned. v 70 residential bridge courses for Visually Impaired and Hiring Impaired children of 6 month duration. v Construction of ramps in 4565 schools. v Braille text books for blind children v Enlarge & bold print text books for low vision children v Strengthening of resource centre at the district level 68
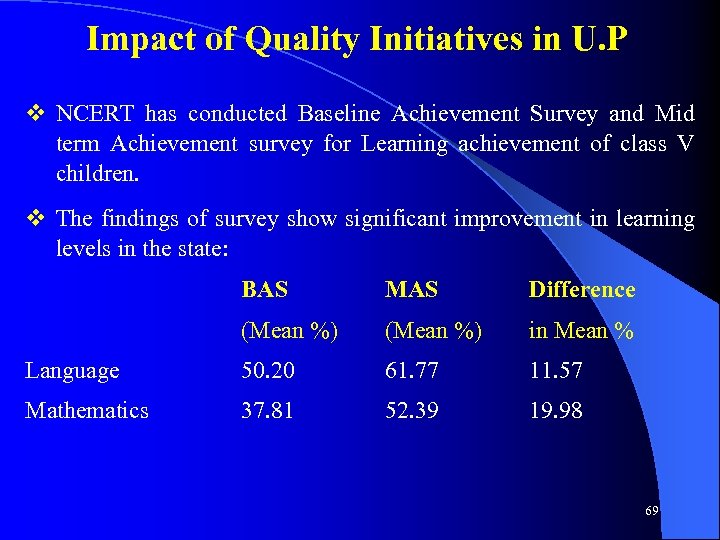 Impact of Quality Initiatives in U. P v NCERT has conducted Baseline Achievement Survey and Mid term Achievement survey for Learning achievement of class V children. v The findings of survey show significant improvement in learning levels in the state: BAS MAS Difference (Mean %) in Mean % Language 50. 20 61. 77 11. 57 Mathematics 37. 81 52. 39 19. 98 69
Impact of Quality Initiatives in U. P v NCERT has conducted Baseline Achievement Survey and Mid term Achievement survey for Learning achievement of class V children. v The findings of survey show significant improvement in learning levels in the state: BAS MAS Difference (Mean %) in Mean % Language 50. 20 61. 77 11. 57 Mathematics 37. 81 52. 39 19. 98 69
 Secondary Education 1. To impart quality education to more than 50 lacs left out children, the state government has taken a decision to establish “State Open School Board”. – The objective of establishing State Open School Board is to provide opportunity of education to working children especially rural children of deprived sections of society including girls. 2. The state has taken a decision to provide computer facilities in 5000 government and aided secondary schools. 3. The state has taken a decision to upgrade 278 government secondary schools to senior secondary schools. 4. The state government has plans to provide a grant of Rs. 20 lacs in two installments for opening of girls’ schools in unserved nyaya panchayats of blocks. 70
Secondary Education 1. To impart quality education to more than 50 lacs left out children, the state government has taken a decision to establish “State Open School Board”. – The objective of establishing State Open School Board is to provide opportunity of education to working children especially rural children of deprived sections of society including girls. 2. The state has taken a decision to provide computer facilities in 5000 government and aided secondary schools. 3. The state has taken a decision to upgrade 278 government secondary schools to senior secondary schools. 4. The state government has plans to provide a grant of Rs. 20 lacs in two installments for opening of girls’ schools in unserved nyaya panchayats of blocks. 70
 5. State Government plans to establish 50 schools in educationally backwards blocks with concentration of scheduled caste population under P. P. P. mode. – Each school to cost Rs. 1. 5 crores, of which the state will bear 33% – Only those blocks will be selected which have female literacy rate below 40% and gender gap more than 20%. – 10% SC children, 10% OBC children and 10% children from general category shall be given free education in these schools 6. A detailed proposal of Rs. 3011. 25 crores has been sent to GOI regarding SUCCESS, an expansion programme of secondary education under 11 th five year plan. 71
5. State Government plans to establish 50 schools in educationally backwards blocks with concentration of scheduled caste population under P. P. P. mode. – Each school to cost Rs. 1. 5 crores, of which the state will bear 33% – Only those blocks will be selected which have female literacy rate below 40% and gender gap more than 20%. – 10% SC children, 10% OBC children and 10% children from general category shall be given free education in these schools 6. A detailed proposal of Rs. 3011. 25 crores has been sent to GOI regarding SUCCESS, an expansion programme of secondary education under 11 th five year plan. 71
 HIGHER EDUCATION • Permission granted for opening of three private universities; • Grant sanctioned for opening 60 degree colleges by private management in unserved blocks and permission granted for opening 150 colleges in self-financing scheme and 7 new Government degree colleges sanctioned in unserved districts. • Grant released for online education through EDUSAT to all state universities. • To expand higher education : Establish new universities in • • private sector and permit new colleges in self-financing scheme. To improve quality of education : Establish Centre of Excellence in 5 state universities. Develop 10 government degree colleges and 10 aided degree colleges as Centres of Excellence. To increase employment potential of students : Establish career guidance bureau/placement cell in all the Universities. Open BBA & BCA courses in 51 government colleges. 72
