caa79800b3530fb108557ac89b42e4cc.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 75
 US and WWII Chapter 13 and 14
US and WWII Chapter 13 and 14
 Isolationism and Neutrality n n Traditional policy of isolationism Wilson and WWI n n n German submarines League of Nations Pacifism, 1920 s n America First
Isolationism and Neutrality n n Traditional policy of isolationism Wilson and WWI n n n German submarines League of Nations Pacifism, 1920 s n America First
 Rise of Dictatorships n n Fascism: glorifies war, preaches extreme nationalism, call for obedience to a dictator Italy n n Germany n n Mussolini Hitler Russia n Stalin
Rise of Dictatorships n n Fascism: glorifies war, preaches extreme nationalism, call for obedience to a dictator Italy n n Germany n n Mussolini Hitler Russia n Stalin
 The Rise of Adolf Hitler Hitler’s Early Years Born in Austria in 1889 Failed artist Fought in WWI Became an extreme nationalist Hitler & Nazi Party Became involved with Nazis in 1921 Made it a super party Hitler becomes dictator Nazis elected as largest single party Hitler appointed chancellor When president dies takes total power Anti-Semitic policies Resulted in Kristallnacht Promised economic recovery
The Rise of Adolf Hitler Hitler’s Early Years Born in Austria in 1889 Failed artist Fought in WWI Became an extreme nationalist Hitler & Nazi Party Became involved with Nazis in 1921 Made it a super party Hitler becomes dictator Nazis elected as largest single party Hitler appointed chancellor When president dies takes total power Anti-Semitic policies Resulted in Kristallnacht Promised economic recovery
 The Rise of Adolf Hitler U. S. Response Focus on domestic concerns FDR & New Deal Low military spending Security through disarmament Most Americans wanted to stay out of European affairs Policymakers supported disarmament, arms control, & international agreements to maintain world peace 1921 -22: US, France, GB, Japan, & Italy negotiated treaty placing limits on # of ships each country could build 1928: US joins 62 nations & signs Kellog-Briand Pact condemning war as a solution to international conflicts & national policy Supporters: first step in outlawing war Critics: no enforcement provisions
The Rise of Adolf Hitler U. S. Response Focus on domestic concerns FDR & New Deal Low military spending Security through disarmament Most Americans wanted to stay out of European affairs Policymakers supported disarmament, arms control, & international agreements to maintain world peace 1921 -22: US, France, GB, Japan, & Italy negotiated treaty placing limits on # of ships each country could build 1928: US joins 62 nations & signs Kellog-Briand Pact condemning war as a solution to international conflicts & national policy Supporters: first step in outlawing war Critics: no enforcement provisions
 Fascism in Italy Turmoil in Italy Severe economic & political problems Govt. not living up to promises Treaty of Versailles didn’t grant all land wanted Socialism gaining power but couldn’t stop worker revolts Mussolini & Fascism Socialist when young; WWI became nationalist member of Fascist Party Goal to unite Italians reminding them of glories of ancient Rome Mussolini’s Rise to Power 1922 led March on Rome led to king naming him prime minister Increased power & became totalitarian dictator Introduced economic programs to stimulate economy Italian Imperialism Fascist policies didn’t solve many economic problems so blamed world economy Wanted to distract people through aggressive foreign policy by building an empire attacked Ethiopia League of Nations imposed sanctions which forbid arms sales & money lending to Italy but didn’t cut off oil supplies to Italy (surely would’ve slowed the invasion) After fall of Ethiopia, League did not try to rescue it & later removed sanctions on Italy
Fascism in Italy Turmoil in Italy Severe economic & political problems Govt. not living up to promises Treaty of Versailles didn’t grant all land wanted Socialism gaining power but couldn’t stop worker revolts Mussolini & Fascism Socialist when young; WWI became nationalist member of Fascist Party Goal to unite Italians reminding them of glories of ancient Rome Mussolini’s Rise to Power 1922 led March on Rome led to king naming him prime minister Increased power & became totalitarian dictator Introduced economic programs to stimulate economy Italian Imperialism Fascist policies didn’t solve many economic problems so blamed world economy Wanted to distract people through aggressive foreign policy by building an empire attacked Ethiopia League of Nations imposed sanctions which forbid arms sales & money lending to Italy but didn’t cut off oil supplies to Italy (surely would’ve slowed the invasion) After fall of Ethiopia, League did not try to rescue it & later removed sanctions on Italy
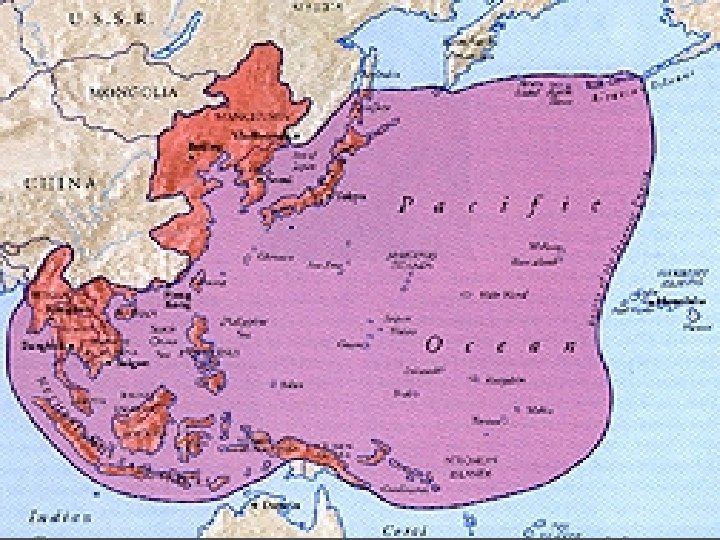
 Japanese Expansion n n n War with Russia (1905) 1931 with the invasion of Manchuria 1937 with attack on China (Rape of Nanking) On September 27, 1940, Japan signed the Tripartite Pact with Germany and Italy, thus entering the military alliance known as the "Axis. " n United States imposed economic sanctions on Japan wants to become dominate power in Pacific n Need oil and other natural resources December 7, 1941 Japanese attack Pearl Harbor. n The attack severely damaged the American fleet and prevented, at least for the short term, serious American interference with Japanese military operations. n The United States declared war on Japan. Following Germany's declaration of war on the United States, the United States also declared war on Germany. After the attack on Pearl Harbor, Japan achieved a long series of military successes. In December 1941, Guam and Wake Island fell to the Japanese, followed in the first half of 1942 by the Philippines, the Dutch East Indies, Hong Kong, Malaya, Singapore, and Burma. Only in mid-1942 were Australian and New Zealander forces in New Guinea and British forces in India able to halt the Japanese advance. Hirohito Tojo
