81646b37a3f8109ac01976d8dae95130.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 38

URANIUM AND RADON: A PUBLIC HEALTH PERSPECTIVE Jean-Claude Dessau, md MSSS

Uranium Heavy metal, radioactive, occurs naturally anywhere on earth 3 natural radio-isotopes : 238 U (99, 28 %), 235 U (0, 71 %), 234 U (0, 0054 %) Estimated World production: 44 000 Tons/Year Canada Currently the largest producer of uranium in the world (9000 tons of U 3 O 8 in 2008, representing 20% of world production) before Australia and Kazakhstan Canada has nearly 10% of global reserve Saskatchewan The Canadian company Cameco (subsidiary of Areva), which operates mines that are among the largest in the world. In 2011, the province will have ten operating sites Athabasca Basin : Uranium content 12% Nova Scotia and British Columbia Moratorium: real potential unknown Québec Intense exploration activity and development (no exploitation) 2 2

Regulatory Process Approvals required before opening a uranium mine Prospecting Licence (MRNF - Ministère des ressources naturelles et de la faune) Environmental Certificate of Authorization for advanced exploration work (excavation and stripping)(MDDEP - Ministère du développement durable, (CNSC-Canadian Nuclear Safety Commission) Obtaining a mining lease (MRNF) Filing a restoration plan and financial guarantees (Investors) Consultation of the Public Health Department (Direction de santé publique. DSP) Assessment and approvals at each stage of the project (CNSC - MDDEP) Mandatory public hearings (BAPE or its equivalent in Federal Territory) Laws applying to uranium mining projects Mining Law, Forest Law (MRNF), Law on Environmental Quality, Order 019 on the mining industry (MDDEP) Metal Mining Effluent Regulations (REMM), Health, safety and Security Law (LSST) and Nuclear safety and Control Law (CNSC) 3 3
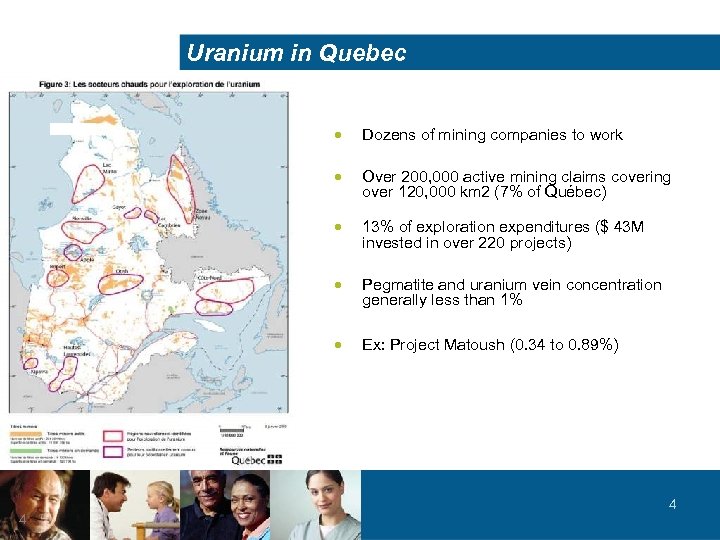
Uranium in Quebec · Dozens of mining companies to work · Over 200, 000 active mining claims covering over 120, 000 km 2 (7% of Québec) · 13% of exploration expenditures ($ 43 M invested in over 220 projects) · Pegmatite and uranium vein concentration generally less than 1% · 4 Ex: Project Matoush (0. 34 to 0. 89%) 4

Key Issues · Climatic · Economic · Energy · Environmental · Industrial / Technology · Medical (isotopes) · Public health · Societal and ethical 5 5

Toxicological Risk of Uranium Chemical toxicity occurs at much lower doses than the radiological toxicity This is why the Provincial Norm for drinking water is based on toxicity as inorganic metal (20 µg / L) and not as radionuclide Mainly due to the ingestion of water rich in uranium Institut National de Santé Publique du Québec - INSPQ has produced a factsheet on the toxicity of uranium in water. 6 6

Radiological risk of Uranium · Radiological risk associated with ingestion, inhalation and exposure to external radiation · Risk potentially more important during periods of exploitation · The exploration does not pose a risk to health or the environment · Health Hazard · · Risk modulated by the concentration, duration of exposure and smoking · 7 Radon and its decay products are historically responsible for high levels of lung cancer listed among uranium miners Nowadays all mines are well ventilated and lung cancer associated with Radon in mines is not an issue anymore 7

