269fd213cc07368720d18bd3829a2e7f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 32
 ® Using Systems Engineering Data Standards with Do. DAF Ian Bailey (Eurostep) Fatma Dandashi (Mitre Corp) Dwayne Hardy (American Systems Corp) David Price (Eurostep) All Presentation Material Copyright Eurostep Group AB
® Using Systems Engineering Data Standards with Do. DAF Ian Bailey (Eurostep) Fatma Dandashi (Mitre Corp) Dwayne Hardy (American Systems Corp) David Price (Eurostep) All Presentation Material Copyright Eurostep Group AB
 Disclaimers • Most of the following is from the co-authors of a white paper on this subject – – Ian Bailey, Eurostep Dwayne Hardy, American Systems Corp Fatma Dandashi and Huei-Wan Ang, Mitre and, based on a Dwayne Hardy quote, “Hundreds of like minded individuals who are contributing to the vision of model-driven SE championed by the INCOSE MDSD WG” – including your own Sandy Friedenthal and others ® All Presentation Material Copyright Eurostep Group AB
Disclaimers • Most of the following is from the co-authors of a white paper on this subject – – Ian Bailey, Eurostep Dwayne Hardy, American Systems Corp Fatma Dandashi and Huei-Wan Ang, Mitre and, based on a Dwayne Hardy quote, “Hundreds of like minded individuals who are contributing to the vision of model-driven SE championed by the INCOSE MDSD WG” – including your own Sandy Friedenthal and others ® All Presentation Material Copyright Eurostep Group AB
 Standards and SE data • Do. DAF - Do. D Architecture Framework – Defines standardized views of systems information • International Council on Systems Engineering (INCOSE) and Model-Driven System Design – Model-Driven SE Semantic Dictionary and Concept Model – Group work results in Sys. ML/AP 233 and alignment activity • Sys. ML - from Object Management Group – Provide a standard modelling language and notation for systems engineers • AP 233 Systems Engineering - ISO 10303 -233 – Defines a neutral information model for complex systems engineering structures ® All Presentation Material Copyright Eurostep Group AB
Standards and SE data • Do. DAF - Do. D Architecture Framework – Defines standardized views of systems information • International Council on Systems Engineering (INCOSE) and Model-Driven System Design – Model-Driven SE Semantic Dictionary and Concept Model – Group work results in Sys. ML/AP 233 and alignment activity • Sys. ML - from Object Management Group – Provide a standard modelling language and notation for systems engineers • AP 233 Systems Engineering - ISO 10303 -233 – Defines a neutral information model for complex systems engineering structures ® All Presentation Material Copyright Eurostep Group AB
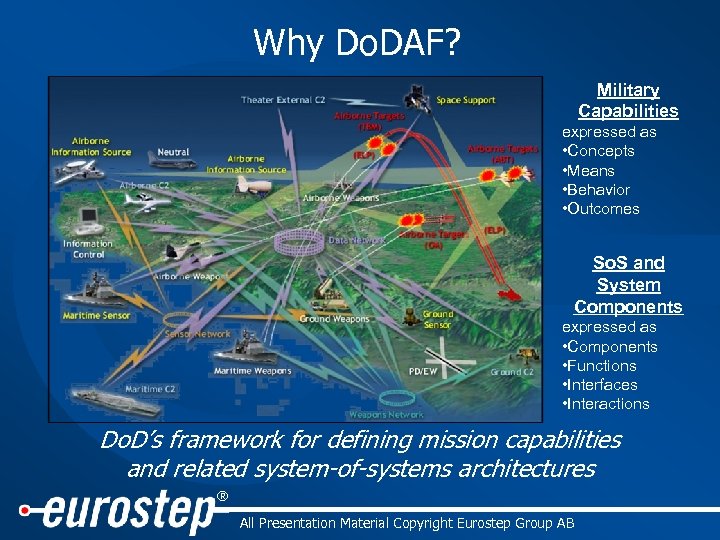 Why Do. DAF? Military Capabilities expressed as • Concepts • Means • Behavior • Outcomes So. S and System Components expressed as • Components • Functions • Interfaces • Interactions Do. D’s framework for defining mission capabilities and related system-of-systems architectures ® All Presentation Material Copyright Eurostep Group AB