Japanese Expansion n n n War with Russia (1905) 1931 with the invasion of Manchuria 1937 with attack on China (Rape of Nanking) On September 27, 1940, Japan signed the Tripartite Pact with Germany and Italy, thus entering the military alliance known as the "Axis. " n United States imposed economic sanctions on Japan wants to become dominate power in Pacific n Need oil and other natural resources December 7, 1941 Japanese attack Pearl Harbor. n The attack severely damaged the American fleet and prevented, at least for the short term, serious American interference with Japanese military operations. n The United States declared war on Japan. Following Germany's declaration of war on the United States, the United States also declared war on Germany. After the attack on Pearl Harbor, Japan achieved a long series of military successes. In December 1941, Guam and Wake Island fell to the Japanese, followed in the first half of 1942 by the Philippines, the Dutch East Indies, Hong Kong, Malaya, Singapore, and Burma. Only in mid-1942 were Australian and New Zealander forces in New Guinea and British forces in India able to halt the Japanese advance. Hirohito Tojo
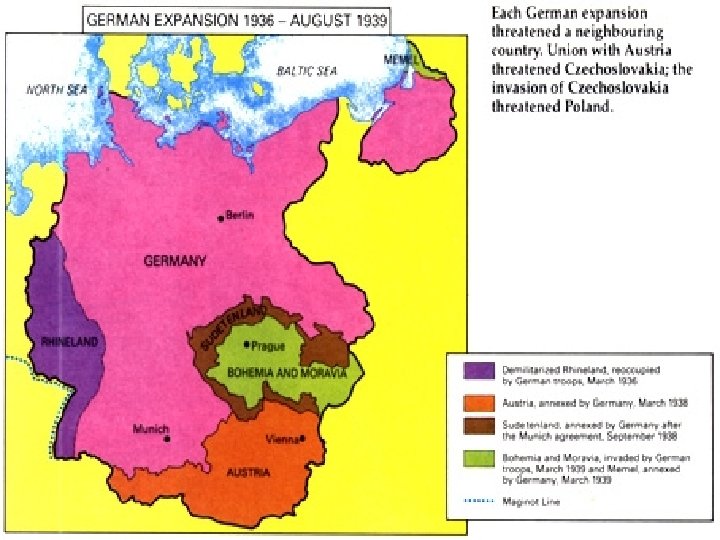
 Triumph of Aggression n n Timid policies of the democracies Germany n n Italy n n Ignore Treaty of Versailles Rhineland (1936) Austria, Czechoslovakia (1938) Ethiopia (1936) Japan n Manchuria (1931) China (1937) Japan withdraws from the League of Nations
Triumph of Aggression n n Timid policies of the democracies Germany n n Italy n n Ignore Treaty of Versailles Rhineland (1936) Austria, Czechoslovakia (1938) Ethiopia (1936) Japan n Manchuria (1931) China (1937) Japan withdraws from the League of Nations
 Neutrality Acts of 1935 -1937 In response to occurrences in Europe, Congress enacted the following Neutrality Acts n No sale or shipment of arms to belligerents n No loans or credits to belligerents n No travel by US citizens on belligerents’ ships n Purchase of non-military goods by belligerents to be paid in cash and transported in their ships n CASH AND CARRY
Neutrality Acts of 1935 -1937 In response to occurrences in Europe, Congress enacted the following Neutrality Acts n No sale or shipment of arms to belligerents n No loans or credits to belligerents n No travel by US citizens on belligerents’ ships n Purchase of non-military goods by belligerents to be paid in cash and transported in their ships n CASH AND CARRY
 Spanish Civil War n n n 1936 Fascists tried to overturn the Republican government Russia aid the Republicans (comprised of socialists and communists) Italy and Germany aid the Fascists n n Try out new weapons Tanks and airplanes 1939 Spain fell to Fascism Leader – Francisco Franco
Spanish Civil War n n n 1936 Fascists tried to overturn the Republican government Russia aid the Republicans (comprised of socialists and communists) Italy and Germany aid the Fascists n n Try out new weapons Tanks and airplanes 1939 Spain fell to Fascism Leader – Francisco Franco
 FDR’s “Quarantine” Speech n n n Concern over aggression by Germany, Italy, Fascist Spain, and Japan Speech given after Japan invaded China Proposed that democratic nations “quarantine” aggressors to “protect the health of the international community against the spread of the disease”
FDR’s “Quarantine” Speech n n n Concern over aggression by Germany, Italy, Fascist Spain, and Japan Speech given after Japan invaded China Proposed that democratic nations “quarantine” aggressors to “protect the health of the international community against the spread of the disease”
 Munich Conference n n n Appeasement – yield to demands in order to avoid conflict British and French leaders applied this policy Gave in to Hitler’s annexation of the Sudetenland Hitler claimed it was the last act of expansion he would make Few months later, Germany threatened Poland Clear that Hitler could only be stopped with force
Munich Conference n n n Appeasement – yield to demands in order to avoid conflict British and French leaders applied this policy Gave in to Hitler’s annexation of the Sudetenland Hitler claimed it was the last act of expansion he would make Few months later, Germany threatened Poland Clear that Hitler could only be stopped with force
 Start of WWII n n September 1939, Germany invaded Poland Blitzkrieg Britain and France declared war on Germany German victories
Start of WWII n n September 1939, Germany invaded Poland Blitzkrieg Britain and France declared war on Germany German victories
 Non-Aggression Pact n n n Prewar, 1939 Signed between Russia and Germany Agreed not to attack each other if war broke out
Non-Aggression Pact n n n Prewar, 1939 Signed between Russia and Germany Agreed not to attack each other if war broke out
 Invasion of Britain? n n n France defeated Soviet Union uninvolved in war Britain alone had to defend Europe against Italy and Germany planned a heavy bombing of England RAF- Royal Air Force Called off by Hitler – destroy infastructure
Invasion of Britain? n n n France defeated Soviet Union uninvolved in war Britain alone had to defend Europe against Italy and Germany planned a heavy bombing of England RAF- Royal Air Force Called off by Hitler – destroy infastructure
 Gradual US Involvement n n Would a German victory in Europe threaten US security? Neutrality Act of 1939 n n n Sell war materials Cash Carry Lend Lease n n Lend war materials to Britain Is the US still neutral?
