db66fa9fe9ea2bf9c12a0214ccc17c3c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 60

Using the Web to Maximize Your Regional Group's Effectiveness Prepared by Fleishman-Hillard December 9, 2009

Eight Common Questions about Web Sites 1. What is a Web site? 2. Why do I need a Web site? 3. What are the building blocks of a Web site? 4. Who builds Web sites? 5. How is a Web site created? 6. Who will host my Web site? 7. How do I grow my Web site? 8. How do I manage and maintain my Web site? 2

WHAT IS A WEB SITE? A website (also spelled web site) is a collection of related web pages, images, videos or other digital assets that are addressed with a common domain name or IP address in an Internet Protocol-based network. A web site is hosted on at least one web server, accessible via a network such as the Internet or a private local area network. 1 Source: Wikipedia, http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/Website 3

WHY DO I NEED A WEB SITE? 4

WEB SITE ATTRACT ENGAGE SPEAK LISTEN TRANSACT IT’S ALL ABOUT YOUR USERS 5

WHAT ARE THE BUILDING BLOCKS OF A WEB SITE? 6
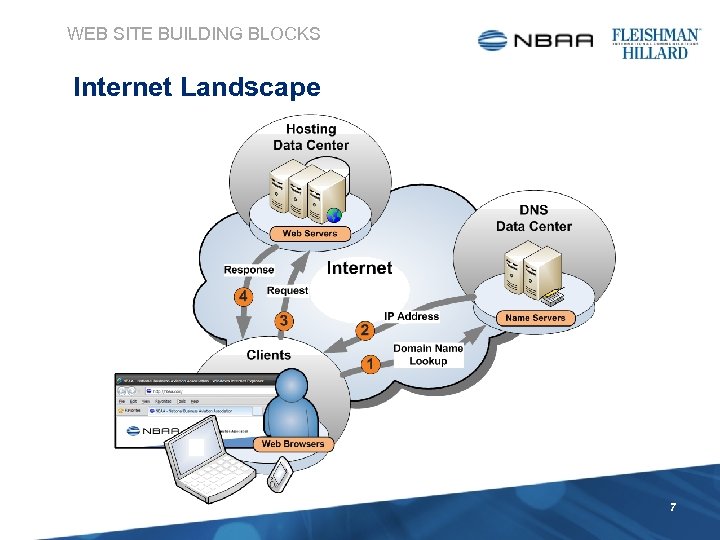
WEB SITE BUILDING BLOCKS Internet Landscape 7
WEB SITE BUILDING BLOCKS Domain Name Registration Providers Include • Network Solutions, http: //www. networksolutions. com • Go Daddy, http: //www. godaddy. com • Hundreds of others available 8
WEB SITE BUILDING BLOCKS WHOIS Lookup Providers Include • Network Solutions, http: //www. networksolutions. com/whois • Who Is, http: //www. whois. net/ 9

WEB SITE BUILDING BLOCKS Content Video Audio Text CONTENT IS KING if you don’t have good content, you don’t have a good Web site 10
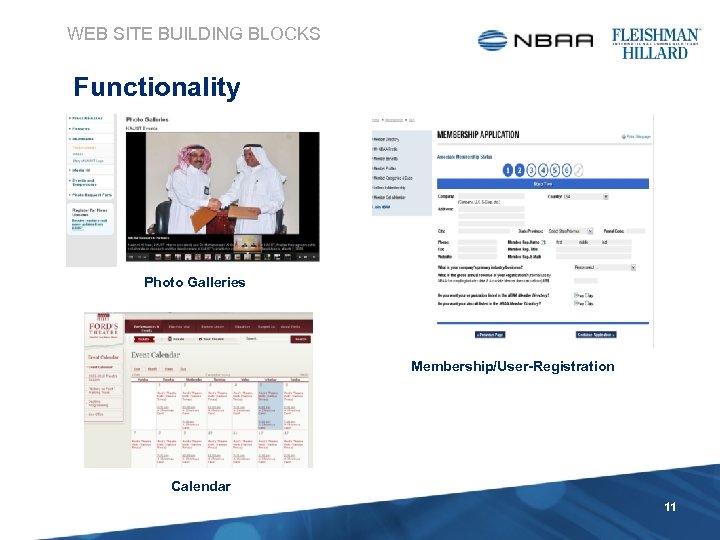
WEB SITE BUILDING BLOCKS Functionality Photo Galleries Membership/User-Registration Calendar 11

