9f8317407f3ccc67eabd5424e3b0dad4.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 17
 Using Healthcare Analytics to Determine an Effective Diagnostic Model for Adult ADHD Diane Mitchnick, MSc. IS Athabasca University October 25, 2014
Using Healthcare Analytics to Determine an Effective Diagnostic Model for Adult ADHD Diane Mitchnick, MSc. IS Athabasca University October 25, 2014
 Introduction • ADHD – Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (causing inventiveness, hyperactivity, and impulsiveness) • Healthcare analytics used for physical diseases (brain cancer, diabetes, etc. ) [1] • Many tools do data mining (collect and filter data through single algorithm) [2] • Proposing a meta-analysis on existing adult ADHD screening tools to produce a more effective model from accuracy in the indicator data from these tools.
Introduction • ADHD – Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (causing inventiveness, hyperactivity, and impulsiveness) • Healthcare analytics used for physical diseases (brain cancer, diabetes, etc. ) [1] • Many tools do data mining (collect and filter data through single algorithm) [2] • Proposing a meta-analysis on existing adult ADHD screening tools to produce a more effective model from accuracy in the indicator data from these tools.
 Research Goal Current diagnostic tools for adult ADHD are varied and do not explicitly interoperate or interrelate with each other. Goal: To demonstrate that an analytics based approach will be more beneficial in key areas of healthcare in addition to data mining based approaches.
Research Goal Current diagnostic tools for adult ADHD are varied and do not explicitly interoperate or interrelate with each other. Goal: To demonstrate that an analytics based approach will be more beneficial in key areas of healthcare in addition to data mining based approaches.
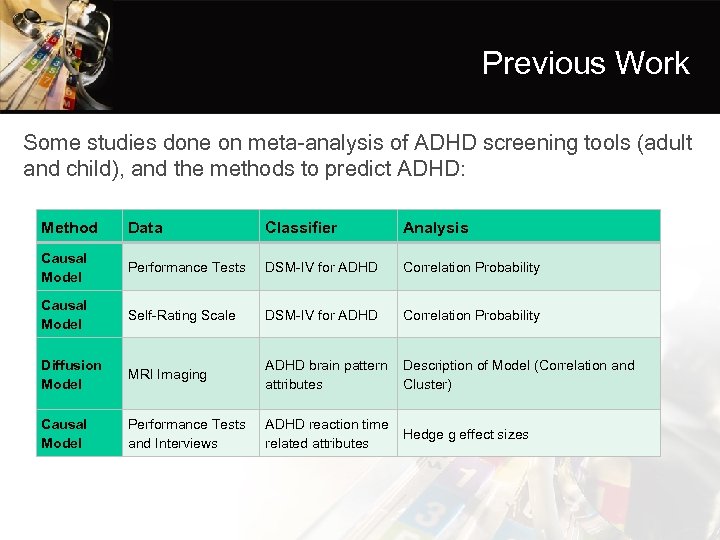 Previous Work Some studies done on meta-analysis of ADHD screening tools (adult and child), and the methods to predict ADHD: Method Data Classifier Analysis Causal Model Performance Tests DSM-IV for ADHD Correlation Probability Causal Model Self-Rating Scale DSM-IV for ADHD Correlation Probability Diffusion Model MRI Imaging ADHD brain pattern attributes Description of Model (Correlation and Cluster) Causal Model Performance Tests and Interviews ADHD reaction time Hedge g effect sizes related attributes