Gradual US Involvement n n Would a German victory in Europe threaten US security? Neutrality Act of 1939 n n n Sell war materials Cash Carry Lend Lease n n Lend war materials to Britain Is the US still neutral?
 Atlantic Charter n n n Aboard ship near Newfoundland Meeting between Churchill and FDR Goals n n Right of all nations to self determination Not seek territory from war Disarmament of aggressors “permanent system of general security”
Atlantic Charter n n n Aboard ship near Newfoundland Meeting between Churchill and FDR Goals n n Right of all nations to self determination Not seek territory from war Disarmament of aggressors “permanent system of general security”
 Pearl Harbor n n n Japanese aggressions in China violate Open Door Policy 1940: US embargo Surprise attack on American fleet to keep US out of Asia December 7, 1941 Sink 19 ships, destroy 150 planes, killed 2, 335 soldiers
Pearl Harbor n n n Japanese aggressions in China violate Open Door Policy 1940: US embargo Surprise attack on American fleet to keep US out of Asia December 7, 1941 Sink 19 ships, destroy 150 planes, killed 2, 335 soldiers
 “Arsenal of Democracy” n n n Allied victory depended upon how fast the US could turn out war goods Government encouraged every industry to stop production of consumer goods Build ships, planes, bombs, bullets, etc.
“Arsenal of Democracy” n n n Allied victory depended upon how fast the US could turn out war goods Government encouraged every industry to stop production of consumer goods Build ships, planes, bombs, bullets, etc.
 Rosie the Riveter n n n Young men joined armed forces Women became the chief producers of ships, aircrafts, etc. 15 million in 1941 to 19 million in 1945 Nurses New attitudes toward gender roles
Rosie the Riveter n n n Young men joined armed forces Women became the chief producers of ships, aircrafts, etc. 15 million in 1941 to 19 million in 1945 Nurses New attitudes toward gender roles
 Mobilization n n n End of the Depression! Congress enacted a draft (selective service) in 1940 Every man between 21 and 35 was required to register for service 1/3 eligible were in service 500, 000 African Americans served Continued Great Migration
Mobilization n n n End of the Depression! Congress enacted a draft (selective service) in 1940 Every man between 21 and 35 was required to register for service 1/3 eligible were in service 500, 000 African Americans served Continued Great Migration
 War Agencies n n War Powers Act War Production Board n “use it up, wear it out, make do, or do without!”
War Agencies n n War Powers Act War Production Board n “use it up, wear it out, make do, or do without!”
 Financing the War n n n Growth of government debt Buy war bonds! Taxes Impact of War on the economy Bob Hope and USO shows n Entertain US soldiers
Financing the War n n n Growth of government debt Buy war bonds! Taxes Impact of War on the economy Bob Hope and USO shows n Entertain US soldiers
 Rationing n n n n Clothing Sugar Meat Rubber Gasoline Receive coupon books Office of Price Administration
Rationing n n n n Clothing Sugar Meat Rubber Gasoline Receive coupon books Office of Price Administration
 Military Service n n Harsh conditions/ environment Psychological Problems Wounded disabled for life Goal – Save Democracy!
Military Service n n Harsh conditions/ environment Psychological Problems Wounded disabled for life Goal – Save Democracy!
 Assistance to the Soviet Union n Hitler violated his nonaggression pact in June, 1941 when he invaded the Soviet Union US give Soviet’s military aid US followed up with Lend Lease
Assistance to the Soviet Union n Hitler violated his nonaggression pact in June, 1941 when he invaded the Soviet Union US give Soviet’s military aid US followed up with Lend Lease
 Europe First Strategy n n Despite attack on Pearl Harbor, US wanted to defeat Nazis first Take three years to win back what took Germany months to acquire
Europe First Strategy n n Despite attack on Pearl Harbor, US wanted to defeat Nazis first Take three years to win back what took Germany months to acquire
 Important Battles n Stalingrad n n El Alamein n n Hitler want to control, gain access to Middle East First time anyone achieve victory against Hitler No one allowed to retreat North Africa Turning point Montgomery (B) vs. Rommel (G) Invasion of Sicily Liberation of Italy
Important Battles n Stalingrad n n El Alamein n n Hitler want to control, gain access to Middle East First time anyone achieve victory against Hitler No one allowed to retreat North Africa Turning point Montgomery (B) vs. Rommel (G) Invasion of Sicily Liberation of Italy
 North African Campaign n n Dwight D. Eisenhower Meeting in Casablanca n n US and Britain Italy Unconditional Surrender The Battle of the Atlantic n Allied Advantages
North African Campaign n n Dwight D. Eisenhower Meeting in Casablanca n n US and Britain Italy Unconditional Surrender The Battle of the Atlantic n Allied Advantages
 Invasion of Sicily and Italy n n n Invasion of Sicily Italy’s surrender Northern Italy n n n Mussolini flee to North Hitler sets up puppet government Where is Hitler fighting? The Battle of Rome Bombing of Europe
Invasion of Sicily and Italy n n n Invasion of Sicily Italy’s surrender Northern Italy n n n Mussolini flee to North Hitler sets up puppet government Where is Hitler fighting? The Battle of Rome Bombing of Europe
 Cairo and Tehran Conference n n Cairo n Big Three? n FDR n Churchill n Chiang Kai-shek – why not Stalin? n Make decisions about post war Asia n Islands; China (Manchuria, etc); Korea n Unconditional Surrender Tehran (2 days after Cairo Conference) n The Big Three n Stalin n FDR n Churchill n Planning D-Day n Want to make it a 2 front war for Germany n Russia enters war against Japan
Cairo and Tehran Conference n n Cairo n Big Three? n FDR n Churchill n Chiang Kai-shek – why not Stalin? n Make decisions about post war Asia n Islands; China (Manchuria, etc); Korea n Unconditional Surrender Tehran (2 days after Cairo Conference) n The Big Three n Stalin n FDR n Churchill n Planning D-Day n Want to make it a 2 front war for Germany n Russia enters war against Japan
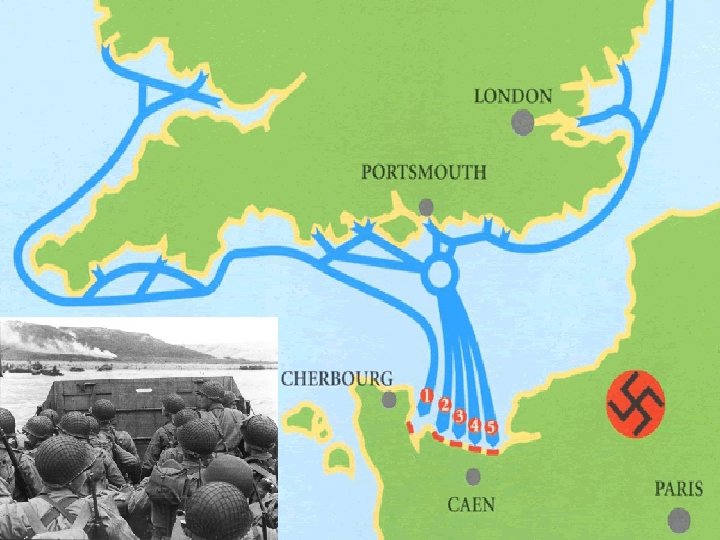
 n D-Day n June 6, 1944 Largest amphibious force in history crossed the English Channel to secure beaches of Normandy n n n Stubborn Hitler General Dwight D. Eisenhower n n n Germany heavily fortified area Knew invasion along beaches likely – cliffs Patton Calais Does most of planning Speech Liberated Paris by August n n Fight for every inch of land! Germans had been in area 4 years
n D-Day n June 6, 1944 Largest amphibious force in history crossed the English Channel to secure beaches of Normandy n n n Stubborn Hitler General Dwight D. Eisenhower n n n Germany heavily fortified area Knew invasion along beaches likely – cliffs Patton Calais Does most of planning Speech Liberated Paris by August n n Fight for every inch of land! Germans had been in area 4 years
 Yalta Conference n Big Three n n Roosevelt’s Ideas n n n Meet in Crimea United Nations Plans for Japan What to do with Germany?