WEB SITE BUILDING BLOCKS Functionality Search Functionality E-commerce Transaction 12

WHO BUILDS WEB SITES? 13

WHO BUILDS WEBSITES • In-house Web Team • Full-time staff or contractors • Agencies • YOU USUALLY GET WHAT YOU PAY FOR a. k. a. , Web Development, Web Design, Digital Development, Digital Media Agencies • Freelancers • One or more part-time independent contractor(s) • “Site-in-a-box” • • • www. webs. com sites. google. com www. networksolutions. com/business-solutions 14
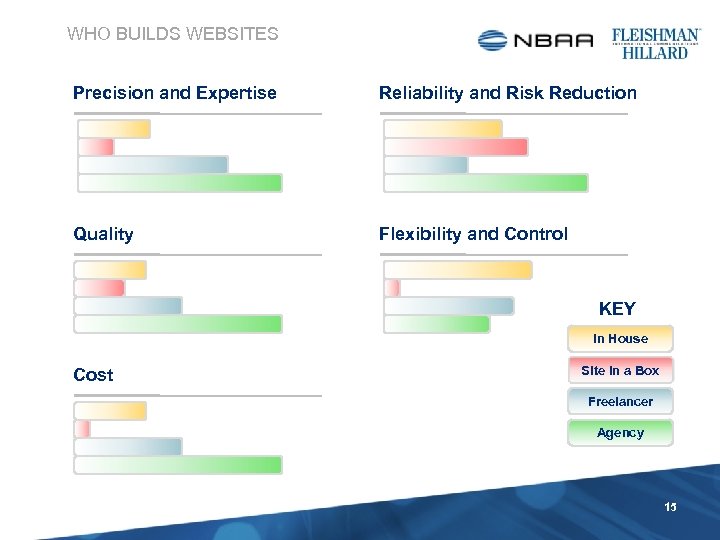
WHO BUILDS WEBSITES Precision and Expertise Reliability and Risk Reduction Quality Flexibility and Control KEY In House Cost Site in a Box Freelancer Agency 15

HOW IS A WEB SITE CREATED? 16
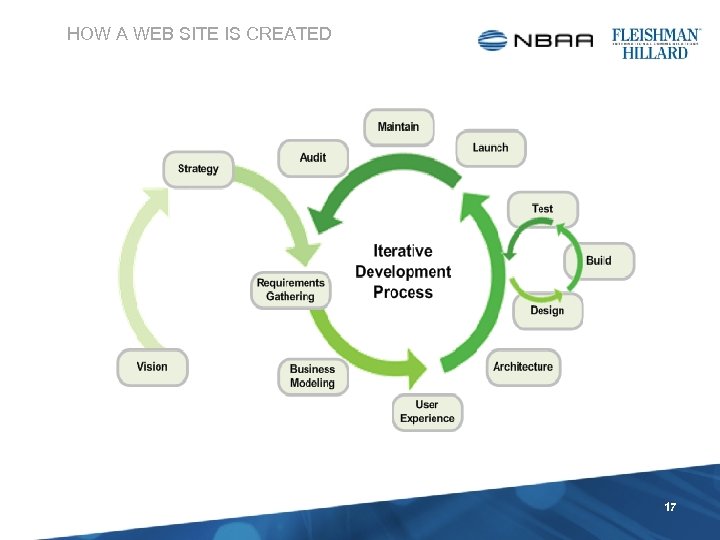
HOW A WEB SITE IS CREATED 17
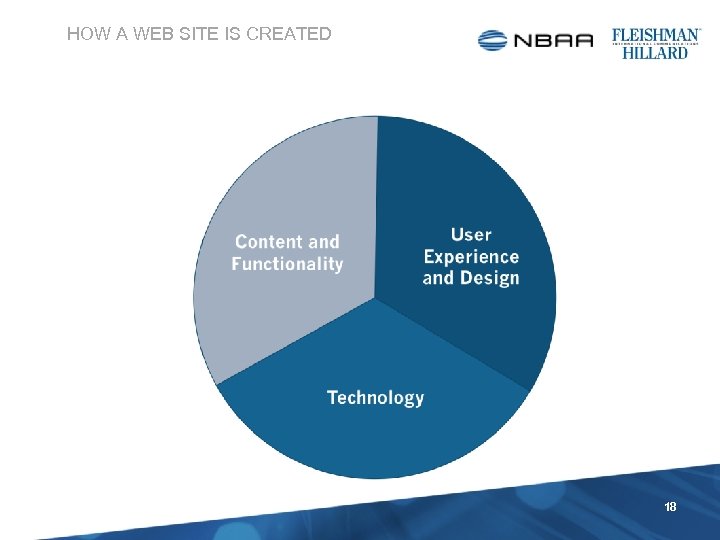
HOW A WEB SITE IS CREATED 18

