9b3a9bc12a2c44620796b7b7d79a493e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 18
 User Centered Design at Elsevier The End-user in the Driver’s Seat Jaco Zijlstra Colloque de l'Académie des sciences "Évolution des publications scientifiques - Le regard des chercheurs“ – Les 14 -15 mai 2007
User Centered Design at Elsevier The End-user in the Driver’s Seat Jaco Zijlstra Colloque de l'Académie des sciences "Évolution des publications scientifiques - Le regard des chercheurs“ – Les 14 -15 mai 2007
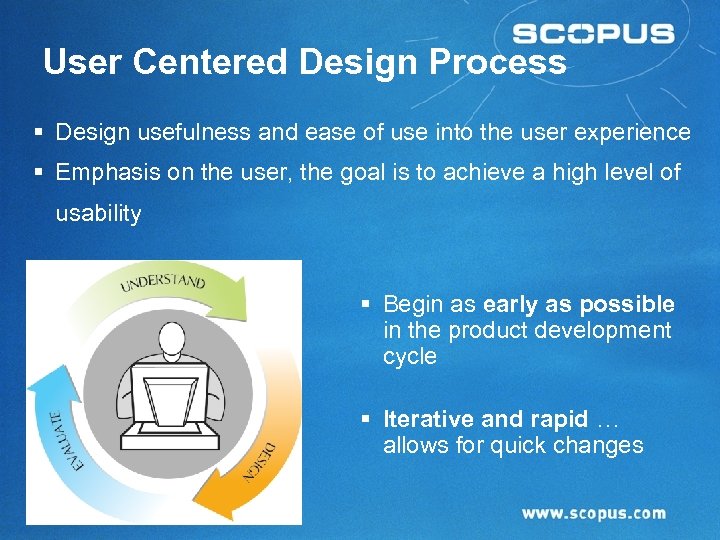 User Centered Design Process § Design usefulness and ease of use into the user experience § Emphasis on the user, the goal is to achieve a high level of usability § Begin as early as possible in the product development cycle § Iterative and rapid … allows for quick changes 1
User Centered Design Process § Design usefulness and ease of use into the user experience § Emphasis on the user, the goal is to achieve a high level of usability § Begin as early as possible in the product development cycle § Iterative and rapid … allows for quick changes 1
 Understand § Know the users, their tasks, and their goals § What information resources and tools do they currently use? § What are their organization’s procedures? § What are their key tasks and how do they accomplish them? § What problems do they encounter daily? 2
Understand § Know the users, their tasks, and their goals § What information resources and tools do they currently use? § What are their organization’s procedures? § What are their key tasks and how do they accomplish them? § What problems do they encounter daily? 2
 Design § Design to fit the user and their tasks § Decisions based on user data § Basic Design Principles § Simplicity § Consistency § Accessibility § User control (undo, exit) § Task efficiency § Clear error communication § Readability (visual presentation) § Aesthetics (graphics) 3
Design § Design to fit the user and their tasks § Decisions based on user data § Basic Design Principles § Simplicity § Consistency § Accessibility § User control (undo, exit) § Task efficiency § Clear error communication § Readability (visual presentation) § Aesthetics (graphics) 3
