f37437e40c6ae6ebcce70046d02b6468.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 54
 Using LEAN Techniques to Improve Office Flow and Efficiency Lucy Loomis MD MSPH Morris Askenazi MD STFM & AAFP Conference on Practice Improvement. Savannah, GA December 6, 2008
Using LEAN Techniques to Improve Office Flow and Efficiency Lucy Loomis MD MSPH Morris Askenazi MD STFM & AAFP Conference on Practice Improvement. Savannah, GA December 6, 2008
 Presentation Objectives n Overview: • Denver Health & Hospitals • ‘Lean’ framework for redesign n Lean Tools Results/Lessons Learned at DH n Lean Activity n Glossary and Handout n December 6, 2008
Presentation Objectives n Overview: • Denver Health & Hospitals • ‘Lean’ framework for redesign n Lean Tools Results/Lessons Learned at DH n Lean Activity n Glossary and Handout n December 6, 2008
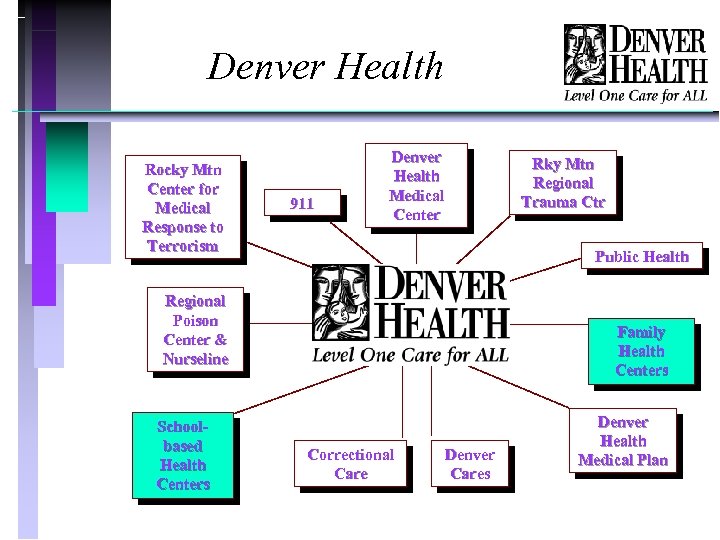 Denver Health Rocky Mtn Center for Medical Response to Terrorism 911 Denver Health Medical Center Public Health Regional Poison Center & Nurseline Schoolbased Health Centers Rky Mtn Regional Trauma Ctr Family Health Centers Correctional Care Denver Cares Denver Health Medical Plan
Denver Health Rocky Mtn Center for Medical Response to Terrorism 911 Denver Health Medical Center Public Health Regional Poison Center & Nurseline Schoolbased Health Centers Rky Mtn Regional Trauma Ctr Family Health Centers Correctional Care Denver Cares Denver Health Medical Plan
 Denver Community Health Services (DCHS) n n Network of 8 Community Health Centers, 12 School-based Health Centers and 2 Urgent Care Centers Underserved population: 42% uninsured, balance primarily Medicaid and Medicare Clinics include all primary care disciplines, dental services and OB/GYN specialty services Resident training in all services but not all sites
Denver Community Health Services (DCHS) n n Network of 8 Community Health Centers, 12 School-based Health Centers and 2 Urgent Care Centers Underserved population: 42% uninsured, balance primarily Medicaid and Medicare Clinics include all primary care disciplines, dental services and OB/GYN specialty services Resident training in all services but not all sites
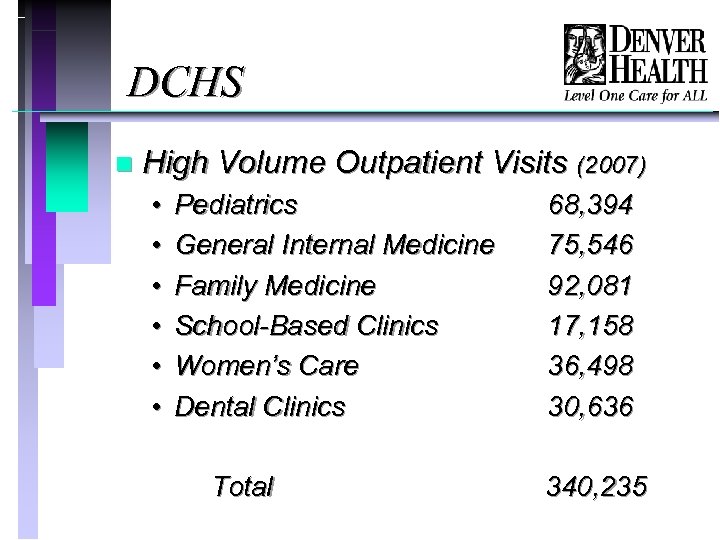 DCHS n High Volume Outpatient Visits (2007) • • • Pediatrics General Internal Medicine Family Medicine School-Based Clinics Women’s Care Dental Clinics Total 68, 394 75, 546 92, 081 17, 158 36, 498 30, 636 340, 235
DCHS n High Volume Outpatient Visits (2007) • • • Pediatrics General Internal Medicine Family Medicine School-Based Clinics Women’s Care Dental Clinics Total 68, 394 75, 546 92, 081 17, 158 36, 498 30, 636 340, 235
 Clinical Office Redesign at DCHS n Advanced Access (Open Access): 2001 • Dramatic drop in no show rates, and nurse time on triage • Decrease in overbooking improved flow and cycle time n n Advanced Access only one component of office redesign, to sustain gains need to address clinic efficiency Barriers to improving efficiency: • Competing demands (tyranny of the urgent) • Lack of tools for change • Classical PDSA process: – Difficult to apply to complex processes • When only meet monthly, change take too long, and team members lose focus December 6, 2008
Clinical Office Redesign at DCHS n Advanced Access (Open Access): 2001 • Dramatic drop in no show rates, and nurse time on triage • Decrease in overbooking improved flow and cycle time n n Advanced Access only one component of office redesign, to sustain gains need to address clinic efficiency Barriers to improving efficiency: • Competing demands (tyranny of the urgent) • Lack of tools for change • Classical PDSA process: – Difficult to apply to complex processes • When only meet monthly, change take too long, and team members lose focus December 6, 2008