HOW A WEB SITE IS CREATED: User Experience: Scalable for any project 19

HOW A WEB SITE IS CREATED: User Experience Persona Example: Investors 20

HOW A WEB SITE IS CREATED: User Experience Persona Example: The Investment Researcher 21
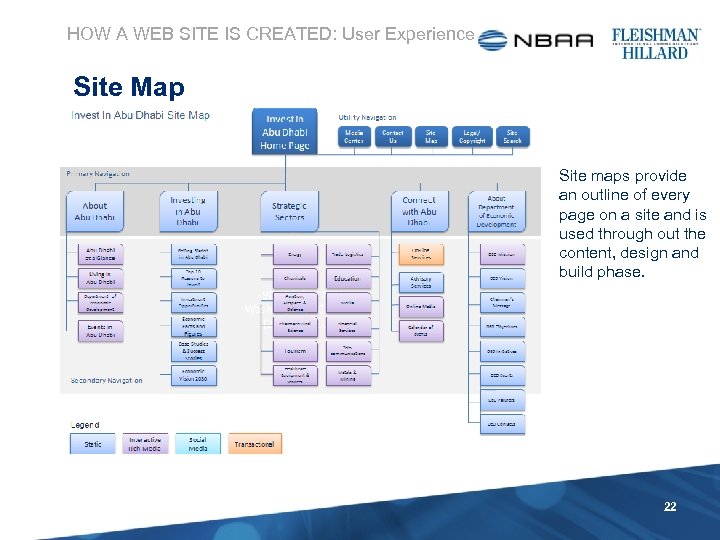
HOW A WEB SITE IS CREATED: User Experience Site Map Site maps provide an outline of every page on a site and is used through out the content, design and build phase. 22
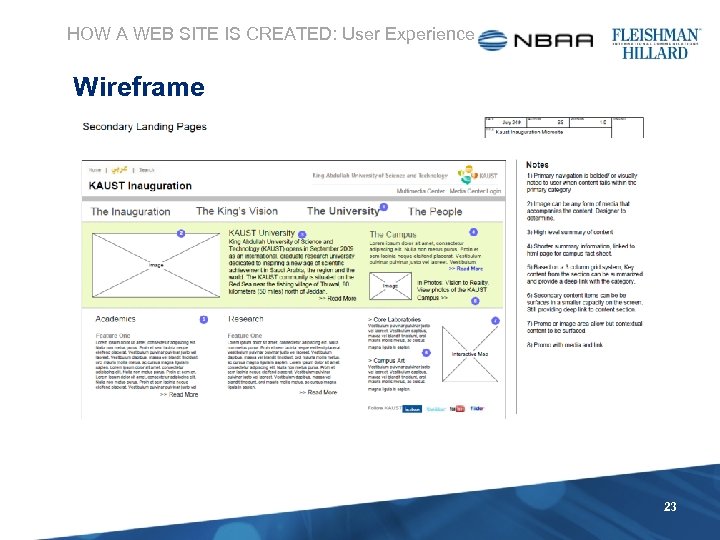
HOW A WEB SITE IS CREATED: User Experience Wireframe 23