 Evaluate § Evaluate the UI, not the user § Key measures – § Efficiency § Effectiveness, Error Rate § Satisfaction § Pitfalls – § Design change based on one comment § Observation is best, users can’t report what they actually do § Over design for non-critical or uncommon tasks 4
Evaluate § Evaluate the UI, not the user § Key measures – § Efficiency § Effectiveness, Error Rate § Satisfaction § Pitfalls – § Design change based on one comment § Observation is best, users can’t report what they actually do § Over design for non-critical or uncommon tasks 4
 Scopus: a case study 5
Scopus: a case study 5
 Who were involved? § § § 20 Development partners 30+ rounds of user testing 5 institutes per test 25 users per test Librarians, professors, researchers, Ph. D students, graduate students, … § Pour comprendre comment les scientifiques: § Recherchent § Trouvent et § Évaluent les documents et les informations scientifiques 6
Who were involved? § § § 20 Development partners 30+ rounds of user testing 5 institutes per test 25 users per test Librarians, professors, researchers, Ph. D students, graduate students, … § Pour comprendre comment les scientifiques: § Recherchent § Trouvent et § Évaluent les documents et les informations scientifiques 6
 Most common search frustrations § There is too much, it is overwhelming § How can I narrow down sensibly and exactly? § How much have I missed ? § Good searching is too complicated § Difficult to find all articles from one author § Why can’t I search everything from one point ? 7
Most common search frustrations § There is too much, it is overwhelming § How can I narrow down sensibly and exactly? § How much have I missed ? § Good searching is too complicated § Difficult to find all articles from one author § Why can’t I search everything from one point ? 7
 High level use cases § Finding (new) articles in a familiar subject field § Getting an overview/understanding of a new subject field § Finding author-related information § Articles by a specific author § Information to help evaluating a specific author § Author contact information § Staying up-to-date 8
High level use cases § Finding (new) articles in a familiar subject field § Getting an overview/understanding of a new subject field § Finding author-related information § Articles by a specific author § Information to help evaluating a specific author § Author contact information § Staying up-to-date 8
