58de04ac2aa96e040d7321123898e1c8.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 38

Urban Models

How are Cities Organized, and How do they Function?

Functional Zonation The division of the city into certain regions (zones) for certain purposes (functions).

Zones of the City • Central business district (CBD) • Central City (the CBD + older housing zones) • Suburb (outlying, functionally uniform zone outside of the central city)
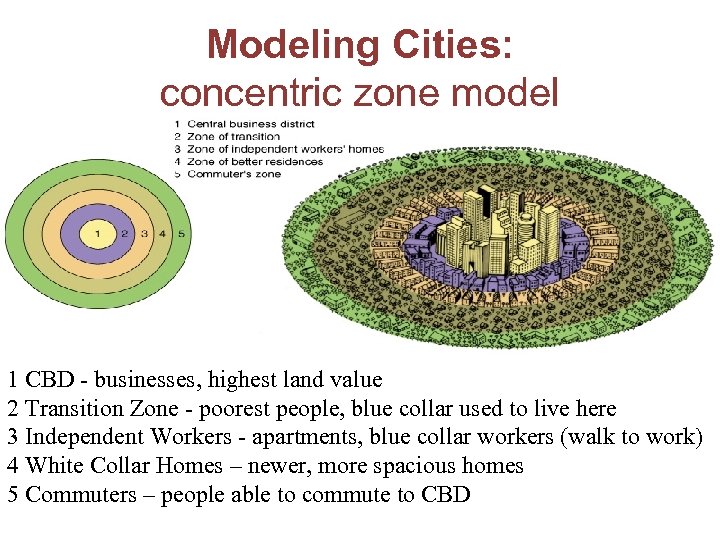
Modeling Cities: concentric zone model 1 CBD - businesses, highest land value 2 Transition Zone - poorest people, blue collar used to live here 3 Independent Workers - apartments, blue collar workers (walk to work) 4 White Collar Homes – newer, more spacious homes 5 Commuters – people able to commute to CBD
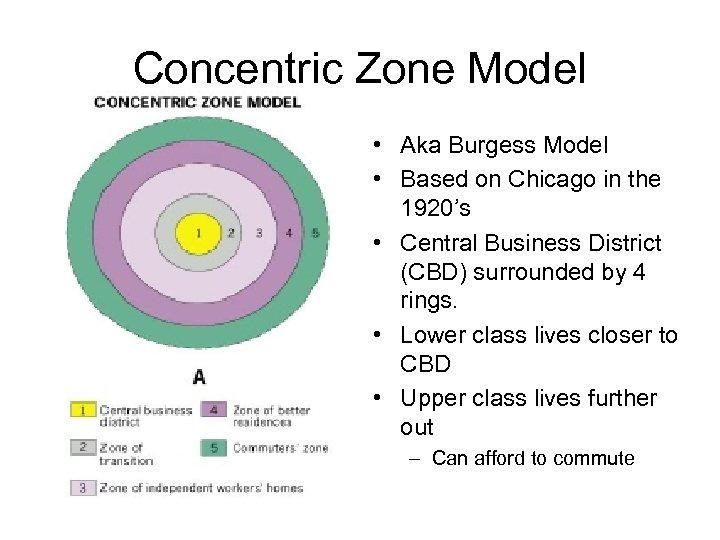
