f5e07c81c16a3709ff81606216b30772.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 47
 Using UNCRC Rights in Early Childhood as a tool for achieving ‘equity from the start’ Clyde Hertzman Human Early Learning Partnership Council for Early Child Development
Using UNCRC Rights in Early Childhood as a tool for achieving ‘equity from the start’ Clyde Hertzman Human Early Learning Partnership Council for Early Child Development
 What influences early child development? The experiences children have in the environments where they grow up, live and learn.
What influences early child development? The experiences children have in the environments where they grow up, live and learn.
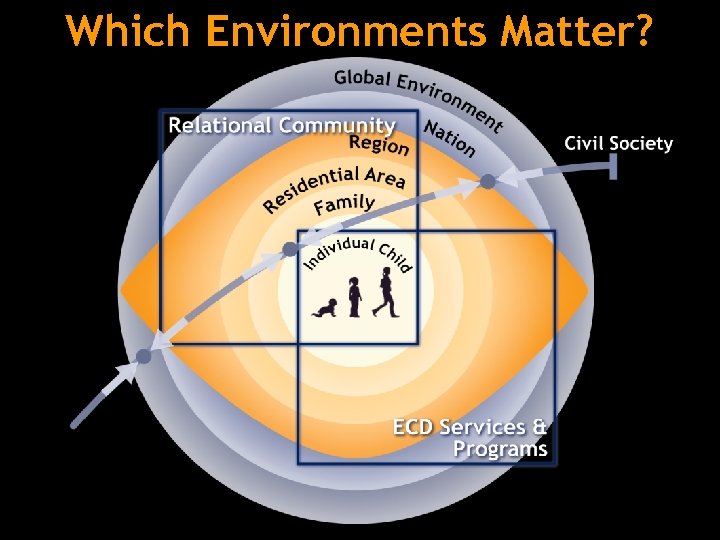 Which Environments Matter?
Which Environments Matter?
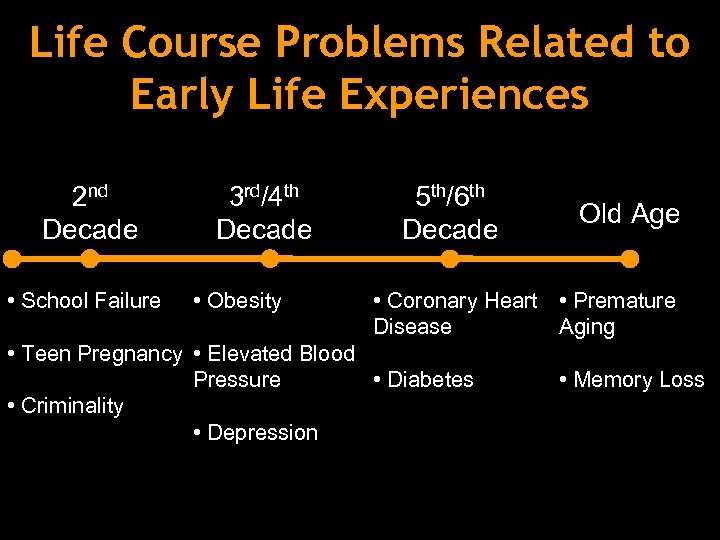 Life Course Problems Related to Early Life Experiences 2 nd Decade • School Failure 3 rd/4 th Decade • Obesity 5 th/6 th Decade Old Age • Coronary Heart • Premature Disease Aging • Teen Pregnancy • Elevated Blood Pressure • Diabetes • Criminality • Depression • Memory Loss
Life Course Problems Related to Early Life Experiences 2 nd Decade • School Failure 3 rd/4 th Decade • Obesity 5 th/6 th Decade Old Age • Coronary Heart • Premature Disease Aging • Teen Pregnancy • Elevated Blood Pressure • Diabetes • Criminality • Depression • Memory Loss
 “Equity from the Start”
“Equity from the Start”
 The Early Development Instrument
The Early Development Instrument
 Early Development Instrument • 104 items • Extensive validity and reliability data from several countries • Not a test • Teacher at age 5 is respondent • Five developmental domains, with sixteen subdomains • A guide with explanations available
Early Development Instrument • 104 items • Extensive validity and reliability data from several countries • Not a test • Teacher at age 5 is respondent • Five developmental domains, with sixteen subdomains • A guide with explanations available
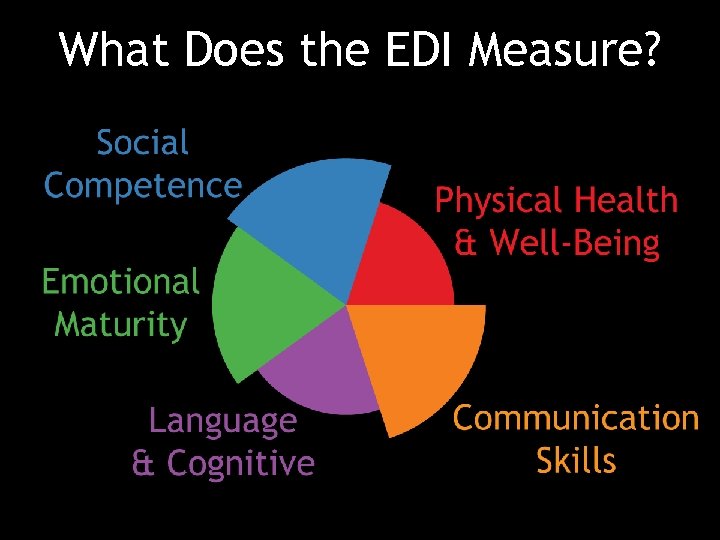 What Does the EDI Measure?