HOW A WEB SITE IS CREATED: CONTENT Creating Content for the Web Attributes IMMEDIACY RELEVANCE UTILITY Value Creation Value can be created through delivering content in an “ondemand” format. Users can get what they want, when they want it. Value can be created through contextual relevance. Users come to a site for one purpose, but are served with additional targeted, relevant content. Value can also be created through providing a service or information that users are in need of, but cannot find elsewhere. Content provider becomes an facilitator resource instrument entertainer Results APPEAL Value can also be created through enjoyment or entertainment, resulting in an enriched and positive user experience. 24

HOW A WEB SITE IS CREATED: CONTENT • People don’t read the Web, they scan • To keep your audience’s attention you must: • • • Keep content relevant and fresh Keep it short Use bullets, short paragraphs and simple sentences Uses photos, video and multi-media Use links to cross-promote other content Use SEO 25

HOW A WEB SITE IS CREATED: CONTENT Short Paragraphs Bullets Imagery Cross Promotion 26
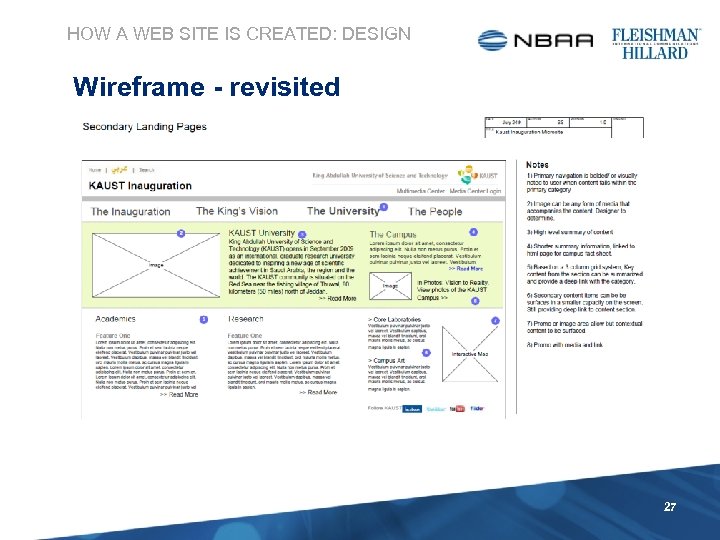
HOW A WEB SITE IS CREATED: DESIGN Wireframe - revisited 27
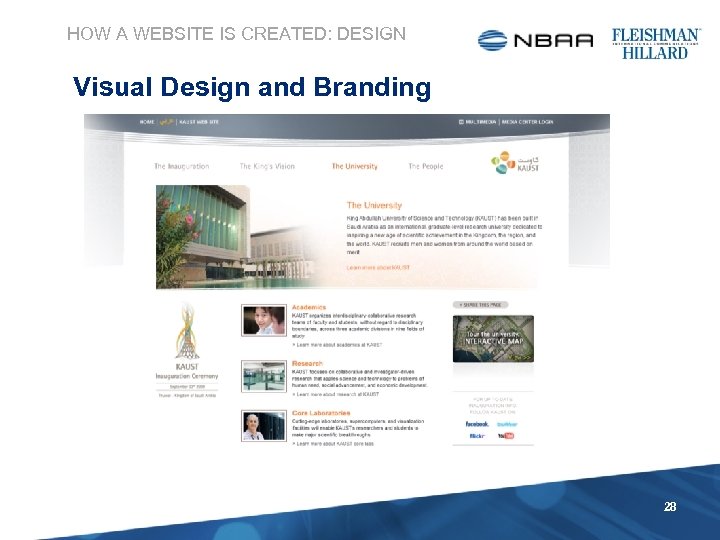
HOW A WEBSITE IS CREATED: DESIGN Visual Design and Branding 28