Concentric Zone Model • Aka Burgess Model • Based on Chicago in the 1920’s • Central Business District (CBD) surrounded by 4 rings. • Lower class lives closer to CBD • Upper class lives further out – Can afford to commute
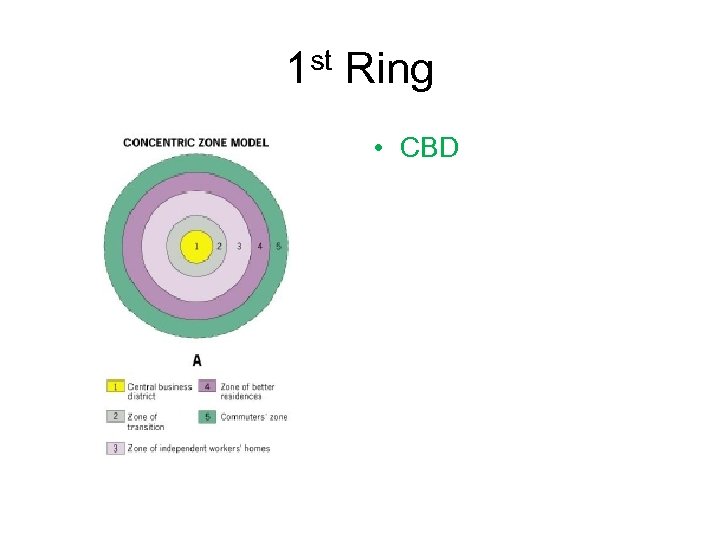
1 st Ring • CBD
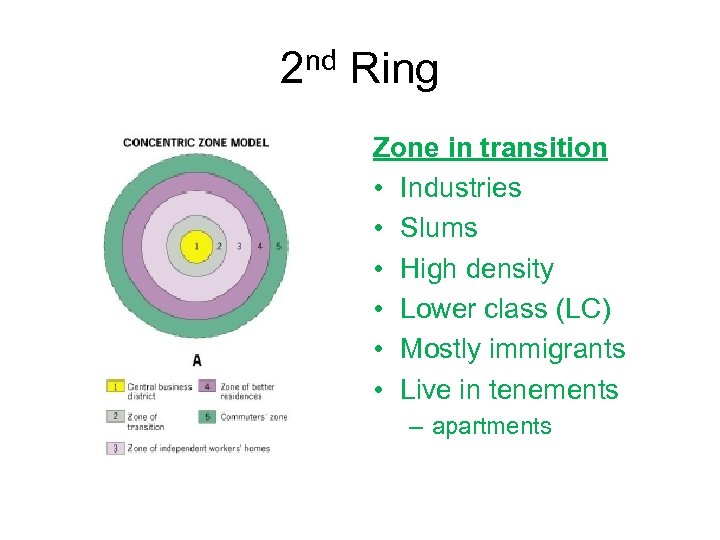
2 nd Ring Zone in transition • Industries • Slums • High density • Lower class (LC) • Mostly immigrants • Live in tenements – apartments
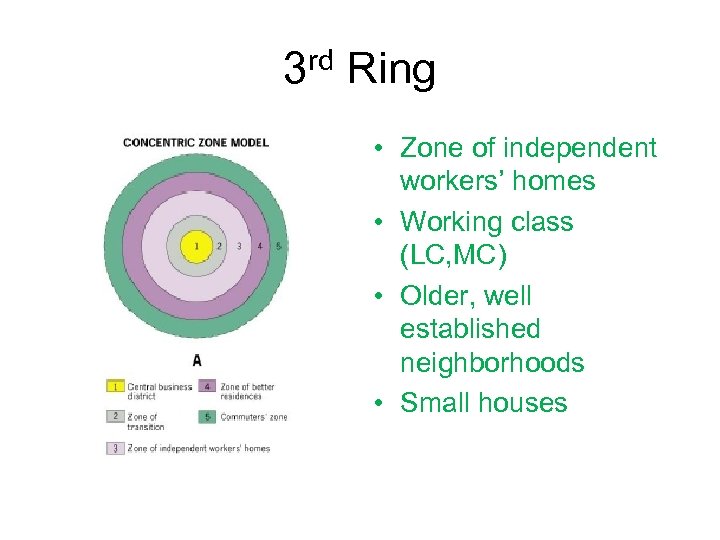
3 rd Ring • Zone of independent workers’ homes • Working class (LC, MC) • Older, well established neighborhoods • Small houses
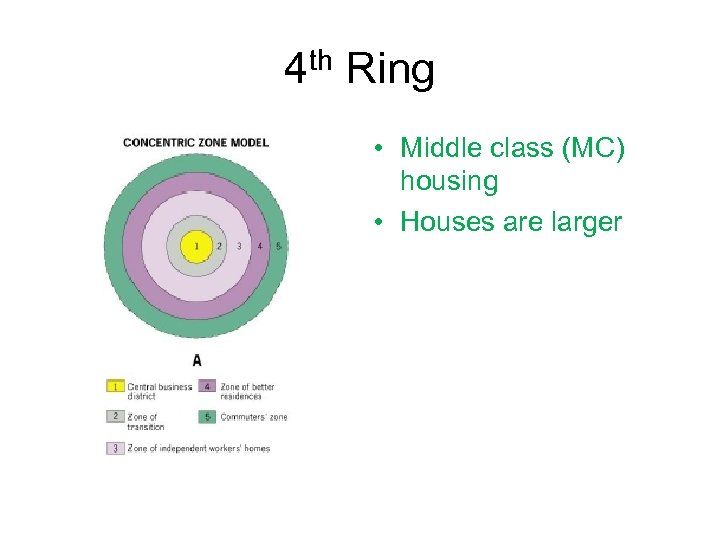
4 th Ring • Middle class (MC) housing • Houses are larger
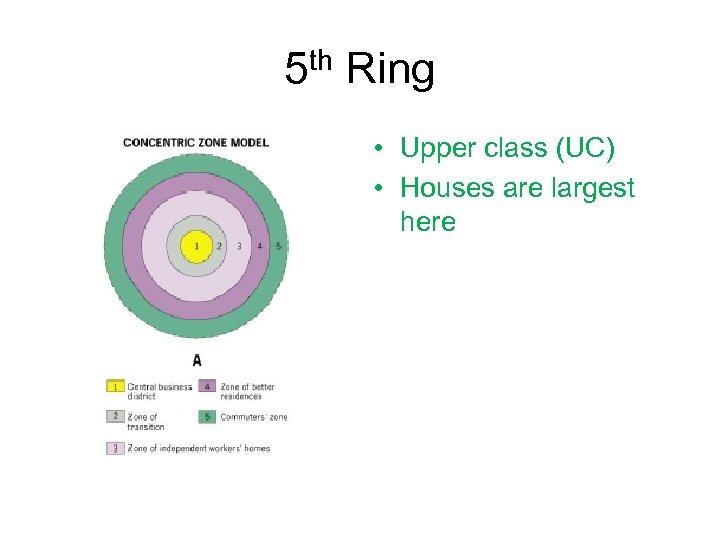
5 th Ring • Upper class (UC) • Houses are largest here
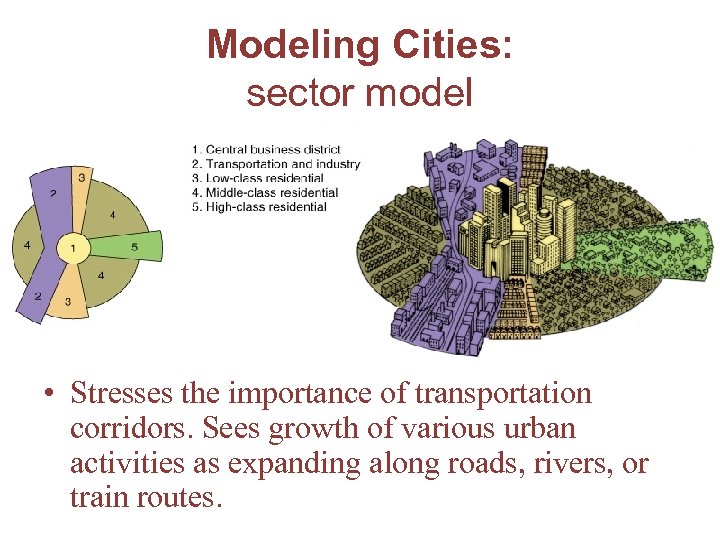
Modeling Cities: sector model • Stresses the importance of transportation corridors. Sees growth of various urban activities as expanding along roads, rivers, or train routes.
