9d62def33b8e1c3f447e6af5807b3172.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 52
 Urinary Tract Infection 2 nd Affiliated Hospital ZJ University Yu Gong
Urinary Tract Infection 2 nd Affiliated Hospital ZJ University Yu Gong
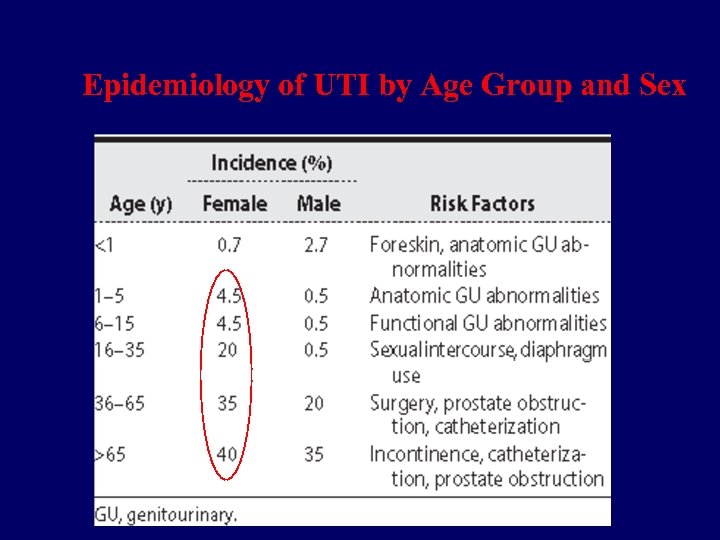 Epidemiology of UTI by Age Group and Sex
Epidemiology of UTI by Age Group and Sex
 Balance Host Pathogen
Balance Host Pathogen

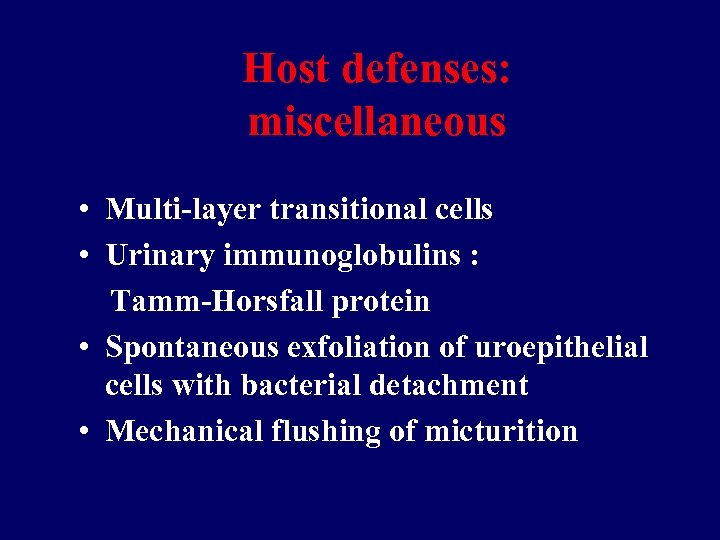 Host defenses: miscellaneous • Multi-layer transitional cells • Urinary immunoglobulins : Tamm-Horsfall protein • Spontaneous exfoliation of uroepithelial cells with bacterial detachment • Mechanical flushing of micturition
Host defenses: miscellaneous • Multi-layer transitional cells • Urinary immunoglobulins : Tamm-Horsfall protein • Spontaneous exfoliation of uroepithelial cells with bacterial detachment • Mechanical flushing of micturition
 Come with a rush, go with a flush!
Come with a rush, go with a flush!