Previous Work Some studies done on meta-analysis of ADHD screening tools (adult and child), and the methods to predict ADHD: Method Data Classifier Analysis Causal Model Performance Tests DSM-IV for ADHD Correlation Probability Causal Model Self-Rating Scale DSM-IV for ADHD Correlation Probability Diffusion Model MRI Imaging ADHD brain pattern attributes Description of Model (Correlation and Cluster) Causal Model Performance Tests and Interviews ADHD reaction time Hedge g effect sizes related attributes
 Methodology • Determine classifier to determine diagnosis (DSM-V for adult ADHD through the American Psychiatric Association). • Obtain patient data information of other screening tool studies for metaanalysis (Pub. Med, EMBASE, Research. Gate), and refine it through Excel (ex. sample size, method results, indicator for diagnosis) • Apply causation and correlation techniques (R) to refined data to determine the best method to model the ADHD screening tool off of - Co-variation on method results calculated through ANCOVA tests [7] - Each process subject a number of rules, determined by the data (algorithms) • Results will be displayed in a web-based tool
Methodology • Determine classifier to determine diagnosis (DSM-V for adult ADHD through the American Psychiatric Association). • Obtain patient data information of other screening tool studies for metaanalysis (Pub. Med, EMBASE, Research. Gate), and refine it through Excel (ex. sample size, method results, indicator for diagnosis) • Apply causation and correlation techniques (R) to refined data to determine the best method to model the ADHD screening tool off of - Co-variation on method results calculated through ANCOVA tests [7] - Each process subject a number of rules, determined by the data (algorithms) • Results will be displayed in a web-based tool
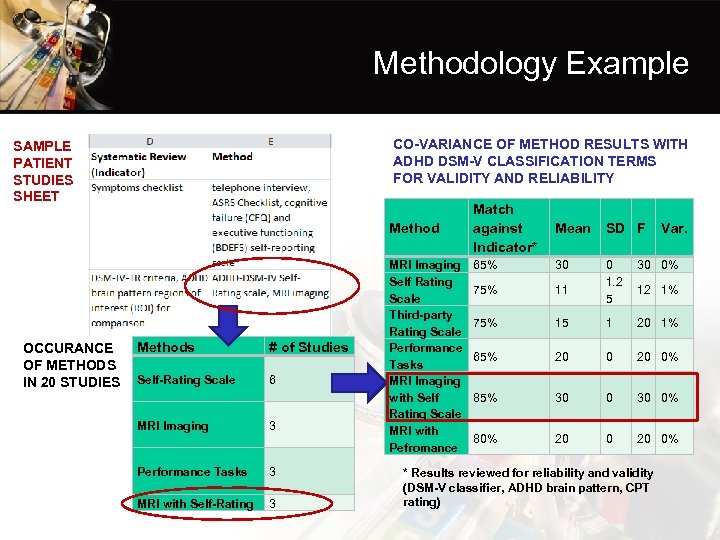 Methodology Example CO-VARIANCE OF METHOD RESULTS WITH ADHD DSM-V CLASSIFICATION TERMS FOR VALIDITY AND RELIABILITY SAMPLE PATIENT STUDIES SHEET Method OCCURANCE OF METHODS IN 20 STUDIES Methods # of Studies Self-Rating Scale 6 MRI Imaging 3 Performance Tasks 3 MRI with Self-Rating 3 MRI Imaging Self Rating Scale Third-party Rating Scale Performance Tasks MRI Imaging with Self Rating Scale MRI with Pefromance Match against Indicator* Mean SD F 65% 30 30 0% 75% 11 0 1. 2 5 75% 15 1 20 1% 65% 20 0% 85% 30 0% 80% 20 0% Var. 12 1% * Results reviewed for reliability and validity (DSM-V classifier, ADHD brain pattern, CPT rating)