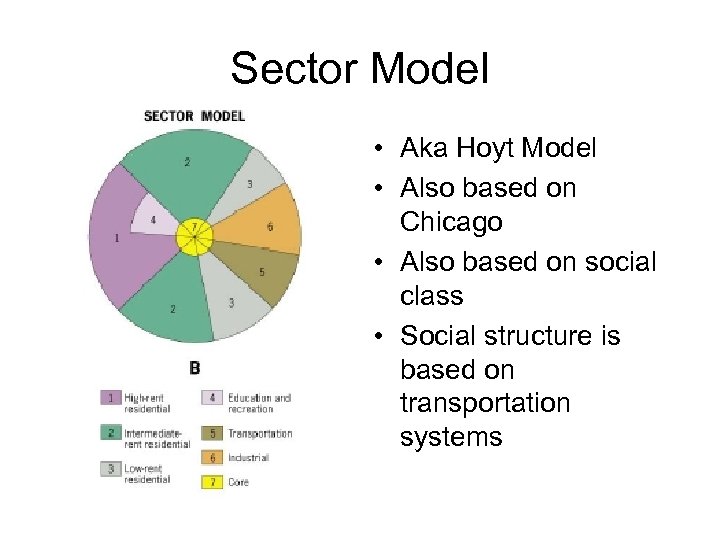
Sector Model • Aka Hoyt Model • Also based on Chicago • Also based on social class • Social structure is based on transportation systems
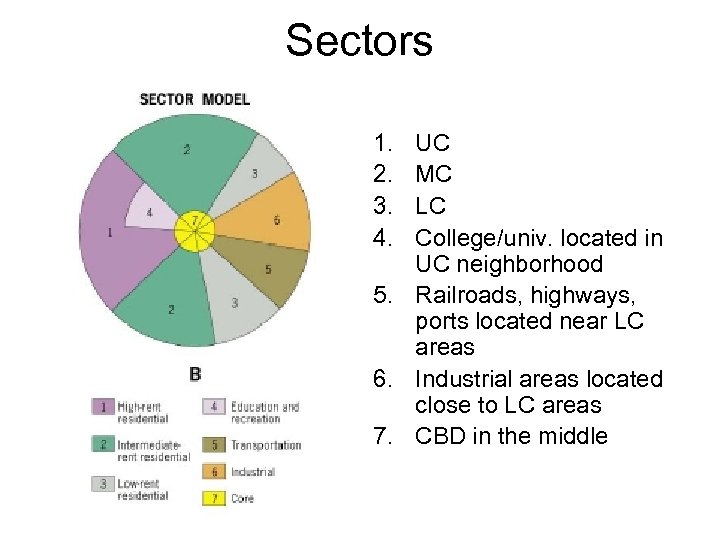
Sectors 1. 2. 3. 4. UC MC LC College/univ. located in UC neighborhood 5. Railroads, highways, ports located near LC areas 6. Industrial areas located close to LC areas 7. CBD in the middle
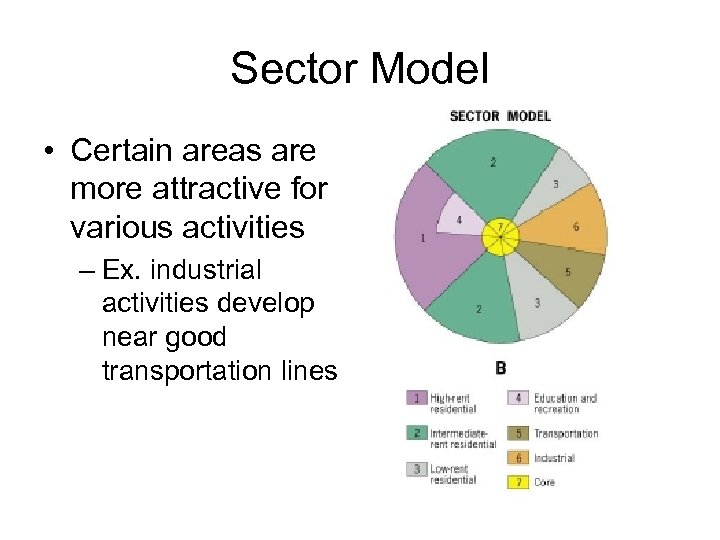
Sector Model • Certain areas are more attractive for various activities – Ex. industrial activities develop near good transportation lines
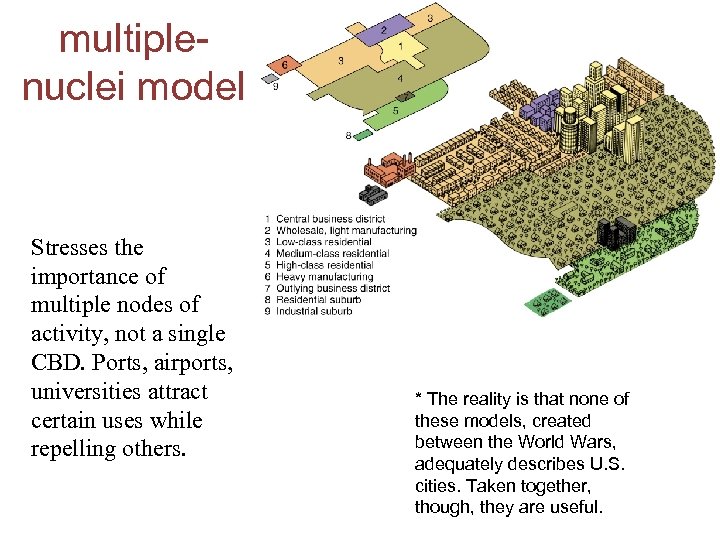
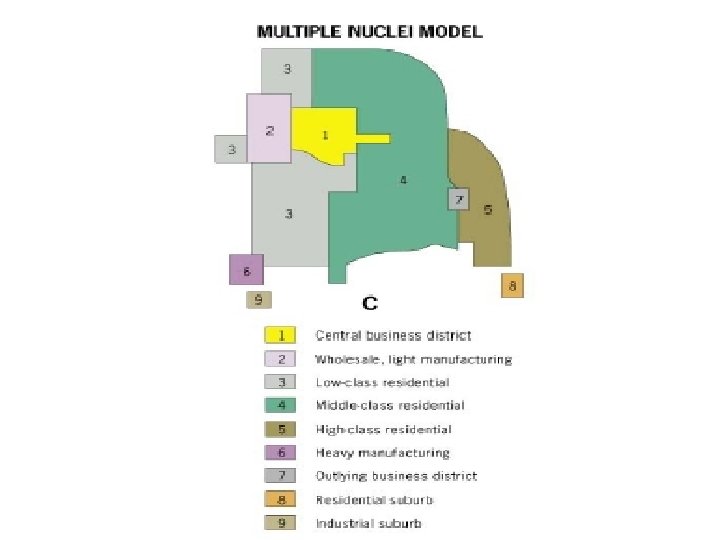
