321b501a08199ddd06581eab4301811f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 31

Using NCBI Resources for Gene Discovery Kim D. Pruitt Transcriptome 2002 National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) National Library of Medicine National Institutes of Health NCBI Genome Resources http: //www. ncbi. nlm. nih. gov/

Fundamental resources Primary Databases - Gen. Bank, db. EST, db. STS, Pub. Med u Archival - original data submissions u Database staff organize, but don’t additional information Derivative Databases – Ref. Seq, Locus. Link, Uni. Gene, Map Viewer u Curated/expert F compilation and correction of data u Computationally u Combinations review Derived
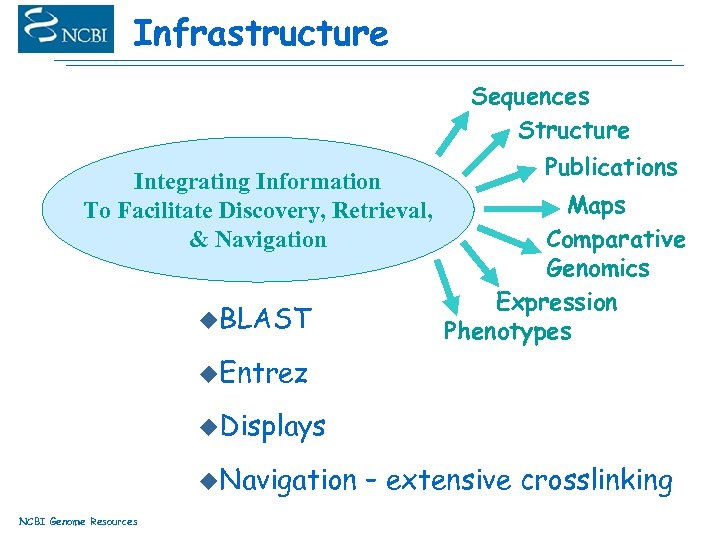
Infrastructure Sequences Structure Integrating Information To Facilitate Discovery, Retrieval, & Navigation u. BLAST Publications Maps Comparative Genomics Expression Phenotypes u. Entrez u. Displays u. Navigation NCBI Genome Resources – extensive crosslinking
Increasing Discovery Space NCBI Map Viewer NCBI Genome Resources
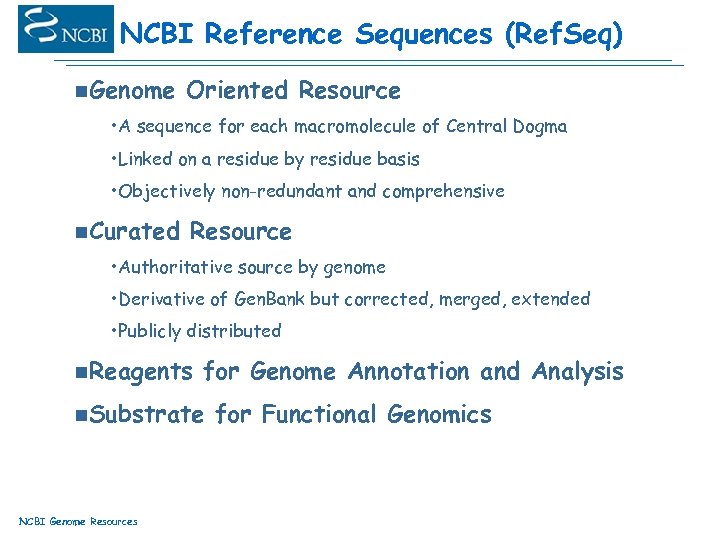