Methodology Example CO-VARIANCE OF METHOD RESULTS WITH ADHD DSM-V CLASSIFICATION TERMS FOR VALIDITY AND RELIABILITY SAMPLE PATIENT STUDIES SHEET Method OCCURANCE OF METHODS IN 20 STUDIES Methods # of Studies Self-Rating Scale 6 MRI Imaging 3 Performance Tasks 3 MRI with Self-Rating 3 MRI Imaging Self Rating Scale Third-party Rating Scale Performance Tasks MRI Imaging with Self Rating Scale MRI with Pefromance Match against Indicator* Mean SD F 65% 30 30 0% 75% 11 0 1. 2 5 75% 15 1 20 1% 65% 20 0% 85% 30 0% 80% 20 0% Var. 12 1% * Results reviewed for reliability and validity (DSM-V classifier, ADHD brain pattern, CPT rating)
 Expected Results • Controlled study size should reduce bias on results • ANCOVA tests should reduce variance on relationship patterns and validate relationships [8] • Analytics will assist medical community with better diagnoses, with trial being run on nursing and psychology students at Athabasca University in an evaluation study
Expected Results • Controlled study size should reduce bias on results • ANCOVA tests should reduce variance on relationship patterns and validate relationships [8] • Analytics will assist medical community with better diagnoses, with trial being run on nursing and psychology students at Athabasca University in an evaluation study
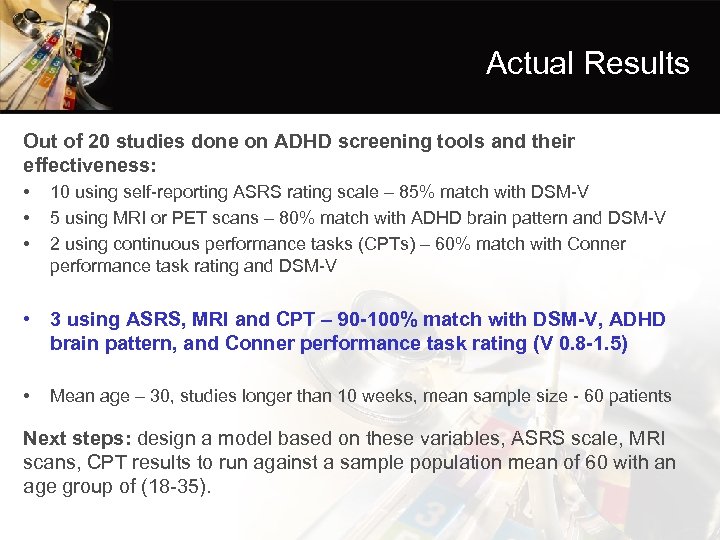 Actual Results Out of 20 studies done on ADHD screening tools and their effectiveness: • • • 10 using self-reporting ASRS rating scale – 85% match with DSM-V 5 using MRI or PET scans – 80% match with ADHD brain pattern and DSM-V 2 using continuous performance tasks (CPTs) – 60% match with Conner performance task rating and DSM-V • 3 using ASRS, MRI and CPT – 90 -100% match with DSM-V, ADHD brain pattern, and Conner performance task rating (V 0. 8 -1. 5) • Mean age – 30, studies longer than 10 weeks, mean sample size - 60 patients Next steps: design a model based on these variables, ASRS scale, MRI scans, CPT results to run against a sample population mean of 60 with an age group of (18 -35).
Actual Results Out of 20 studies done on ADHD screening tools and their effectiveness: • • • 10 using self-reporting ASRS rating scale – 85% match with DSM-V 5 using MRI or PET scans – 80% match with ADHD brain pattern and DSM-V 2 using continuous performance tasks (CPTs) – 60% match with Conner performance task rating and DSM-V • 3 using ASRS, MRI and CPT – 90 -100% match with DSM-V, ADHD brain pattern, and Conner performance task rating (V 0. 8 -1. 5) • Mean age – 30, studies longer than 10 weeks, mean sample size - 60 patients Next steps: design a model based on these variables, ASRS scale, MRI scans, CPT results to run against a sample population mean of 60 with an age group of (18 -35).