 Pathogens
Pathogens
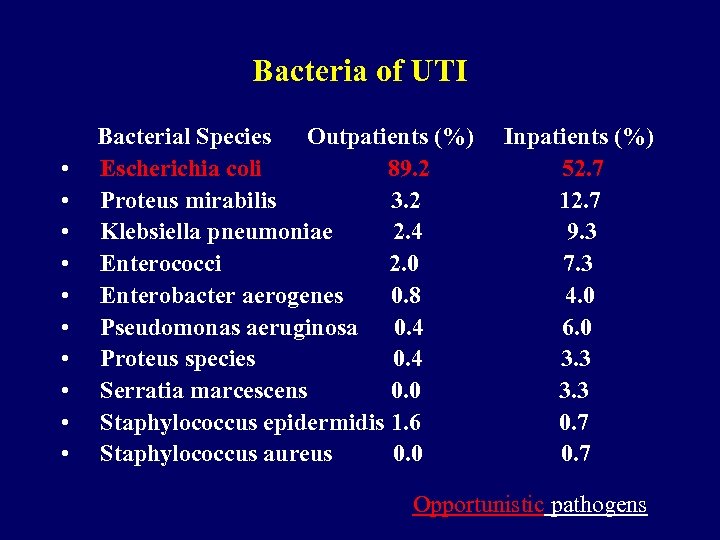 Bacteria of UTI • • • Bacterial Species Outpatients (%) Escherichia coli 89. 2 Proteus mirabilis 3. 2 Klebsiella pneumoniae 2. 4 Enterococci 2. 0 Enterobacter aerogenes 0. 8 Pseudomonas aeruginosa 0. 4 Proteus species 0. 4 Serratia marcescens 0. 0 Staphylococcus epidermidis 1. 6 Staphylococcus aureus 0. 0 Inpatients (%) 52. 7 12. 7 9. 3 7. 3 4. 0 6. 0 3. 3 0. 7 Opportunistic pathogens
Bacteria of UTI • • • Bacterial Species Outpatients (%) Escherichia coli 89. 2 Proteus mirabilis 3. 2 Klebsiella pneumoniae 2. 4 Enterococci 2. 0 Enterobacter aerogenes 0. 8 Pseudomonas aeruginosa 0. 4 Proteus species 0. 4 Serratia marcescens 0. 0 Staphylococcus epidermidis 1. 6 Staphylococcus aureus 0. 0 Inpatients (%) 52. 7 12. 7 9. 3 7. 3 4. 0 6. 0 3. 3 0. 7 Opportunistic pathogens
 Fungal Pathogens Most such infection occurs in patients : • with long indwelling Foley catheters • receiving broad-spectrum antibacterial therapy • diabetes mellitus • on corticosteroids
Fungal Pathogens Most such infection occurs in patients : • with long indwelling Foley catheters • receiving broad-spectrum antibacterial therapy • diabetes mellitus • on corticosteroids
 Other Pathogens • C. Trachomatis • U. Urealyticum Chronic Urethritis Chronic Prostatitis
Other Pathogens • C. Trachomatis • U. Urealyticum Chronic Urethritis Chronic Prostatitis
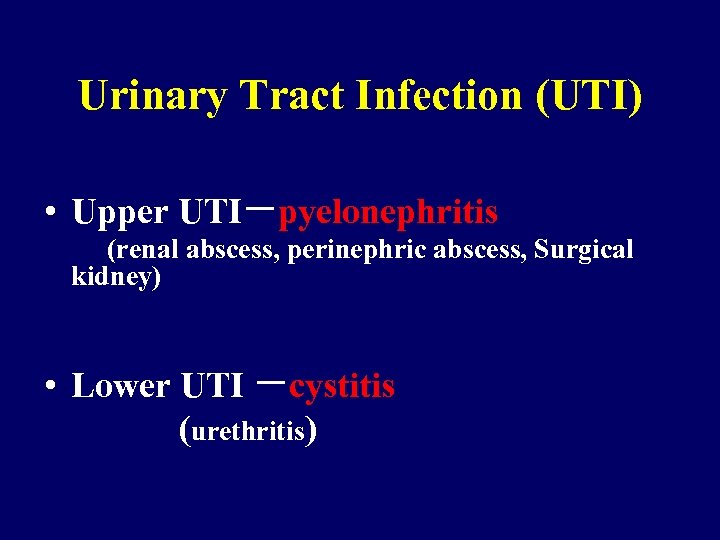 Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) • Upper UTI-pyelonephritis (renal abscess, perinephric abscess, Surgical kidney) • Lower UTI -cystitis (urethritis)
Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) • Upper UTI-pyelonephritis (renal abscess, perinephric abscess, Surgical kidney) • Lower UTI -cystitis (urethritis)
