9d55aa7acd4984dabec8526f309a002b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 53

US Birth Outcomes in a Comparative Context Update of Data from Birth By the Numbers. These slides largely mirror those used in the video, but update them with the most recent available data as of January 1, 2012 Gene Declercq, Ph. D NOTE: There is a lag of 2 -4 years in the reporting of vital statistics from the US and abroad Birth. By. The. Numbers. org

Key Question Is the U. S. really doing as badly as it seems in international comparisons? Birth. By. The. Numbers. org

Is the U. S. really doing that badly? How Do we Compare Outcomes? Neonatal Mortality Rate Infant Deaths in First 28 days X 1, 000 ________ Live Births Birth. By. The. Numbers. org
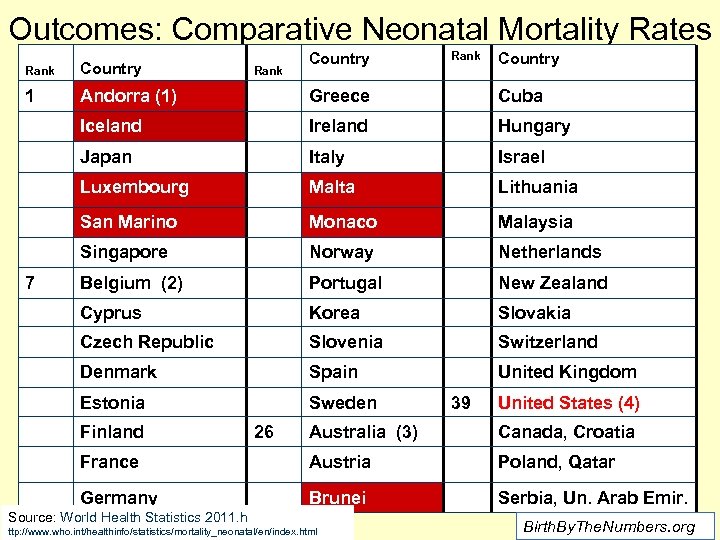
Outcomes: Comparative Neonatal Mortality Rates Country Rank Country 1 Andorra (1) Greece Cuba Iceland Ireland Hungary Japan Italy Israel Luxembourg Malta Lithuania San Marino Monaco Malaysia Singapore Norway Netherlands Belgium (2) Portugal New Zealand Cyprus Korea Slovakia Czech Republic Slovenia Switzerland Denmark Spain United Kingdom Estonia Sweden 7 Finland Rank 26 39 United States (4) Australia (3) Canada, Croatia France Austria Poland, Qatar Germany Brunei Serbia, Un. Arab Emir. Source: World Health Statistics 2011. h ttp: //www. who. int/healthinfo/statistics/mortality_neonatal/en/index. html Birth. By. The. Numbers. org
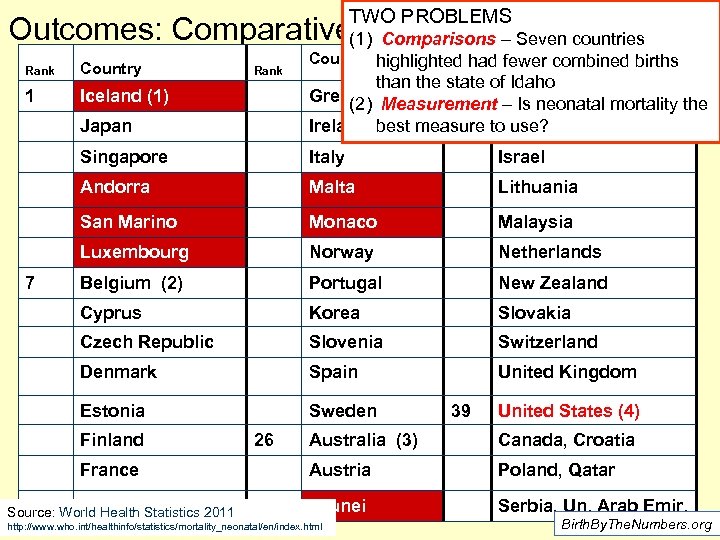
TWO PROBLEMS Outcomes: Comparative(1) Comparisons Mortality Rates Neonatal – Seven countries Rank Country 1 Iceland (1) Rank Country highlighted had. Country fewer combined births Japan Singapore Italy Israel Andorra Malta Lithuania San Marino Monaco Malaysia Luxembourg Norway Netherlands Belgium (2) Portugal New Zealand Cyprus Korea Slovakia Czech Republic Slovenia Switzerland Denmark Spain United Kingdom Estonia 7 than the state of Idaho Greece Measurement Cuba (2) – Is neonatal mortality the Ireland best measure to use? Hungary Sweden Finland France Germany Source: World Health Statistics 2011 26 39 United States (4) Australia (3) Canada, Croatia Austria Poland, Qatar Brunei Serbia, Un. Arab Emir. http: //www. who. int/healthinfo/statistics/mortality_neonatal/en/index. html Birth. By. The. Numbers. org

Outcomes Seven countries in red background share a particular characteristic – almost no one actually lives there. Total Births in these countries in 2009 were 23, 549 or fewer than the 23, 731 in Idaho in ‘ 09 Country Andorra 2009 Births 828 Iceland 5, 027 Luxembourg 5, 639 San Marino Malta Monaco 334 4, 143 298 Brunei 7, 280 TOTAL 23, 549 Birth. By. The. Numbers. org