 Possible Dissemination • Tool intended for medical assistance • Tool possible study aid (analytic tool in education) • If effective, similar models for analytic tools may follow [10] • Thesis as primary publication • May inspire more publications on data analytics (learning/forecasting) • May inspire research on causation and possible prevention of mental illness/diseases • May be used for ADHD students’ performance in writing analytics
Possible Dissemination • Tool intended for medical assistance • Tool possible study aid (analytic tool in education) • If effective, similar models for analytic tools may follow [10] • Thesis as primary publication • May inspire more publications on data analytics (learning/forecasting) • May inspire research on causation and possible prevention of mental illness/diseases • May be used for ADHD students’ performance in writing analytics
 Challenges • Obtaining quality studies to use for refining model • Ensuring quality testing on model • Obtaining approval for student trial – will require new Research Ethics Board (REB) application
Challenges • Obtaining quality studies to use for refining model • Ensuring quality testing on model • Obtaining approval for student trial – will require new Research Ethics Board (REB) application
 Timeline Phase 1 (1 year) Phase 2 (1 year) Phase 3 (1 year) Collection and Analysis of Data Application development of Diagnostic Tool evaluation on study groups
Timeline Phase 1 (1 year) Phase 2 (1 year) Phase 3 (1 year) Collection and Analysis of Data Application development of Diagnostic Tool evaluation on study groups
![References [1] A. R. Hasan, S. M. Kamruzzaman, E. H. Mazumder and A. B. References [1] A. R. Hasan, S. M. Kamruzzaman, E. H. Mazumder and A. B.](https://present5.com/presentation/9f8317407f3ccc67eabd5424e3b0dad4/image-12.jpg) References [1] A. R. Hasan, S. M. Kamruzzaman, E. H. Mazumder and A. B. Siddiquee, "Medical Diagnosis Uising Neural Network, " in International Conference on Electrical & Computing Engineering, Dhaka, 2004. [2] J. C. Goodman, L. Gorman and D. M. Herrick, "Health Information Technology: Benefits and Problems, " National Center for Policy Analysis, Washington, 2010. [3] F. Mirzazadeh, Using SNP Data to Predict Radiation Toxicity for Prostate Cancer Patients, Edmonton, Alberta: University of Alberta, 2010. [4] M. Cooper, O. Eyre, K. Langley and A. Thapar, "Practitioner Review: What have we learnt about the causes of ADHD, " The Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, pp. 3 -16, 2013. [5] S. Thorne, "Data Analysis in Qualitative Research, " Evidence Based Nursing, pp. 68 -70, 2000. [6] M. Egger, G. D. Smith and A. N. Phillips, "Meta-analysis: Principles and Procedures, " BMJ, p. 315, 1997. [7] D. Pollard, "Variances and covariances, " in Statistics 241, New Haven, Yale University, 1997, pp. 1 -6. [8] American Psychiatric Association, "Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder, " in Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Arlington, American Psychiatric Publishing, 2013, pp. 59 -66. [9] A. Field, "Analysis of Covariance (ANCOVA), " in Discovering Statistics, London, Sage Publications Ltd. , 2012, pp. 1 -16.
References [1] A. R. Hasan, S. M. Kamruzzaman, E. H. Mazumder and A. B. Siddiquee, "Medical Diagnosis Uising Neural Network, " in International Conference on Electrical & Computing Engineering, Dhaka, 2004. [2] J. C. Goodman, L. Gorman and D. M. Herrick, "Health Information Technology: Benefits and Problems, " National Center for Policy Analysis, Washington, 2010. [3] F. Mirzazadeh, Using SNP Data to Predict Radiation Toxicity for Prostate Cancer Patients, Edmonton, Alberta: University of Alberta, 2010. [4] M. Cooper, O. Eyre, K. Langley and A. Thapar, "Practitioner Review: What have we learnt about the causes of ADHD, " The Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, pp. 3 -16, 2013. [5] S. Thorne, "Data Analysis in Qualitative Research, " Evidence Based Nursing, pp. 68 -70, 2000. [6] M. Egger, G. D. Smith and A. N. Phillips, "Meta-analysis: Principles and Procedures, " BMJ, p. 315, 1997. [7] D. Pollard, "Variances and covariances, " in Statistics 241, New Haven, Yale University, 1997, pp. 1 -6. [8] American Psychiatric Association, "Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder, " in Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Arlington, American Psychiatric Publishing, 2013, pp. 59 -66. [9] A. Field, "Analysis of Covariance (ANCOVA), " in Discovering Statistics, London, Sage Publications Ltd. , 2012, pp. 1 -16.
