4b0c117b5285b7470173d8b0d1d4104f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 21
 USING THE METADATA IN STATISTICAL PROCESSING CYCLE – THE PRODUCTION TOOLS PERSPECTIVE Matjaž Jug, Pavle Kozjek, Tomaž Špeh Statistical Office of the Republic of Slovenia
USING THE METADATA IN STATISTICAL PROCESSING CYCLE – THE PRODUCTION TOOLS PERSPECTIVE Matjaž Jug, Pavle Kozjek, Tomaž Špeh Statistical Office of the Republic of Slovenia
 Overview n n n Current statistical production cycle in SORS Using the metadata in Blaise applications The role of metadata in automatic editing system in SAS Metadata connected with the data in Oracle data warehouse Lessons learnt Questions
Overview n n n Current statistical production cycle in SORS Using the metadata in Blaise applications The role of metadata in automatic editing system in SAS Metadata connected with the data in Oracle data warehouse Lessons learnt Questions
 Current statistical production cycle n n n Entry and micro editing (Blaise) Macro and statistical editing (SAS) Storing and analysis (Oracle) Dissemination (PC-Axis) Central metadata stores (Klasje & Metis)
Current statistical production cycle n n n Entry and micro editing (Blaise) Macro and statistical editing (SAS) Storing and analysis (Oracle) Dissemination (PC-Axis) Central metadata stores (Klasje & Metis)
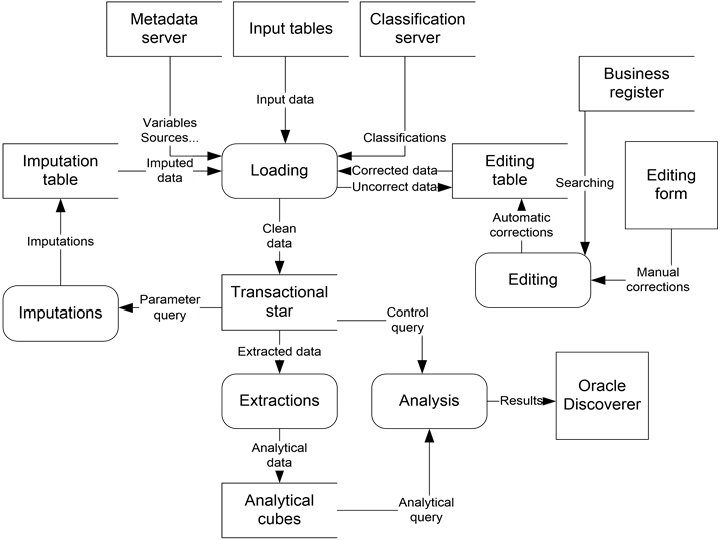
 Using the metadata in Blaise applications n n Generation of (high speed) data-entry applications using Gentry (using by non-IT personnel) Metadata-based transformations between different data structures (EXTRA-FAT, THIN)
Using the metadata in Blaise applications n n Generation of (high speed) data-entry applications using Gentry (using by non-IT personnel) Metadata-based transformations between different data structures (EXTRA-FAT, THIN)
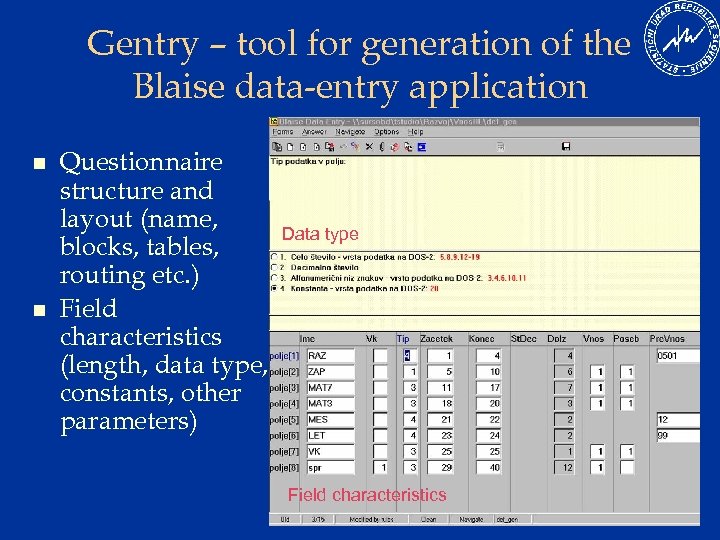 Gentry – tool for generation of the Blaise data-entry application n n Questionnaire structure and layout (name, blocks, tables, routing etc. ) Field characteristics (length, data type, constants, other parameters) Data type Field characteristics
Gentry – tool for generation of the Blaise data-entry application n n Questionnaire structure and layout (name, blocks, tables, routing etc. ) Field characteristics (length, data type, constants, other parameters) Data type Field characteristics
