463cf2805cd29d054919e56fee8cc1e0.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 38
 Using MIS 4 e Chapter 3 Information Systems for Competitive Advantage
Using MIS 4 e Chapter 3 Information Systems for Competitive Advantage
 Study Questions Q 1: How does organizational strategy determine information systems structure? Q 2: What five forces determine industry structure? Q 3: How does analysis of industry structure determine competitive strategy? Q 4: How does competitive strategy determine value chain structure? Q 5: How do business processes generate value? Q 6: How does competitive strategy determine business processes and the structure of information systems? Q 7: How do information systems provide competitive advantages? Q 8: 2021? Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 3 -2
Study Questions Q 1: How does organizational strategy determine information systems structure? Q 2: What five forces determine industry structure? Q 3: How does analysis of industry structure determine competitive strategy? Q 4: How does competitive strategy determine value chain structure? Q 5: How do business processes generate value? Q 6: How does competitive strategy determine business processes and the structure of information systems? Q 7: How do information systems provide competitive advantages? Q 8: 2021? Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 3 -2
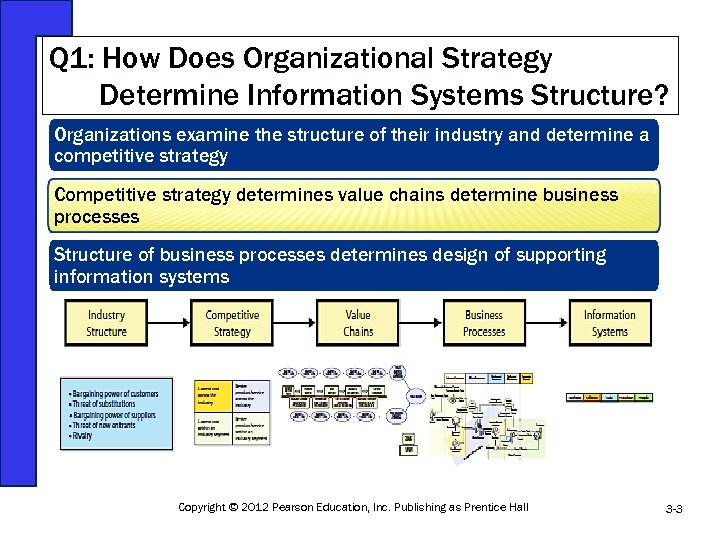 Q 1: How Does Organizational Strategy Determine Information Systems Structure? Organizations examine the structure of their industry and determine a competitive strategy Competitive strategy determines value chains determine business processes Structure of business processes determines design of supporting information systems Figure 3 -1 Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 3 -3
Q 1: How Does Organizational Strategy Determine Information Systems Structure? Organizations examine the structure of their industry and determine a competitive strategy Competitive strategy determines value chains determine business processes Structure of business processes determines design of supporting information systems Figure 3 -1 Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 3 -3
 Q 2: What Five Forces Determine Industry Structure? Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 3 -4
Q 2: What Five Forces Determine Industry Structure? Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 3 -4
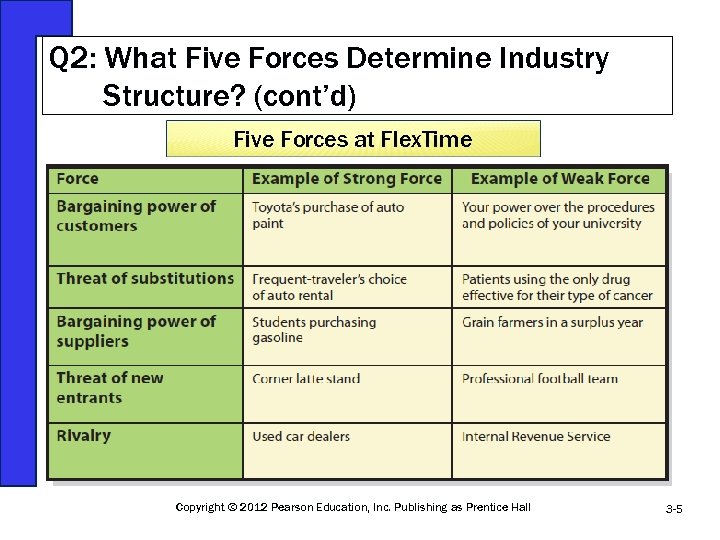 Q 2: What Five Forces Determine Industry Structure? (cont’d) Five Forces at Flex. Time Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 3 -5
Q 2: What Five Forces Determine Industry Structure? (cont’d) Five Forces at Flex. Time Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 3 -5
 Q 3: How Does Analysis of Industry Structure Determine Competitive Strategy? Porter’s Four Competitive Strategies Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 3 -6