 LEAN: Background n n Based on the Toyota Corporation efforts to eliminate waste Continuous Improvement to achieve improvement in the process • There is no end to this continued improvements n “At Toyota we get brilliant results from average people managing a brilliant process. Others get average results from brilliant people managing broken processes. ” Source: Toyota Motor Co. December 6, 2008
LEAN: Background n n Based on the Toyota Corporation efforts to eliminate waste Continuous Improvement to achieve improvement in the process • There is no end to this continued improvements n “At Toyota we get brilliant results from average people managing a brilliant process. Others get average results from brilliant people managing broken processes. ” Source: Toyota Motor Co. December 6, 2008
 Toyota Production System Approach to Production • Build only what is needed • Stop if something goes wrong • Eliminate anything which does not add value n n Philosophy of Work • Respect for Workers • Full utilization of workers’ capabilities • Entrust workers with responsibility & authority Taiichi Ohno
Toyota Production System Approach to Production • Build only what is needed • Stop if something goes wrong • Eliminate anything which does not add value n n Philosophy of Work • Respect for Workers • Full utilization of workers’ capabilities • Entrust workers with responsibility & authority Taiichi Ohno
 Right Process n Why did Denver Health chose Lean? • A philosophy, set of principles and a tool set • Philosophy fits for health care • Tool set is intuitive • Meaningful employee engagement • Initial rapid results • Power to change culture
Right Process n Why did Denver Health chose Lean? • A philosophy, set of principles and a tool set • Philosophy fits for health care • Tool set is intuitive • Meaningful employee engagement • Initial rapid results • Power to change culture
 Denver Health Steps in Lean n Consulted with Simpler • “Sensei's” n Formed the Lean Systems Improvement department in May 2006 • Senior Lean Facilitator • 7 Lean Facilitators n Trained Denver Health Staff • Executive Staff and Directors of Service: Lean 101 • Mid-managers: Lean Overview • 131 “Black Belts”: The Fundamental of Lean December 6, 2008
Denver Health Steps in Lean n Consulted with Simpler • “Sensei's” n Formed the Lean Systems Improvement department in May 2006 • Senior Lean Facilitator • 7 Lean Facilitators n Trained Denver Health Staff • Executive Staff and Directors of Service: Lean 101 • Mid-managers: Lean Overview • 131 “Black Belts”: The Fundamental of Lean December 6, 2008
 How DH implements these principles n n No downsizing of staff Staff not expected to work faster or harder Focus on process – and understanding root causes Beware of the CAVE people • (Citizens Against Virtually Everything) December 6, 2008
How DH implements these principles n n No downsizing of staff Staff not expected to work faster or harder Focus on process – and understanding root causes Beware of the CAVE people • (Citizens Against Virtually Everything) December 6, 2008
 Core Concepts of Lean n n n n Create continuous process flow to bring problems to the surface Use “pull” to avoid overproduction Level out the workload (hejunka) Get quality right the first time Standardize tasks Use visual controls so no problems are hidden Use only reliable, thoroughly tested technology that serves your people and processes In pursuit of perfection
Core Concepts of Lean n n n n Create continuous process flow to bring problems to the surface Use “pull” to avoid overproduction Level out the workload (hejunka) Get quality right the first time Standardize tasks Use visual controls so no problems are hidden Use only reliable, thoroughly tested technology that serves your people and processes In pursuit of perfection
