b3516dabfe5ec3bdd88d877645447edc.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 59

Using IT as a Competitive Advantage By Marisa Anekratchadaporn Nolan Bayliss Bill Burgard Tony Mercadante

How can IT create a competitive advantage? Ø IT can differentiate a product or service. Ø IT can improve business processes. Ø IT can change a business structure. Ø IT can spawn new business. Source : Lecture and notes, Mary Lacity, 2002
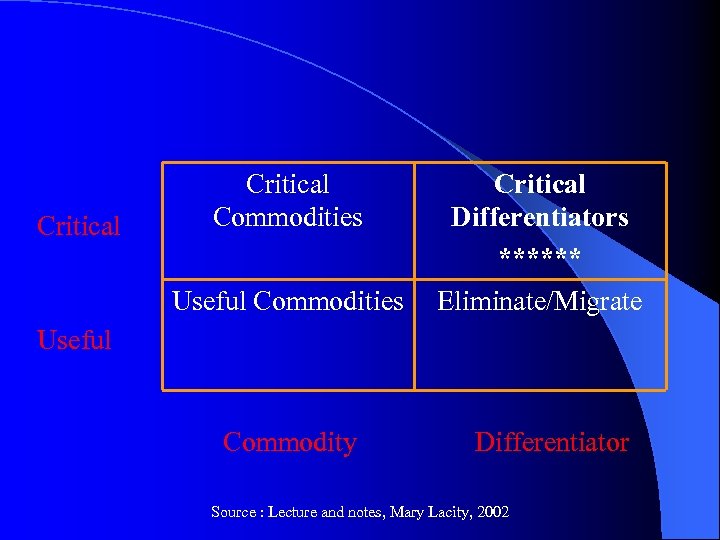
Critical Differentiators ****** Useful Commodities Critical Commodities Eliminate/Migrate Useful Commodity Differentiator Source : Lecture and notes, Mary Lacity, 2002

Outstanding case studies American Airlines – SABRE Bergen Brunswig Walmart
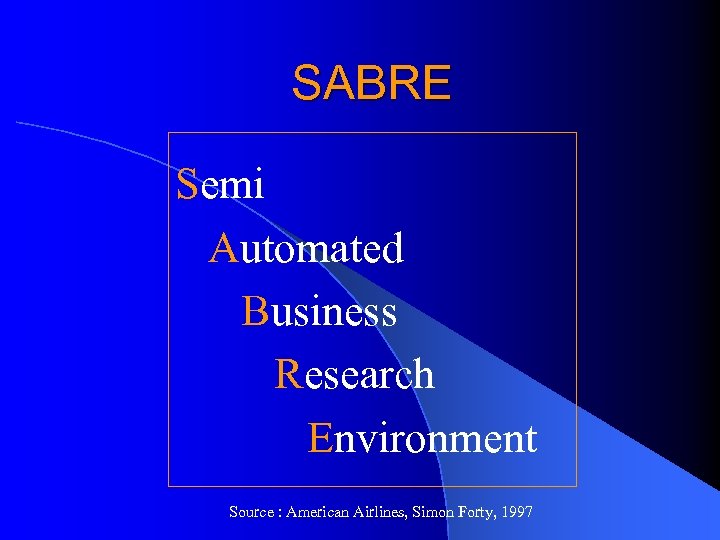
SABRE Semi Automated Business Research Environment Source : American Airlines, Simon Forty, 1997

SABRE : What is it? SABRE is a completely automatic , centralized , electronic airlines reservations system developed by IBM for American Airlines. Source : IBM Corporate Archives, New York