What’s a Fair Comparison with the US? In the most recent year available (2009): • Countries with at least 100, 000 births • Countries with a total per capita annual expenditure on health of at least $1, 500 in US dollars. Birth. By. The. Numbers. org
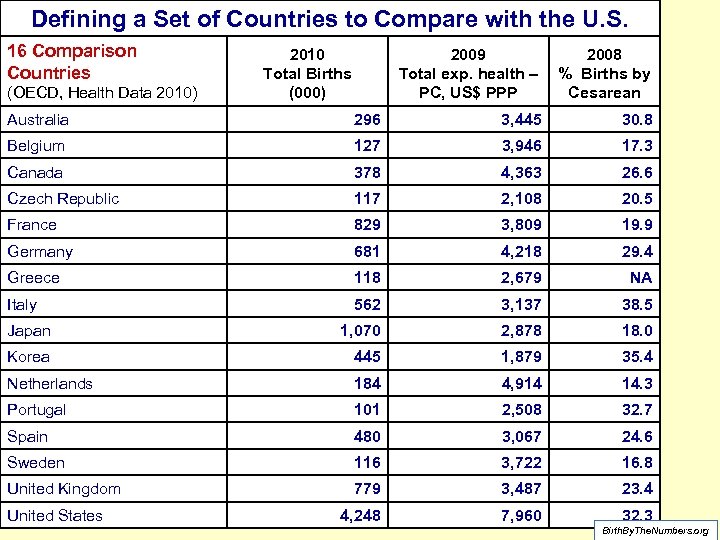
Defining a Set of Countries to Compare with the U. S. 16 Comparison Countries (OECD, Health Data 2010) 2010 Total Births (000) 2009 Total exp. health – PC, US$ PPP 2008 % Births by Cesarean Australia 296 3, 445 30. 8 Belgium 127 3, 946 17. 3 Canada 378 4, 363 26. 6 Czech Republic 117 2, 108 20. 5 France 829 3, 809 19. 9 Germany 681 4, 218 29. 4 Greece 118 2, 679 NA Italy 562 3, 137 38. 5 Japan 1, 070 2, 878 18. 0 Korea 445 1, 879 35. 4 Netherlands 184 4, 914 14. 3 Portugal 101 2, 508 32. 7 Spain 480 3, 067 24. 6 Sweden 116 3, 722 16. 8 United Kingdom 779 3, 487 23. 4 4, 248 7, 960 United States 32. 3 Birth. By. The. Numbers. org
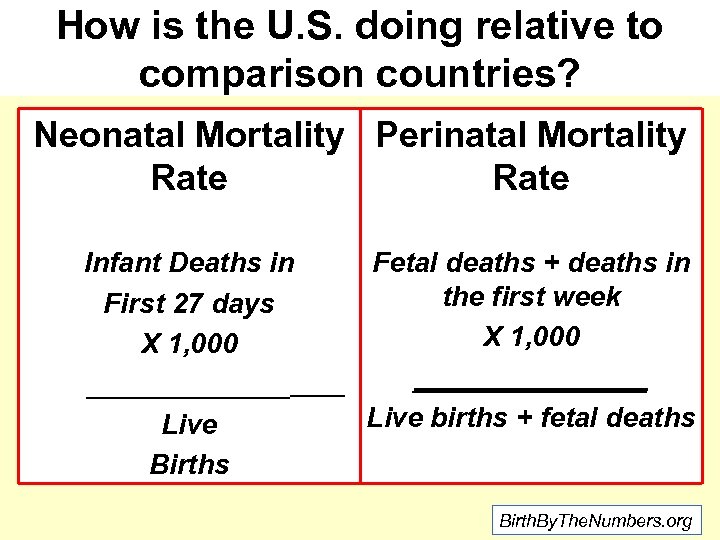
How is the U. S. doing relative to comparison countries? Neonatal Mortality Perinatal Mortality Rate Infant Deaths in First 27 days X 1, 000 _______ Live Births Fetal deaths + deaths in the first week X 1, 000 ________ Live births + fetal deaths Birth. By. The. Numbers. org
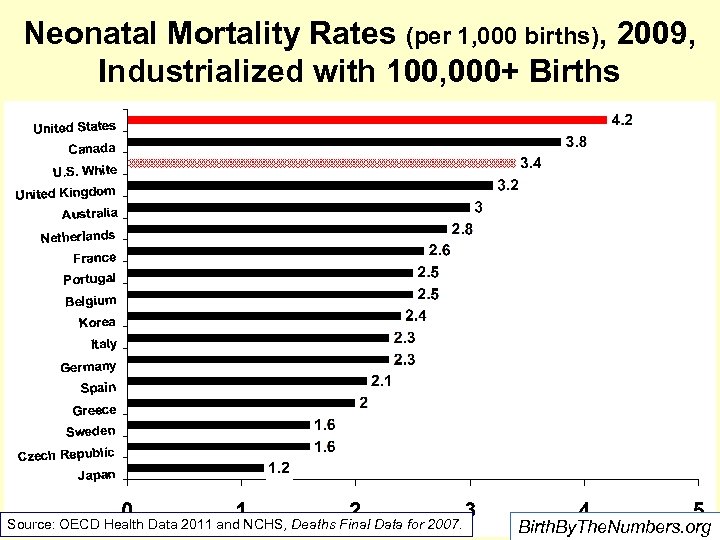
Neonatal Mortality Rates (per 1, 000 births), 2009, Industrialized with 100, 000+ Births Source: OECD Health Data 2011 and NCHS, Deaths Final Data for 2007. Birth. By. The. Numbers. org
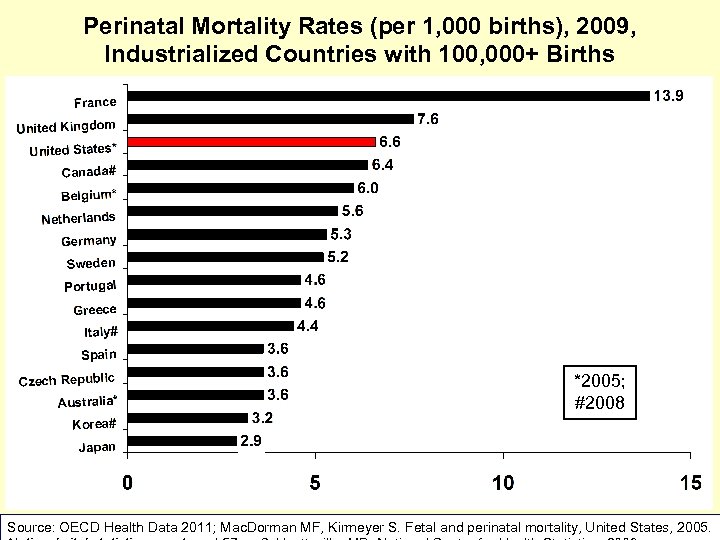
Perinatal Mortality Rates (per 1, 000 births), 2009, Industrialized Countries with 100, 000+ Births *2005; #2008 Source: OECD Health Data 2011; Mac. Dorman MF, Kirmeyer S. Fetal and perinatal mortality, United States, 2005.

Maternal Mortality Ratios Maternal Mortality Ratio Maternal Deaths all causes X 100, 000 ________ Live births
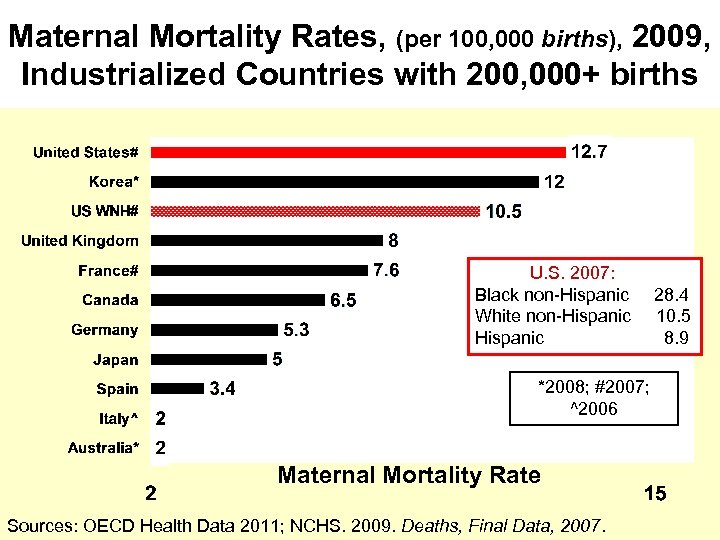
Maternal Mortality Rates, (per 100, 000 births), 2009, Industrialized Countries with 200, 000+ births U. S. 2007: Black non-Hispanic White non-Hispanic *2008; #2007; ^2006 Maternal Mortality Rate Sources: OECD Health Data 2011; NCHS. 2009. Deaths, Final Data, 2007. 28. 4 10. 5 8. 9