multiplenuclei model Stresses the importance of multiple nodes of activity, not a single CBD. Ports, airports, universities attract certain uses while repelling others. * The reality is that none of these models, created between the World Wars, adequately describes U. S. cities. Taken together, though, they are useful.
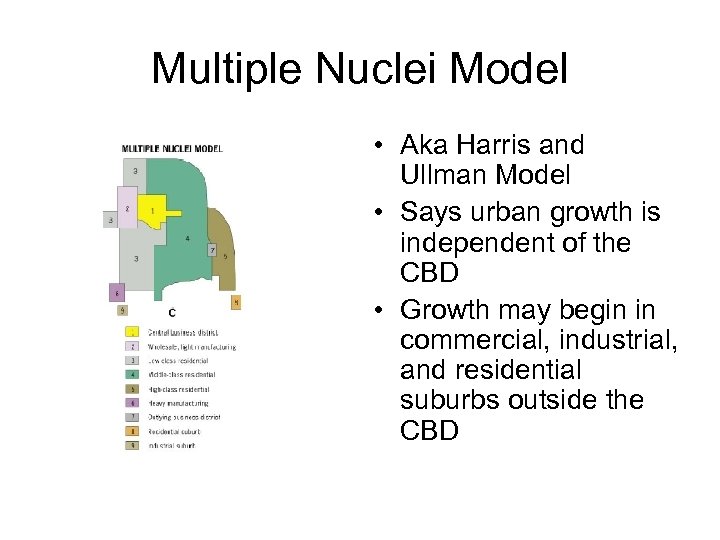
Multiple Nuclei Model • Aka Harris and Ullman Model • Says urban growth is independent of the CBD • Growth may begin in commercial, industrial, and residential suburbs outside the CBD
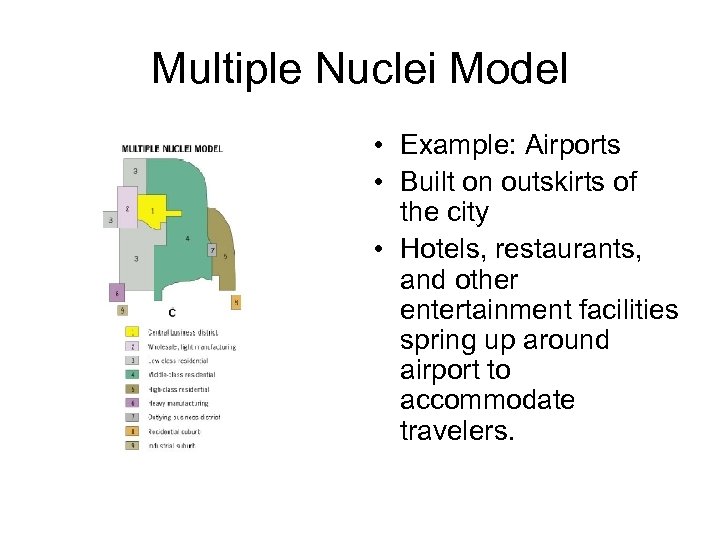
Multiple Nuclei Model • Example: Airports • Built on outskirts of the city • Hotels, restaurants, and other entertainment facilities spring up around airport to accommodate travelers.
