7b5a9d79d78ec18e16bf2391b3d88e97.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 29

URBAN REGENERATION AS A TOOL OF URBAN DENSITY MANAGEMENT Maciej Huculak Wojciech Jarczewski Institute of Urban Development 27 th of November 2013 r. Bratislava 30 -015 Kraków, ul. Cieszyńska 2 www. irm. krakow. pl

[ Urban Regeneration Definition: Coordinated process conducted jointly by the local government, local community, and other stakeholders, being an element of development policy and intended to oppose urbanized space degradation and crisis phenomena, stimulate development and quality changes by increasing social and business activities, improve residential environment and protect national heritage, with preservation of the sustainable development principles.

[ Urban Regeneration Definition: Coordinated process conducted jointly by the local government, local community, and other stakeholders, being an element of development policy and intended to oppose urbanized space degradation and crisis phenomena, stimulate development and quality changes by increasing social and business activities, improve residential environment and protect national heritage, with preservation of the sustainable development principles.

[ Urban Regeneration in Urban Density context Why Urban Regeneration? 1. Efficient space recycling tool 2. Prevents urban sprawl by suppressing ‘push’ stimulants of the process 3. Saves the greenfield areas 4. Prevents reduction of urban density in cities
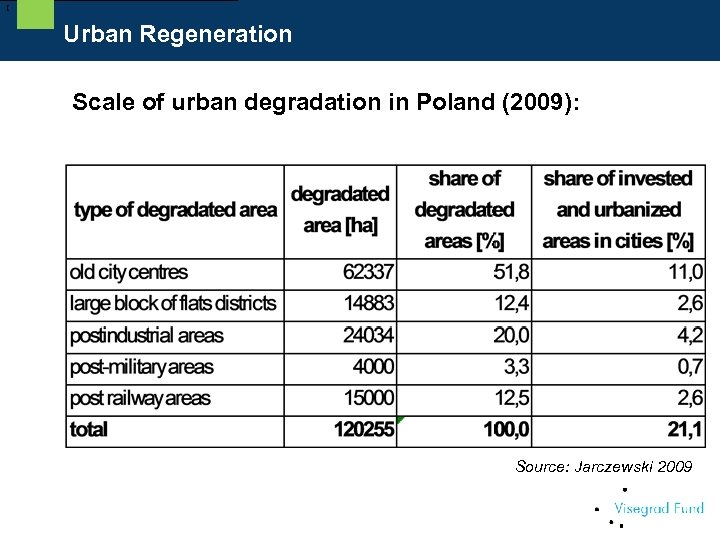
[ Urban Regeneration Scale of urban degradation in Poland (2009): Source: Jarczewski 2009
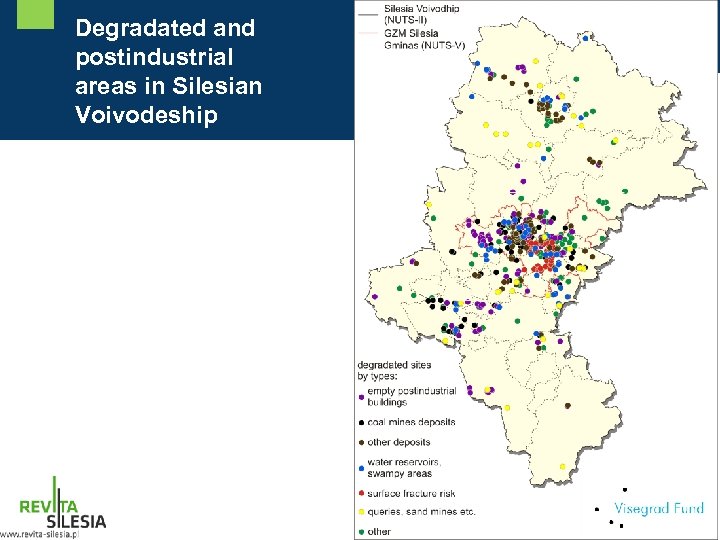
Degradated and postindustrial areas in Silesian Voivodeship
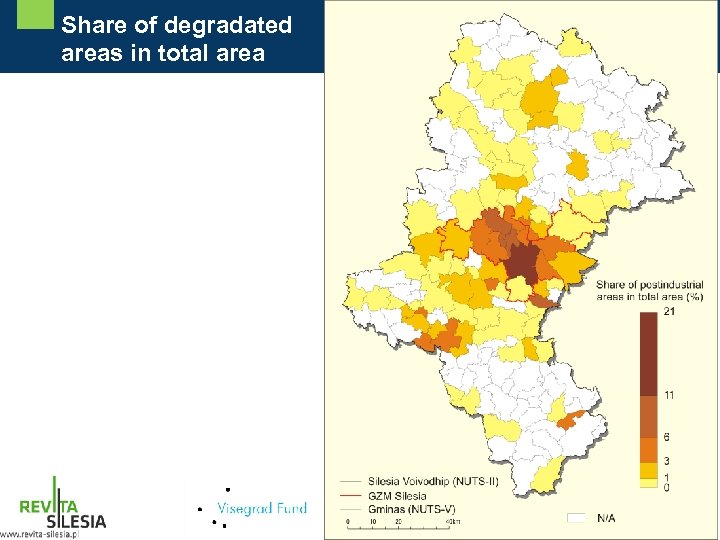
Share of degradated areas in total area
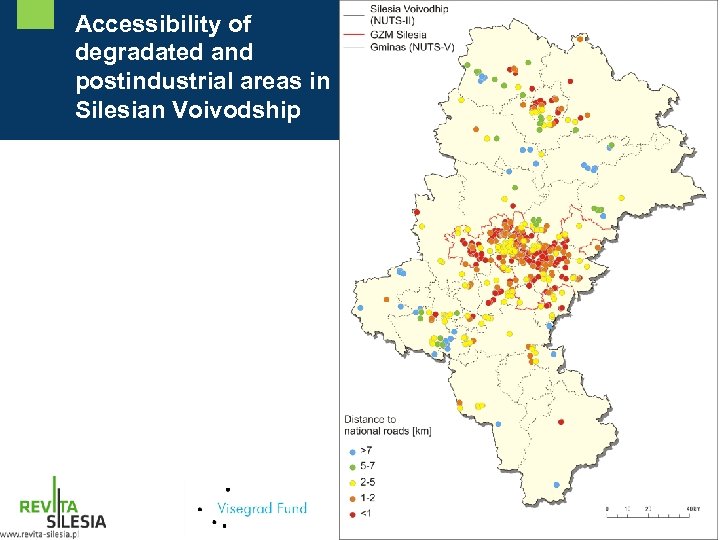
Accessibility of degradated and postindustrial areas in Silesian Voivodship
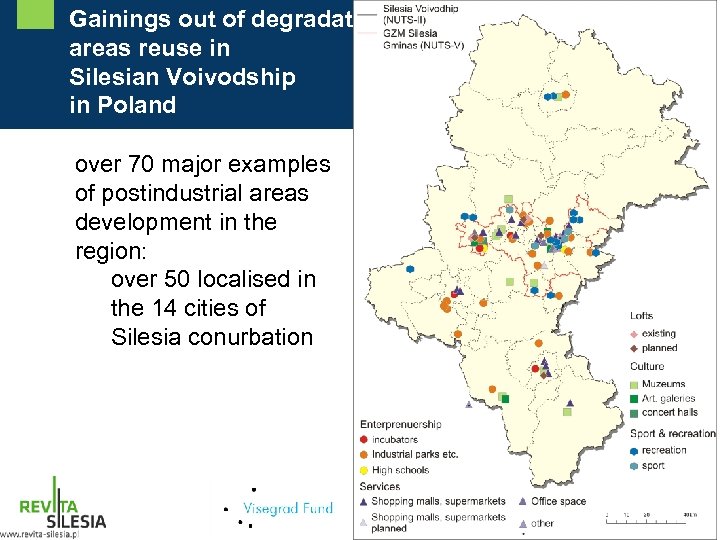
Gainings out of degradated areas reuse in Silesian Voivodship in Poland over 70 major examples of postindustrial areas development in the region: over 50 localised in the 14 cities of Silesia conurbation