Overview v v v Size of company : $ 2. 1 billion revenue in 2001 Employee : Approximately 5, 500 employees in 45 countries Major Product : Airline ticket Customers : Travelers and Travel agents Headquartered : Southlake, Texas SABRE connects more than 59, 000 travel agents around the world, providing content from 450 airlines, 53, 000 hotels, 54 car rental companies, eight cruise lines, 33 railroads and 228 tour operators Source : www. sabre. com and Business and Company Resource Center, www. infotrac. galegroup. com
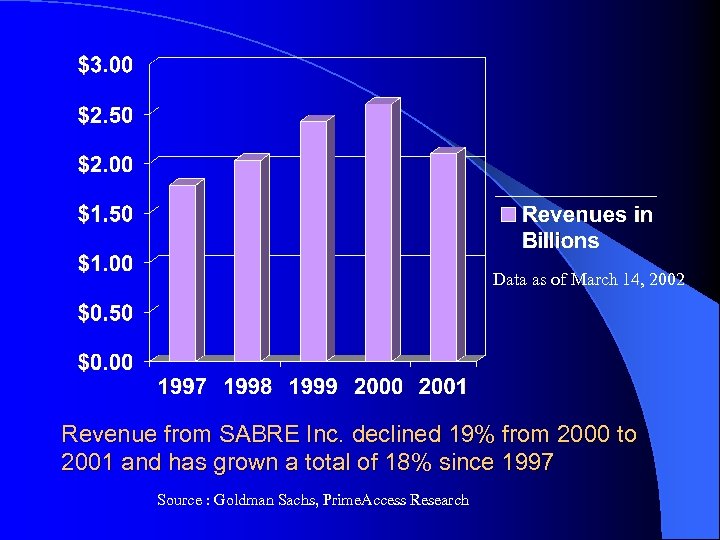
Data as of March 14, 2002 Revenue from SABRE Inc. declined 19% from 2000 to 2001 and has grown a total of 18% since 1997 Source : Goldman Sachs, Prime. Access Research
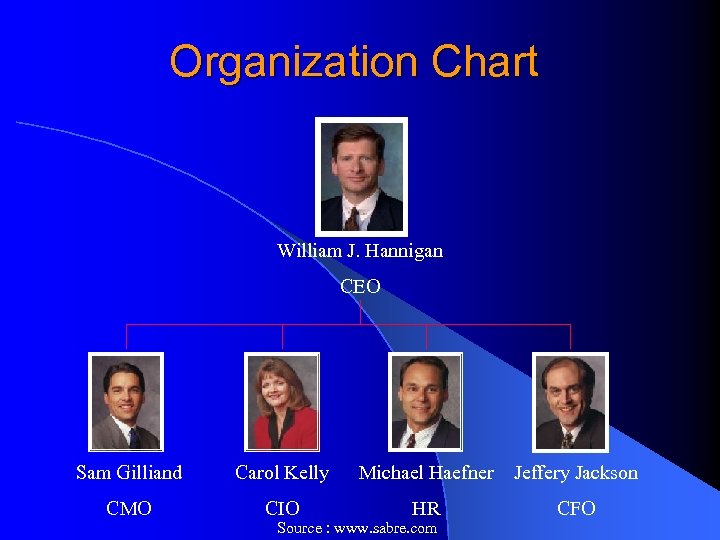
Organization Chart William J. Hannigan CEO Sam Gilliand Carol Kelly Michael Haefner Jeffery Jackson CMO CIO HR CFO Source : www. sabre. com

What prompted change? v Needed a system to regulate the flow of passengers due to the increasing number of people who want to travel by plane. v Lost millions of dollars due to the manual reservation system. Source : High Technology Business, Wheeler Helen, Boston, 1987 Historical Dictionary of Data Processing Technology p. 331 -332, James W. Cortada, New York

The History of “SABRE”

SABRE 1959 -1969 1959 1960 - American Airlines and IBM signed contract for the development of a communications-bases reservation system - The first SABRE system is installed. SABRE becomes one of the first of the large , online , realtime applications using computer developed in the United States.

SABRE 1959 -1969 1964 - SABRE system is complete. - The initial research, development and installation investment in this system took a 400 person staff and cost almost $40 million Source : Historical Dictionary of Data Processing Technology p. 331 -332, James W. Cortada, New York www. sabre. com

SABRE 1959 -1969 Initial startup success v Once the system was complete in 1964, AA saved 30% on its investments in staff alone. v Average time required to complete the processing of reservations transaction reduce from 45 minutes to 3 seconds. v Error rate reduce to less than 1% v Automatically reminds AA agents at various locations to advise their scheduled passengers of any changes affecting them.