What Does the EDI Measure?
 EDI is: -a population-based tool -a mobilisation tool -a monitoring tool EDI is not: -an individual assessment -a prescription for action -perfect
EDI is: -a population-based tool -a mobilisation tool -a monitoring tool EDI is not: -an individual assessment -a prescription for action -perfect
 Question: Does the following represent a rights violation under the UN-CRC?
Question: Does the following represent a rights violation under the UN-CRC?
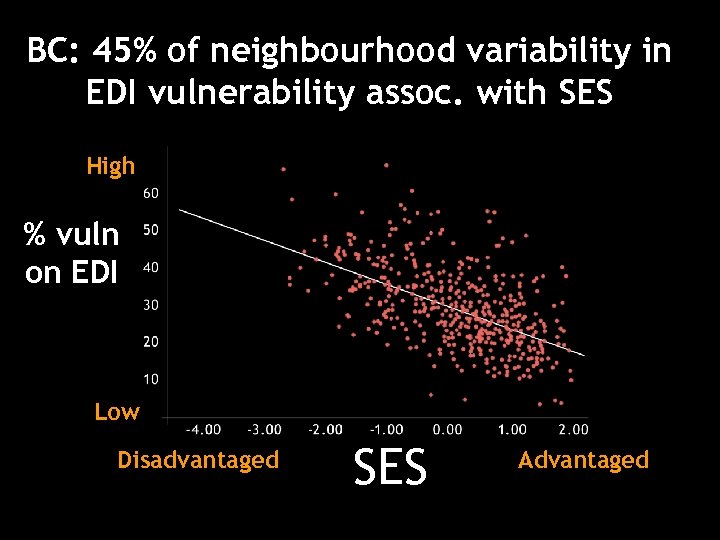 BC: 45% of neighbourhood variability in EDI vulnerability assoc. with SES High % vuln on EDI Low Disadvantaged SES Advantaged
BC: 45% of neighbourhood variability in EDI vulnerability assoc. with SES High % vuln on EDI Low Disadvantaged SES Advantaged
 According to UN-CRC: GC 7 …………the answer is ‘yes’ thus……. UN-CRC GC: 7 Indicators Group
According to UN-CRC: GC 7 …………the answer is ‘yes’ thus……. UN-CRC GC: 7 Indicators Group
 Who is involved in UN-CRC GC: 7 Indicators group?
Who is involved in UN-CRC GC: 7 Indicators group?
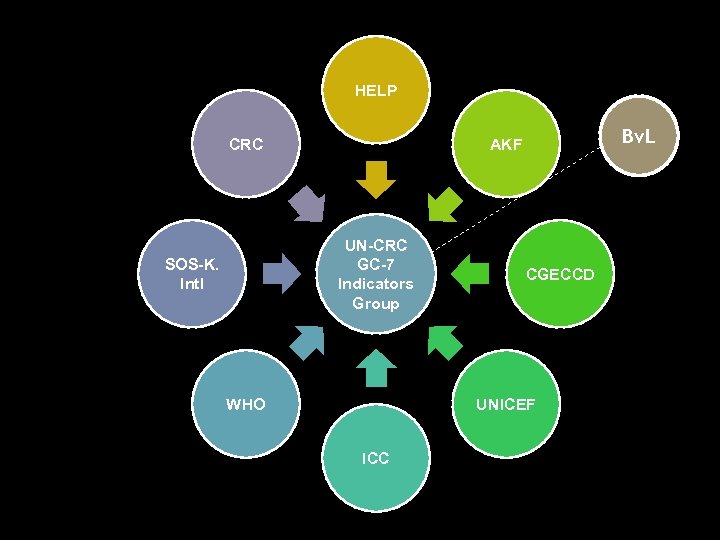 HELP CRC UN-CRC GC-7 Indicators Group SOS-K. Intl Bv. L AKF WHO CGECCD UNICEF ICC
HELP CRC UN-CRC GC-7 Indicators Group SOS-K. Intl Bv. L AKF WHO CGECCD UNICEF ICC
 What is a CRC General Comment? 1989: The Child Right Convention, CRC 2004: General Comment 7 (GC: 7); Implementing child rights in early childhood General Comments: Are usually developed to address specific issues or overarching problems with CRC Are also meant to assist the States Parties with their analyses of the problems with respect to specific issues and improve reporting to CRC. There are 14 GCs to date in CRC
What is a CRC General Comment? 1989: The Child Right Convention, CRC 2004: General Comment 7 (GC: 7); Implementing child rights in early childhood General Comments: Are usually developed to address specific issues or overarching problems with CRC Are also meant to assist the States Parties with their analyses of the problems with respect to specific issues and improve reporting to CRC. There are 14 GCs to date in CRC