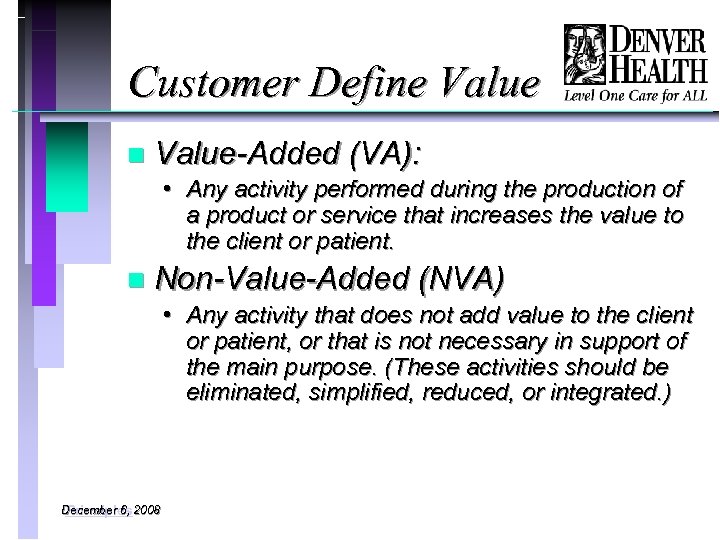 Customer Define Value n Value-Added (VA): • Any activity performed during the production of a product or service that increases the value to the client or patient. n Non-Value-Added (NVA) • Any activity that does not add value to the client or patient, or that is not necessary in support of the main purpose. (These activities should be eliminated, simplified, reduced, or integrated. ) December 6, 2008 Principles
Customer Define Value n Value-Added (VA): • Any activity performed during the production of a product or service that increases the value to the client or patient. n Non-Value-Added (NVA) • Any activity that does not add value to the client or patient, or that is not necessary in support of the main purpose. (These activities should be eliminated, simplified, reduced, or integrated. ) December 6, 2008 Principles
 Sample Lean Event Tools n Waste Walk n Rapid Improvement Events (RIE) n 5 S n Process Mapping December 6, 2008
Sample Lean Event Tools n Waste Walk n Rapid Improvement Events (RIE) n 5 S n Process Mapping December 6, 2008
 Waste n Waste is disrespectful of humanity • - Because it squanders scarce resources n Waste is disrespectful of individuals • - Because it asks them to do work with no value - President Toyota n Waste is disrespectful to patients • - By asking them to endure processes with no value December 6, 2008
Waste n Waste is disrespectful of humanity • - Because it squanders scarce resources n Waste is disrespectful of individuals • - Because it asks them to do work with no value - President Toyota n Waste is disrespectful to patients • - By asking them to endure processes with no value December 6, 2008
 Waste Walk (U-WIT-D-MOP) A process to critically look at a process and eliminate waste. A waste is any process or operation that does not add value. n n Unused Human Talent- Under utilizing people’s knowledge and skills Waiting- idle time (when no value is added to service or product) Inventory- unnecessary materials and work in process Transportation-handling more than once, delays in moving, unnecessary moving or handling December 6, 2008
Waste Walk (U-WIT-D-MOP) A process to critically look at a process and eliminate waste. A waste is any process or operation that does not add value. n n Unused Human Talent- Under utilizing people’s knowledge and skills Waiting- idle time (when no value is added to service or product) Inventory- unnecessary materials and work in process Transportation-handling more than once, delays in moving, unnecessary moving or handling December 6, 2008
 Waste Walk (U-WIT-D-MOP) n n Defects-equipment that does not work properly, errors in procedures Motion-movement of people or equipment that adds no value Overproduction- early production and producing unordered services and goods Processing-unnecessary processing or procedures that do not add value, such as duplicate orders of xrays or lab tests December 6, 2008
Waste Walk (U-WIT-D-MOP) n n Defects-equipment that does not work properly, errors in procedures Motion-movement of people or equipment that adds no value Overproduction- early production and producing unordered services and goods Processing-unnecessary processing or procedures that do not add value, such as duplicate orders of xrays or lab tests December 6, 2008
 Rapid Improvement Event (RIE) n n n Goal: Generate ideas for improvements and test changes at the work site Typically 4 days and report out event Appropriate scope Prework and data gathering key Cross-functional team (8 -10) • • • Black Belt team leader Process owner 1/3 fresh eyes 1/3 Lean experience 1/3 team doing the work
Rapid Improvement Event (RIE) n n n Goal: Generate ideas for improvements and test changes at the work site Typically 4 days and report out event Appropriate scope Prework and data gathering key Cross-functional team (8 -10) • • • Black Belt team leader Process owner 1/3 fresh eyes 1/3 Lean experience 1/3 team doing the work