Main directions of degradated areas reuse in Silesian Voivodship in Poland - Services (shopping malls, supermarkets, office space etc. ) - Enterpreneurship development (incubators, industrial parks, economic activity zones, high schools, greenfields) - Culture (museums, art. galleries, concert halls) - Recreation (water reservoirs) - Housing
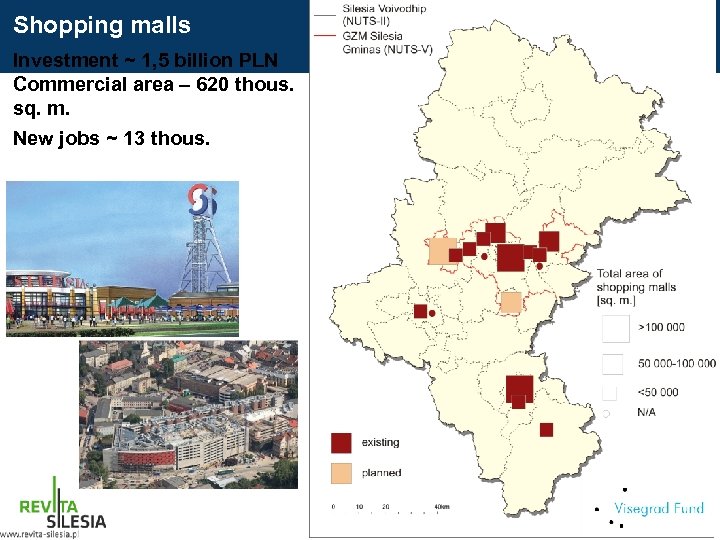
Shopping malls Investment ~ 1, 5 billion PLN Commercial area – 620 thous. sq. m. New jobs ~ 13 thous.
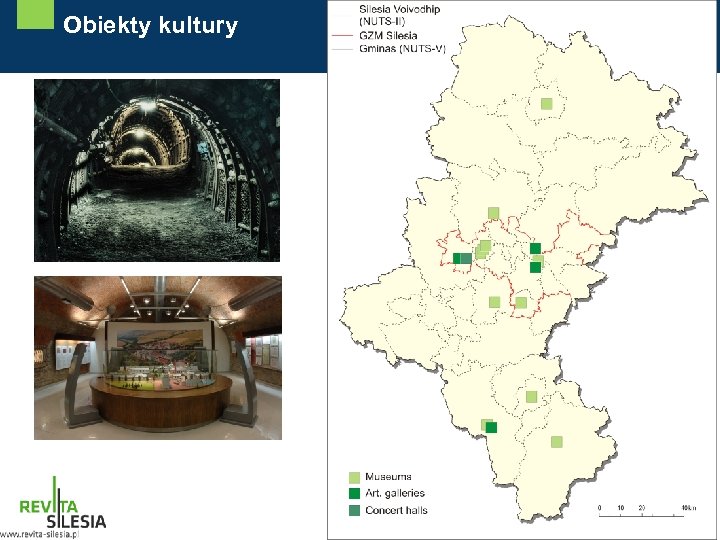
Obiekty kultury
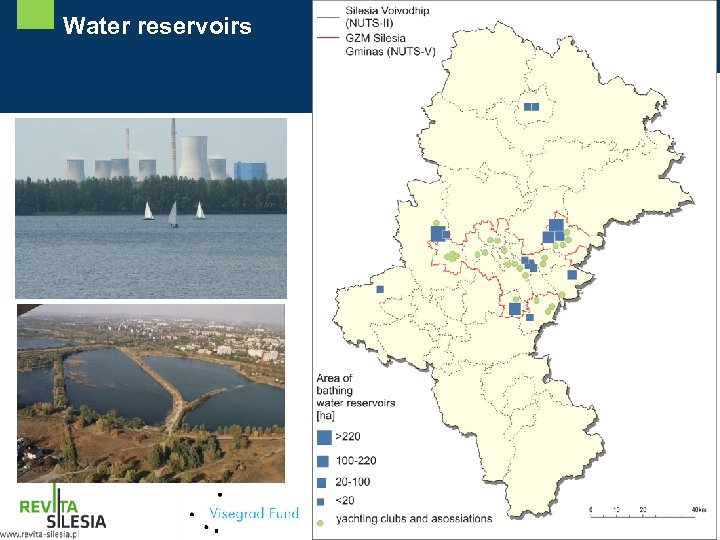
Water reservoirs