NCBI Reference Sequences (Ref. Seq) n. Genome Oriented Resource • A sequence for each macromolecule of Central Dogma • Linked on a residue by residue basis • Objectively non-redundant and comprehensive n. Curated Resource • Authoritative source by genome • Derivative of Gen. Bank but corrected, merged, extended • Publicly distributed n. Reagents for Genome Annotation and Analysis n. Substrate NCBI Genome Resources for Functional Genomics
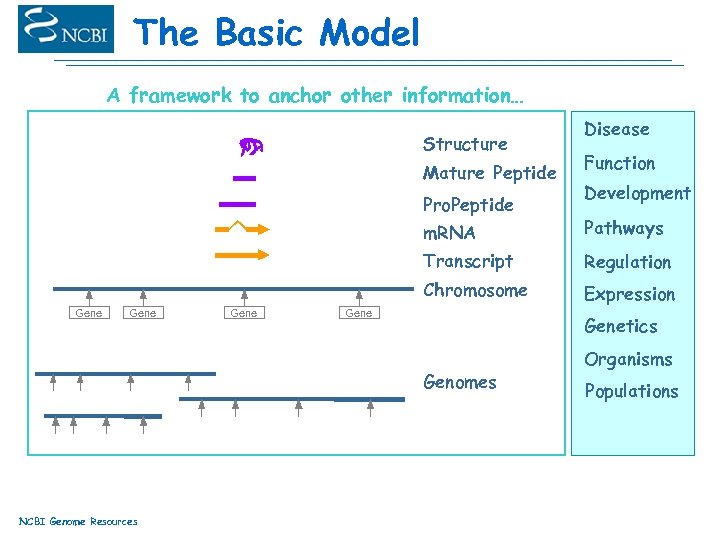
The Basic Model A framework to anchor other information… Structure Mature Peptide Pro. Peptide Disease Function Development m. RNA Transcript Gene Regulation Chromosome Gene Pathways Expression Genetics Genomes NCBI Genome Resources Organisms Populations

Ref. Seq: Scope The NCBI Reference Sequence (Ref. Seq) project provides non-redundant sequence data including bacterial and viral genomes, mitochondrion, chromosomes, constructed genomic contigs, transcripts, and proteins. Ref. Seq as a protein database over 280, 000 proteins NCBI Genome Resources
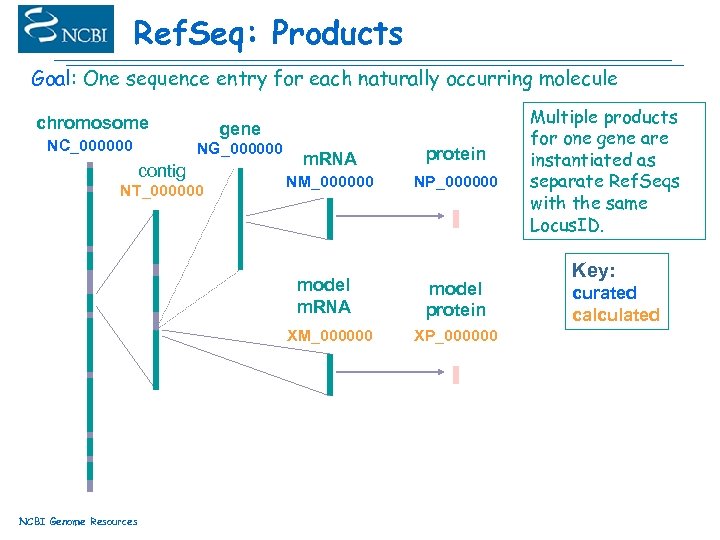
Ref. Seq: Products Goal: One sequence entry for each naturally occurring molecule chromosome NC_000000 gene NG_000000 contig NT_000000 m. RNA protein NM_000000 NP_000000 model m. RNA XM_000000 NCBI Genome Resources model protein XP_000000 Multiple products for one gene are instantiated as separate Ref. Seqs with the same Locus. ID. Key: curated calculated