 Why a General Comment on Rights in Early Childhood? In response to the observation that children<8 were often overlooked in States Parties’ reporting Where discussed, references were limited to child mortality and …, neglecting the broad scope of child right The States Parties simply overlooked their obligations towards young children
Why a General Comment on Rights in Early Childhood? In response to the observation that children<8 were often overlooked in States Parties’ reporting Where discussed, references were limited to child mortality and …, neglecting the broad scope of child right The States Parties simply overlooked their obligations towards young children
 Why indicators? Why monitoring? Procedural rights vs Substantive rights
Why indicators? Why monitoring? Procedural rights vs Substantive rights
 Why indicators? Why monitoring? Procedural rights = immediate realization Substantive rights = ‘progressive realization’
Why indicators? Why monitoring? Procedural rights = immediate realization Substantive rights = ‘progressive realization’
 Why indicators? Why monitoring? UNCRC: GC 7 is mostly about substantive rights You can only tell if there is ‘progressive realization’ by monitoring over time. Monitoring can create a bridge between population health and human rights.
Why indicators? Why monitoring? UNCRC: GC 7 is mostly about substantive rights You can only tell if there is ‘progressive realization’ by monitoring over time. Monitoring can create a bridge between population health and human rights.
 UN-CRC GC-7 Indicators • 2005: group approached CRC, arguing that GC: 7 is impractical and underused………. . need user-friendly and useful GC: 7 indicators • 2006: UN-CRC invites us to develop indicators • 2006 -2008: indicators of GC: 7 were completed • May 2008: GC: 7 indicators were presented to CRC