Yalta Conference n Big Three n n Roosevelt’s Ideas n n n Meet in Crimea United Nations Plans for Japan What to do with Germany?
 End of War in Europe n n Britain and US push from West Soviet troops move in from East n n n Gain miles a day Love of Stalin Legacy April 1945 - US and Soviet troops met on German soil Hitler committed suicide in Berlin
End of War in Europe n n Britain and US push from West Soviet troops move in from East n n n Gain miles a day Love of Stalin Legacy April 1945 - US and Soviet troops met on German soil Hitler committed suicide in Berlin
 Collapse of Third Reich n FDR dies! n n Mussolini dies! n n Admiral of Navy sign German surrender April 28 Hitler dies! n n April 12 April 30 Dreams of World Domination die!
Collapse of Third Reich n FDR dies! n n Mussolini dies! n n Admiral of Navy sign German surrender April 28 Hitler dies! n n April 12 April 30 Dreams of World Domination die!
 Discovery of Nazi Holocaust These charred bodies were found by U. S. troops of the 80 th Division in furnace of horror chamber at the Buchenwald concentration camp near Jena, Germany. 4/16/45 This pile of clothes belonged to prisoners of the Dachau concentration camp, recently liberated by troops of the U. S. Seventh Army.
Discovery of Nazi Holocaust These charred bodies were found by U. S. troops of the 80 th Division in furnace of horror chamber at the Buchenwald concentration camp near Jena, Germany. 4/16/45 This pile of clothes belonged to prisoners of the Dachau concentration camp, recently liberated by troops of the U. S. Seventh Army.
 During the latter part of our imprisonment, the daily ration consisted of very watery soup given out once daily, and the usual small bread ration. In addition to that, there was the so-called "extra allowance, " consisting of three-fourths of an ounce of margarine, or a slice of poor quality sausage, or of a little piece of cheese, or a bit of synthetic honey, or a spoonful of watery jam, varying daily. In calories, this diet was absolutely inadequate, especially taking into consideration our heavy manual work and our constant exposure to the cold in inadequate clothing. The sick who were "under special care"--that is, those who were allowed to lie in the huts instead of leaving the camp for work-were worse off. When the last layers of subcutaneous fat had vanished and we looked like skeletons disguised with skin and rags, we could watch our bodies beginning to devour themselves. The organism digested its own protein, and the muscles disappeared. Then the body had no powers of resistance left. .
During the latter part of our imprisonment, the daily ration consisted of very watery soup given out once daily, and the usual small bread ration. In addition to that, there was the so-called "extra allowance, " consisting of three-fourths of an ounce of margarine, or a slice of poor quality sausage, or of a little piece of cheese, or a bit of synthetic honey, or a spoonful of watery jam, varying daily. In calories, this diet was absolutely inadequate, especially taking into consideration our heavy manual work and our constant exposure to the cold in inadequate clothing. The sick who were "under special care"--that is, those who were allowed to lie in the huts instead of leaving the camp for work-were worse off. When the last layers of subcutaneous fat had vanished and we looked like skeletons disguised with skin and rags, we could watch our bodies beginning to devour themselves. The organism digested its own protein, and the muscles disappeared. Then the body had no powers of resistance left. .