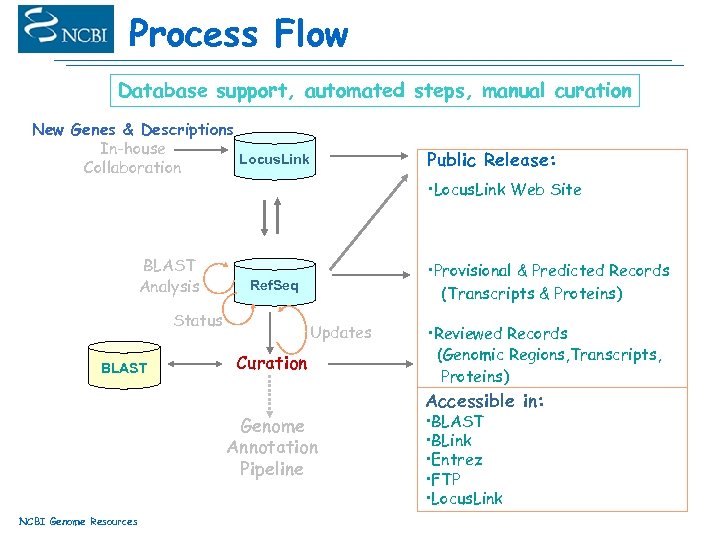
Process Flow Database support, automated steps, manual curation New Genes & Descriptions In-house Locus. Link Collaboration BLAST Analysis • Locus. Link Web Site • Provisional & Predicted Records (Transcripts & Proteins) Ref. Seq Status BLAST Public Release: Updates Curation Genome Annotation Pipeline NCBI Genome Resources • Reviewed Records (Genomic Regions, Transcripts, Proteins) Accessible in: • BLAST • BLink • Entrez • FTP • Locus. Link
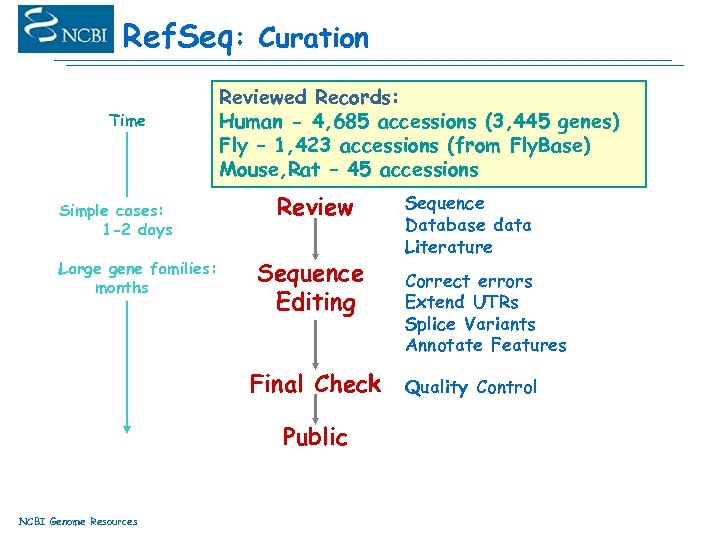
Ref. Seq: Curation Time Simple cases: 1 -2 days Large gene families: months Reviewed Records: Known Genes Assignment Gene Families Human - 4, 685 accessions (3, 445 genes) Fly – 1, 423 accessions (from Fly. Base) Gene Clusters Mouse, Rat – 45 accessions Problems Identified Review Sequence Editing Final Check Public NCBI Genome Resources Sequence Database data Literature Correct errors Extend UTRs Splice Variants Annotate Features Quality Control
New Type of Ref. Seq: Genomic Regions Why? Correct Assembly through Duplications, Paralogous Gene Clusters Optimize Annotation in Gene Clusters Used in Genome Annotation Process NCBI Genome Resources