 RIE – Rapid Improvement Event Day 1 n n Day 2 n Day 3 n n n Day 4 n Examine a process/function or area Identify areas of waste, non-customer value and metrics Develop new process, standard work and communication to eliminate identified waste and increase value Implement the new processes, standard work Monitor production board and communicate standards Observe new process and any change in metrics Adjust and fine tune new standards
RIE – Rapid Improvement Event Day 1 n n Day 2 n Day 3 n n n Day 4 n Examine a process/function or area Identify areas of waste, non-customer value and metrics Develop new process, standard work and communication to eliminate identified waste and increase value Implement the new processes, standard work Monitor production board and communicate standards Observe new process and any change in metrics Adjust and fine tune new standards
 RIE Day 4 December 6, 2008
RIE Day 4 December 6, 2008
 Transformational Learning n n 174 Total Rapid Improvement Events 749 Employees on teams 383 Employees involved 900 Total Employees Engaged/Involved December 6, 2008
Transformational Learning n n 174 Total Rapid Improvement Events 749 Employees on teams 383 Employees involved 900 Total Employees Engaged/Involved December 6, 2008
 5 S Typically 1 day initial events n Engage an entire team / site n Support visual controls and flow n Not a “spring cleaning” n • Not a one time event • Relevant to “us and our process” • Measures
5 S Typically 1 day initial events n Engage an entire team / site n Support visual controls and flow n Not a “spring cleaning” n • Not a one time event • Relevant to “us and our process” • Measures
 5 S Sort (does it belong here) n Set in Order (organize) n Shine (clean) n Standardize (repetition process) n Sustain (metrics posted, accountability) n (Safety): Sometimes the 6 th “S” n
5 S Sort (does it belong here) n Set in Order (organize) n Shine (clean) n Standardize (repetition process) n Sustain (metrics posted, accountability) n (Safety): Sometimes the 6 th “S” n
 Exam Rooms - Before
Exam Rooms - Before
 Exam Rooms - After
Exam Rooms - After
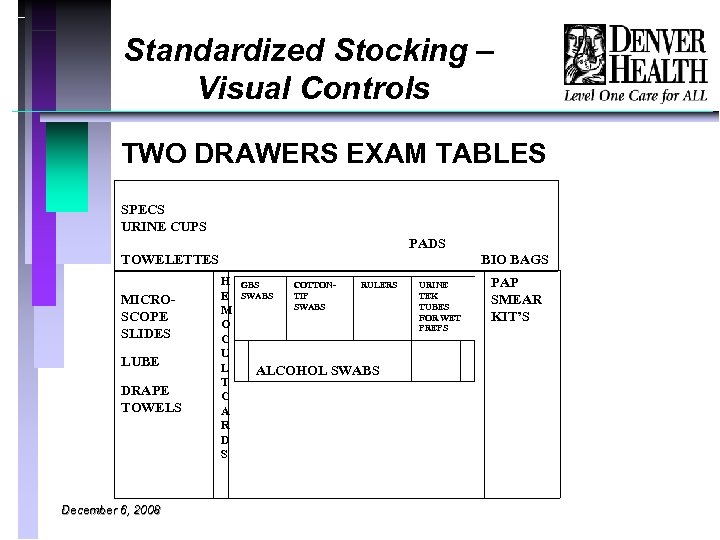 Standardized Stocking – Visual Controls TWO DRAWERS EXAM TABLES SPECS URINE CUPS PADS TOWELETTES MICROSCOPE SLIDES LUBE DRAPE TOWELS December 6, 2008 BIO BAGS H GBS COTTONRULERS TIP E SWABS M O C U L ALCOHOL SWABS T C A R D S PAP SMEAR KIT’S URINE TEK TUBES FOR WET PREPS
Standardized Stocking – Visual Controls TWO DRAWERS EXAM TABLES SPECS URINE CUPS PADS TOWELETTES MICROSCOPE SLIDES LUBE DRAPE TOWELS December 6, 2008 BIO BAGS H GBS COTTONRULERS TIP E SWABS M O C U L ALCOHOL SWABS T C A R D S PAP SMEAR KIT’S URINE TEK TUBES FOR WET PREPS
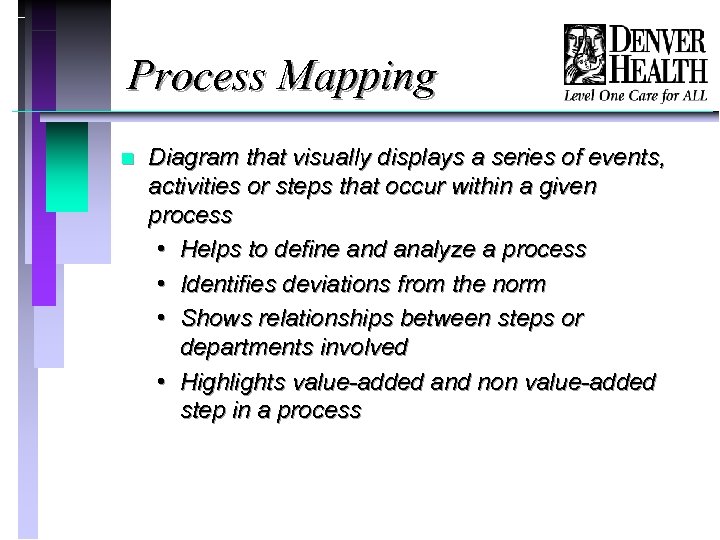 Process Mapping n Diagram that visually displays a series of events, activities or steps that occur within a given process • Helps to define and analyze a process • Identifies deviations from the norm • Shows relationships between steps or departments involved • Highlights value-added and non value-added step in a process
Process Mapping n Diagram that visually displays a series of events, activities or steps that occur within a given process • Helps to define and analyze a process • Identifies deviations from the norm • Shows relationships between steps or departments involved • Highlights value-added and non value-added step in a process
 Process Mapping Yellow notes: steps in the process Pink notes: identify opportunities for improvement
Process Mapping Yellow notes: steps in the process Pink notes: identify opportunities for improvement
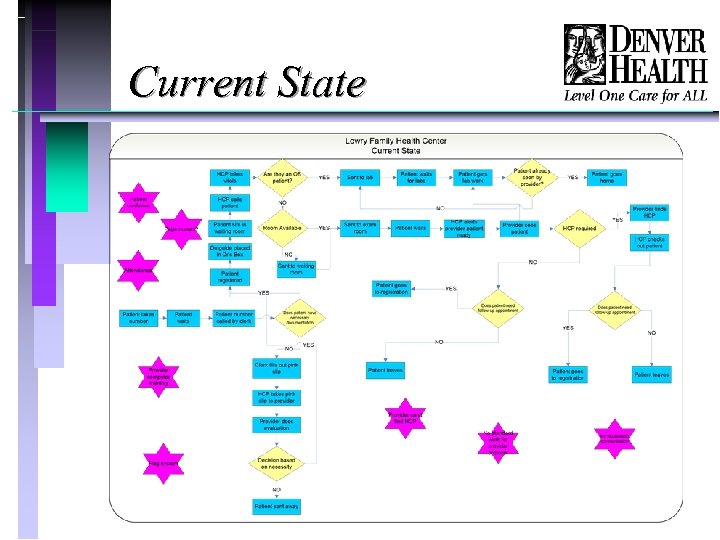 Current State
Current State
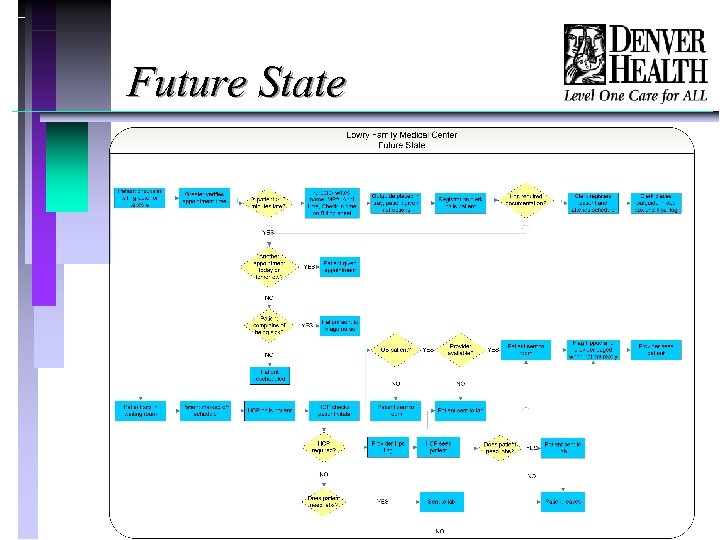 Future State
Future State