 First step: content is king § 15. 000 revues académiques § Dont plus de 550 revues en « Accès Libre » § Dont presque 600 de revues Françaises § 30 millions de résumés portant sur les 40 dernières années § Dont 800. 000 de résumés en Anglais portant sur des articles en Français § 265 millions de références ajoutées à tous les résumés depuis 1996 § 250 millions de pages Web scientifiques via Scirus § 13 millions de brevets § Contenu mis à jour quotidiennement 9
First step: content is king § 15. 000 revues académiques § Dont plus de 550 revues en « Accès Libre » § Dont presque 600 de revues Françaises § 30 millions de résumés portant sur les 40 dernières années § Dont 800. 000 de résumés en Anglais portant sur des articles en Français § 265 millions de références ajoutées à tous les résumés depuis 1996 § 250 millions de pages Web scientifiques via Scirus § 13 millions de brevets § Contenu mis à jour quotidiennement 9
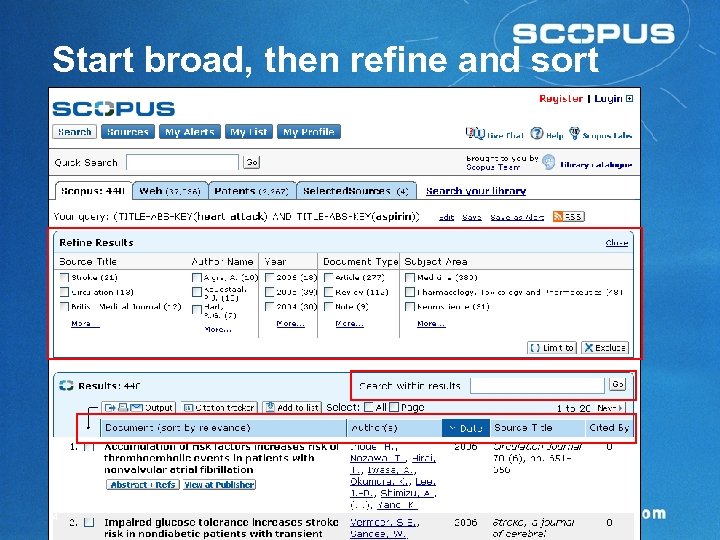 Start broad, then refine and sort 14
Start broad, then refine and sort 14
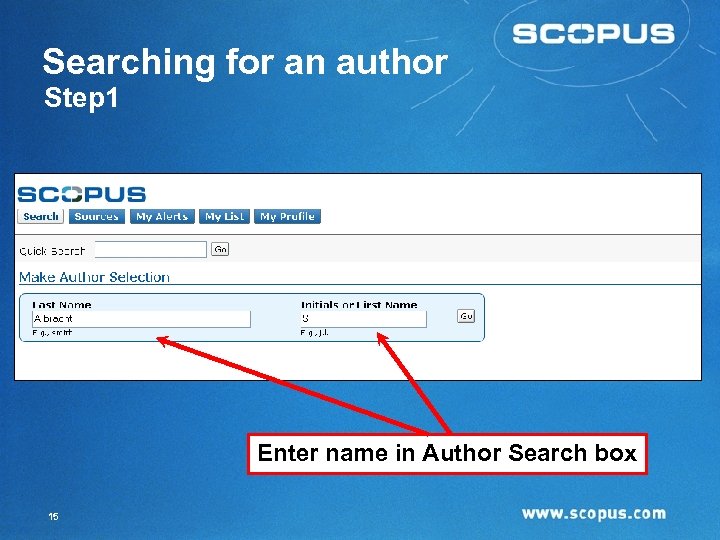 Searching for an author Step 1 Enter name in Author Search box 15
Searching for an author Step 1 Enter name in Author Search box 15
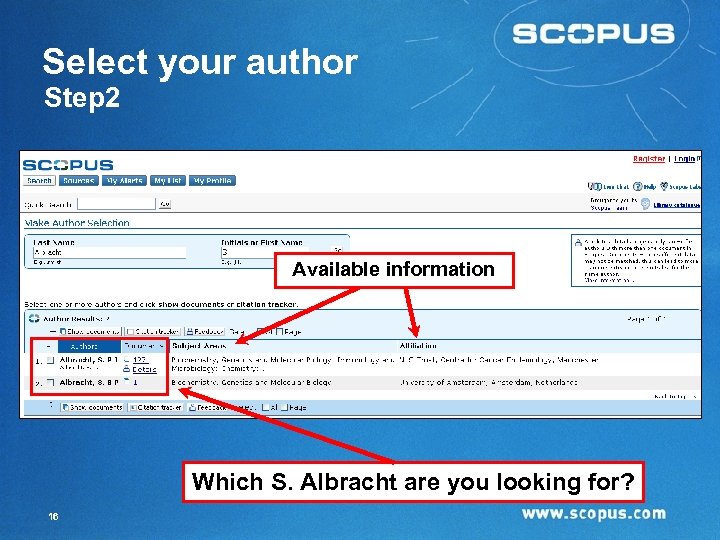 Select your author Step 2 Available information Which S. Albracht are you looking for? 16
Select your author Step 2 Available information Which S. Albracht are you looking for? 16
 Author details Step 3 Unique Author ID & matched documents 17
Author details Step 3 Unique Author ID & matched documents 17
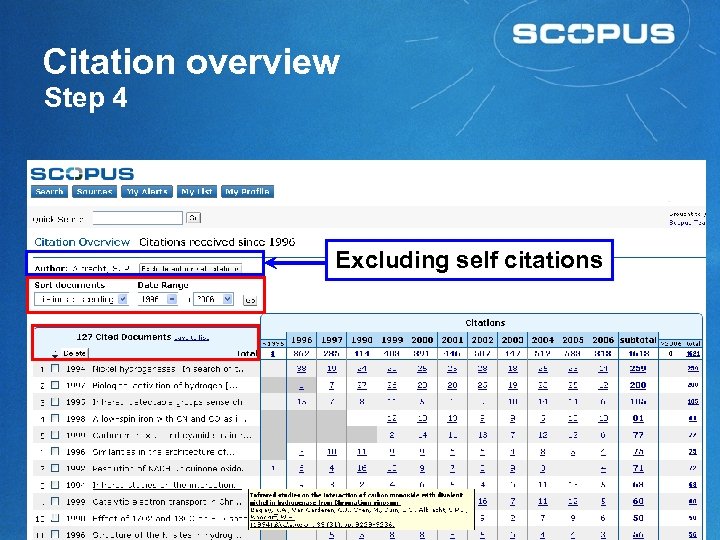 Citation overview Step 4 Excluding self citations 18
Citation overview Step 4 Excluding self citations 18
 Conclusions § Benefits of user-centered design § Ensures that what is developed is useful § Improves the user experience § Gives ownership where it belongs: the eventual users § Reduces the need for librarians to train their users on the products they buy 19
Conclusions § Benefits of user-centered design § Ensures that what is developed is useful § Improves the user experience § Gives ownership where it belongs: the eventual users § Reduces the need for librarians to train their users on the products they buy 19
 20
20
 Nous vous remercions de votre attention!
Nous vous remercions de votre attention!