Maintenance New Genes: Updates: Gen. Bank updates Uni. Gene Collaboration Genome Annotation Ongoing curation Collaboration Genome Annotation e-mail We welcome feedback, suggestions, collaborations Why Look For Ref. Seqs? Enhanced Discovery Space: What do we already known? Predicted Ref. Seqs – where do we need to know more? Genome Annotation Products (Model Ref. Seqs) Analysis: transcript, protein, annotation, gene index NCBI Genome Resources
Increasing Discovery Space NCBI Map Viewer NCBI Genome Resources
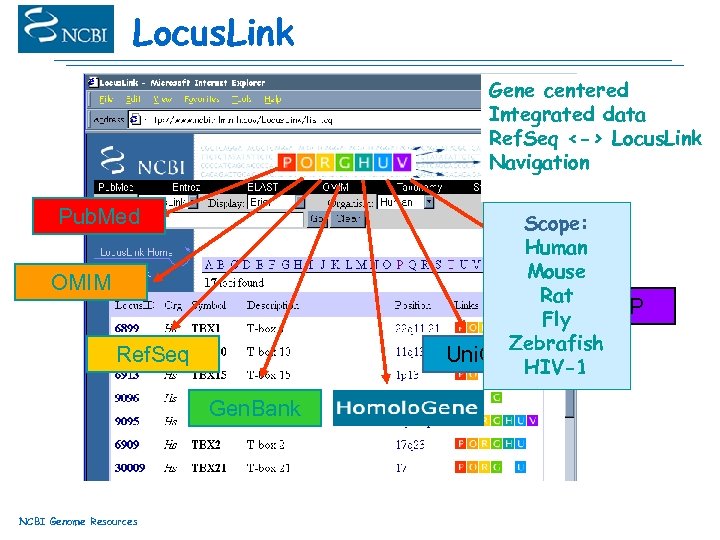
Locus. Link Gene centered Integrated data Ref. Seq <-> Locus. Link Navigation Pub. Med Scope: Human Mouse Rat db. SNP Fly Zebrafish Uni. Gene HIV-1 OMIM Ref. Seq Gen. Bank NCBI Genome Resources

Locus. Link: Maintenance Data Collection: Extensive Collaborations with authoritative groups In-house computation In-house curation effort (Ref. Seq review) NCBI Genome Resources
![Locus. Link: Discovery Find novel uncharacterized genes on a finished chromosome QUERY= 21[chr] NOT Locus. Link: Discovery Find novel uncharacterized genes on a finished chromosome QUERY= 21[chr] NOT](https://present5.com/presentation/321b501a08199ddd06581eab4301811f/image-16.jpg)
Locus. Link: Discovery Find novel uncharacterized genes on a finished chromosome QUERY= 21[chr] NOT has_omim AND has_homol AND type_gene_protein AND predicted AND model AND provisional AND C 21 orf* OR MGC* NCBI Genome Resources