HIGHER EDUCATION • Permission granted for opening of three private universities; • Grant sanctioned for opening 60 degree colleges by private management in unserved blocks and permission granted for opening 150 colleges in self-financing scheme and 7 new Government degree colleges sanctioned in unserved districts. • Grant released for online education through EDUSAT to all state universities. • To expand higher education : Establish new universities in • • private sector and permit new colleges in self-financing scheme. To improve quality of education : Establish Centre of Excellence in 5 state universities. Develop 10 government degree colleges and 10 aided degree colleges as Centres of Excellence. To increase employment potential of students : Establish career guidance bureau/placement cell in all the Universities. Open BBA & BCA courses in 51 government colleges. 72
 ASSISTANCE REQUIRED • Government of India will setup thirty central universities to improve Gross Enrolment Ratio (GER). State of U. P. with huge student population in age group (18 -24) of around 2 crore and a GER of 9% against national average of 11% will make available adequate land for setting up 3 central universities- one each in Bundelkhand, Western Uttar Pradesh and Eastern Uttar Pradesh. • Government of India has identified 41 districts in Uttar Pradesh with low GER where Government of India will provide Rs. 2. 67 crore to set up a model degree college; rest amount including cost of land to be provided by State. Government of India may kindly sanction 8 colleges for 2008 -09, for which land balance cost will be arranged by Uttar Pradesh. 73
ASSISTANCE REQUIRED • Government of India will setup thirty central universities to improve Gross Enrolment Ratio (GER). State of U. P. with huge student population in age group (18 -24) of around 2 crore and a GER of 9% against national average of 11% will make available adequate land for setting up 3 central universities- one each in Bundelkhand, Western Uttar Pradesh and Eastern Uttar Pradesh. • Government of India has identified 41 districts in Uttar Pradesh with low GER where Government of India will provide Rs. 2. 67 crore to set up a model degree college; rest amount including cost of land to be provided by State. Government of India may kindly sanction 8 colleges for 2008 -09, for which land balance cost will be arranged by Uttar Pradesh. 73
 Technical Education 60 Govt. polytechnics, 19 aided and 27 Pvt. Polytechnics. Intake- 20400 l 7 Govt. Engineering Colleges, 279 Pvt. Technical & management colleges Intake - 65777 l 258 ITIs in Govt. Sector; 232 Pvt. ITIs Intake - 77702 l 74
Technical Education 60 Govt. polytechnics, 19 aided and 27 Pvt. Polytechnics. Intake- 20400 l 7 Govt. Engineering Colleges, 279 Pvt. Technical & management colleges Intake - 65777 l 258 ITIs in Govt. Sector; 232 Pvt. ITIs Intake - 77702 l 74
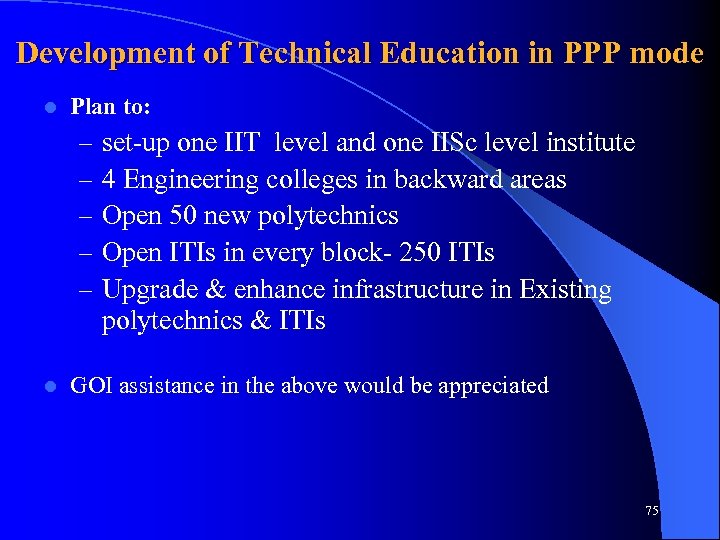 Development of Technical Education in PPP mode l Plan to: – – – l set-up one IIT level and one IISc level institute 4 Engineering colleges in backward areas Open 50 new polytechnics Open ITIs in every block- 250 ITIs Upgrade & enhance infrastructure in Existing polytechnics & ITIs GOI assistance in the above would be appreciated 75
Development of Technical Education in PPP mode l Plan to: – – – l set-up one IIT level and one IISc level institute 4 Engineering colleges in backward areas Open 50 new polytechnics Open ITIs in every block- 250 ITIs Upgrade & enhance infrastructure in Existing polytechnics & ITIs GOI assistance in the above would be appreciated 75
 ASSISTANCE REQUIRED FROM Go. I l l l l l Opening of polytechnics in 14 unserved districts- Rs 126 Crores required - proposal sent Upgradation of Infrastructure of polytechnics - Proposal for Rs 132 Crore sent to Go. I Hostels for girls in polytechnics- Rs 70 Crores required - Proposal sent. Improving the quality of engineering education- TEQIP- State should get substantial funds in TEQIP II Upgradation of infrastructure of ITIs - Go. I assistance required Bundelkhand as educational HUB : One IIT, One IIM, One IIIT 4 Other IIITs sought from Go. I under PPP mode State plans to launch SKILL development mission- SKILL development centre for cluster of villages- Go. I assistance would be required Establishment of one Research & Development Institute for Bio. Technology - Rs 250 Crores Establishment of one Research & Development Institute for Nano. Technology - Rs 250 Crores 76