Other countries do better because the U. S. is different: -- more diversity, -- weaker social support system, -- inequality in our health care system. What if we compared subgroups in the U. S. to other countries? Birth. By. The. Numbers. org
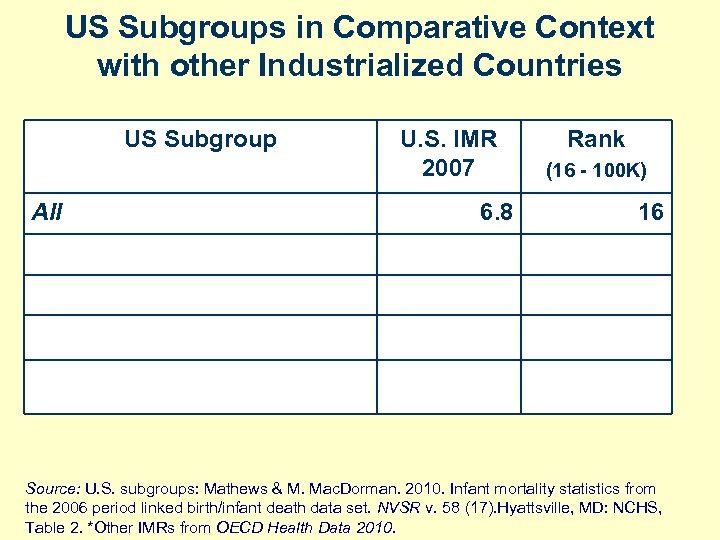
US Subgroups in Comparative Context with other Industrialized Countries US Subgroup All U. S. IMR 2007 6. 8 Rank (16 - 100 K) 16 Source: U. S. subgroups: Mathews & M. Mac. Dorman. 2010. Infant mortality statistics from the 2006 period linked birth/infant death data set. NVSR v. 58 (17). Hyattsville, MD: NCHS, Table 2. *Other IMRs from OECD Health Data 2010.
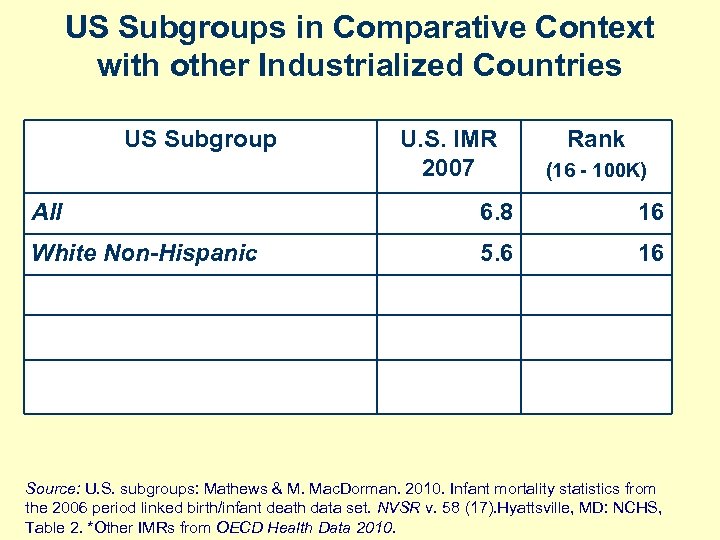
US Subgroups in Comparative Context with other Industrialized Countries US Subgroup U. S. IMR 2007 Rank (16 - 100 K) All 6. 8 16 White Non-Hispanic 5. 6 16 Source: U. S. subgroups: Mathews & M. Mac. Dorman. 2010. Infant mortality statistics from the 2006 period linked birth/infant death data set. NVSR v. 58 (17). Hyattsville, MD: NCHS, Table 2. *Other IMRs from OECD Health Data 2010.
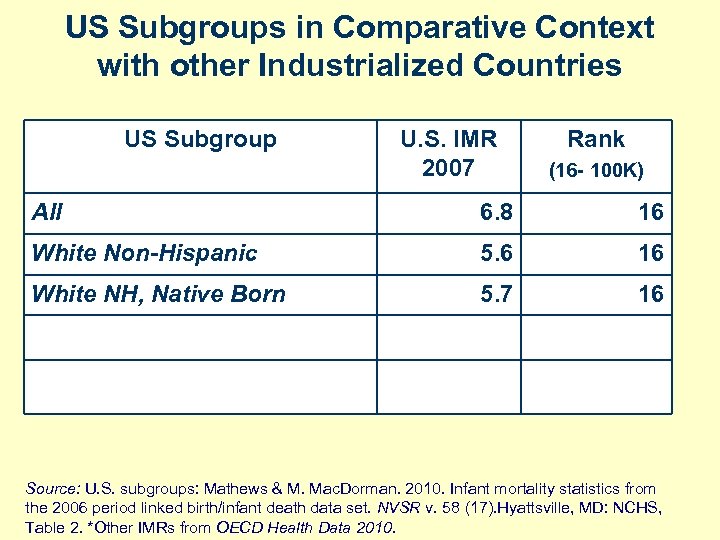
US Subgroups in Comparative Context with other Industrialized Countries US Subgroup U. S. IMR 2007 Rank (16 - 100 K) All 6. 8 16 White Non-Hispanic 5. 6 16 White NH, Native Born 5. 7 16 Source: U. S. subgroups: Mathews & M. Mac. Dorman. 2010. Infant mortality statistics from the 2006 period linked birth/infant death data set. NVSR v. 58 (17). Hyattsville, MD: NCHS, Table 2. *Other IMRs from OECD Health Data 2010.
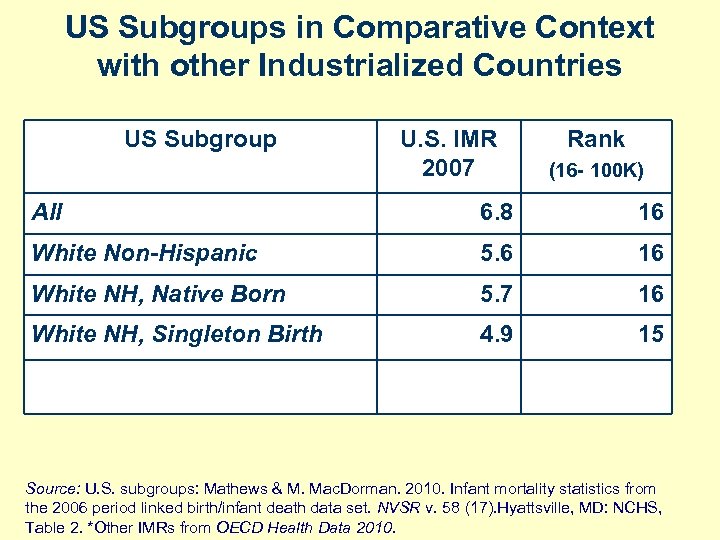
US Subgroups in Comparative Context with other Industrialized Countries US Subgroup U. S. IMR 2007 Rank (16 - 100 K) All 6. 8 16 White Non-Hispanic 5. 6 16 White NH, Native Born 5. 7 16 White NH, Singleton Birth 4. 9 15 Source: U. S. subgroups: Mathews & M. Mac. Dorman. 2010. Infant mortality statistics from the 2006 period linked birth/infant death data set. NVSR v. 58 (17). Hyattsville, MD: NCHS, Table 2. *Other IMRs from OECD Health Data 2010.
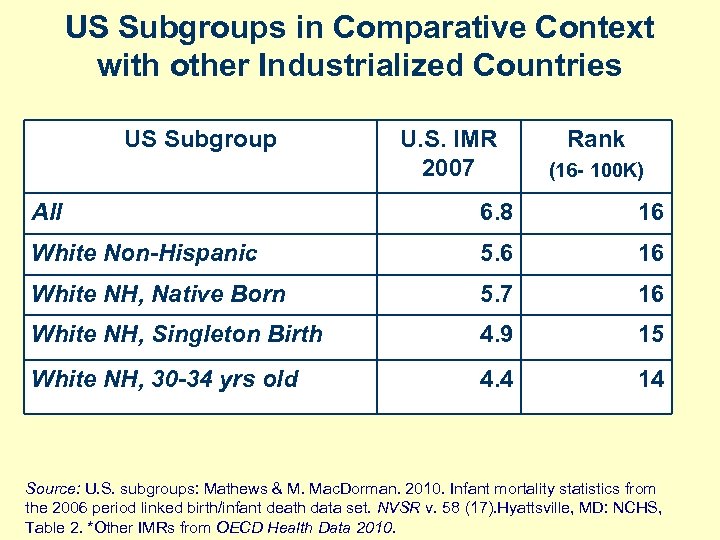
US Subgroups in Comparative Context with other Industrialized Countries US Subgroup U. S. IMR 2007 Rank (16 - 100 K) All 6. 8 16 White Non-Hispanic 5. 6 16 White NH, Native Born 5. 7 16 White NH, Singleton Birth 4. 9 15 White NH, 30 -34 yrs old 4. 4 14 Source: U. S. subgroups: Mathews & M. Mac. Dorman. 2010. Infant mortality statistics from the 2006 period linked birth/infant death data set. NVSR v. 58 (17). Hyattsville, MD: NCHS, Table 2. *Other IMRs from OECD Health Data 2010.