Increasing Discovery Space NCBI Map Viewer NCBI Genome Resources
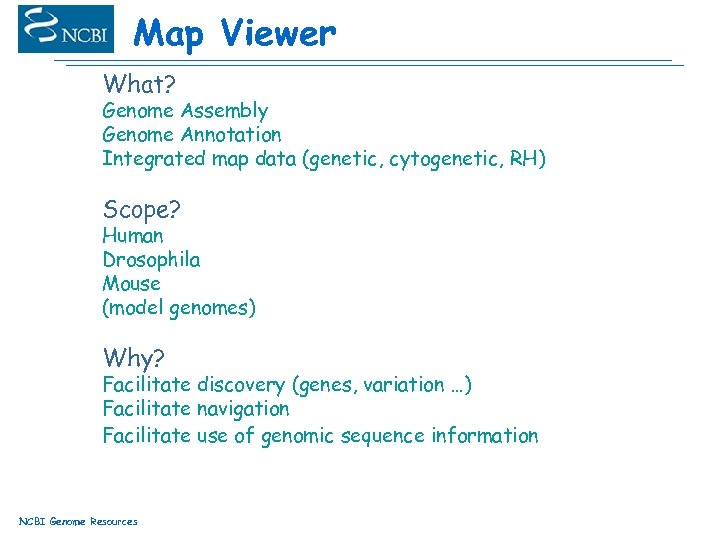
Map Viewer What? Genome Assembly Genome Annotation Integrated map data (genetic, cytogenetic, RH) Scope? Human Drosophila Mouse (model genomes) Why? Facilitate discovery (genes, variation …) Facilitate navigation Facilitate use of genomic sequence information NCBI Genome Resources
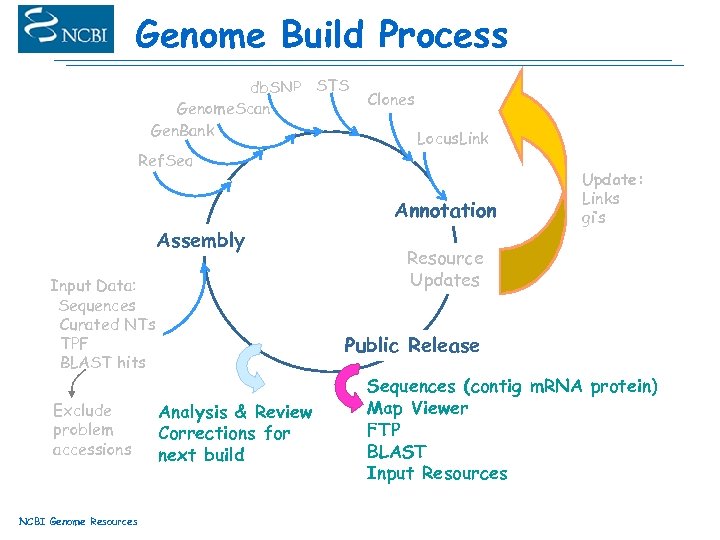
Genome Build Process db. SNP STS Genome. Scan Gen. Bank Ref. Seq Clones Locus. Link Annotation Assembly Input Data: Sequences Curated NTs TPF BLAST hits Exclude problem accessions NCBI Genome Resources Update: Links gi’s Resource Updates Public Release Analysis & Review Corrections for next build Sequences (contig m. RNA protein) Map Viewer FTP BLAST Input Resources
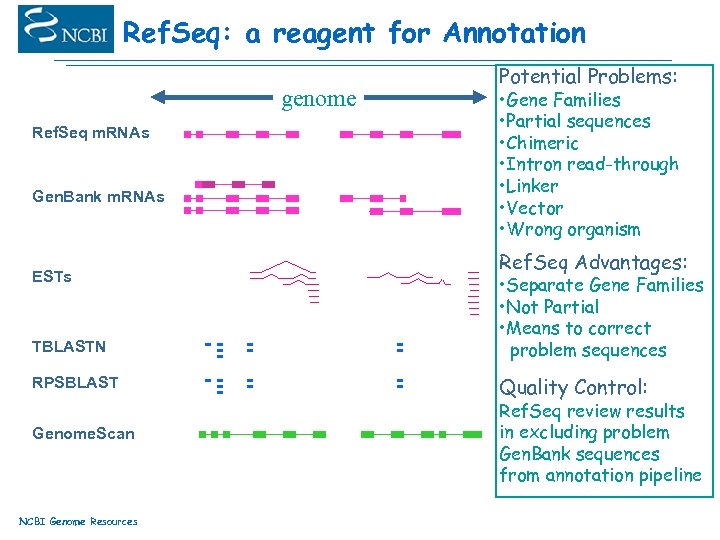
Ref. Seq: a reagent for Annotation genome Ref. Seq m. RNAs Gen. Bank m. RNAs ESTs TBLASTN RPSBLAST Genome. Scan NCBI Genome Resources Potential Problems: • Gene Families • Partial sequences • Chimeric • Intron read-through • Linker • Vector • Wrong organism Ref. Seq Advantages: • Separate Gene Families • Not Partial • Means to correct problem sequences Quality Control: Ref. Seq review results in excluding problem Gen. Bank sequences from annotation pipeline