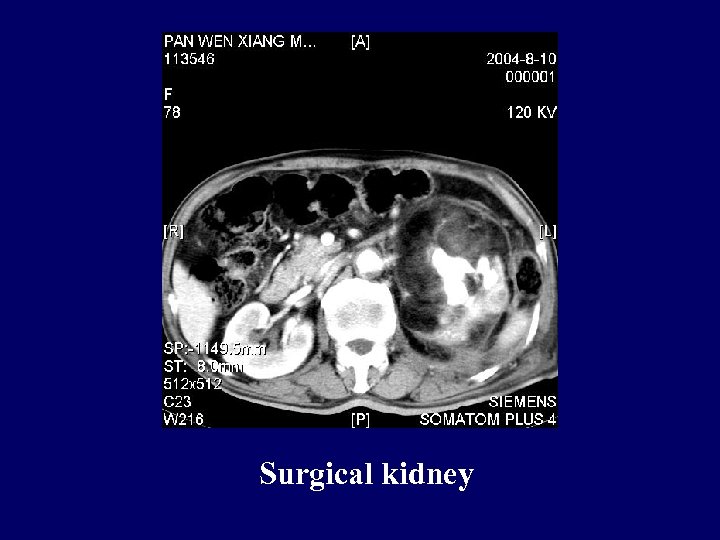 Surgical kidney
Surgical kidney
 Pyelonephritis
Pyelonephritis
 Pyelonephritis —— inflammation of the kidney and its pelvis
Pyelonephritis —— inflammation of the kidney and its pelvis
 PATHOGENESIS How bacteria reach the urinary tract in general and the kidney in particular?
PATHOGENESIS How bacteria reach the urinary tract in general and the kidney in particular?
 Pathogenesis Two potential routes : (1) hematogenous infection bacteremia → kidney (Descending) (2) retrograde infection urethra→bladder→ ureter →kidney (ascending)
Pathogenesis Two potential routes : (1) hematogenous infection bacteremia → kidney (Descending) (2) retrograde infection urethra→bladder→ ureter →kidney (ascending)
 Hematogenous Infection Because the kidneys receive 20% to 25% of the cardiac output, any microorganism that reaches the bloodstream can be delivered to the kidneys.
Hematogenous Infection Because the kidneys receive 20% to 25% of the cardiac output, any microorganism that reaches the bloodstream can be delivered to the kidneys.
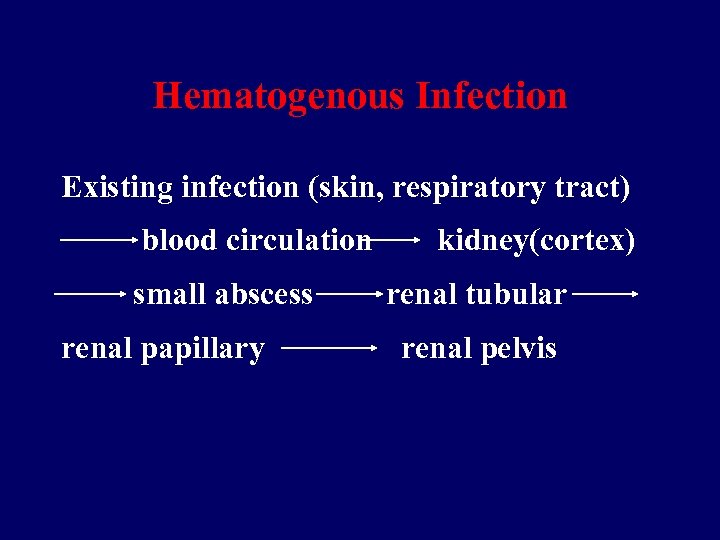 Hematogenous Infection Existing infection (skin, respiratory tract) blood circulation small abscess renal papillary kidney(cortex) renal tubular renal pelvis
Hematogenous Infection Existing infection (skin, respiratory tract) blood circulation small abscess renal papillary kidney(cortex) renal tubular renal pelvis
 PATHOGENESIS Factors predisposing to pyelonephritis • Urinary Tract Obstruction • Vesicoureteral Reflux • Instrumentation of the Urinary Tract • Pregnancy • Diabetes Mellitus How long will there be possibility of UTI after urethral catheterization?
