3744f13f76cd9993f05c98794575cff3.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 7

Update on Helium Management and Tungsten Bonded Ferritic Presented by Lance Snead Oak Ridge National Laboratory HAPL e-meeting June 6, 2003
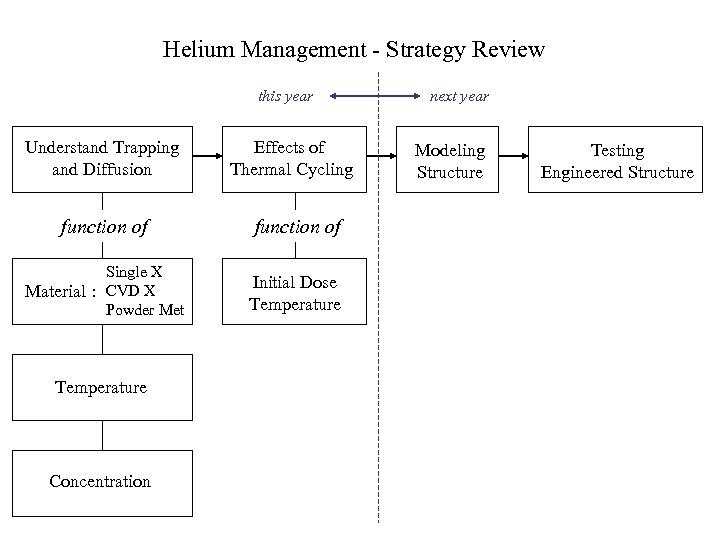
Helium Management - Strategy Review this year Understand Trapping and Diffusion Effects of Thermal Cycling function of Single X Material : CVD X Powder Met Initial Dose Temperature Concentration next year Modeling Structure Testing Engineered Structure

Helium Management - Results Update Previous Result CVD produced 238 counts Polycrystalline produced 82 counts Single crystal produced no counts Repeat of Experiment CVD produced 480 counts Polycrystalline produced 355 counts Single crystal produced 303 counts
Helium Management - Results Update • The error in the original data was confirmed by a third test. While there is a dependence of microstructure on retained helium is not dramatic. • Work to be completed this year: - Implantation system to be automated for continual irradiation/anneal, simulating IFE implantation dose, temperature and thermal spike. - Samples of CVD W, powder met W, and single crystal tungsten were implanted at 1013, 1014, and 1015 /cm 2 at room temperature and shipped to DELFT for thermal desorption studies (underway. ) - Elevated dose/annealing and TEM microstructural analysis continues. - Trapping sites and diffusion coefficients by end of year for modeling…. .
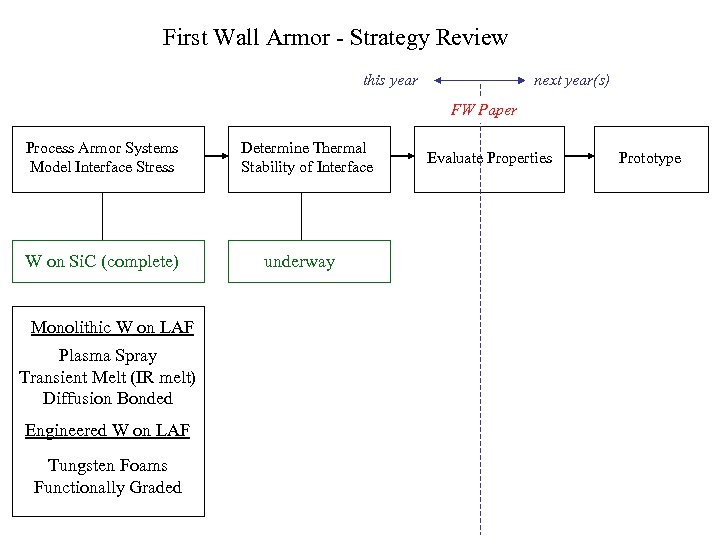
First Wall Armor - Strategy Review this year next year(s) FW Paper Process Armor Systems Model Interface Stress W on Si. C (complete) Monolithic W on LAF Plasma Spray Transient Melt (IR melt) Diffusion Bonded Engineered W on LAF Tungsten Foams Functionally Graded Determine Thermal Stability of Interface underway Evaluate Properties Prototype

First Wall Armor - Plasma Spray • The potential for failure of a tungsten cladding on F 82 H steel is driven by strain mismatch at the coating interface. This strain mismatch arises from the cladding process as well as nominal and transient operating conditions. The CTE of F 82 H Steel at 600 C is 11 ppm/K compared to 4. 7 ppm/K for tungsten. In addition, the alpha and gamma iron phase transformations must be considered for F 82 H Steel at temperatures associated with cladding. • Plasma spraying under inert gas and vacuum allow for the deposition of pure tungsten and tungsten/steel composite microstructures. Graded layers can mitigate concentrated strain mismatches. • Plasma spraying of preheated substrates can be used to manage the magnitude and direction of interfacial stress. --> Samples have been sprayed at various substrate temperatures. --> Metallography has been carried out. X-ray diffraction and annealing pending. • Transient powder melt may allow porosity near surface. --> Samples have been sprayed at various substrate temperatures. --> Metallography has been carried out. • Diffusion bonding of tungsten foil as the top layer would result in the highest surface integrity if strain mismatch could be managed by plasma sprayed, composite inter-layers.
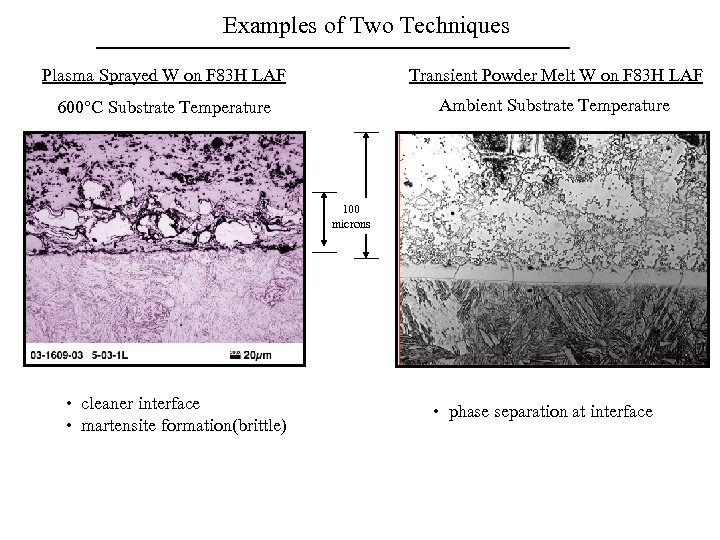
Examples of Two Techniques Plasma Sprayed W on F 83 H LAF Transient Powder Melt W on F 83 H LAF 600°C Substrate Temperature Ambient Substrate Temperature 100 microns • cleaner interface • martensite formation(brittle) • phase separation at interface
3744f13f76cd9993f05c98794575cff3.ppt