ASSISTANCE REQUIRED FROM Go. I l l l l l Opening of polytechnics in 14 unserved districts- Rs 126 Crores required - proposal sent Upgradation of Infrastructure of polytechnics - Proposal for Rs 132 Crore sent to Go. I Hostels for girls in polytechnics- Rs 70 Crores required - Proposal sent. Improving the quality of engineering education- TEQIP- State should get substantial funds in TEQIP II Upgradation of infrastructure of ITIs - Go. I assistance required Bundelkhand as educational HUB : One IIT, One IIM, One IIIT 4 Other IIITs sought from Go. I under PPP mode State plans to launch SKILL development mission- SKILL development centre for cluster of villages- Go. I assistance would be required Establishment of one Research & Development Institute for Bio. Technology - Rs 250 Crores Establishment of one Research & Development Institute for Nano. Technology - Rs 250 Crores 76
 Vocational Education Council 1. 2. 3. 4. To contract and Grant permission to Vocational institutions To prepare syllabus of vocational education institution Conduct Examination of Vocational education institution To grant certificate to the students passed from vocational education institution 77
Vocational Education Council 1. 2. 3. 4. To contract and Grant permission to Vocational institutions To prepare syllabus of vocational education institution Conduct Examination of Vocational education institution To grant certificate to the students passed from vocational education institution 77
 Medical Health & Family Welfare 78
Medical Health & Family Welfare 78
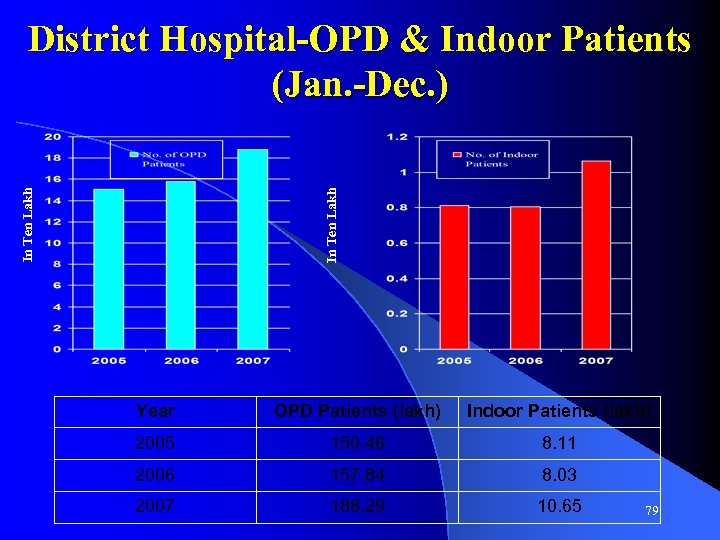 In Ten Lakh District Hospital-OPD & Indoor Patients (Jan. -Dec. ) Year OPD Patients (lakh) Indoor Patients (lakh) 2005 150. 46 8. 11 2006 157. 84 8. 03 2007 188. 29 10. 65 79
In Ten Lakh District Hospital-OPD & Indoor Patients (Jan. -Dec. ) Year OPD Patients (lakh) Indoor Patients (lakh) 2005 150. 46 8. 11 2006 157. 84 8. 03 2007 188. 29 10. 65 79
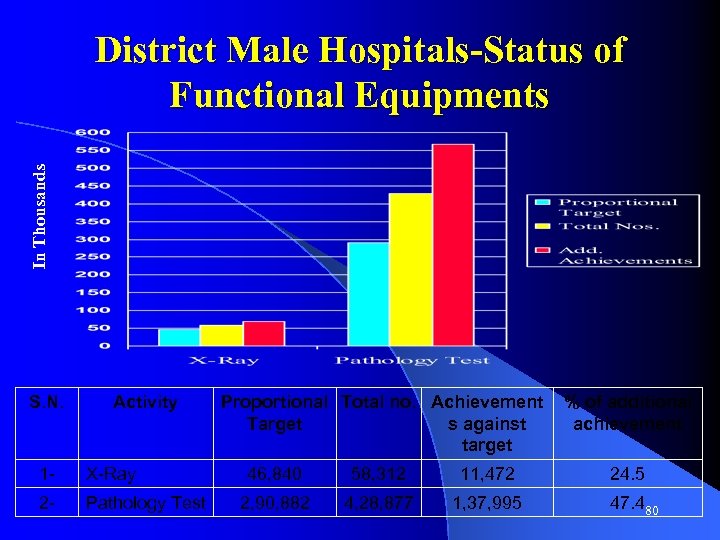 In Thousands District Male Hospitals-Status of Functional Equipments S. N. Activity 1 - X-Ray 2 - Pathology Test Proportional Total no. Achievement Target s against target 46, 840 58, 312 11, 472 2, 90, 882 4, 28, 877 1, 37, 995 % of additional achievement 24. 5 47. 480
In Thousands District Male Hospitals-Status of Functional Equipments S. N. Activity 1 - X-Ray 2 - Pathology Test Proportional Total no. Achievement Target s against target 46, 840 58, 312 11, 472 2, 90, 882 4, 28, 877 1, 37, 995 % of additional achievement 24. 5 47. 480
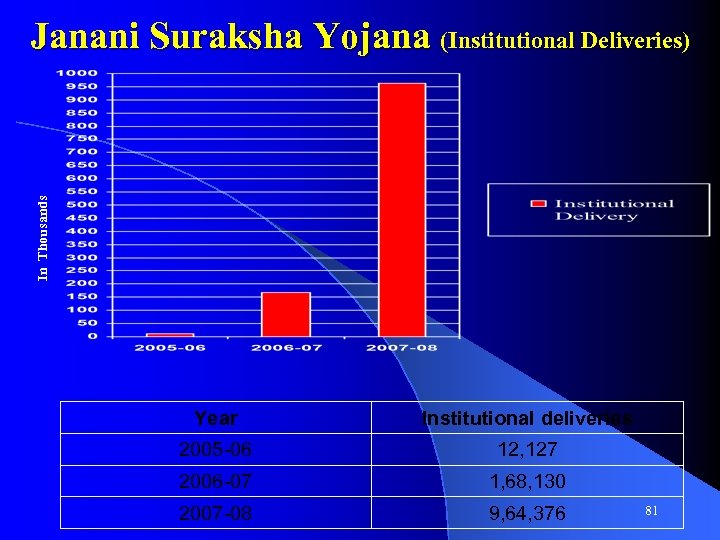 In Thousands Janani Suraksha Yojana (Institutional Deliveries) Year Institutional deliveries 2005 -06 12, 127 2006 -07 1, 68, 130 2007 -08 9, 64, 376 81
In Thousands Janani Suraksha Yojana (Institutional Deliveries) Year Institutional deliveries 2005 -06 12, 127 2006 -07 1, 68, 130 2007 -08 9, 64, 376 81
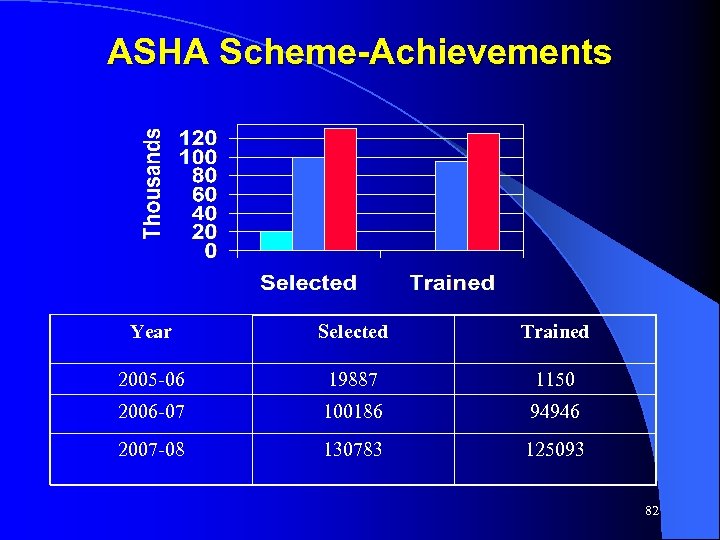 ASHA Scheme-Achievements Year Selected Trained 2005 -06 19887 1150 2006 -07 100186 94946 2007 -08 130783 125093 82
ASHA Scheme-Achievements Year Selected Trained 2005 -06 19887 1150 2006 -07 100186 94946 2007 -08 130783 125093 82
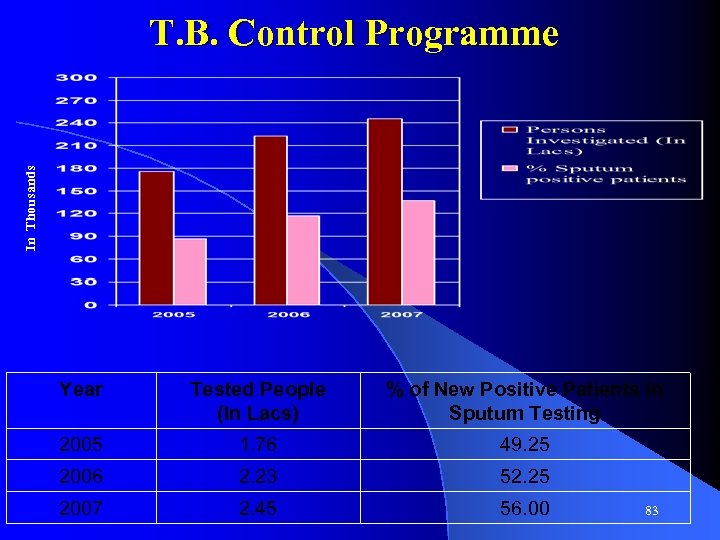 In Thousands T. B. Control Programme Year Tested People (In Lacs) % of New Positive Patients in Sputum Testing 2005 1. 76 49. 25 2006 2. 23 52. 25 2007 2. 45 56. 00 83
In Thousands T. B. Control Programme Year Tested People (In Lacs) % of New Positive Patients in Sputum Testing 2005 1. 76 49. 25 2006 2. 23 52. 25 2007 2. 45 56. 00 83
 Key Achievements under NRHM (2007 -08) l 1. 30 lakh ASHA selected and trained in first module. l Contractual appointment of 1410 staff nurses, 960 ANMs, 155 Lady doctors & 82 Lab Technicians l 63 DFH /CHCs functional as FRUs l 9. 64 lakh women benefitted under JSY in 2007 -08 in comparison to 1. 67 lakh in 2006 -07 l RKS constituted at all districts hospitals & CHCs/BPHCs l 28600 Village Health & Sanitation Committees constituted l Comprehensive child survival programme in 17 selected districts started in the 2007 -08 to reduce the Infant Mortality Rate l Accreditation of private facilities has been initiated for JSY l Divisional PMUs Established 84