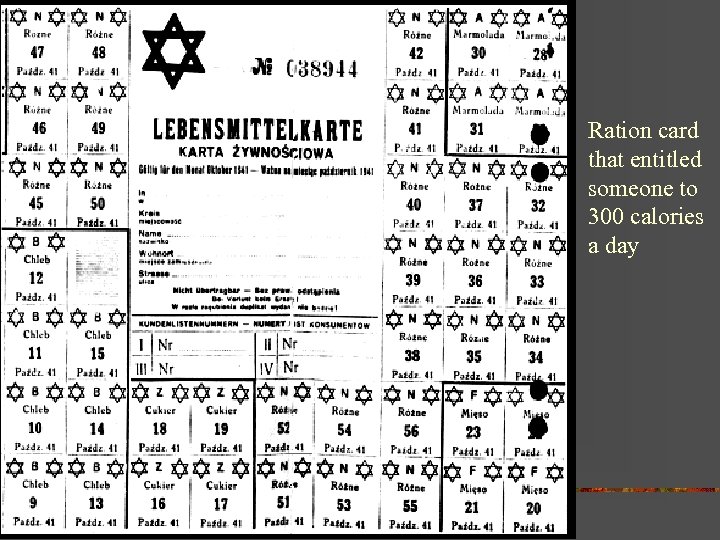 Ration card that entitled someone to 300 calories a day
Ration card that entitled someone to 300 calories a day
 US soldiers with Hitler Youth examining bodies that have been starved to death
US soldiers with Hitler Youth examining bodies that have been starved to death
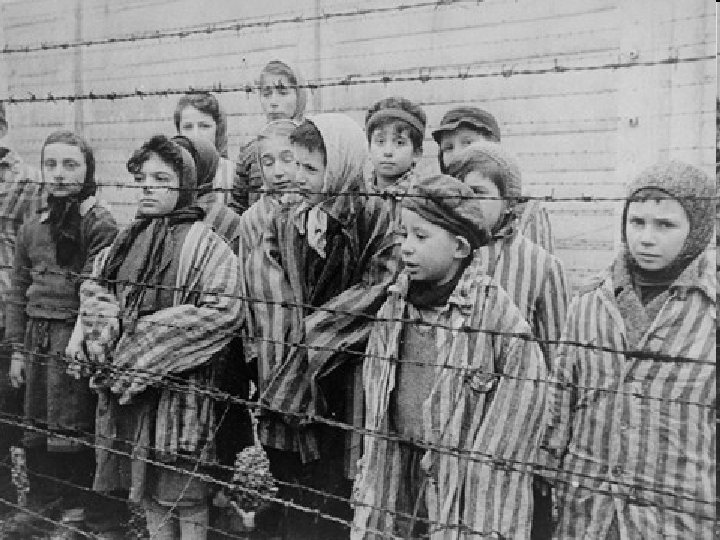

 Nuremburg Trials n n n What do we do with Germany? Nazis? 21 War Criminals How should the proceed? n n Agree to trial at Yalta Why Nuremburg? Set down the principle that there were such things as crimes against humanity and systematic crimes against civilians that can occur inside a country but that might be tried anywhere else Since Holocaust there has been genocide in Yugoslavia, Rwanda, and Cambodia
Nuremburg Trials n n n What do we do with Germany? Nazis? 21 War Criminals How should the proceed? n n Agree to trial at Yalta Why Nuremburg? Set down the principle that there were such things as crimes against humanity and systematic crimes against civilians that can occur inside a country but that might be tried anywhere else Since Holocaust there has been genocide in Yugoslavia, Rwanda, and Cambodia
 VE Day n n May 7, 1945 Ended the war in Europe
VE Day n n May 7, 1945 Ended the war in Europe
 WWII in the Pacific n n 1942, Japan occupied much of Asia and the islands of the South Pacific Island Hopping n n Want islands of strategic importance Want islands that put is in range of Japan
WWII in the Pacific n n 1942, Japan occupied much of Asia and the islands of the South Pacific Island Hopping n n Want islands of strategic importance Want islands that put is in range of Japan
 Early American Battles n n n Douglas Macarthur and the Philippines Japanese Strategy Battle of the Coral Sea
Early American Battles n n n Douglas Macarthur and the Philippines Japanese Strategy Battle of the Coral Sea
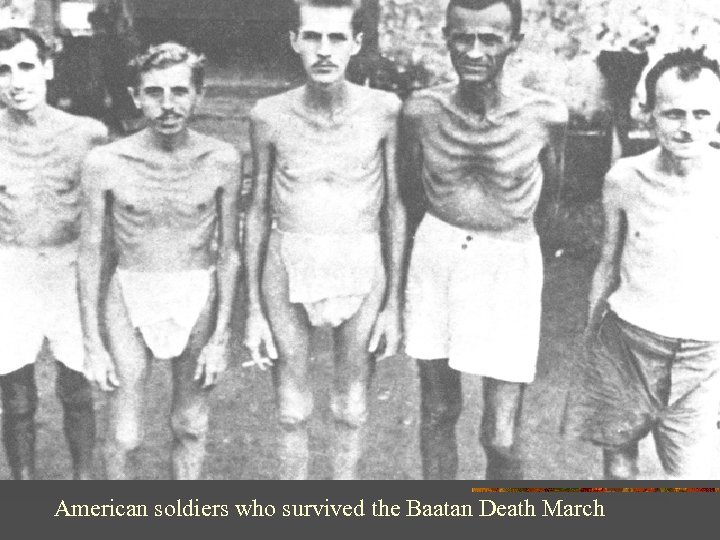 American soldiers who survived the Baatan Death March
American soldiers who survived the Baatan Death March
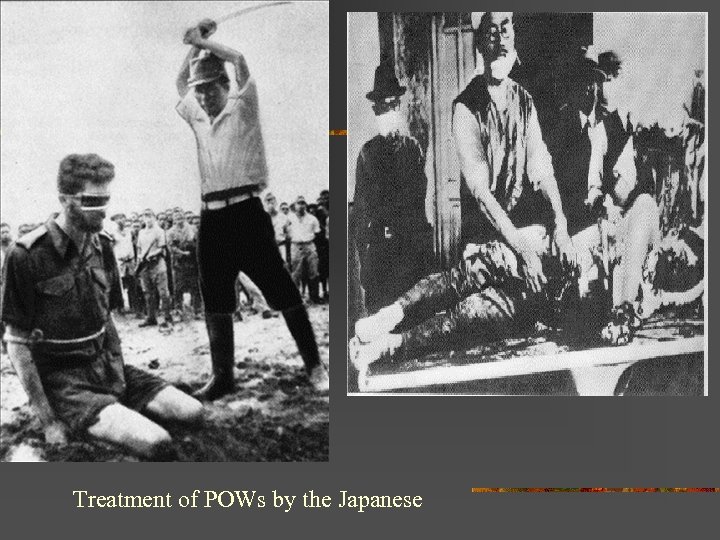 Treatment of POWs by the Japanese
Treatment of POWs by the Japanese
 Battle of Midway n n June 4, 1942 Goal of Capturing Midway Cryptologists Turning Point of War in the Pacific
Battle of Midway n n June 4, 1942 Goal of Capturing Midway Cryptologists Turning Point of War in the Pacific
 War in the Pacific n n Guadalcanal Offensive Leapfrogging n n General Mac. Arthur Central Pacific n n n Nimitz Battle of Phillipine Sea Battle of Leyte Gulf
War in the Pacific n n Guadalcanal Offensive Leapfrogging n n General Mac. Arthur Central Pacific n n n Nimitz Battle of Phillipine Sea Battle of Leyte Gulf
 Toward an Invasion of Japan? n n Philippines Iwo Jima Okinawa Kamikazee
Toward an Invasion of Japan? n n Philippines Iwo Jima Okinawa Kamikazee
 To drop or not drop an atomic bomb? n Manhattan Project n n n Albert Einstein Los Alamos, New Mexico Decision to use n n Invade Japan? Bomb’s destructiveness would force a surrender
To drop or not drop an atomic bomb? n Manhattan Project n n n Albert Einstein Los Alamos, New Mexico Decision to use n n Invade Japan? Bomb’s destructiveness would force a surrender
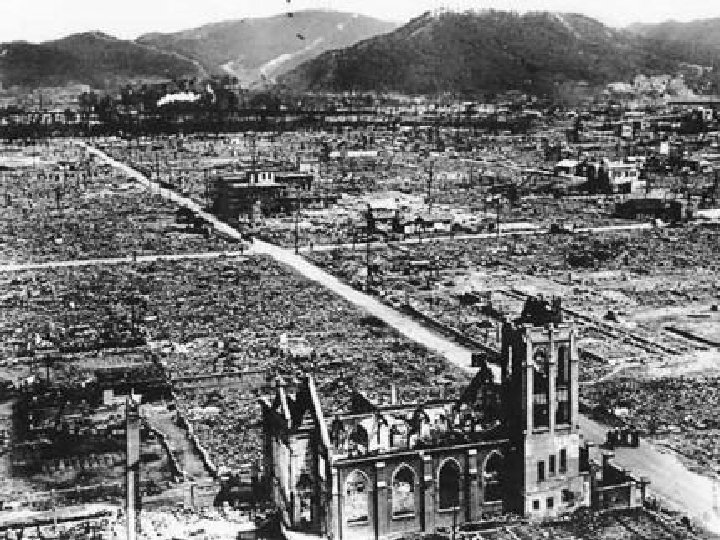
 Quick end to the War? n n Truman did decide to use the Atomic Bomb August 6, 1945 n n n Hiroshima Enola Gay August 9, 1945 n n Nagasaki 100, 000 deaths
Quick end to the War? n n Truman did decide to use the Atomic Bomb August 6, 1945 n n n Hiroshima Enola Gay August 9, 1945 n n Nagasaki 100, 000 deaths
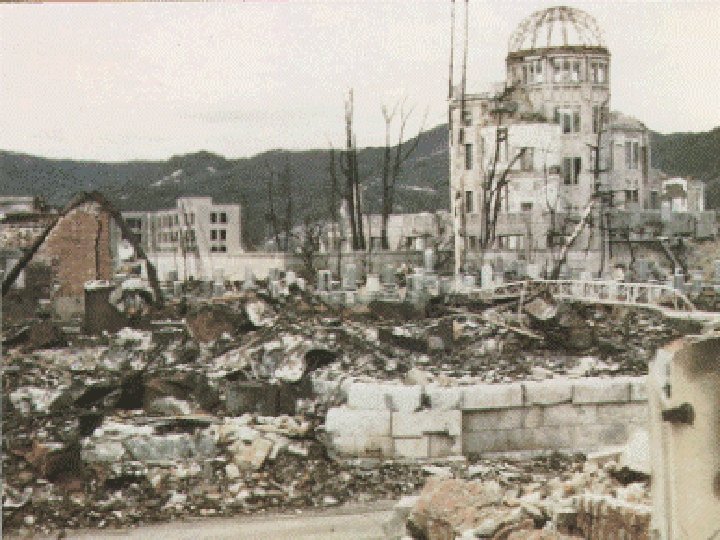


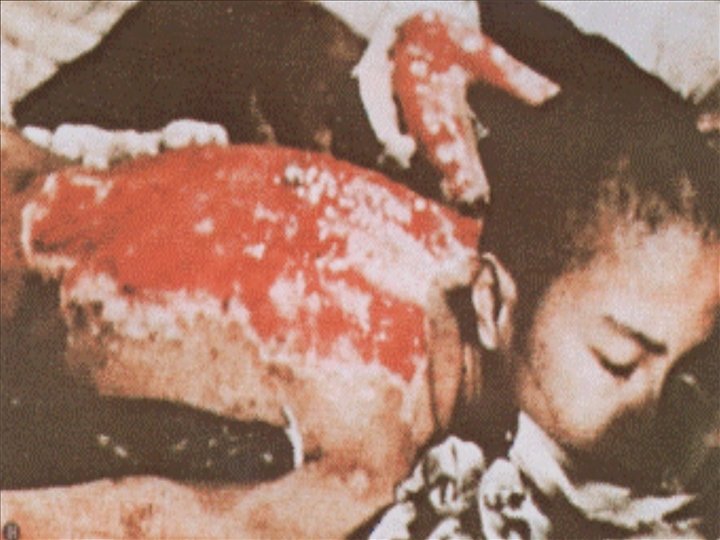
 A girl with her skin hanging in strips after the bombing of Hiroshima
A girl with her skin hanging in strips after the bombing of Hiroshima