![References (continued) [10] R. R. Engel and C. Schoechlin, References (continued) [10] R. R. Engel and C. Schoechlin,](https://present5.com/presentation/9f8317407f3ccc67eabd5424e3b0dad4/image-13.jpg) References (continued) [10] R. R. Engel and C. Schoechlin, "Neuropsychological performance in adult attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder: Metaanalysis of empirical data, " Archives of Clinical Neuropsychology, vol. 20, no. 6, pp. 727 -744, August 2005. [11] [S. Bálint, I. Bitter, P. Czobor, Á. Mészáros and V. Simon, "Prevalence and correlates of adult attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder: meta-analysis, " The British Journal of Psychiatry, vol. 194, pp. 204 -211, 2009. [12] C. Kelly, M. P. Milham, et al. "Toward Systems Neuroscience of ADHD: A Meta-Analysis of 55 f. MRI Studies", American Journal of Psychiatry, vol. 169, no. 10, pp. 1038 -1055, 2012. [13] L. M. Friedman, M. J. Kofler, E. G. Kolomeyer, S. A. Orban, J. S. Raiker, M. D. Rapport and D. E. Sarver, "Reaction time variability in ADHD: A meta-analytic review of 319 studies, " Clinical Psychology Review, vol. 33, pp. 795 -811, 2013. [14] B. N. Carpenter, R. Gilliland, K. Reef and R. C. Reid, "Problems of Self-Concept in a Patient Sample of Hypersexual Men With Attention-Deficit Disorder, " Americian Society of Addiction Medicine, vol. 4, no. 3, pp. 1 -8, 2010. [15] T. Edgünlü, M. E. Erdal, H. Herken and A. N. I. Kenar, "Association of Synapsin III Gene with Adult Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder, " DNA and Cell Biology, vol. 32, no. 8, pp. 430 -434, 2013. [16] M. Dey, D. Eich-Höchli, N. Estévez, G. Gmel, M. Mohler-Kuo and J. Studer, "Prevalence of and Associated Factors for Adult Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder in Young Swiss Men, " PLOS ONE, vol. 9, no. 2, pp. 1 -8, 2014. [17] I. -Y. Ahn, B. -S. Cha, B. -J. Kim, C. -S. Lee, S. -J. Lee, C. -S. Park and J. -Y. Seo, "Mediating Effect of Depressive Symptoms on the Relationship between Adult Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder and Quality of Life, " Psychiatry Investig, vol. 11, no. 2, pp. 131 -136, 2014.
References (continued) [10] R. R. Engel and C. Schoechlin, "Neuropsychological performance in adult attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder: Metaanalysis of empirical data, " Archives of Clinical Neuropsychology, vol. 20, no. 6, pp. 727 -744, August 2005. [11] [S. Bálint, I. Bitter, P. Czobor, Á. Mészáros and V. Simon, "Prevalence and correlates of adult attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder: meta-analysis, " The British Journal of Psychiatry, vol. 194, pp. 204 -211, 2009. [12] C. Kelly, M. P. Milham, et al. "Toward Systems Neuroscience of ADHD: A Meta-Analysis of 55 f. MRI Studies", American Journal of Psychiatry, vol. 169, no. 10, pp. 1038 -1055, 2012. [13] L. M. Friedman, M. J. Kofler, E. G. Kolomeyer, S. A. Orban, J. S. Raiker, M. D. Rapport and D. E. Sarver, "Reaction time variability in ADHD: A meta-analytic review of 319 studies, " Clinical Psychology Review, vol. 33, pp. 795 -811, 2013. [14] B. N. Carpenter, R. Gilliland, K. Reef and R. C. Reid, "Problems of Self-Concept in a Patient Sample of Hypersexual Men With Attention-Deficit Disorder, " Americian Society of Addiction Medicine, vol. 4, no. 3, pp. 1 -8, 2010. [15] T. Edgünlü, M. E. Erdal, H. Herken and A. N. I. Kenar, "Association of Synapsin III Gene with Adult Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder, " DNA and Cell Biology, vol. 32, no. 8, pp. 430 -434, 2013. [16] M. Dey, D. Eich-Höchli, N. Estévez, G. Gmel, M. Mohler-Kuo and J. Studer, "Prevalence of and Associated Factors for Adult Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder in Young Swiss Men, " PLOS ONE, vol. 9, no. 2, pp. 1 -8, 2014. [17] I. -Y. Ahn, B. -S. Cha, B. -J. Kim, C. -S. Lee, S. -J. Lee, C. -S. Park and J. -Y. Seo, "Mediating Effect of Depressive Symptoms on the Relationship between Adult Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder and Quality of Life, " Psychiatry Investig, vol. 11, no. 2, pp. 131 -136, 2014.