HOW A WEBSITE IS CREATED: DESIGN Visual Design and Branding Good Design and Branding consists of four steps 1. Defining and Researching your concept and Brand 2. Honing and Translating those findings into memorable and meaningful online experiences 3. Designing the online experience through a tried and tested series of steps and iterative process to get it right 4. Synthesizing the final product to ensure the site and message are ready for engagement. 29
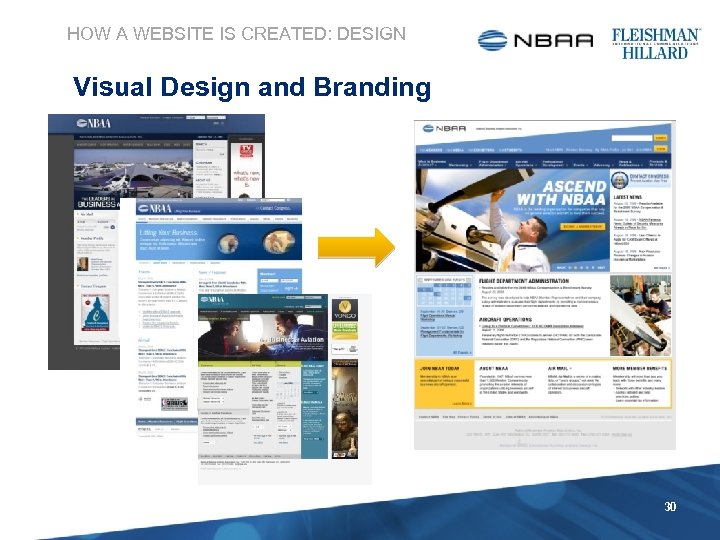
HOW A WEBSITE IS CREATED: DESIGN Visual Design and Branding 30
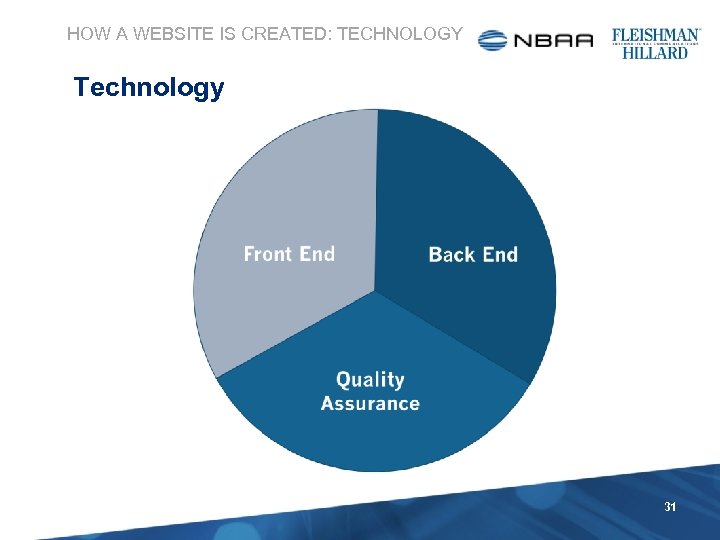
HOW A WEBSITE IS CREATED: TECHNOLOGY Technology 31
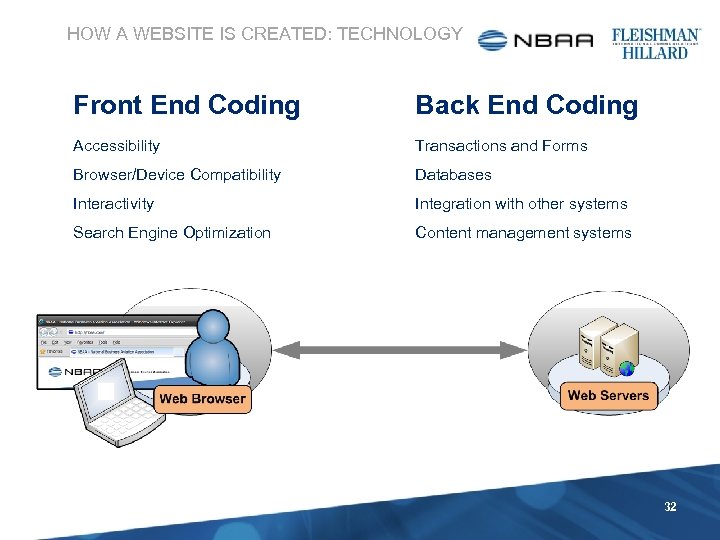
HOW A WEBSITE IS CREATED: TECHNOLOGY Front End Coding Back End Coding Accessibility Transactions and Forms Browser/Device Compatibility Databases Interactivity Integration with other systems Search Engine Optimization Content management systems 32