Key Achievements under NRHM (2007 -08) l 1. 30 lakh ASHA selected and trained in first module. l Contractual appointment of 1410 staff nurses, 960 ANMs, 155 Lady doctors & 82 Lab Technicians l 63 DFH /CHCs functional as FRUs l 9. 64 lakh women benefitted under JSY in 2007 -08 in comparison to 1. 67 lakh in 2006 -07 l RKS constituted at all districts hospitals & CHCs/BPHCs l 28600 Village Health & Sanitation Committees constituted l Comprehensive child survival programme in 17 selected districts started in the 2007 -08 to reduce the Infant Mortality Rate l Accreditation of private facilities has been initiated for JSY l Divisional PMUs Established 84
 Priorities under NRHM- 2008 -09 l l l To facilitate 15 lacs beneficiaries under Janani Suraksha Yojana. All 823 CHC/BPHC to be made functional for 24 x 7 services. Atleast 2 facilities in each district (total 140 no. ) to be made functional as FRU. Training of 5000 ANMs & 900 male workers to be started with the help of private sector. Construction of buildings for 3315 Sub Centres Medical mobile units in each district 10 clinical training centres to be established at district level ASHA Support System will be established with the help of NGO at the Block level. Fixed day family planning services to be provided at CHC level Adolescent counseling center in each district School health programme in 36000 schools. Pilot of conditional cash transfer scheme for addressing 85 malnutrition among girls
Priorities under NRHM- 2008 -09 l l l To facilitate 15 lacs beneficiaries under Janani Suraksha Yojana. All 823 CHC/BPHC to be made functional for 24 x 7 services. Atleast 2 facilities in each district (total 140 no. ) to be made functional as FRU. Training of 5000 ANMs & 900 male workers to be started with the help of private sector. Construction of buildings for 3315 Sub Centres Medical mobile units in each district 10 clinical training centres to be established at district level ASHA Support System will be established with the help of NGO at the Block level. Fixed day family planning services to be provided at CHC level Adolescent counseling center in each district School health programme in 36000 schools. Pilot of conditional cash transfer scheme for addressing 85 malnutrition among girls
 Issues • Major Bottlenecks in Procurement • Vaccines for RI not available timely, especially DT & Measles. • Vaccines for JE campaign not available in time – has affected the program. • IFA Tablets. Ø Cold Chain replacement not approved by GOI. Ø Release of funds (Rs. 24 Cr) for NPCB to clear past liabilities not approved. ØStates initiative for handling cases of drug resistant TB not approved. 86
Issues • Major Bottlenecks in Procurement • Vaccines for RI not available timely, especially DT & Measles. • Vaccines for JE campaign not available in time – has affected the program. • IFA Tablets. Ø Cold Chain replacement not approved by GOI. Ø Release of funds (Rs. 24 Cr) for NPCB to clear past liabilities not approved. ØStates initiative for handling cases of drug resistant TB not approved. 86
 Information Technology 87
Information Technology 87
 I. T & Electronics – e. Governance: Core Infrastructure Projects SWAN The project envisages setting up of a backbone network of 3 Hubs with 885 nodes connecting all the blocks, tehsils & districts to the state capital over a 2 Mbps bandwidth. Implementation by NIC. l Data, Video and Voice (IP based) network, which shall be reaching to all the districts and ultimately more than 100, 000 villages of the state l l All the 70 districts are linked with HQ and are operational. The Tehsil level NOC shall be operational by June, 2008 and all the Block level NOC shall be operational by July 2008. Jan Sewa Kendras (Common Service Centres-CSC) The State is implementing CSC project in which a total of 17909 CSCs shall be setup in rural areas during the year 2008 -09. l The CSCs shall be known as 'Jan Seva Kendra' in the State. These Kendras shall be the delivery points of various services to citizens at their doorstep. l 25% of the centres shall be rolled out by 08 -09 -08, another 25% by 08 -11 -08, 25% by 08 -01 -09 and the rest 25% by 08 -04 -09 l Since the revenue support is based on the availability of G 2 C services, the State has to develop appropriate G 2 C service enablement plans, at least for key 88 government services l