![References (continued) [18] L. A. Adler, R. A. Barkley, S. Chatterji, S. V. Faraone, References (continued) [18] L. A. Adler, R. A. Barkley, S. Chatterji, S. V. Faraone,](https://present5.com/presentation/9f8317407f3ccc67eabd5424e3b0dad4/image-14.jpg) References (continued) [18] L. A. Adler, R. A. Barkley, S. Chatterji, S. V. Faraone, M. Finkelman, J. G. Green, L. L. Greenhill, M. J. Gruber, M. Jewell, R. C. Kessler, L. J. Russo, N. A. Sampson and D. L. Van Brunt, "Structure and diagnosis of adult attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: analysis of expanded symptom criteria from the Adult ADHD Clinical Diagnostic Scale, " ARCH GEN PSYCHIATRY, vol. 67, no. 11, pp. 1168 -1178, 2010. [19] S. Abdi, S. Amiri, A. Asadollahi, M. A. Ghoreishizadeh, J. Golmirzaei, M. Jonggoo, H. Sadeghi-Bazargani and S. Safikhanlo, "Prevalence of Adult Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (Adult ADHD): Tabriz, " Iran J Psychiatry, vol. 9, no. 2, pp. 83 -88, 2014. [20] C. Dodds, S. Morein-Zamir, U. Müller, T. Robbins, B. Sahakian, W. Schwarzkopf and T. J. van Hartevelt, "Hypoactivation in right inferior frontal cortex is specifically associated with motor response inhibition in adult ADHD, " Human Brain Mapping, pp. 1 -12, 2014. [21] A. M. H. Onnink, M. P. Zwiers, M. Hoogman, J. C. Mostert, C. C. Kan, J. Buitelaar and B. Franke, "Brain alterations in adult ADHD: Effects of gender, treatment and comorbid depression, " European Neuropsychopharmacology(2014), vol. 24, pp. 397 -409, 2014. [22] S. Gray, K. Mawjee, S. Woltering and R. Tannock, "The Adult ADHD Self-Report Scale (ASRS): utility in college students with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, " Peer. J, pp. 1 -17, 2014. [23] M. Fischer, V. S. Knopik, R. C. Mulligan, S. M. Rao, M. Seidenberg and L. H. Sweet, "Neural correlates of inhibitory control in adult ADHD: Evidence from the Milwaukee longitudinal sample, " Psychiatry Res, vol. 194, no. 2, pp. 119 -129, 2011.