Examining Trends over Time
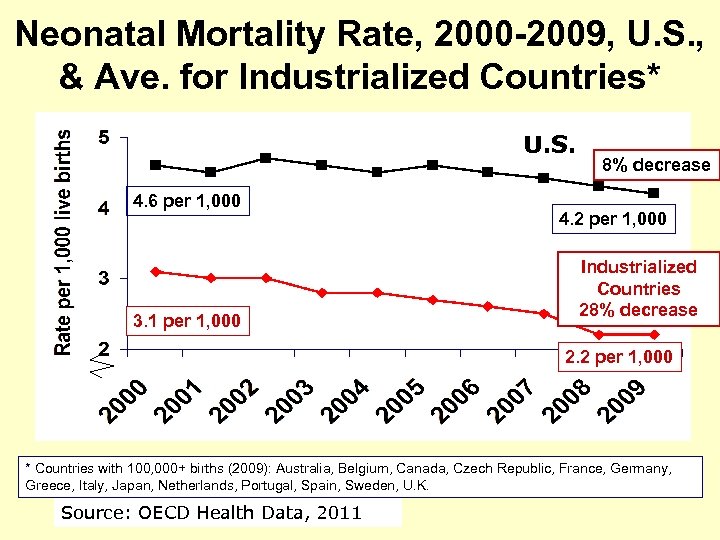
Neonatal Mortality Rate, 2000 -2009, U. S. , & Ave. for Industrialized Countries* U. S. 4. 6 per 1, 000 3. 1 per 1, 000 8% decrease 4. 2 per 1, 000 Industrialized Countries 28% decrease 2. 2 per 1, 000 * Countries with 100, 000+ births (2009): Australia, Belgium, Canada, Czech Republic, France, Germany, Greece, Italy, Japan, Netherlands, Portugal, Spain, Sweden, U. K. Source: OECD Health Data, 2011
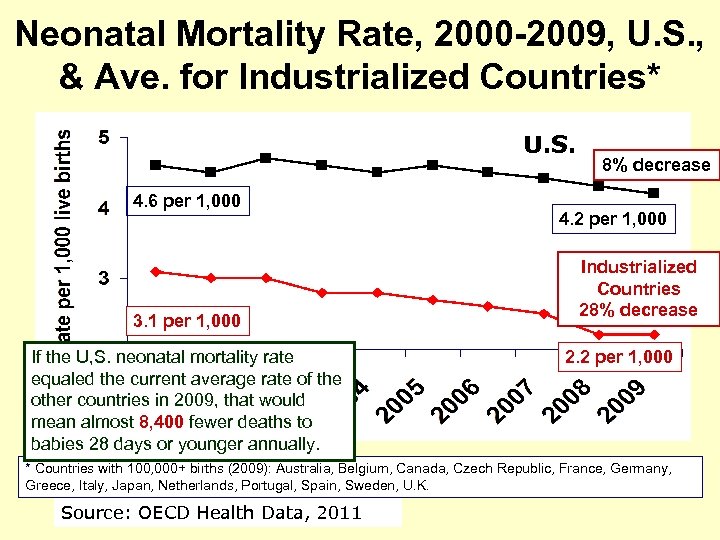
Neonatal Mortality Rate, 2000 -2009, U. S. , & Ave. for Industrialized Countries* U. S. 4. 6 per 1, 000 3. 1 per 1, 000 If the U, S. neonatal mortality rate equaled the current average rate of the other countries in 2009, that would mean almost 8, 400 fewer deaths to babies 28 days or younger annually. 8% decrease 4. 2 per 1, 000 Industrialized Countries 28% decrease 2. 2 per 1, 000 * Countries with 100, 000+ births (2009): Australia, Belgium, Canada, Czech Republic, France, Germany, Greece, Italy, Japan, Netherlands, Portugal, Spain, Sweden, U. K. Source: OECD Health Data, 2011
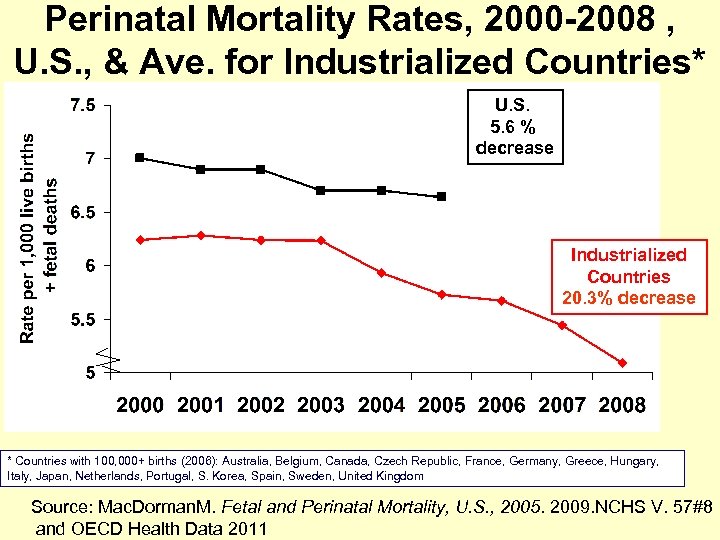
Perinatal Mortality Rates, 2000 -2008 , U. S. , & Ave. for Industrialized Countries* U. S. 5. 6 % decrease Industrialized Countries 20. 3% decrease * Countries with 100, 000+ births (2006): Australia, Belgium, Canada, Czech Republic, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Italy, Japan, Netherlands, Portugal, S. Korea, Spain, Sweden, United Kingdom Source: Mac. Dorman. M. Fetal and Perinatal Mortality, U. S. , 2005. 2009. NCHS V. 57#8 and OECD Health Data 2011
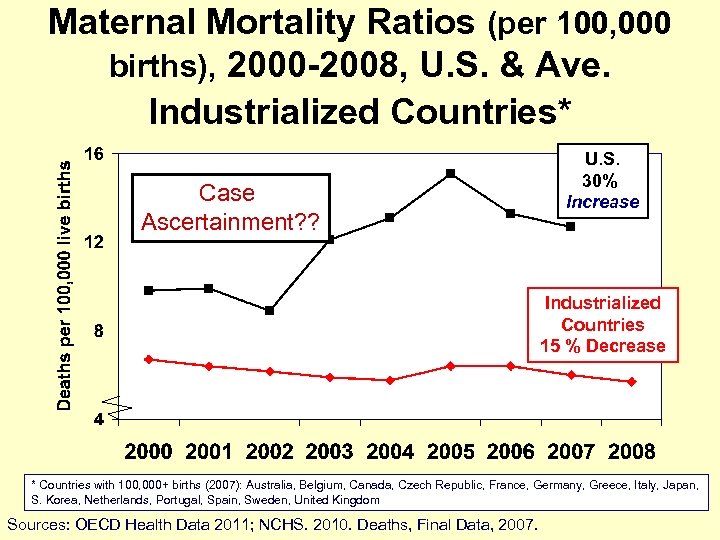
Maternal Mortality Ratios (per 100, 000 births), 2000 -2008, U. S. & Ave. Industrialized Countries* Case Ascertainment? ? U. S. 30% Increase Industrialized Countries 15 % Decrease * Countries with 100, 000+ births (2007): Australia, Belgium, Canada, Czech Republic, France, Germany, Greece, Italy, Japan, S. Korea, Netherlands, Portugal, Spain, Sweden, United Kingdom Sources: OECD Health Data 2011; NCHS. 2010. Deaths, Final Data, 2007.
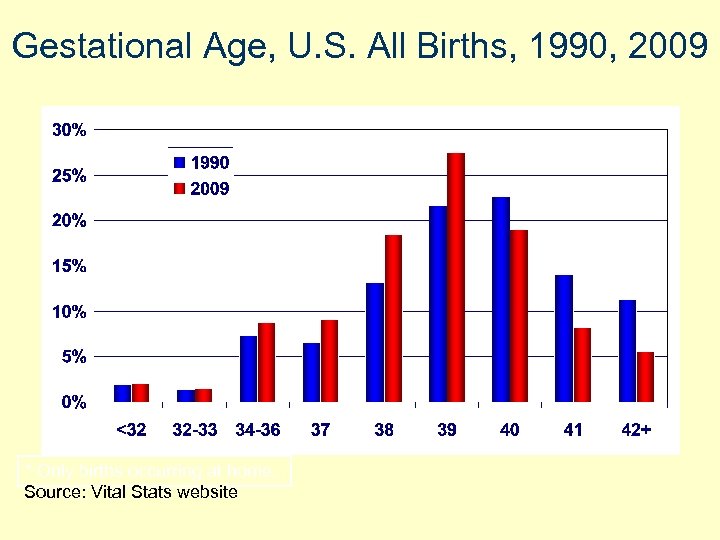
Gestational Age, U. S. All Births, 1990, 2009 * Only births occurring at home. Source: Vital Stats website