UN-CRC GC-7 Indicators • 2005: group approached CRC, arguing that GC: 7 is impractical and underused………. . need user-friendly and useful GC: 7 indicators • 2006: UN-CRC invites us to develop indicators • 2006 -2008: indicators of GC: 7 were completed • May 2008: GC: 7 indicators were presented to CRC
 UN-CRC GC: 7 Indicators were meant to: • Assist States Parties with preparation of their report to UN-CRC • Monitor the progressive realization of rights in early childhood
UN-CRC GC: 7 Indicators were meant to: • Assist States Parties with preparation of their report to UN-CRC • Monitor the progressive realization of rights in early childhood
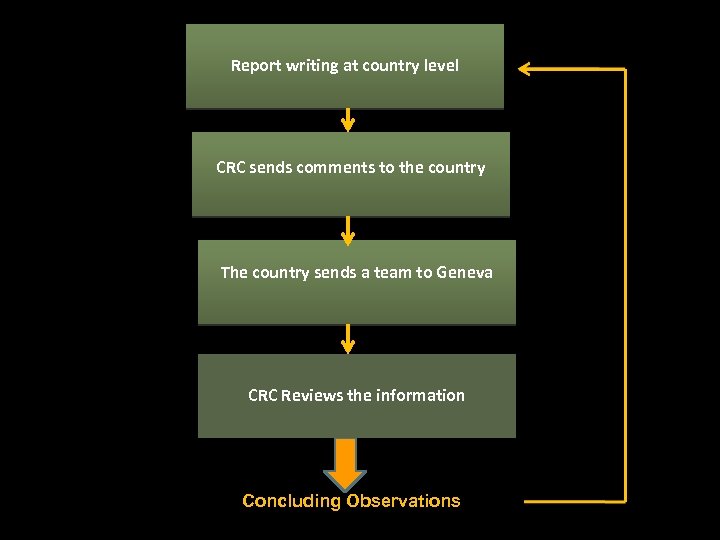 Report writing at country level CRC sends comments to the country The country sends a team to Geneva CRC Reviews the information Concluding Observations
Report writing at country level CRC sends comments to the country The country sends a team to Geneva CRC Reviews the information Concluding Observations
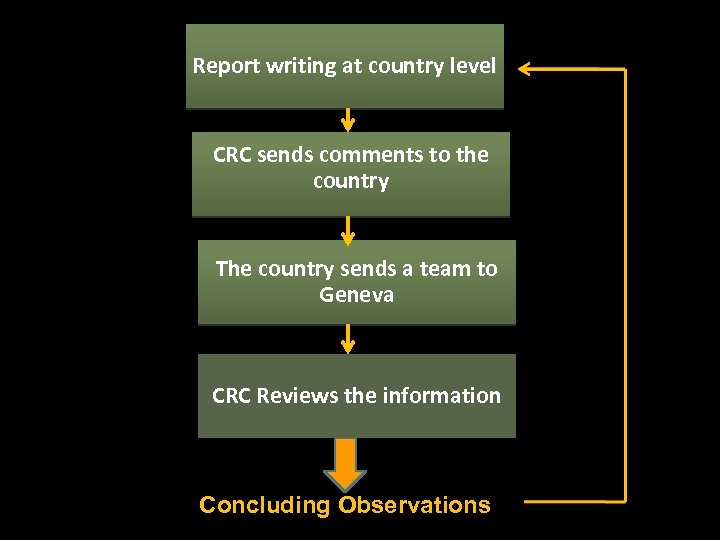 Report writing at country level CRC sends comments to the country The country sends a team to Geneva CRC Reviews the information Concluding Observations
Report writing at country level CRC sends comments to the country The country sends a team to Geneva CRC Reviews the information Concluding Observations
 We created 15 Indicator Clusters matching CRC reporting guidelines • General Measures of Implementation (4) 1. Dissemination of GC 7 • Civil rights and implementing the positive agenda 2. Constructing freedoms (1) Birth registration 3. Human Rights training • Family environment and alternative care (2) 4. Data collection system 1. Participation in household decision making 2. Violence against welfare (3) • Basic health and young children 1. Basic material needs 2. Child survival and • Education, leisurehealth cultural activities (4) 3. Age-appropriate health education 1. Early education service provision • Special protection measures vulnerable 2. Educational service provision for (1) Inclusive policy andright and capacity to support it 3. Knowledge of provisions for vulnerable groups 4. Play, leisure and rest opportunitites