SABRE 1959 -1969 Initial startup success 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. More airline seats will be available to the customers. Automatically advise agents to check on passengers who have not picked up their tickets within the time limit. Maintain and automatically process waiting lists of passengers desiring space on fully-booked flights. Automatically supply fare quotations for most flights. Automatically supply information on arrival and Source : IBM Corporate Archives, New York departure time for the current day’s flight. www. sabre. com The story of American Airlines, Serling Robert, New York, 1985

SABRE 1970 -1979 1975 - AA began marketing SABRE to travel agencies and airlines throughout the US. 1976 - The SABRE system is installed in a travel agency for the first time. Passengers can also ask for hotel reservations, car rentals, special meals etc. - 86% of the top 100 agency accounts located in highly competitive markets elect to use SABRE system. - United Airlines introduces their Apollo System. Source : Datacomm Advisor, Waltham, June 1976 www. sabre. com
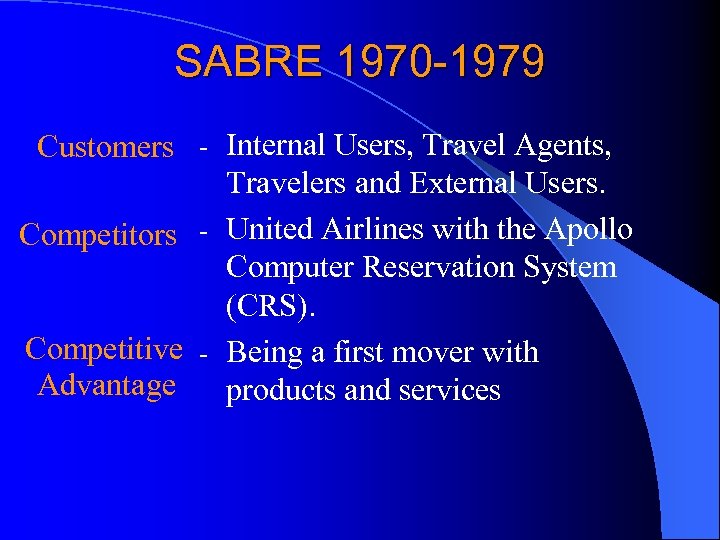
SABRE 1970 -1979 Customers - Internal Users, Travel Agents, Travelers and External Users. Competitors - United Airlines with the Apollo Computer Reservation System (CRS). Competitive - Being a first mover with Advantage products and services

SABRE 1980 -1989 1981 - - 1982 1985 1987 - SABRE had 41% of the market share & Apollo had 39%, started offering computer terminals to travel agents. Started to market a travel awards program AADVANTAGE Unveiled AAirpass with 5 year to lifetime options Reorganized to AMR Corporation 10, 000 travel agencies were now using SABRE AMR builds worlds largest private data base in Tulsa Ok. Source : Business Week, Transportation, August 1982 www. sabre. com

SABRE 1980 -1989 Customers - Internal Users, External Users, Travel Agents and Travelers. Competitors - Apollo, PARS (TWA) and Amadeus. Competitive - Being a first mover with Advantage products and services

SABRE 1990 -1999 1992 1995 1996 SABRE introduces SABRE Air. Flite a flight scheduling system - To prepare for Y 2 K, new software is sent to 40, 000 travel agents - SABRE becomes a separate legal entity of AMR followed by an IPO of 18 percent of its stock. - Travelocity. com is launched - Source : Air Transport World, Sabre Unleashed, Nov. 1996 www. sabre. com

SABRE 1990 -1999 Customers - External Users, Travel Agents and Travelers. - Apollo, Galileo (buys Apollo in Competitors 1993), Amadeus, Expedia. com (Microsoft) Competitive - Being a first mover with products and services Advantage

SABRE 2000 - Present SABRE acquires Get. There. com a B 2 B internet provider of travel services. 2. SABRE is completely spun off from AMR Corporation. 1. AMR spun off SABRE due to decrease in options Reasons “SABRE is guiding AMR and it should be the other way around”. 2. AMR looking for ways to expand profits. 3. Internet allows access to more people without travel agents. 4. AMR is to retain 25 leading developers 2000 1. Source : Air Transport World, AAdios to Sabre, Feb. 2000 www. sabre. com

SABRE 2000 - Present 2001 AMR now competes against SABRE with Orbitz. com 2. SABRE signs a long term contract with AMR 3. SABRE sells IT outsourcing business to EDS, SABRE will focus on software, distribution, travel marketing and reservation hosting 1. transfer 4, 200 employees to EDS 2. transfer 250 employees to AMR Corp. 3. Selling the Data Center“They obviously don’t view anything as a sacred cow” 1. Source : Computerworld, Sabre sells IT business to EDS, March, 2001