What about process? Birth. By. The. Numbers. org
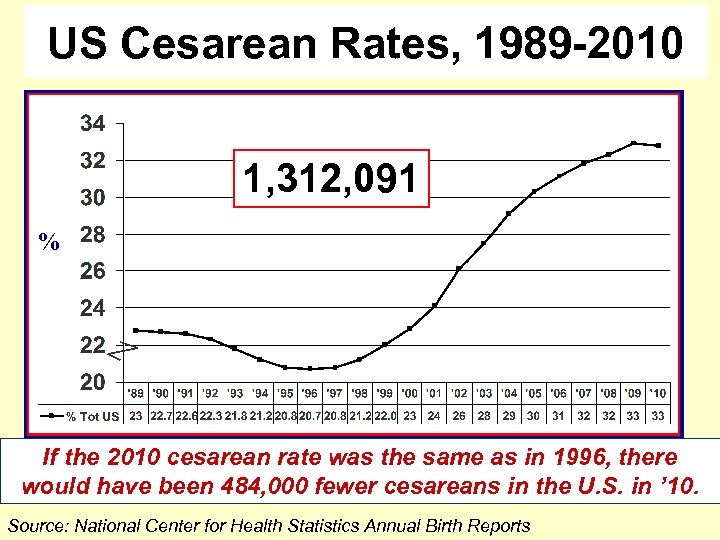
US Cesarean Rates, 1989 -2010 1, 312, 091 % If the 2010 cesarean rate was the same as in 1996, there would have been 484, 000 fewer cesareans in the U. S. in ’ 10. Source: National Center for Health Statistics Annual Birth Reports
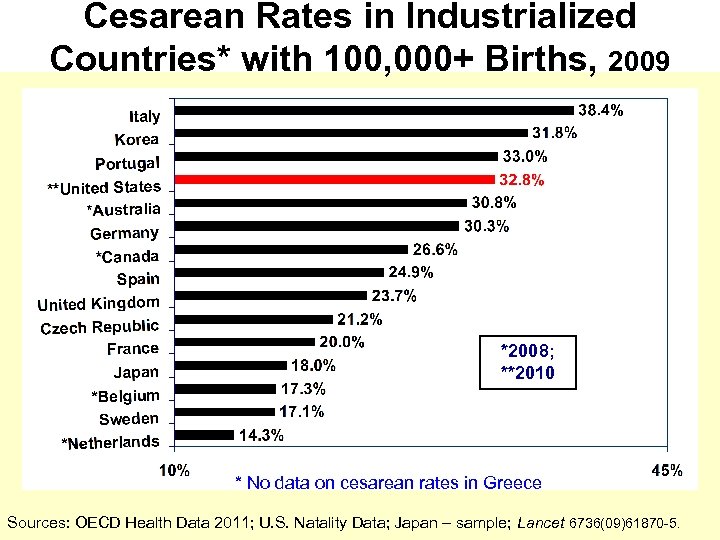
Cesarean Rates in Industrialized Countries* with 100, 000+ Births, 2009 *2008; **2010 * No data on cesarean rates in Greece Sources: OECD Health Data 2011; U. S. Natality Data; Japan – sample; Lancet 6736(09)61870 -5.
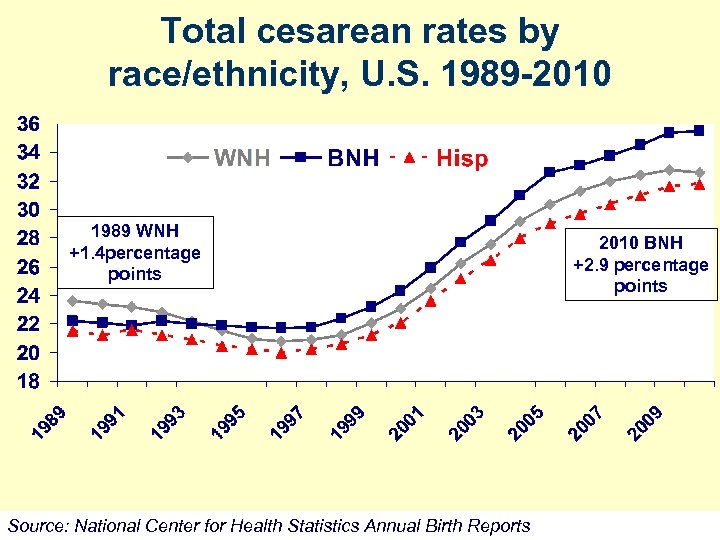
Total cesarean rates by race/ethnicity, U. S. 1989 -2010 1989 WNH +1. 4 percentage points Source: National Center for Health Statistics Annual Birth Reports 2010 BNH +2. 9 percentage points
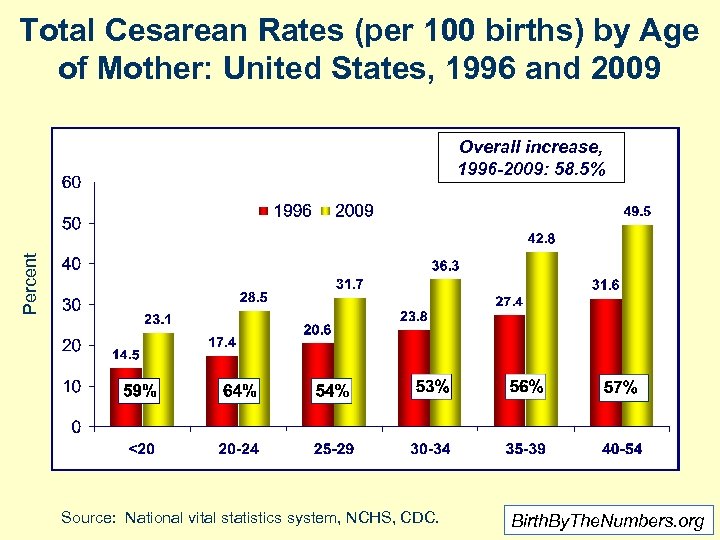
Total Cesarean Rates (per 100 births) by Age of Mother: United States, 1996 and 2009 Percent Overall increase, 1996 -2009: 58. 5% Source: National vital statistics system, NCHS, CDC. Birth. By. The. Numbers. org
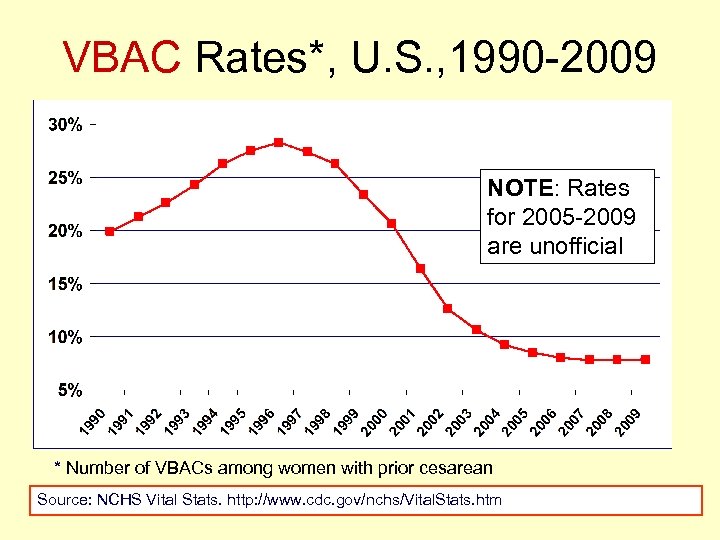
VBAC Rates*, U. S. , 1990 -2009 NOTE: Rates for 2005 -2009 are unofficial * Number of VBACs among women with prior cesarean Source: NCHS Vital Stats. http: //www. cdc. gov/nchs/Vital. Stats. htm
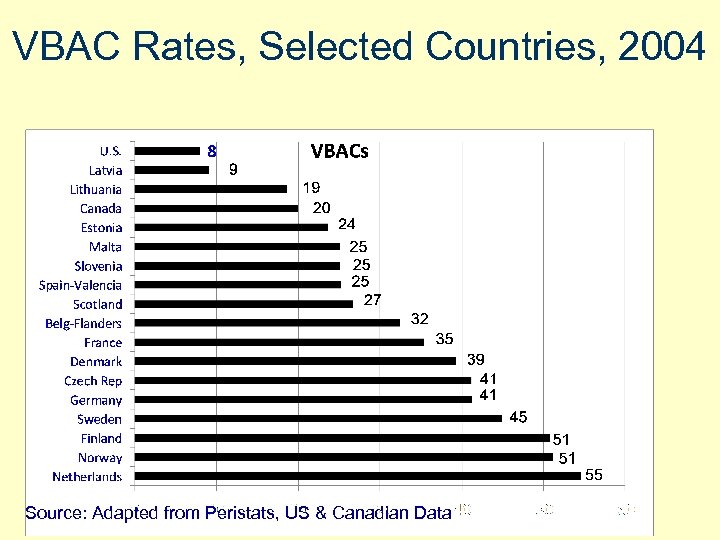
VBAC Rates, Selected Countries, 2004 Source: Adapted from Peristats, US & Canadian Data