Q 3: How Does Analysis of Industry Structure Determine Competitive Strategy? Porter’s Four Competitive Strategies Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 3 -6
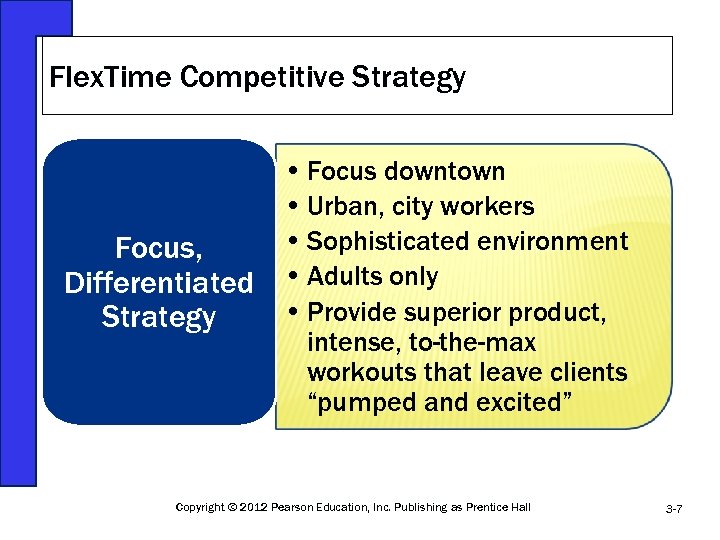 Flex. Time Competitive Strategy Focus, Differentiated Strategy • Focus downtown • Urban, city workers • Sophisticated environment • Adults only • Provide superior product, intense, to-the-max workouts that leave clients “pumped and excited” Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 3 -7
Flex. Time Competitive Strategy Focus, Differentiated Strategy • Focus downtown • Urban, city workers • Sophisticated environment • Adults only • Provide superior product, intense, to-the-max workouts that leave clients “pumped and excited” Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 3 -7
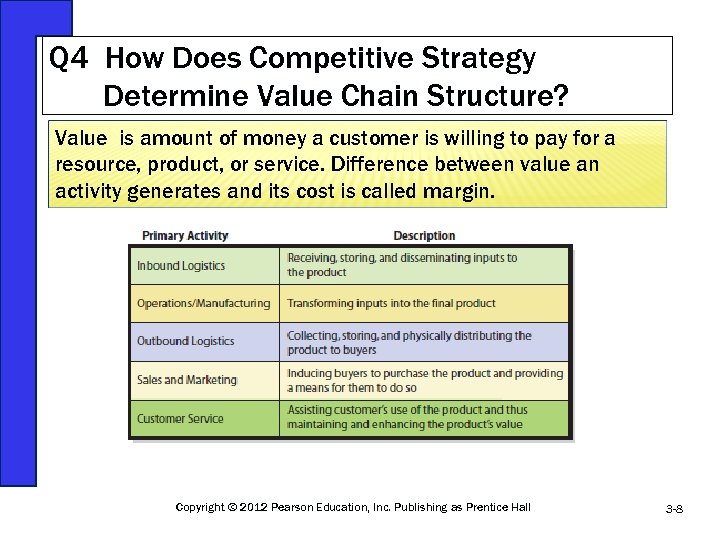 Q 4 How Does Competitive Strategy Determine Value Chain Structure? Value is amount of money a customer is willing to pay for a resource, product, or service. Difference between value an activity generates and its cost is called margin. Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 3 -8
Q 4 How Does Competitive Strategy Determine Value Chain Structure? Value is amount of money a customer is willing to pay for a resource, product, or service. Difference between value an activity generates and its cost is called margin. Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 3 -8
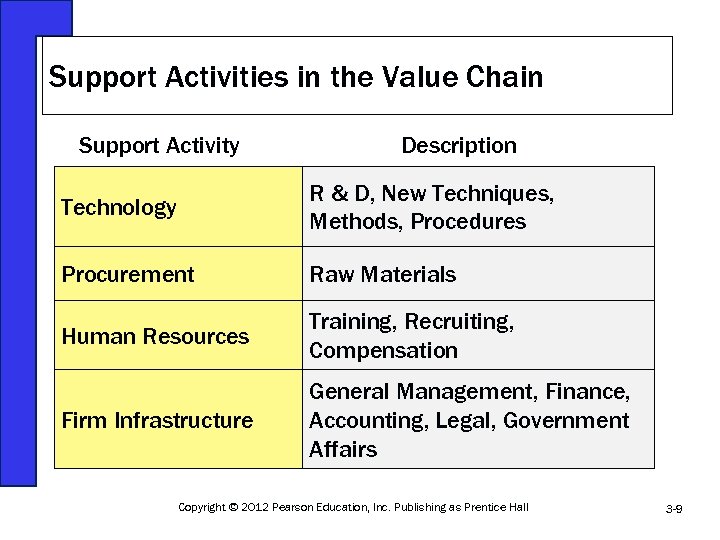 Support Activities in the Value Chain Support Activity Description Technology R & D, New Techniques, Methods, Procedures Procurement Raw Materials Human Resources Training, Recruiting, Compensation Firm Infrastructure General Management, Finance, Accounting, Legal, Government Affairs Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 3 -9
Support Activities in the Value Chain Support Activity Description Technology R & D, New Techniques, Methods, Procedures Procurement Raw Materials Human Resources Training, Recruiting, Compensation Firm Infrastructure General Management, Finance, Accounting, Legal, Government Affairs Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 3 -9
 Bicycle Maker’s Value Chain Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 3 -10
Bicycle Maker’s Value Chain Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 3 -10
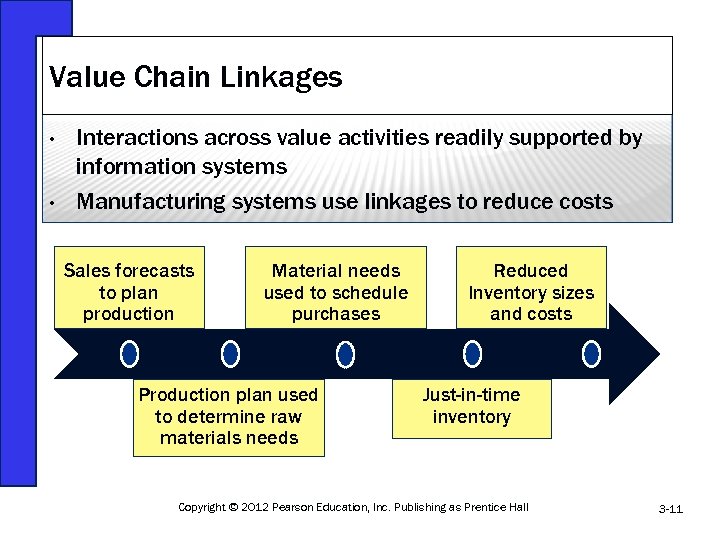 Value Chain Linkages • • Interactions across value activities readily supported by information systems Manufacturing systems use linkages to reduce costs Sales forecasts to plan production Material needs used to schedule purchases Production plan used to determine raw materials needs Reduced Inventory sizes and costs Just-in-time inventory Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 3 -11