Why Do. DAF? Military Capabilities expressed as • Concepts • Means • Behavior • Outcomes So. S and System Components expressed as • Components • Functions • Interfaces • Interactions Do. D’s framework for defining mission capabilities and related system-of-systems architectures ® All Presentation Material Copyright Eurostep Group AB
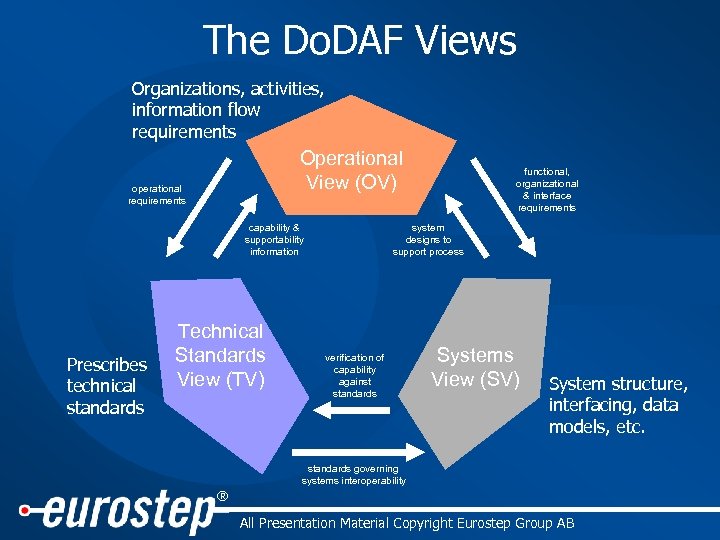 The Do. DAF Views Organizations, activities, information flow requirements Operational View (OV) operational requirements capability & supportability information Prescribes technical standards Technical Standards View (TV) functional, organizational & interface requirements system designs to support process verification of capability against standards Systems View (SV) System structure, interfacing, data models, etc. standards governing systems interoperability ® All Presentation Material Copyright Eurostep Group AB
The Do. DAF Views Organizations, activities, information flow requirements Operational View (OV) operational requirements capability & supportability information Prescribes technical standards Technical Standards View (TV) functional, organizational & interface requirements system designs to support process verification of capability against standards Systems View (SV) System structure, interfacing, data models, etc. standards governing systems interoperability ® All Presentation Material Copyright Eurostep Group AB
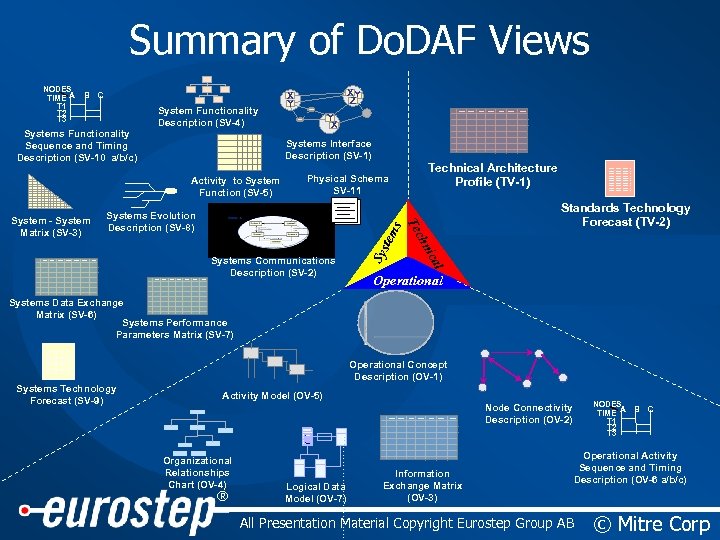 Summary of Do. DAF Views B C System Functionality Description (SV-4) Systems Functionality Sequence and Timing Description (SV-10 a/b/c) Y X Systems Interface Description (SV-1) Activity to System Function (SV-5) Physical Schema SV-11 s Systems Evolution Description (SV-8) Standards Technology Forecast (TV-2) l ica Systems Communications Description (SV-2) Technical Architecture Profile (TV-1) chn Te System - System Matrix (SV-3) XY Z X Y Sys tem NODES TIME A T 1 T 2 T 3 Operational Systems Data Exchange Matrix (SV-6) Systems Performance Parameters Matrix (SV-7) Operational Concept Description (OV-1) Systems Technology Forecast (SV-9) Activity Model (OV-5) NODES TIME A T 1 T 2 T 3 Node Connectivity Description (OV-2) • . . . Organizational Relationships Chart (OV-4) ® • - Logical Data Model (OV-7) Information Exchange Matrix (OV-3) B C Operational Activity Sequence and Timing Description (OV-6 a/b/c) All Presentation Material Copyright Eurostep Group AB © Mitre Corp