References (continued) [18] L. A. Adler, R. A. Barkley, S. Chatterji, S. V. Faraone, M. Finkelman, J. G. Green, L. L. Greenhill, M. J. Gruber, M. Jewell, R. C. Kessler, L. J. Russo, N. A. Sampson and D. L. Van Brunt, "Structure and diagnosis of adult attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: analysis of expanded symptom criteria from the Adult ADHD Clinical Diagnostic Scale, " ARCH GEN PSYCHIATRY, vol. 67, no. 11, pp. 1168 -1178, 2010. [19] S. Abdi, S. Amiri, A. Asadollahi, M. A. Ghoreishizadeh, J. Golmirzaei, M. Jonggoo, H. Sadeghi-Bazargani and S. Safikhanlo, "Prevalence of Adult Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (Adult ADHD): Tabriz, " Iran J Psychiatry, vol. 9, no. 2, pp. 83 -88, 2014. [20] C. Dodds, S. Morein-Zamir, U. Müller, T. Robbins, B. Sahakian, W. Schwarzkopf and T. J. van Hartevelt, "Hypoactivation in right inferior frontal cortex is specifically associated with motor response inhibition in adult ADHD, " Human Brain Mapping, pp. 1 -12, 2014. [21] A. M. H. Onnink, M. P. Zwiers, M. Hoogman, J. C. Mostert, C. C. Kan, J. Buitelaar and B. Franke, "Brain alterations in adult ADHD: Effects of gender, treatment and comorbid depression, " European Neuropsychopharmacology(2014), vol. 24, pp. 397 -409, 2014. [22] S. Gray, K. Mawjee, S. Woltering and R. Tannock, "The Adult ADHD Self-Report Scale (ASRS): utility in college students with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, " Peer. J, pp. 1 -17, 2014. [23] M. Fischer, V. S. Knopik, R. C. Mulligan, S. M. Rao, M. Seidenberg and L. H. Sweet, "Neural correlates of inhibitory control in adult ADHD: Evidence from the Milwaukee longitudinal sample, " Psychiatry Res, vol. 194, no. 2, pp. 119 -129, 2011.
![References (continued) [24] P. Alleman, S. Allsop, M. Auriacombe, C. Barta, E. -T. Bu, References (continued) [24] P. Alleman, S. Allsop, M. Auriacombe, C. Barta, E. -T. Bu,](https://present5.com/presentation/9f8317407f3ccc67eabd5424e3b0dad4/image-15.jpg) References (continued) [24] P. Alleman, S. Allsop, M. Auriacombe, C. Barta, E. -T. Bu, P. -J. Carpentier, S. Carruthers, M. Casas, L. Degenhardt, Z. Demetrovics, G. Dom, S. V. Faraone, M. Fatséas, J. Franck, M. Kapitány-Fövény, B. Johnson, S. Kaye, M. W. Koeter, M. Konstenius, F. R. Levin, F. Moggi, M. Møller, J. A. Ramos-Quiroga, A. Schillinger, R. A. Schoevers, A. Skutle, G. van de Glind, W. van den Brink, K. van Emmerik-van Oortmerssen, S. Verspreet and S. Wallhed, "Variability in the prevalence of adult ADHD in treatment seekingsubstance use disorder patients: Results from an internationalmulti-center study exploring DSM-IV and DSM-5 criteria, " Drug and Alcohol Dependence, vol. 134, pp. 158 -166, 2014. [25] L. A. Adler, M. Dauphin, P. Deas, B. Dirks, A. Raychaudhuri, K. Saylor and R. Weisler, "Self-Reported quality of life in adults with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and executive function impairment treated with lisdexamfetamine dimesylate: a randomized, double-blind, multicenter, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study, " BMC Psychiatry, vol. 13, no. 253, pp. 1 -11, 2013. [26] J. Acosta-Cabronero, F. I. Aigbirhio, J. -C. Baron, L. Brichard, N. d. Campo, S. R. Chamberlain, J. Dowson, T. D. Fryer, Y. T. Hong, D. Izquierdo, U. Müller, R. Regenthal, T. W. Robbins, B. J. Sahakian, R. Smith, J. Suckling and R. Tait, "A positron emission tomography study of nigro-striatal dopaminergic mechanisms underlying attention: implications for ADHD and its treatment, " Brain, vol. 136, pp. 3252 -3270, 2013. [27] A. Abramovitch, G. Goldzweig and A. Schweiger, "Correlates of Physical Activity with Intrusive Thoughts, Worry and Impulsivity in Adults with Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder: A Cross-sectional Pilot Study, " Israel Annals of Psychiatry and Related Disciplines, vol. 50, no. 1, pp. 47 -54, 2013. [28] E. J. Goodwin, G. H. Gudjonsson, O. Sedgwick and S. Young, "The effectiveness of police custody assessments in identifying suspects with intellectual disabilities and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, " BMC Medicine, vol. 11, pp. 1 -11, 2013.