We created 15 Indicator Clusters matching CRC reporting guidelines • General Measures of Implementation (4) 1. Dissemination of GC 7 • Civil rights and implementing the positive agenda 2. Constructing freedoms (1) Birth registration 3. Human Rights training • Family environment and alternative care (2) 4. Data collection system 1. Participation in household decision making 2. Violence against welfare (3) • Basic health and young children 1. Basic material needs 2. Child survival and • Education, leisurehealth cultural activities (4) 3. Age-appropriate health education 1. Early education service provision • Special protection measures vulnerable 2. Educational service provision for (1) Inclusive policy andright and capacity to support it 3. Knowledge of provisions for vulnerable groups 4. Play, leisure and rest opportunitites
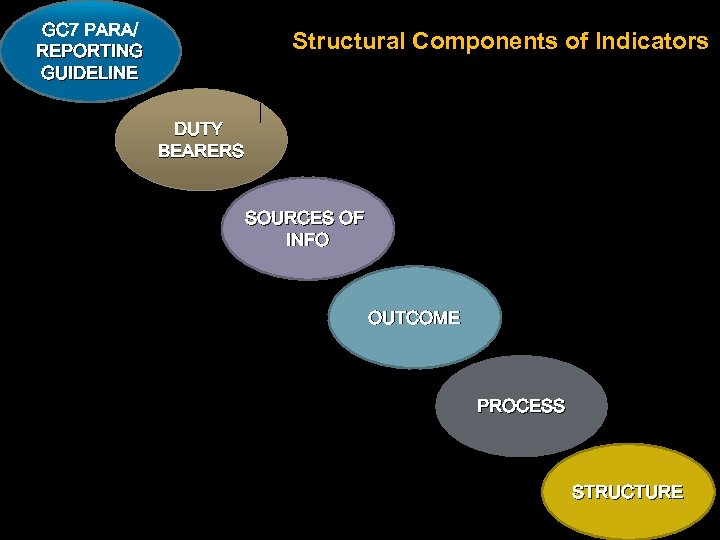 GC 7 PARA/ REPORTING GUIDELINE Structural Components of Indicators DUTY BEARERS SOURCES OF INFO OUTCOME PROCESS STRUCTURE
GC 7 PARA/ REPORTING GUIDELINE Structural Components of Indicators DUTY BEARERS SOURCES OF INFO OUTCOME PROCESS STRUCTURE
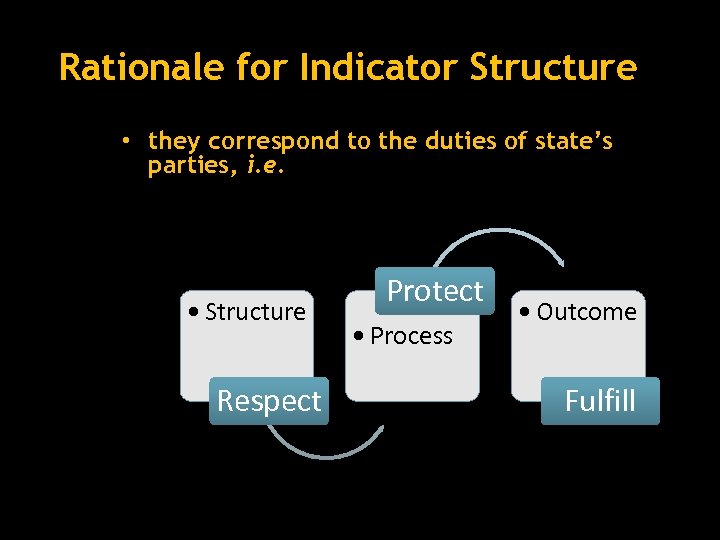 Rationale for Indicator Structure • they correspond to the duties of state’s parties, i. e. • Structure Respect Protect • Process • Outcome Fulfill
Rationale for Indicator Structure • they correspond to the duties of state’s parties, i. e. • Structure Respect Protect • Process • Outcome Fulfill
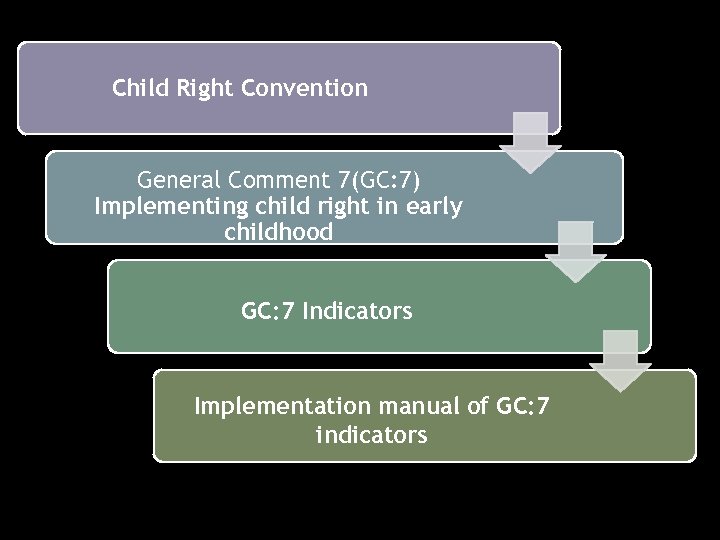 Child Right Convention General Comment 7(GC: 7) Implementing child right in early childhood GC: 7 Indicators Implementation manual of GC: 7 indicators
Child Right Convention General Comment 7(GC: 7) Implementing child right in early childhood GC: 7 Indicators Implementation manual of GC: 7 indicators
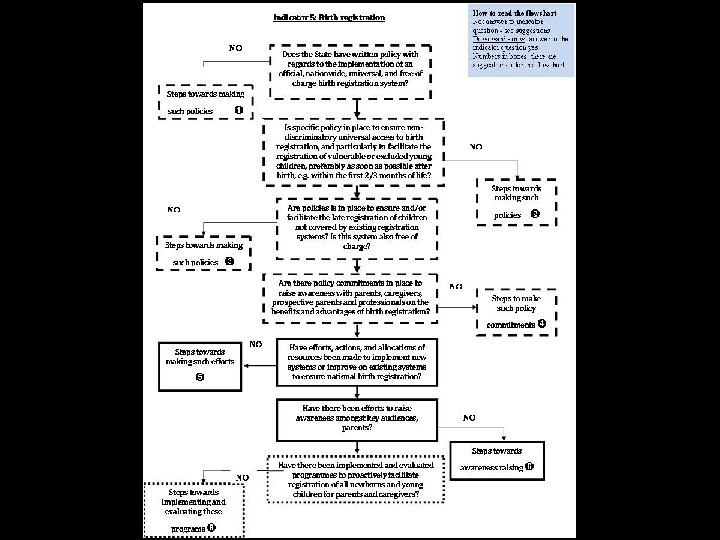