SABRE Summary - - American Airlines designed the system initially to be a competitive advantage to increase the number of reservations and reduce transaction errors Sold CRS to external vendors (first mover) Gave travel agents a terminal (first mover) Added services, travel, hotel, etc. (first mover) Added features – Eaasy. SABRE, SABRE Air. Flite (first mover) Added Travelocity. com (first mover)

SABRE’s Competitive Advantage - New products - Set the market and make change – prefer not to follow the competitors - Need continued change to keep customers - Customers like new ideas and “better” services - Update products & services - Add extra features to feel continued “value added”

BERGEN BRUNSWIG Pharmaceutical Distributor

Bergen Brunswig l Founded in 1969 from Lucien Brunswig’s Brunswig Drug Co in Los Angeles; merged with Emil Martini’s Bergen Drug Co. in New Jersey. l Today : now called Amerisource. Bergen as of 8/01 l 3 rd largest pharmaceutical distributor in the world. Source : bergenbrunswig. com

Company Officers Source : bergenbrunswig. com

IT Organization l CIO- Linda Burkett l 12, 200 Employees for entire corporation l 300 IT Employees l 1999 Annual IT Budget : $58 million Source : schwab. com/bergenbrunswig. com/Drug Store News 12/13/99 v 21 i 20 p 36.

Major Products Being Sold v Generic Pharmaceuticals v Pharmaceutical Services v Pharmaceutical Solutions Source : Bergenbrunswig. com

History of the System l 1995 Linda Burkett promoted to CIO. l 1996 Interlinx first implemented. l 1999 Interlinx evolved into COE (Catalog & Order Entry), when Bergen moved from a desktop application to the web. l Known to customers as IBERGEN. COM Source : Brooke Walton, Bergenbrunswig Marketing dept
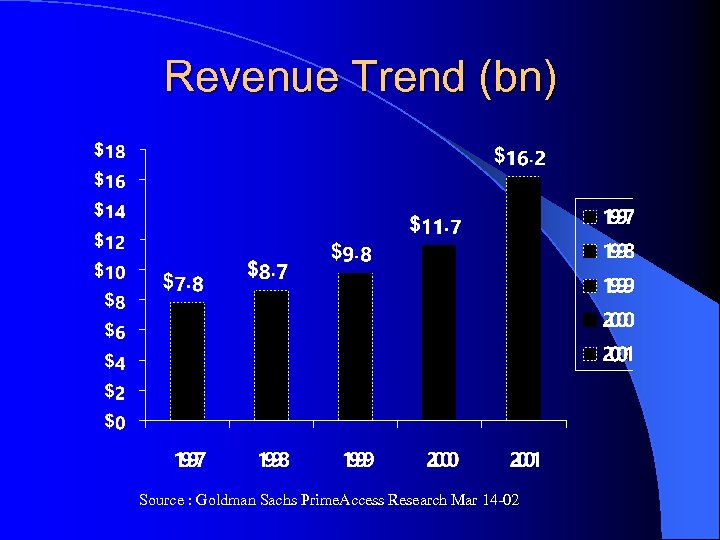
Revenue Trend (bn) Source : Goldman Sachs Prime. Access Research Mar 14 -02
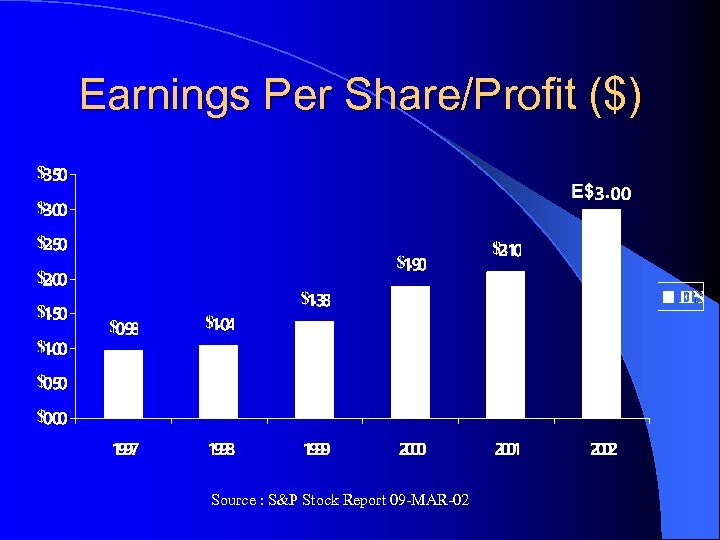
Earnings Per Share/Profit ($) Source : S&P Stock Report 09 -MAR-02
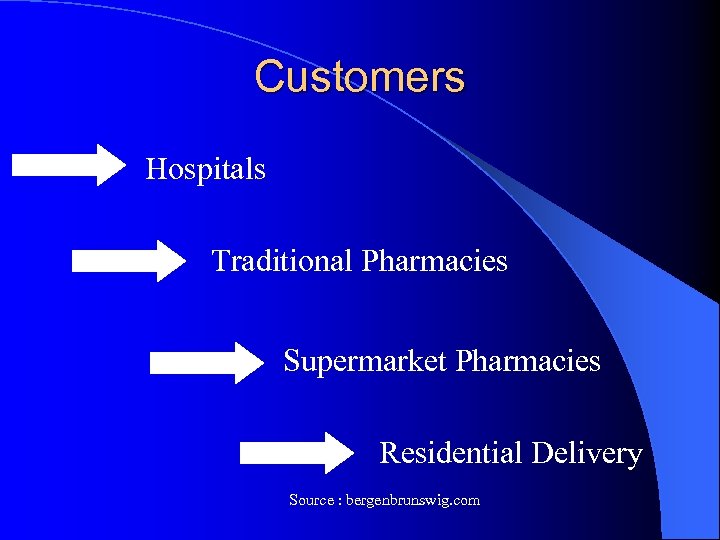
Customers Hospitals Traditional Pharmacies Supermarket Pharmacies Residential Delivery Source : bergenbrunswig. com