PATHOGENESIS Factors predisposing to pyelonephritis • Urinary Tract Obstruction • Vesicoureteral Reflux • Instrumentation of the Urinary Tract • Pregnancy • Diabetes Mellitus How long will there be possibility of UTI after urethral catheterization?
 Diabetes Mellitus • 3 -4 times UTIs in DM than in non-diabetes • Diabetic neuropathy and vascular injury affects bladder emptying(paralytic bladder) • hyperglycemia impact host immuno system
Diabetes Mellitus • 3 -4 times UTIs in DM than in non-diabetes • Diabetic neuropathy and vascular injury affects bladder emptying(paralytic bladder) • hyperglycemia impact host immuno system
 Clinical Presentation • • • fever back pain colicky abdominal pain nausea and vomiting Sepsis, septic shock
Clinical Presentation • • • fever back pain colicky abdominal pain nausea and vomiting Sepsis, septic shock
 Clinical Presentation Cystitis • Suprapubic region pain • frequency, urgent urination, odynuria and dysuria
Clinical Presentation Cystitis • Suprapubic region pain • frequency, urgent urination, odynuria and dysuria
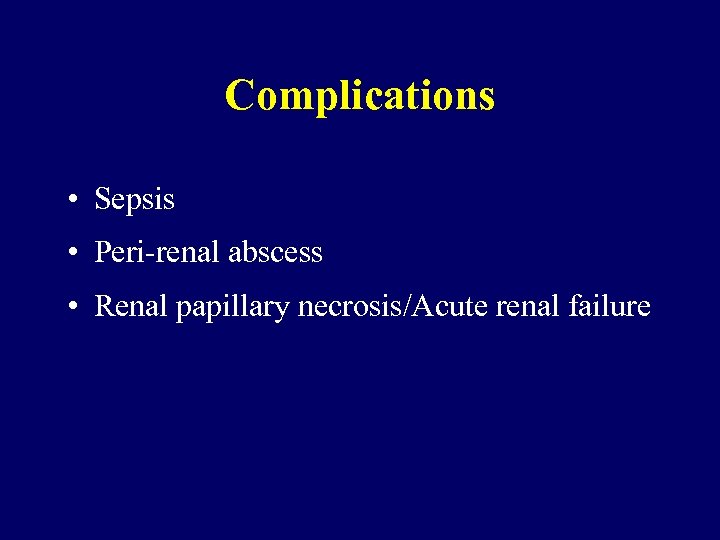 Complications • Sepsis • Peri-renal abscess • Renal papillary necrosis/Acute renal failure
Complications • Sepsis • Peri-renal abscess • Renal papillary necrosis/Acute renal failure
 Laboratory findings • Urine dipstick pyuria on microscopic examination urine WBC > 3 WBC/high-power field • Middle stream urine culture bacterial account > 105 cfu/ml (cfu: clony-forming units) • blood culture
Laboratory findings • Urine dipstick pyuria on microscopic examination urine WBC > 3 WBC/high-power field • Middle stream urine culture bacterial account > 105 cfu/ml (cfu: clony-forming units) • blood culture

 Treatment • Rest • Drinking large amount of water • Antibiotics: 2 weeks / until symptom free • Treat related diseases: diabetes, renal stones, etc
Treatment • Rest • Drinking large amount of water • Antibiotics: 2 weeks / until symptom free • Treat related diseases: diabetes, renal stones, etc
 Antibiotic therapy • Objective - prevention of sepsis - eradication of organism - prevention if recurrences • Medications - trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole(SMZ) - fluoroquinolones - ampicillin
Antibiotic therapy • Objective - prevention of sepsis - eradication of organism - prevention if recurrences • Medications - trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole(SMZ) - fluoroquinolones - ampicillin

 Catheter-associated UTI • Over 1 million catheter-associated UTIs occur in the US each year • Risk factors: duration of catheterization: mostly at 72 hours after catheterization (Bacteria film)
Catheter-associated UTI • Over 1 million catheter-associated UTIs occur in the US each year • Risk factors: duration of catheterization: mostly at 72 hours after catheterization (Bacteria film)
 Remove catheter as early as possible Change catheter
Remove catheter as early as possible Change catheter
 Any abnormalities of structural, or functional causes should be excluded when UTI was diagnosed and treated.