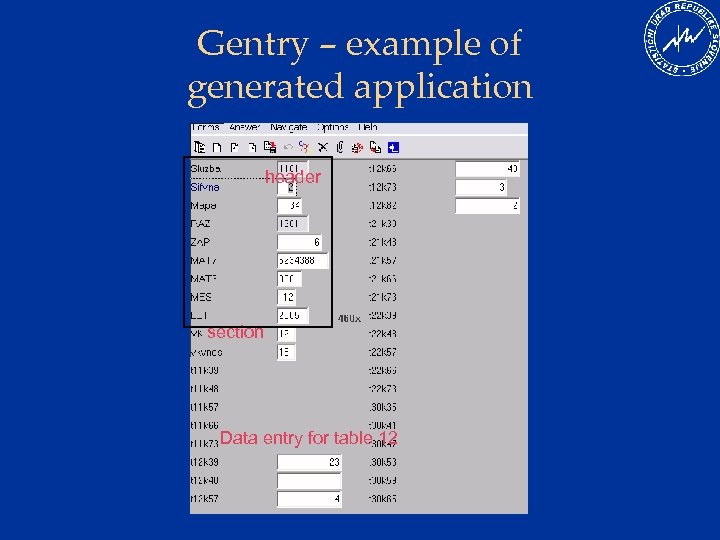 Gentry – example of generated application header section Data entry for table 12
Gentry – example of generated application header section Data entry for table 12
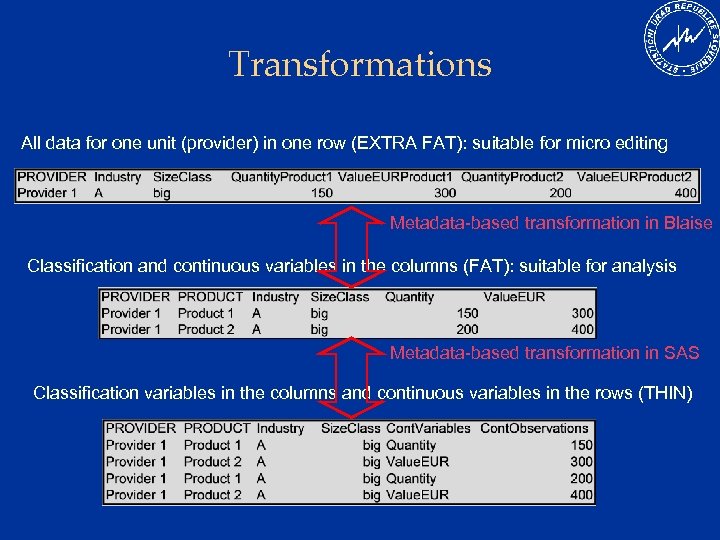 Transformations All data for one unit (provider) in one row (EXTRA FAT): suitable for micro editing Metadata-based transformation in Blaise Classification and continuous variables in the columns (FAT): suitable for analysis Metadata-based transformation in SAS Classification variables in the columns and continuous variables in the rows (THIN)
Transformations All data for one unit (provider) in one row (EXTRA FAT): suitable for micro editing Metadata-based transformation in Blaise Classification and continuous variables in the columns (FAT): suitable for analysis Metadata-based transformation in SAS Classification variables in the columns and continuous variables in the rows (THIN)
 The role of metadata in automatic editing system in SAS n n General system for automated editing Process metadata
The role of metadata in automatic editing system in SAS n n General system for automated editing Process metadata
 The role of metadata in automatic editing system in SAS n In order to be general the tool must be able to: - recognize the data which are due to be subjected to editing and/or imputation; recognize which editing method should be applied, and with what parameters
The role of metadata in automatic editing system in SAS n In order to be general the tool must be able to: - recognize the data which are due to be subjected to editing and/or imputation; recognize which editing method should be applied, and with what parameters
 Process indicators – level 1 n Mode of data collection - 1 data provided directly by reporting unit 2 data from administrative source 3 data computed from original values 4 imputed data – imputation of non-response 5 imputed data – imputation due to invalid values detected through the editing process 6 data missing because the unit is not eligible for the item (logical skip)
Process indicators – level 1 n Mode of data collection - 1 data provided directly by reporting unit 2 data from administrative source 3 data computed from original values 4 imputed data – imputation of non-response 5 imputed data – imputation due to invalid values detected through the editing process 6 data missing because the unit is not eligible for the item (logical skip)