The “Sievert” The « Sievert » is the measure of the effect of radiation on humans One sievert (Sv) is a very large dose The effects caused by short-term exposure to very high doses of radiation (acute exposure) vary depending on the dose. Here are some examples: 10 Sv (Sievert) : risk of death within days or weeks; 1 Sv : risk of cancer occurring later in life (5 out of 100); 0, 1 Sv : risk of cancer occurring later in life (5 out of 1000); Fortunately no one is exposed to such high doses

The “Sievert” Even workers who are generally more exposed than the general population are exposed to much lower doses What are the limits of exposure to radiation? For Radiation Workers: The Threshold Limit Values (TLVs) published by the ACGIH (American Conference of Governmental Industrial Hygienists) are used in many jurisdictions occupational exposure limits or guidelines: 50 m. Sv - TLV for the annual dose of radiation workers during any year; 20 m. Sv - TLV for average annual dose for radiation workers, averaged over five years The actual exposure of workers is only one to two m. Sv per year (See next slide) For general public: To the order of a thousandth of a Sievert 1 m. Sv - Recommended annual dose limit for general public (ICRP International Commission on Radiological Protection).
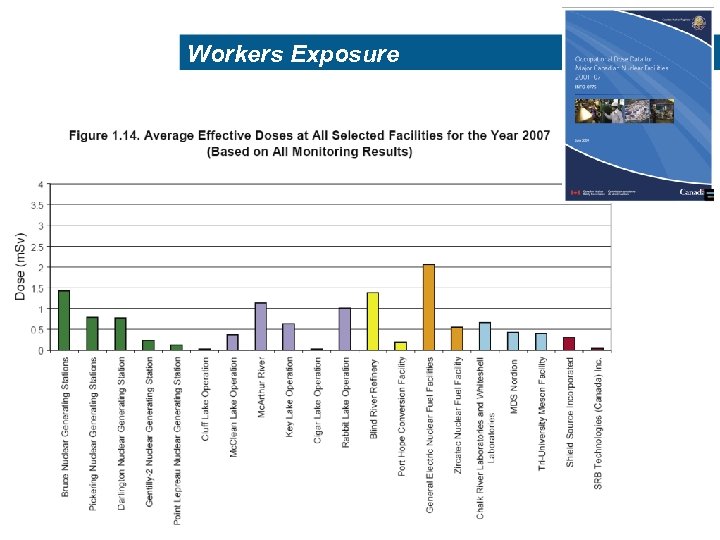
Workers Exposure 10 10

Conclusions · Quebec uranium potential is substantial · Perception of uranium industry non-uniform in the population · Uranium mining subject to numerous laws and regulations · There a lot of information to evaluate the risk of exposure to uranium in the industry · Currently, on average, the uranium miners are exposed to lower levels of radon in the workplace than in their homes 11 11

Press Review: Protégez-vous, mai 2009 12

Press Review: La facture: 20 octobre 2009
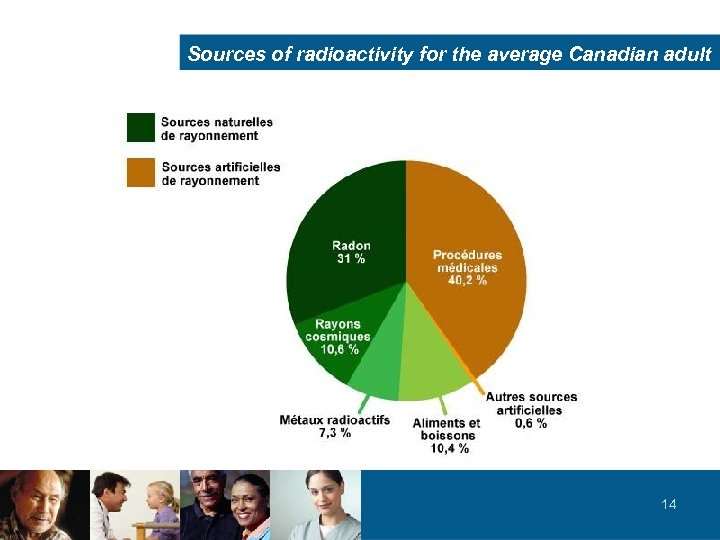
Sources of radioactivity for the average Canadian adult 14

Question What is Radon ?