Any abnormalities of structural, or functional causes should be excluded when UTI was diagnosed and treated.
 Take radical measures, insted of providing temporary solutions 治标,更要治本
Take radical measures, insted of providing temporary solutions 治标,更要治本
 Genitourinary Tuberculosis
Genitourinary Tuberculosis
 Epidemiology • 8~10 million new active cases of TB each year(WHO) • TB is the most common opportunistic infection in AIDS patients(WHO)
Epidemiology • 8~10 million new active cases of TB each year(WHO) • TB is the most common opportunistic infection in AIDS patients(WHO)
 Transmission and Development • Genitourinary TB is caused by metastatic spread of the organism through bloodstream during initial infection (hematogenous). • Kidney is usually the primary organ infected in urinary disease • Primary site for infection of genital system is often the epididymis in men and the fallopian tubes in women
Transmission and Development • Genitourinary TB is caused by metastatic spread of the organism through bloodstream during initial infection (hematogenous). • Kidney is usually the primary organ infected in urinary disease • Primary site for infection of genital system is often the epididymis in men and the fallopian tubes in women
 Pathological renal TB Parenchyma to Collecting system Clinical renal TB
Pathological renal TB Parenchyma to Collecting system Clinical renal TB
 Clinical Features • • Most patients are aged 20~40 years Some cases with Pulmonary tuberculosis Bladder is always the spokesman for renal TB Urologist should always consider the diagnosis of genitourinary TB in a patient presenting with vague, long-standing urinary symptoms for which there is no obvious cause
Clinical Features • • Most patients are aged 20~40 years Some cases with Pulmonary tuberculosis Bladder is always the spokesman for renal TB Urologist should always consider the diagnosis of genitourinary TB in a patient presenting with vague, long-standing urinary symptoms for which there is no obvious cause
 Diagnosis • Urine examination (Sterile pyuria, p. H<7, WBC, RBC, Pro) • Urine : Acid-fast bacilli (AFB) • Blood: TB-Antibody • Imageology (Ultrasonography, Plain film, IVU, RGP, CU, CTU, ) • Cystoscopy and Biopsy