 Process indicators – level 2 n Data status - 1 original value 2 corrected value
Process indicators – level 2 n Data status - 1 original value 2 corrected value
 Process indicators – level 3 n Method of data correction - 11 correction after telephone contact 12 data reported at a later stage
Process indicators – level 3 n Method of data correction - 11 correction after telephone contact 12 data reported at a later stage
 Process indicators – level 3 n Reporting methods - 11 reporting by mail questionnaire 12 computer assisted telephone interview(CATI) 13 telephone interview without computer assistance 14 paper assisted personal interview (PAPI) 15 computer assisted personal interview (CAPI) 16 paper assisted self interviewing 17 computer assisted self interviewing 18 web reporting
Process indicators – level 3 n Reporting methods - 11 reporting by mail questionnaire 12 computer assisted telephone interview(CATI) 13 telephone interview without computer assistance 14 paper assisted personal interview (PAPI) 15 computer assisted personal interview (CAPI) 16 paper assisted self interviewing 17 computer assisted self interviewing 18 web reporting
 Process indicators – level 3 n Imputation methods - 10 method of zero values 11 logical imputation 12 historical data imputation 13 mean values imputation 14 nearest neighbour imputation 15 hot-deck imputation 16 cold-deck imputation 17 regression imputation 18 method of the most frequent value 19 estimation of anual value based on infraanual data 21 stochastic hot-deck (random donor) 22 regression imputation with random residuals 23 multiple imputation
Process indicators – level 3 n Imputation methods - 10 method of zero values 11 logical imputation 12 historical data imputation 13 mean values imputation 14 nearest neighbour imputation 15 hot-deck imputation 16 cold-deck imputation 17 regression imputation 18 method of the most frequent value 19 estimation of anual value based on infraanual data 21 stochastic hot-deck (random donor) 22 regression imputation with random residuals 23 multiple imputation
 Process indicators examples - xy. zz n 11. 15 means: 1 - data provided directly by reporting unit 11 - original value 11. 15 - computer assisted personal interview (CAPI) n 42. 19 means: 4 - imputed data – imputation of nonresponse 42 - corrected value 42. 19 - estimation of anual value based on infraanual data