HOW A WEBSITE IS CREATED: TECHNOLOGY What is a Content Management System (CMS) A Web Content Management System (CMS or WCMS) is software, implemented as a Web application, for creating and managing HTML content. It is used to manage and control a large, dynamic collection of Web material (HTML documents and their associated images). A WCMS facilitates content creation, content control, editing, and essential Web maintenance functions. Source: Wikipedia, http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/Web_content_management_system 33

HOW A WEBSITE IS CREATED: TECHNOLOGY Why do I need a CMS? • Allow non-technical people to create new pages • Allow a large number contributors with controlled access • Reduce repetitive tasks and duplicative input • Support workflow and publishing • Maintain consistency • Separate content from presentation 34

HOW A WEBSITE IS CREATED: TECHNOLOGY CMS Examples CMS products range from little or no cost to high-end commercial solutions. Three Open Source CMS platforms with no license fee: • Drupal, http: //www. drupal. org • Wordpress, http: //www. wordpress. org • Joomla!, http: //www. joomla. org 35
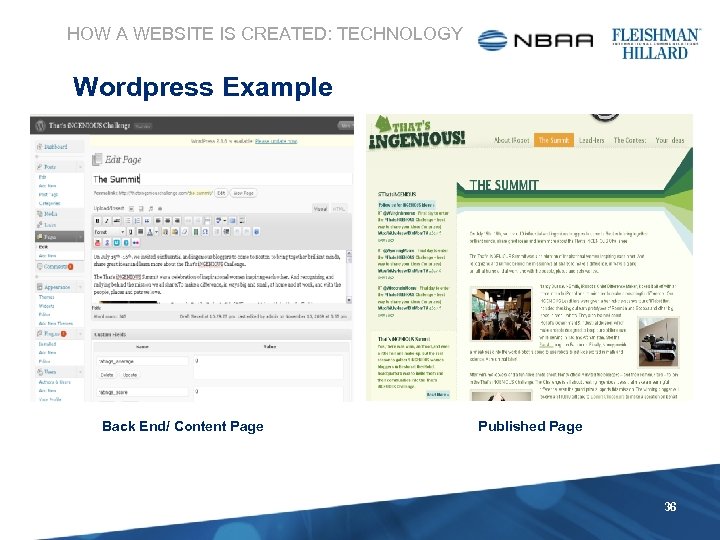
HOW A WEBSITE IS CREATED: TECHNOLOGY Wordpress Example Back End/ Content Page Published Page 36
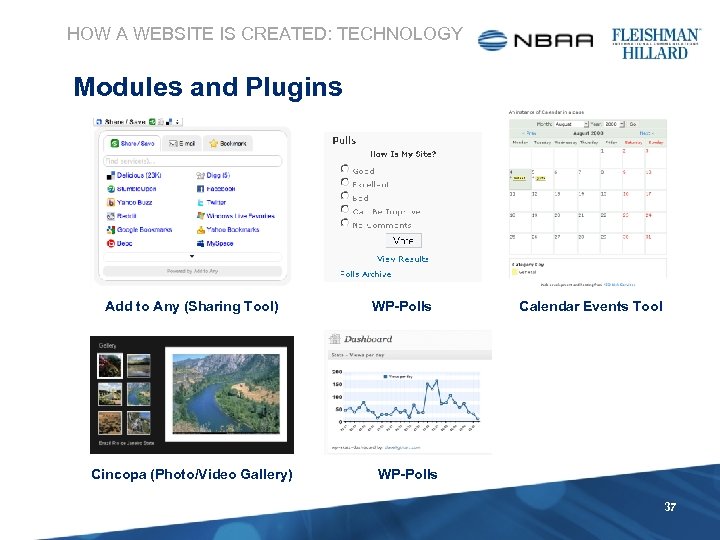
HOW A WEBSITE IS CREATED: TECHNOLOGY Modules and Plugins Add to Any (Sharing Tool) Cincopa (Photo/Video Gallery) WP-Polls Calendar Events Tool WP-Polls 37