Physical characteristics of radon Radioactive gas Everywhere on the earth's crust From natural uranium Imperceptible by the senses Colorless Odorless Inert (chemically unreactive) 16

Physical characteristics of radon Half-life: 3. 8 days Half a given amount of radon is disintegrated in 3. 8 days Unit of measure: Bq/m 3 (Becquerel per cubic meter) Measurement of radon activity 1 Bq = 1 disintegration per second
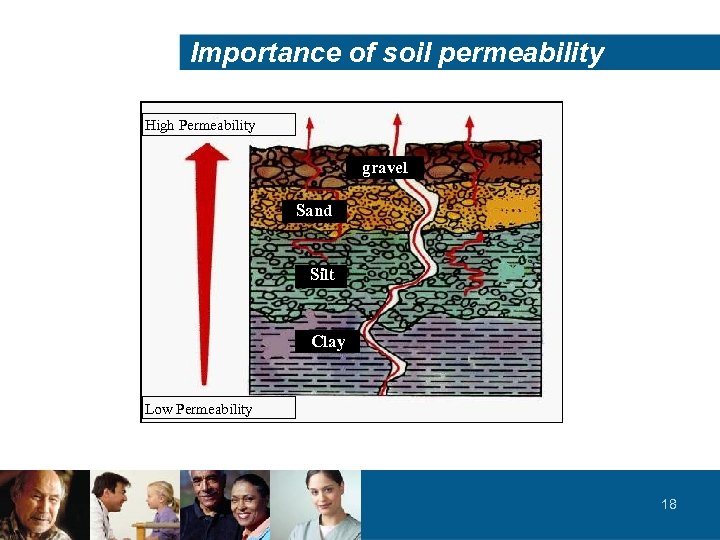
Importance of soil permeability High Permeability gravel Sand Silt Clay Low Permeability 18
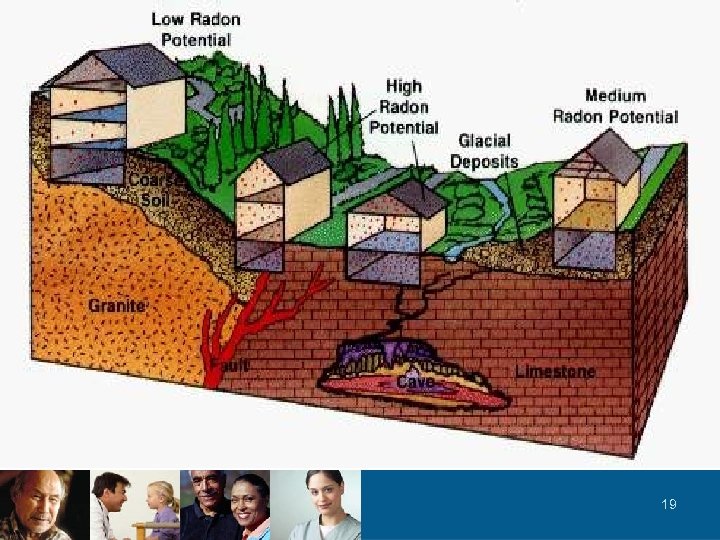
19
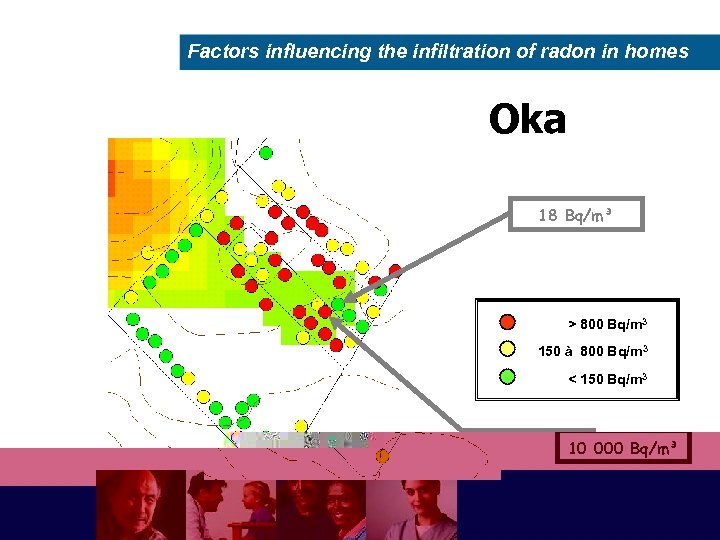
Factors influencing the infiltration of radon in homes Oka 18 Bq/m³ > 800 Bq/m 3 150 à 800 Bq/m 3 < 150 Bq/m 3 10 000 Bq/m³
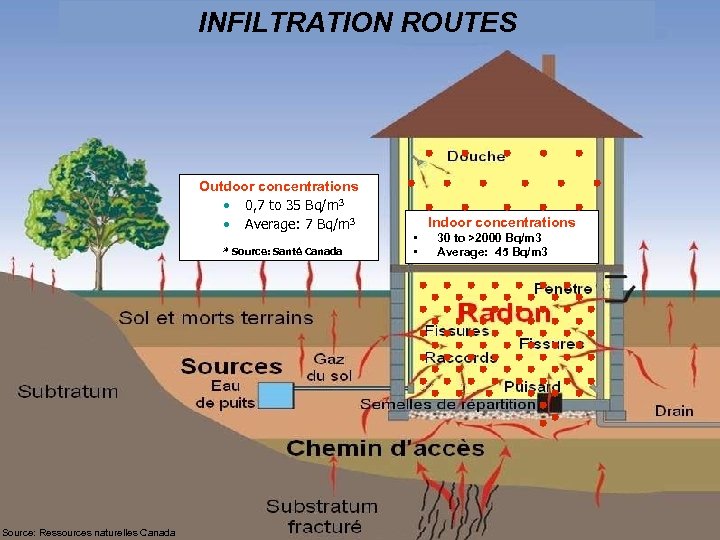
INFILTRATION ROUTES Outdoor concentrations • 0, 7 to 35 Bq/m 3 • Average: 7 Bq/m 3 * Source: Santé Canada Indoor concentrations • 30 to >2000 Bq/m 3 • Average: 45 Bq/m 3 21 Source: Ressources naturelles Canada