Proinvestment policy on degradated areas Sosnowiec Postindustrial areas: Coal mines (KWK): Saturn, Niwka-Modrzejów, Sosnowiec, Porąbka-Klimontów, Other: Sand Filling Mine Maczki-Bór, Low Power Engines factory Silma, House Factory (prefabricated) Effects: • 18 investors • ~1 billion PLN invested • 4500 new jobs • 80% of effects – Katowicka Special Economic Zone

Polityka proinwestycyjna na terenach zdegradowanych

[ International Perspective Lviv-Pidzamche
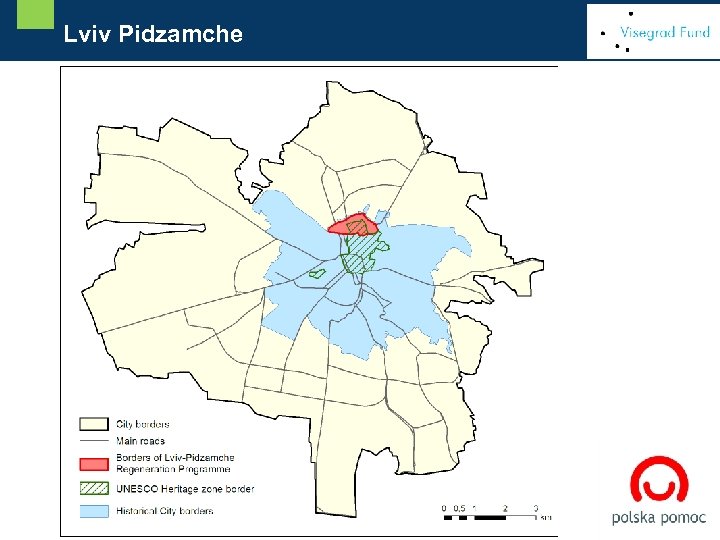
[ Delimitacja obszaru rewitalizacji Lviv Pidzamche
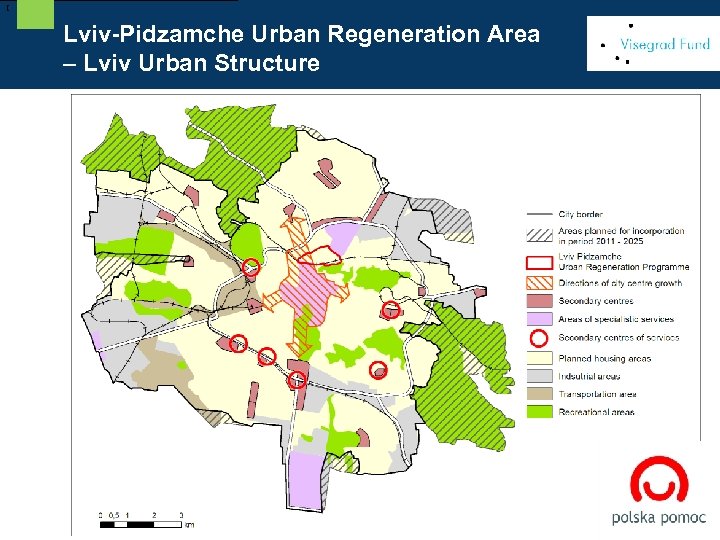
[ Lviv-Pidzamche Urban Regeneration Area – Lviv Urban Structure