Summary of Do. DAF Views B C System Functionality Description (SV-4) Systems Functionality Sequence and Timing Description (SV-10 a/b/c) Y X Systems Interface Description (SV-1) Activity to System Function (SV-5) Physical Schema SV-11 s Systems Evolution Description (SV-8) Standards Technology Forecast (TV-2) l ica Systems Communications Description (SV-2) Technical Architecture Profile (TV-1) chn Te System - System Matrix (SV-3) XY Z X Y Sys tem NODES TIME A T 1 T 2 T 3 Operational Systems Data Exchange Matrix (SV-6) Systems Performance Parameters Matrix (SV-7) Operational Concept Description (OV-1) Systems Technology Forecast (SV-9) Activity Model (OV-5) NODES TIME A T 1 T 2 T 3 Node Connectivity Description (OV-2) • . . . Organizational Relationships Chart (OV-4) ® • - Logical Data Model (OV-7) Information Exchange Matrix (OV-3) B C Operational Activity Sequence and Timing Description (OV-6 a/b/c) All Presentation Material Copyright Eurostep Group AB © Mitre Corp
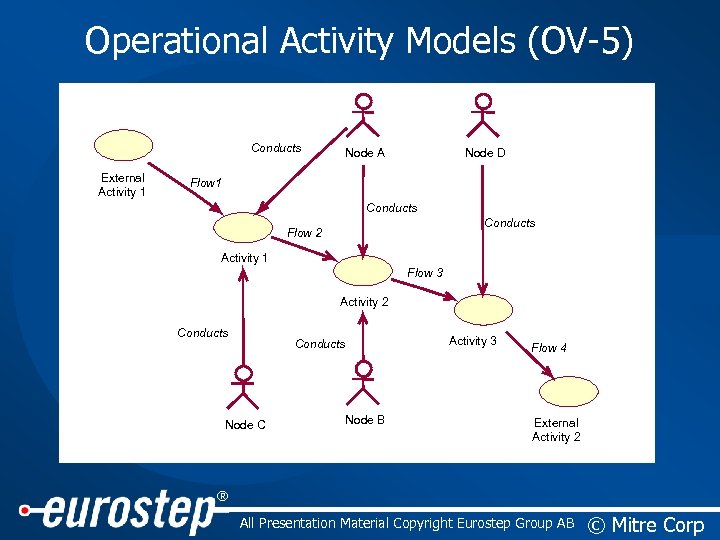 Operational Activity Models (OV-5) Conducts External Activity 1 Node A Node D Flow 1 Conducts Flow 2 Activity 1 Flow 3 Activity 2 Conducts Node C Node B Activity 3 Flow 4 External Activity 2 ® All Presentation Material Copyright Eurostep Group AB © Mitre Corp
Operational Activity Models (OV-5) Conducts External Activity 1 Node A Node D Flow 1 Conducts Flow 2 Activity 1 Flow 3 Activity 2 Conducts Node C Node B Activity 3 Flow 4 External Activity 2 ® All Presentation Material Copyright Eurostep Group AB © Mitre Corp
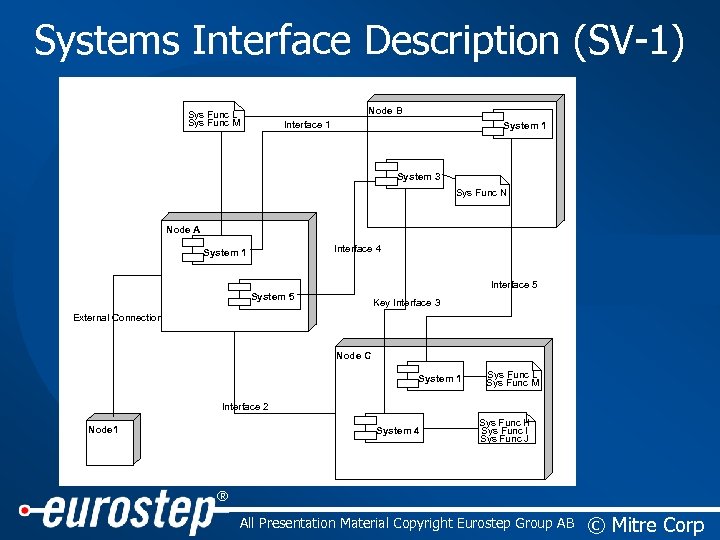 Systems Interface Description (SV-1) Node B Sys Func L Sys Func M Interface 1 System 3 Sys Func N Node A Interface 4 System 1 Interface 5 System 5 Key Interface 3 External Connection Node C System 1 Sys Func L Sys Func M Interface 2 Node 1 System 4 Sys Func H Sys Func I Sys Func J ® All Presentation Material Copyright Eurostep Group AB © Mitre Corp
Systems Interface Description (SV-1) Node B Sys Func L Sys Func M Interface 1 System 3 Sys Func N Node A Interface 4 System 1 Interface 5 System 5 Key Interface 3 External Connection Node C System 1 Sys Func L Sys Func M Interface 2 Node 1 System 4 Sys Func H Sys Func I Sys Func J ® All Presentation Material Copyright Eurostep Group AB © Mitre Corp
 Sys. ML • System Modeling Language being standardized in OMG – “a general-purpose systems modeling language” – “supports the specification, analysis, design, verification and validation of a broad range of complex systems” – “systems may include hardware, software, data, personnel, procedures, and facilities” • Based on UML 2. 0 with extensions (i. e. a UML Profile): – To define engineering semantics for existing UML concepts – To add requirements and parametric capabilities • AP 233 and Sys. ML based on the common Concept Model from INCOSE which defines their scope ® All Presentation Material Copyright Eurostep Group AB
Sys. ML • System Modeling Language being standardized in OMG – “a general-purpose systems modeling language” – “supports the specification, analysis, design, verification and validation of a broad range of complex systems” – “systems may include hardware, software, data, personnel, procedures, and facilities” • Based on UML 2. 0 with extensions (i. e. a UML Profile): – To define engineering semantics for existing UML concepts – To add requirements and parametric capabilities • AP 233 and Sys. ML based on the common Concept Model from INCOSE which defines their scope ® All Presentation Material Copyright Eurostep Group AB