I. T & Electronics – e. Governance: Core Infrastructure Projects SWAN The project envisages setting up of a backbone network of 3 Hubs with 885 nodes connecting all the blocks, tehsils & districts to the state capital over a 2 Mbps bandwidth. Implementation by NIC. l Data, Video and Voice (IP based) network, which shall be reaching to all the districts and ultimately more than 100, 000 villages of the state l l All the 70 districts are linked with HQ and are operational. The Tehsil level NOC shall be operational by June, 2008 and all the Block level NOC shall be operational by July 2008. Jan Sewa Kendras (Common Service Centres-CSC) The State is implementing CSC project in which a total of 17909 CSCs shall be setup in rural areas during the year 2008 -09. l The CSCs shall be known as 'Jan Seva Kendra' in the State. These Kendras shall be the delivery points of various services to citizens at their doorstep. l 25% of the centres shall be rolled out by 08 -09 -08, another 25% by 08 -11 -08, 25% by 08 -01 -09 and the rest 25% by 08 -04 -09 l Since the revenue support is based on the availability of G 2 C services, the State has to develop appropriate G 2 C service enablement plans, at least for key 88 government services l
 I. T & Electronics – e. Governance: Core Infrastructure Projects STATE DATA CENTER l l l The third major core infrastructure project under e. Governance plan of the State Government is the State Data Centre which is being set up to consolidate services, applications and infrastructure to provide efficient delivery of Government-to-Government (G 2 G), Governmentto-Citizen (G 2 C) and Government-to-Business (G 2 B) services Ensure high Data and Application availability to all e. Governance applications Go. I has given approval for establishment of SDC at a cost of Rs. 55. 33 crores. The Date Centre shall be installed at Updesco premises. DIT share of Rs 4. 20 cr has been transferred to the State by Go. I. RFP under preparation by Ms Wipro the selected consultants E-District (a Mission Mode Project) Being implemented in 6 districts viz. Gorakhpur, Noida, Ghaziabad, Sultanpur, Sitapur & Raibareilly. It will provide 10 services/32 sub-services to citizens electronically. It shall become operational in September, 2008. Once implemented on pilot basis and upon its success, it shall be rolled out in other districts of the state. l Data digitization work at district level is under progress l The application development is being carried out by State NIC with active support from Consultants l One Jan Soochana Kendra at each district level is being established with an estimated cost of Rs. 40. 00 lacs for each centre. 89 l
I. T & Electronics – e. Governance: Core Infrastructure Projects STATE DATA CENTER l l l The third major core infrastructure project under e. Governance plan of the State Government is the State Data Centre which is being set up to consolidate services, applications and infrastructure to provide efficient delivery of Government-to-Government (G 2 G), Governmentto-Citizen (G 2 C) and Government-to-Business (G 2 B) services Ensure high Data and Application availability to all e. Governance applications Go. I has given approval for establishment of SDC at a cost of Rs. 55. 33 crores. The Date Centre shall be installed at Updesco premises. DIT share of Rs 4. 20 cr has been transferred to the State by Go. I. RFP under preparation by Ms Wipro the selected consultants E-District (a Mission Mode Project) Being implemented in 6 districts viz. Gorakhpur, Noida, Ghaziabad, Sultanpur, Sitapur & Raibareilly. It will provide 10 services/32 sub-services to citizens electronically. It shall become operational in September, 2008. Once implemented on pilot basis and upon its success, it shall be rolled out in other districts of the state. l Data digitization work at district level is under progress l The application development is being carried out by State NIC with active support from Consultants l One Jan Soochana Kendra at each district level is being established with an estimated cost of Rs. 40. 00 lacs for each centre. 89 l
 I. T & Electronics – e. Governance: Core Infrastructure Projects E-Procurement (a Mission Mode Project) To be implemented in 6 departments viz. PWD, Irrigation, Medical & Health, Industries, IT & Electronics & Printing & Stationary on pilot basis in the State l Government directives issued and departmental level infrastructure created l l Methodologies finalized, training program and resource persons finalized in the State l Tender Notice published in Newspapers for registered tenderers/bidders to get Digital Signature issued and thereafter to get trained on e-Procurement Application Software usage from 20/05/2008 90