 VJ Day n n September 2, 1945 Japan surrender after the US dropped bombs on Hiroshima and Nagasaki
VJ Day n n September 2, 1945 Japan surrender after the US dropped bombs on Hiroshima and Nagasaki
 US occupation of Japan n n n General Douglas Macarthur responsible for New Constitution took all power from the Emperor Guaranteed free elections Ban Japanese Army/Navy Millions of dollars spent rebuilding economy Recovery by 1955
US occupation of Japan n n n General Douglas Macarthur responsible for New Constitution took all power from the Emperor Guaranteed free elections Ban Japanese Army/Navy Millions of dollars spent rebuilding economy Recovery by 1955
 WWII Home front n n Rosie the Riveter Cease production of peace time goods Factories produce bombers, fighter planes, ships Children helped by planting victory gardens, collecting scrap metal, or paper
WWII Home front n n Rosie the Riveter Cease production of peace time goods Factories produce bombers, fighter planes, ships Children helped by planting victory gardens, collecting scrap metal, or paper

 African Americans in the War n n Military Service War Industries “Double V” Tuskegee Airmen
African Americans in the War n n Military Service War Industries “Double V” Tuskegee Airmen
 Mobilization of African Americans and Hispanic Americans n n The scale of the United States' war production effort during World War II touched every corner of the nation and millions of people. When traditional farm workers left for military service or higher paying jobs in war industries, the U. S. government looked south to Mexico. Several thousands braceros were invited to work in the United States, primarily in agriculture. This photograph of braceros in Texas cotton country, though, shows that in some places African Americans (especially men who were too young to join the army) worked alongside Mexican laborers. A bracero later recalled that harvesting cotton was the hardest work of all; one bracero corridista sang, "But I too came to pick cotton / and they have to pay me / for each hundred pounds a dollar / You can see I am quite skinny / From lack of food to eat. "
Mobilization of African Americans and Hispanic Americans n n The scale of the United States' war production effort during World War II touched every corner of the nation and millions of people. When traditional farm workers left for military service or higher paying jobs in war industries, the U. S. government looked south to Mexico. Several thousands braceros were invited to work in the United States, primarily in agriculture. This photograph of braceros in Texas cotton country, though, shows that in some places African Americans (especially men who were too young to join the army) worked alongside Mexican laborers. A bracero later recalled that harvesting cotton was the hardest work of all; one bracero corridista sang, "But I too came to pick cotton / and they have to pay me / for each hundred pounds a dollar / You can see I am quite skinny / From lack of food to eat. "
 Bracero Program n Aaron Castañeda Gamez and thousands of other Mexican workers had to pass a series of examinations to enter the bracero program. Recruits reported to centers in Mexico where they were inspected for lice and disease. Braceros' hands were inspected to see if they had calluses, indicating they were familiar with manual labor. They were told to disrobe and were then sprayed with the pesticide DDT. The processing stage lasted for several days, most of which were spent standing in line. Finally, if the man passed all the exams, he was given an identification card that certified his acceptance in the program. This card notes that Castañeda was to perform "railroad track labor only" and, like all braceros, was exempt from the wartime requirement of registering for the draft.