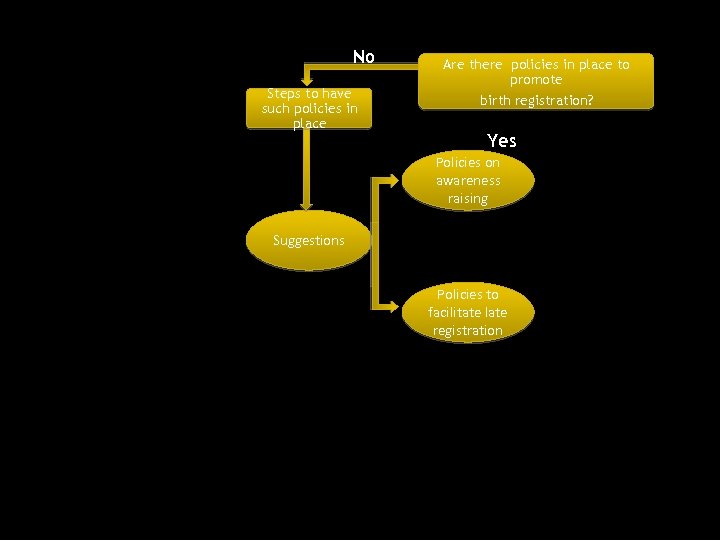 No Steps to have such policies in place Are there policies in place to promote birth registration? Yes Policies on awareness raising Suggestions Policies to facilitate late registration
No Steps to have such policies in place Are there policies in place to promote birth registration? Yes Policies on awareness raising Suggestions Policies to facilitate late registration
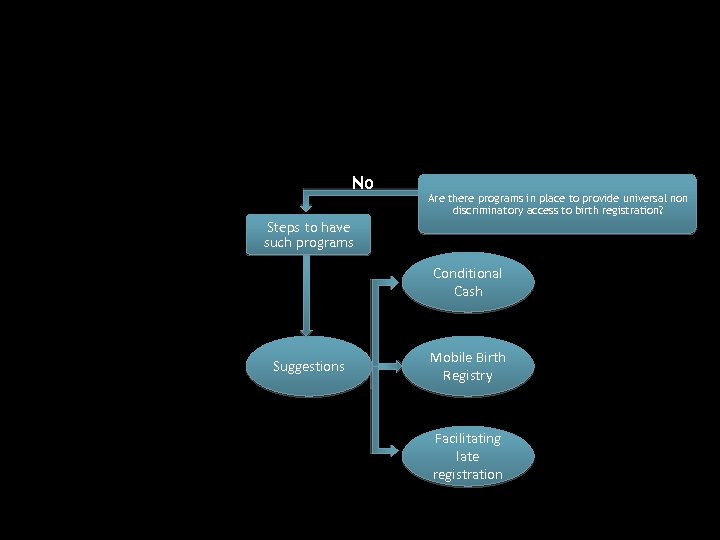 No Are there programs in place to provide universal non discriminatory access to birth registration? Steps to have such programs Conditional Cash Suggestions Mobile Birth Registry Facilitating late registration
No Are there programs in place to provide universal non discriminatory access to birth registration? Steps to have such programs Conditional Cash Suggestions Mobile Birth Registry Facilitating late registration
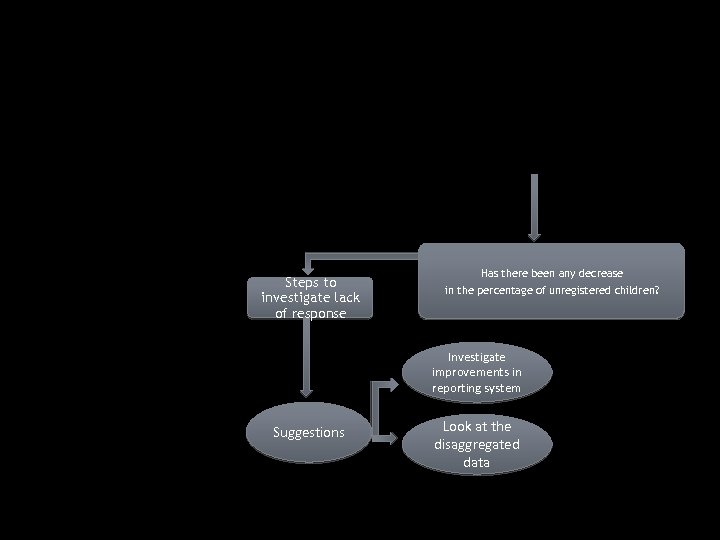 Steps to investigate lack of response Has there been any decrease in the percentage of unregistered children? Investigate improvements in reporting system Suggestions Look at the disaggregated data
Steps to investigate lack of response Has there been any decrease in the percentage of unregistered children? Investigate improvements in reporting system Suggestions Look at the disaggregated data
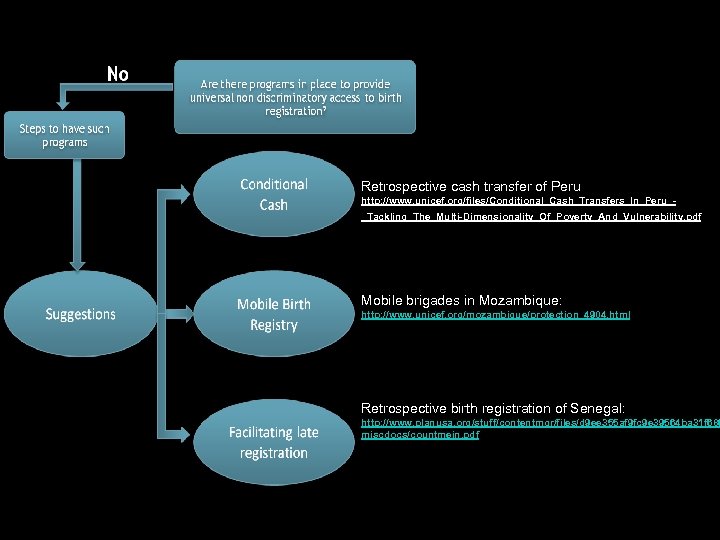 Retrospective cash transfer of Peru http: //www. unicef. org/files/Conditional_Cash_Transfers_In_Peru__Tackling_The_Multi-Dimensionality_Of_Poverty_And_Vulnerability. pdf Mobile brigades in Mozambique: http: //www. unicef. org/mozambique/protection_4904. html Retrospective birth registration of Senegal: http: //www. planusa. org/stuff/contentmgr/files/d 9 ee 355 af 9 fc 9 e 39564 ba 31 f 686 miscdocs/countmein. pdf
Retrospective cash transfer of Peru http: //www. unicef. org/files/Conditional_Cash_Transfers_In_Peru__Tackling_The_Multi-Dimensionality_Of_Poverty_And_Vulnerability. pdf Mobile brigades in Mozambique: http: //www. unicef. org/mozambique/protection_4904. html Retrospective birth registration of Senegal: http: //www. planusa. org/stuff/contentmgr/files/d 9 ee 355 af 9 fc 9 e 39564 ba 31 f 686 miscdocs/countmein. pdf