References (continued) [24] P. Alleman, S. Allsop, M. Auriacombe, C. Barta, E. -T. Bu, P. -J. Carpentier, S. Carruthers, M. Casas, L. Degenhardt, Z. Demetrovics, G. Dom, S. V. Faraone, M. Fatséas, J. Franck, M. Kapitány-Fövény, B. Johnson, S. Kaye, M. W. Koeter, M. Konstenius, F. R. Levin, F. Moggi, M. Møller, J. A. Ramos-Quiroga, A. Schillinger, R. A. Schoevers, A. Skutle, G. van de Glind, W. van den Brink, K. van Emmerik-van Oortmerssen, S. Verspreet and S. Wallhed, "Variability in the prevalence of adult ADHD in treatment seekingsubstance use disorder patients: Results from an internationalmulti-center study exploring DSM-IV and DSM-5 criteria, " Drug and Alcohol Dependence, vol. 134, pp. 158 -166, 2014. [25] L. A. Adler, M. Dauphin, P. Deas, B. Dirks, A. Raychaudhuri, K. Saylor and R. Weisler, "Self-Reported quality of life in adults with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and executive function impairment treated with lisdexamfetamine dimesylate: a randomized, double-blind, multicenter, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study, " BMC Psychiatry, vol. 13, no. 253, pp. 1 -11, 2013. [26] J. Acosta-Cabronero, F. I. Aigbirhio, J. -C. Baron, L. Brichard, N. d. Campo, S. R. Chamberlain, J. Dowson, T. D. Fryer, Y. T. Hong, D. Izquierdo, U. Müller, R. Regenthal, T. W. Robbins, B. J. Sahakian, R. Smith, J. Suckling and R. Tait, "A positron emission tomography study of nigro-striatal dopaminergic mechanisms underlying attention: implications for ADHD and its treatment, " Brain, vol. 136, pp. 3252 -3270, 2013. [27] A. Abramovitch, G. Goldzweig and A. Schweiger, "Correlates of Physical Activity with Intrusive Thoughts, Worry and Impulsivity in Adults with Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder: A Cross-sectional Pilot Study, " Israel Annals of Psychiatry and Related Disciplines, vol. 50, no. 1, pp. 47 -54, 2013. [28] E. J. Goodwin, G. H. Gudjonsson, O. Sedgwick and S. Young, "The effectiveness of police custody assessments in identifying suspects with intellectual disabilities and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, " BMC Medicine, vol. 11, pp. 1 -11, 2013.
![References (continued) [29] Karakus, G. , Ozpoyraz, N. , Tamam L. , ” Comorbidity References (continued) [29] Karakus, G. , Ozpoyraz, N. , Tamam L. , ” Comorbidity](https://present5.com/presentation/9f8317407f3ccc67eabd5424e3b0dad4/image-16.jpg) References (continued) [29] Karakus, G. , Ozpoyraz, N. , Tamam L. , ” Comorbidity of adult attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder and bipolar disorder: prevalence and clinical correlates”, European Archives of Psychiatry and Clinical Neuroscience, vol. 258, no. 7, pp. 385 -393, 2008. [30] Barendregt, H. P. , Cornelis, C. K. , et al. , “Effects of mindfulness-based cognitive therapy on neurophysiological correlates of performance monitoring in adult attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder”, Clinical neurophysiology, pp. 1 -10, 2014.
References (continued) [29] Karakus, G. , Ozpoyraz, N. , Tamam L. , ” Comorbidity of adult attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder and bipolar disorder: prevalence and clinical correlates”, European Archives of Psychiatry and Clinical Neuroscience, vol. 258, no. 7, pp. 385 -393, 2008. [30] Barendregt, H. P. , Cornelis, C. K. , et al. , “Effects of mindfulness-based cognitive therapy on neurophysiological correlates of performance monitoring in adult attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder”, Clinical neurophysiology, pp. 1 -10, 2014.
 Questions?
Questions?