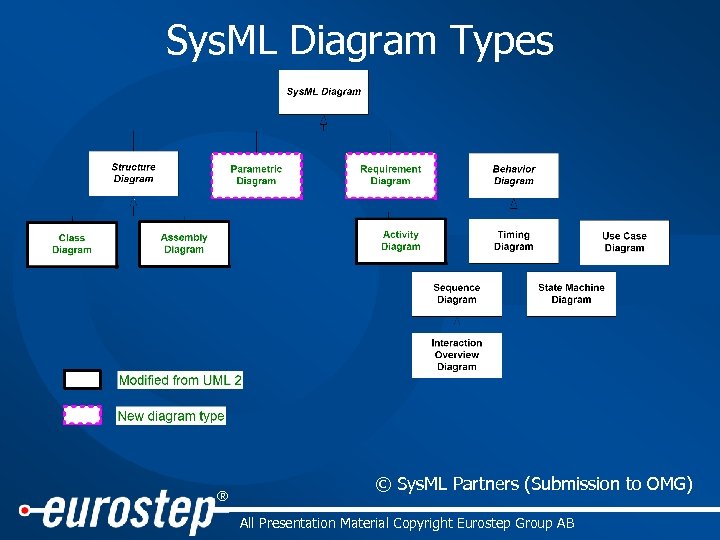 Sys. ML Diagram Types ® © Sys. ML Partners (Submission to OMG) All Presentation Material Copyright Eurostep Group AB
Sys. ML Diagram Types ® © Sys. ML Partners (Submission to OMG) All Presentation Material Copyright Eurostep Group AB
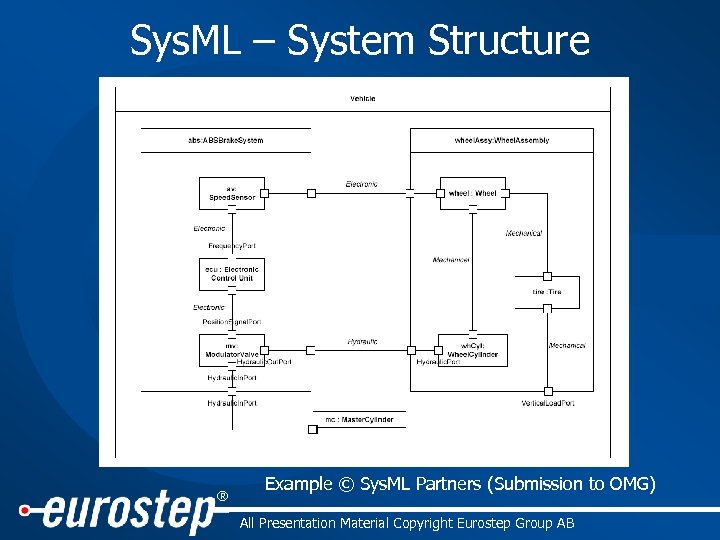 Sys. ML – System Structure ® Example © Sys. ML Partners (Submission to OMG) All Presentation Material Copyright Eurostep Group AB
Sys. ML – System Structure ® Example © Sys. ML Partners (Submission to OMG) All Presentation Material Copyright Eurostep Group AB
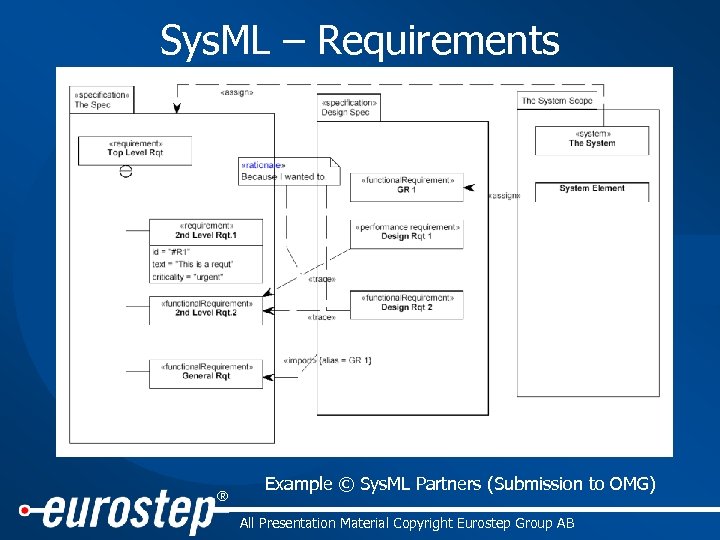 Sys. ML – Requirements ® Example © Sys. ML Partners (Submission to OMG) All Presentation Material Copyright Eurostep Group AB
Sys. ML – Requirements ® Example © Sys. ML Partners (Submission to OMG) All Presentation Material Copyright Eurostep Group AB
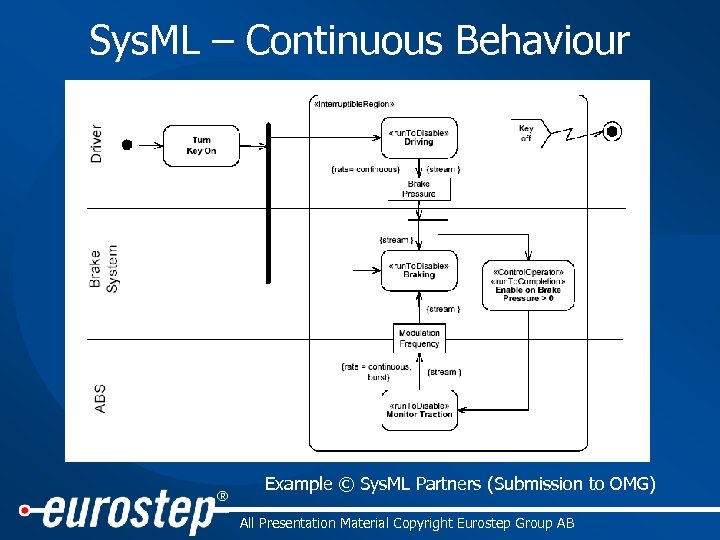 Sys. ML – Continuous Behaviour ® Example © Sys. ML Partners (Submission to OMG) All Presentation Material Copyright Eurostep Group AB
Sys. ML – Continuous Behaviour ® Example © Sys. ML Partners (Submission to OMG) All Presentation Material Copyright Eurostep Group AB
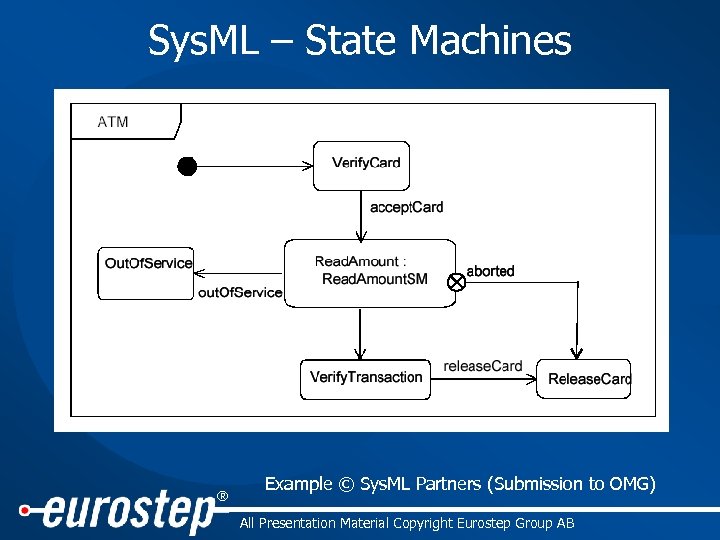 Sys. ML – State Machines ® Example © Sys. ML Partners (Submission to OMG) All Presentation Material Copyright Eurostep Group AB
Sys. ML – State Machines ® Example © Sys. ML Partners (Submission to OMG) All Presentation Material Copyright Eurostep Group AB
 AP 233 Systems Engineering • AP 233 is the Systems Engineering part of the new suite of ISO 10303 STEP Application Protocols built from modules – Shared constructs guarantee interoperability between disciplines such as Systems Engineering, Product Life Cycle Support and Configuration Controlled Design • Defines a formal, strict information model intended to prevent ambiguity when used for exchange between engineering systems • As part of STEP, AP 233 links to standards with a vast scope ® All Presentation Material Copyright Eurostep Group AB
AP 233 Systems Engineering • AP 233 is the Systems Engineering part of the new suite of ISO 10303 STEP Application Protocols built from modules – Shared constructs guarantee interoperability between disciplines such as Systems Engineering, Product Life Cycle Support and Configuration Controlled Design • Defines a formal, strict information model intended to prevent ambiguity when used for exchange between engineering systems • As part of STEP, AP 233 links to standards with a vast scope ® All Presentation Material Copyright Eurostep Group AB