WHO WILL HOST MY WEB SITE? 38

WHO HOSTS A WEB SITE Levels of Service • In-house Data Center • Physical Hosting (Managed or Self-Managed) (examples: IBM, AT&T) • Shared or “Dedicated Virtual” Web Hosting Service (examples: Media Temple, Go Daddy, Dream. Host) • Free Web Hosting (examples: Webs. com, Google Sites, Geo. Cities, Wordpress. com) 39

WHO HOSTS A WEB SITE Media Temple http: //www. mediatemple. net • Good tech support • Easy upgrade path • Developer-friendly, full control 40

WHO HOSTS A WEB SITE Go Daddy http: //www. godaddy. com/hosting/wordpress-hosting. aspx • Pre-installed Wordpress • Low price 41
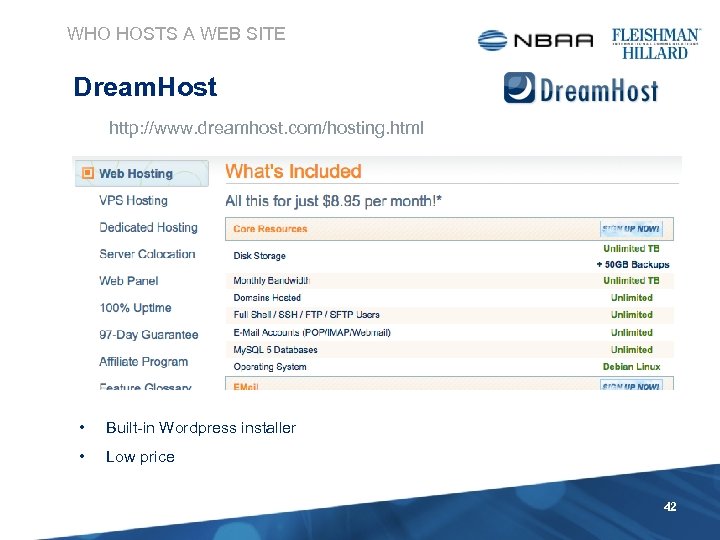
WHO HOSTS A WEB SITE Dream. Host http: //www. dreamhost. com/hosting. html • Built-in Wordpress installer • Low price 42

WHO HOSTS A WEB SITE Wordpress. com vs. Wordpress. org Wordpress. com provides hosting and management of Wordpress software, which can be downloaded from Wordpress. org and installed on your own server BENEFITS CONS Wordpress. com • Free, easy setup • Managed upgrades, backups, spam, security, etc. • Scales for traffic spikes • No custom themes • Limited plugins Wordpress. org • Custom themes • Access to all plugins • Complete control • Requires hosting plan • Self-managed upgrades, backups, spam, security Source: Wordpress. com 43

HOW DO I GROW MY WEB SITE? 44

GROWING A WEB SITE As important as building your Web site, is sharing and promoting it: • Google Analytics • Evaluating Your Web site based on metrics • Search engine optimization and marketing • Using language to attract missed opportunities • Link Building • Cross-promoting the site internally and externally 45

Google Analytics and Search Engine Marketing (SEM) 46

GROWING A WEB SITE Distributing Content and Conversation • Email programs • Social media • Widgets, Facebook, Twitter, You. Tube • Content Aggregation • RSS Feeds DON’T BUILD YOUR WEB SITE IN A SILO 47

Twitter and Facebook 48

HOW DO I MANAGE AND MAINTAIN MY WEB SITE? 49

MANAGING AND MAINTAING A WEB SITE • Assign an in-house Web Manager • Retain technical and design support • Keep your content fresh • Get to know your users • Pay attention to your Web analytics • Visit your own Web site every day! DON’T UNDERESTIMATE THE TOTAL COST OF OWNERSHIP 50

THINGS TO REMEMBER IT’S ALL ABOUT YOUR USERS YOU USUALLY GET WHAT YOU PAY FOR CONTENT IS KING DON’T BUILD YOUR WEB SITE IN A SILO DON’T UNDERESTIMATE THE TOTAL COST OF OWNERSHIP 51