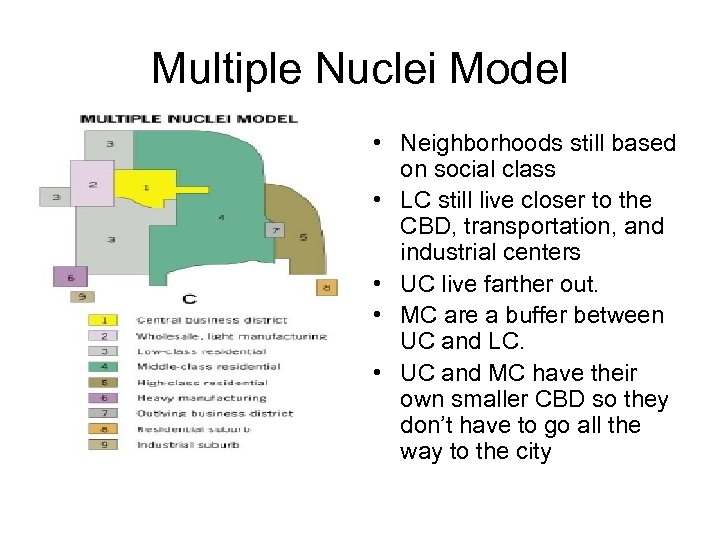
Multiple Nuclei Model • Neighborhoods still based on social class • LC still live closer to the CBD, transportation, and industrial centers • UC live farther out. • MC are a buffer between UC and LC. • UC and MC have their own smaller CBD so they don’t have to go all the way to the city
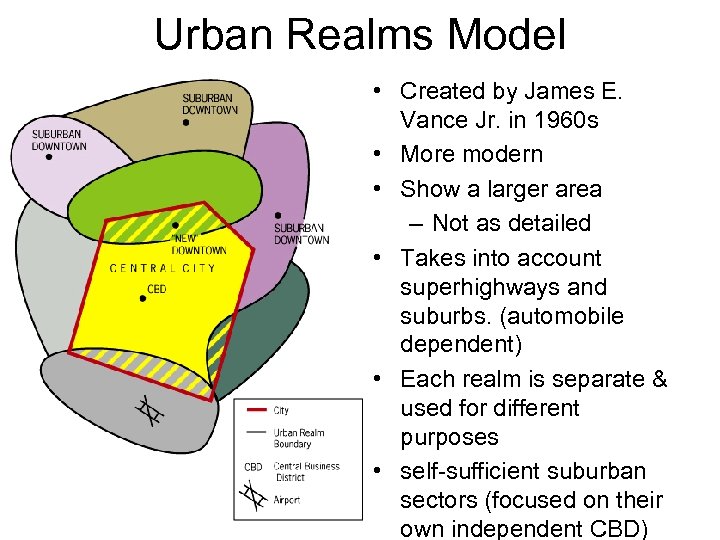
Urban Realms Model • Created by James E. Vance Jr. in 1960 s • More modern • Show a larger area – Not as detailed • Takes into account superhighways and suburbs. (automobile dependent) • Each realm is separate & used for different purposes • self-sufficient suburban sectors (focused on their own independent CBD)
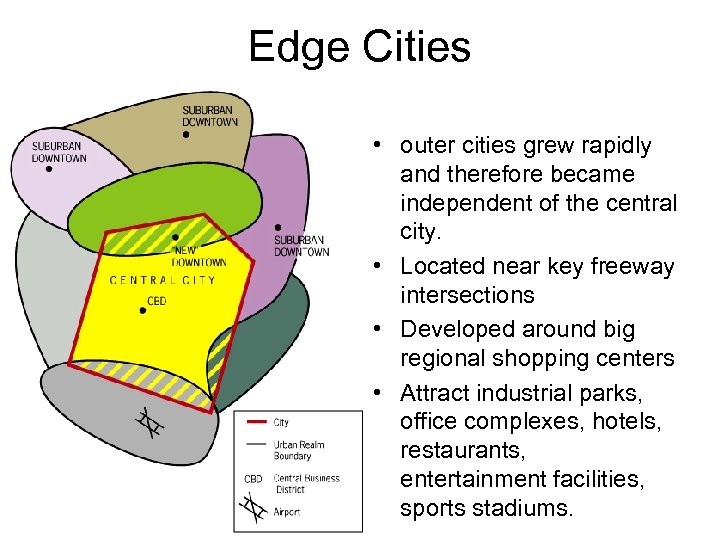
Edge Cities • outer cities grew rapidly and therefore became independent of the central city. • Located near key freeway intersections • Developed around big regional shopping centers • Attract industrial parks, office complexes, hotels, restaurants, entertainment facilities, sports stadiums.