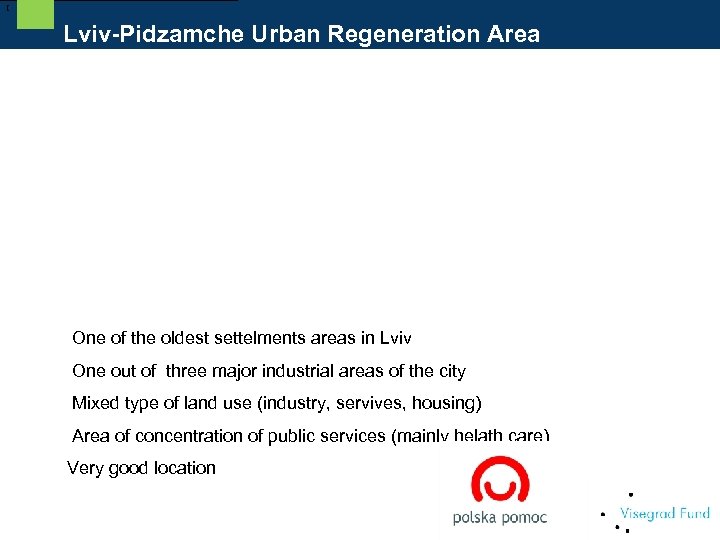
[ Lviv-Pidzamche Urban Regeneration Area – Facts & Figures One of the oldest settelments areas in Lviv One out of three major industrial areas of the city Mixed type of land use (industry, servives, housing) Area of concentration of public services (mainly helath care) Very good location
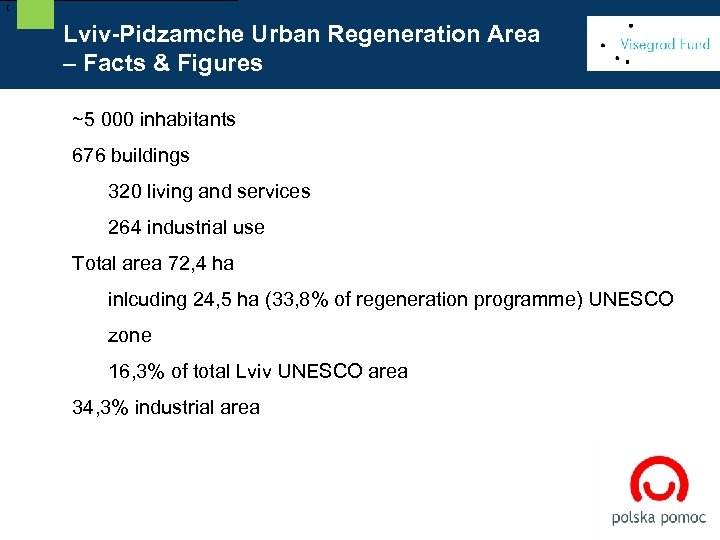
[ Lviv-Pidzamche Urban Regeneration Area – Facts & Figures ~5 000 inhabitants 676 buildings 320 living and services 264 industrial use Total area 72, 4 ha inlcuding 24, 5 ha (33, 8% of regeneration programme) UNESCO zone 16, 3% of total Lviv UNESCO area 34, 3% industrial area