Do High Rates of Intervention Matter? 1. Outcomes (NMR & GA) 2. Costs Birth. By. The. Numbers. org
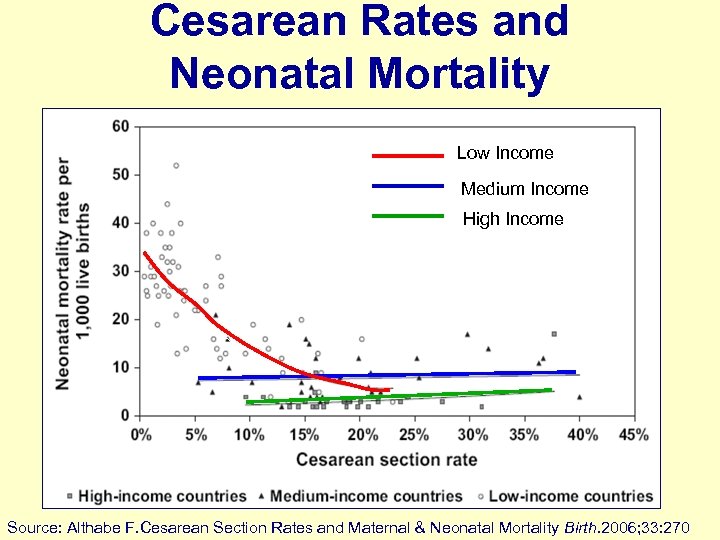
Cesarean Rates and Neonatal Mortality Low Income Medium Income High Income Source: Althabe F. Cesarean Section Rates and Maternal & Neonatal Mortality Birth. 2006; 33: 270
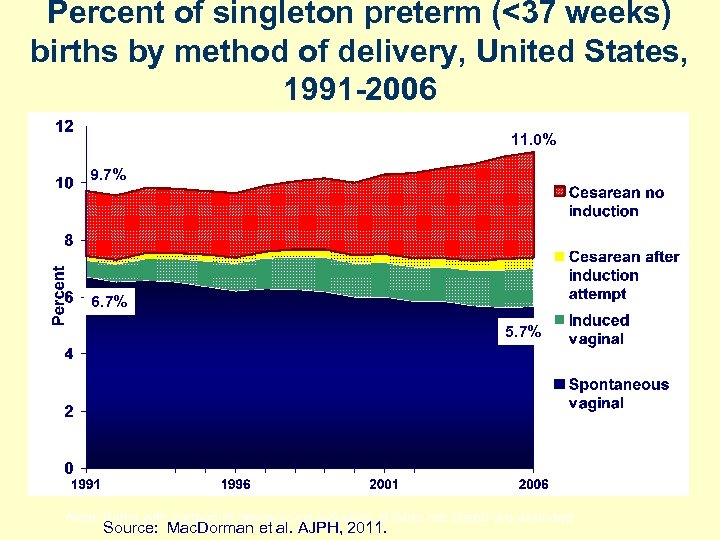
Percent of singleton preterm (<37 weeks) births by method of delivery, United States, 1991 -2006 11. 0% 9. 7% 6. 7% 5. 7% Note: Births with method of delivery and induction of labor not stated are excluded. Source: Mac. Dorman et al. AJPH, 2011.