Customer Interaction l Orders placed through worldwide web. l Customers enter order, receive next day, sometimes same day. l Patients pickup prescription at pharmacy, store, hospital, or have home delivery.

Economic Forces on Bergen (1990 -present) l 1990 -1992 Recession l Clinton’s Healthcare Plan l Mergers/Acquisitions l FTC Antitrust concerns l 1990’s Price fixing lawsuits l FTC m&a approvals during G. W. Bush era l HMOs, third party payers’ lower payments Source : Drug Topics, Dec 13, 1993 v 137 n 23 p 102(3) ; Wall Street Journal

Critical Differentiator Rather than be acquired, Bergen Brunswig decided to invest in IT to lower costs/maximize profit; 1. 2. Build the best pharmaceutical distribution platform through inventory/regional distribution centers; 3. Moved from telephone ordering to desktop networks, and then onward to the worldwide web. 4. Sources : Brady, R. “The Strategic Use of Information : Seizing the Competitive Edge, ” Information Week May 26, 1986 pp 26 -62. Kettinger, William J. MIS Quarterly, Minneapolis; Mra 1994; Vol 18 Iss. 1; pg 31, 28 pgs

Key Features of a Successful System l l l l l Building relationships/Brand recognition. Mass of Force. Ability to grow leaps and bounds in a short time. Showing customers how Bergen can save them money which keeps customers in business for the long run. Investing in IT to compete in low margin environment. Fulfillment. Regional distribution centers. Competitive pricing. Same Day Service/Next day service (bulk shipments). Solid supplier agreements as well as 3 rd party carrier agreements. Source : Drug Store News, Dec 13, 1999 v 21 i 20 p 20
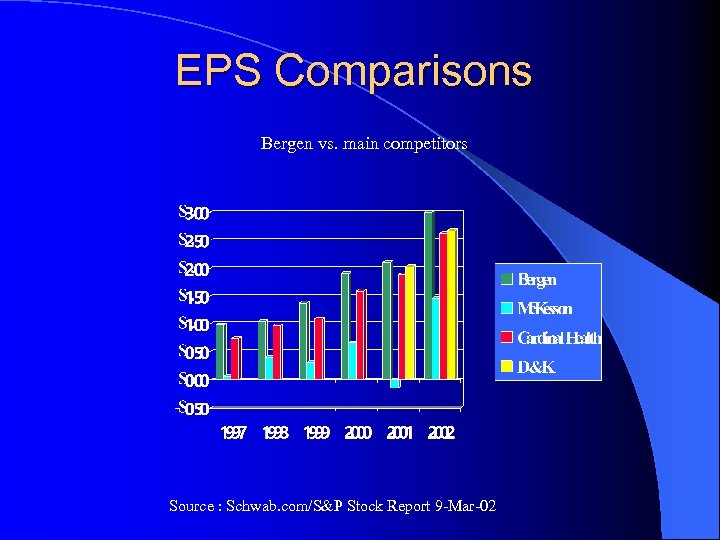
EPS Comparisons Bergen vs. main competitors Source : Schwab. com/S&P Stock Report 9 -Mar-02