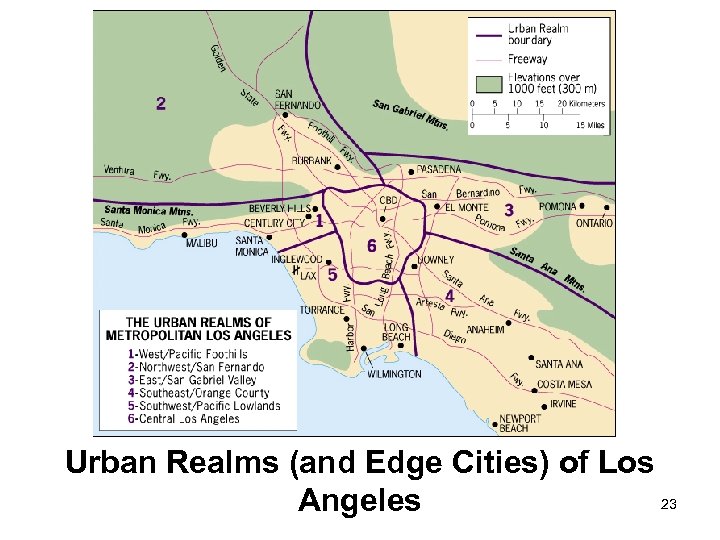
Urban Realms (and Edge Cities) of Los 23 Angeles
Geographic Application of the Models • Social scientists & geographers can use data from a census to help in identifying where people live and their demographic information • The usage of all 3 models can help pinpoint where a specific type of person will most likely live • Segmentation: process of partitioning markets into groups of potential customers w/ similar needs & characteristics who are likely to exhibit similar purchasing behavior • Putting it all together: – Concentric model: housing is newer most likely in outer rings of the city (development) – Sector model: deals w/ income – Multiple nuclei model: similar ethnicity or racial background tend to live near one another Nielsen Claritas PRIZM

CBDs in Europe • Less skyscrapers • More public/semipublic services • More people live downtown & contain more consumer services • Shopping streets w/ no vehicles are common • Renovation of older buildings to stay centrally located • Higher rents for business & consumer service locations • What do cities look like: – Wealthy people still live in the inner portions, not just in the suburbs – New housing in