Urban regeneration projects 2012 -2020

[ Lviv Pidzamche 2013 Implementation phase 3 courtyards 1 playground 1 public space Pidzamche Guidebook Courtyards Regeneration – best practices handbook 3 day study visit Kraków-Wrocław-Katowice Stakeholders: Institut Mista – coordinator (UA) Lvivska Miska Rada Schevchenski Rajon Administration Citizens
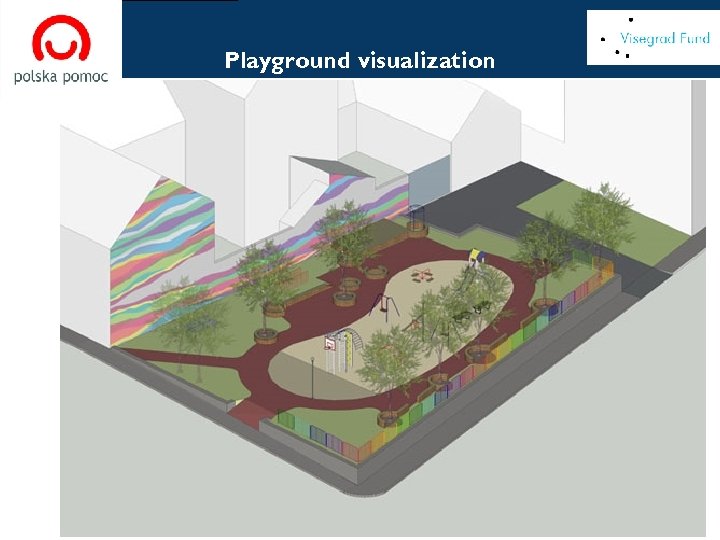
[ Playground visualization
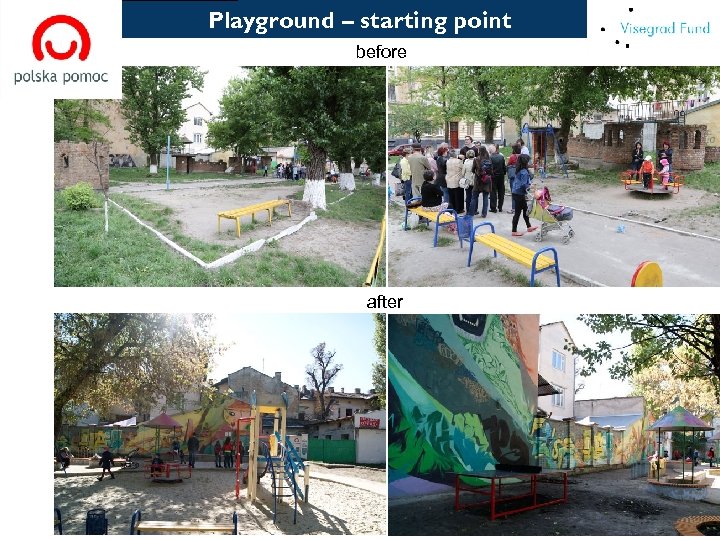

[ Playground – starting point before after

[ Playground – starting point before after
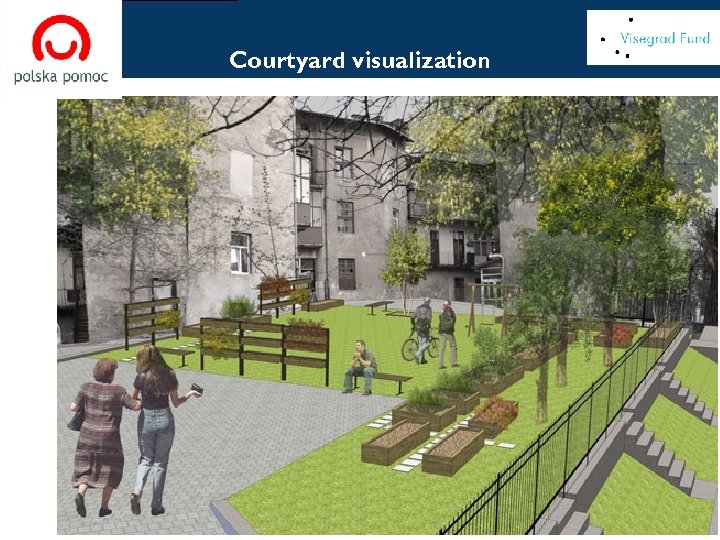
[ Courtyard visualization

[ Courtyard before after

[ Concluding remarks 1. Urban regeneration can be an efficient tool of urban density management in Central and Eastern Europe 2. Improves the attractiveness of degradated urban space for business and housing purposes 3. Can trigger introduction of new functions to postindustrial, post military and other types of degradated areas 4. Encreases sustainability by using existing infrastructure: housing, transportation, water, heating, electricity etc. supply 5. May reduce the urban sprawl push effects by improving the quality of life in urbanised areas

URBAN REGENERATION AS A TOOL OF URBAN DENSITY MANAGEMENT Thank you for your attention Maciej Huculak Wojciech Jarczewski Institute of Urban Development 27 th of November 2013 r. Bratislava 30 -015 Kraków, ul. Cieszyńska 2 www. irm. krakow. pl
7b5a9d79d78ec18e16bf2391b3d88e97.ppt