What questions can be asked? n n n What genes (markers, SNPs) are between 2 markers? What BAC clones are available on Xq 28? Where are there serine kinases? I’ve cloned gene xyz in my favorite organism. What is related in human? What is the evidence that there is a gene at position n? I have found a phenotype of interest between markers x and y; what is known about this region? NCBI Genome Resources
Fanconi Syndrome Genetic Mapping Pathology in proximal renal tubular transport NCBI Genome Resources
Query Map Viewer Look for genes in the region NCBI Genome Resources
NCBI Genome Resources
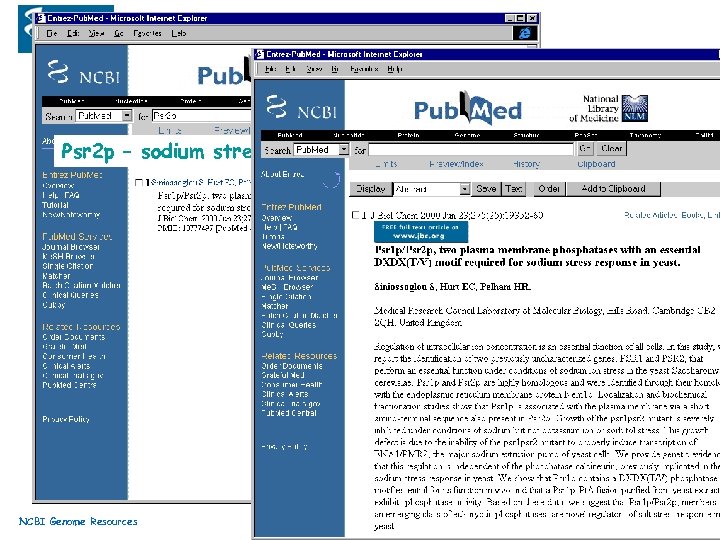
Psr 2 p – sodium stress response in yeast NCBI Genome Resources
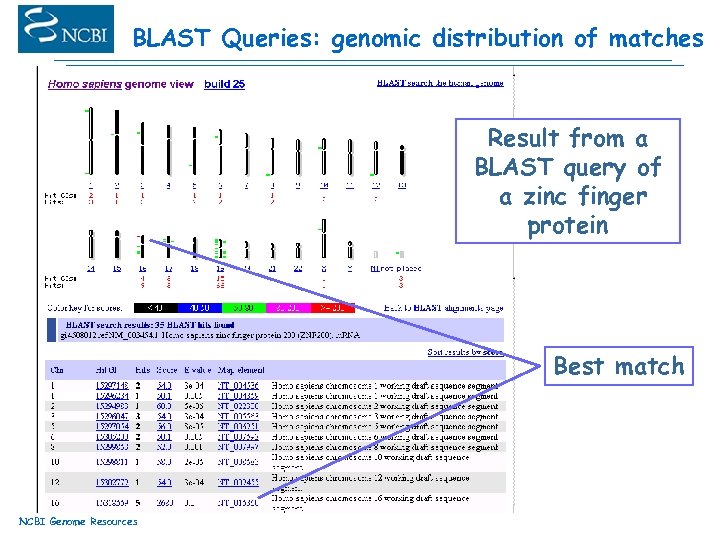
BLAST Queries: genomic distribution of matches Result from a BLAST query of a zinc finger protein Best match NCBI Genome Resources
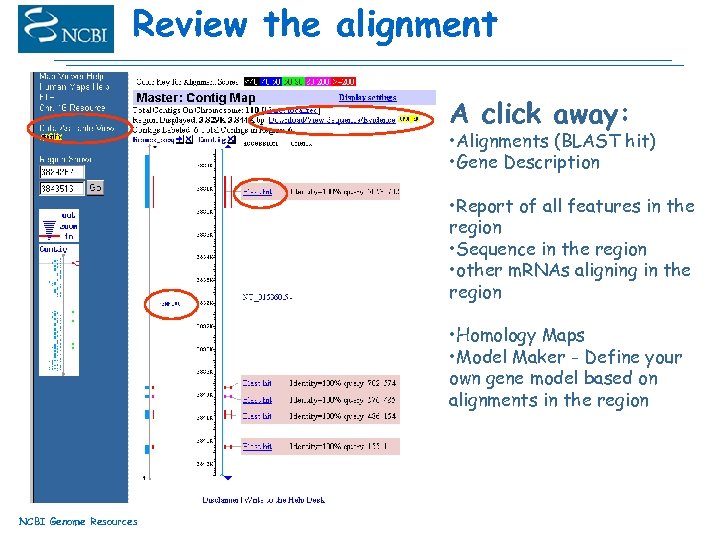
Review the alignment A click away: • Alignments (BLAST hit) • Gene Description • Report of all features in the region • Sequence in the region • other m. RNAs aligning in the region • Homology Maps • Model Maker - Define your own gene model based on alignments in the region NCBI Genome Resources