Bracero Program n Aaron Castañeda Gamez and thousands of other Mexican workers had to pass a series of examinations to enter the bracero program. Recruits reported to centers in Mexico where they were inspected for lice and disease. Braceros' hands were inspected to see if they had calluses, indicating they were familiar with manual labor. They were told to disrobe and were then sprayed with the pesticide DDT. The processing stage lasted for several days, most of which were spent standing in line. Finally, if the man passed all the exams, he was given an identification card that certified his acceptance in the program. This card notes that Castañeda was to perform "railroad track labor only" and, like all braceros, was exempt from the wartime requirement of registering for the draft.
 Hispanics n n n People moved to the cities Mexicans recruited to be farm laborers “Bracero” Program n n 200, 000 Mexicans came legally n n 1942 -1964 More came illegally “Zoot Suit” riots
Hispanics n n n People moved to the cities Mexicans recruited to be farm laborers “Bracero” Program n n 200, 000 Mexicans came legally n n 1942 -1964 More came illegally “Zoot Suit” riots
 Native Americans n n Support for War Code talkers
Native Americans n n Support for War Code talkers
 Japanese Americans n n Executive Order 9066 (1942) FDR bend to nativist pressures Forced removal of 110, 000 Japanese Americans from their homes to “relocation centers” Korematsu vs. US ruled that removal was justified by military necessity
Japanese Americans n n Executive Order 9066 (1942) FDR bend to nativist pressures Forced removal of 110, 000 Japanese Americans from their homes to “relocation centers” Korematsu vs. US ruled that removal was justified by military necessity
 Source: In 1941 President Roosevelt ordered the State Department to investigate the loyalty of Japanese Americans. Special Representative of the State Department Curtis B. Munson carried out the investigation in October and November of 1941 and presented what came to be known as the “Munson Report” to the President on November 7, 1941. The excerpt above is from the 25 -page report. n There is no Japanese `problem' on the Coast. There will be no armed uprising of Japanese. There will undoubtedly be some sabotage financed by Japan and executed largely by imported agents. . . In each Naval District there about 250 to 300 suspects under surveillance. It is easy to get on the suspect list, merely a speech in favor of Japan at some banquet being sufficient to land one there. The Intelligence Services are generous with the title of suspect and are taking no chances. Privately, they believe that only 50 or 60 in each district can be classed as really dangerous. The Japanese are hampered as saboteurs because of their easily recognized physical appearance. It will be hard for them to get near anything to blow up if it is guarded. There is far more danger from Communists and people of the Bridges type on the Coast than there is from Japanese. The Japanese here is almost exclusively a farmer, a fisherman or a small businessman. He has no entree to plants or intricate machinery
Source: In 1941 President Roosevelt ordered the State Department to investigate the loyalty of Japanese Americans. Special Representative of the State Department Curtis B. Munson carried out the investigation in October and November of 1941 and presented what came to be known as the “Munson Report” to the President on November 7, 1941. The excerpt above is from the 25 -page report. n There is no Japanese `problem' on the Coast. There will be no armed uprising of Japanese. There will undoubtedly be some sabotage financed by Japan and executed largely by imported agents. . . In each Naval District there about 250 to 300 suspects under surveillance. It is easy to get on the suspect list, merely a speech in favor of Japan at some banquet being sufficient to land one there. The Intelligence Services are generous with the title of suspect and are taking no chances. Privately, they believe that only 50 or 60 in each district can be classed as really dangerous. The Japanese are hampered as saboteurs because of their easily recognized physical appearance. It will be hard for them to get near anything to blow up if it is guarded. There is far more danger from Communists and people of the Bridges type on the Coast than there is from Japanese. The Japanese here is almost exclusively a farmer, a fisherman or a small businessman. He has no entree to plants or intricate machinery
 Source: Harry Paxton Howard, “Americans in Concentration Camps, ” The Crisis, September, 1942. Founded in 1910, The Crisis is one of the oldest black periodicals in America. The publication is dedicated to promoting civil rights. The excerpt above is from an editorial that appeared soon after the establishment of internment camps. n Along the eastern coast of the United States, where the numbers of Americans of Japanese ancestry is comparatively small, no concentration camps have been established. From a military point of view, the only danger on this coast is from Germany and Italy…But the American government has not taken any such high-handed action against Germans and Italians – and their American-born descendants – on the East Coast, as has been taken against Japanese and their American-born descendants on the West Coast. Germans and Italians are “white. ” Color seems to be the only possible reason why thousands of American citizens of Japanese ancestry are in concentration camps. Anyway, there are no Italian. American, or German-American citizens in such camps
Source: Harry Paxton Howard, “Americans in Concentration Camps, ” The Crisis, September, 1942. Founded in 1910, The Crisis is one of the oldest black periodicals in America. The publication is dedicated to promoting civil rights. The excerpt above is from an editorial that appeared soon after the establishment of internment camps. n Along the eastern coast of the United States, where the numbers of Americans of Japanese ancestry is comparatively small, no concentration camps have been established. From a military point of view, the only danger on this coast is from Germany and Italy…But the American government has not taken any such high-handed action against Germans and Italians – and their American-born descendants – on the East Coast, as has been taken against Japanese and their American-born descendants on the West Coast. Germans and Italians are “white. ” Color seems to be the only possible reason why thousands of American citizens of Japanese ancestry are in concentration camps. Anyway, there are no Italian. American, or German-American citizens in such camps
 Korematsu Ruling We uphold the exclusion order as of the time it was made and when the petitioner violated it…. In doing so, we are not unmindful of the hardships imposed by it upon a large group of American citizens…. But hardships are part of war, and war is an aggregation of hardships. All citizens alike, both in and out of uniform, feel the impact of war in greater or lesser measure. Citizenship has its responsibilities, as well as its privileges, and, in time of war, the burden is always heavier. Compulsory exclusion of large groups of citizens from their homes, except under circumstances of direst emergency and peril, is inconsistent with our basic governmental institutions. But when, under conditions of modern warfare, our shores are threatened by hostile forces, the power to protect must be commensurate with the threatened danger… To cast this case into outlines of racial prejudice, without reference to the real military dangers which were presented, merely confuses the issue. Korematsu was not excluded from the Military Area because of hostility to him or his race. He was excluded because we are at war with the Japanese Empire, because the properly constituted military authorities feared an invasion of our West Coast and felt constrained to take proper security measures, because they decided that the military urgency of the situation demanded that all citizens of Japanese ancestry be segregated from the West Coast temporarily, and, finally, because Congress, reposing its confidence in this time of war in our military leaders -- as inevitably it must -- determined that they should have the power to do just this.