Value Chain Linkages • • Interactions across value activities readily supported by information systems Manufacturing systems use linkages to reduce costs Sales forecasts to plan production Material needs used to schedule purchases Production plan used to determine raw materials needs Reduced Inventory sizes and costs Just-in-time inventory Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 3 -11
 Q 5 How Do Business Processes Generate Value? Business process Cost of a business process Margin of a business process Activity • Network of activities that generate value by transforming inputs into outputs • Cost of inputs plus cost of activities • Equals value of the outputs minus cost • Transforms input resources into output resources Resources • Flow between or among activities Facilities store resources • Inventories, store physical items Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 3 -12
Q 5 How Do Business Processes Generate Value? Business process Cost of a business process Margin of a business process Activity • Network of activities that generate value by transforming inputs into outputs • Cost of inputs plus cost of activities • Equals value of the outputs minus cost • Transforms input resources into output resources Resources • Flow between or among activities Facilities store resources • Inventories, store physical items Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 3 -12
 Three Examples of Business Processes for Bicycle Manufacturer 1. Materials ordering process transforms cash into a raw materials inventory 2. Manufacturing process transforms raw materials into finished goods 3. Sales process transforms finished goods into cash Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 3 -13
Three Examples of Business Processes for Bicycle Manufacturer 1. Materials ordering process transforms cash into a raw materials inventory 2. Manufacturing process transforms raw materials into finished goods 3. Sales process transforms finished goods into cash Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 3 -13
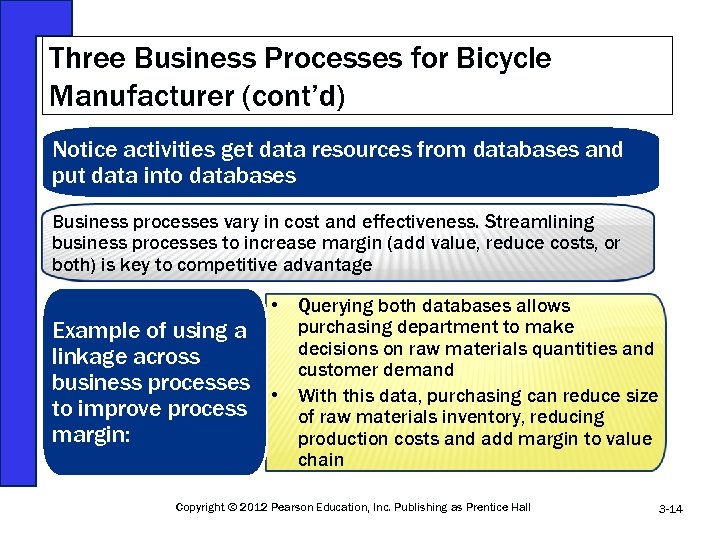 Three Business Processes for Bicycle Manufacturer (cont’d) Notice activities get data resources from databases and put data into databases Business processes vary in cost and effectiveness. Streamlining business processes to increase margin (add value, reduce costs, or both) is key to competitive advantage Example of using a linkage across business processes to improve process margin: • Querying both databases allows purchasing department to make decisions on raw materials quantities and customer demand • With this data, purchasing can reduce size of raw materials inventory, reducing production costs and add margin to value chain Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 3 -14