 Applying Lean to Clinic Flow n Define the Value Stream • Clinic Flow Initial definition: Registration through the end of visit n Determine desired improvements (Metrics) • Decrease patient cycle time – (Drop non-value added time by 50%) • Increase clinical productivity by 15% • Increase users per FTE by 5% • Improve outcomes in selected chronic disease and prevention indicators • Improve staff satisfaction December 6, 2008
Applying Lean to Clinic Flow n Define the Value Stream • Clinic Flow Initial definition: Registration through the end of visit n Determine desired improvements (Metrics) • Decrease patient cycle time – (Drop non-value added time by 50%) • Increase clinical productivity by 15% • Increase users per FTE by 5% • Improve outcomes in selected chronic disease and prevention indicators • Improve staff satisfaction December 6, 2008
 Clinic Flow Value Stream High Level Mapping of the Value Stream (2 -3 day event) n Identify wastes (non-value added activity) • • • n n Uneven Flow Many types of clinics all operating differently Variations in processes even in similar clinics Poor use of skills of staff involved Limited value-added time for patients Develop plans to address the identified wastes, using the appropriate lean tools. Collect baseline metrics December 6, 2008
Clinic Flow Value Stream High Level Mapping of the Value Stream (2 -3 day event) n Identify wastes (non-value added activity) • • • n n Uneven Flow Many types of clinics all operating differently Variations in processes even in similar clinics Poor use of skills of staff involved Limited value-added time for patients Develop plans to address the identified wastes, using the appropriate lean tools. Collect baseline metrics December 6, 2008
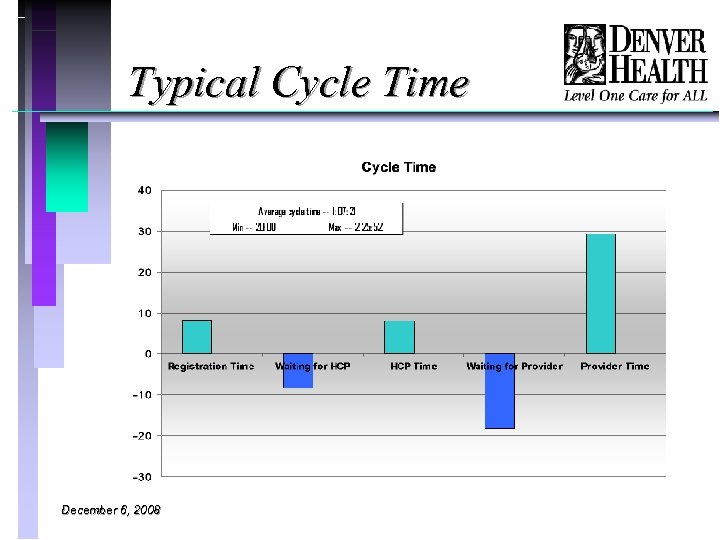 Typical Cycle Time December 6, 2008
Typical Cycle Time December 6, 2008
 Clinic Flow RIE’s n 2006: • Clinic Flow: (8 sites) – Increase visits per session, reduce cycle time • Appointment scheduling efficiency – Decrease abandoned call rates • Provider-MA flow cell (3 sites) – Improve cycle time, standardize dyad process n 2007 • Registration (1 site) • Desk Top Management (3 sites) – Streamline panel management tasks • New patient sorting – Process to direct new patients to closest clinic with capacity • Lab flow and follow-up • 3 P: Flow mapping for design on a new facility. December 6, 2008
Clinic Flow RIE’s n 2006: • Clinic Flow: (8 sites) – Increase visits per session, reduce cycle time • Appointment scheduling efficiency – Decrease abandoned call rates • Provider-MA flow cell (3 sites) – Improve cycle time, standardize dyad process n 2007 • Registration (1 site) • Desk Top Management (3 sites) – Streamline panel management tasks • New patient sorting – Process to direct new patients to closest clinic with capacity • Lab flow and follow-up • 3 P: Flow mapping for design on a new facility. December 6, 2008
 Clinic Flow RIE’s n 2008: • Centralized medication refill process • Clinic flow revisited(3 sites) – Focus on implementing new processes in pediatric care, and defining what MA and RN roles in panel management. • Forms management • Telephone visits (pilot project only) n Quality Improvement RIE’s • Diabetes care • Cancer screening • Anticoagulation December 6, 2008
Clinic Flow RIE’s n 2008: • Centralized medication refill process • Clinic flow revisited(3 sites) – Focus on implementing new processes in pediatric care, and defining what MA and RN roles in panel management. • Forms management • Telephone visits (pilot project only) n Quality Improvement RIE’s • Diabetes care • Cancer screening • Anticoagulation December 6, 2008
 Clinic Flow Focus Areas n Patient flow • Registration, check in, rooming Provider-MA dyad function n Desk Top (or Panel) Management (DTM) n • Follow up, medication refills, forms and phone calls. December 6, 2008
Clinic Flow Focus Areas n Patient flow • Registration, check in, rooming Provider-MA dyad function n Desk Top (or Panel) Management (DTM) n • Follow up, medication refills, forms and phone calls. December 6, 2008