Diagnosis • Urine examination (Sterile pyuria, p. H<7, WBC, RBC, Pro) • Urine : Acid-fast bacilli (AFB) • Blood: TB-Antibody • Imageology (Ultrasonography, Plain film, IVU, RGP, CU, CTU, ) • Cystoscopy and Biopsy
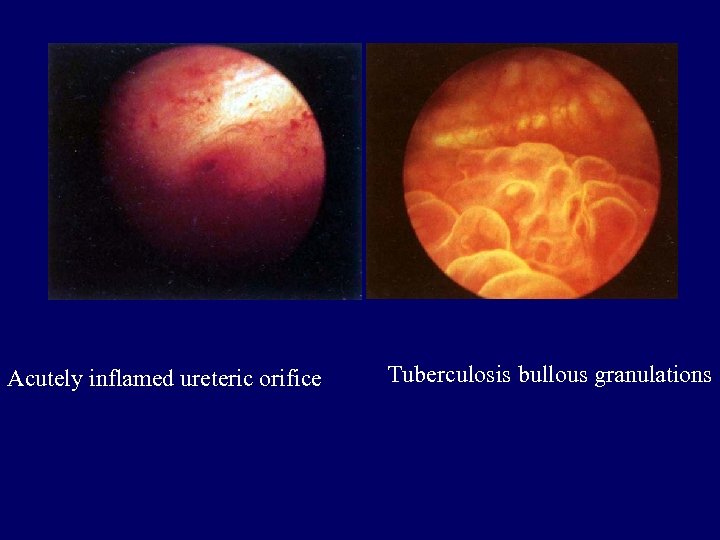 Acutely inflamed ureteric orifice Tuberculosis bullous granulations
Acutely inflamed ureteric orifice Tuberculosis bullous granulations
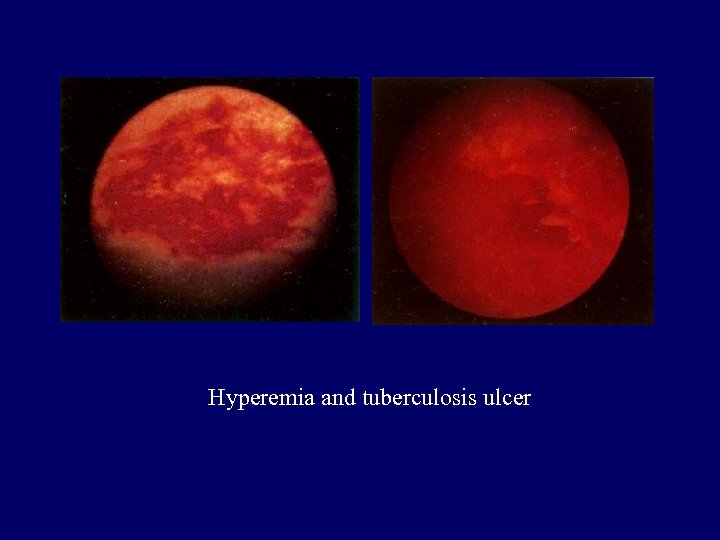 Hyperemia and tuberculosis ulcer
Hyperemia and tuberculosis ulcer
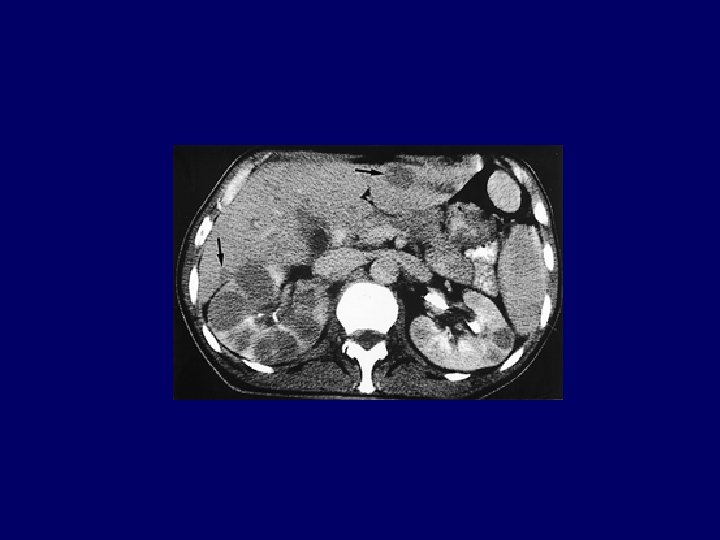
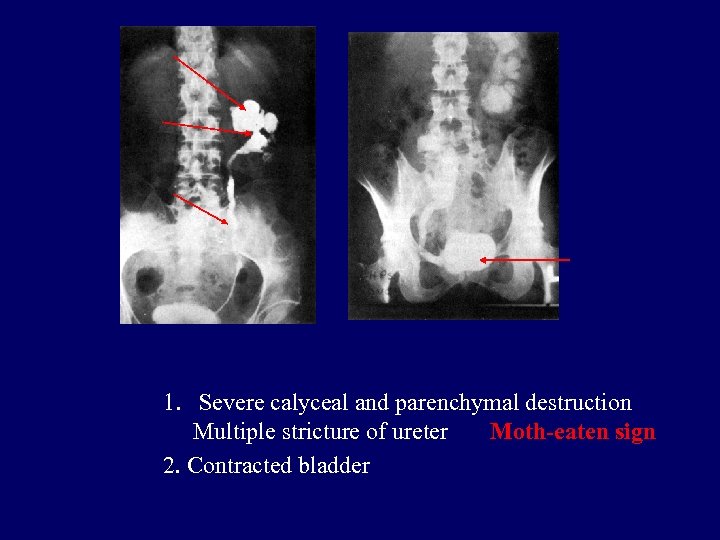 1. Severe calyceal and parenchymal destruction Multiple stricture of ureter Moth-eaten sign 2. Contracted bladder
1. Severe calyceal and parenchymal destruction Multiple stricture of ureter Moth-eaten sign 2. Contracted bladder
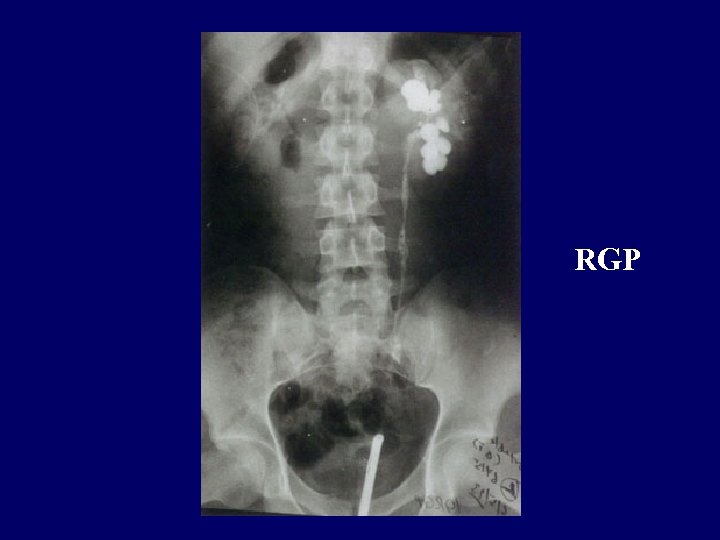 RGP
RGP
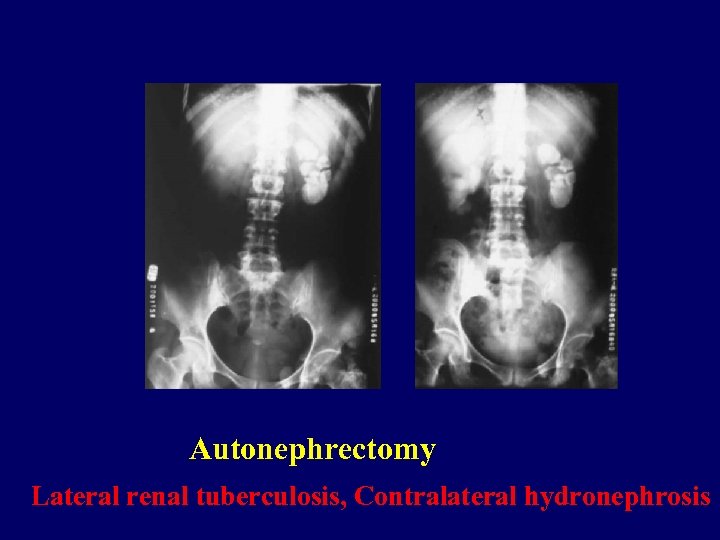 Autonephrectomy Lateral renal tuberculosis, Contralateral hydronephrosis
Autonephrectomy Lateral renal tuberculosis, Contralateral hydronephrosis