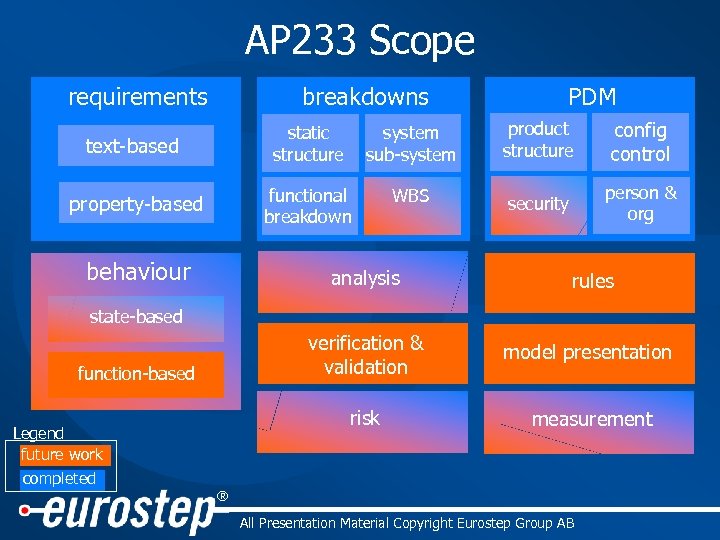 AP 233 Scope breakdowns requirements PDM text-based static structure system sub-system product structure config control property-based functional breakdown WBS security person & org behaviour analysis rules verification & validation model presentation risk measurement state-based function-based Legend future work completed ® All Presentation Material Copyright Eurostep Group AB
AP 233 Scope breakdowns requirements PDM text-based static structure system sub-system product structure config control property-based functional breakdown WBS security person & org behaviour analysis rules verification & validation model presentation risk measurement state-based function-based Legend future work completed ® All Presentation Material Copyright Eurostep Group AB
 How Does AP 233 Help? • Defines a reliable, automated way to move data between SE software tools – Eliminates the need for data re-entry • • Provides a system-independent format for archiving data Can be specified in a contract Unlocks data stored in uncompetitive systems Allows movement of data along the design process – e. g. requirements->systems->budgeting->design • Introduces functionality never before possible – All systems engineering data can be integrated together – Allows whole-system, whole-lifecycle design and analysis ® All Presentation Material Copyright Eurostep Group AB
How Does AP 233 Help? • Defines a reliable, automated way to move data between SE software tools – Eliminates the need for data re-entry • • Provides a system-independent format for archiving data Can be specified in a contract Unlocks data stored in uncompetitive systems Allows movement of data along the design process – e. g. requirements->systems->budgeting->design • Introduces functionality never before possible – All systems engineering data can be integrated together – Allows whole-system, whole-lifecycle design and analysis ® All Presentation Material Copyright Eurostep Group AB
 Using Them Together • One obvious scenario – Use Do. DAF to specify requirements for the different views of a system – Use Sys. ML to model the system – Use AP 233 to exchange data between Sys. ML, legacy SE tools and other Do. DAF views Sys. ML Do. DAF OV 2 SV 4 • • . . . OV 7 • . . . TV 2 AP 233 • - ® All Presentation Material Copyright Eurostep Group AB -
Using Them Together • One obvious scenario – Use Do. DAF to specify requirements for the different views of a system – Use Sys. ML to model the system – Use AP 233 to exchange data between Sys. ML, legacy SE tools and other Do. DAF views Sys. ML Do. DAF OV 2 SV 4 • • . . . OV 7 • . . . TV 2 AP 233 • - ® All Presentation Material Copyright Eurostep Group AB -
 How Well do They Fit ? • AP 233 and Sys. ML are being aligned by the development teams • Initial analysis indicates good coverage of the relevant Do. DAF views with Sys. ML • AP 233 aligned with Sys. ML scope but can also exchange the Do. DAF Technical Views – AP 233 is independent of modelling technique or representation and so can exchange data between non. Sys. ML tools also ® All Presentation Material Copyright Eurostep Group AB