 Clinic Flow: Common Wastes n Patient Flow • • • n Late starts Frequent interruptions for providers Wasted motion Uneven patient flow High no show rates Dyading • Staff not working at highest skill level • Lack of standard work n Desk Top Management. • • December 6, 2008 Work not going to right person Delays in response to requests result in re-work Lack of clarity on standards for notification of patients Forms and requests often lost
Clinic Flow: Common Wastes n Patient Flow • • • n Late starts Frequent interruptions for providers Wasted motion Uneven patient flow High no show rates Dyading • Staff not working at highest skill level • Lack of standard work n Desk Top Management. • • December 6, 2008 Work not going to right person Delays in response to requests result in re-work Lack of clarity on standards for notification of patients Forms and requests often lost
 Clinic Flow: Process Changes n Late starts: affect flow throughout session • • n Clarified appointment time vs rooming time Staggered start times for staff Template changes to decrease front loading of schedules “Pull Systems” to notify provider when patients ready No shows or late patients • “Work in” procedures to fill open slots • Revised late and no show policies n Frequent interruptions for providers • Standardize room stocking • Assign “Doc of the day” n Wasted Motion: looking for people or stuff • Page staff when patients ready December 6, 2008 • Flags and standardized exit processes
Clinic Flow: Process Changes n Late starts: affect flow throughout session • • n Clarified appointment time vs rooming time Staggered start times for staff Template changes to decrease front loading of schedules “Pull Systems” to notify provider when patients ready No shows or late patients • “Work in” procedures to fill open slots • Revised late and no show policies n Frequent interruptions for providers • Standardize room stocking • Assign “Doc of the day” n Wasted Motion: looking for people or stuff • Page staff when patients ready December 6, 2008 • Flags and standardized exit processes
 Process Changes: Flags December 6, 2008
Process Changes: Flags December 6, 2008
 Provider-MA Dyad n • • • Wastes Identified Duplication of information gathering Wasted staff time looking for each other Excess patient movement, going from check in to waiting area and back to exam room n Process changes • Exam Room Check-in • In-room dyading: provider and MA in room together – Worked to improve cycle time in setting with high need for MA work (preventive care) December 6, 2008
Provider-MA Dyad n • • • Wastes Identified Duplication of information gathering Wasted staff time looking for each other Excess patient movement, going from check in to waiting area and back to exam room n Process changes • Exam Room Check-in • In-room dyading: provider and MA in room together – Worked to improve cycle time in setting with high need for MA work (preventive care) December 6, 2008
 Dyading: Process Changes Standardization of MA work n Standardized check in and check out protocols – Acute visits – Chronic care (planned visits) • • • Allow MA to give IZ’s before provider sees pts • n Ordering diabetic tests Performing foot exams (eg Cancer screening) Preventive care: – Immunization protocols: – Ordering tests n n December 6, 2008 Tracking follow-up Colocation of Provider and MA • (When possible, given clinic layout).
Dyading: Process Changes Standardization of MA work n Standardized check in and check out protocols – Acute visits – Chronic care (planned visits) • • • Allow MA to give IZ’s before provider sees pts • n Ordering diabetic tests Performing foot exams (eg Cancer screening) Preventive care: – Immunization protocols: – Ordering tests n n December 6, 2008 Tracking follow-up Colocation of Provider and MA • (When possible, given clinic layout).