Effect on health The only known effect of radon is an increased risk of lung cancer This risk depends on: Concentration exposure time Smoking 22

Global Consensus Radon is a serious public health 2 nd leading cause of lung cancer after smoking First rank among non-smokers We can not identify a level below which the risk of exposure to radon is nonexistent; Combined exposure to radon and tobacco: The health effects are greater than the sum of their individual effects.
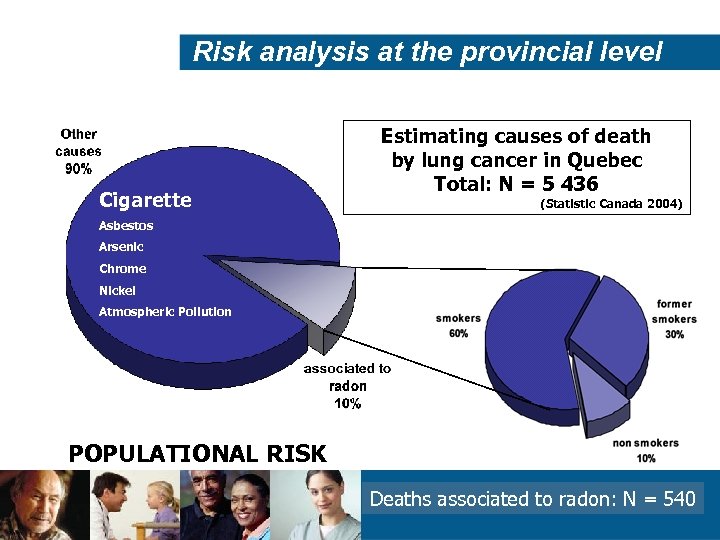
Risk analysis at the provincial level Cigarette Estimating causes of death by lung cancer in Quebec Total: N = 5 436 (Statistic Canada 2004) Asbestos Arsenic Chrome Nickel Atmospheric Pollution POPULATIONAL RISK Deaths associated to radon: N = 24 540
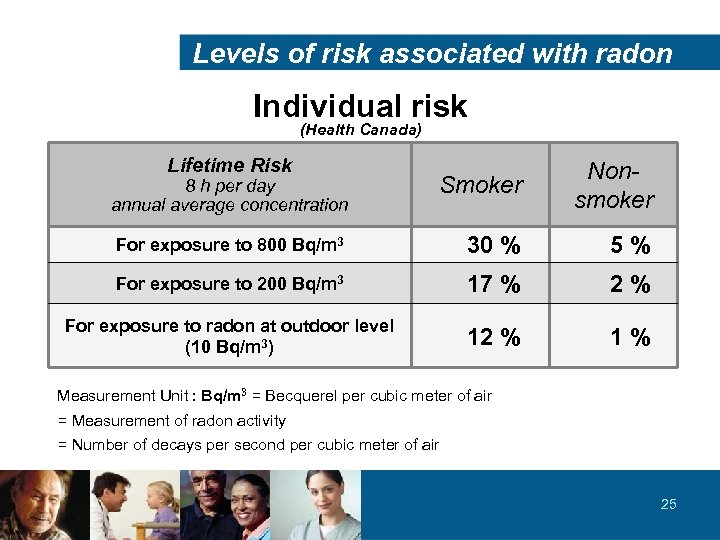
Levels of risk associated with radon Individual risk (Health Canada) Lifetime Risk Smoker Nonsmoker For exposure to 800 Bq/m 3 30 % 5 % For exposure to 200 Bq/m 3 17 % 2 % For exposure to radon at outdoor level (10 Bq/m 3) 12 % 1 % 8 h per day annual average concentration Measurement Unit : Bq/m 3 = Becquerel per cubic meter of air = Measurement of radon activity = Number of decays per second per cubic meter of air 25