National Costs and Hospitalizations
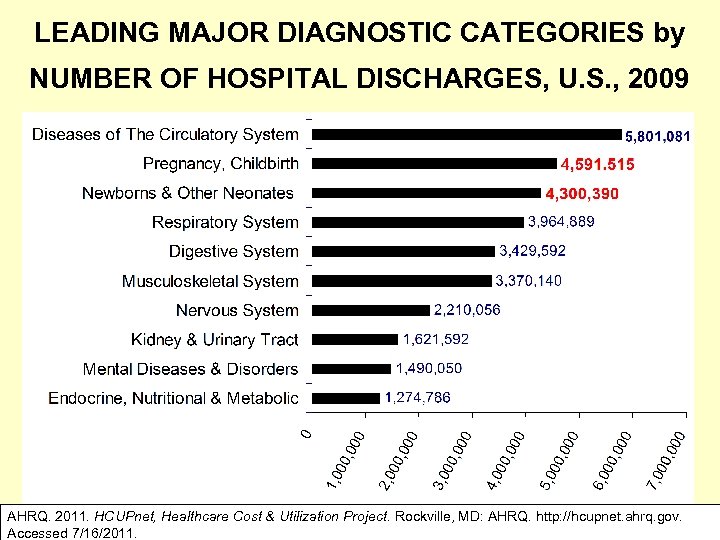
LEADING MAJOR DIAGNOSTIC CATEGORIES by NUMBER OF HOSPITAL DISCHARGES, U. S. , 2009 AHRQ. 2011. HCUPnet, Healthcare Cost & Utilization Project. Rockville, MD: AHRQ. http: //hcupnet. ahrq. gov. Accessed 7/16/2011.
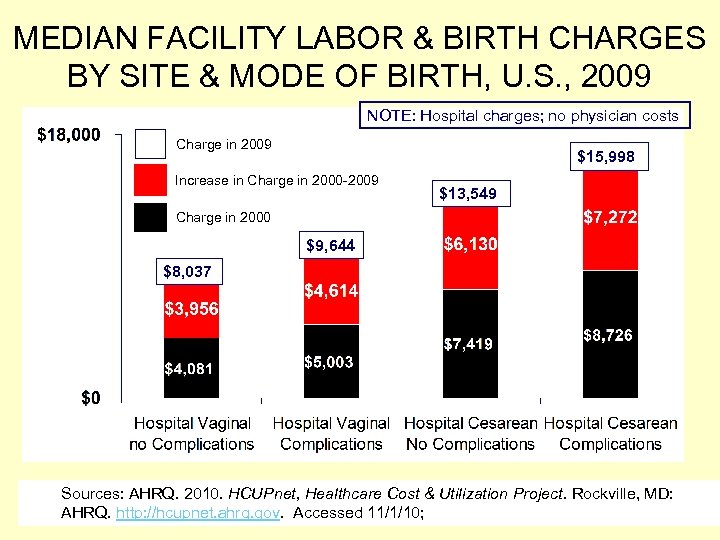
MEDIAN FACILITY LABOR & BIRTH CHARGES BY SITE & MODE OF BIRTH, U. S. , 2009 NOTE: Hospital charges; no physician costs Charge in 2009 $15, 998 Increase in Charge in 2000 -2009 $13, 549 Charge in 2000 $9, 644 $8, 037 Sources: AHRQ. 2010. HCUPnet, Healthcare Cost & Utilization Project. Rockville, MD: AHRQ. http: //hcupnet. ahrq. gov. Accessed 11/1/10;
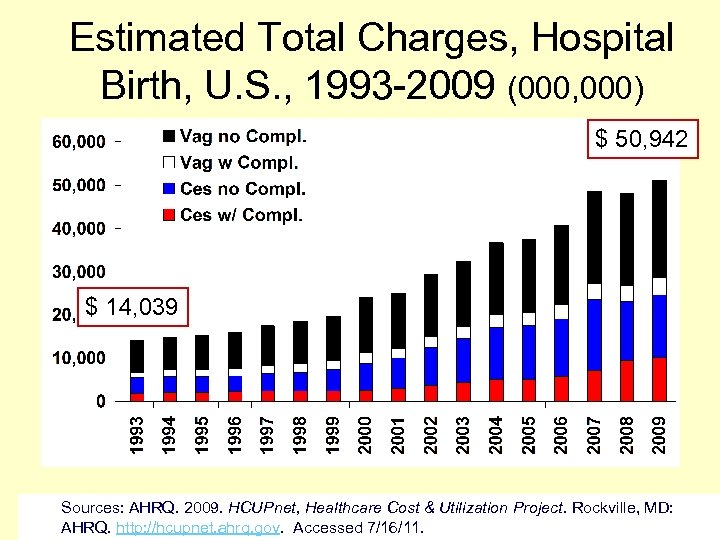
Estimated Total Charges, Hospital Birth, U. S. , 1993 -2009 (000, 000) $ 50, 942 $ 14, 039 Sources: AHRQ. 2009. HCUPnet, Healthcare Cost & Utilization Project. Rockville, MD: AHRQ. http: //hcupnet. ahrq. gov. Accessed 7/16/11.

Have maternal request cesareans played a major role in these increases? Birth. By. The. Numbers. org

Asking Mothers about Maternal Request Cesareans http: //www. childbirthconnection. org

Two Components to Maternal Request Primary Cesarean 1. Mother made request for planned cesarean before labor Birth. By. The. Numbers. org

Two Components to Maternal Request Primary Cesarean 1. Mother made request for planned cesarean before labor 2. Cesarean for no medical reason Birth. By. The. Numbers. org

Patient Choice Primary Cesareans • Combining reason for cesarean and timing of decision found only 1 respondent of 252 (0. 4%) had a planned primary cesarean for no medical reason. “I think that [cesarean] is… the best way … to give birth. It is a planned way, no hassle, no pain, the baby doesn’t struggle to come out, the baby is not pressed to come out …I think that … everybody should have the baby by cesarean section. ” Studies from England Canada confirm very low rates of maternal request cesareans Birth. By. The. Numbers. org
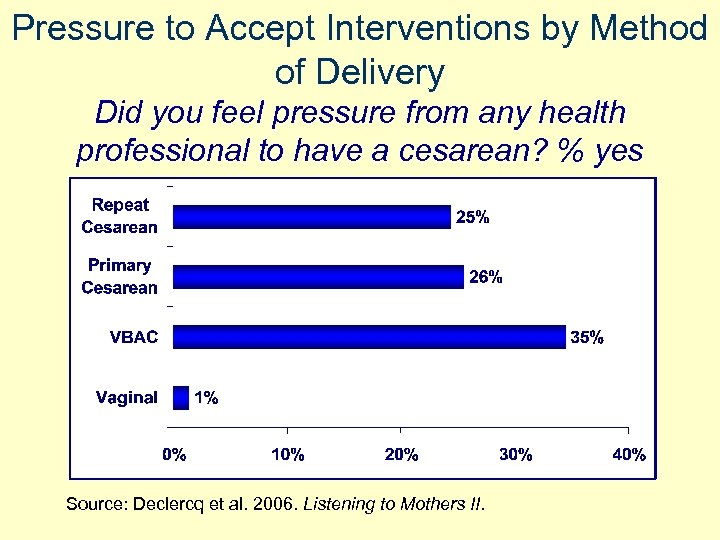
Pressure to Accept Interventions by Method of Delivery Did you feel pressure from any health professional to have a cesarean? % yes Source: Declercq et al. 2006. Listening to Mothers II.