Competitive Advantage System Designed for Competitive Advantage from the beginning to continue brand recognition and dominance while building solid long term relationships.

l Background Information l Financials l Customers/Suppliers/Competitors l IT Organization and Architecture l IT Strategic Advantage – EDI

Background l Founded by Sam Walton in 1962 l Company founded with first store in Rogers, AR l Headquarters: Bentonville, AR l 38 stores in 1970 l 4732 stores today http: //www. walmartstores. com/wmstores/Mainabout. jsp

Financials l $191 Billion in Sales in 2001 – Five Times that of AOL Time Warner l $8 billion in capital spending in 2001 – Market Expansion l Cash flow of $9. 8 billion – Up 17 % from 2000 (5)

Competitors/Suppliers l Competitors – Kmart – Sears – Target l Suppliers – P & G – Thousands of others (4)

IT Organization Most powerful computer system in the corporate world l Second largest data warehouse l Logistics Technology l – Retail Link. TM – Enormous Network Infrastructure CIO: Kevin Turner l $500 million IT budget l l . 26 % of Annual Sales Revenue (6)
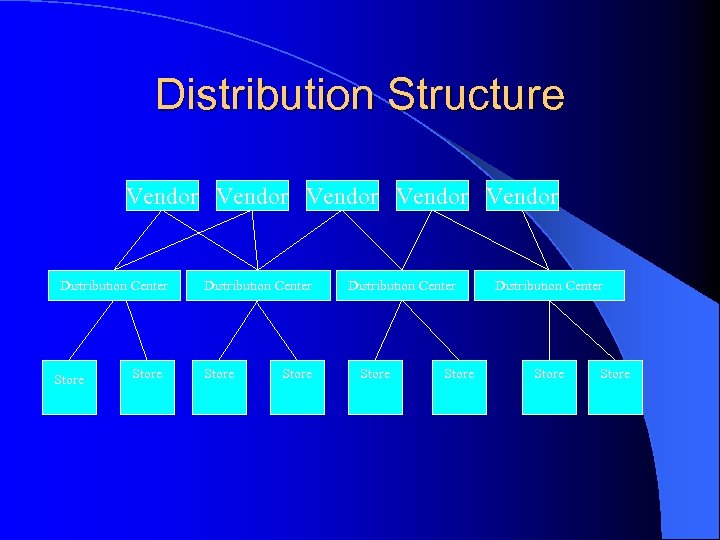
Distribution Structure Vendor Vendor Distribution Center Store Store

Distribution Structure • Supply Chain Management l Create superior efficiencies through SCM 1. Decentralize distribution through multiple distribution centers 2. Centralize management and control 3. Excellent coordination with multiple suppliers (4)(3)(2)
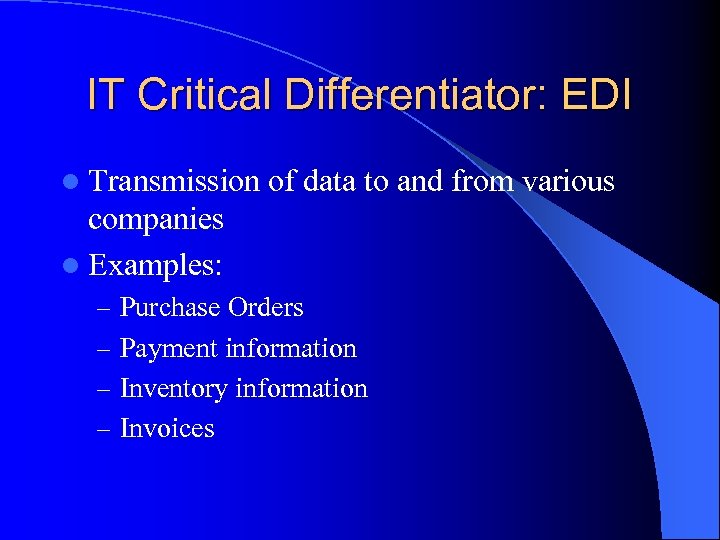
IT Critical Differentiator: EDI l Transmission of data to and from various companies l Examples: – Purchase Orders – Payment information – Inventory information – Invoices