Three Business Processes for Bicycle Manufacturer (cont’d) Notice activities get data resources from databases and put data into databases Business processes vary in cost and effectiveness. Streamlining business processes to increase margin (add value, reduce costs, or both) is key to competitive advantage Example of using a linkage across business processes to improve process margin: • Querying both databases allows purchasing department to make decisions on raw materials quantities and customer demand • With this data, purchasing can reduce size of raw materials inventory, reducing production costs and add margin to value chain Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 3 -14
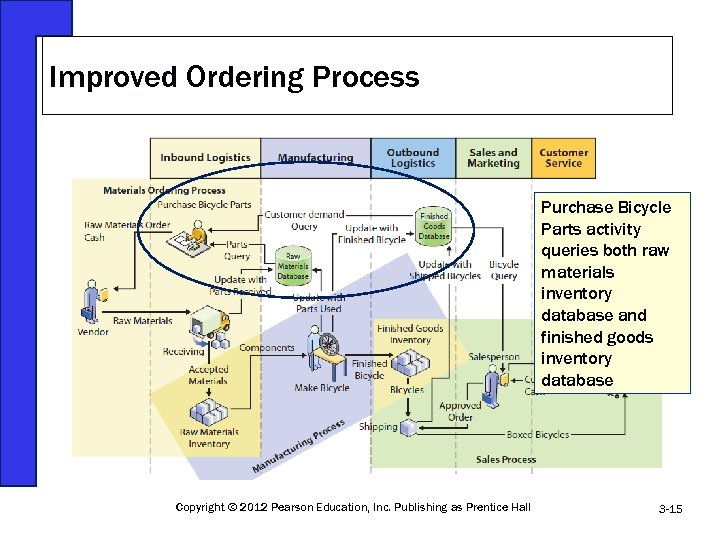 Improved Ordering Process Purchase Bicycle Parts activity queries both raw materials inventory database and finished goods inventory database Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 3 -15
Improved Ordering Process Purchase Bicycle Parts activity queries both raw materials inventory database and finished goods inventory database Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 3 -15
 Ethics Guide: Yikes! Bikes You are the operations manager for Yikes! Bikes, a manufacturer of high-end mountain bicycles New owners being deceitful about their plans to turn company into a low-cost, low-service producer. Most employees will lose their job, but new owners not being honest with employees about that New owners say you might be promoted to new general manager. Should you trust them? Q: Should you tell employees what you know? Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 3 -16
Ethics Guide: Yikes! Bikes You are the operations manager for Yikes! Bikes, a manufacturer of high-end mountain bicycles New owners being deceitful about their plans to turn company into a low-cost, low-service producer. Most employees will lose their job, but new owners not being honest with employees about that New owners say you might be promoted to new general manager. Should you trust them? Q: Should you tell employees what you know? Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 3 -16
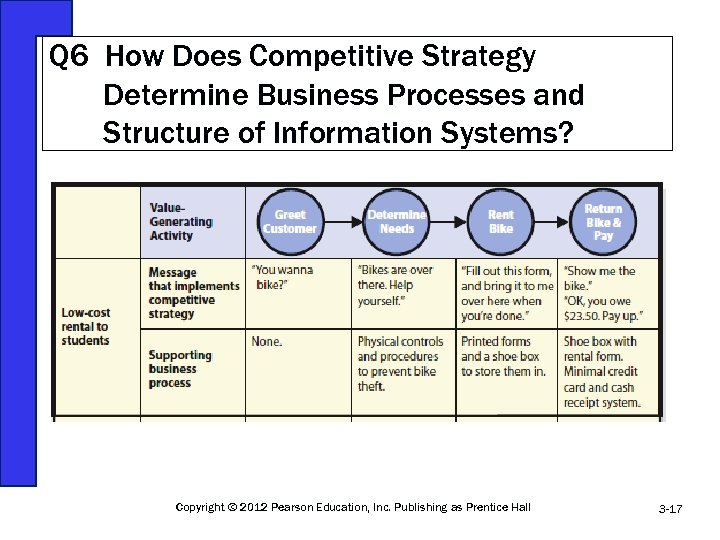 Q 6 How Does Competitive Strategy Determine Business Processes and Structure of Information Systems? Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 3 -17
Q 6 How Does Competitive Strategy Determine Business Processes and Structure of Information Systems? Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 3 -17
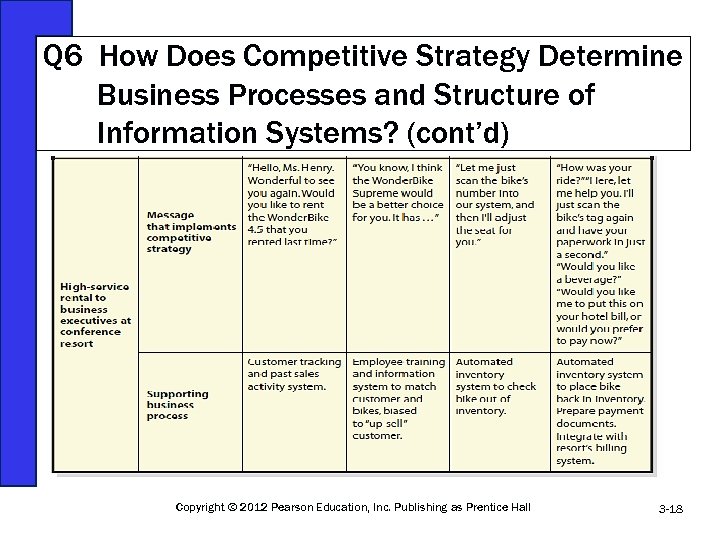 Q 6 How Does Competitive Strategy Determine Business Processes and Structure of Information Systems? (cont’d) Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 3 -18
Q 6 How Does Competitive Strategy Determine Business Processes and Structure of Information Systems? (cont’d) Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 3 -18
 High-Service Business Bike Rental Extensive use of information systems Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 3 -19
High-Service Business Bike Rental Extensive use of information systems Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 3 -19