I. T & Electronics – e. Governance: Core Infrastructure Projects E-Procurement (a Mission Mode Project) To be implemented in 6 departments viz. PWD, Irrigation, Medical & Health, Industries, IT & Electronics & Printing & Stationary on pilot basis in the State l Government directives issued and departmental level infrastructure created l l Methodologies finalized, training program and resource persons finalized in the State l Tender Notice published in Newspapers for registered tenderers/bidders to get Digital Signature issued and thereafter to get trained on e-Procurement Application Software usage from 20/05/2008 90
 National e. Governance Plan – Issues with Go. I NEGAP Under the CSC scheme the project for UP has been sanctioned in 2007 -08 with a total cost of Rs. 284 crores for 4 years. The open bids received by Go. UP in 5 of the 7 zones are either negative or have no fiscal liability towards Go. UP. This shall result in saving of about Rs 250 crores from the sanctioned amount as calculated at normative value. Go. I may consider the saving thus derived to be used in Back end Computerisation for e-Governance services. l Go. I has released an installment of ACA for State Data Centre Scheme for some States. UP may also be given the Ist Installment of ACA of approx Rs. 4. 20 crores as approved. l Bandwidth cost of SWAN was to be reimbursed by Go. I. A payment of approx Rs. 11 crores is due from Go. I on this account. l 91
National e. Governance Plan – Issues with Go. I NEGAP Under the CSC scheme the project for UP has been sanctioned in 2007 -08 with a total cost of Rs. 284 crores for 4 years. The open bids received by Go. UP in 5 of the 7 zones are either negative or have no fiscal liability towards Go. UP. This shall result in saving of about Rs 250 crores from the sanctioned amount as calculated at normative value. Go. I may consider the saving thus derived to be used in Back end Computerisation for e-Governance services. l Go. I has released an installment of ACA for State Data Centre Scheme for some States. UP may also be given the Ist Installment of ACA of approx Rs. 4. 20 crores as approved. l Bandwidth cost of SWAN was to be reimbursed by Go. I. A payment of approx Rs. 11 crores is due from Go. I on this account. l 91
 Urban Development 92
Urban Development 92
 Urban Infrastructure and Governance (UIG) l Cities Covered 7 Project Submitted (No) 30 Project Cost of Submitted Project Rs 3910. 42 Cr. Sanctioned Project (No) 16 Sanctioned Project Cost Rs. 1912. 27 Cr. Go. I Share against Sanctioned Project Rs. 1368. 59 Cr. Released by Go. I against (6) Rs. 232. 26 Cr. Project Pending in Go. I 3 Project Cost of Pending Project Rs. 266. 35 Cr. l UC submitted to Go. I l l l l Rs. 85. 00 Cr 93
Urban Infrastructure and Governance (UIG) l Cities Covered 7 Project Submitted (No) 30 Project Cost of Submitted Project Rs 3910. 42 Cr. Sanctioned Project (No) 16 Sanctioned Project Cost Rs. 1912. 27 Cr. Go. I Share against Sanctioned Project Rs. 1368. 59 Cr. Released by Go. I against (6) Rs. 232. 26 Cr. Project Pending in Go. I 3 Project Cost of Pending Project Rs. 266. 35 Cr. l UC submitted to Go. I l l l l Rs. 85. 00 Cr 93
 Urban Infrastructure Development Scheme for Small and Medium Towns (UIDSSMT) l l l l l Project Submitted (No. ) 66 Project Cost of Submitted Project Rs. 1155. 96 Cr. Sanctioned Project (No) 49 Sanctioned Project Cost Rs. 995. 00 Cr. Go. I Share against Sanctioned Project Rs. 796. 00 Cr. Released by Go. I against (6) Rs. 308. 74 Cr. Project Pending in Go. I (No) 17 Project Cost of Pending Project Rs. 200. 0 Cr. UC Submitted to Go. I Rs. 13. 02 Cr. Go. I has only released the funds for 33 projects against the 49 sanctioned projects 94
Urban Infrastructure Development Scheme for Small and Medium Towns (UIDSSMT) l l l l l Project Submitted (No. ) 66 Project Cost of Submitted Project Rs. 1155. 96 Cr. Sanctioned Project (No) 49 Sanctioned Project Cost Rs. 995. 00 Cr. Go. I Share against Sanctioned Project Rs. 796. 00 Cr. Released by Go. I against (6) Rs. 308. 74 Cr. Project Pending in Go. I (No) 17 Project Cost of Pending Project Rs. 200. 0 Cr. UC Submitted to Go. I Rs. 13. 02 Cr. Go. I has only released the funds for 33 projects against the 49 sanctioned projects 94
 l l l l Basic Services for Urban Poor (BSUP) Cities Covered 7 Project Submitted (No. ) 12 Project Cost of Submitted Project Rs. 437. 71 Cr. Sanctioned Project (No) 12 Sanctioned Project Cost Rs. 437. 71 Cr. Go. I Share against Sanctioned Project Rs. 218. 75 Cr. Released by Go. I against (6) Rs. 43. 86 Cr. UC Submitted to Go. I Rs. 26. 48 Cr. 95
l l l l Basic Services for Urban Poor (BSUP) Cities Covered 7 Project Submitted (No. ) 12 Project Cost of Submitted Project Rs. 437. 71 Cr. Sanctioned Project (No) 12 Sanctioned Project Cost Rs. 437. 71 Cr. Go. I Share against Sanctioned Project Rs. 218. 75 Cr. Released by Go. I against (6) Rs. 43. 86 Cr. UC Submitted to Go. I Rs. 26. 48 Cr. 95