How Well do They Fit ? • AP 233 and Sys. ML are being aligned by the development teams • Initial analysis indicates good coverage of the relevant Do. DAF views with Sys. ML • AP 233 aligned with Sys. ML scope but can also exchange the Do. DAF Technical Views – AP 233 is independent of modelling technique or representation and so can exchange data between non. Sys. ML tools also ® All Presentation Material Copyright Eurostep Group AB
 Proof-of-concept 1. AP 233 Demonstrator 2. Sys. ML Assembly/AP 233 project 3. Do. DAF CADM/AP 233 project ® All Presentation Material Copyright Eurostep Group AB
Proof-of-concept 1. AP 233 Demonstrator 2. Sys. ML Assembly/AP 233 project 3. Do. DAF CADM/AP 233 project ® All Presentation Material Copyright Eurostep Group AB
 1. AP 233 Demonstrator • Initial work sponsored by NASA JPL – further development sponsored by UK MOD and Eurostep • Intended to: – showcase AP 233 functionality – enable creation of test data and to test AP 233 functionality – provide target/source for vendor i/f implementations • Uses High Level API – native format is AP 233 STEP ASCII File – High Level API has also been used for DOORS, Cradle and Requisite Pro interfaces ® All Presentation Material Copyright Eurostep Group AB
1. AP 233 Demonstrator • Initial work sponsored by NASA JPL – further development sponsored by UK MOD and Eurostep • Intended to: – showcase AP 233 functionality – enable creation of test data and to test AP 233 functionality – provide target/source for vendor i/f implementations • Uses High Level API – native format is AP 233 STEP ASCII File – High Level API has also been used for DOORS, Cradle and Requisite Pro interfaces ® All Presentation Material Copyright Eurostep Group AB
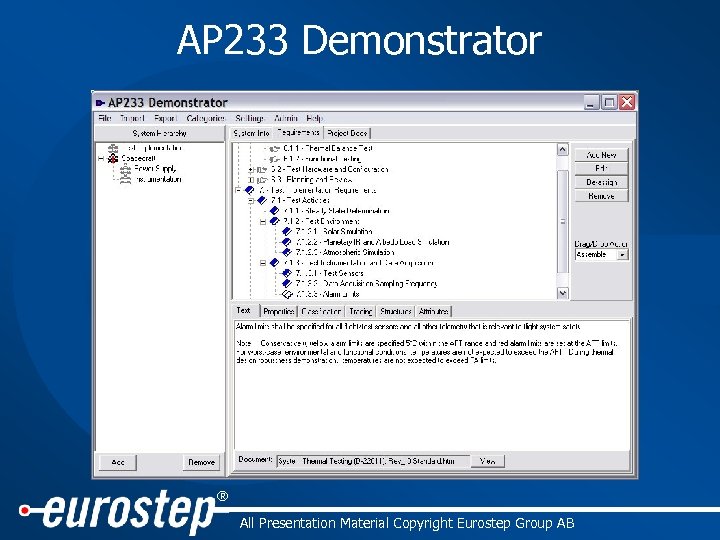 AP 233 Demonstrator ® All Presentation Material Copyright Eurostep Group AB
AP 233 Demonstrator ® All Presentation Material Copyright Eurostep Group AB
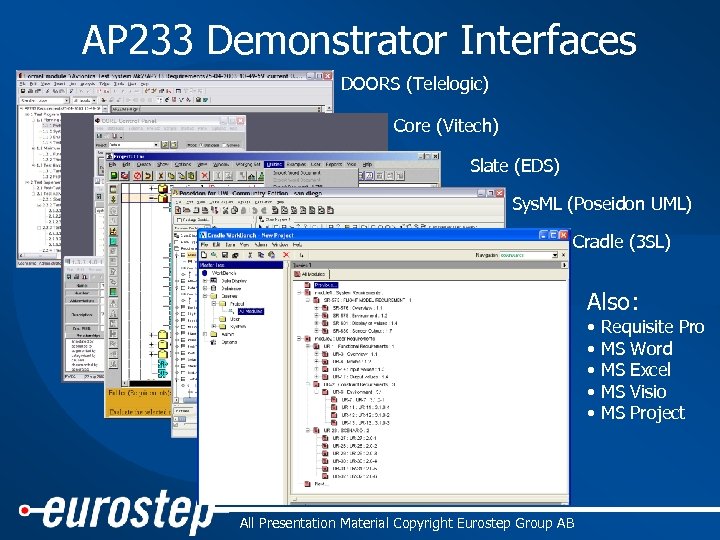 AP 233 Demonstrator Interfaces DOORS (Telelogic) Core (Vitech) Slate (EDS) Sys. ML (Poseidon UML) Cradle (3 SL) Also: • • • ® All Presentation Material Copyright Eurostep Group AB Requisite Pro MS Word MS Excel MS Visio MS Project
AP 233 Demonstrator Interfaces DOORS (Telelogic) Core (Vitech) Slate (EDS) Sys. ML (Poseidon UML) Cradle (3 SL) Also: • • • ® All Presentation Material Copyright Eurostep Group AB Requisite Pro MS Word MS Excel MS Visio MS Project
 2. Sys. ML Assembly/AP 233 project • For John Deere research – Sys. ML team member • Define a mapping from Sys. ML Assembly to STEP AP 233/Sys. Eng Structures • Implement mapping using an early UML 2/Sys. ML tool • Import resulting data into “AP 233 Demonstrator” to show what’s possible ® All Presentation Material Copyright Eurostep Group AB
