secondary data.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 16

Using Secondary Data and Online Information Databases

Primary Versus Secondary Data • Primary data: information that is developed or gathered by the researcher specifically for the research project at hand. • Secondary data: information that has previously been gathered by someone other than the researcher and/or for some other purpose than the research project at hand. Ch 6 2

Uses of Secondary Data • Secondary data has many uses in marketing research and sometimes the entire research project may depend on the use of secondary data. • Applications include economic-trend forecasting, corporate intelligence, international data, public opinion, and historical data. • See www. secondarydata. com. Ch 6 3

Classification of Secondary Data • Internal secondary data are data that have been collected within the firm such as sales records, purchase requisitions, and invoices. – Internal secondary data is used for database marketing. Ch 6 4

Classification of Secondary Data – Database marketing is the process of building, maintaining customer (internal) databases and other (internal) databases for the purpose of contacting, transacting, and building relationships. CRM and DATA Mining – Ethical Issue? How much information should companies have about consumers? http: //www. adcritic. com/interactive/view. php? id =5927 Ch 6 5

Internal Databases • Database refers to a collection of data and information describing items of interest. – Vehicle Registration Database • Record: is a unit of information in a database. – SS#XXX YY ZZZZ • Fields: subcomponents of information composing records. – Brand– Color – Year Ch 6 6 – Model – Violations
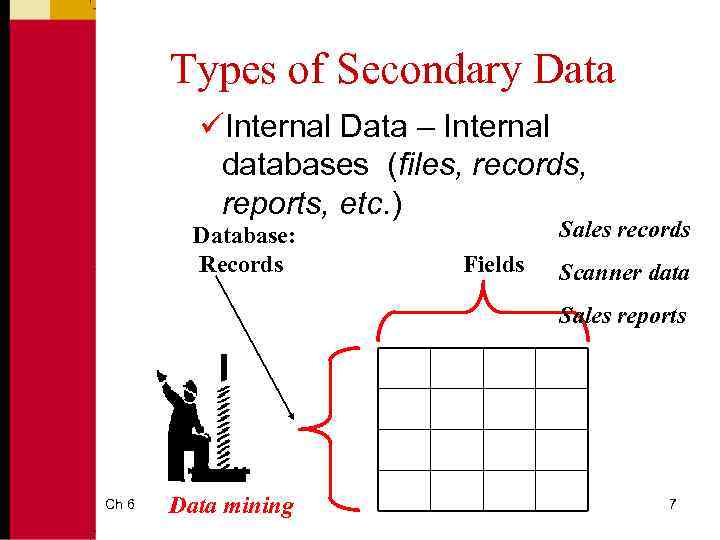
Types of Secondary Data üInternal Data – Internal databases (files, records, reports, etc. ) Database: Records Sales records Fields Scanner data Sales reports Ch 6 Data mining 7

External Secondary Data • Published: are sources of information prepared for public distribution and normally found in libraries or a variety of other entities such as trade organizations. Ch 6 8

External Secondary Data • Syndicated Services Data: are provided by firms that collect data in a standard format and make them available to subscribing firms -- highly specialized and not available in libraries. Ch 6 9

External Secondary Data • External databases: are databases supplied by organizations outside the firm such as online information databases such as FACTIVA and Lexis Nexis. Ch 6 10

Different Types of Publications Ch 6 11

Advantages of Secondary Data • • • Ch 6 Obtained quickly Inexpensive Usually available Enhances existing primary data May achieve research objective 12

Disadvantages of Secondary Data • Incompatible reporting units…need zip code data and only have County data. • Measurement units do not match…need per capita income and only have household income. • Class definitions are not usable…need to know percent of population with income above $100 k and only have $50 k and over. Ch 6 13 • Data are outdated.

Evaluating Secondary Data • • • Ch 6 What was the purpose of the study? Who collected the information? What information was collected? How was the information attained? How consistent is the information with other information? 14

Locating Secondary Data Sources • Step 1: • Step 2: • Step 3: Ch 6 Identify what you wish to know and what you already know about your topic. Develop a list of key words and names. Begin your search using several library sources. 15

Locating Secondary Data Sources • Step 4: • Step 5: • Step 6: Ch 6 Compile the literature you have found and evaluate your findings. If you are unhappy with what you have found or are otherwise having trouble and the reference librarian has not been able to identify sources, use an authority. 16 Report results.
secondary data.ppt