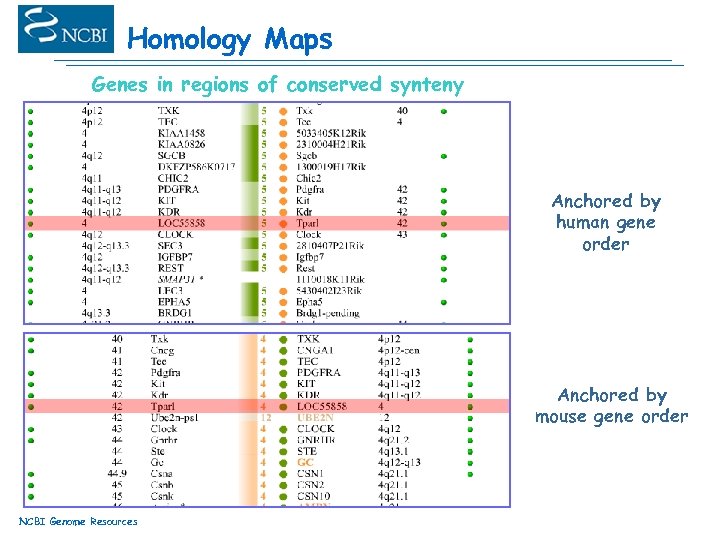
Homology Maps Genes in regions of conserved synteny Anchored by human gene order Anchored by mouse gene order NCBI Genome Resources
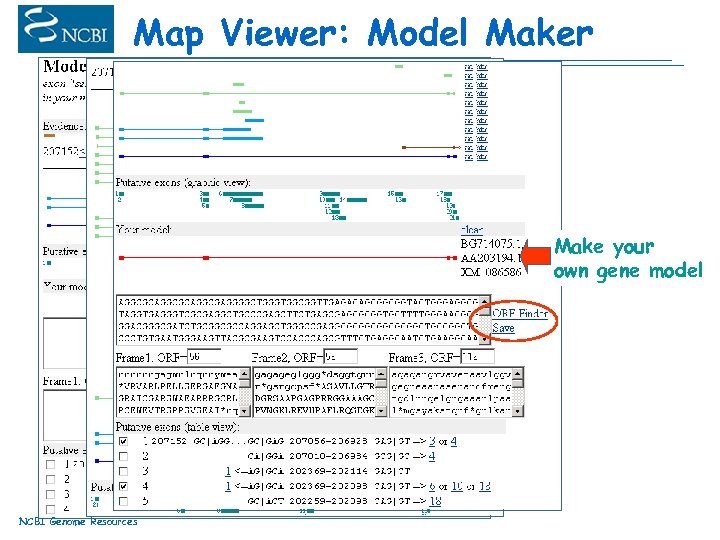
Map Viewer: Model Maker Make your own gene model NCBI Genome Resources
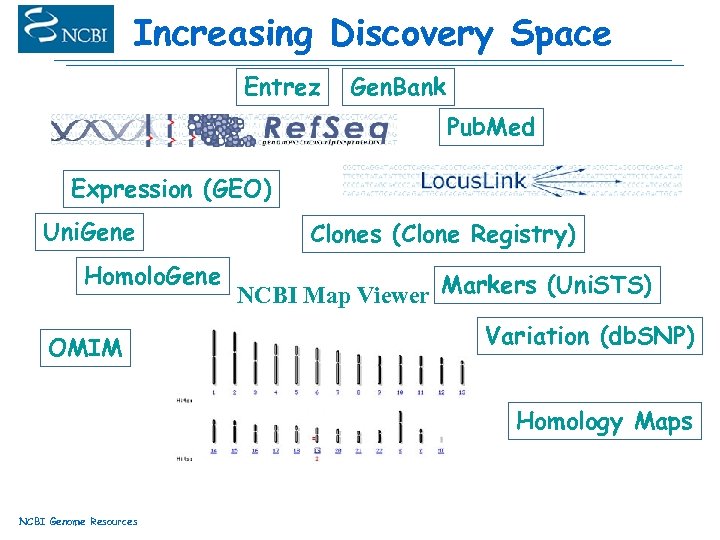
Increasing Discovery Space Entrez Gen. Bank Pub. Med Expression (GEO) Uni. Gene Homolo. Gene OMIM Clones (Clone Registry) NCBI Map Viewer Markers (Uni. STS) Variation (db. SNP) Homology Maps NCBI Genome Resources

Genome Build Team: Acknowledgments Ref. Seq Curator Staff BLAST Team Entrez Team NCBI Service Desk Staff Collaborators: Human Gene Nomenclature Committee OMIM Staff The Jackson Laboratory Rat Genome Database http: //www. ncbi. nlm. nih. gov/ NCBI Genome Resources Richa Agarwala Hsiu-Chuan Chen Slava Chetvernin Deanna Church Olga Ermolaeva Renata Geer Wratko Hlavina Wonhee Jang Jonathan Kans Ken Katz Paul Kitts David Lipman Adam Lowe Donna Maglott Jim Ostell Kim Pruitt Sergey Resenchuk Victor Sapojnikov Greg Schuler Steve Sherry Andrei Shkeda Tatiana Tatusova Lukas Wagner Sarah Wheelan
321b501a08199ddd06581eab4301811f.ppt