 Bottom Line Organizations analyze their industry and choose a competitive strategy Given a strategy, business processes to span value -generating activities are designed Those processes determine scope and requirements of each organization’s information systems Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 3 -20
Bottom Line Organizations analyze their industry and choose a competitive strategy Given a strategy, business processes to span value -generating activities are designed Those processes determine scope and requirements of each organization’s information systems Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 3 -20
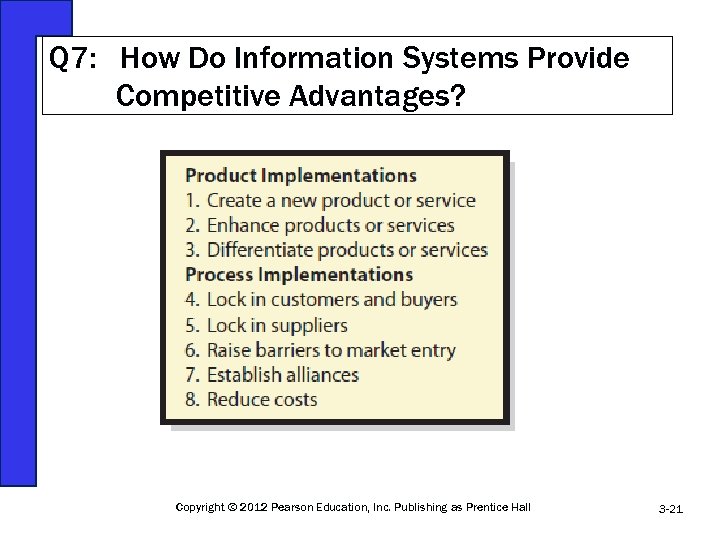 Q 7: How Do Information Systems Provide Competitive Advantages? Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 3 -21
Q 7: How Do Information Systems Provide Competitive Advantages? Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 3 -21
 Two Ways to Respond to the Five Competitive Forces Creating new products or services • Enhancing existing products or services • Differentiating • By cost • By quality Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 3 -22
Two Ways to Respond to the Five Competitive Forces Creating new products or services • Enhancing existing products or services • Differentiating • By cost • By quality Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 3 -22
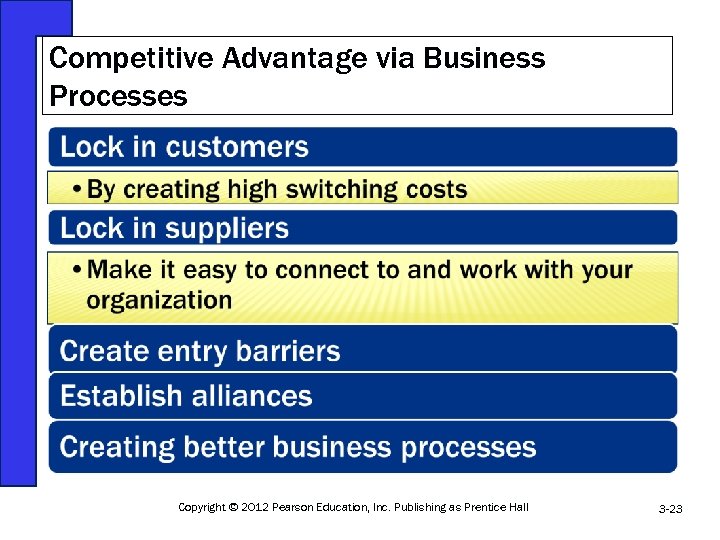 Competitive Advantage via Business Processes Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 3 -23
Competitive Advantage via Business Processes Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 3 -23
 How Does an Actual Company Use IS to Create Competitive Advantages? ABC, Inc. , an • Superior customer service actual company, • Making it easy for customers to do created a business by minimizing data entry: competitive Ø Drop-down lists, automatic fill-ins, advantage in contact lists for customers shipping industry Ø Minimizing data-entry errors by: Following slides shows some web pages of ABC’s information system Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 3 -24
How Does an Actual Company Use IS to Create Competitive Advantages? ABC, Inc. , an • Superior customer service actual company, • Making it easy for customers to do created a business by minimizing data entry: competitive Ø Drop-down lists, automatic fill-ins, advantage in contact lists for customers shipping industry Ø Minimizing data-entry errors by: Following slides shows some web pages of ABC’s information system Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 3 -24
 ABC, Inc. Web Page to Select Recipient from Customer Records Fig 3 -14 Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 3 -25
ABC, Inc. Web Page to Select Recipient from Customer Records Fig 3 -14 Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 3 -25
 ABC, Inc. Web Page to Select Contact from Customer Records Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 3 -26