2. Sys. ML Assembly/AP 233 project • For John Deere research – Sys. ML team member • Define a mapping from Sys. ML Assembly to STEP AP 233/Sys. Eng Structures • Implement mapping using an early UML 2/Sys. ML tool • Import resulting data into “AP 233 Demonstrator” to show what’s possible ® All Presentation Material Copyright Eurostep Group AB
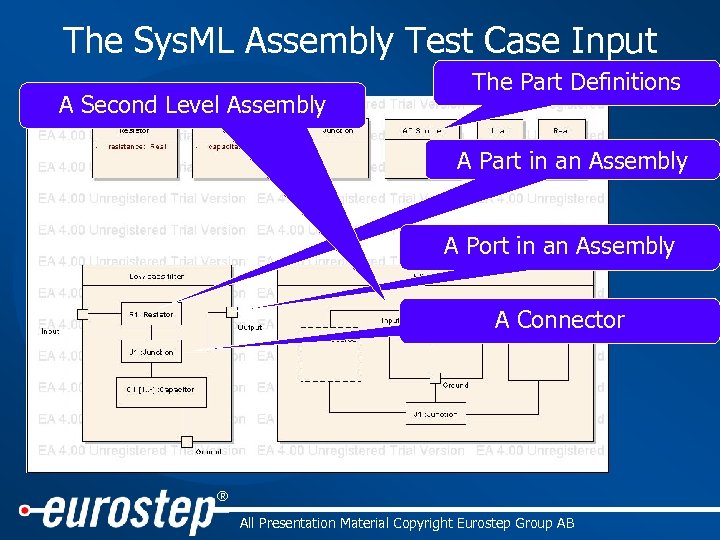 The Sys. ML Assembly Test Case Input A Second Level Assembly The Part Definitions A Part in an Assembly A Port in an Assembly A Connector ® All Presentation Material Copyright Eurostep Group AB
The Sys. ML Assembly Test Case Input A Second Level Assembly The Part Definitions A Part in an Assembly A Port in an Assembly A Connector ® All Presentation Material Copyright Eurostep Group AB
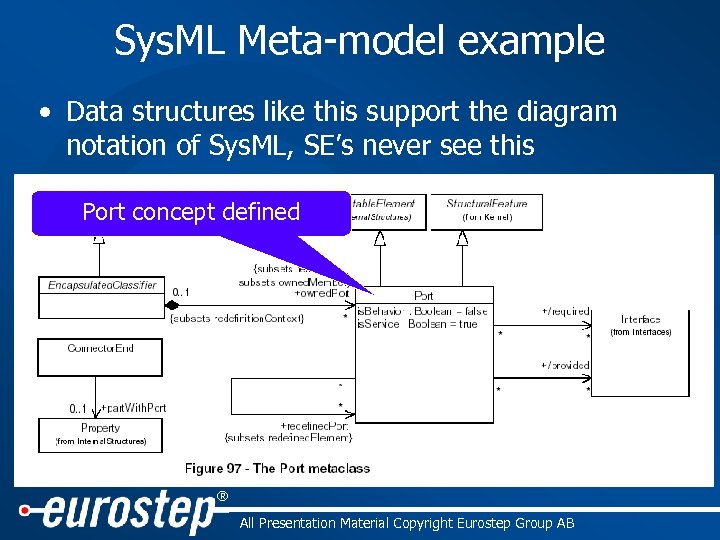 Sys. ML Meta-model example • Data structures like this support the diagram notation of Sys. ML, SE’s never see this Port concept defined ® All Presentation Material Copyright Eurostep Group AB
Sys. ML Meta-model example • Data structures like this support the diagram notation of Sys. ML, SE’s never see this Port concept defined ® All Presentation Material Copyright Eurostep Group AB
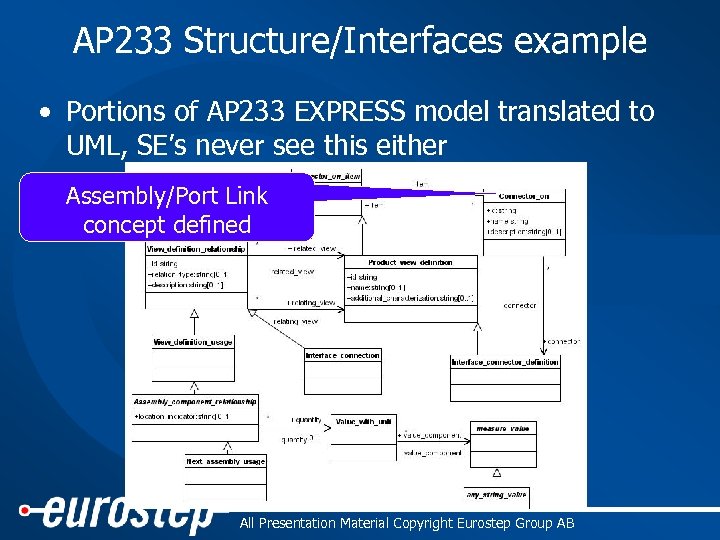 AP 233 Structure/Interfaces example • Portions of AP 233 EXPRESS model translated to UML, SE’s never see this either Assembly/Port Link concept defined ® All Presentation Material Copyright Eurostep Group AB
AP 233 Structure/Interfaces example • Portions of AP 233 EXPRESS model translated to UML, SE’s never see this either Assembly/Port Link concept defined ® All Presentation Material Copyright Eurostep Group AB
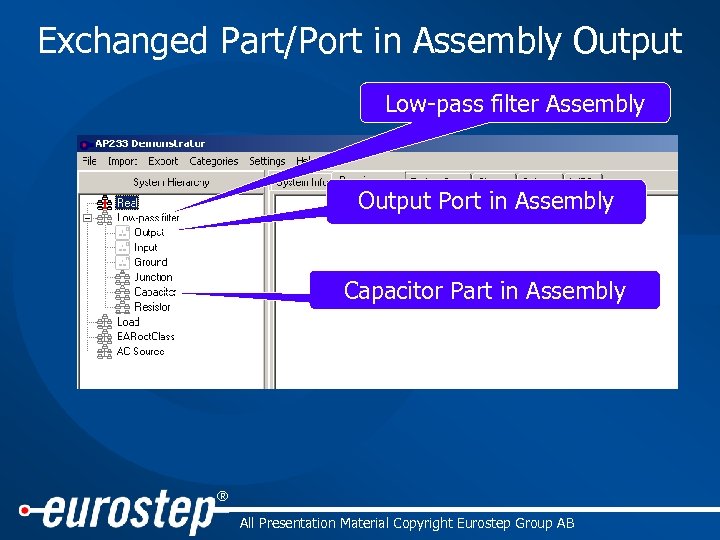 Exchanged Part/Port in Assembly Output Low-pass filter Assembly Output Port in Assembly Capacitor Part in Assembly ® All Presentation Material Copyright Eurostep Group AB
Exchanged Part/Port in Assembly Output Low-pass filter Assembly Output Port in Assembly Capacitor Part in Assembly ® All Presentation Material Copyright Eurostep Group AB
 3. Do. DAF CADM/AP 233 project • For Do. D/American Systems Corporation – Sys. ML team member • Project currently underway – First demonstration planned for joint INCOSE/OMG conference early November 2004 • Define mapping from several Do. DAF Views to AP 233 • Implement two-way mapping between Do. DAF CADM XML format and AP 233 XML format ® All Presentation Material Copyright Eurostep Group AB
3. Do. DAF CADM/AP 233 project • For Do. D/American Systems Corporation – Sys. ML team member • Project currently underway – First demonstration planned for joint INCOSE/OMG conference early November 2004 • Define mapping from several Do. DAF Views to AP 233 • Implement two-way mapping between Do. DAF CADM XML format and AP 233 XML format ® All Presentation Material Copyright Eurostep Group AB