QUESTIONS 52

GLOSSARY 53

GLOSSARY 3 x 3’s – Three different conceptual screen layouts that organize the information in varying ways that follow a simple task 3 layers deep. Aggregator – Software or a Web application that aggregates syndicated Web content such as news headlines, blogs or podcasts in a single location for easy viewing. Also feed reader, news reader. Application (social network) – A mini-program that leverages a social network’s platform to deliver customized experience and content. Content Optimization – The editing or altering of Internet content, including text, graphics and interactive assets, to improve a Web site’s usability and effectiveness. Also site language analysis, link strategy. Dedicated Virtual Hosting – A hosting service that partitions a server into multiple operating systems and resource units that are each dedicated to a single customer. 54

GLOSSARY Data Center – A facility where servers and computer components are housed (telecommunications, security devices, back-up power, etc. ). Also known as a server farm. Domain Name – An identification label that defines authority or control in the Internet (e. g. nbaa. org). A domain name is based on the Domain Name System (DNS). DNS – Domain Name System (DNS) is a hierarchical naming convention for computers, services, or any resource connected to the Internet or a private network. DNS makes it possible to assign domain names to groups of Internet users in a meaningful way, independent of each user's physical location. E-mail Marketing – A form of direct marketing that uses e-mail as a means of communicating with an audience. Can be used to deliver a message, promote a service or product or enhance relationships with the audience. HTML – The most popular front-end language for Web sites. Stands for Hyper. Text Markup Language. 55

GLOSSARY HTTP – Defines how Web servers and browsers should transmit messages on Web sites. Stands for Hyper. Text Transfer Protocol. Information Architecture – The blueprint that describes how information is organized and structured on a website. Mashup – A derivative work consisting of two pieces of media conjoined, such as a video clip with a different soundtrack applied for humorous effect, or a digital map overlaid with user-supplied data. Online Advertising – A Web-based equivalent of traditional advertising. Advertisers purchase Web site real estate, typically from online advertising networks, for the purpose of displaying brand messages. 56

GLOSSARY Open Source – Started as the notion of a free program with source code available to the general public for use and/ or modification; programmers improve upon the software code collaboratively and share changes with the community. Personas – Profiles of user types including key tasks, goals, pain points, search behaviors and activities. They help the team keep the intended consumer of the programs that we are creating in mind also to remind us that we are not the users. Podcast – Audio recording, hosted on a Web page and accessible for individual downloads by using “pull” technology, such as RSS feeds and MP 3 players. 57

GLOSSARY RSS – An acronym for Really Simple Syndication. Plug and play technology, typically called a “reader” which allows users to easily pull in (by way of subscription) select Web content such as a blog, Twitter feed, news, press releases, etc. Search Engine Optimization (SEO) – The act of editing or altering Web site content, including text, graphics, interactive assets, to improve a Web site’s natural visibility and rank or prominence in search engine results. Shared Web Hosting – A service or offering where multiple sites are hosted on one Web server. Social Media – An online tool and digital platform used to share opinions, insights, experiences and perspectives. Includes blogs, message boards, podcasts, social networking sites, and wiki sites. Tags – Keywords or phrases assigned to Web content, such as blog posts, wiki entries, photos, podcasts, etc. , to facilitate easy organization, called indexing and searching. 58

GLOSSARY URL – An address identifying a location of a page or site on the Internet. Stands for Uniform Resource Locator (example, http: //www. nbaa. org/folder/page. html) User experience – A term used to describe the overarching experience a person has as a result of his or her interactions with a particular product or service, its delivery and related artifacts, according to their design. Also UX, or UE. User Requirements – The “must haves” governing the project's deliverable or product as expressed or demonstrated by the users. Web 2. 0 – A term coined to loosely describe Web-based services such as wiki sites and social networks that emphasize online collaboration and content sharing among users. 59
GLOSSARY Web Syndication – A form of syndication in which a section of a Web site is made available to other sites, often by information feeds. Subscribers receive a regularly scheduled summary of the most recently added news and posts. WHOIS – A query that is used for determining the registrant and contact information (where applicable) of domain names or IP addresses. Widget – A “mini-Web page” or piece of content that can be embedded in personal Web sites. Distribution usually includes tools that allow users to easily port or grab code to embed the widget across their own sites and social network profiles. Wireframes – Sketches of screens that help visualize the structure, function , organization, navigation and interaction. 60
db66fa9fe9ea2bf9c12a0214ccc17c3c.ppt