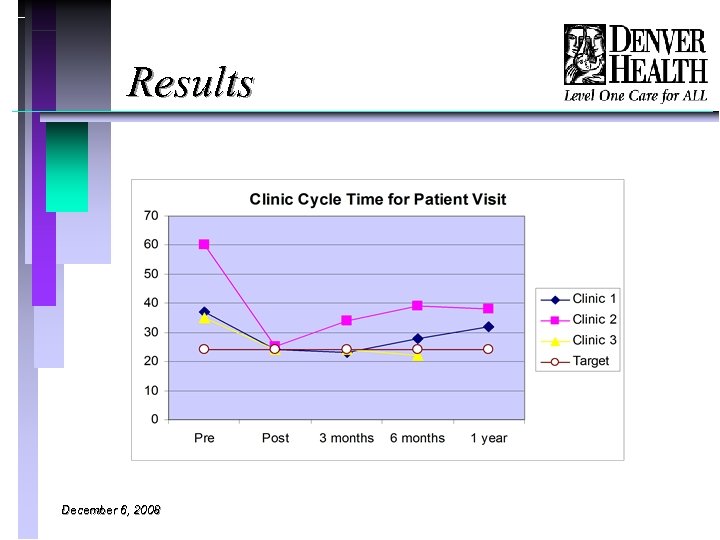 Results December 6, 2008
Results December 6, 2008
 Benefits of Dyading n Improved flow through: • • n n n Setting agenda for visit: keeping provider on time, Less time looking for each other MA assisting with orders concurrently Knocking on door periodically Improved working relationship between MA and provider MAs’ skills and ability to anticipate provider needs improved Patient identifies MA as part of team More preventive health care, as MA assists in tracking, ordering preventive measures Improved exam room readiness December 6, 2008
Benefits of Dyading n Improved flow through: • • n n n Setting agenda for visit: keeping provider on time, Less time looking for each other MA assisting with orders concurrently Knocking on door periodically Improved working relationship between MA and provider MAs’ skills and ability to anticipate provider needs improved Patient identifies MA as part of team More preventive health care, as MA assists in tracking, ordering preventive measures Improved exam room readiness December 6, 2008
 Desk Top Management: Process Changes n Medication Refill requests • Developed protocols for RN’s to authorize med refill requests • Standard scripting for med refills: – Patients directed to pharmacies to send fax requests • Narcotic refill processes improved n n Developed cross coverage policies for part time provider staff: For refills and follow-up Improved utilization of staff capabilities: Right work to right person • Clerical staff assigned to clinical area to help with paperwork. • Forms management: improved turnaround by flagging forms, and delegating form completion to support staff. • Developed Processes to assign patients to appropriate level provider (MD, Midlevel, RN) n Developed standard message to patients regarding lab follow -up and med refill process December 6, 2008
Desk Top Management: Process Changes n Medication Refill requests • Developed protocols for RN’s to authorize med refill requests • Standard scripting for med refills: – Patients directed to pharmacies to send fax requests • Narcotic refill processes improved n n Developed cross coverage policies for part time provider staff: For refills and follow-up Improved utilization of staff capabilities: Right work to right person • Clerical staff assigned to clinical area to help with paperwork. • Forms management: improved turnaround by flagging forms, and delegating form completion to support staff. • Developed Processes to assign patients to appropriate level provider (MD, Midlevel, RN) n Developed standard message to patients regarding lab follow -up and med refill process December 6, 2008
 Desk Top Management: Challenges n n n Limitations of EMR make documentation of lab review and follow-up time consuming Staff are not ‘paid’ or credited for DTM work, so harder to measure the benefits of improving it. Much of the DTM work generated from processes outside of clinical control – IS issues – Standardized system requirements – EMR limitations December 6, 2008
Desk Top Management: Challenges n n n Limitations of EMR make documentation of lab review and follow-up time consuming Staff are not ‘paid’ or credited for DTM work, so harder to measure the benefits of improving it. Much of the DTM work generated from processes outside of clinical control – IS issues – Standardized system requirements – EMR limitations December 6, 2008
 Lean and Quality n n Improved quality is one of goals of all lean efforts Used lean techniques to address how we can improve processes of care management • Diabetes Care (Rapid Improvement Event) • Medication reconciliation (Project) • Lab follow-up • Cancer Screening: • Anticoagulation Management. December 6, 2008
Lean and Quality n n Improved quality is one of goals of all lean efforts Used lean techniques to address how we can improve processes of care management • Diabetes Care (Rapid Improvement Event) • Medication reconciliation (Project) • Lab follow-up • Cancer Screening: • Anticoagulation Management. December 6, 2008
 Lessons Learned n n n No magic bullets for clinic redesign Lean is one of many possible tools Advantages of lean: • • n Structure for analysis, focus on removing waste Customer centered focus on improving processes Great tool for sequential processes Imposes discipline to the process of improvement, with clearer expectations Need to increase input (ie templates) to start to see the productivity and access benefits of the changes. December 6, 2008
Lessons Learned n n n No magic bullets for clinic redesign Lean is one of many possible tools Advantages of lean: • • n Structure for analysis, focus on removing waste Customer centered focus on improving processes Great tool for sequential processes Imposes discipline to the process of improvement, with clearer expectations Need to increase input (ie templates) to start to see the productivity and access benefits of the changes. December 6, 2008
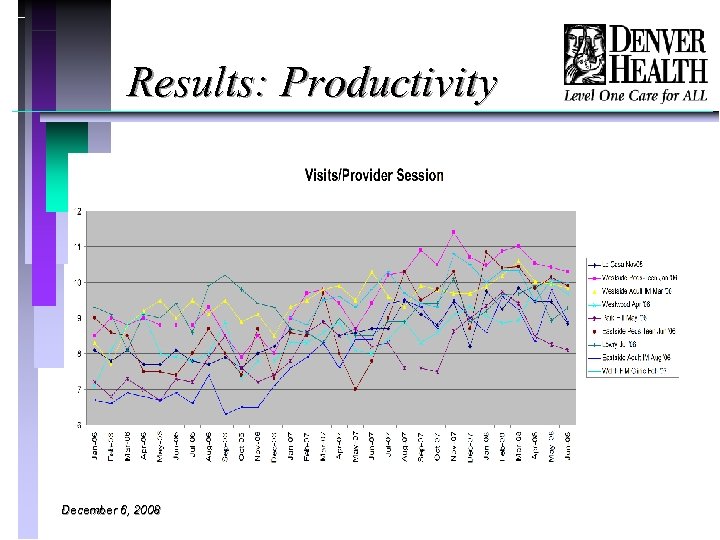 Results: Productivity December 6, 2008
Results: Productivity December 6, 2008