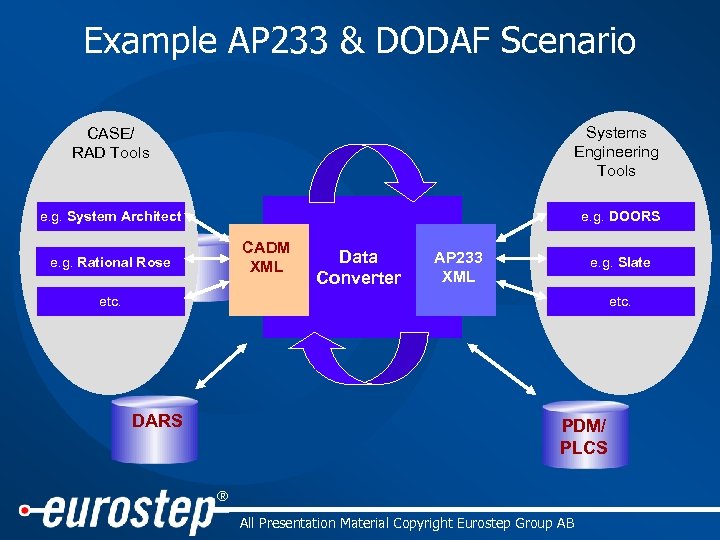 Example AP 233 & DODAF Scenario CASE/ RAD Tools Systems Engineering Tools e. g. System Architect e. g. DOORS CADM XML e. g. Rational Rose Data Converter AP 233 XML e. g. Slate etc. DARS PDM/ PLCS ® All Presentation Material Copyright Eurostep Group AB
Example AP 233 & DODAF Scenario CASE/ RAD Tools Systems Engineering Tools e. g. System Architect e. g. DOORS CADM XML e. g. Rational Rose Data Converter AP 233 XML e. g. Slate etc. DARS PDM/ PLCS ® All Presentation Material Copyright Eurostep Group AB
 Conclusions • Do. DAF, Sys. ML and AP 233 – Improve the systems engineering of Systems – Support related analyses and project management decisions – Have different roles in the systems engineering process • Do. DAF provides larger context/framework for SE • Sys. ML is tool for SEs enabling consistency across Do. DAF and other architectures/processes • AP 233 for SE system integrators supporting a broad scope – enables Sys. ML/other SE modeling paradigm exchange and legacy data extraction – opens up possibility of standardized shared data environments based on Sys. ML and Do. DAF – Proof-of-concepts show that they do work together ® All Presentation Material Copyright Eurostep Group AB
Conclusions • Do. DAF, Sys. ML and AP 233 – Improve the systems engineering of Systems – Support related analyses and project management decisions – Have different roles in the systems engineering process • Do. DAF provides larger context/framework for SE • Sys. ML is tool for SEs enabling consistency across Do. DAF and other architectures/processes • AP 233 for SE system integrators supporting a broad scope – enables Sys. ML/other SE modeling paradigm exchange and legacy data extraction – opens up possibility of standardized shared data environments based on Sys. ML and Do. DAF – Proof-of-concepts show that they do work together ® All Presentation Material Copyright Eurostep Group AB
 More Information • AP 233 – david. price@eurostep. com – NASA AP 233 Page at http: //step. jpl. nasa. gov/AP 233/ – Eurostep AP 233 Page at http: //ap 233. eurostep. com • Do. DAF – Fatma. Dandashi@pentagon. af. mil – Do. D NII Archive at http: //www. defenselink. mil/nii/doc • Sys. ML – Dwayne. Hardy. CTR@osd. mil – Sys. ML Partners Page at http: //www. sysml. org – OMG Sys. Eng SIG at http: //syseng. omg. org/ • The International Council on Systems Engineering – INCOSE at http: //www. incose. org ® All Presentation Material Copyright Eurostep Group AB
More Information • AP 233 – david. price@eurostep. com – NASA AP 233 Page at http: //step. jpl. nasa. gov/AP 233/ – Eurostep AP 233 Page at http: //ap 233. eurostep. com • Do. DAF – Fatma. Dandashi@pentagon. af. mil – Do. D NII Archive at http: //www. defenselink. mil/nii/doc • Sys. ML – Dwayne. Hardy. CTR@osd. mil – Sys. ML Partners Page at http: //www. sysml. org – OMG Sys. Eng SIG at http: //syseng. omg. org/ • The International Council on Systems Engineering – INCOSE at http: //www. incose. org ® All Presentation Material Copyright Eurostep Group AB