ABC, Inc. Web Page to Select Contact from Customer Records Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 3 -26
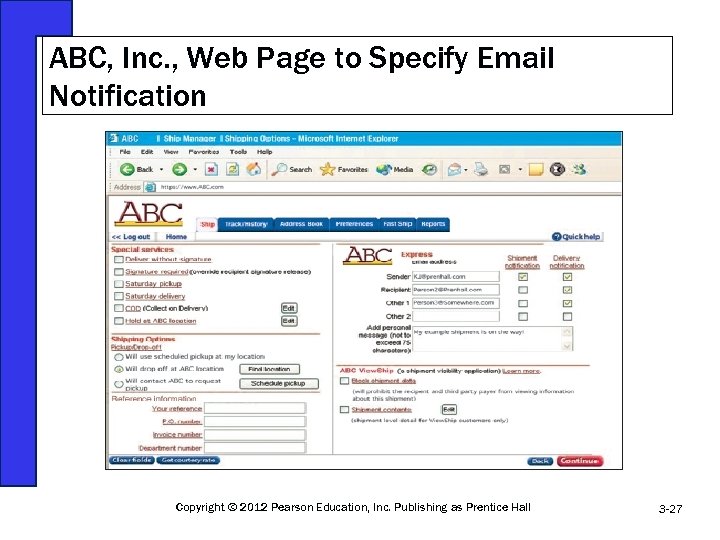 ABC, Inc. , Web Page to Specify Email Notification Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 3 -27
ABC, Inc. , Web Page to Specify Email Notification Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 3 -27
 ABC, Inc. , Web Page to Print a Shipping Label Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 3 -28
ABC, Inc. , Web Page to Print a Shipping Label Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 3 -28
 How Does This System Create a Competitive Advantage? Enhancing existing products Differentiating products Locking in customers Raising barriers to market entry Increasing profit margins by decreasing costs and decreasing errors Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 3 -29
How Does This System Create a Competitive Advantage? Enhancing existing products Differentiating products Locking in customers Raising barriers to market entry Increasing profit margins by decreasing costs and decreasing errors Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 3 -29
 Q 8 2021? What Does Flextime Look Like in 2021? Assume Flex. Time keeps pace with emerging research on optimal workout schedules (www. angelfire. com/wa 3/loserschallenge/cardio. html, www. sportsci. org/jour/0101/cf. htm) Optimist view • Could develop information systems to track client workouts and intensity, then relate data into net cardiovascular benefits. • Could correlate workout data with dietary data and client weight loss or gain. • Maybe provide data to medical insurers and help its active clients to obtain reductions in medical insurance premiums. • Flex. Time could, but should it? Is it worthwhile for Flex. Time to develop such systems? Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 3 -30
Q 8 2021? What Does Flextime Look Like in 2021? Assume Flex. Time keeps pace with emerging research on optimal workout schedules (www. angelfire. com/wa 3/loserschallenge/cardio. html, www. sportsci. org/jour/0101/cf. htm) Optimist view • Could develop information systems to track client workouts and intensity, then relate data into net cardiovascular benefits. • Could correlate workout data with dietary data and client weight loss or gain. • Maybe provide data to medical insurers and help its active clients to obtain reductions in medical insurance premiums. • Flex. Time could, but should it? Is it worthwhile for Flex. Time to develop such systems? Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 3 -30
 Pessimistic View Suppose economic downturn proves too much for Flex. Time and it is forced to reconfigure into a shadow of former self • No longer a single business entity. Maybe it becomes a federation of trainers, workout spaces, dieticians, and recreational sports leagues. • Federation uses free data storage, data communication, and emerging collaboration tools and systems to appear as a virtual organization to clients, but is composed of independently owned and operated small business entities. • Who knows? Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 3 -31