suburbs are high-rises for lowincome people, many who are immigrants – Gov’t encourages high density suburban development to preserve countryside – Worse in suburbs: increased crime, drug dealing, less consumer services
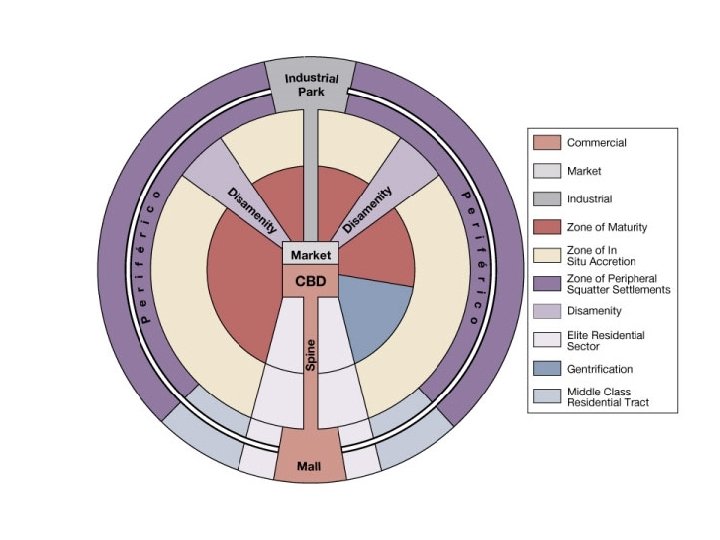
Latin American City Model • AKA Griffin-Ford Model • Central spine extends out from the CBD • UC housing surrounds the spine

Latin American City Model • Outermost sector made up of LC housing – Squatter settlements • Called barrios or favelas • few services & primitive amenities • Migrants from other parts of country come looking for jobs
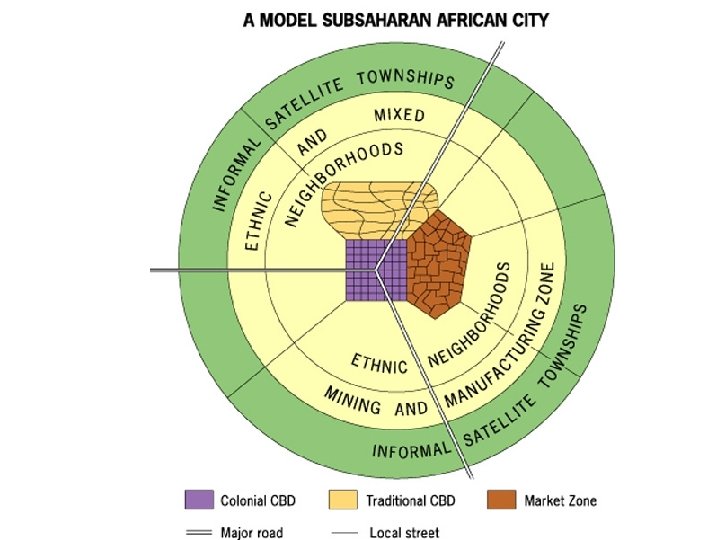
Sub-Saharan African City Model • Can still see relics of colonialism • 3 distinct CBDs:
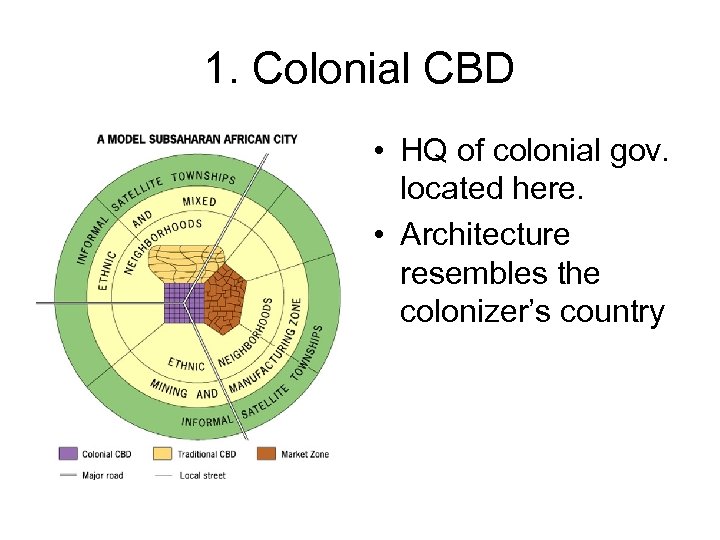
1. Colonial CBD • HQ of colonial gov. located here. • Architecture resembles the colonizer’s country
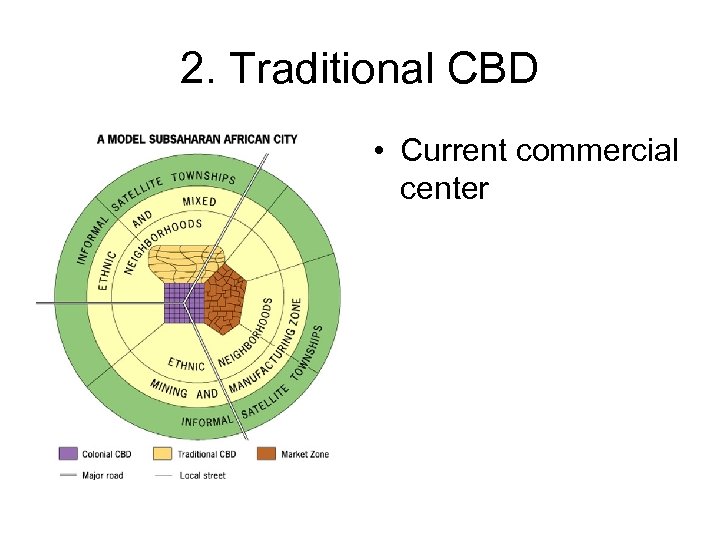
2. Traditional CBD • Current commercial center

3. Market or Bazaar CBD • Open air markets that sell just about everything • Informal economy – No taxes paid
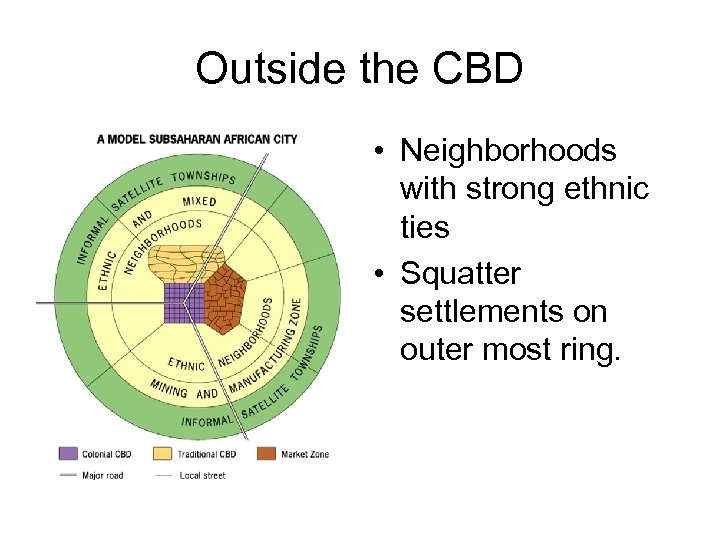
Outside the CBD • Neighborhoods with strong ethnic ties • Squatter settlements on outer most ring.