Korematsu Ruling We uphold the exclusion order as of the time it was made and when the petitioner violated it…. In doing so, we are not unmindful of the hardships imposed by it upon a large group of American citizens…. But hardships are part of war, and war is an aggregation of hardships. All citizens alike, both in and out of uniform, feel the impact of war in greater or lesser measure. Citizenship has its responsibilities, as well as its privileges, and, in time of war, the burden is always heavier. Compulsory exclusion of large groups of citizens from their homes, except under circumstances of direst emergency and peril, is inconsistent with our basic governmental institutions. But when, under conditions of modern warfare, our shores are threatened by hostile forces, the power to protect must be commensurate with the threatened danger… To cast this case into outlines of racial prejudice, without reference to the real military dangers which were presented, merely confuses the issue. Korematsu was not excluded from the Military Area because of hostility to him or his race. He was excluded because we are at war with the Japanese Empire, because the properly constituted military authorities feared an invasion of our West Coast and felt constrained to take proper security measures, because they decided that the military urgency of the situation demanded that all citizens of Japanese ancestry be segregated from the West Coast temporarily, and, finally, because Congress, reposing its confidence in this time of war in our military leaders -- as inevitably it must -- determined that they should have the power to do just this.
 Source: In 1980, Congress established the Commission on Wartime Relocation and Internment of Civilians to investigate the detention program and the constitutionality of Executive Order 9066. The Commission released its report “Personal Justice Denied: The Report of the Commission on Wartime Relocation and Internment of Civilians” on February 24, 1983. The passage above is an excerpt from this report The Commission held 20 days of hearings in cities across the country, particularly on the West Coast, hearing testimony from more than 750 witnesses: evacuees, former government officials, public figures, interested citizens, and historians and other professionals who have studied the subjects of Commission inquiry. An extensive effort was made to locate and to review the records of government action and to analyze other sources of information including contemporary writings, personal accounts and historical analyses…. . . Executive Order 9066 was not justified by military necessity, and the decisions which followed from it—detention, ending detention and ending exclusion—were not driven by analysis of military conditions. The broad historical causes which shaped these decisions were race prejudice, war hysteria and a failure of political leadership. Widespread ignorance of Japanese Americans contributed to a policy conceived in haste and executed in an atmosphere of fear and anger at Japan. A grave injustice was done to American citizens and resident aliens of Japanese ancestry who, without individual review or any…evidence against them, were excluded, removed and detained by the United States during World War II.
Source: In 1980, Congress established the Commission on Wartime Relocation and Internment of Civilians to investigate the detention program and the constitutionality of Executive Order 9066. The Commission released its report “Personal Justice Denied: The Report of the Commission on Wartime Relocation and Internment of Civilians” on February 24, 1983. The passage above is an excerpt from this report The Commission held 20 days of hearings in cities across the country, particularly on the West Coast, hearing testimony from more than 750 witnesses: evacuees, former government officials, public figures, interested citizens, and historians and other professionals who have studied the subjects of Commission inquiry. An extensive effort was made to locate and to review the records of government action and to analyze other sources of information including contemporary writings, personal accounts and historical analyses…. . . Executive Order 9066 was not justified by military necessity, and the decisions which followed from it—detention, ending detention and ending exclusion—were not driven by analysis of military conditions. The broad historical causes which shaped these decisions were race prejudice, war hysteria and a failure of political leadership. Widespread ignorance of Japanese Americans contributed to a policy conceived in haste and executed in an atmosphere of fear and anger at Japan. A grave injustice was done to American citizens and resident aliens of Japanese ancestry who, without individual review or any…evidence against them, were excluded, removed and detained by the United States during World War II.

 Toward an Everlasting Peace? n n Estimates of Death and Destruction Impacts on the US and the Soviets
Toward an Everlasting Peace? n n Estimates of Death and Destruction Impacts on the US and the Soviets
 Death Toll Soviet Union n n 15 million civilians 7. 5 million soldiers Germany n n 300, 000 civilians 1. 59 million soldiers Great Britain n 5 million civilians 2. 85 million soldiers Japan n n France n n n 65, 000 civilians 398, 000 soldiers 108, 000 civilians 211, 111 soldiers US n n 0 civilians 292, 000 soldiers
Death Toll Soviet Union n n 15 million civilians 7. 5 million soldiers Germany n n 300, 000 civilians 1. 59 million soldiers Great Britain n 5 million civilians 2. 85 million soldiers Japan n n France n n n 65, 000 civilians 398, 000 soldiers 108, 000 civilians 211, 111 soldiers US n n 0 civilians 292, 000 soldiers