Pessimistic View Suppose economic downturn proves too much for Flex. Time and it is forced to reconfigure into a shadow of former self • No longer a single business entity. Maybe it becomes a federation of trainers, workout spaces, dieticians, and recreational sports leagues. • Federation uses free data storage, data communication, and emerging collaboration tools and systems to appear as a virtual organization to clients, but is composed of independently owned and operated small business entities. • Who knows? Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 3 -31
 Guide: Limiting Access to Those Who Have Access Digital divide segregates “haves” and “have-nots” Using the Internet is a matter of access to knowledge Advantages accrue to those who have easy access Digital divide between those who have Internet access and those who don’t • Divide deepens education, income, social differences • Internet access might be available at public places, but: Ø Not everyone served Ø Not as convenient as home access Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 3 -32
Guide: Limiting Access to Those Who Have Access Digital divide segregates “haves” and “have-nots” Using the Internet is a matter of access to knowledge Advantages accrue to those who have easy access Digital divide between those who have Internet access and those who don’t • Divide deepens education, income, social differences • Internet access might be available at public places, but: Ø Not everyone served Ø Not as convenient as home access Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 3 -32
 Benefits of Access Intellectual capital resides on Internet readily available Benefits for businesses • Cheaper product customer support • Reduces warehousing costs • Reduces mailings costs Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 3 -33
Benefits of Access Intellectual capital resides on Internet readily available Benefits for businesses • Cheaper product customer support • Reduces warehousing costs • Reduces mailings costs Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 3 -33
 Issues to Think About What groups of people in the United States are not connected to the Internet? Does it make sense for benefactors, such as Bill and Melinda Gates, to provide access to those in poverty? What keeps the elderly from accessing the Internet? Should the government help the elderly? What could be done to provide Internet access for the poorly educated? What role, if any, could local governments have? State? Federal? United Nations? Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 3 -34