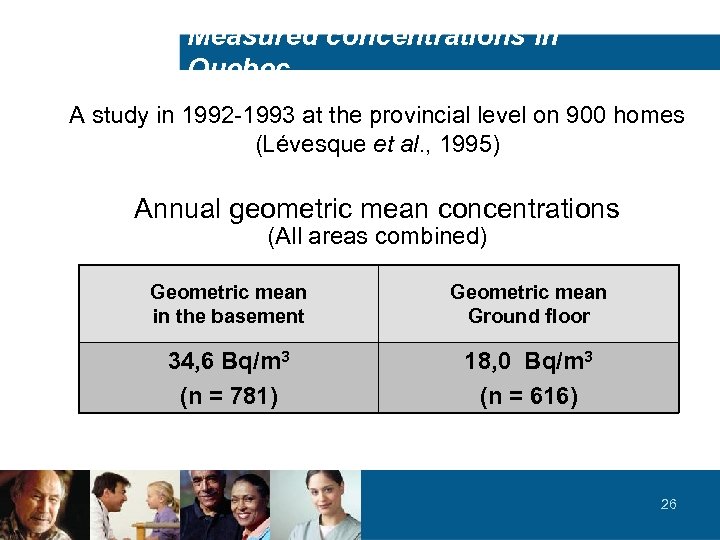
Measured concentrations in Quebec A study in 1992 -1993 at the provincial level on 900 homes (Lévesque et al. , 1995) Annual geometric mean concentrations (All areas combined) Geometric mean in the basement Geometric mean Ground floor 34, 6 Bq/m 3 (n = 781) 18, 0 Bq/m 3 (n = 616) 26
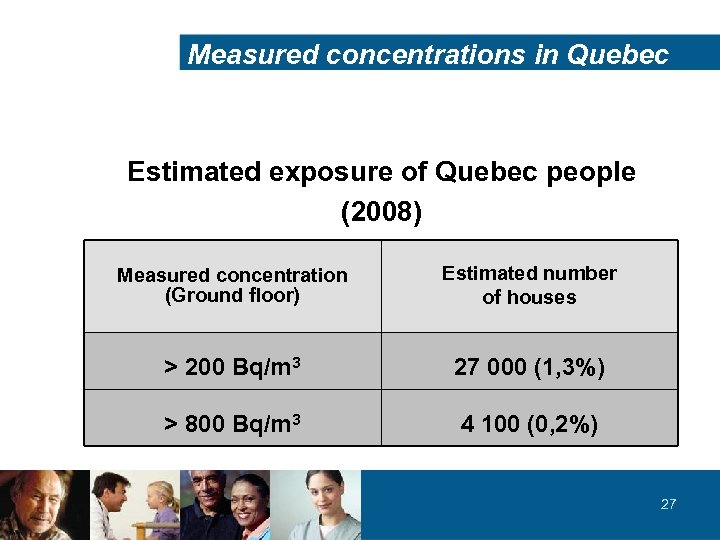
Measured concentrations in Quebec Estimated exposure of Quebec people (2008) Measured concentration (Ground floor) Estimated number of houses > 200 Bq/m 3 27 000 (1, 3%) > 800 Bq/m 3 4 100 (0, 2%) 27

Initiatives about radon Question 28

Health Canada Strategy 1. Developing policy on radon Lowering the directive 800 to 200 Bq/m 3 2. Data collection and advice Federal Buildings in Quebec Measures in 15, 000 homes - national study Measurement guides and radon mitigation guide 3. Education and public awareness Workshops, exhibitions, conferences, website and printed documents Québec real estate brokers Information campaign for the MRC