 INTEGRATED HOUSING AND SLUM DEVELOPMENT PROGRAMME (IHSDP) l l l l Cities Covered 9 Project Submitted (No. ) 9 Project Cost of Submitted Project Rs. 33. 30 Cr. Sanctioned Project (No) 9 Sanctioned Project Cost Rs. 33. 30 Cr. Go. I Share against Sanctioned Project Rs. 26. 64 Cr. Released by Go. I against (6) Rs. 11. 05 Cr. UC Submitted to Go. I Rs. 9. 47 Cr. Same specifications are adopted under BSUP and IHSDP dwelling units but the unit cost under IHSDP is only Rs 80000 whereas in BSUP the unit cost is Rs 2 lakh. . This needs to revised and made the same as that under BSUP. 96
INTEGRATED HOUSING AND SLUM DEVELOPMENT PROGRAMME (IHSDP) l l l l Cities Covered 9 Project Submitted (No. ) 9 Project Cost of Submitted Project Rs. 33. 30 Cr. Sanctioned Project (No) 9 Sanctioned Project Cost Rs. 33. 30 Cr. Go. I Share against Sanctioned Project Rs. 26. 64 Cr. Released by Go. I against (6) Rs. 11. 05 Cr. UC Submitted to Go. I Rs. 9. 47 Cr. Same specifications are adopted under BSUP and IHSDP dwelling units but the unit cost under IHSDP is only Rs 80000 whereas in BSUP the unit cost is Rs 2 lakh. . This needs to revised and made the same as that under BSUP. 96
 Social Welfare 97
Social Welfare 97
 Issues • State has introduced scholarship schemes for general students, which should be shared by GOI on 50% basis. anticipated expenditure for pre-matric classes is expected to be Rs. 200 crores and for post-matric classes nearly Rs. 250 crores. • Coaching scheme for different competitive examinations for poor general candidates has bee introduced, in which anticipated expenditure is expected to be Rs. 13. 50 crores, which should also be shared by GOI on 50% basis. • State provides Old Age Pension to persons above the age of 60 years. GOI provides Central assistance of Rs. 200/- per beneficiary for persons above the age of 65 years. GOI should reduce age limit from 65 to 60 years. 98
Issues • State has introduced scholarship schemes for general students, which should be shared by GOI on 50% basis. anticipated expenditure for pre-matric classes is expected to be Rs. 200 crores and for post-matric classes nearly Rs. 250 crores. • Coaching scheme for different competitive examinations for poor general candidates has bee introduced, in which anticipated expenditure is expected to be Rs. 13. 50 crores, which should also be shared by GOI on 50% basis. • State provides Old Age Pension to persons above the age of 60 years. GOI provides Central assistance of Rs. 200/- per beneficiary for persons above the age of 65 years. GOI should reduce age limit from 65 to 60 years. 98
 • GOI should provide 50 % of construction cost of Ashram Type School for scheduled caste as is admissible for scheduled tribes ATS. • It is requested that GOI should bear 50% of running cost of Hostel and ATS. • State Govt. provides grant for daughter's marriage and treatment of illness to Sc/ST/General caste families below poverty line. It is requested that GOI should bear at least 50% amount of the grant. 99
• GOI should provide 50 % of construction cost of Ashram Type School for scheduled caste as is admissible for scheduled tribes ATS. • It is requested that GOI should bear 50% of running cost of Hostel and ATS. • State Govt. provides grant for daughter's marriage and treatment of illness to Sc/ST/General caste families below poverty line. It is requested that GOI should bear at least 50% amount of the grant. 99
 Women & Child Welfare 100
Women & Child Welfare 100
 Ø For Women Welfare empowerment of women to ensure women’s participation in all decision making processes and economic activities, State Women Policy formulated. Ø 13. 52 lakh destitute women living below poverty line are being covered under pension scheme. Ø Need to build and strengthen observation homes in each district as per JJ Act Ø As per Go. I norms, NGOs not willing to bear 50% of land cost under Working Womens Hostel hence GOI to bear entire land cost. 101
Ø For Women Welfare empowerment of women to ensure women’s participation in all decision making processes and economic activities, State Women Policy formulated. Ø 13. 52 lakh destitute women living below poverty line are being covered under pension scheme. Ø Need to build and strengthen observation homes in each district as per JJ Act Ø As per Go. I norms, NGOs not willing to bear 50% of land cost under Working Womens Hostel hence GOI to bear entire land cost. 101