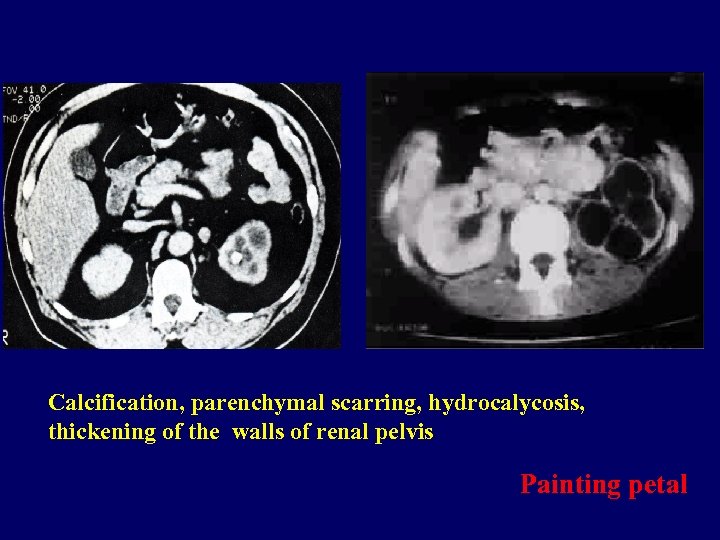 Calcification, parenchymal scarring, hydrocalycosis, thickening of the walls of renal pelvis Painting petal
Calcification, parenchymal scarring, hydrocalycosis, thickening of the walls of renal pelvis Painting petal
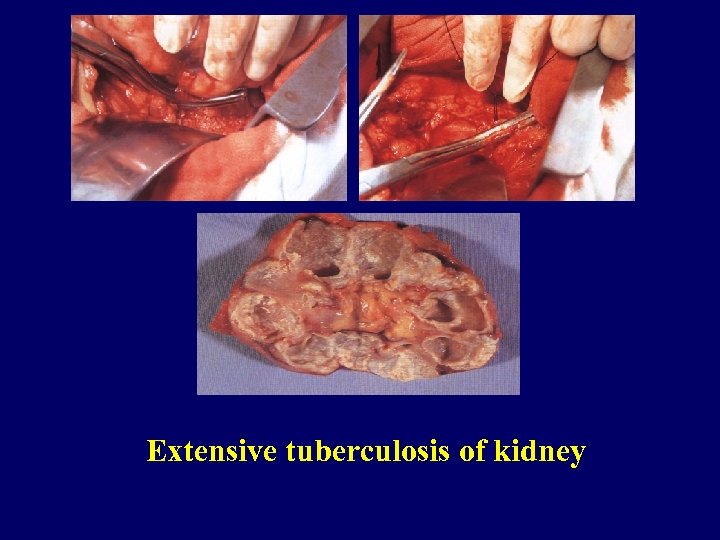 Extensive tuberculosis of kidney
Extensive tuberculosis of kidney
 Antituberculous drugs Isoniazid(INH), Rifampicin(RFP), Streptomycin(SM), Pyrazinamide(PZA), Ethambutol(EMB), PAS
Antituberculous drugs Isoniazid(INH), Rifampicin(RFP), Streptomycin(SM), Pyrazinamide(PZA), Ethambutol(EMB), PAS
 Surgery 1. Excision of diseased tissue (Partial )Nephrectomy, Abscess Drainage, Epididymectomy 2. Reconstructive Surgery Ureteral stricture, Augmentation cystoplasty, Urinary conduit diversion(Bricker’s procedure, ileum conduit), orthotopic Neobladder
Surgery 1. Excision of diseased tissue (Partial )Nephrectomy, Abscess Drainage, Epididymectomy 2. Reconstructive Surgery Ureteral stricture, Augmentation cystoplasty, Urinary conduit diversion(Bricker’s procedure, ileum conduit), orthotopic Neobladder
 Thank You
Thank You