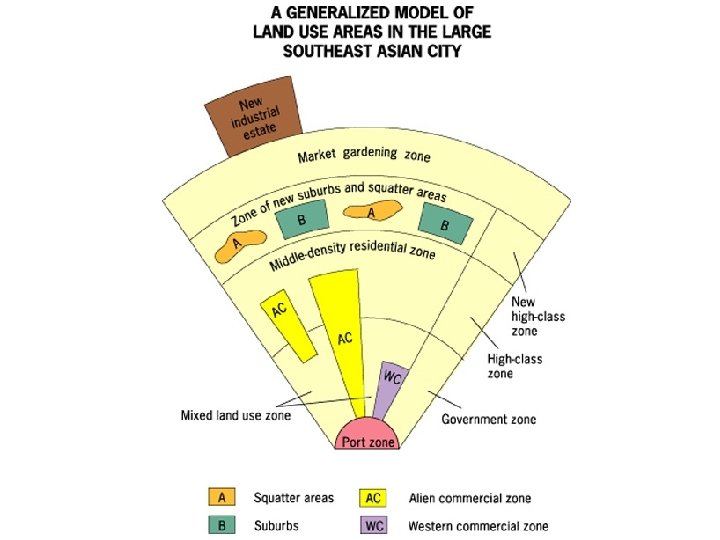
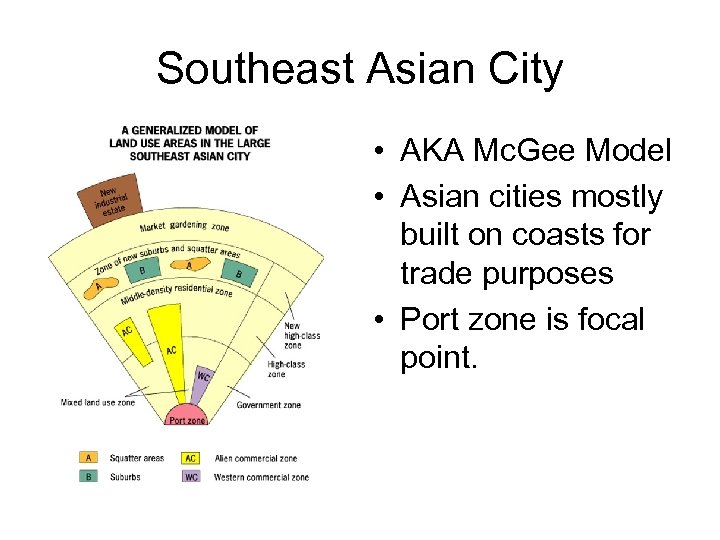
Southeast Asian City • AKA Mc. Gee Model • Asian cities mostly built on coasts for trade purposes • Port zone is focal point.
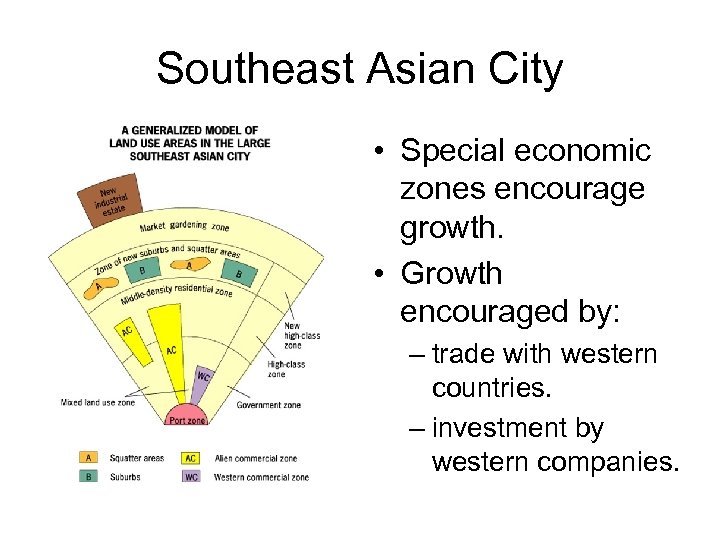
Southeast Asian City • Special economic zones encourage growth. • Growth encouraged by: – trade with western countries. – investment by western companies.
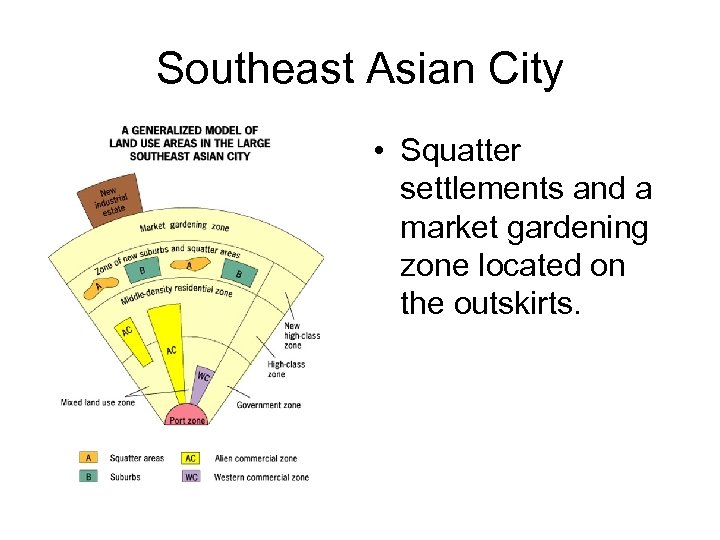
Southeast Asian City • Squatter settlements and a market gardening zone located on the outskirts.
58de04ac2aa96e040d7321123898e1c8.ppt