Process indicators examples - xy. zz n 11. 15 means: 1 - data provided directly by reporting unit 11 - original value 11. 15 - computer assisted personal interview (CAPI) n 42. 19 means: 4 - imputed data – imputation of nonresponse 42 - corrected value 42. 19 - estimation of anual value based on infraanual data
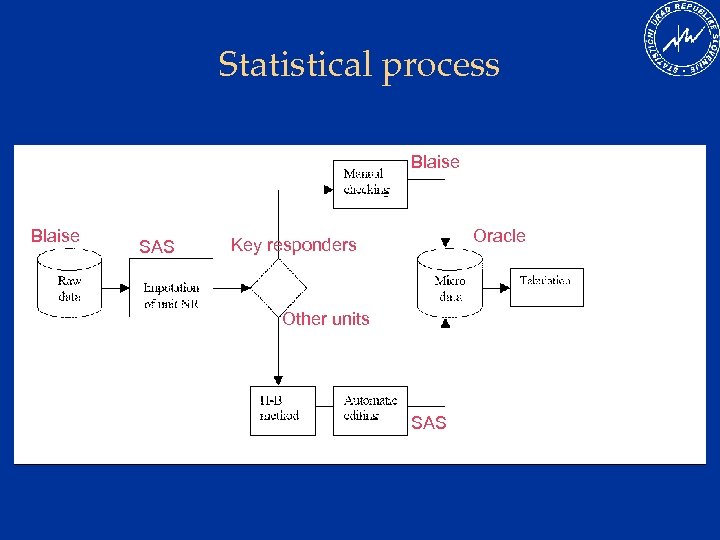 Statistical process Blaise SAS Oracle Key responders Other units SAS
Statistical process Blaise SAS Oracle Key responders Other units SAS
 Metadata connected with the data in Oracle data warehouse n On-line access to: - n Historical data Data from different phases (not only final data) Data for multiple surveys (not only data marts) Statistical (variables & classifications) and process (time stamps, status indicators. . . ) metadata connected with the data . . . accessible for third-party tools
Metadata connected with the data in Oracle data warehouse n On-line access to: - n Historical data Data from different phases (not only final data) Data for multiple surveys (not only data marts) Statistical (variables & classifications) and process (time stamps, status indicators. . . ) metadata connected with the data . . . accessible for third-party tools
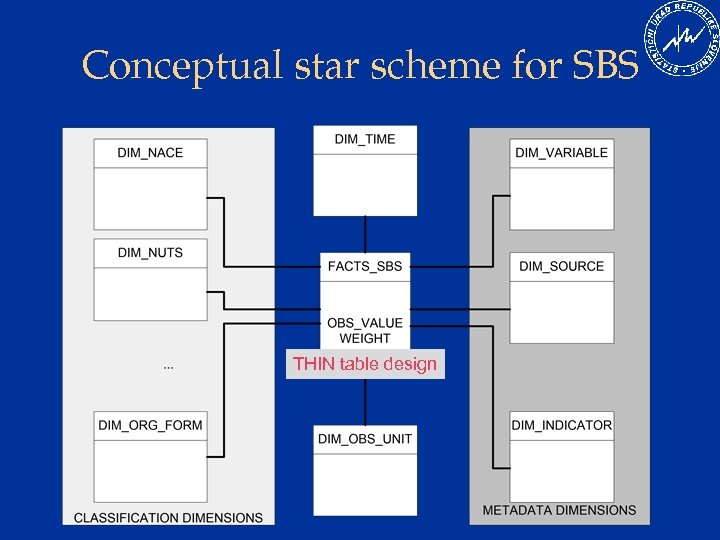 Conceptual star scheme for SBS THIN table design
Conceptual star scheme for SBS THIN table design
 Lessons learnt n The role of central repositories for metadata - n Harmonisation of metadata concepts - n Natural source of conceptual metadata Metadata have to be exact, complete and consistant Process metadata should be connected with the data Local metadata vs. global metadata The cultural change is needed Technical considerations - The possibilities for metadata exchange and system integration are good (XML, SQL)
Lessons learnt n The role of central repositories for metadata - n Harmonisation of metadata concepts - n Natural source of conceptual metadata Metadata have to be exact, complete and consistant Process metadata should be connected with the data Local metadata vs. global metadata The cultural change is needed Technical considerations - The possibilities for metadata exchange and system integration are good (XML, SQL)
 Questions
Questions