 Child Welfare-ICDS Ø Through 897 operational projects and 150460 Anganwadi Centres, 218 lakh beneficiaries are being provided various services under ICDS programme. . Ø Out of 150460 operational Anganwadi centres, 11000 centres have their own buildings constructed/under construction. Ø There is an urgent need to construct the remaining centres with child friendly toilets and kitchen sheds. Go. I should provide assistance 102
Child Welfare-ICDS Ø Through 897 operational projects and 150460 Anganwadi Centres, 218 lakh beneficiaries are being provided various services under ICDS programme. . Ø Out of 150460 operational Anganwadi centres, 11000 centres have their own buildings constructed/under construction. Ø There is an urgent need to construct the remaining centres with child friendly toilets and kitchen sheds. Go. I should provide assistance 102
 Problems & Issues Ø As per directions of Hon’ble Supreme Court, all ICDS projects to provide hot cooked meal by 2009. Ø Under Phase-I, hot cooked meal is being provided in 470 projects. Conversion cost @ Rs. 0. 50 per beneficiary per day (67. 68 lac beneficiaries, excluding children below 3 years), a total amount of Rs. 101. 52 Crores and for utensils Rs 23. 56 Cr. is required. Ø During 2008 -09, to cover the remaining 427 projects, Rs. 88. 16 crores and Rs 20. 99 Cr for utensils is required. 103
Problems & Issues Ø As per directions of Hon’ble Supreme Court, all ICDS projects to provide hot cooked meal by 2009. Ø Under Phase-I, hot cooked meal is being provided in 470 projects. Conversion cost @ Rs. 0. 50 per beneficiary per day (67. 68 lac beneficiaries, excluding children below 3 years), a total amount of Rs. 101. 52 Crores and for utensils Rs 23. 56 Cr. is required. Ø During 2008 -09, to cover the remaining 427 projects, Rs. 88. 16 crores and Rs 20. 99 Cr for utensils is required. 103
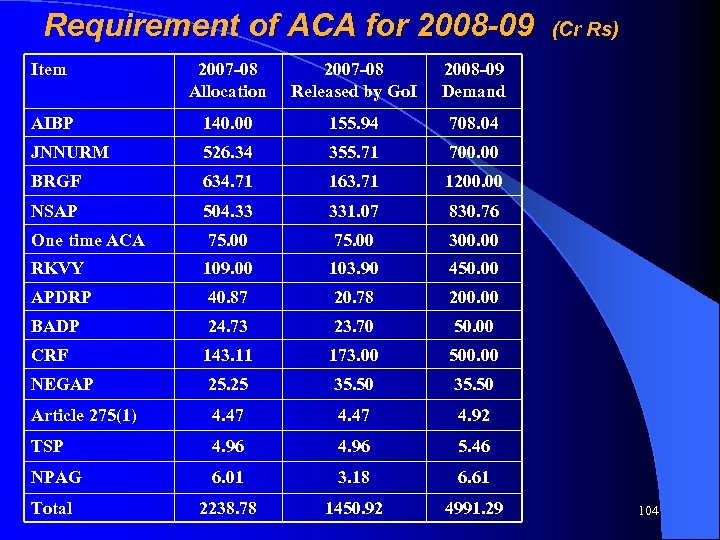 Requirement of ACA for 2008 -09 Item 2007 -08 Allocation 2007 -08 Released by Go. I 2008 -09 Demand AIBP 140. 00 155. 94 708. 04 JNNURM 526. 34 355. 71 700. 00 BRGF 634. 71 163. 71 1200. 00 NSAP 504. 33 331. 07 830. 76 One time ACA 75. 00 300. 00 RKVY 109. 00 103. 90 450. 00 APDRP 40. 87 20. 78 200. 00 BADP 24. 73 23. 70 50. 00 CRF 143. 11 173. 00 500. 00 NEGAP 25. 25 35. 50 Article 275(1) 4. 47 4. 92 TSP 4. 96 5. 46 NPAG 6. 01 3. 18 6. 61 Total 2238. 78 1450. 92 4991. 29 (Cr Rs) 104
Requirement of ACA for 2008 -09 Item 2007 -08 Allocation 2007 -08 Released by Go. I 2008 -09 Demand AIBP 140. 00 155. 94 708. 04 JNNURM 526. 34 355. 71 700. 00 BRGF 634. 71 163. 71 1200. 00 NSAP 504. 33 331. 07 830. 76 One time ACA 75. 00 300. 00 RKVY 109. 00 103. 90 450. 00 APDRP 40. 87 20. 78 200. 00 BADP 24. 73 23. 70 50. 00 CRF 143. 11 173. 00 500. 00 NEGAP 25. 25 35. 50 Article 275(1) 4. 47 4. 92 TSP 4. 96 5. 46 NPAG 6. 01 3. 18 6. 61 Total 2238. 78 1450. 92 4991. 29 (Cr Rs) 104
 Projects Proposed to be Financed Under One time ACA (Grant ) § Water Supply & Irrigation facilities in Bundelkhand- Rs 300 Cr. § Setting up Agriculture University in Banda – Rs 100 Cr § Providing assistance for drip and sprinkler irrigation to small and marginal farmers in Vindhyanchal region- Rs 50 Cr § One solar light for every Indira Awas- Rs 50 Cr § Creation of permanent infrastructure in Allahabad for Kumbh Mela/Tourism Development - Rs 200 Cr. § Setting up a World University of Religion and Culture at Sarnath, Varanasi - Rs 200 Cr § Development of state of art tourism infrastructure in Agra- Rs 100 Cr. 105
Projects Proposed to be Financed Under One time ACA (Grant ) § Water Supply & Irrigation facilities in Bundelkhand- Rs 300 Cr. § Setting up Agriculture University in Banda – Rs 100 Cr § Providing assistance for drip and sprinkler irrigation to small and marginal farmers in Vindhyanchal region- Rs 50 Cr § One solar light for every Indira Awas- Rs 50 Cr § Creation of permanent infrastructure in Allahabad for Kumbh Mela/Tourism Development - Rs 200 Cr. § Setting up a World University of Religion and Culture at Sarnath, Varanasi - Rs 200 Cr § Development of state of art tourism infrastructure in Agra- Rs 100 Cr. 105
 SIZE OF ANNUAL PLAN 2008 -09 § Additional Central Assistance to the tune of Rs 4991. 27 Cr needed under different programmes § Annual Plan size should be fixed at-least at Rs 35000 Cr 106
SIZE OF ANNUAL PLAN 2008 -09 § Additional Central Assistance to the tune of Rs 4991. 27 Cr needed under different programmes § Annual Plan size should be fixed at-least at Rs 35000 Cr 106
 THANK YOU 107
THANK YOU 107


