07567ffebdb523fab173c943e74eccdb.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 18
 User-Centered Development Methodology A user interface comprises “those aspects of the system that the user comes in contact with. ” ●Moran [1981]
User-Centered Development Methodology A user interface comprises “those aspects of the system that the user comes in contact with. ” ●Moran [1981]
 User-Centered Development Methodology ● Centered on the USER not the Data – – ● Involves users in the whole process Usability can be quantified =>measured Interdisciplinary – ● Draws from many disciplines Highly iterative – Involves repeated testing and revision – Techniques to test and debug interfaces before implementing them
User-Centered Development Methodology ● Centered on the USER not the Data – – ● Involves users in the whole process Usability can be quantified =>measured Interdisciplinary – ● Draws from many disciplines Highly iterative – Involves repeated testing and revision – Techniques to test and debug interfaces before implementing them
 Fields HCI builds upon ● Computer Science – ● Engineering – ● Design for human factors Graphic design – ● Faster, cheaper equipment Ergonomics – ● Implementation of website or other interface Visual communication Technical writing – Textual communication
Fields HCI builds upon ● Computer Science – ● Engineering – ● Design for human factors Graphic design – ● Faster, cheaper equipment Ergonomics – ● Implementation of website or other interface Visual communication Technical writing – Textual communication
 Fields HCI builds upon ● Linguistics, artificial intelligence – ● Cognitive psychology – ● Perception, memory, mental models Sociology – ● Speech recognition, natural language processing How people interact in groups Anthropology – Study of people in their work settings A highly eclectic field which offers both challenges and satisfactions
Fields HCI builds upon ● Linguistics, artificial intelligence – ● Cognitive psychology – ● Perception, memory, mental models Sociology – ● Speech recognition, natural language processing How people interact in groups Anthropology – Study of people in their work settings A highly eclectic field which offers both challenges and satisfactions
 User-Centered Methodology ● Initial stages involve gathering of information ● ● ● Needs Analysis User and task analysis Functional analysis Requirements analysis Setting usability specifications Later stages involve designing, building, and testing ● ● Design Prototyping Implementation Evaluation
User-Centered Methodology ● Initial stages involve gathering of information ● ● ● Needs Analysis User and task analysis Functional analysis Requirements analysis Setting usability specifications Later stages involve designing, building, and testing ● ● Design Prototyping Implementation Evaluation
 Needs analysis ● Summarizes the nature and purpose of the system – – – ● Type of system (website, video game, spreadsheet) People it will serve Benefits it will provide This is normally very brief. Two or three sentences explaining why it is a good idea.
Needs analysis ● Summarizes the nature and purpose of the system – – – ● Type of system (website, video game, spreadsheet) People it will serve Benefits it will provide This is normally very brief. Two or three sentences explaining why it is a good idea.
 User and task analysis ● User analysis - characterizes those who will use the site: – – ● General considerations (age, education, experience with computers) Users' experience and expectations Task analysis - what users will do – – User’s goals - what they want to accomplish Tasks or activities carried out to achieve the goals
User and task analysis ● User analysis - characterizes those who will use the site: – – ● General considerations (age, education, experience with computers) Users' experience and expectations Task analysis - what users will do – – User’s goals - what they want to accomplish Tasks or activities carried out to achieve the goals
 Functional analysis ● Functionality -computer services needed by users – ● What to automate – ● on-line reservation or phone call Examples: travel site task: “find all flights to xyz, ordered by price” – ● Close correspondence between functions and tasks Needs search function and sorting capability Music CD site: task “buy a CD” – Needs secure on-line transaction functionality
Functional analysis ● Functionality -computer services needed by users – ● What to automate – ● on-line reservation or phone call Examples: travel site task: “find all flights to xyz, ordered by price” – ● Close correspondence between functions and tasks Needs search function and sorting capability Music CD site: task “buy a CD” – Needs secure on-line transaction functionality
 Requirements analysis ● Describes the formal specifications required to implement the system: – – – ● Data dictionaries Entity-relationship diagrams Object oriented modeling Covered in great detail in software engineering courses.
Requirements analysis ● Describes the formal specifications required to implement the system: – – – ● Data dictionaries Entity-relationship diagrams Object oriented modeling Covered in great detail in software engineering courses.