Issues to Think About What groups of people in the United States are not connected to the Internet? Does it make sense for benefactors, such as Bill and Melinda Gates, to provide access to those in poverty? What keeps the elderly from accessing the Internet? Should the government help the elderly? What could be done to provide Internet access for the poorly educated? What role, if any, could local governments have? State? Federal? United Nations? Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 3 -34
 Issues to Think About If you are from outside the United States, what is the connectivity situation in your country? Is there a digital divide there? Are some countries more behind in connectivity trends than others? What does this mean for their ability to compete? What does this mean for citizens of those countries? Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 3 -35
Issues to Think About If you are from outside the United States, what is the connectivity situation in your country? Is there a digital divide there? Are some countries more behind in connectivity trends than others? What does this mean for their ability to compete? What does this mean for citizens of those countries? Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 3 -35
 Take Away from Guide Knowledge grows exponentially—just like capital Digital divide can create or worsen social problems Businesses and government should explore their responsibilities with respect to the digital divide Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 3 -36
Take Away from Guide Knowledge grows exponentially—just like capital Digital divide can create or worsen social problems Businesses and government should explore their responsibilities with respect to the digital divide Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 3 -36
 Guide: Your Personal Competitive Advantage Who will be your competitors when you seek a job after you graduate from college? What will be your competitive advantage in the job market? What can you do before you graduate to develop your competitive advantage? Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 3 -37
Guide: Your Personal Competitive Advantage Who will be your competitors when you seek a job after you graduate from college? What will be your competitive advantage in the job market? What can you do before you graduate to develop your competitive advantage? Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 3 -37
 Guide: Your Personal Competitive Advantage (cont’d) How could these concepts help you get and keep a job? • Switching costs? • Differentiating products? • Creating barriers? • Establishing alliances? • Reducing costs, increasing revenues? Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 3 -38
Guide: Your Personal Competitive Advantage (cont’d) How could these concepts help you get and keep a job? • Switching costs? • Differentiating products? • Creating barriers? • Establishing alliances? • Reducing costs, increasing revenues? Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 3 -38