 Spread and Sustaining n n Challenge to spread to 21 separate teams Variations in culture of change across clinics • Resistance from teams to perceived outside intervention in their processes n n Need process to harvest “least waste ways”, and create a change package that can be adapted at a variety of sites. Keys to spread • Ongoing evaluation of changes • Communication strategy • Champion at each site to adopt and try new ways n Holding RIE’s at different sites helps speed adoption of the change packages December 6, 2008
Spread and Sustaining n n Challenge to spread to 21 separate teams Variations in culture of change across clinics • Resistance from teams to perceived outside intervention in their processes n n Need process to harvest “least waste ways”, and create a change package that can be adapted at a variety of sites. Keys to spread • Ongoing evaluation of changes • Communication strategy • Champion at each site to adopt and try new ways n Holding RIE’s at different sites helps speed adoption of the change packages December 6, 2008
 Ongoing Challenges n Team buy in for change • Resistance can occur if team perceives process as being externally driven. n Standardization vs. customization • To accommodate differences in staffing patterns, or patient populations n Meeting increasing demands for primary care December 6, 2008
Ongoing Challenges n Team buy in for change • Resistance can occur if team perceives process as being externally driven. n Standardization vs. customization • To accommodate differences in staffing patterns, or patient populations n Meeting increasing demands for primary care December 6, 2008
 Keys for Success n Institutional commitment to process • Leadership training in lean (black belts) • All black belts expected to use lean analysis in their regular work • In house facilitators to work with staff in each of the major value streams Multiple efforts simultaneously n Time for process improvement work n
Keys for Success n Institutional commitment to process • Leadership training in lean (black belts) • All black belts expected to use lean analysis in their regular work • In house facilitators to work with staff in each of the major value streams Multiple efforts simultaneously n Time for process improvement work n
 Further Reading n n n n Bibliography: Rother and Shook. (2003). Learning To See. Cambridge, MA: The Lean Enterprise Institute. Womack and Jones. (2003). Lean Thinking. Northampton, MA: Free Press. Kilpatrick. (2003) Lean Principles. Orem, Utah: Utah Manufacturing Extension Partnership. Poppendieck. (2002). Principles of Lean Thinking. Eden Prairie, MN: Poppendieck. LLC. Spear, (2004). Learning to Lead at Toyota. Boston, MA: Harvard Business Review. Miller, D. (Ed. ). (2005). Going Lean in Health Care. (Innovation Series 2005). Cambridge, MA: Institute for Healthcare Improvement. December 6, 2008
Further Reading n n n n Bibliography: Rother and Shook. (2003). Learning To See. Cambridge, MA: The Lean Enterprise Institute. Womack and Jones. (2003). Lean Thinking. Northampton, MA: Free Press. Kilpatrick. (2003) Lean Principles. Orem, Utah: Utah Manufacturing Extension Partnership. Poppendieck. (2002). Principles of Lean Thinking. Eden Prairie, MN: Poppendieck. LLC. Spear, (2004). Learning to Lead at Toyota. Boston, MA: Harvard Business Review. Miller, D. (Ed. ). (2005). Going Lean in Health Care. (Innovation Series 2005). Cambridge, MA: Institute for Healthcare Improvement. December 6, 2008
 Resources Lean Training Programs With Health Care Focus n n n Denver Health Medical Center/University of Denver/Simpler Healthcare Medical LEAN Institute http: //www. denverhealth. org/portal/Profession als/Lean. Institute/tabid/1716/Default. aspx Contact: Phil Goodman-Senior Lean Facilitator 777 Bannock St- Mail Code 8702 Denver, CO, 80204303 -602 -7032 pgoodman@dhha. org Lean Health. Care Services http: //www. leanhealthcareservices. com/leans cm_com/index. php Belmont University Massey Graduate School of Business Pittsburgh Regional Health Initiative The Lean Healthcare Certificate Program http: //www. buleancourse. com/ Traditional Lean in Manufacturing: Lean Enterprise Institute (Jim Womack et al) www. lean. org December 6, 2008 Lean Consultants: n Simpler Consulting Inc www. simpler. com Steve Matteson 339 -337 -5159 n GE Healthcare www. gehealthcare. com n gembutsu (manufacturing) info@gembutsu. com n HPK Group-Lean Healthcare Consultants http: //www. hpkgroupllc. com/leanhealthcare. ht ml
Resources Lean Training Programs With Health Care Focus n n n Denver Health Medical Center/University of Denver/Simpler Healthcare Medical LEAN Institute http: //www. denverhealth. org/portal/Profession als/Lean. Institute/tabid/1716/Default. aspx Contact: Phil Goodman-Senior Lean Facilitator 777 Bannock St- Mail Code 8702 Denver, CO, 80204303 -602 -7032 pgoodman@dhha. org Lean Health. Care Services http: //www. leanhealthcareservices. com/leans cm_com/index. php Belmont University Massey Graduate School of Business Pittsburgh Regional Health Initiative The Lean Healthcare Certificate Program http: //www. buleancourse. com/ Traditional Lean in Manufacturing: Lean Enterprise Institute (Jim Womack et al) www. lean. org December 6, 2008 Lean Consultants: n Simpler Consulting Inc www. simpler. com Steve Matteson 339 -337 -5159 n GE Healthcare www. gehealthcare. com n gembutsu (manufacturing) info@gembutsu. com n HPK Group-Lean Healthcare Consultants http: //www. hpkgroupllc. com/leanhealthcare. ht ml
 Questions?
Questions?