 Setting usability specifications ● ● Answers question “How good is your site? ” Set usability specifications: – Performance measures: Observable user behavior such as number of tasks completed, number of errors, etc. – Preference measures insights into user opinion about site such as first impression, overall satisfaction.
Setting usability specifications ● ● Answers question “How good is your site? ” Set usability specifications: – Performance measures: Observable user behavior such as number of tasks completed, number of errors, etc. – Preference measures insights into user opinion about site such as first impression, overall satisfaction.
 Design Make decisions about: ● Organization – – – ● Visual organization to create clarity and consistency Layout navigation Appearance – “Look and feel” Now you can begin to sketch the pages ● Because you know your users and what they want to do
Design Make decisions about: ● Organization – – – ● Visual organization to create clarity and consistency Layout navigation Appearance – “Look and feel” Now you can begin to sketch the pages ● Because you know your users and what they want to do
 Prototyping ● Prototype is an original model or pattern – – ● Global: entire site Local: selected parts of the site Prototypes – – Evolutionary: becomes the final project Throw-away: serves as a pattern High fidelity: resembles final product Low fidelity: just rough sketch - not close to final
Prototyping ● Prototype is an original model or pattern – – ● Global: entire site Local: selected parts of the site Prototypes – – Evolutionary: becomes the final project Throw-away: serves as a pattern High fidelity: resembles final product Low fidelity: just rough sketch - not close to final
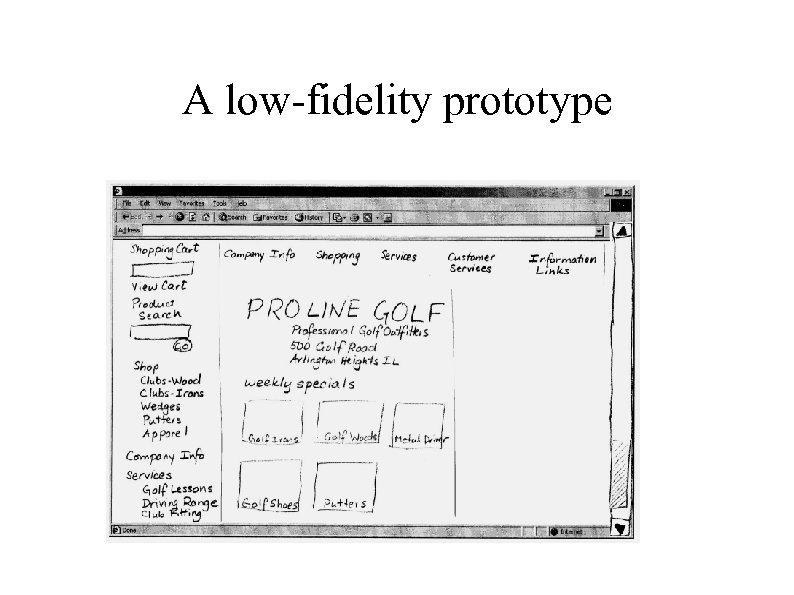 A low-fidelity prototype
A low-fidelity prototype
 A high-fidelity prototype
A high-fidelity prototype
 Implementation ● This is where the website or other interface is implemented, in HTML or a programming language
Implementation ● This is where the website or other interface is implemented, in HTML or a programming language
 Evaluation ● Expert-based evaluation – ● User-based evaluation – ● Bring in a usability expert Test the website or other interface with users In this class we will emphasize user-based evaluation
Evaluation ● Expert-based evaluation – ● User-based evaluation – ● Bring in a usability expert Test the website or other interface with users In this class we will emphasize user-based evaluation
 User-Centered Characteristics ● Highly iterative NO YES
User-Centered Characteristics ● Highly iterative NO YES
 User-Centered Design ● ● ● Is industry-proven Lets you build websites or interfaces that meet user expectations Leads to cost-effective and timely implementation Is highly interactive You have also learned that HCI is a highly eclectic field, building on a dozen other disciplines
User-Centered Design ● ● ● Is industry-proven Lets you build websites or interfaces that meet user expectations Leads to cost-effective and timely implementation Is highly interactive You have also learned that HCI is a highly eclectic field, building on a dozen other disciplines