 Experience of Senegal
Experience of Senegal
 Sample flowchart: www. childrightsimpact. info/ecrim/flowchart 5
Sample flowchart: www. childrightsimpact. info/ecrim/flowchart 5
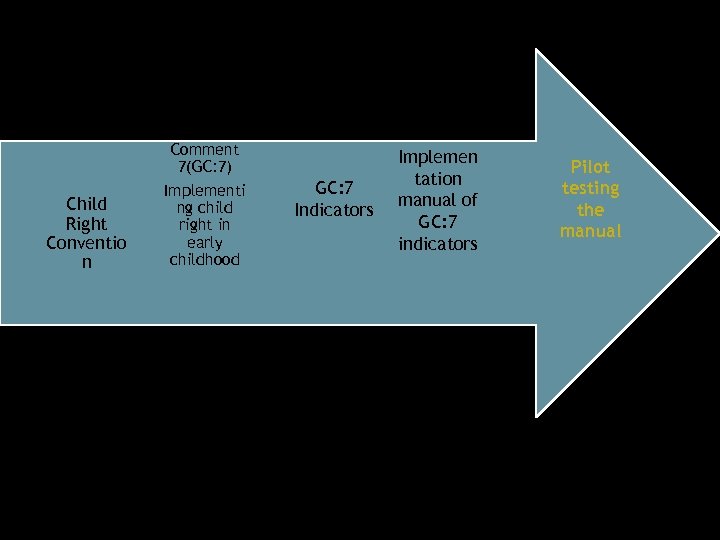 General Comment 7(GC: 7) Child Right Conventio n Implementi ng child right in early childhood GC: 7 Indicators Implemen tation manual of GC: 7 indicators Pilot testing the manual
General Comment 7(GC: 7) Child Right Conventio n Implementi ng child right in early childhood GC: 7 Indicators Implemen tation manual of GC: 7 indicators Pilot testing the manual
 Tanzania as a suitable pilot country • Has ratified CRC in 1991 • Suitable reporting timeline (next report due 2012) • National awareness to invest in ECD (Integrated ECD strategy, Child Act and…) • Number of on-going projects by international agencies to build up ECD capacity (CRED-PRO, EFA of WB…)
Tanzania as a suitable pilot country • Has ratified CRC in 1991 • Suitable reporting timeline (next report due 2012) • National awareness to invest in ECD (Integrated ECD strategy, Child Act and…) • Number of on-going projects by international agencies to build up ECD capacity (CRED-PRO, EFA of WB…)
 Objectives of the pilot • To test the relevance and feasibility of each indicator • To further refine the indicators and the flow charts • To understand whether or not the process serves as an effective means of report writing as well as a national, institutional self-study
Objectives of the pilot • To test the relevance and feasibility of each indicator • To further refine the indicators and the flow charts • To understand whether or not the process serves as an effective means of report writing as well as a national, institutional self-study
 What was our pilot testing strategy? • To achieve maximum government & civil society buy-in for the pilot. • To strengthen initiatives around the early childhood policies, training, services and rights.