Canadian Guideline on radon Applies to new and existing buildings 1. Remedial measures should be undertaken in a dwelling whenever the average annual radon concentration exceeds 200 Bq/m³ in the normal occupancy area (where a person can spend more than four hours per day ). 30

Canadian Guideline on radon 2. The higher the radon concentration, the sooner remedial measures should be undertaken radon Concentration (Bq/m 3) Time to take corrective measures Over 600 In less than a year Between 200 and 600 In less than 2 years Less than 200 No action required Bq/m 3 = Becquerel per cubic meter of air 31

Canadian Guideline on radon 3. When remedial action is taken, the radon level should be reduced to a value as low as practicable. 4. The construction of new dwellings should employ techniques that will minimize radon entry and will facilitate post-construction radon removal, should this subsequently prove necessary. 32

Radon Measurement Measuring time Radon levels in a building can vary significantly with time Health Canada recommends a long-term measurement from three to twelve months (preferred) The ideal time to perform a test of three months is during the heating season which extends from October to April For more information, see the guides at Health Canada: www. hc-sc. gc. ca/ewh-semt/radiation/radon/index-eng. php 33
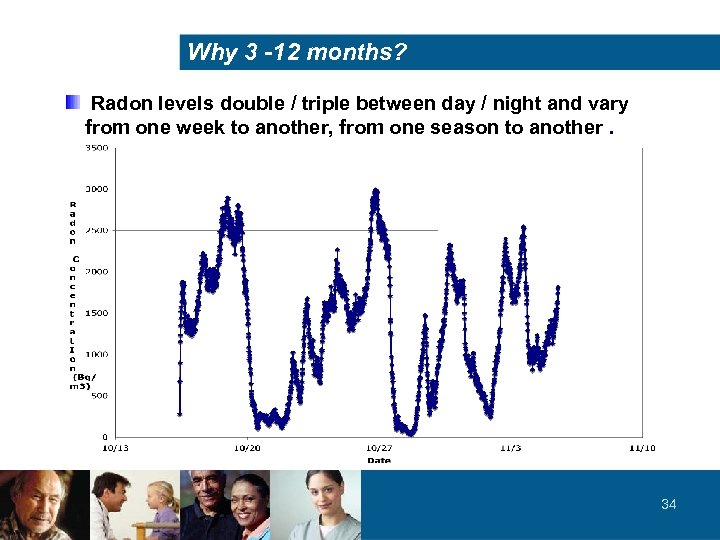
Why 3 -12 months? Radon levels double / triple between day / night and vary from one week to another, from one season to another. 34

Radon Measurement The types of long term detectors a) Electret Ion Chamber b) Alpha-track detector a b In general, the cost of a radon test can vary between $ 50 and $ 100 Other measurement methods available which require specialized services of a competent technician (see Health Canada measures Guides) 35
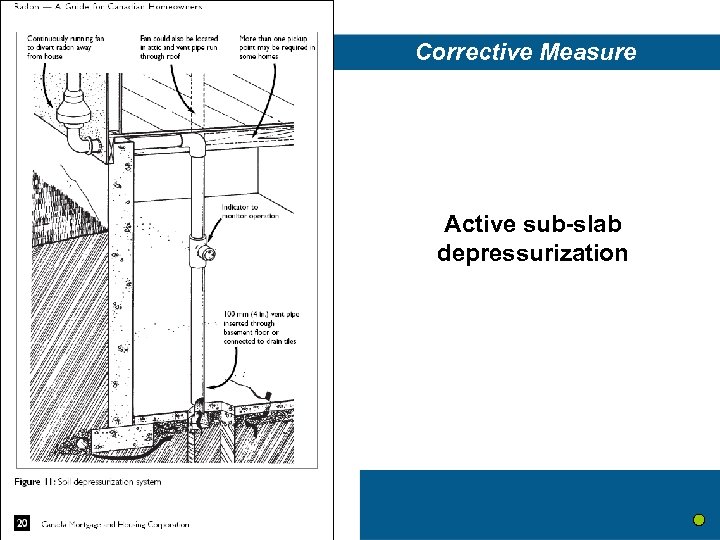
Corrective Measure Active sub-slab depressurization

Key messages for citizens Radon is the leading cause of lung cancer among non -smoker, second only to smoking Measure radon in your home to protect your family. It's simple and cheap If the level exceeds the guideline, there are solutions: mitigate 37

Thank you ! 38
81646b37a3f8109ac01976d8dae95130.ppt