Have maternal request cesareans played a major role in these increases? NO! So what is the reason for the increasing cesarean rate? Birth. By. The. Numbers. org

Have maternal request cesareans played a major role in these increases? NO! So what is the reason for the increasing cesarean rate? Practice Changes Birth. By. The. Numbers. org
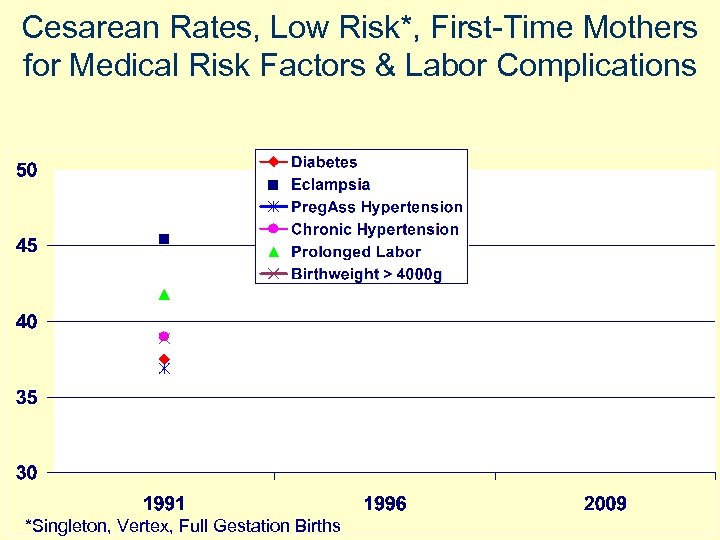
Cesarean Rates, Low Risk*, First-Time Mothers for Medical Risk Factors & Labor Complications *Singleton, Vertex, Full Gestation Births
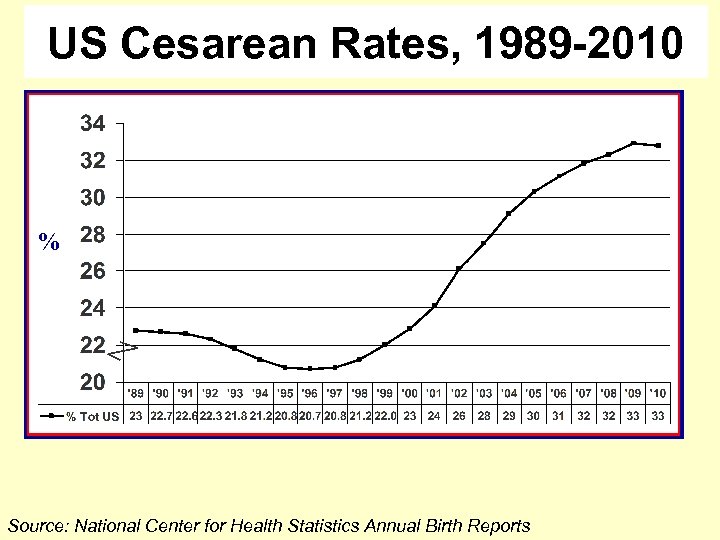
US Cesarean Rates, 1989 -2010 % Source: National Center for Health Statistics Annual Birth Reports
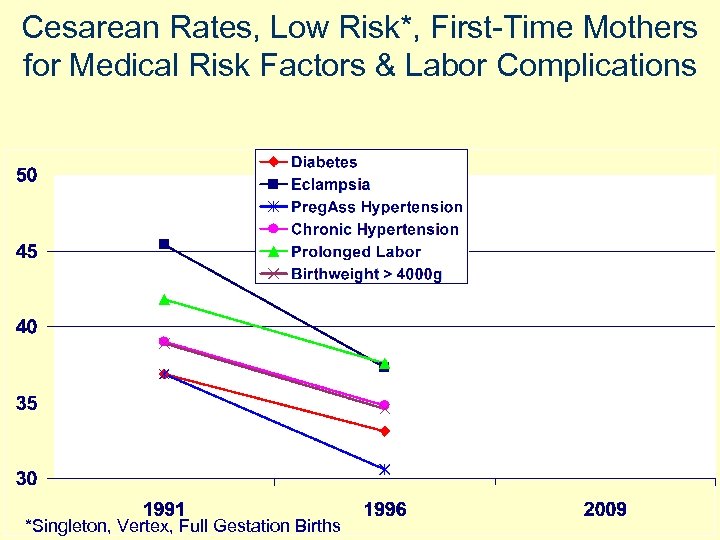
Cesarean Rates, Low Risk*, First-Time Mothers for Medical Risk Factors & Labor Complications *Singleton, Vertex, Full Gestation Births
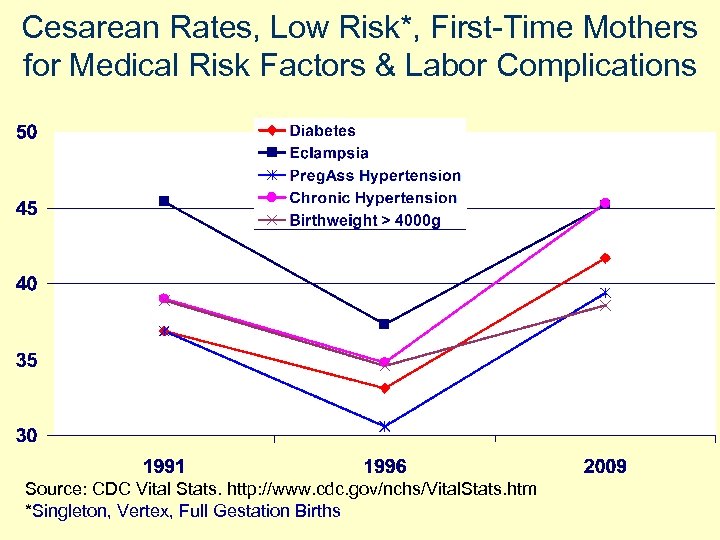
Cesarean Rates, Low Risk*, First-Time Mothers for Medical Risk Factors & Labor Complications Source: CDC Vital Stats. http: //www. cdc. gov/nchs/Vital. Stats. htm *Singleton, Vertex, Full Gestation Births
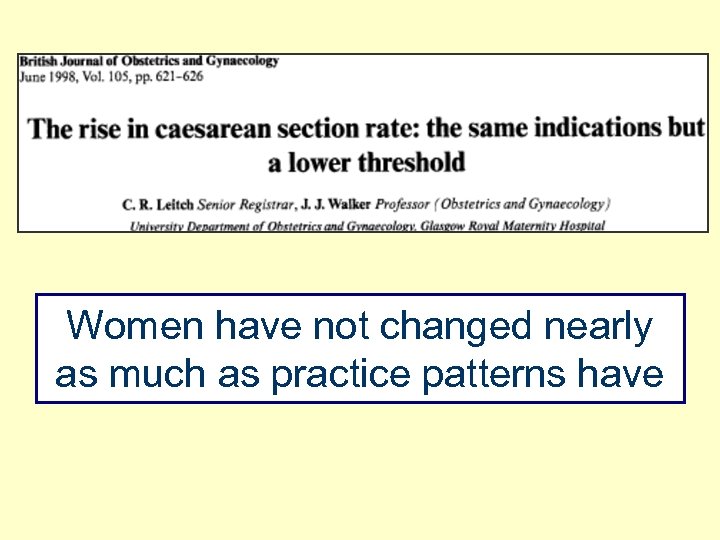
Women have not changed nearly as much as practice patterns have

For more information and additional resources regularly check: Birth. By. The. Numbers. org The site is updated as additional data becomes available.
9d55aa7acd4984dabec8526f309a002b.ppt