What was our pilot testing strategy? • To achieve maximum government & civil society buy-in for the pilot. • To strengthen initiatives around the early childhood policies, training, services and rights.
 How did we structure the pilot?
How did we structure the pilot?
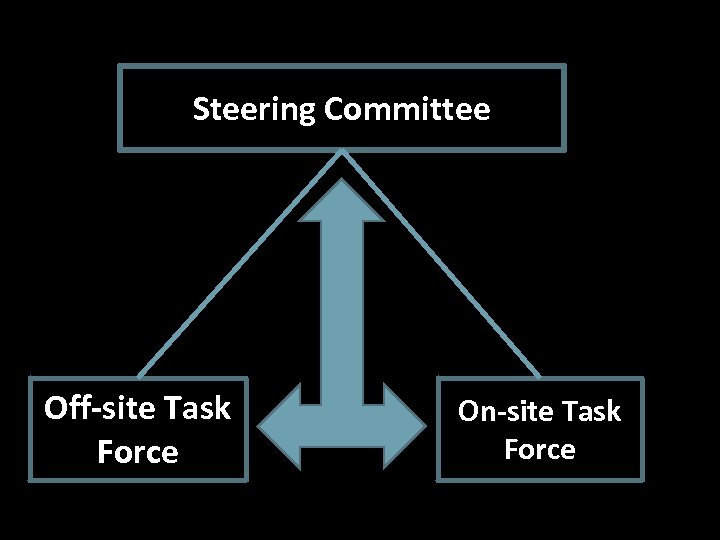 Steering Committee Off-site Task Force On-site Task Force
Steering Committee Off-site Task Force On-site Task Force
 Sequence of the events: • Feasibility assessment, February 2009 • Face-to-face meeting of the team to finalize the pilot country and plan the pilot, April 2009 • Identifying the stakeholders and bringing them around What should our pilot one table, September 2009 testing strategy be? • Establishing the project team in the country, Sept 2009 • Formation and training of the task force, Dec 2009 • Face validation of the flow charts, Jan, 2010
Sequence of the events: • Feasibility assessment, February 2009 • Face-to-face meeting of the team to finalize the pilot country and plan the pilot, April 2009 • Identifying the stakeholders and bringing them around What should our pilot one table, September 2009 testing strategy be? • Establishing the project team in the country, Sept 2009 • Formation and training of the task force, Dec 2009 • Face validation of the flow charts, Jan, 2010
 Sequence of the events…. • The pilot, January-May 2010 • Mid-term evaluation, March 2010 • Review of the What should our pilot testing strategy pilot data, May 2010 be? • Informing CRC on the outcome of the pilot, June 14 th 2010 • Informing the country on the outcome of the pilot and wrapping up the pilot, June 22 nd 2010
Sequence of the events…. • The pilot, January-May 2010 • Mid-term evaluation, March 2010 • Review of the What should our pilot testing strategy pilot data, May 2010 be? • Informing CRC on the outcome of the pilot, June 14 th 2010 • Informing the country on the outcome of the pilot and wrapping up the pilot, June 22 nd 2010
 Benefits for pilot country Awareness raising How many “No”s, how many “Yes”s in the system? Capacity building • How to turn “No’s to “Yes”s? Better reporting system How to use “Yes”s and “No”s to describe the status of child • rights in the country and communicate it to UN-CRC?
Benefits for pilot country Awareness raising How many “No”s, how many “Yes”s in the system? Capacity building • How to turn “No’s to “Yes”s? Better reporting system How to use “Yes”s and “No”s to describe the status of child • rights in the country and communicate it to UN-CRC?
 The Forward Plan • Revise Indicators and Manual in light of Tanzanian pilot • Identify 2 -3 middle and upper income countries for second stage implementation…Canada? ? • Complete second stage implementation in 2010/2011 • Present final Indicators and Manual to UN-CRC Monitoring Committee • Have Indicators promulgated for use in all 193 signatory countries
The Forward Plan • Revise Indicators and Manual in light of Tanzanian pilot • Identify 2 -3 middle and upper income countries for second stage implementation…Canada? ? • Complete second stage implementation in 2010/2011 • Present final Indicators and Manual to UN-CRC Monitoring Committee • Have Indicators promulgated for use in all 193 signatory countries
 For further info: visit the Global Knowledge Hub for ECD at : http: //www. earlylearning. ubc. ca/globalknowledgehub or contact -ziba. vaghri@ubc. ca
For further info: visit the Global Knowledge Hub for ECD at : http: //www. earlylearning. ubc. ca/globalknowledgehub or contact -ziba. vaghri@ubc. ca