WHY EDI? l Realized the complexity of their supply chain – Thousands of Stores, Suppliers and Products l Inventory management removed from store level l Also: – – Transaction Costs Paperless Environment Inventory Management Efficiencies JIT of Retail l “Everyday low price strategy” through up-to- date sales information (1)(4)

EDI • • How does it work? Through telephone line: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Item is purchased Computer Adjusts Inventory Need To Order Level reached Purchase Order sent to vendor Vendor replenishes and sends invoice Wal-Mart sends electronic funds transfer (2)(4)

Retail Link. Tm l Software that enhances EDI functionality l Provided to vendor in 1991 l Allows for much better forecasting and reporting abilities l Faster replenishment l Better communication between Wal-Mart and Vendors (1)(3)(5)

EDI and Retail Link. TM Today l No longer through telephone lines – Cisco Networking – Web Enabled l Most vendors now utilize Retail Link. Tm l Required enrollment: EDI (1)(2)

EDI l Critical Differentiator? YES – Has allowed for a 2 -3 percent reduction in costs – Allowed for increased vendor responsiveness – Resulted in Wal-Mart out pricing it’s competitors – Superior Customer Satification – Sales Revenues tell the story (3)(4)(5)
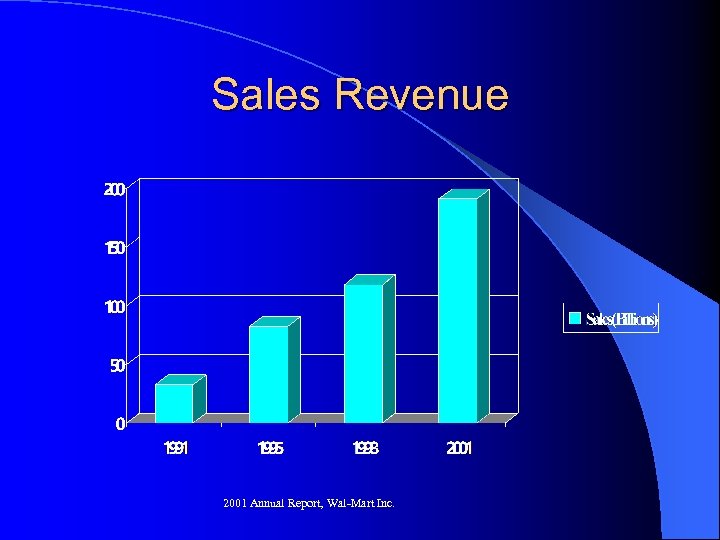
Sales Revenue 2001 Annual Report, Wal-Mart Inc.

EDI l Sustainable Differentiator? YES – Logistics System impossible to replicate – Most efficient infrastructure network – Continues to enhance traditional EDI – JIT? …. Close

References (1) Ehrens, J. Scott, Wal-Mart: Beyond Regional Merchandizing, Apr 1992, Pg. 1 -3 (2) Gilbert, A. , Retail’s Super Supply Chain, Informationweek, Oct, 2000, Pg. 1 -5 (3) www. cisco. com/warp/public/779/ibs/vertical/retail/Wal-Mart. PDF (4) Caldwell, B. , Wal-Mart Ups the Pace, Informationweek, Dec 9, 1996, Pg 1 -6 (5) Janoff, B. , High-tech Knowledge, Progressive Grocer, Dec 2000, Pg. 1 -5 (6) 2001 Annual Report, Wal-Mart Inc.

Best Practice: IT might need a large budget but also can yield a prosperous benefit for the company. Ø The competitive advantage always works for the company that willing to be an innovator. Ø IT needs to be improved all the time, otherwise the competitor can catch up and the competitive advantage will no longer exist. Ø

Best practice: Ø CIO who pay close attention to IT and has a good capability in managing IT will lead the company to success. Ø Only a few number of company can sustain their competitive advantage for a long time.

Why most companies cannot sustain their competitive advantage so long? Ø Lack of managing skill Ø Competitors Ø IT become obsolete
b3516dabfe5ec3bdd88d877645447edc.ppt